Seismic Characteristics and Optimal Design of Ballastless Track Simply-rigid-frame Composite Girder Bridge
-
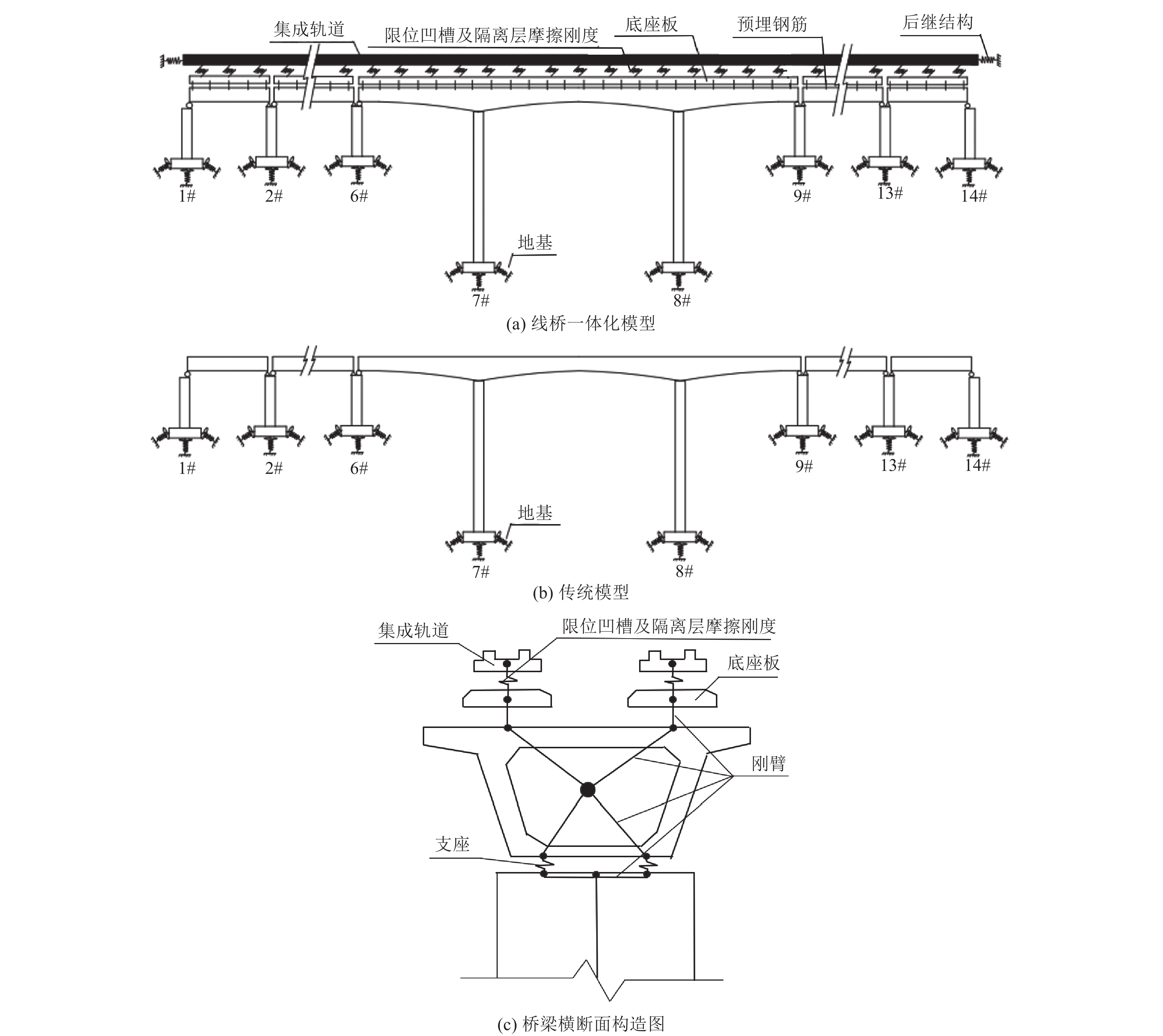
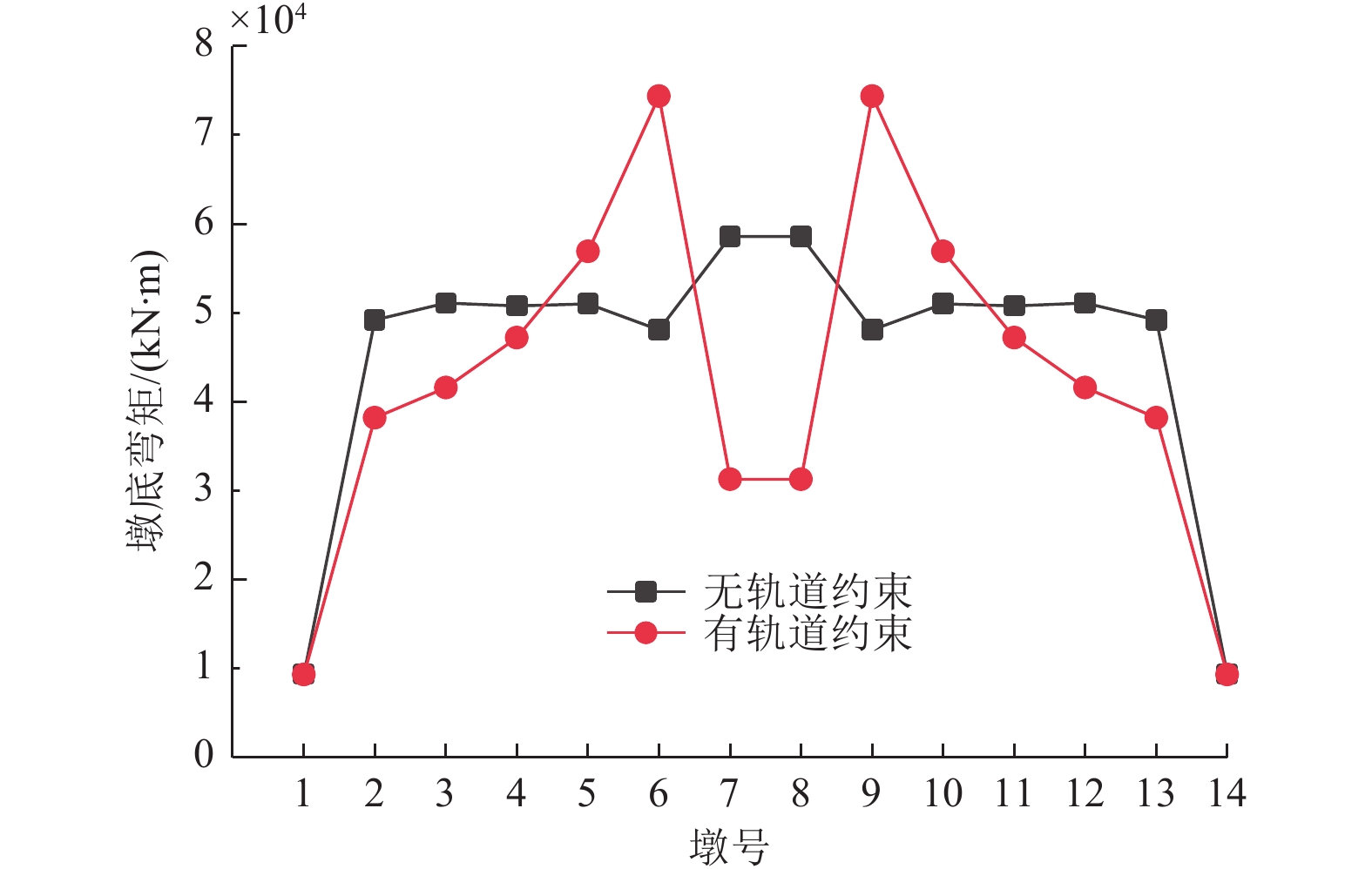
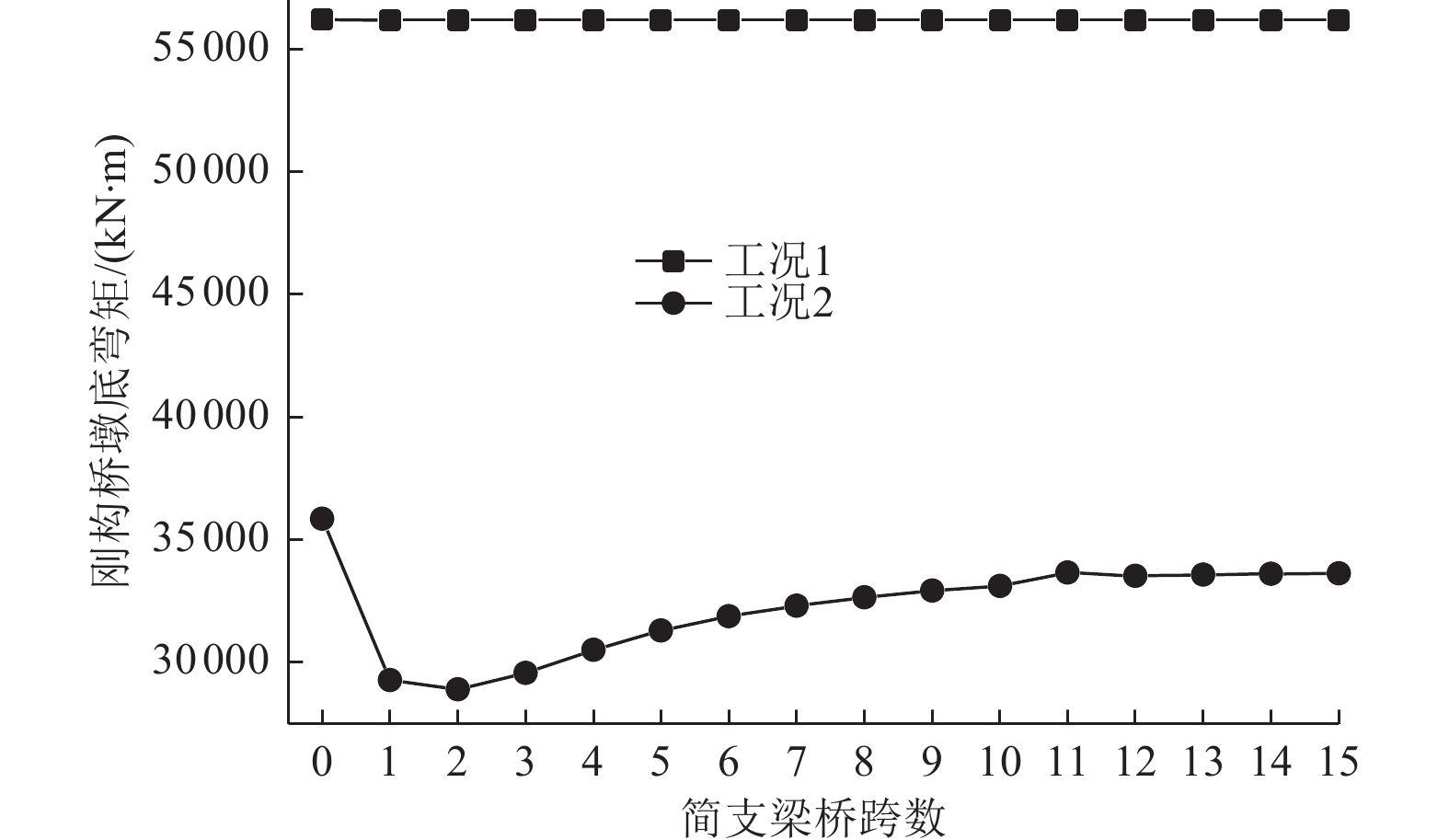
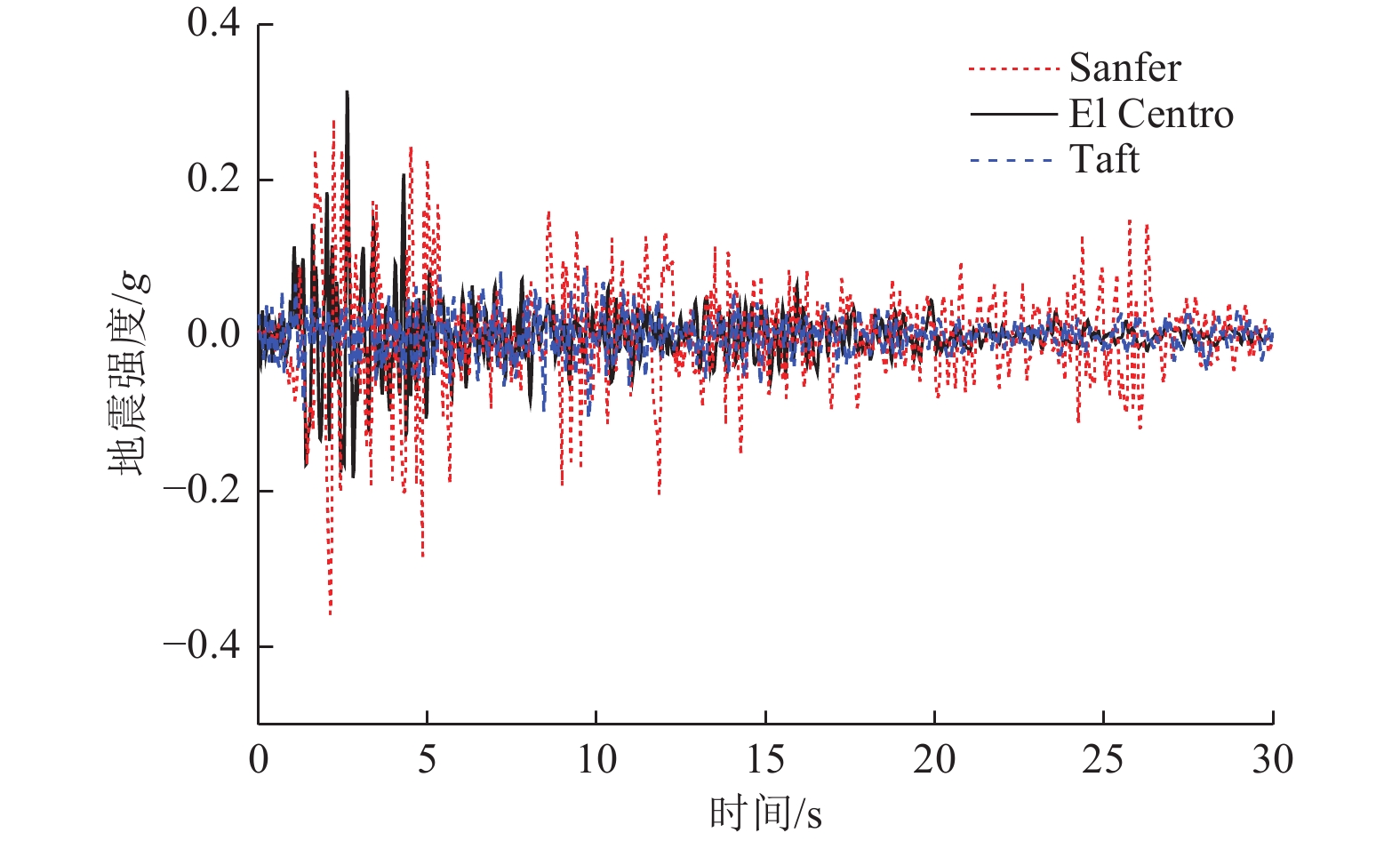
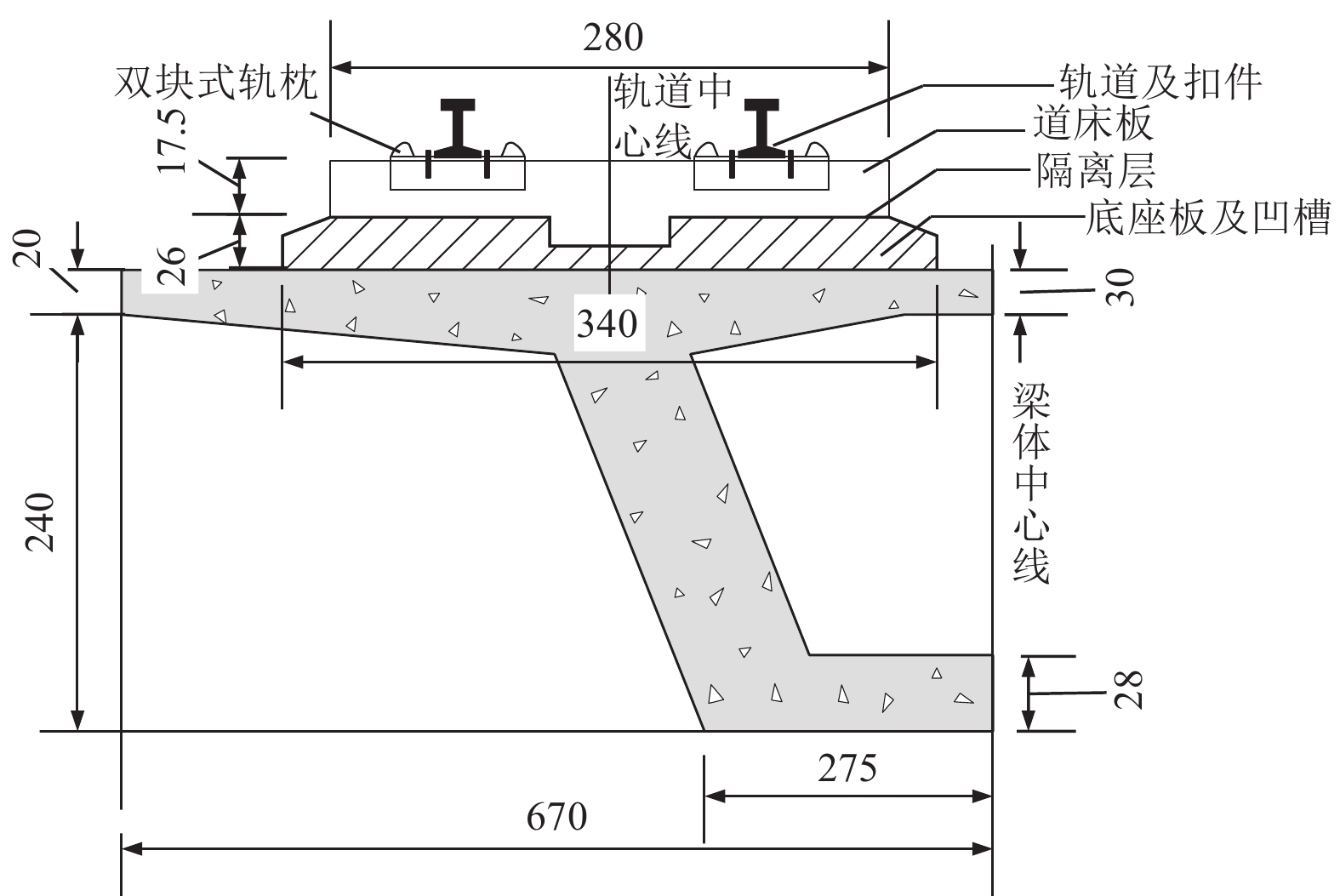
摘要: 为探究高速铁路简支-刚构组合梁桥抗震优化设计方法,以我国西部地区一座跨越沟谷的高速铁路简支-刚构组合梁桥为实际工程背景,建立考虑CRTS Ⅰ型双块式无砟轨道的简支-刚构组合梁桥线桥一体化计算模型。采用反应谱法、非线性时程法及IDA法对比分析了线桥一体化模型和传统模型的抗震特性并进行优化设计。结果表明:①轨道约束改变了桥梁体系的受力行为和高、低阶振型对桥梁动力特性的影响;②对刚构桥进行抗震研究时,可选择邻近10~11跨简支梁桥作为边界条件,以消解桥跨数对刚构桥抗震性能的影响;③针对6度区地震及7度区小震、中震,刚构桥抗震研究建议不考虑轨道约束效应,而在8度、9度区中震及7度、8度、9度区大震中,轨道约束对刚构桥地震响应影响较大,进行抗震计算时建议考虑轨道约束效应;④轨道约束放大了过渡桥墩的地震响应,在过渡桥墩墩顶设置减隔震支座不仅能有效降低结构体系地震响应,同时节约其他桥跨减隔震支座的购买及施工成本;⑤轨道层间的传力及耗能部件主要是凹槽垫片和隔离层,为防止这些构件在能量传递过程中发生严重损伤,可考虑在轨道层间设置减隔震装置或植入耗能钢筋。Abstract: To explore the optimal seismic design method for simply-rigid-frame composite girder bridges in high-speed railways, this study takes a simply-rigid-frame bridge spanning a gully in western China as a case study. An integrated calculation model incorporating a CRTS Type I double-block ballastless track is developed. The response spectrum method, nonlinear time history analysis, and incremental dynamic analysis (IDA) method are used to compare the seismic characteristics of the integrated model and the traditional model, optimizing the seismic design. The key findings are as follows: ①Rail constraints alter the mechanical behavior of the bridge system, influencing both higher- and lower-order modes in the bridge’s dynamic response; ②In seismic research on rigid-frame bridges, selecting an adjacent 10- to 11-span simply supported beam bridge as the boundary condition eliminates the influence of bridge span count on seismic performance;③For seismic intensity zones of 6 degrees and small to moderate earthquakes in the 7-degree zone, rail constraints have minimal impact and can be neglected in seismic calculations. However, for moderate earthquakes in the 8-degree and 9-degree zones and large earthquakes in the 7-degree, 8-degree, and 9-degree zones, rail constraints significantly affect the seismic response of rigid-frame bridges and should be considered in seismic analysis; ④Rail constraints amplify the seismic response of transition piers. Installing seismic isolation bearings at the top of transition piers effectively reduces the structural seismic response while lowering the cost of seismic isolation supports for other bridge spans; ⑤The primary force transfer and energy dissipation components between track layers are fluted gaskets and isolation layers. To prevent severe damage during energy transfer, vibration reduction and isolation devices or energy-dissipating steel bars can be incorporated between track layers. These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing the seismic design of simply-rigid-frame composite girder bridges in high-speed railways.
-
表 1 各部件刚度取值
Table 1. Stiffness values of each component
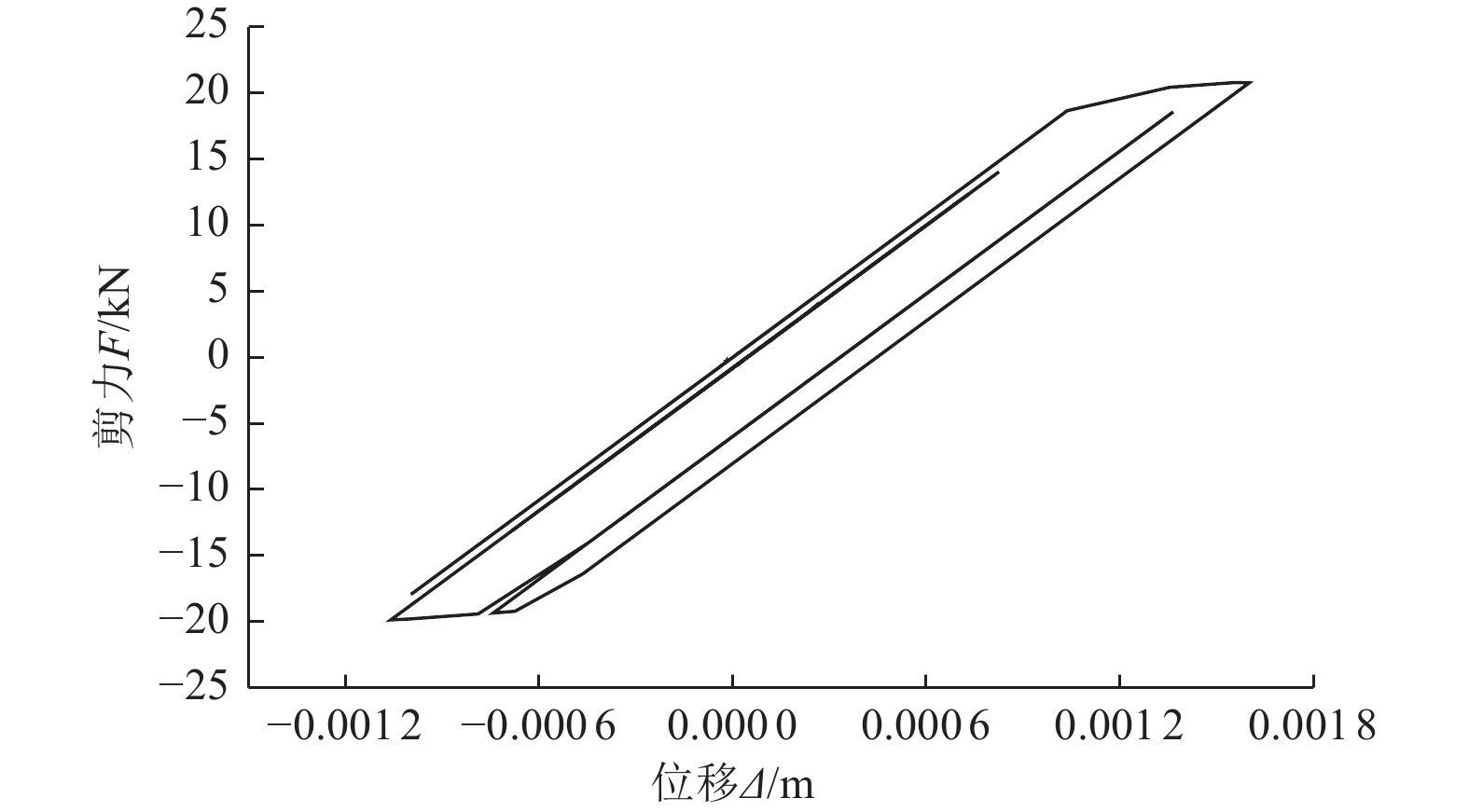
隔离摩擦层刚度/(kN·m−1) 凹槽垫片刚度/(kN·m−1) 后继结构刚度/(kN·m−1) 9.5 1.8×105 7.72×104 表 2 HRB335钢筋参数表
Table 2. HRB335 reinforcement parameters
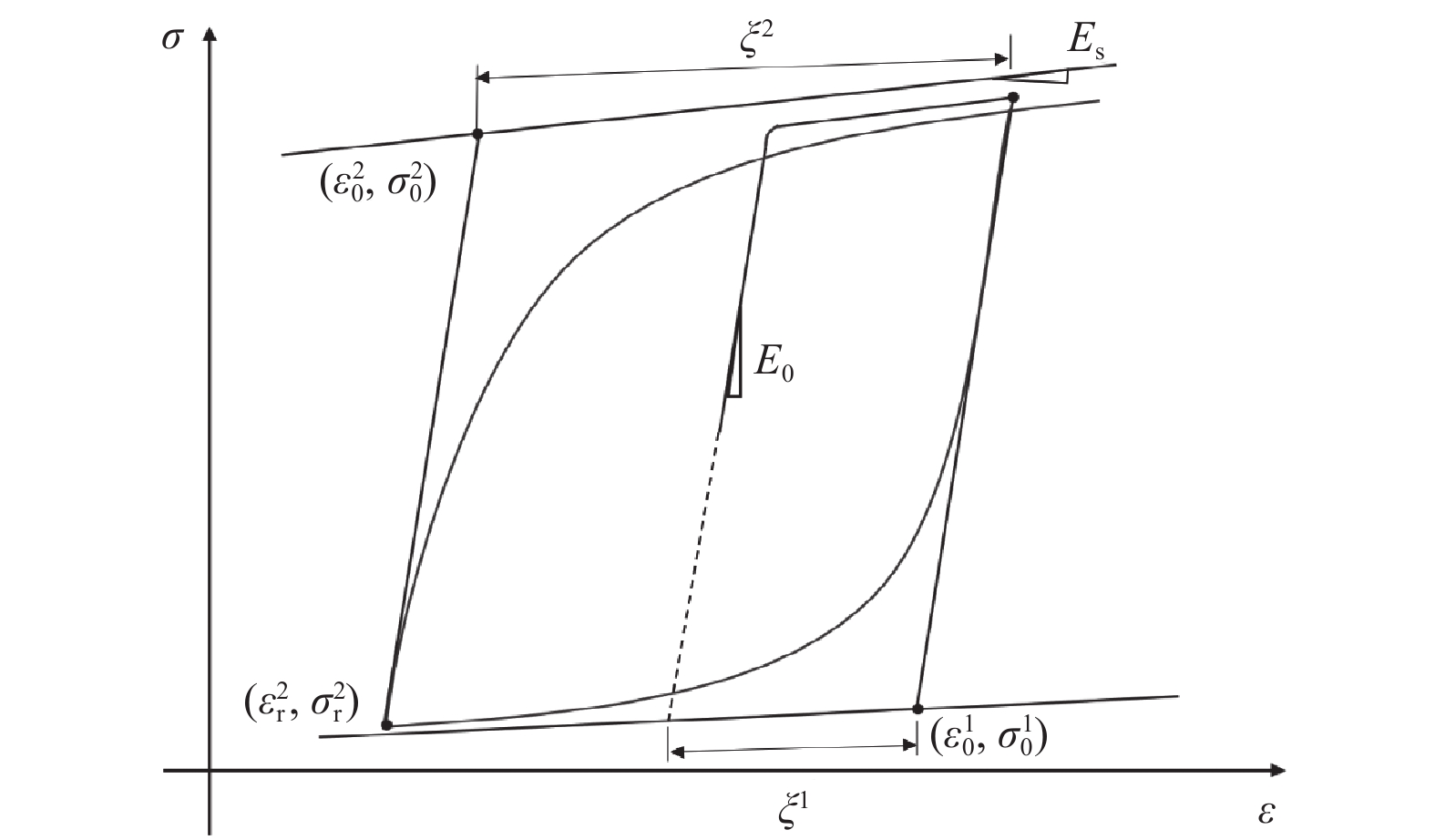
弹性模量E0/GPa 抗拉强度$ \mathit{\text{σ}}_0 $/MPa 横截面积b/m2 直径$ {{R}}_{\text{0}} $/mm 材料常数cR1 材料常数cR2 200 455 0.01 20 0.925 0.15 表 3 混凝土参数表
Table 3. Concrete parameters
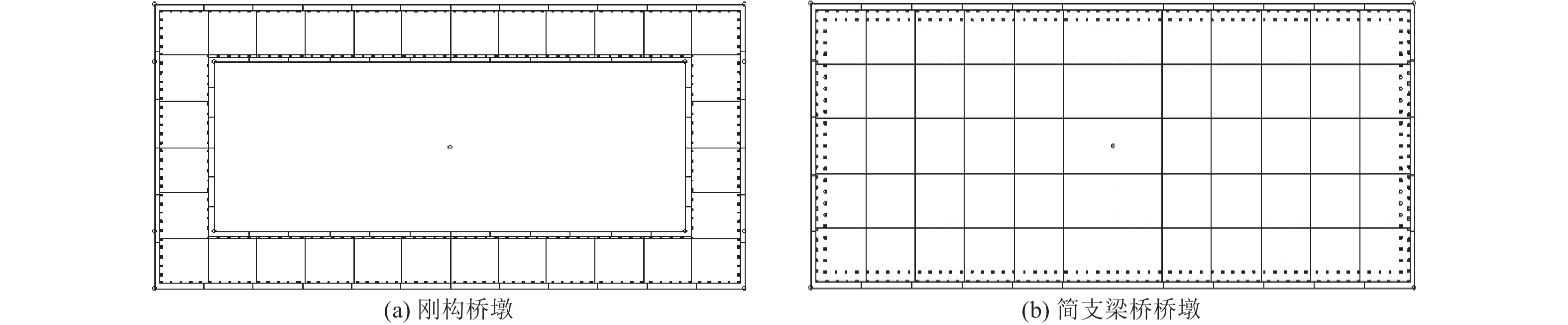
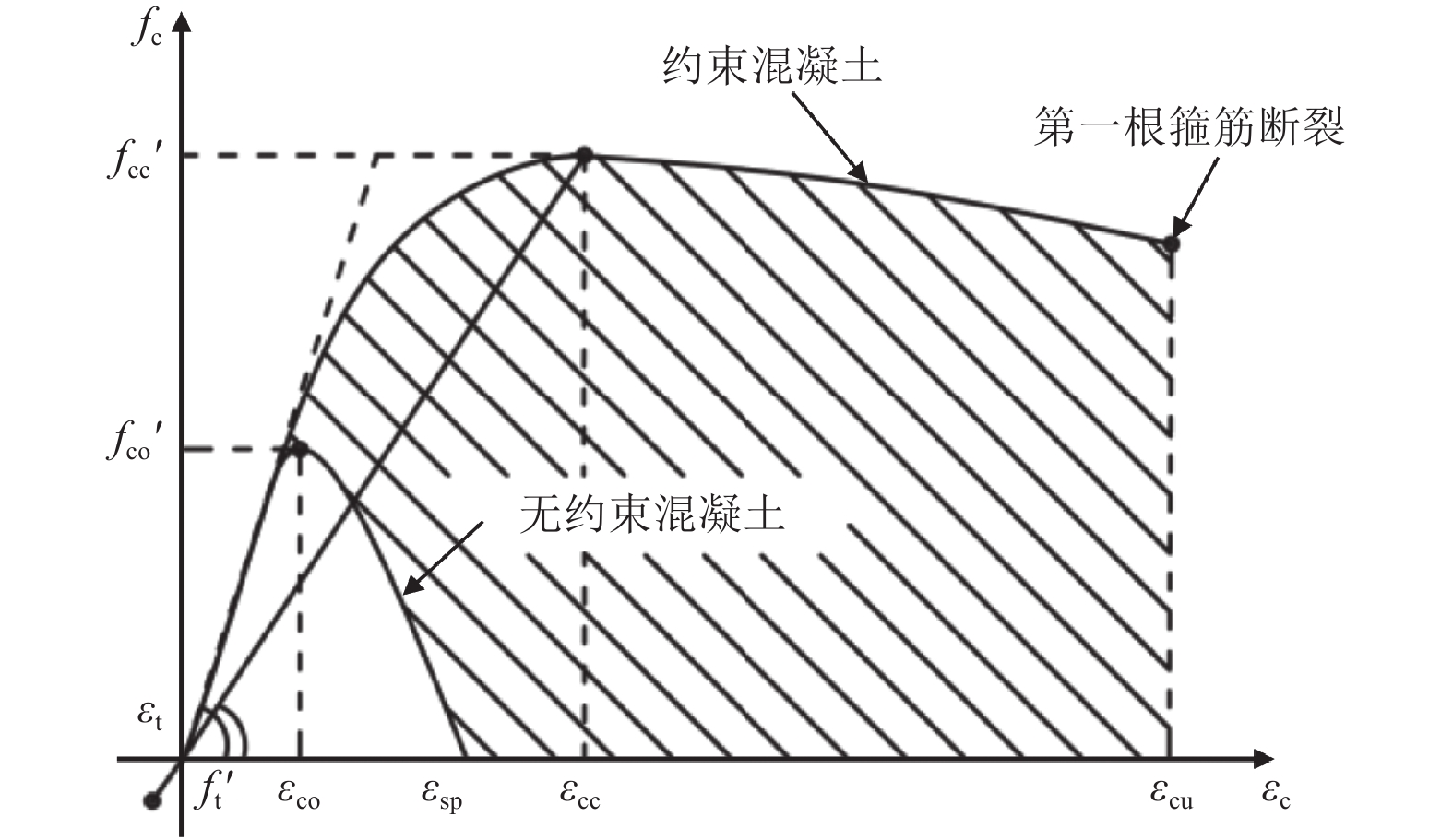
桥墩类型 $ f'_{{\mathrm{co}}} $/MPa $ f'_{{\text{cc}}}$/MPa 刚构桥墩 (C40) 35.5 41.4 简支梁桥桥墩 (C35) 30 36.5 表 4 2种模型的前10阶振型
Table 4. The first ten longitudinal natural vibration periods of two models
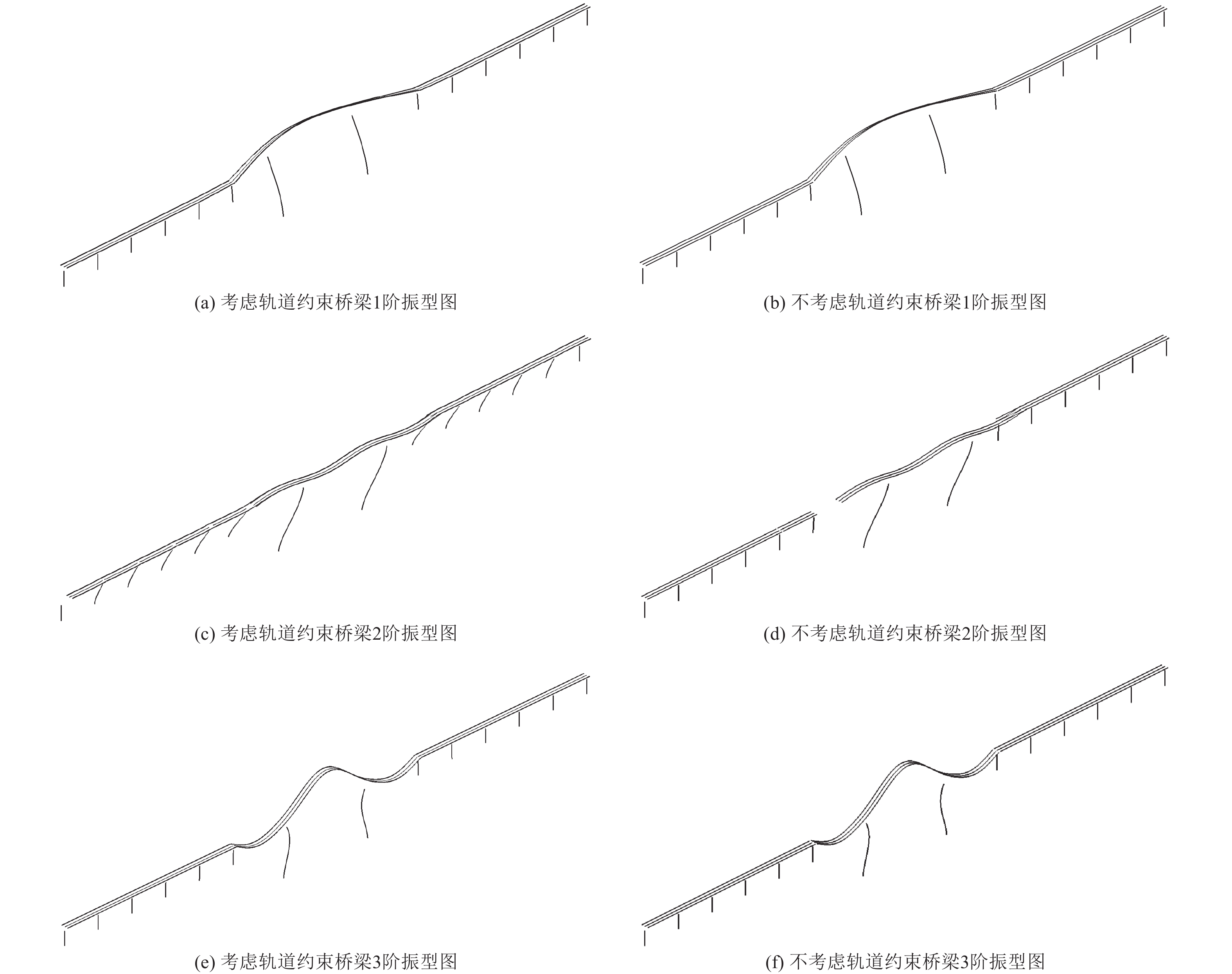
振型阶数 考虑轨道约束 不考虑轨道约束 自振周期/s 质量参与系数/% 振型 自振周期/s 质量参与系数/% 振型 1 1.107 0 桥梁横向正对称振动 1.362 30.84 桥梁横向正对称振动 2 0.507 72.98 桥梁纵向反对称振动 1.095 0 桥梁纵向反对称振动 3 0.486 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 0.482 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 4 0.441 0 桥梁横向反对称振动 0.432 0 桥梁横向反对称振动 5 0.280 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 0.307 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 6 0.274 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 0.307 49.07 桥梁纵向正对称振动 7 0.254 11.76 桥梁横向正对称振动 0.305 0 桥梁横向正对称振动 8 0.241 0 桥梁横向正对称振动 0.304 0 桥梁横向正对称振动 9 0.224 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 0.301 0 桥梁纵向正对称振动 10 0.187 0 桥梁横向正对称振动 0.302 3.3 桥梁横向正对称振动 表 5 水平设计地震基本加速度
Table 5. Basic earthquake acceleration of horizontal design
设计地震基本加速度/g 6度 7度 8度 9度 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.30 0.40 -
国巍,王阳,葛苍瑜等,2020. 近断层地震动下高速铁路多跨简支梁桥震致破坏特征. 振动与冲击,39(17):210−218.Guo W., Wang Y., Ge C. Y., et al., 2020. Seismic failure features of multi-span simply supported girder bridges of high-speed railway under near-fault earthquake. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 39(17): 210−218. (in Chinese) 焦习龙,王荣霞,马海龙等,2023. 断层走向对刚构桥地震反应的影响. 地震工程学报,45(1):50−57.Jiao X. L., Wang R. X., Ma H. L., et al., 2023. Influence of fault strike on the seismic response of rigid-frame bridges. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 45(1): 50−57. (in Chinese) 雷燕云,谢旭,2018. 修正的Giuffre-Menegotto-Pinto钢筋滞回本构模型. 浙江大学学报(工学版),52(10):1926−1934. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2018.10.012Lei Y. Y., Xie X., 2018. Improved method of Giuffre-Menegotto-Pinto hysteretic constitutive model. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 52(10): 1926−1934. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2018.10.012 梁岩,闫佳磊,班亚云等,2019. 多跨连续刚构桥梁地震易损性损伤指标计算方法. 铁道科学与工程学报,16(6):1466−1475.Liang Y., Yan J. L., Ban Y. Y., et al., 2019. Analysis of calculation method for seismic fragility index of multi span continuous rigid frame bridge. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 16(6): 1466−1475. (in Chinese) 刘尊稳,2020. 基于线桥一体化模型的高速铁路桥梁抗震性能及设计方法研究. 岩石力学与工程学报,39(5):1080.Liu Z. W., 2020. Research on seismic performance and design method for high-speed railway bridges based on track-bridge integrated model. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(5): 1080. (in Chinese) 卢永飞,秦亮,2020. T形刚构桥桥墩参数对车-桥动力响应影响研究. 震灾防御技术,15(4):718−730.Lu Y. F., Qin L., 2020. Study on influence of pier parameters of t-shaped rigid frame bridge on vehicle bridge dynamic response. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(4): 718−730. (in Chinese) 彭有开,吴超垚,于佳傲等,2020. 箍筋约束再生混凝土受压应力-应变本构关系模型. 建筑结构学报,41(12):174−183.Peng Y. K., Wu C. Y., Yu J. A., et al., 2020. Stress-strain constitutive model for stirrup-confined recycled concrete under compression. Journal of Building Structures, 41(12): 174−183. (in Chinese) 全伟,王东升,2018. 高烈度震区高速铁路中小跨桥梁结构选型研究. 桥梁建设,48(2):43−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.02.008Quan W., Wang D. S., 2018. Study of structural type selection for short and medium span high-speed railway bridges in high-intensity seismic region. Bridge Construction, 48(2): 43−48. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.02.008 王帅,宋帅,张巍,2021. 高承台下自由桩长对双薄壁墩连续刚构桥地震响应的影响. 世界地震工程,37(1):103−110.Wang S., Song S., Zhang W., 2021. Influence of free length of piles under high platform on seismic response of continuous rigid frame bridges with double thin-wall piers. World Earthquake Engineering, 37(1): 103−110. (in Chinese) 魏俊杰,邬晓光,2023. 结构参数对高低墩刚构连续梁桥体系地震响应的影响. 地震工程学报,45(6):1333−1342.Wei J. J., Wu X. G., 2023. Influence of structural parameters on the seismic response of rigid-frame continuous girder bridges with high and low piers. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 45(6): 1333−1342. (in Chinese) 喻梅,吕佳伟,贾宏宇等,2021. 近断层脉冲型地震作用下高速铁路桥梁-轨道系统响应分析. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),48(9):138−146.Yu M., Lü J. W., Jia H. Y., et al., 2021. Response analysis of high-speed railway bridge-rail system subjected to near-fault pulse-type earthquake. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 48(9): 138−146. (in Chinese) 张永亮,王云,陈兴冲等,2018. 双薄壁墩连续刚构桥地震反应影响参数分析. 桥梁建设,48(4):17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.04.004Zhang Y. L., Wang Y., Chen X. C., et al., 2018. Analysis of parameters having influence on seismic responses of continuous rigid-frame bridges with double thin-wall piers. Bridge Construction, 48(4): 17−21. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.04.004 张玥,薛磊,陈帅等,2020. 地震作用下高烈度区连续刚构桥参数敏感性分析. 地震工程学报,42(2):311−317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.02.311Zhang Y., Xue L., Chen S., et al., 2020. Parameter sensitivity analysis of continuous rigid-frame bridges in high seismic intensity regions under seismic action. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(2): 311−317. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.02.311 赵金钢,贾宏宇,占玉林,2023. 近场旋转地震波对多跨高墩连续刚构桥地震易损性的影响. 振动与冲击,42(1):146−159.Zhao J. G., Jia H. Y., Zhan Y. L., 2023. Effects of near-field rotating seismic waves on seismic vulnerability of multi-span high-pier continuous rigid frame bridge. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 42(1): 146−159. (in Chinese) 周旺保,彭东航,蒋丽忠等,2023. 横向地震作用下高速铁路CRTS Ⅲ型无砟轨道-桥梁系统震致轨道不平顺研究. 铁道科学与工程学报,20(8):2773−2784.Zhou W. B., Peng D. H., Jiang L. Z., et al., 2023. Study on track irregularity of CRTS Ⅲ ballastless track-bridge system of high-speed railway under transverse earthquake. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 20(8): 2773−2784. (in Chinese) Gao Q., Yang M. G., Meng D. L., 2023. Seismic optimization of high-speed railway bridges considering the running safety of trains in normal service. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 19(9): 1283−1298. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2021.2023587 Guo W., Gao X., Hu P., et al., 2020. Seismic damage features of high-speed railway simply supported bridge–track system under near-fault earthquake. Advances in Structural Engineering, 23(8): 1573−1586. doi: 10.1177/1369433219896166 Jiang L. Z., Zhang Y. T., Feng Y. L., et al., 2020. Simplified calculation modeling method of multi-span bridges on high-speed railways under earthquake condition. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 18(5): 2303−2328. doi: 10.1007/s10518-019-00779-x Liu W. S., Lai H., Dai G. L., et al., 2021. Numerical study on track–bridge interaction of integral railway rigid-frame bridge. Applied Sciences, 11(3): 922. doi: 10.3390/app11030922 Livingston E., Sasani M., Bazan M., et al., 2015. Progressive collapse resistance of RC beams. Engineering Structures, 95: 61−70. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.03.044 Zhou W. B., Peng D. H., Liu L. L., et al., 2023. Transverse seismic analysis of high-speed railway bridge in China based on a simplified calculation model. Journal of Central South University, 30(1): 351−364. doi: 10.1007/s11771-023-5226-7 -



 下载:
下载: