Seismic Damage Assessment of Regional RC Frame Structures Based on TCN
-
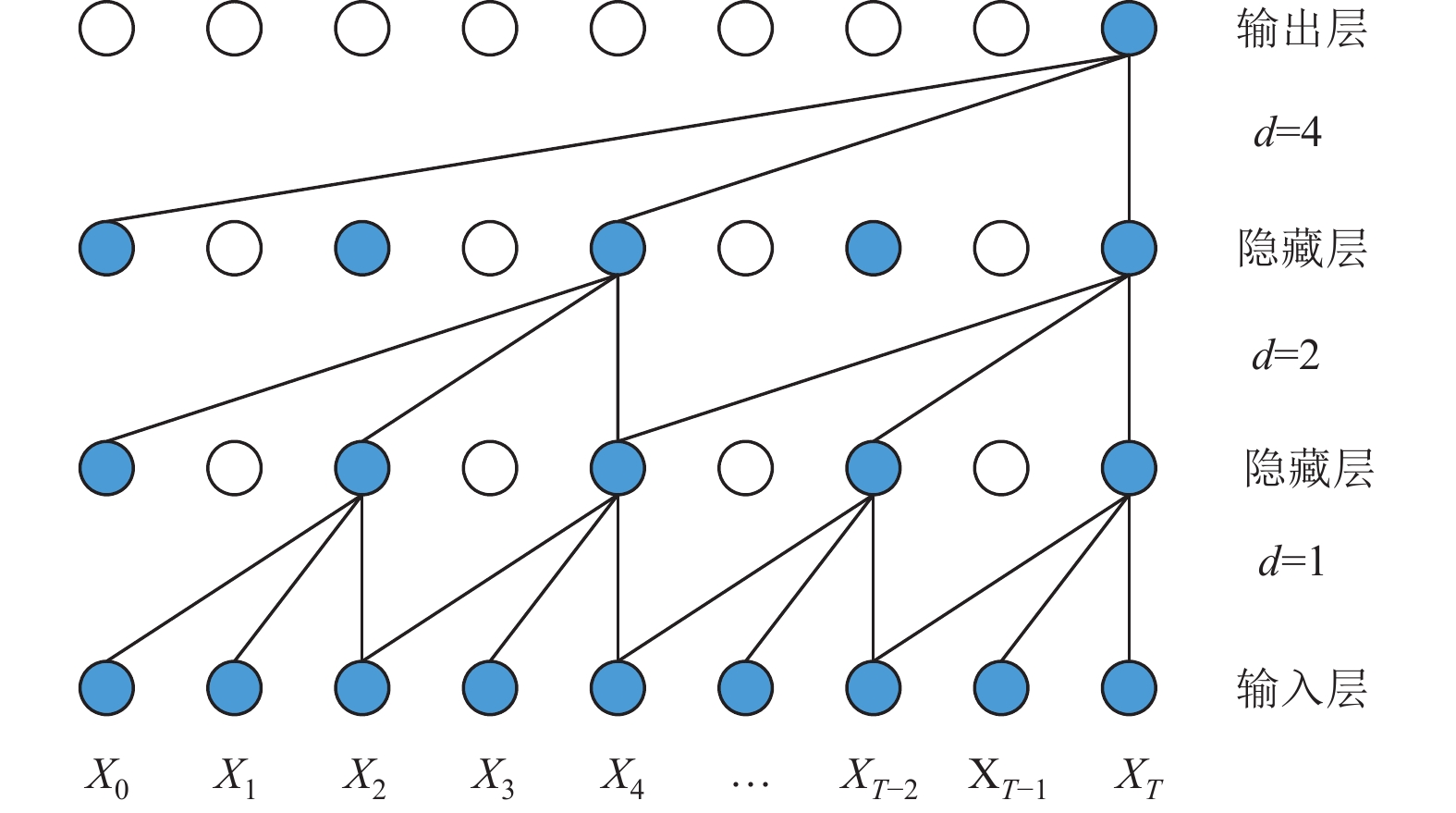
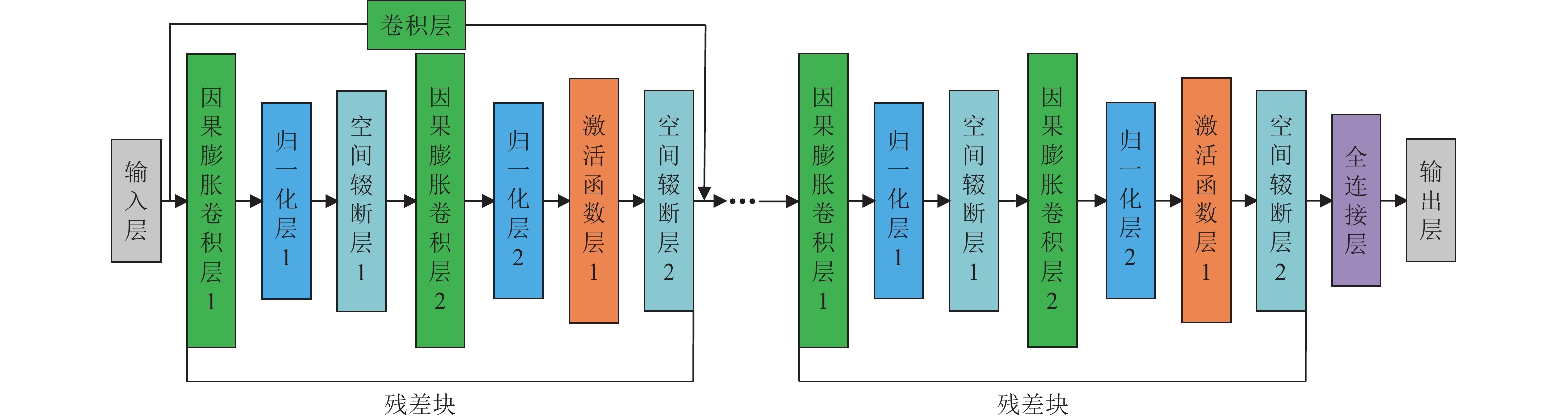
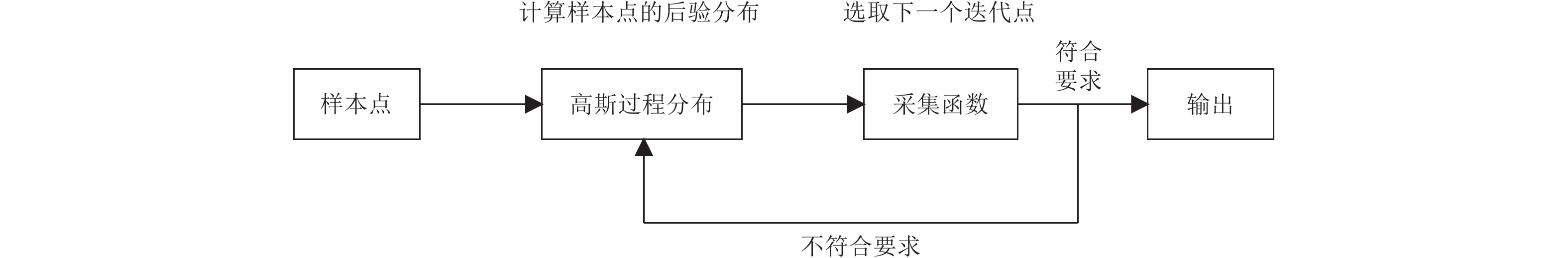
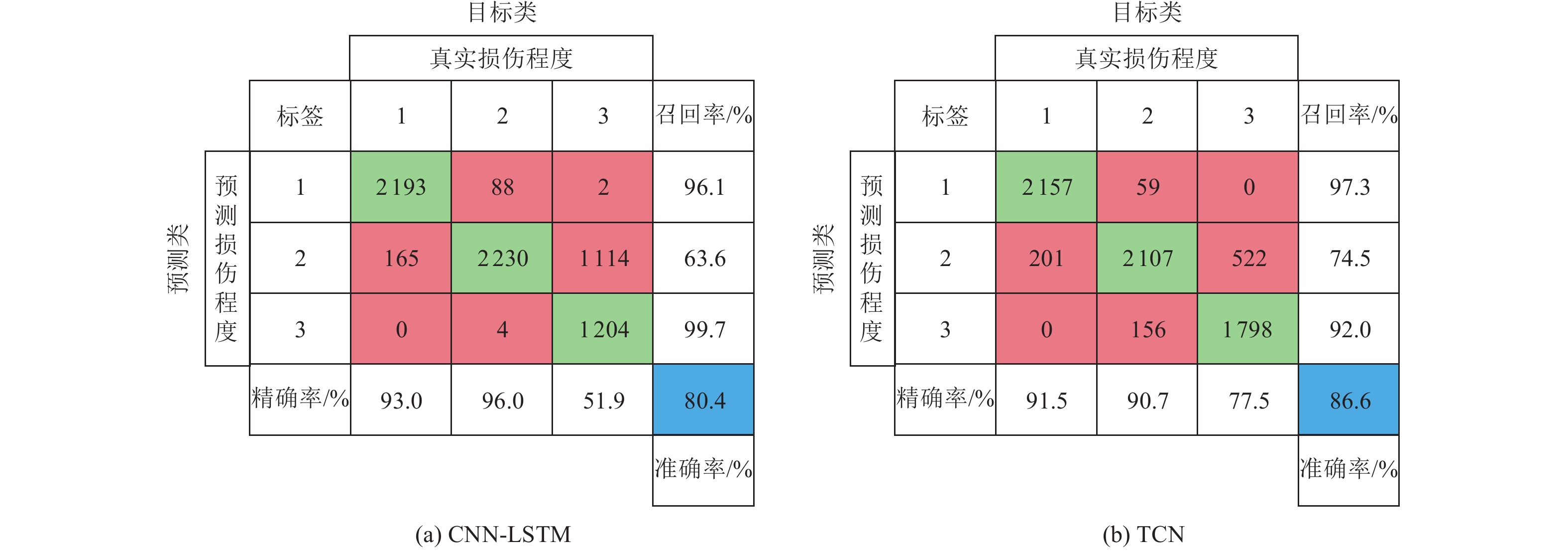
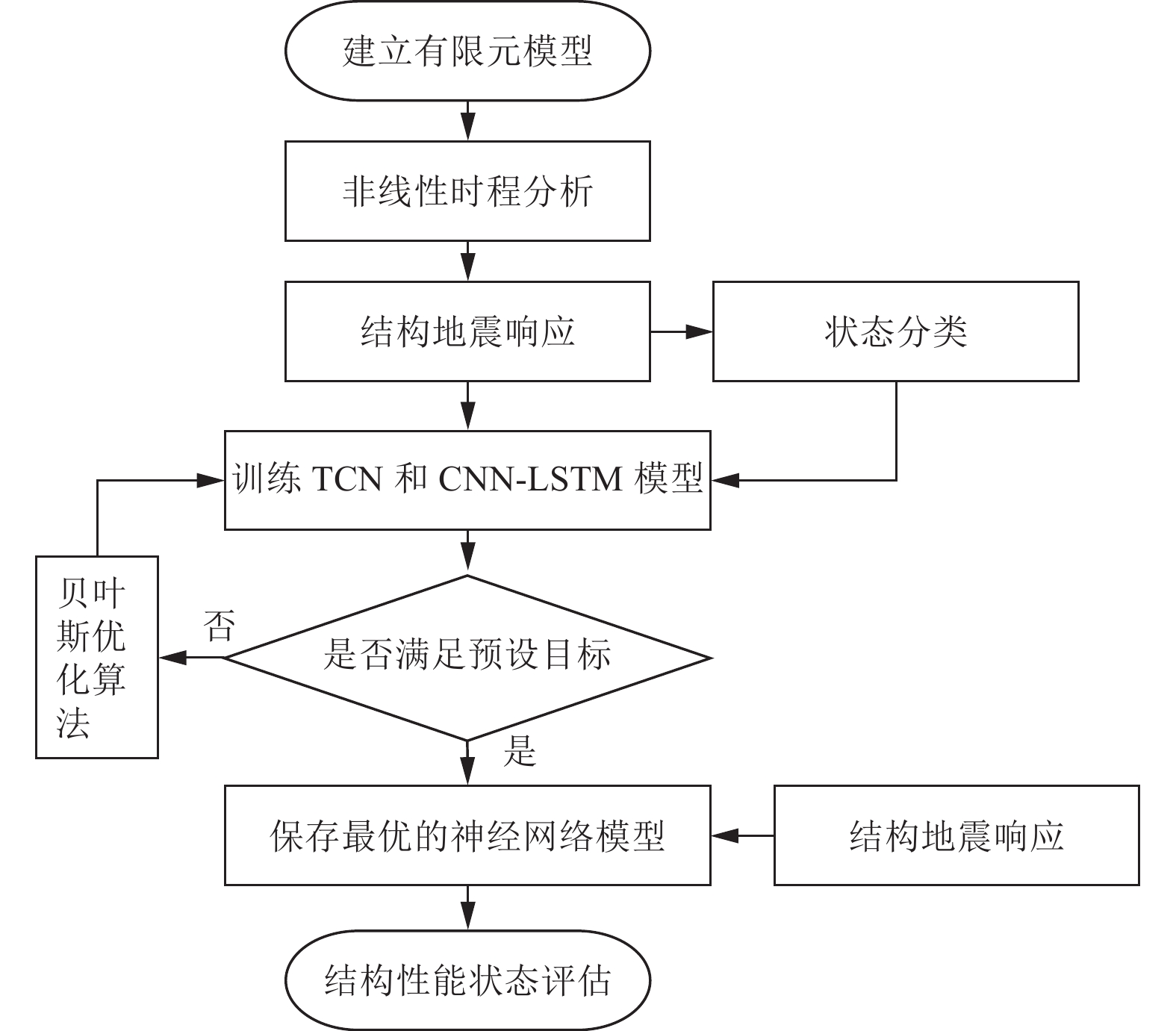
摘要: 为准确评估区域RC框架结构震后损伤状态,提出了基于时序卷积神经网络(Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks,TCN)模型的结构地震损伤评估方法。首先选取几何参数中的结构高度、x向跨度和设计参数中的抗震设防烈度、场地类别作为结构特征参数,设计了48个RC框架结构模型;然后用OpenSees软件计算结构在地震过程中的加速度响应数据,采用最大层间位移角作为结构损伤指标,并建立结构损伤指标与加速度响应数据之间的映射关系,以此得到震损数据集;最后通过建立基于TCN模型的区域RC框架结构震损评估模型,利用贝叶斯优化算法找出模型中的最优参数组合,分析了TCN模型的损伤评估准确率、计算资源及在噪声作用下的泛化能力。研究结果表明,TCN模型损伤评估准确率高达86.6%,评估效果优于CNN-LSTM模型,且具有更少的参数量,在噪声作用下也有较好的鲁棒性。Abstract: To accurately evaluate the post-earthquake damage state of regional reinforced concrete (RC) frame structures, a method based on Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks (TCN) is proposed. First, 48 RC frame structure models were designed by selecting structural height, X-span, seismic fortification intensity, and site category as key geometric parameters. Next, OpenSees software was used to calculate the acceleration response data of the structures during an earthquake. The maximum inter-layer displacement angle was introduced as the structural damage index, and a mapping relationship between this index and the acceleration response data was established to create the seismic damage dataset. A regional RC frame earthquake damage assessment model based on TCN was then developed, and the Bayesian optimization algorithm was employed to identify the optimal parameter combination for the model. The model’s damage assessment accuracy, computational efficiency, and generalization ability under noisy conditions were evaluated. The results show that the TCN model achieves a damage assessment accuracy of 86.6%, outperforming the CNN-LSTM model in terms of accuracy, parameter efficiency, and robustness under noise.
-
表 1 贝叶斯优化参数范围
Table 1. Parameter range of Bayesian optimization
模型名称 参数范围 L2正则化 学习率 卷积核尺寸 卷积块数量 残差块数量 CNN-LSTM [10−4,10−1] [10−4,10−1] [27,35] [1,3] — TCN [10−4,10−1] [10−4,10−1] [3,7] — [5,8] 表 2 框架结构模型结构特征参数
Table 2. Structural characteristic parameters of frame structure model
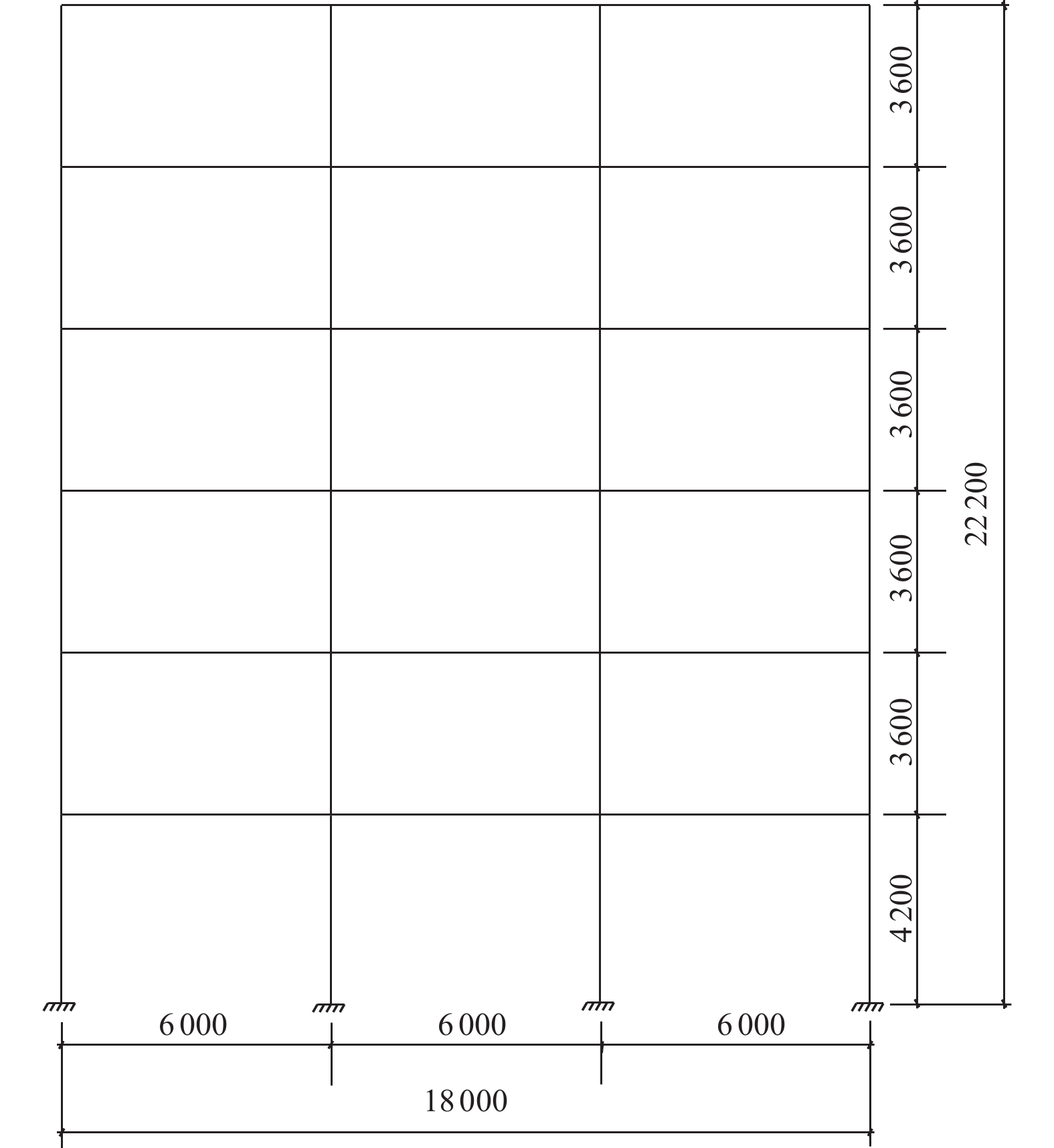
项目 结构特征参数 参数取值范围 几何参数 结构层数/层 4、6、8、10 x向跨度/m 6、8 设计参数 抗震设防烈度 7、8 场地类别 Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ 表 3 不同性能状态下最大层间位移角限值
Table 3. Limits of maximum interlayer displacement angle under different performance states
结构性能状态 轻度损伤
(第1类)中度损伤
(第2类)重度损伤
(第3类)最大层间位移角限值/rad ≤1/200 1/200~1/100 >1/100 表 4 各数据集中加速度响应数据量
Table 4. Data amount of acceleration response in each data set
项目 训练集 验证集 测试集 地震波/条 12 4 4 数据量/组 18 640 4 460 7 000 表 5 CNN-LSTM和TCN模型性能对比
Table 5. Comparison of performance between CNN-LSTM model and TCN model
模型名称 参数量/kb 时间/s 最优准确率/% CNN-LSTM 15 380 099 3 042.2 80.4 TCN 12 419 1 946.0 86.6 -
邓夕胜,赖馨粤,袁凯等,2022. 罕遇地震下高层RC框架结构双地震动强度参数易损性分析. 世界地震工程,38(3):19−29.Deng X. S., Lai X. Y., Yuan K., et al., 2022. Vulnerability analysis of multipleground motion intensity measure rectors for high-rise RC frame structure under rare earthquake. World Earthquake Engineering, 38(3): 19−29. (in Chinese) 韩小雷,吴梓楠,杨明灿等,2020. 基于深度学习的区域RC框架结构震损评估方法研究. 建筑结构学报,41(S2):27−35.Han X. L., Wu Z. N., Yang M. C., et al., 2020. Research on seismic damage assessment of regional RC frame structures based on deep learning. Journal of Building Structures, 41(S2): 27−35. (in Chinese) 李加笑,2023. 基于误差修正的RF-TCN-SA超短期风电功率预测模型. 西安:西安理工大学.Li J. X., 2023. Wind power ultra-short-term prediction model of RF-TCN-SA based on error correction. Xi'an:Xi'an University of Technology. (in Chinese) 任彦洁,唐晓刚,张斌权,等,2023. 基于时间卷积网络的通信信号调制识别算法. 无线电工程,53(4):807−814.Ren Y. J., Tang X. G., Zhang B. Q., et al., 2023. Communication signal modulation recognition algorithm based on temporal convolutional network. Radio Engineering, 53(4): 807−814. (in Chinese) 谢丰蔚,2015. 地震动记录选择和调幅方法的研究及评价. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学.Xie F. W., 2015. Study and evaluation on selecting and scaling of ground motions. Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology. (in Chinese) 叶珊珊,翟国方,2010. 地震经济损失评估研究综述. 地理科学进展,29(6):684−692. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.06.007Ye S. S., Zhai G. F., 2010. A review on seismic economic loss estimation. Progress in Geography, 29(6): 684−692. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.06.007 尹之潜,杨淑文,2004. 地震损失分析与设防标准. 北京:地震出版社,87−92. 周航,程泽,弓清瑞,等,2023. 基于TCN编码的锂离子电池SOH估计方法. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),50(4):185−192.Zhou H., Cheng Z., Gong Q. R., et al., 2023. SOH estimation method of lithium-ion battery based on TCN encoding. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 50(4): 185−192. (in Chinese) 左占宣,李爽,翟长海等,2019. 结构周期延长对倒塌分析中地震动强度指标选择的影响. 建筑结构学报,40(5):141−148.Zuo Z. X., Li S., Zhai C. H., et al., 2019. Influence of structural period elongation on ground motion intensity index in collapse analysis. Journal of Building Structures, 40(5): 141−148. (in Chinese) Lea C. , Vidal R. , Reiter A. , et al. , 2016. Temporal convolutional networks: a unified approach to action segmentation. In: Computer Vision – ECCV 2016 Workshops. Amsterdam: Springer, 47−54. Lu X. Z., Xu Y. J., Tian Y., et al., 2021. A deep learning approach to rapid regional post‐event seismic damage assessment using time‐frequency distributions of ground motions. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 50(6): 1612−1627. Wang C., Xia Y., Wang D. Y., et al., 2021. Dynamic risk assessment of deep-water dual gradient drilling with SMD system using an uncertain DBN-based comprehensive method. Ocean Engineering, 226: 108701. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108701 Xiong C., Zheng J., Xu L. J., et al., 2021. Multiple-input convolutional neural network model for large-scale seismic damage assessment of reinforced concrete frame buildings. Applied Sciences, 11(17): 8258. doi: 10.3390/app11178258 Xu Y. J., Lu X. Z., Cetiner B., et al., 2021. Real-time regional seismic damage assessment framework based on long short-term memory neural network. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 36(4): 504−521. doi: 10.1111/mice.12628 -



 下载:
下载: