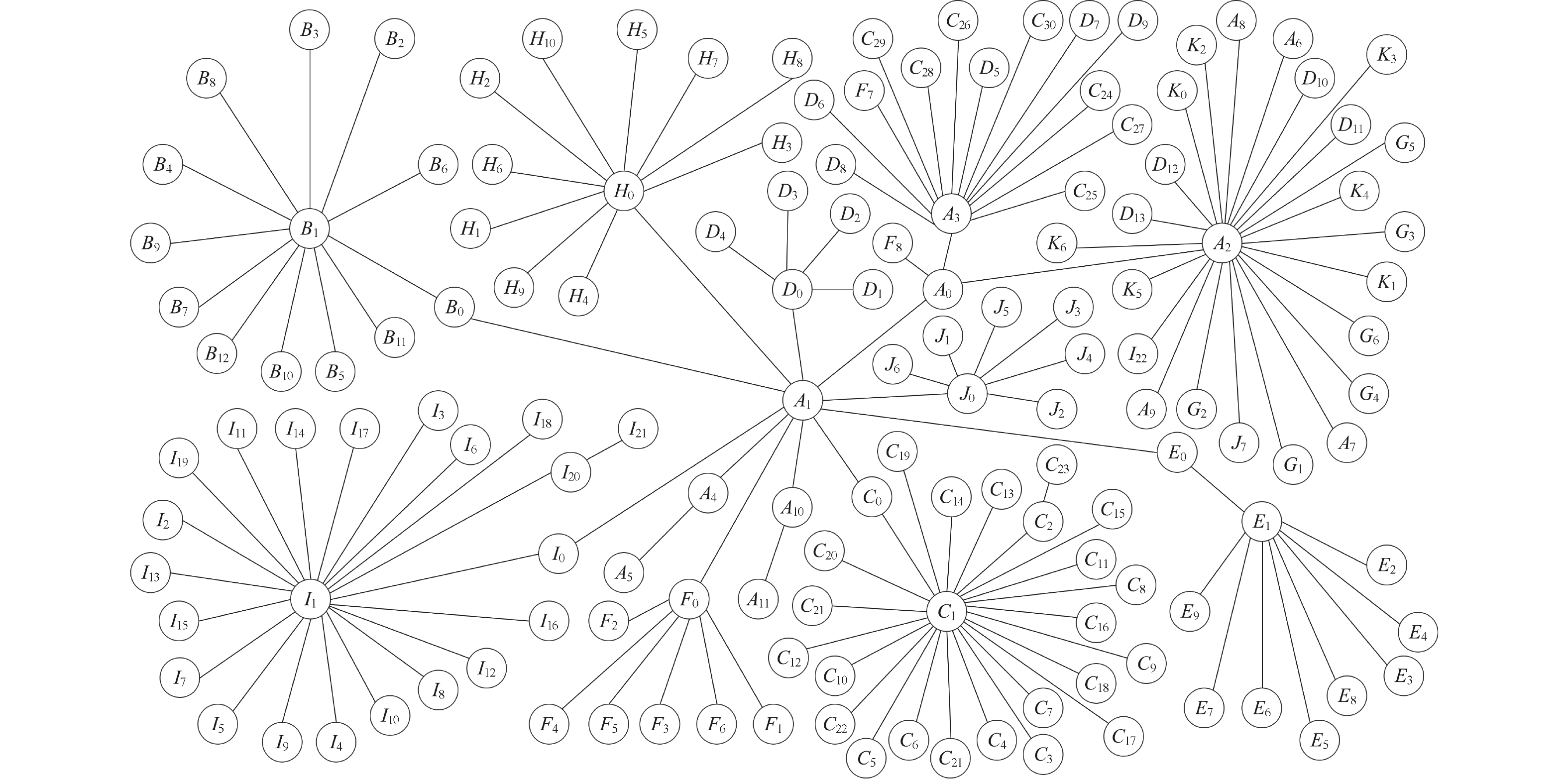
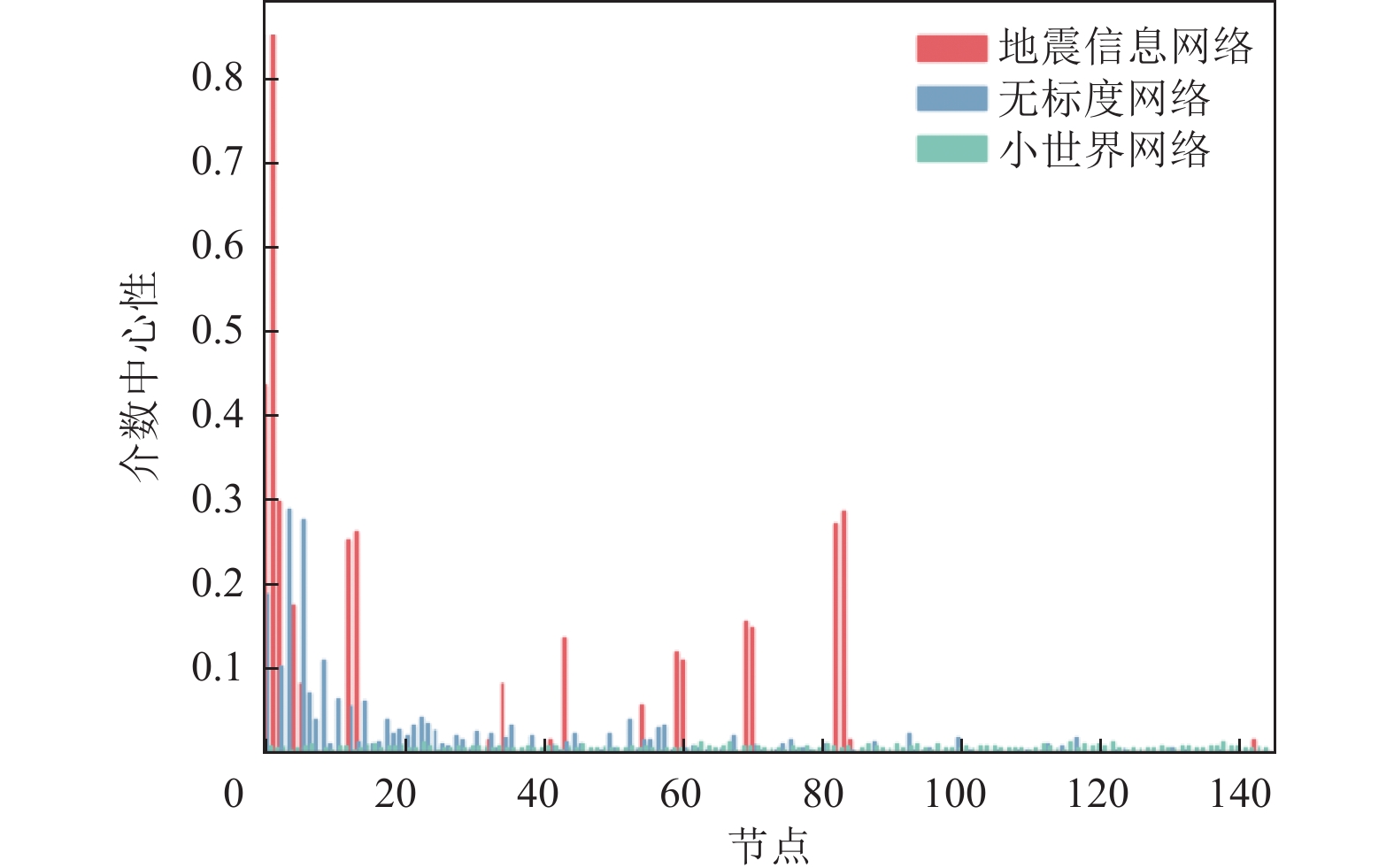
The Key Nodes Identification and Robustness Analysis of Zhejiang Seismic Network Based on Complex Network Theory
-
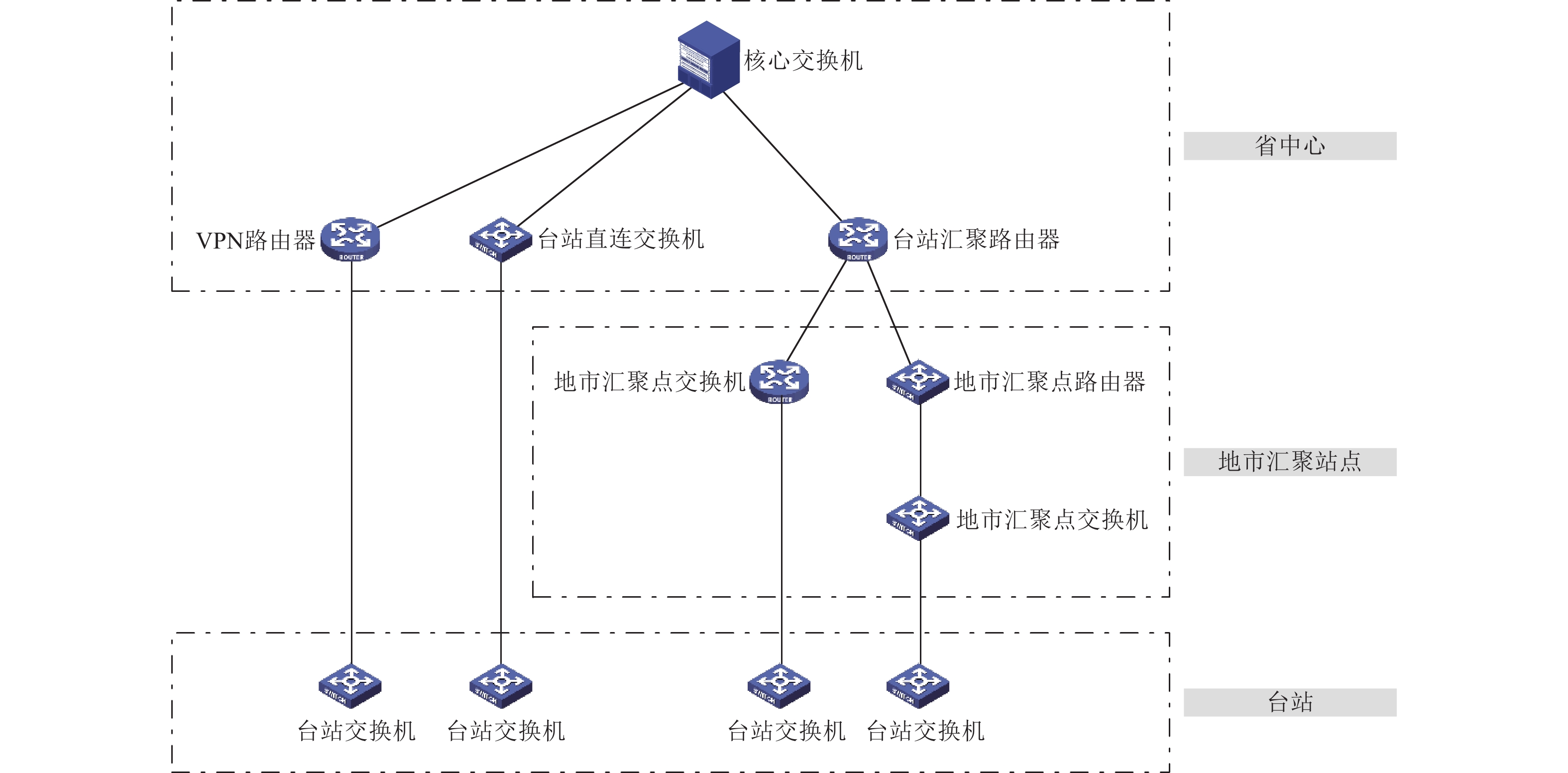
摘要: 信息化是推进地震现代化建设的强力引擎。当前,面对日益复杂的信息网络系统,有效识别网络关键节点和评估网络鲁棒性,对于提高站网运行能力和规划网络建设具有重要现实意义。首先,基于浙江地震信息网络实际运行数据,对网络进行路由器级建模;然后,与小世界网络和无标度网络进行对比,分析其表现的拓扑结构特征;其次,结合复杂网络统计特性和地震业务特性,构建关键节点评价指标体系,并基于主观和客观维度设置指标权重,采用理想逼近排序法,综合评价各节点重要程度;最后,模拟不同攻击方式评估网络的鲁棒性。研究结果表明,相较于传统方法,本研究建立的关键节点评价指标体系和权重计算方法更合理,评价结果更准确;浙江地震信息网络为无标度网络,对蓄意攻击具有脆弱性,但对随机攻击具有较强的鲁棒性。Abstract: Informatization plays a crucial role in advancing seismic modernization. With the increasing complexity of network structures, it is essential to develop and enhance station networks. This study focuses on identifying key nodes and evaluating the robustness of such networks. Using the Zhejiang Seismic Network as a case study, we first developed a model at the router level. We then compared this network with small-world and scale-free networks to analyze its topological characteristics. Next, an evaluation system for key nodes was established by assigning weights based on both subjective and objective criteria. The ideal approximation ranking method was employed to comprehensively assess the importance of each node, taking into account the specific characteristics of complex networks and earthquake-related operations. Finally, network robustness was tested through simulated network attacks. The results indicate that the key node evaluation system and weight calculation method proposed in this study are both reasonable and accurate. The Zhejiang Seismic Network was found to be a scale-free network, vulnerable to deliberate attacks but highly resilient to random attacks.
-
Key words:
- Seismic network /
- Key node /
- Robustness /
- Assessment /
- Identification
-
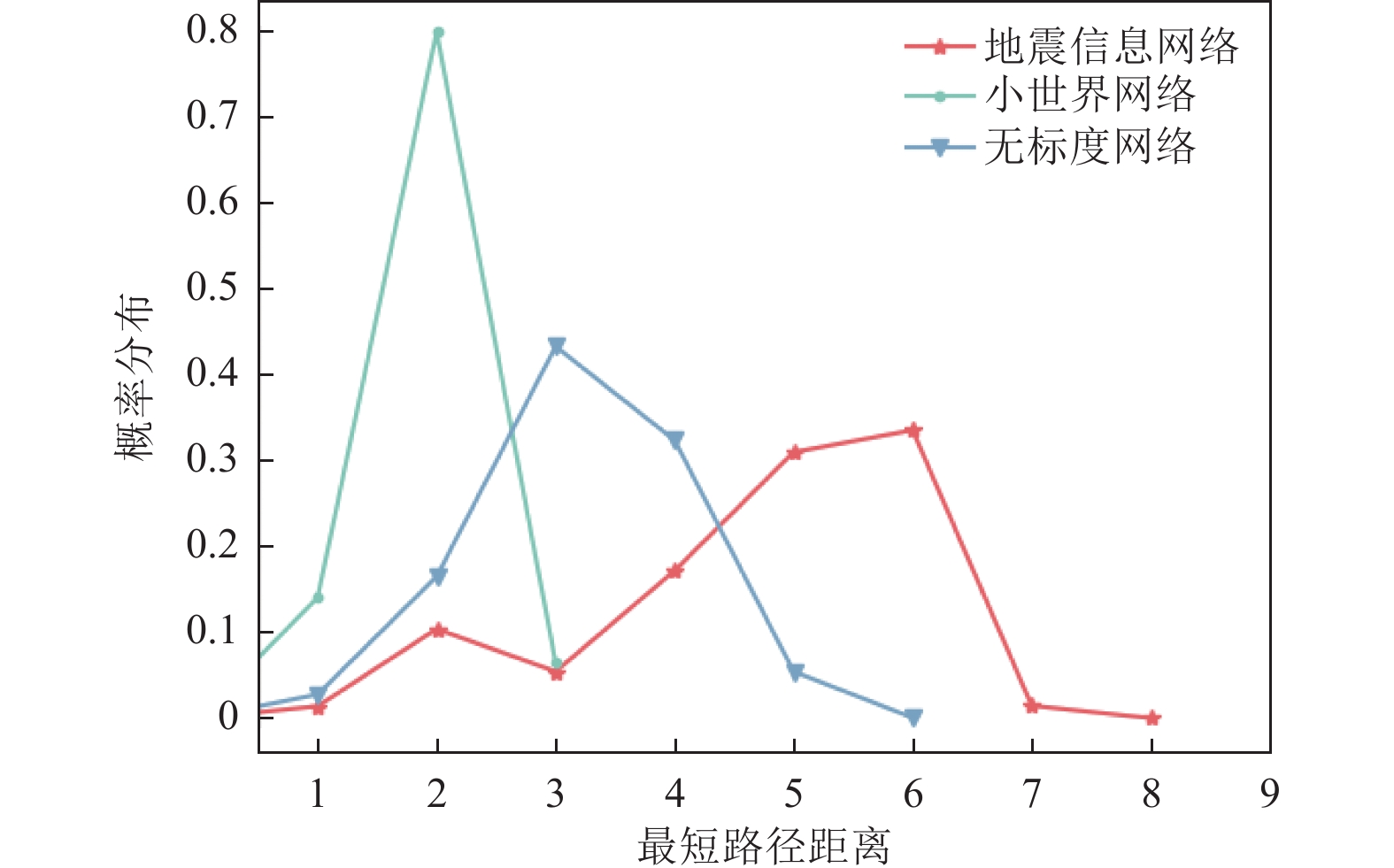
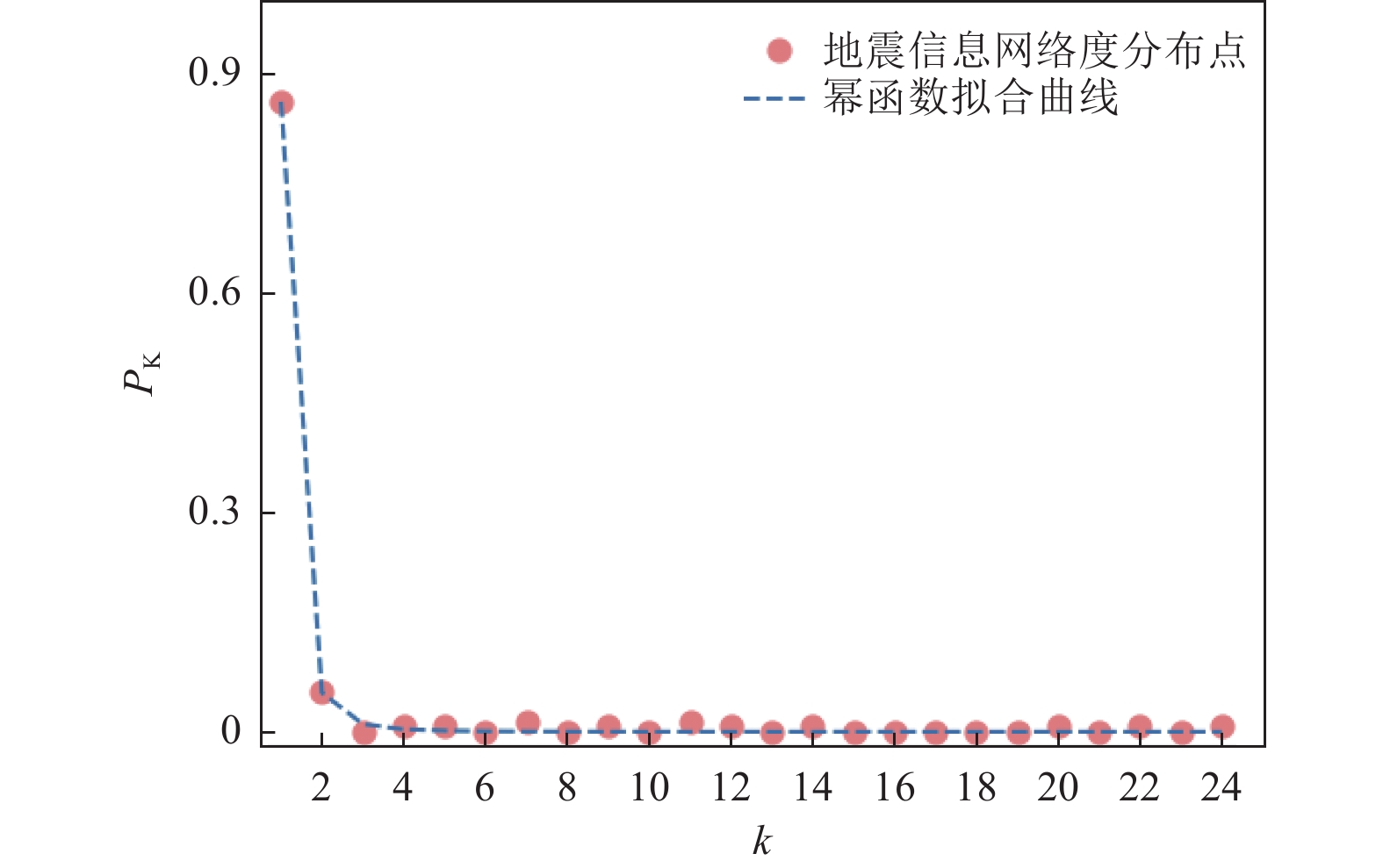
表 1 各网络拓扑特征值
Table 1. The Characteristic topology of each network
网络类型 边数 平均度 最大度 特征路径 网络直径 聚合系数 地震信息网络 143 1.99 24 4.72 8 0 无标度网络 144 3.94 28 3.21 6 0.07 小世界网络 1440 20 29 1.92 3 0.19 表 2 比例标度规则
Table 2. The Proportional scaling rules
尺度aij 含义 1 表示2个指标同等重要 2~3 表示指标$ i $较$ j $稍微重要 4~5 表示指标$ i $较$ j $明显重要 6~7 表示指标$ i $较$ j $强烈重要 8~9 表示指标$ i $较$ j $极端重要 表 3 RI指标
Table 3. The RI indicator
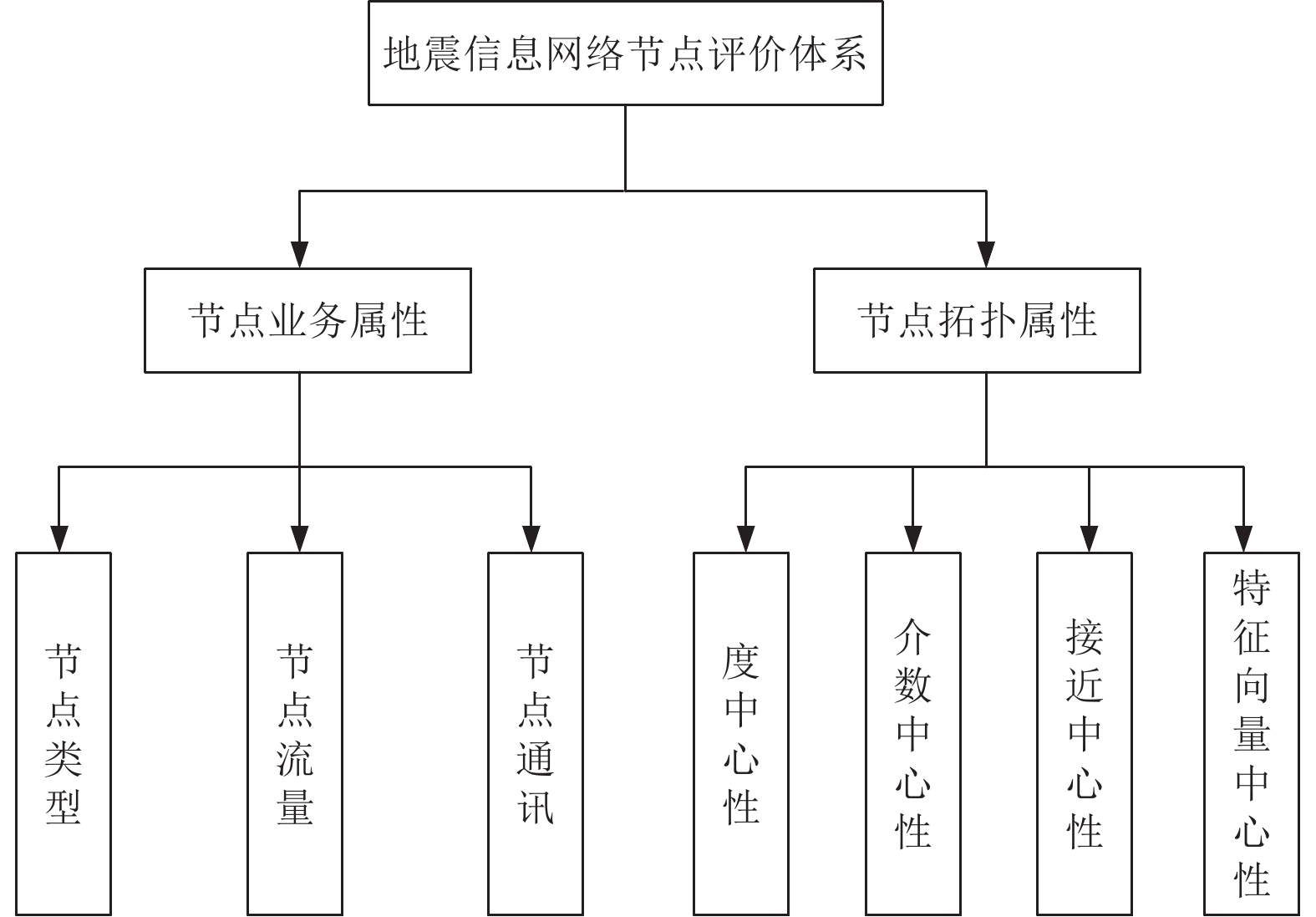
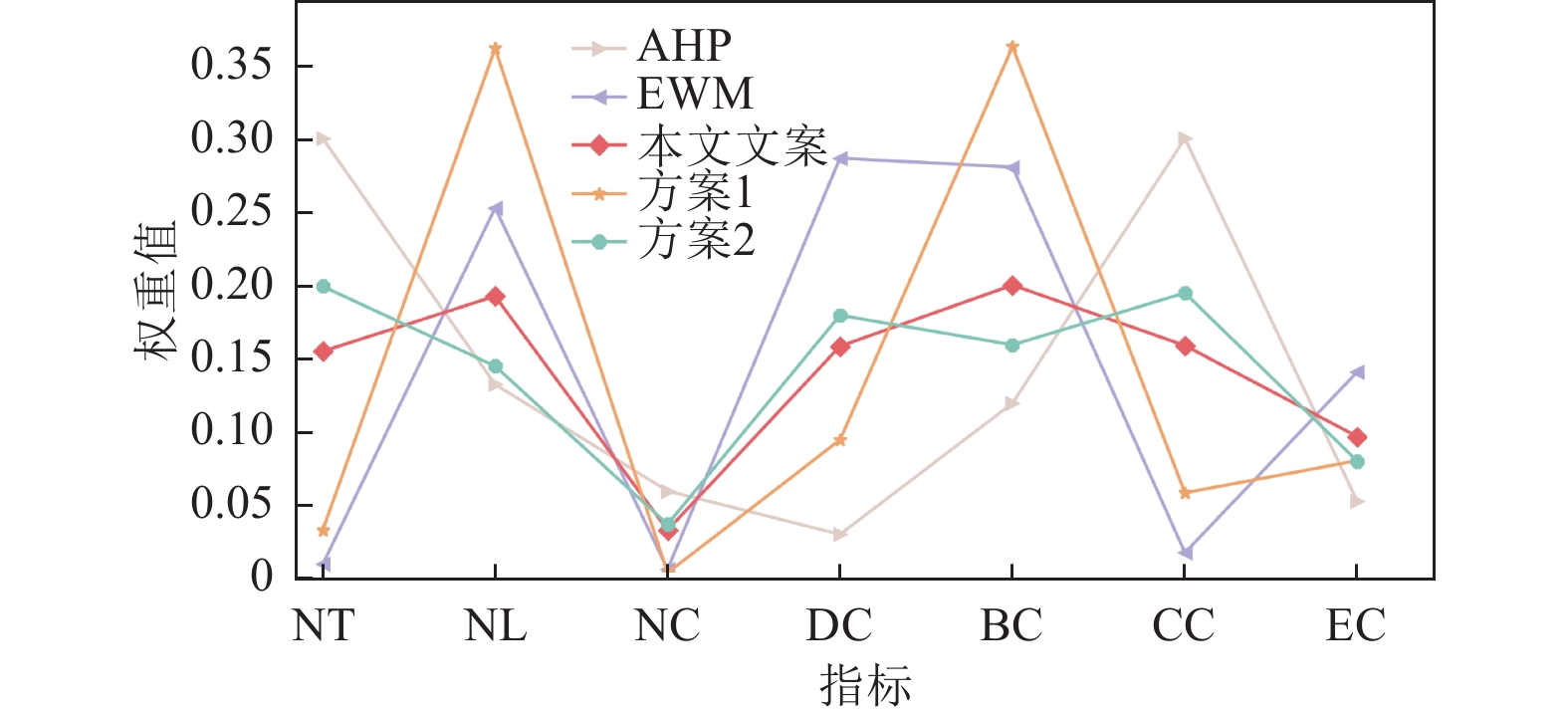
m 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 RI 0 0 0.59 0.9 1.12 1.24 1.32 1.41 1.45 表 4 地震信息网络部分节点标准化后的评价指标分数
Table 4. Evaluation index scores of some nodes in the seismic network
序号 NT NL NC DC BC CC EC A1 0.750 0.696 1 0.435 1 1 0.107 A0 1 1 1 0.130 0.513 0.741 0.258 A2 0.750 0.210 1 1 0.349 0.469 1 C1 0.625 0.129 1 0.913 0.335 0.395 0.048 I1 0.625 0.112 1 0.826 0.307 0.378 0.024 5 A3 0.75 0.071 1 0.565 0.205 0.424 0.002 H0 0.625 0.063 1 0.435 0.159 0.564 0.036 C0 0.625 0.134 1 0.043 0.320 0.638 0.031 I0 0.625 0.120 1 0.043 0.297 0.626 0.026 B1 0.625 0.103 1 0.478 0.175 0.311 0.008 表 5 地震信息网络节点重要性排序结果
Table 5. The top 10 nodes of seismic network
排序 本文方案 TOPSIS-灰色关联分析法 综合中心度法 1 A1 A2 A2 2 A0 A1 A1 3 A2 A0 C1 4 C1 C1 I1 5 I1 I1 A3 6 A3 A3 A0 7 H0 B1 B1 8 C0 H0 H0 9 I0 E1 E1 10 B1 C0 C0 -
丁琳,刘莹慧,2016. 拓扑对复杂通信网络级联故障传播的影响. 南华大学学报(自然科学版),30(4):82−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0062.2016.04.016Ding L., Liu Y. H., 2016. Impact of topology on the propagation of cascading failure in complex communication networks. Journal of University of South China (Science and Technology), 30(4): 82−87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0062.2016.04.016 段东立,2015. 基于负载最近邻偏好分配的复杂网络连锁效应. 复杂系统与复杂性科学,12(1):33−39.Duan D. L., 2015. Cascading failure of complex networks based on load local preferential redistribution rule. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 12(1): 33−39. (in Chinese) 贾开华,于云霞,范秀波等,2023. 基于AHP-EWM综合赋权和TOPSIS法的多能互补系统综合评价. 中国电力,56(7):228−238.Jia K. H., Yu Y. X., Fan X. B., et al., 2023. Multi-criteria comprehensive evaluation of multi-energy complementary system based on AHP-EWM and TOPSIS method. Electric Power, 56(7): 228−238. (in Chinese) 李刚,陈述新,赵洪壮等,2018. 地震行业网络安全全流量监控系统建设与应用. 地震工程学报,40(S1):205−213.Li G., Chen S. X., Zhao H. Z., et al., 2018. Construction and application of a full-flow monitoring system for seismic network safety. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 40(S1): 205−213. (in Chinese) 李莉,2019. 统计学原理与应用. 南京:南京大学出版社. 刘同林,杨芷柔,张虎等,2020. 基于复杂网络的军事通信网络建模与性能分析. 系统工程与电子技术,42(12):2892−2898. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.12.27Liu T. L., Yang Z. R., Zhang H., et al., 2020. Modeling and performance analysis of military communication network based on complex network. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 42(12): 2892−2898. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.12.27 刘欣,徐桂琼,杨平乐,2019. 基于组合赋权VIKOR方法的网络节点重要性评价. 计算机应用研究,36(8):2368−2371,2377.Liu X., Xu G. Q., Yang P. L., 2019. Node importance evaluating of network based on combination weighting VIKOR method. Application Research of Computers, 36(8): 2368−2371,2377. (in Chinese) 罗海秀,赵海兴,肖玉芝等,2021. 基于超图的公交超网络拓扑特性及鲁棒性分析. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),43(10):181−191.Luo H. X., Zhao H. X., Xiao Y. Z., et al., 2021. A hypergraph-based analysis of the topology and robustness of bus hypernetworks. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 43(10): 181−191. (in Chinese) 权治,李艳冠,李保罡等,2022. 空中应急通信网络中基于多属性的关键节点识别. 无线电工程,52(5):904−910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.05.027Quan Z., Li Y. G., Li B. G., et al., 2022. Key node identification based on multiple attributes in air emergency communication network. Radio Engineering, 52(5): 904−910. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.05.027 田文,方琴,周雪芳等,2025. 航路网络关键节点的识别方法. 西南交通大学学报,60(1):1−10.Tian W., Fang Q., Zhou X. F., et al., 2025. Identification method for key nodes in en-route network. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 60(1): 1−10. (in Chinese) 汪小帆,李翔,陈关荣,2006. 复杂网络理论及其应用. 北京:清华大学出版社. 吴晨,董吉文,房晓亮等,2013. 地震行业信息安全体系建设. 地震地磁观测与研究,34(3-4):245−251.Wu C., Dong J. W., Fang X. L., et al., 2013. Earthquake profession information security system construction research. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 34(3-4): 245−251. (in Chinese) 吴凌杰,孟真,严俊峰,2022. 基于混合加密API算法对地震数据安全传输的研究. 华南地震,42(2):46−52.Wu L. J., Meng Z., Yan J. F., 2022. A study on secure transmission of seismic data based on hybrid encryption API algorithm. South China Journal of Seismology, 42(2): 46−52. (in Chinese) 徐凤,朱金福,陈丹,2023. 东航空铁联运双层加权网络的关键节点识别与抗毁性分析. 铁道运输与经济,45(1):93−100.Xu F., Zhu J. F., Chen D., 2023. Identification of key nodes and invulnerability analysis of double-layer weighted network of air-rail inter-modal transport by China eastern airlines. Railway Transport and Economy, 45(1): 93−100. (in Chinese) 于会,刘尊,李勇军,2013. 基于多属性决策的复杂网络节点重要性综合评价方法. 物理学报,62(2):020204. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.020204Yu H., Liu Z., Li Y. J., 2013. Key nodes in complex networks identified by multi-attribute decision-making method. Acta Physica Sinica, 62(2): 020204. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.62.020204 周苗,杨家海,刘洪波等,2009. Internet网络拓扑建模. 软件学报,20(1):109−123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00109Zhou M., Yang J. H., Liu H. B., et al., 2009. Modeling the complex Internet topology. Journal of Software, 20(1): 109−123. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00109 朱沁雨,曹延华,陶海成等,2022. 低轨星座网络拓扑的抗毁性研究进展. 计算机工程与应用,58(17):1−12. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2203-0316Zhu Q. Y., Cao Y. H., Tao H. C., et al., 2022. Research progress on survivability of low-orbit constellation network topology. Computer Engineering and Applications, 58(17): 1−12. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2203-0316 Bian T. , Deng Y. , 2017. A new evidential methodology of identifying influential nodes in complex networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 103 : 101−110. Chen D. B., Lü L. Y., Shang M. S., et al., 2012. Identifying influential nodes in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 391(4): 1777−1787. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.09.017 Chen Z. H., Wu J. J., Xia Y. X., et al., 2018. Robustness of interdependent power grids and communication networks: a complex network perspective. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 65(1): 115−119. Heegaard P. E., Trivedi K. S., 2009. Network survivability modeling. Computer Networks, 53(8): 1215−1234. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2009.02.014 Hu J. T., Du Y. X., Mo H. M., et al., 2016. A modified weighted TOPSIS to identify influential nodes in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 444: 73−85. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.09.028 Hu P., Fan W. L., Mei S. W., 2015. Identifying node importance in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 429: 169−176. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.02.002 Kourtellis N., Alahakoon T., Simha R., et al., 2013. Identifying high betweenness centrality nodes in large social networks. Social Network Analysis and Mining, 3(4): 899−914. doi: 10.1007/s13278-012-0076-6 Liu Z. H., Jiang C., Wang J. Y., et al., 2015. The node importance in actual complex networks based on a multi-attribute ranking method. Knowledge-Based Systems, 84: 56−66. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.03.026 Motter A. E., Lai Y. C., 2002. Cascade-based attacks on complex networks. Physical Review E, 66(6): 065102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.065102 Peng G. S., Wu J., 2016. Optimal network topology for structural robustness based on natural connectivity. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 443: 212−220. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.09.023 Pu C. L., Yang J., Pei W. J., et al., 2013. Robustness analysis of static routing on networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 392(15): 3293−3300. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2013.03.059 Wei D. Q., Luo X. S., Zhang B., 2012. Analysis of cascading failure in complex power networks under the load local preferential redistribution rule. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 391(8): 2771−2777. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.12.030 Wei M. K., Lu Z., Wang W. Y., 2018. On characterizing information dissemination during city-wide cascading failures in smart grid. IEEE Systems Journal, 12(4): 3404−3413. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2763462 Xia Y. X., Fan J., Hill D., 2010. Cascading failure in Watts-Strogatz small-world networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 389(6): 1281−1285. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2009.11.037 -



 下载:
下载: