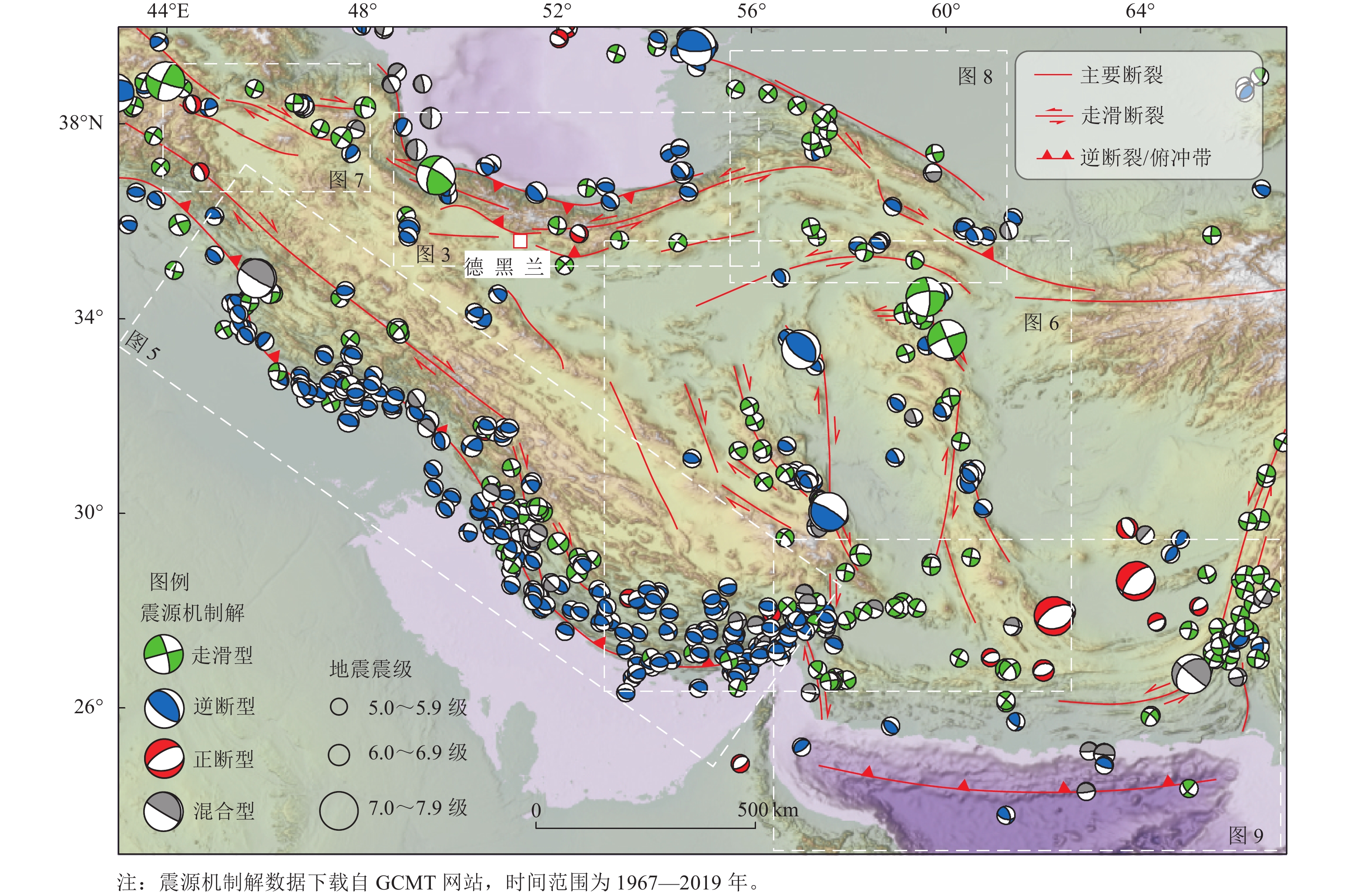
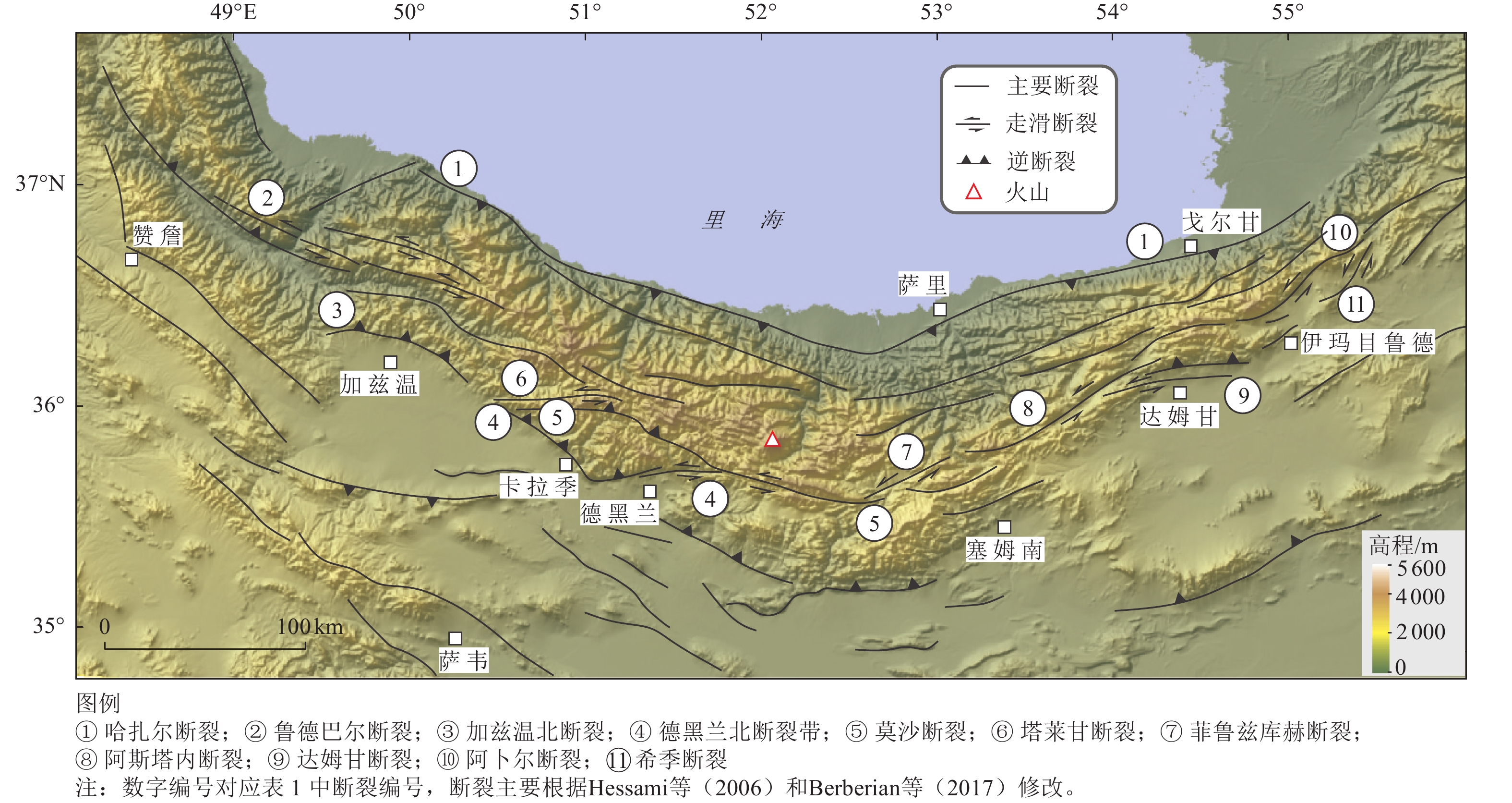
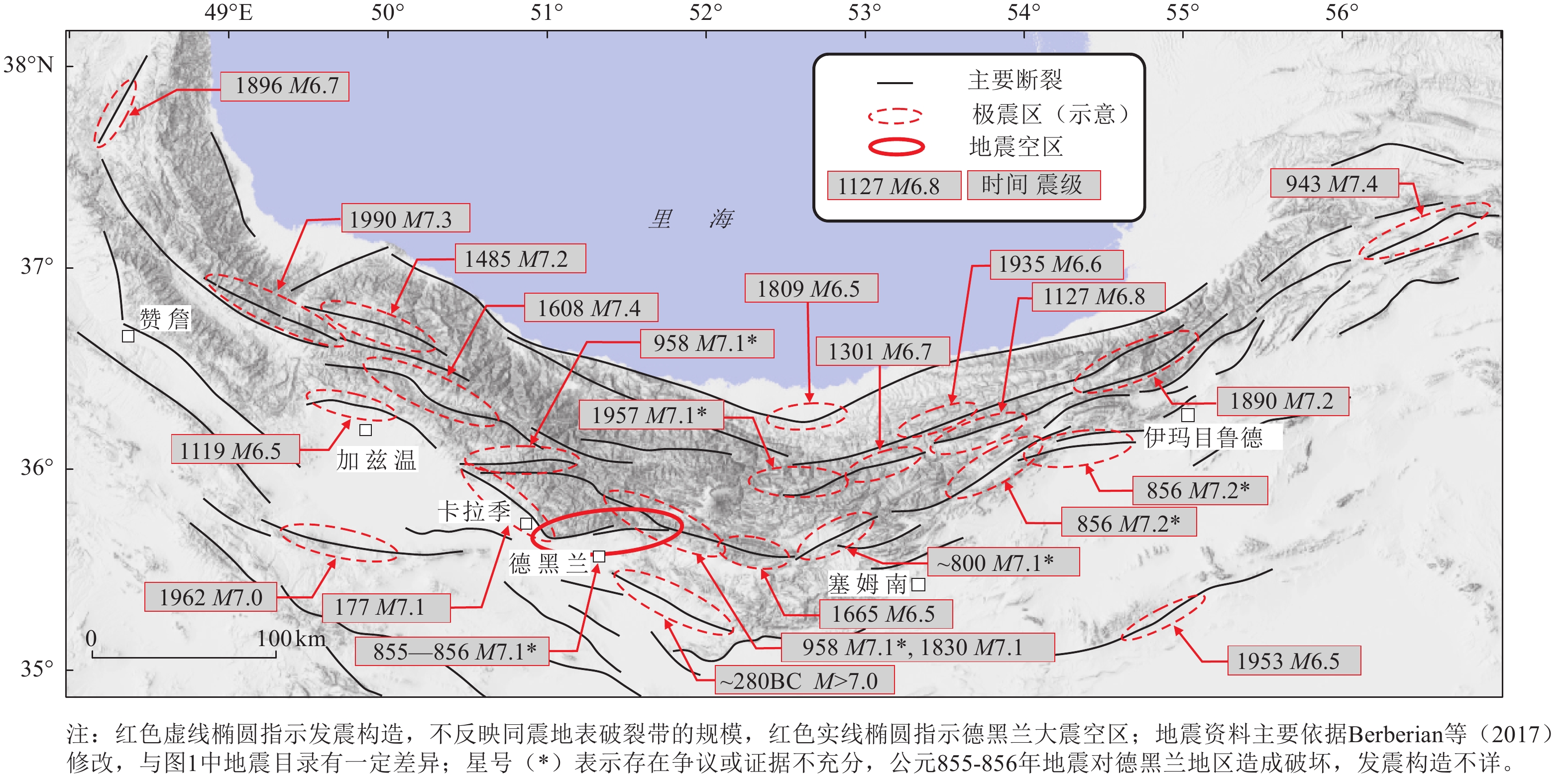
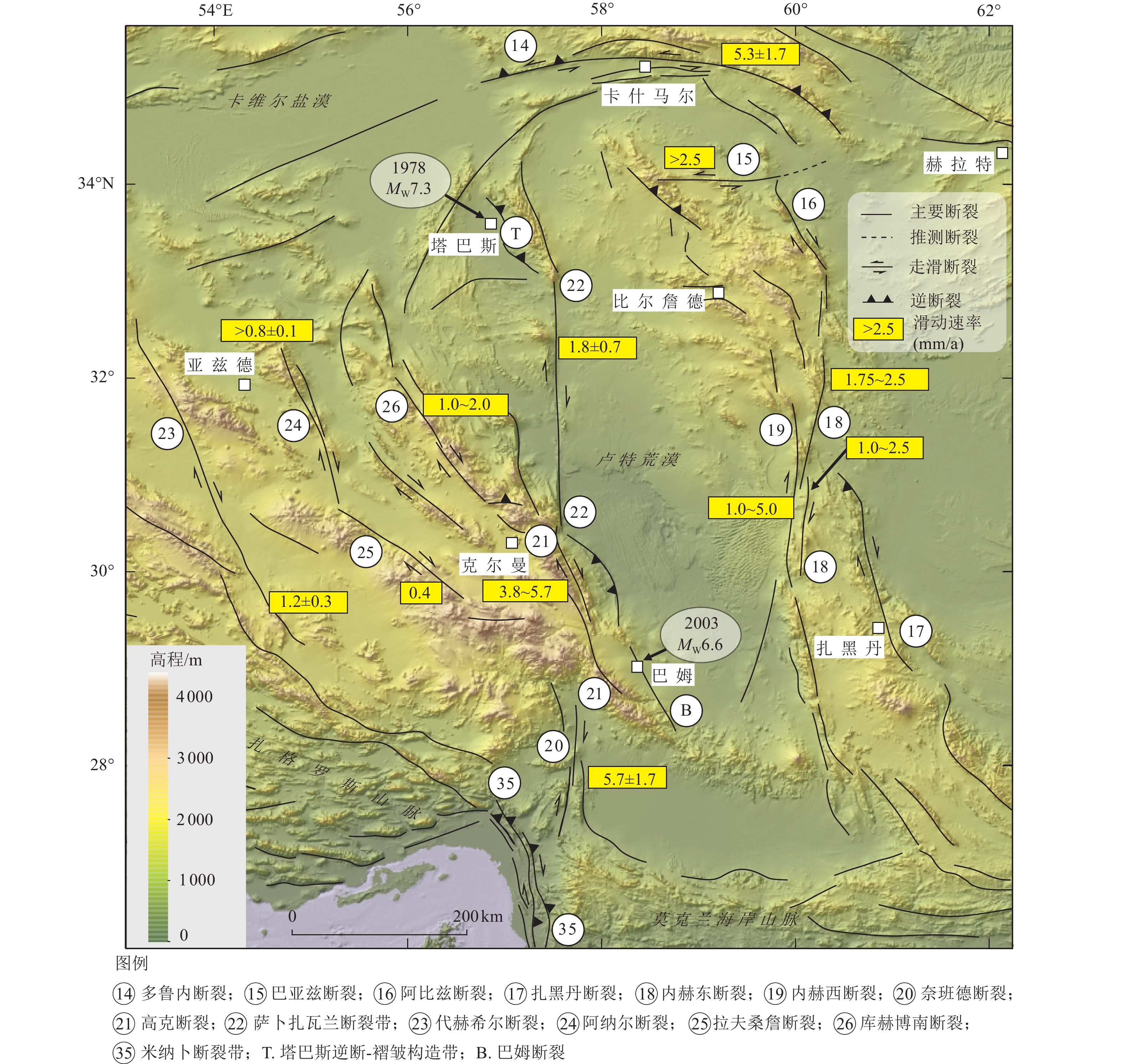
Characteristic features on Iranian Active Tectonics
-
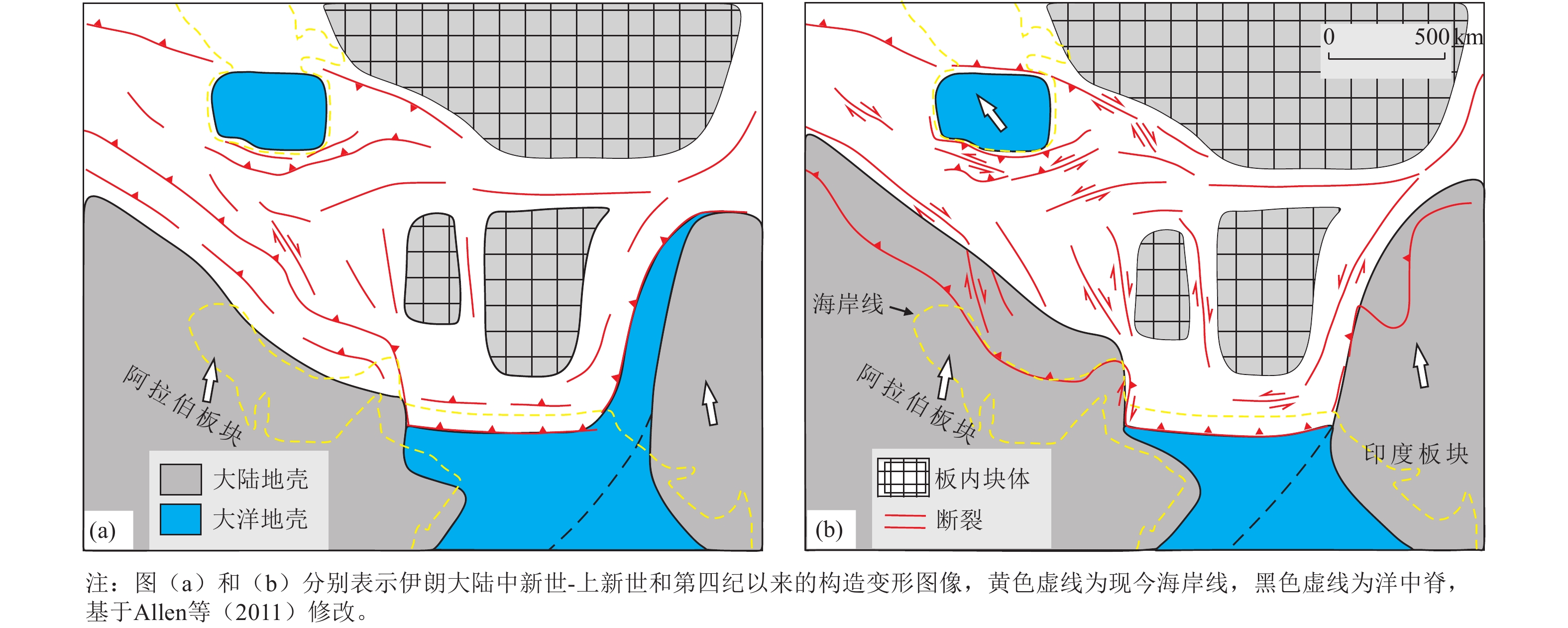
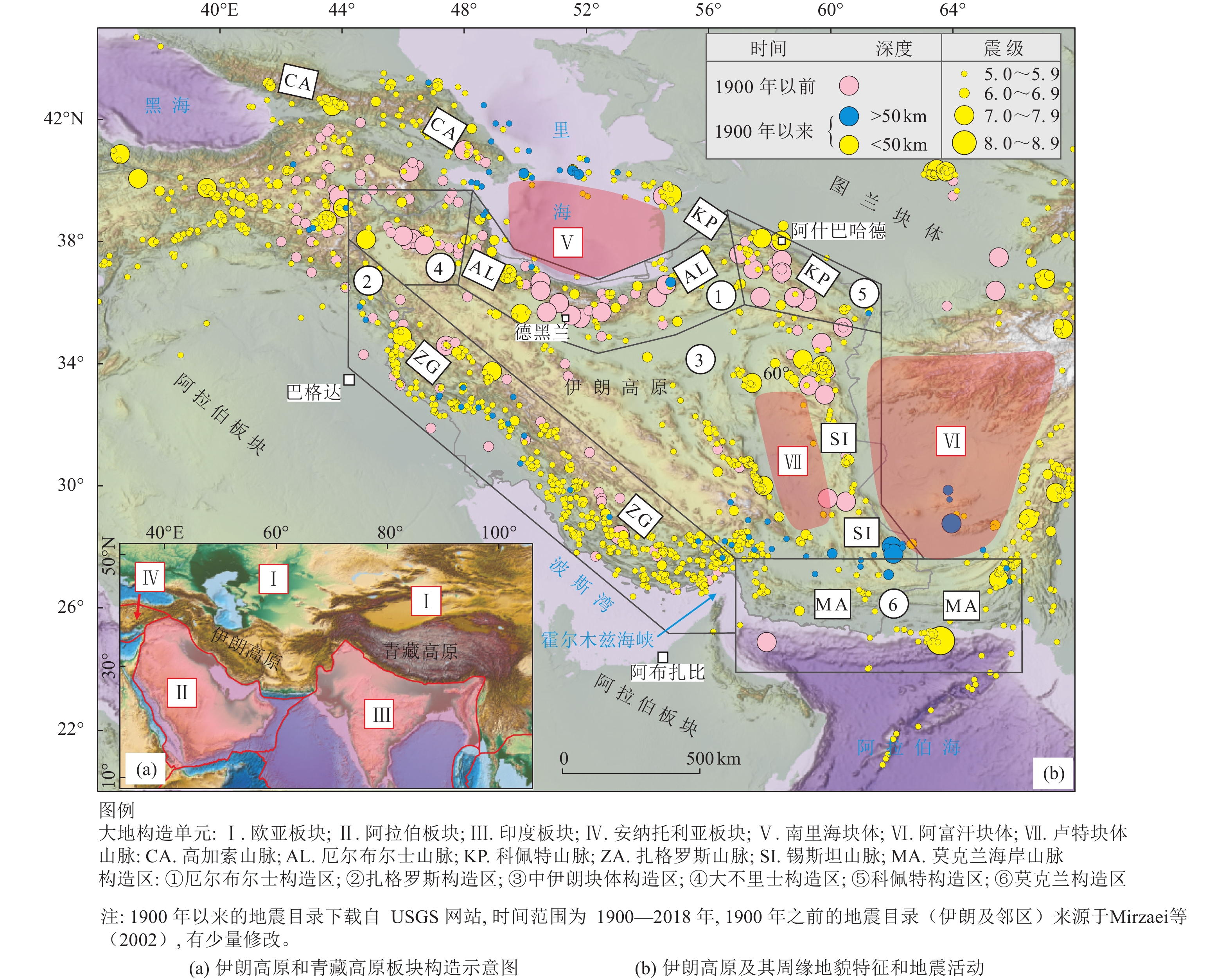
摘要: 伊朗是地震灾害频发的国家之一,有丰富的历史地震记载。按照构造特征与地震活动性的差异可将伊朗划分为6个地震构造区,包括北部的厄尔布尔士构造区、南部的扎格罗斯构造区和莫克兰构造区、中部的中伊朗块体构造区、大不里士构造区以及科佩特构造区,本文简要介绍了各构造区主要活动构造的基本特征和相应地震活动。受新生代阿拉伯板块与欧亚板块碰撞控制,伊朗地区处于挤压构造环境,活动构造以走滑和逆断-褶皱变形为主。根据活动构造特征和地震记录,伊朗地区的主要活动(断裂)构造具有发生7~7.5级地震的发震能力,莫克兰俯冲带具有发生≥8.0级地震的发震能力。伊朗北部主要城市德黑兰和大不里士面临着严峻的地震灾害风险,德黑兰北断裂带和大不里士断裂分别是威胁2个城市的主要活动断裂。伊朗的活动构造研究和防震减灾工作较为薄弱,可进一步加强历史地震与古地震研究、城市活动断层 探测、活断层避让等工作。伊朗高原是研究青藏高原新生代演化的参照模型,中-伊两国都面临着长期的地震风险,两国之间有必要加强防震减灾国际合作,中国研究者可以更广泛地参与伊朗地区的活动构造研究。Abstract: Located in the Alpine-Himalaya seismic zone, Iran suffers from intense earthquake disasters, and there is a wealthy and diverse record of historical earthquakes which can go back for more than two thousand years witnessed by the Iranian civilization. On the basis of tectonic feature, geomorphology and seismicity, we divide Iran and adjacent areas into six tectonic provinces, namely Alborz seismic region in the north, Zagros region in the southwest, Central Iranian block region, Makran region in the southeast, Tabriz region in the northwest and Kopeh Dagh region in the northeast. Then, we briefly present the basic characteristics of major active tectonics in each seismic regions accompanied by main seismic activities. Dictated by the collision-subduction between Arabian plate and Eurasia plate in Cenozoic, Iranian active tectonics are feathered by widespread regional strike-slip and reverse faults which define a compressive kinematic regime. According to the nature of active tectonics and seismicity, major active tectonics in mainland Iran are capable of generating earthquakes with magnitudes of MW7.0~7.5. Meanwhile, the Makran subduction zone could bear great earthquakes with magnitudes larger than MW8.0. Cities in northern Iran, especially Tehran and Tabriz, are confronted with severe earthquake disaster risk. The Tehran North fault zone and Tabriz North fault are the major active faults that threaten Tehran and Tabriz, respectively. The current active tectonic research and earthquake disaster relief work in Iran is insufficient, thus it is strongly recommended that more efforts, such as paleo-seismological research, active fault survey and prospect in urban areas, active fault avoidance strategy, should be applied throughout the whole country. Iranian plateau, built during the continent collision between Eurasia plate and Arabia plate, can serve as a reference model of Tibetan Plateau, which will no doubt improve our knowledge on the Cenozoic tectonic evolutionary history of mainland China. China and Iran both face perpetual earthquake disaster risks, which calls for a more robust international cooperation in the field of protection against and mitigation of earthquake disasters. China could participate extensively in Iranian active tectonic researches and earthquake mitigation work.
-
Key words:
- Iranian plateau /
- Active tectonics /
- Seismicity /
- Alborz tectonic province /
- Zagros tectonic province
-
表 1 伊朗地区主要活动构造特征一览表
Table 1. Characteristics of major active tectonics in Iran
编号 断裂名称 英文名称 性质 走向 长度/km 累积位
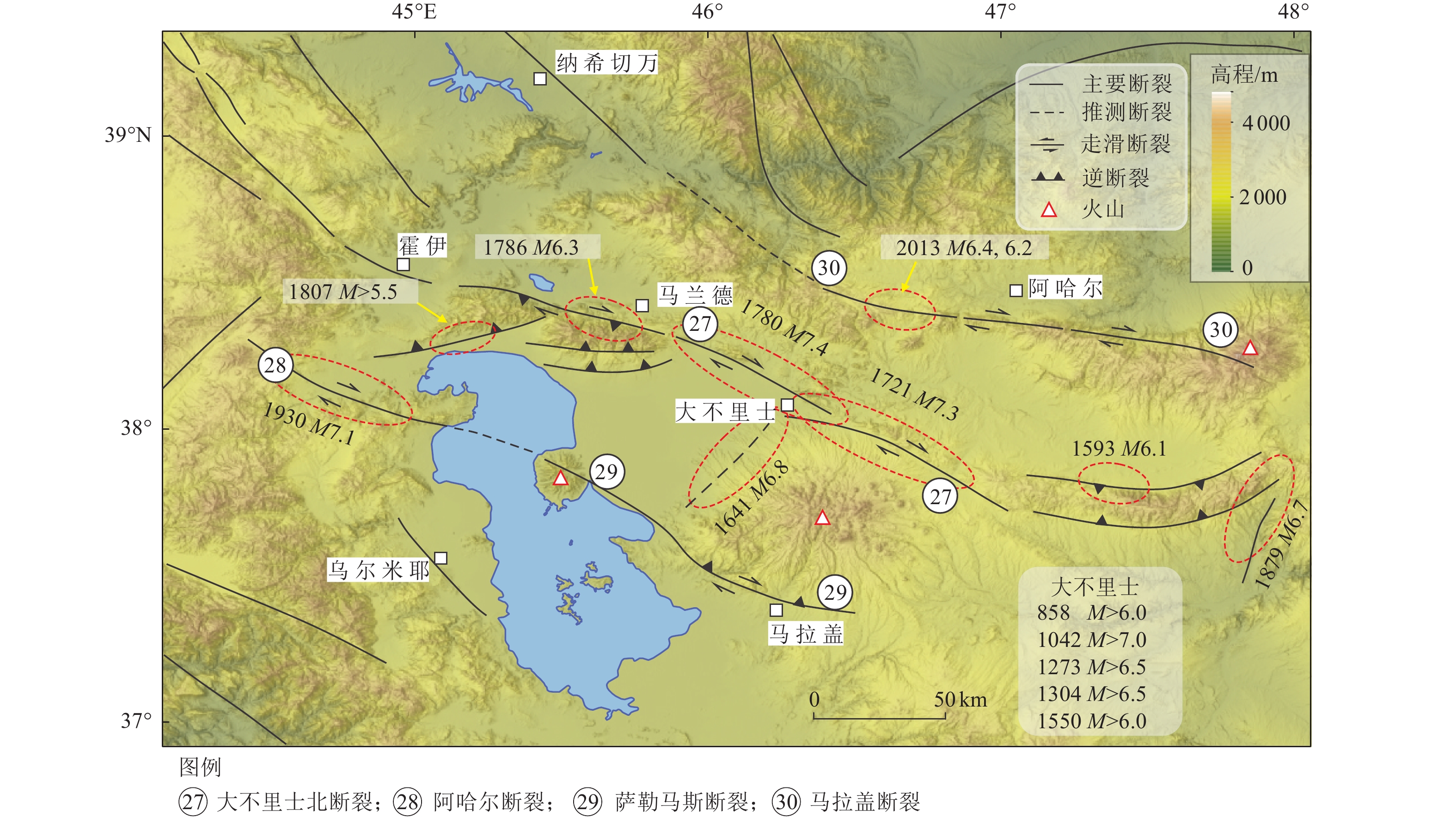
错/km滑动速率/(mm·a−1) 地震活动 水平 垂直 F1 哈扎尔断裂 Khazar 逆断 V型 >500 − − 2.0±0.5 1809年M6.5;2004年5月28日MW6.2 F2 鲁德巴尔断裂 Rudbar 左旋走滑 NW 80 1.0 − − 1990年6月20日MW7.3(>80 km) F3 加兹温北断裂 Qazvin 逆断 NWW-NW 60 − − − 1119年12月10日M6.5 F4 德黑兰北断裂带 North Tehran 左旋逆断 V型 >120 1.0~9.5 − − NE1177年5月1-30日M7.1? F5 莫沙断裂 Mosha 左旋逆断 EW弧形 200 3.0~6.5 2.0 − 958年2月23M7.1?;1665年6-7月M6.5;1830年3月27日M7.0 F6 塔莱甘断裂 Taleghan 左旋正断 EW 80 0.45(V) 0.6~1.6 0.5 958年2月23日 M7.1*? F7 菲鲁兹库赫断裂 Firzuzkuh 左旋走滑 NNE 55 − 1.1~2.2 − 763–819年M7.1*?;
1990年1月20日MW5.9F8 阿斯塔内断裂 Astaneh 左旋走滑 NE-EW >100 − 1.7~2.2 − 12 ka以来3次古地震事件,
最新事件对应856年M7.2*?F9 达姆甘断裂 Damghan 左旋走滑 NE-EW >80 − − − 856年12月22日M7.2? F10 阿卜尔断裂 Abr 左旋走滑 NE 95 − 3.2±0.5 − 无强震资料 F11 希季断裂 Khij 左旋走滑 NE 55 − 1.0~2.4 0.07 无强震资料 F12 扎格罗斯主近断裂 Zagros Main Recent 右旋走滑 NW >600 16~50 3.5~12.5 − 1909年1月23日MW7.4(>40);
1957年12月13日MW6.8;
1958年8月16日MW6.6(20)F13 卡泽伦断裂 Kazerun 右旋走滑 N-S 300 >8 S 2.5~4.0;M 1.5~3.5 − 5~6级地震活动 F14 多鲁内断裂 Doruneh 左旋走滑 EW弧形 400 − 5.3±1.7 − 13世纪以来无强震资料 F15 巴亚兹断裂 Dasht-e Bayaz 左旋走滑 EW 120 4~5 >2.5 − 1968年8月31日MW7.1(80);
1979年11月27日MW7.1(68)F16 阿比兹断裂 Abiz 右旋走滑 NNW 125 − − − 1936年6月30日MW6.0;1979年
11月14日MW6.6(20);1997年5月
10日MW7.2(125)F17 扎黑丹断裂 Zahedan 右旋走滑 N-S 150 13~20 − − 断裂北端逆断裂1994年
2月23日MW6.2F18 内赫东断裂 EastNeh 右旋走滑 N-S 200 50 N 1.75~2.5;S 1.0~2.5 − 无强震资料 F19 内赫西断裂 WestNeh 右旋走滑 N-S 200 10 1.0~5.0 − 无强震资料 F20 奈班德断裂 Nayband 右旋走滑 N-S 290 2~4 1.8±0.7 − 6.5 ka*,6.7 ka*,<0.74 ka*;断裂以北塔巴斯1978年9月16日MW7.3 F21 高克断裂 Gowk 右旋走滑 NNW >150 12~15 3.8~5.7 − 1981年6月11日MW6.6(15);
1981年7月28日MW7.0(65);
1998年3月14日MW6.6(23)F22 萨卜扎瓦兰断裂带 Sabzevran-Jiroft 右旋逆断 N-S 150 − 5.7±1.7 − 无强震资料 F23 代赫希尔断裂 Dehshir 右旋走滑 NNW 400 65±15 1.2±0.3 − 2.8±1.4 ka,~2.0±0.2 ka*,
6000年复发周期F24 阿纳尔断裂 Anar 右旋走滑 NNW 200 25±5 >0.8±0.1 − 9.8±2.0,6.8±1.0,4.4±0.8 ka*,2000~5000年复发周期 F25 拉夫桑詹断裂 Rafsanjan 右旋走滑 NW 200 − 0.4 − 无强震资料 F26 库赫博南断裂 Kuh Banan 右旋走滑 NNW 180 5~7 1.0~2.0 − 1933年11月28日MW6.2;1977年
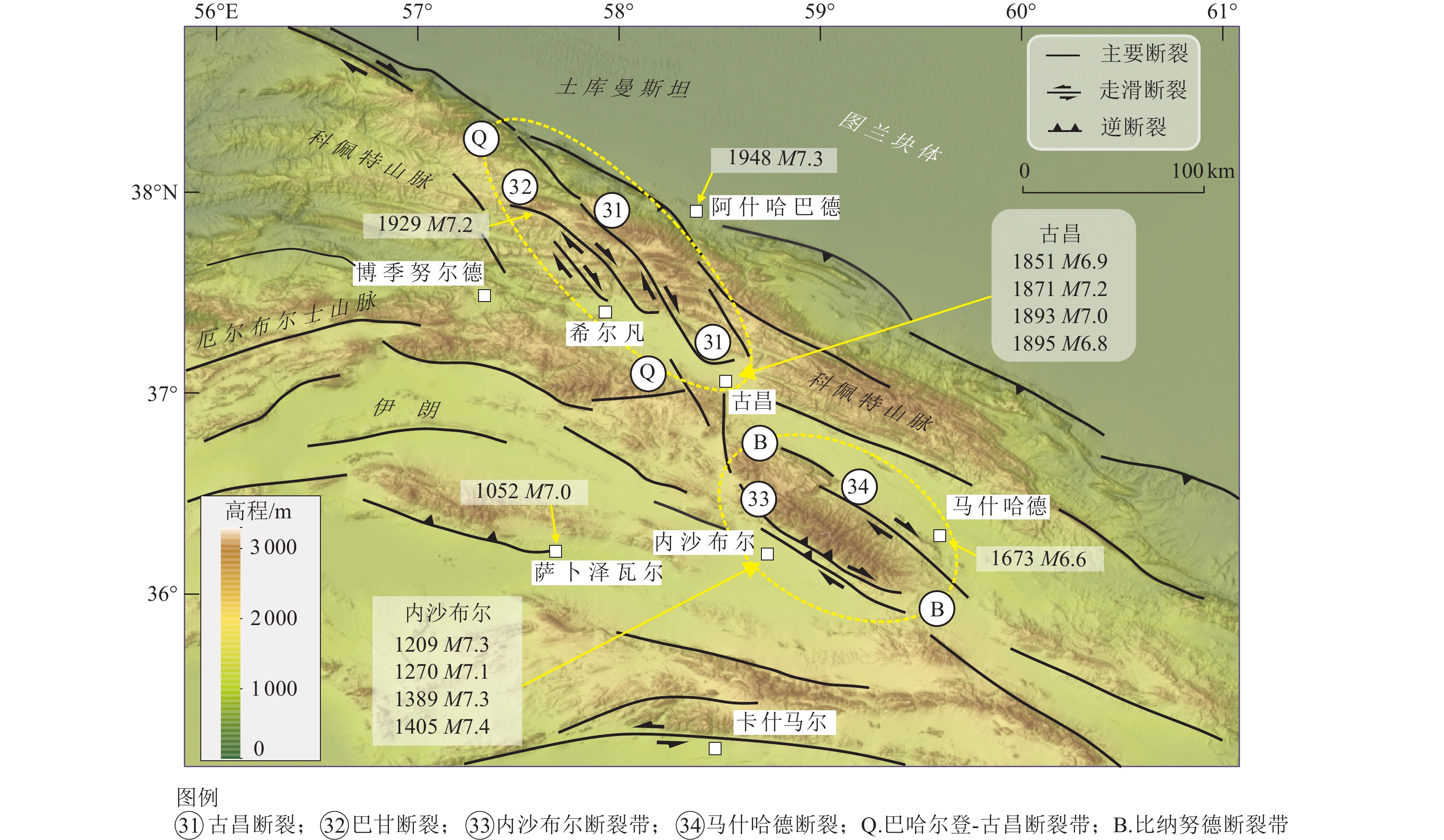
12月19日MW5.9 (19.5)F27 大不里士北断裂 North Tabriz 右旋走滑 NW >120 20~25 NW 6.5~7.3 − SE 1721年4月26日M7.3(>35);NW 1780年1月8日M7.4(>42) F28 阿哈尔断裂 Ahar 右旋走滑 EW >150 − 1.9±0.1 − 2012年8月11日MW6.4,6.2(13) F29 萨勒马斯断裂 Salmas 右旋走滑 NW-NNW 60 − − − 1930年5月6日MW7.1(16~30) F30 马拉盖断裂 Maragheh 右旋走滑 NW-NNW >110 − − − 无强震资料 F31 古昌断裂 Quchan 右旋走滑 NNW >130 15.5 4.3±0.6 − 古昌区域1851,1871,1893,1895年M~7.0 F32 巴甘断裂 Baghan 右旋走滑 NNW 80 9.8 2.8±1.0 − 1929年5月1日MW7.2(74) F33 内沙布尔断裂带 Neyshabur 右旋逆断 NW 90 f 2.4±0.5 2.8±0.6 内沙布尔区域1209,1270,
1389,1405年M>7.0F34 马什哈德断裂 Mashahad 右旋走滑 NW 125 − 1.3±0.1 − 1673年7月30日M6.6 F35 米纳卜断裂带 Minab-Zendan 右旋逆断 N-NNW 250 − 4.7±2.0
(6.3±2.3)− 无强震资料 注:1.断裂中文名称主要依据中国地图出版社发行的世界分国地图册,个别名称参照已有地名翻译,中文名称只保留首个地名;英文名称为波斯语拉丁转写的简化,并省略了断裂(带)对应的英文fault(zone)。累积位错主要为水平位错,仅塔莱甘断裂为垂直位错。各断裂研究资料见正文。
2.滑动速率一栏,数值前的英文字母表示断裂的不同段落,如N表示北段,M表示中段,断裂带的滑动速率为分支断裂的累加速率。
3.地震活动一栏,日期前的字母表示断裂段落,震级之后括号内数字为同震地表破裂带的长度,单位为km,同震地表破裂资料来自Ghassemi(2016);问号(?)表示存在争议或证据不充分,星号(*)表示探槽古地震事件;无强震资料指无6.0级以上地震记录或记载;“区域”指这一地区记载的地震事件,发震构造可能涉及多条活动断裂。
4.历史地震资料主要依据Berberian(2014),通常为里氏震级,需要特别注意伊朗历史地震的震级采用小数表示。 -
陈学忠, 许建东, 2004.2003年12月26日伊朗巴姆地震. 国际地震动态, (2): 21—23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2004.02.006Chen X. Z. , Xu J. D. , 2004. An earthquake occurred in bam of Iran on December 26, 2003. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (2): 21—23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2004.02.006 代欢欢, 陈俊华, 方尹, 2017.1986年~2016年伊朗人口空间分布格局演变特征. 世界地理研究, 26(3): 29—38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2017.03.004Dai H. H. , Chen J. H. , Fang Y. , 2017. Evolution of spatial pattern of province-level population distribution in Iran during 1986-2016. World Regional Studies, 26(3): 29—38. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2017.03.004 邓起东, 张裕明, 许桂林等, 1979. 中国构造应力场特征及其与板块运动的关系. 地震地质, 1(1): 11—22Deng Q. D. , Zhang Y. M. , Xu G. L. , et al. , 1979. On the tectonic stress field in China and its relation to plate movement. Seismology and Geology, 1(1): 11—22. (in Chinese) 邓起东, 卢造勋, 杨主恩, 2007. 城市活动断层探测和断层活动性评价问题. 地震地质, 29(2): 189—200 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.001Deng Q. D. , Lu Z. X. , Yang Z. E. , 2007. Remarks on urban active faults exploration and associated activity assessment. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 189—200. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.001 邓起东, 闻学泽, 2008. 活动构造研究——历史、进展与建议. 地震地质, 30(1): 1—30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.002Deng Q. D. , Wen X. Z. , 2008. A review on the research of active tectonics——history, progress and suggestions. Seismology and Geology, 30(1): 1—30. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.002 刘小兵, 温志新, 贺正军等, 2019. 中东扎格罗斯盆地: 沿走向变化的构造及油气特征. 岩石学报, 35(4): 1269—1278 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.19Liu X. B. , Wen Z. X. , He Z. J. , et al. , 2019. Zagros basin in Middle East: along-strike variations of structure and petroleum accumulation characteristics. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(4): 1269—1278. (in Chinese) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.19 王剑, 赵汝敏, 谢楠等, 2016. 扎格罗斯前陆盆地构造样式与油气成藏规律. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(2): 143—151 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.02.016Wang J. , Zhao R. M. , Xie N. , et al. , 2016. Structural style of Zagros foreland basin and its bearing on oil and gas accumulation. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 36(2): 143—151. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.02.016 王卫民, 郝金来, 何建坤等, 2018.2013年巴基斯坦俾路支MW7.7地震震源过程研究. 地球物理学报, 61(3): 872—879 doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0769Wang W. M. , Hao J. L. , He J. K. , et al. , 2018. Rupture process of the 2013, Balochistan MW7.7 earthquake, Pakistan. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(3): 872—879. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0769 文鑫涛, 李华玥, 段乙好等, 2021.2020年中国大陆地震灾害损失述评. 震灾防御技术, 16(4): 651—656 doi: 10.11899/j.issn.1673-5722.2021.4.zzfyjs202104006Wen X. T. , Li H. Y. , Duan Y. H. , et al. , 2021. Earthquake disasters loss on Chinese mainland in 2020. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(4): 651—656. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/j.issn.1673-5722.2021.4.zzfyjs202104006 徐锡伟, 2006. 活动断层、地震灾害与减灾对策问题. 震灾防御技术, 1(1): 7—14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.01.002Xu X. W. , 2006. Active faults, associated earthquake disaster distribution and policy for disaster reduction. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(1): 7—14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.01.002 张洪瑞, 侯增谦, 2018. 大陆碰撞带成矿作用: 年轻碰撞造山带对比研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(12): 1629—1654.Zhang H. R. , Hou Z. Q. , 2018. Metallogenesis within continental collision zones: comparisons of modern collisional orogens. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(12): 1737—1760. 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊等, 2014. 东亚大陆新生代构造演化. 地震地质, 36(3): 574—585 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003Zhang P. Z. , Zhang H. P. , Zheng W. J. , et al. , 2014. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of continental eastern Asia. Seismology and Geology, 36(3): 574—585. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003 张裕明, 汪良谋, 董瑞树等, 1981. 亚欧地震构造图说明书. 北京: 地图出版社, 1—33Zhang Y. M., Wang L. M., Dong R. S., et al., 1981. The instruction for seismotectonic map of Asia and Europe. Beijing: Cartographic Publishing House, 1—33. (in Chinese) 郑剑东, 1990. 伊朗地震考察简况. 地震地质, 12(4): 380—381Zheng J. D. , 1990. Brief investigation on the 1990 earthquake in Iran. Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 380—381. (in Chinese) Alipoor R., Zaré M., Ghassemi M. R., 2012. Inception of activity and slip rate on the Main Recent Fault of Zagros Mountains, Iran. Geomorphology, 175—176: 86—97. Allen M. B. , Ghassemi M. R. , Shahrabi M. , et al. , 2003. Accommodation of late Cenozoic oblique shortening in the Alborz range, northern Iran. Journal of Structural Geology, 25(5): 659—672. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00064-0 Allen M. B., 2010. Roles of strike-slip faults during continental deformation: examples from the active Arabia–Eurasia collision. In: Kusky T. M., Zhai M. G., Xiao W., eds., The Evolving Continents: Understanding Processes of Continental Growth. London: The Geological Society, 338: 329—344. Allen M. B. , Kheirkhah M. , Emami M. H. , et al. , 2011. Right-lateral shear across Iran and kinematic change in the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone. Geophysical Journal International, 184(2): 555—574. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04874.x Ambraseys N. N., Melville C. P., 1982. A history of Persian earthquakes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1—219. Authemayou C. , Chardon D. , Bellier O. , et al. , 2006. Late Cenozoic partitioning of oblique plate convergence in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt (Iran). Tectonics, 25(3): TC3002. Authemayou C. , Bellier O. , Chardon D. , et al. , 2009. Quaternary slip-rates of the Kazerun and the Main Recent Faults: active strike-slip partitioning in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt. Geophysical Journal International, 178(1): 524—540. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04191.x Barnhart W. D. , Hayes G. P. , Samsonov S. V. , et al. , 2014. Breaking the oceanic lithosphere of a subducting slab: the 2013 Khash, Iran earthquake. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(1): 32—36. doi: 10.1002/2013GL058096 Berberian M., 1981. Active faulting and tectonics of Iran. In: Gupta H. K., Delany F. M., eds., Zagros Hindu Kush Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution. Washington D. C. USA: American Geophysical Union, 33—69. Berberian M., 1995. Master “blind” thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: Active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics. Tectonophysics, 241(3—4): 193—195, 197, 199—224. Berberian M. , Walker R. , 2010. The Rudbār MW 7.3 earthquake of 1990 June 20; seismotectonics, coseismic and geomorphic displacements, and historic earthquakes of the western ‘High-Alborz’, Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 182(3): 1577—1602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04705.x Berberian M., 2014. Earthquakes and coseismic surface faulting on the Iranian plateau: a historical, social, and physical approach. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1—714. Berberian M., Yeats R. S., 2017. Tehran: an earthquake time bomb. In: Sorkhabi R., ed., Tectonic Evolution, Collision, and Seismicity of Southwest Asia: In Honor of Manuel Berberian’s Forty-Five Years of Research Contributions. Boulder: The Geological Society of America, 87—170. Byrne D. E. , Sykes L. R. , Davis D. M. , 1992. Great thrust earthquakes and aseismic slip along the plate boundary of the Makran Subduction Zone. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97(B1): 449—478. doi: 10.1029/91JB02165 Copley A. , Faridi M. , Ghorashi M. , et al. , 2014. The 2012 August 11 Ahar earthquakes: consequences for tectonics and earthquake hazard in the Turkish–Iranian Plateau. Geophysical Journal International, 196(1): 15—21. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt379 Danciu L. , Şeşetyan K. , Demircioglu M. , et al. , 2018. The 2014 earthquake model of the Middle East: seismogenic sources. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 16(8): 3465—3496. doi: 10.1007/s10518-017-0096-8 Farbod Y. , Shabanian E. , Bellier O. , et al. , 2016. Spatial variations in late Quaternary slip rates along the Doruneh Fault System (Central Iran). Tectonics, 35(2): 386—406. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003862 Faridi M. , Nazari H. , Burg J. P. , et al. , 2019. Structural characteristics, paleoseismology and slip rate of the Qoshadagh fault, northwest of Iran. Geotectonics, 53(2): 280—297. doi: 10.1134/S0016852119020031 Fattahi M. , Walker R. T. , Talebian M. , et al. , 2014. Late Quaternary active faulting and landscape evolution in relation to the Gowk Fault in the South Golbaf Basin, S. E. Iran. Geomorphology, 204: 334—343. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.017 Fattahi M. , Walker R. , Khatib M. M. , et al. , 2015. Determination of slip-rate by optical dating of lake bed sediments from the Dasht-E-Bayaz fault, NE Iran. Geochronometria, 42(1): 148—157. Foroutan M. , Meyer B. , Sébrier M. , et al. , 2014. Late Pleistocene-Holocene right slip rate and paleoseismology of the Nayband fault, western margin of the Lut block, Iran. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 119(4): 3517—3560. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010746 Ghassemi M. R. , 2016. Surface ruptures of the Iranian earthquakes 1900–2014: insights for earthquake fault rupture hazards and empirical relationships. Earth-Science Reviews, 156: 1—13. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.03.001 Ghods A. , Shabanian E. , Bergman E. , et al. , 2015. The Varzaghan–Ahar, Iran, Earthquake Doublet (MW 6.4, 6.2): implications for the geodynamics of northwest Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 203(1): 522—540. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv306 Ghorbani M., 2013. The economic geology of Iran: mineral deposits and natural resources. Dordrecht: Springer, 1—572. Hatzfeld D. , Molnar P. , 2010. Comparisons of the kinematics and deep structures of the Zagros and Himalaya and of the Iranian and Tibetan plateaus and geodynamic implications. Reviews of Geophysics, 48(2): RG2005. Hessami K. , Pantosti D. , Tabassi H. , et al. , 2003. Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results. Annals of Geophysics, 46(5): 903—915. Hessami K. , Jamali F. , 2006. Explanatory notes to the map of major active faults of Iran. Journal of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, 8(1): 1—11. Hoffmann G. , Grützner C. , Schneider B. , et al. , 2020. Large Holocene tsunamis in the northern Arabian Sea. Marine Geology, 419: 106068. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.106068 Hollingsworth J. , Jackson J. , Walker R. , et al. , 2006. Strike-slip faulting, rotation, and along-strike elongation in the Kopeh Dagh mountains, NE Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 166(3): 1161—1177. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02983.x Hollingsworth J. , Jackson J. , Walker R. , et al. , 2008. Extrusion tectonics and subduction in the eastern South Caspian region since 10 Ma. Geology, 36(10): 763—766. doi: 10.1130/G25008A.1 Hollingsworth J. , Nazari H. , Ritz J. F. , et al. , 2010. Active tectonics of the east Alborz mountains, NE Iran: Rupture of the left-lateral Astaneh fault system during the great 856 A. D. Qumis earthquake. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(B12): B12313. doi: 10.1029/2009JB007185 Jackson J. , Priestley K. , Allen M. , et al. , 2002. Active tectonics of the South Caspian Basin. Geophysical Journal International, 148(2): 214—245. Javidfakhr B., Bellier O., Shabanian E., et al., 2011. Fault kinematics and active tectonics at the southeastern boundary of the eastern Alborz (Abr and Khij fault zones): geodynamic implications for NNE Iran. Journal of Geodynamics, 52(3—4): 290—303. Karasözen E. , Nissen E. , Bergman E A. , et al. , 2019. Seismotectonics of the Zagros (Iran) from orogen-wide, calibrated earthquake relocations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(8): 9109—9129. doi: 10.1029/2019JB017336 Kopp C., Fruehn J., Flueh E. R., et al., 2000. Structure of the Makran subduction zone from wide-angle and reflection seismic data. Tectonophysics, 329(1—4): 171—191. Landgraf A. , Ballato P. , Strecker M. R. , et al. , 2009. Fault-kinematic and geomorphic observations along the North Tehran Thrust and Mosha Fasham Fault, Alborz mountains Iran: implications for fault-system evolution and interaction in a changing tectonic regime. Geophysical Journal International, 177(2): 676—690. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04089.x Meyer B. , Le Dortz K. , 2007. Strike-slip kinematics in Central and Eastern Iran: estimating fault slip-rates averaged over the Holocene. Tectonics, 26(5): TC5009. Mirzaei N., Gheitanchi M. R., Naserieh S., et al., 2002. Basic parameters of earthquakes in Iran. Tehran: Daneshnegar Publications, 1—183. Mouthereau F., Lacombe O., Vergés J., 2012. Building the Zagros collisional orogen: timing, strain distribution and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence. Tectonophysics, 532—535: 27—60. Nazari H. , Ritz J. F. , Salamati R. , et al. , 2009. Morphological and palaeoseismological analysis along the Taleghan fault (Central Alborz, Iran). Geophysical Journal International, 178(2): 1028—1041. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04173.x Nazari H. , Ritz J. F. , Walker R. T. , et al. , 2014. Palaeoseismic evidence for a medieval earthquake, and preliminary estimate of late Pleistocene slip-rate, on the Firouzkuh strike-slip fault in the Central Alborz region of Iran. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 82: 124—135. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.12.018 Nazari H. , Ritz J. F. , Burg J. P. , et al. , 2021. Active tectonics along the Khazar fault (Alborz, Iran). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 219: 104893. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104893 Nissen E. , Tatar M. , Jackson J. A. , et al. , 2011. New views on earthquake faulting in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt of Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 186(3): 928—944. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05119.x Nissen E. , Ghods A. , Karasözen E. , et al. , 2019. The 12 November 2017 MW 7.3 Ezgeleh-Sarpolzahab (Iran) earthquake and active tectonics of the Lurestan Arc. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(2): 2124—2152. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016221 Page W. D., Alt J. N., Cluff L. S., et al., 1979. Evidence for the recurrence of large-magnitude earthquakes along the Makran Coast of Iran and Pakistan. Tectonophysics, 52(1—4): 533—547. Penney C. , Tavakoli F. , Saadat A. , et al. , 2017. Megathrust and accretionary wedge properties and behaviour in the Makran subduction zone. Geophysical Journal International, 209(3): 1800—1830. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx126 Rashidi A. , Dutykh D. , Shomali Z. H. , et al. , 2020. A review of tsunami hazards in the Makran Subduction Zone. Geosciences, 10(9): 372. doi: 10.3390/geosciences10090372 Regard V. , Bellier O. , Thomas J. C. , et al. , 2005. Cumulative right-lateral fault slip rate across the Zagros-Makran transfer zone: role of the Minab-Zendan fault system in accommodating Arabia-Eurasia convergence in southeast Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 162(1): 177—203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02558.x Ritz J. F. , Nazari H. , Ghassemi A. , et al. , 2006. Active transtension inside central Alborz: a new insight into northern Iran–southern Caspian geodynamics. Geology, 34(6): 477—480. doi: 10.1130/G22319.1 Rizza M. , Vernant P. , Ritz J. F. , et al. , 2013. Morphotectonic and geodetic evidence for a constant slip-rate over the last 45 kyr along the Tabriz fault (Iran). Geophysical Journal International, 193(3): 1083—1094. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt041 Şeşetyan K. , Danciu L. , Demircioğlu Tümsa M. B. , et al. , 2018. The 2014 seismic hazard model of the Middle East: overview and results. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 16(8): 3535—3566. doi: 10.1007/s10518-018-0346-4 Shabanian E. , Siame L. , Bellier O. , et al. , 2009. Quaternary slip rates along the northeastern boundary of the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone (Kopeh Dagh Mountains, Northeast Iran). Geophysical Journal International, 178(2): 1055—1077. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04183.x Shabanian E. , Bellier O. , Siame L. , et al. , 2012. The Binalud Mountains: a key piece for the geodynamic puzzle of NE Iran. Tectonics, 31(6): TC6003. Solaymani Azad S., Ritz J. F., Abbassi M. R., 2011. Left-lateral active deformation along the Mosha–North Tehran fault system (Iran): morphotectonics and paleoseismological investigations. Tectonophysics, 497(1—4): 1—14. Stern R. J. , Moghadam H. S. , Pirouz M. , et al. , 2021. The geodynamic evolution of Iran. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 49: 9—36. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-071620-052109 Stöcklin J. , 1968. Structural history and tectonics of Iran: a review. AAPG Bulletin, 52(7): 1229—1258. Taghipour K., Khatib M. M., Heyhat M., et al., 2018. Evidence for distributed active strike-slip faulting in NW Iran: the Maragheh and Salmas fault zones. Tectonophysics, 742—743: 15—33. Talebian M. , Jackson J. , 2002. Offset on the Main Recent Fault of NW Iran and implications for the Late Cenozoic tectonics of the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone. Geophysical Journal International, 150(2): 422—439. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01711.x Talebian M. , Jackson J. , 2004. A reappraisal of earthquake focal mechanisms and active shortening in the Zagros mountains of Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 156(3): 506—526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02092.x Tatar M. , Jackson J. , Hatzfeld D. , et al. , 2007. The 2004 May 28 Baladeh earthquake (MW 6.2) in the Alborz, Iran: overthrusting the South Caspian Basin margin, partitioning of oblique convergence and the seismic hazard of Tehran. Geophysical Journal International, 170(1): 249—261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03386.x Vernant P. , Nilforoushan F. , Hatzfeld D. , et al. , 2004. Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophysical Journal International, 157(1): 381—398. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02222.x Walker R. , Jackson J. , 2004 a. Active tectonics and late Cenozoic strain distribution in central and eastern Iran. Tectonics, 23(5): TC5010. Walker R. , Jackson J. , Baker C. , 2004 b. Active faulting and seismicity of the Dasht-e-Bayaz region, eastern Iran. Geophysical Journal International, 157(1): 265—282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.02179.x -



 下载:
下载: