Seismic Response of the Adjacent Semi-cylindrical Hill in Layered Half Space for Incident SV Wave
-
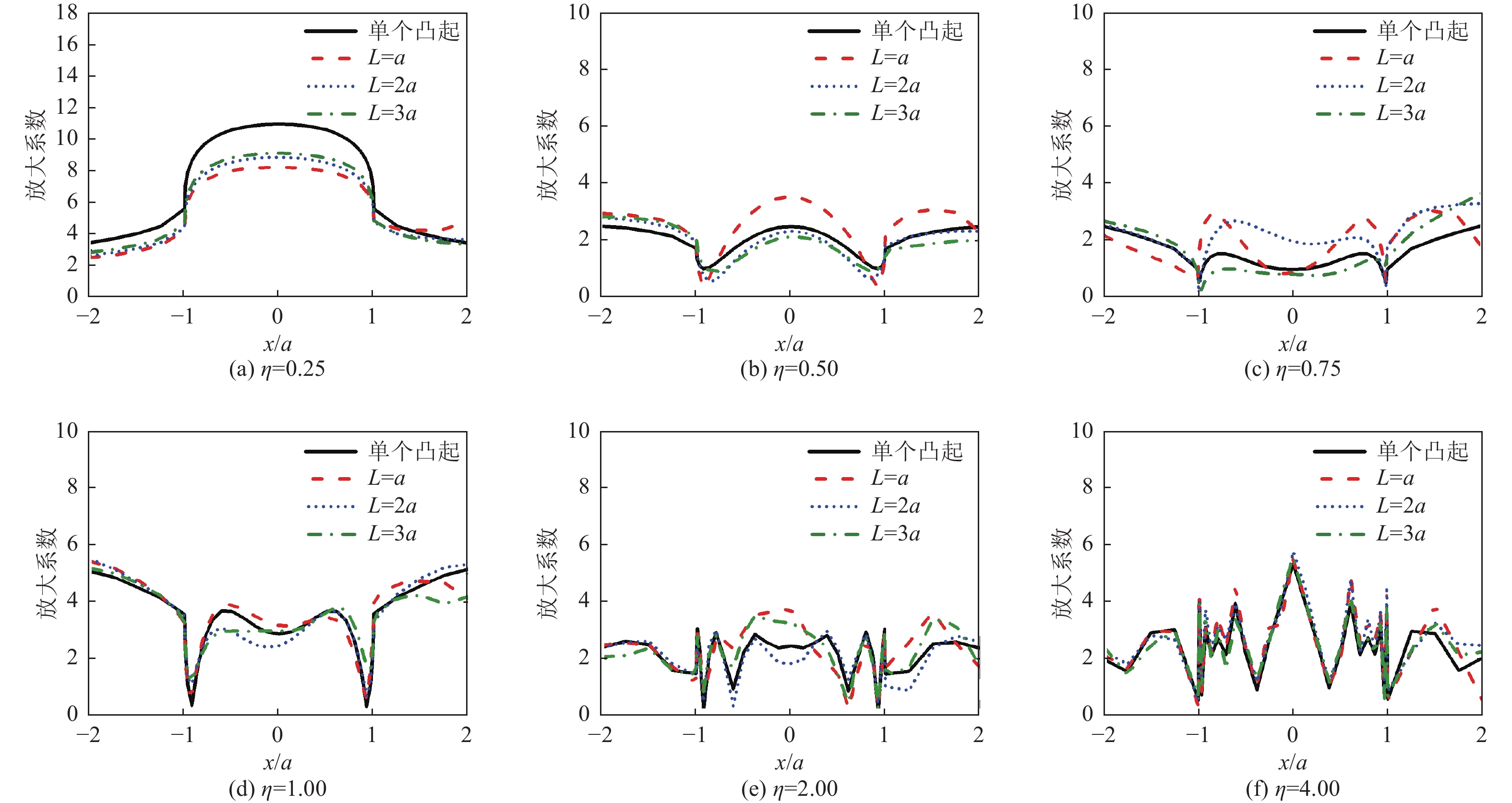
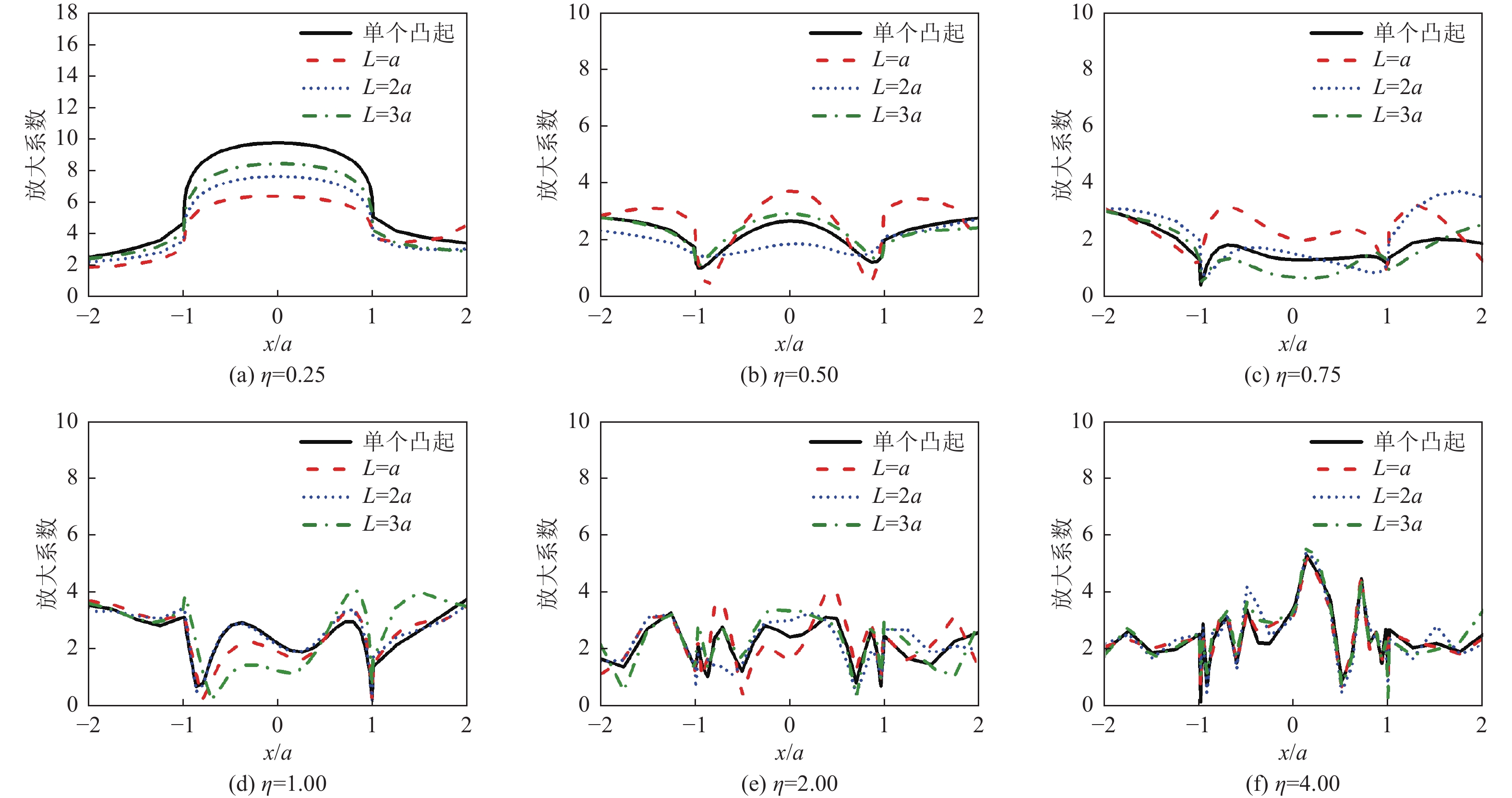
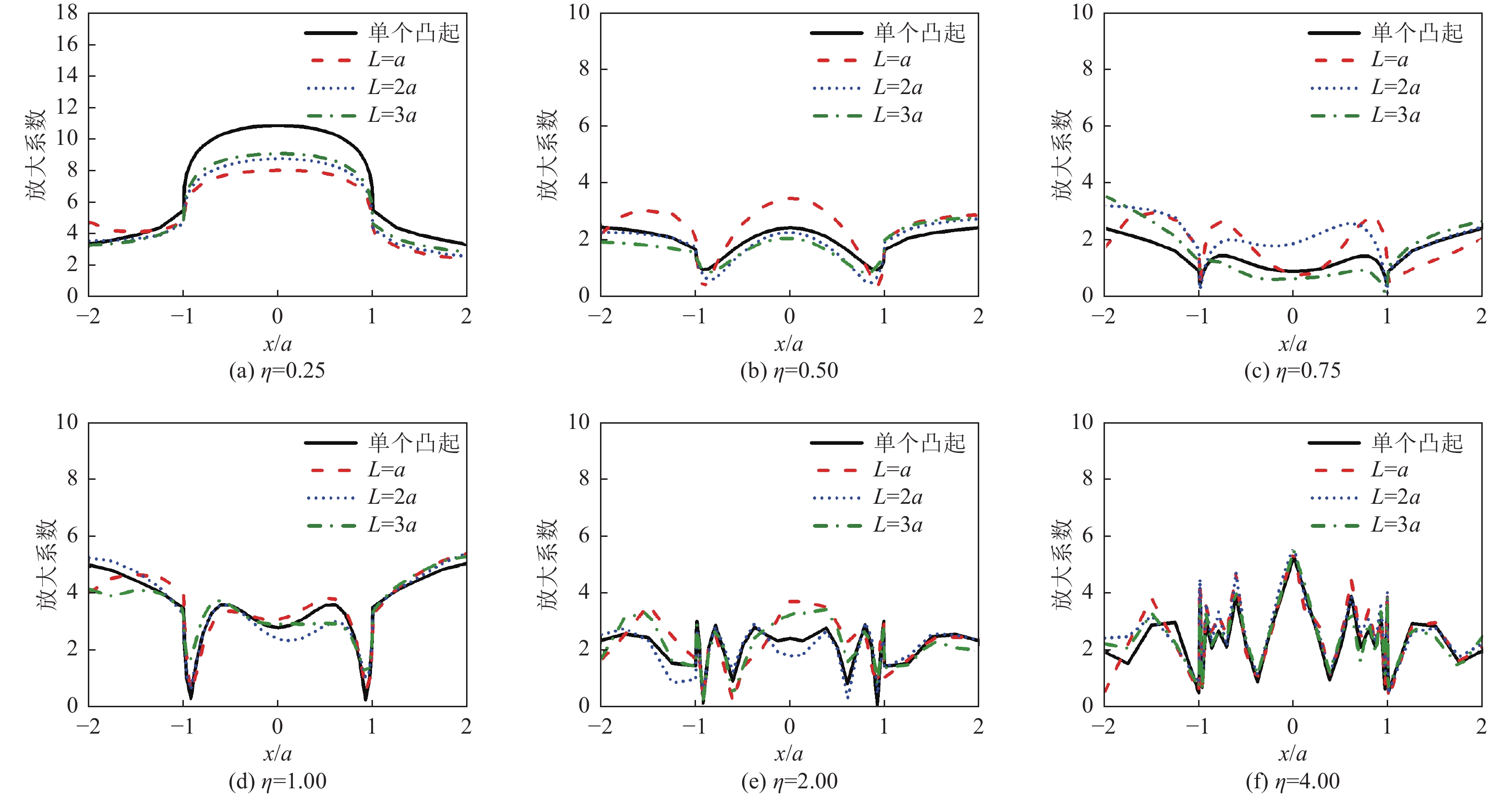
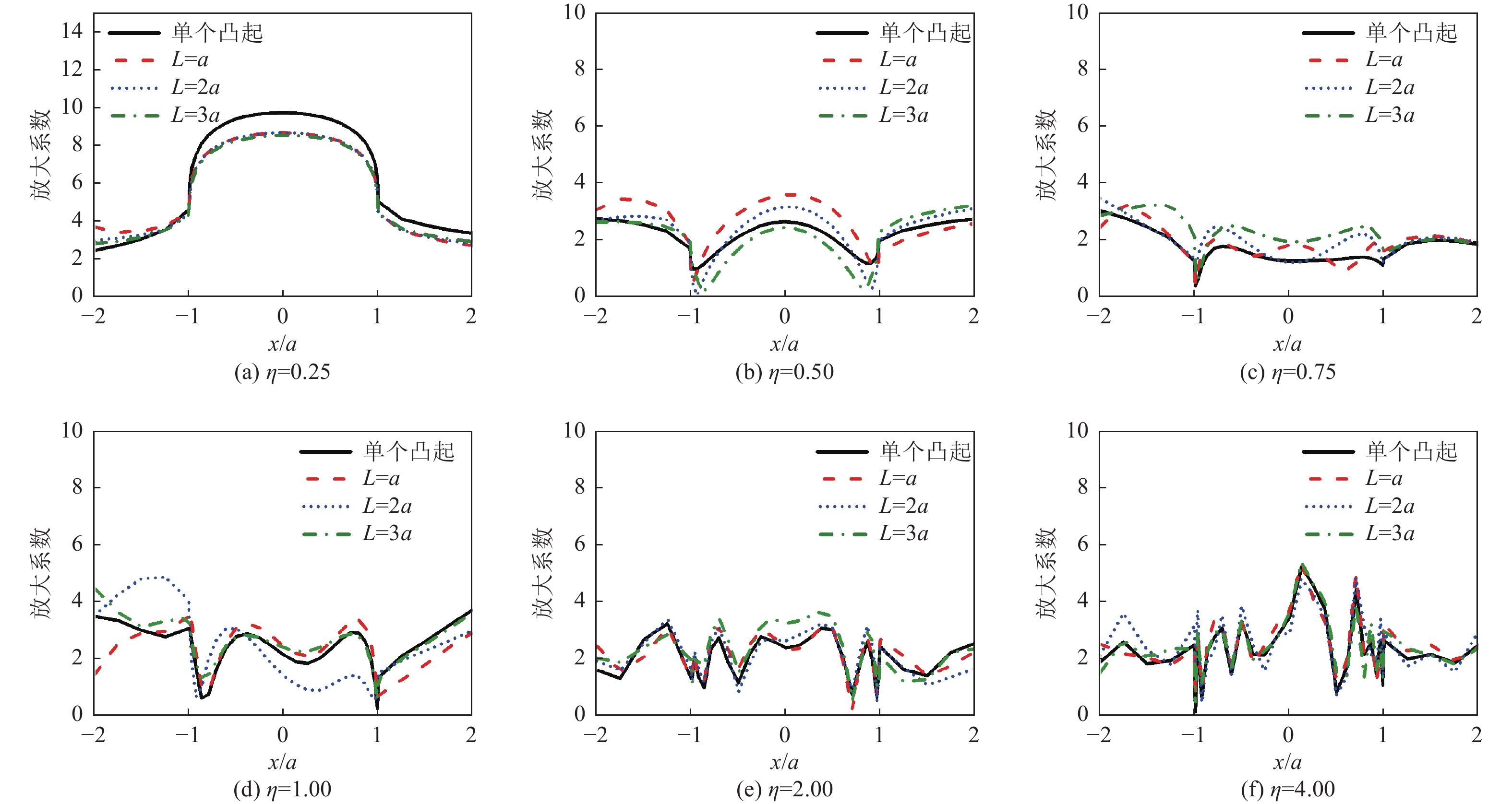
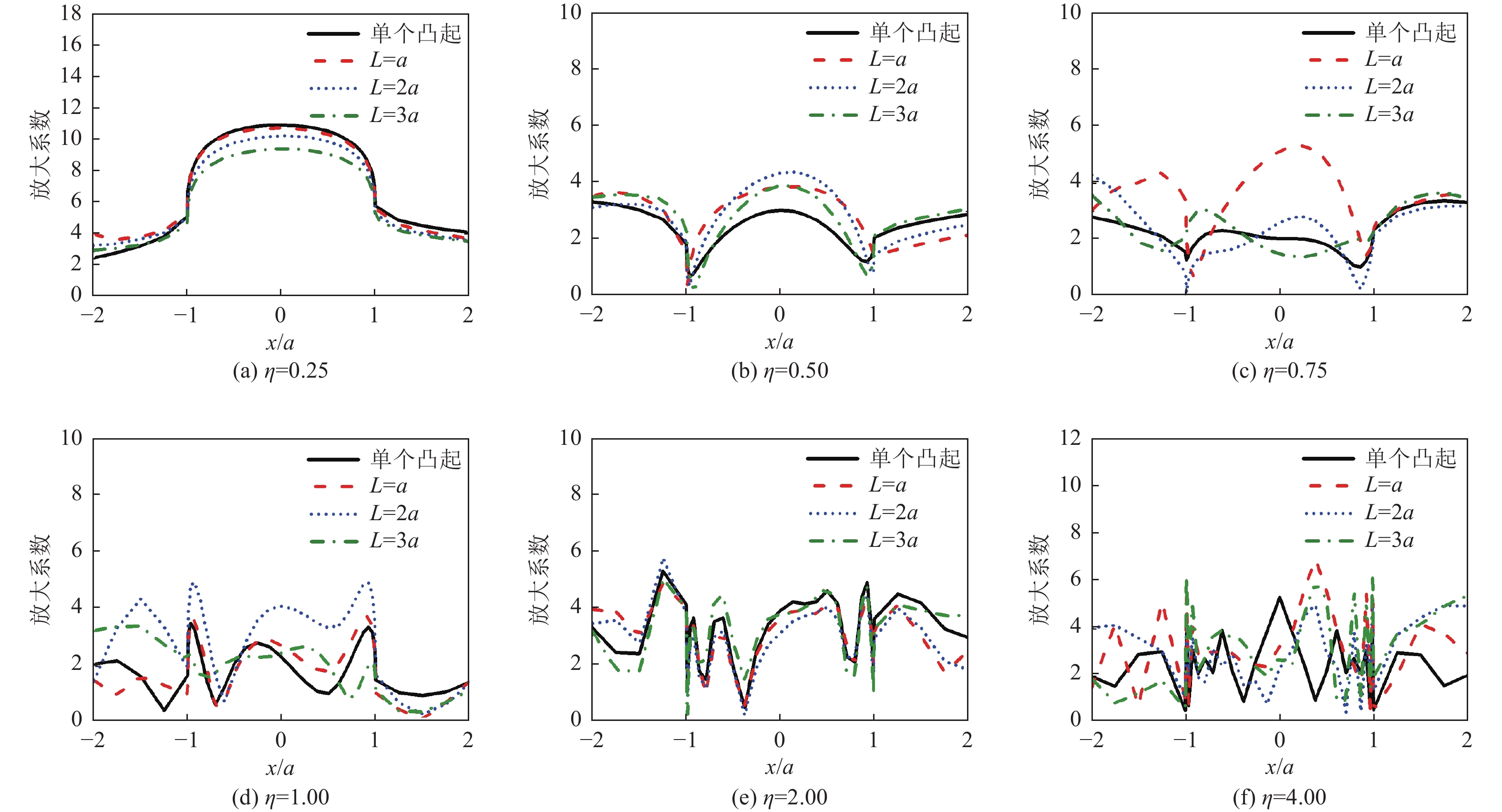
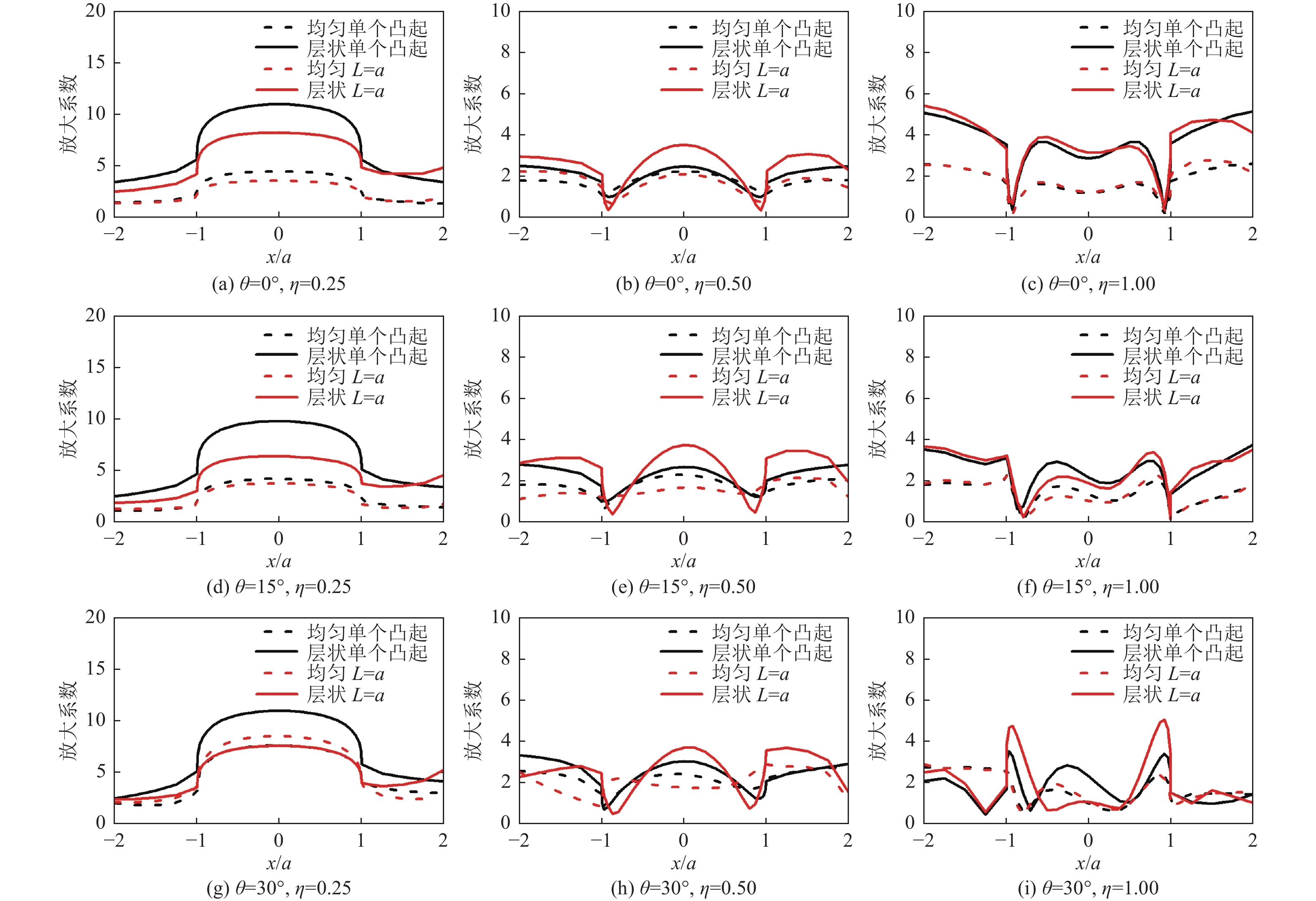
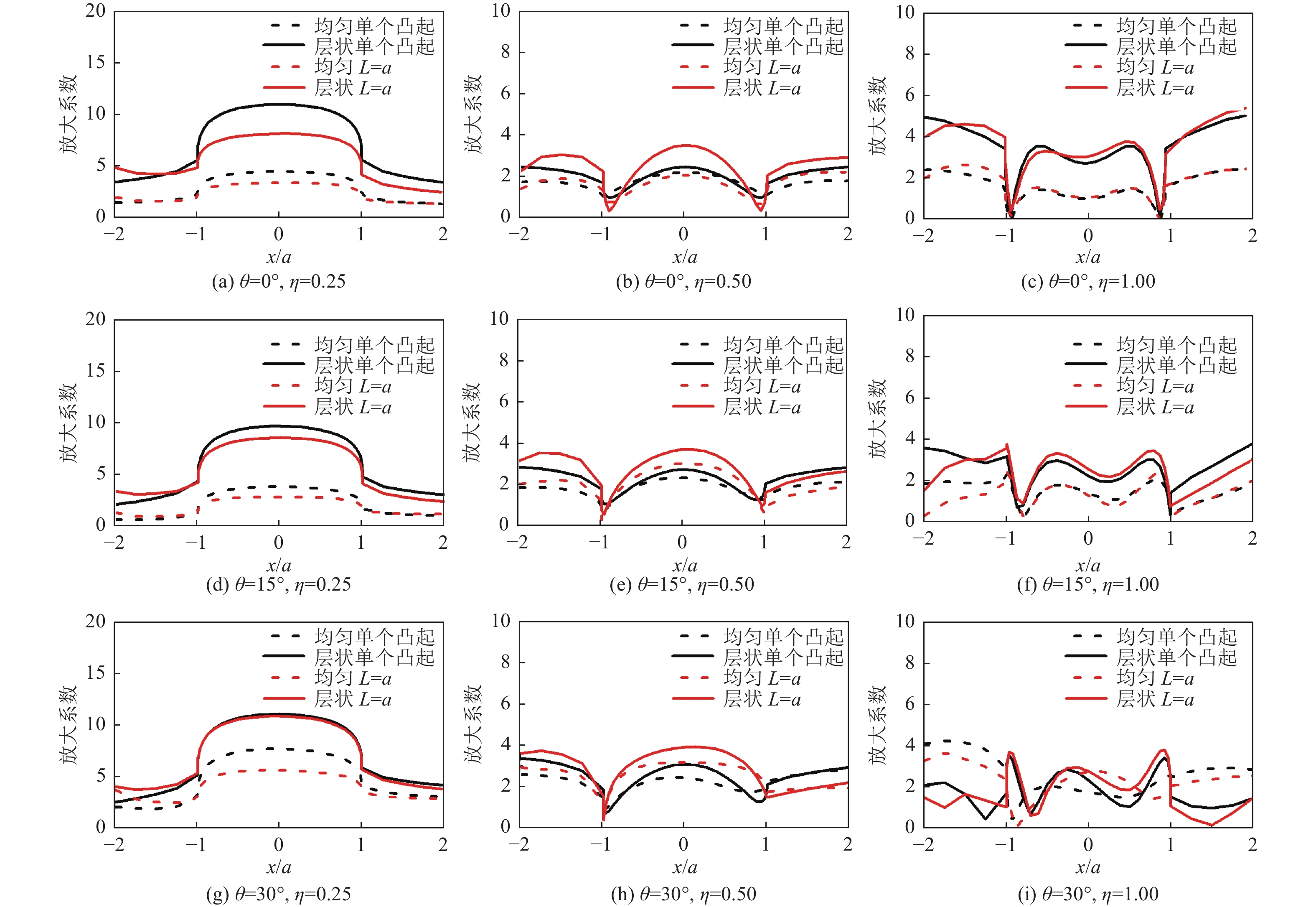
摘要: 采用有限元方法计算SV波入射下层状半空间相邻2个半圆形凸起地形的地震响应,比较分析相邻凸起之间的相互影响。研究结果表明:(1)当无量纲频率
$\eta $ 较小时,凸起间距对地表位移谱放大系数$\beta $ 的影响明显大于高频;凸起间距越小,右侧凸起对左侧凸起的影响越大,而左侧凸起对右侧凸起的影响还受入射角度限制。(2)当无量纲频率$\eta $ > 1.0 时,对于相同的入射波频率和入射角度,凸起间距越大,对谱放大系数的影响越小。(3)当输入地震波波长大于凸起地形宽度时,相邻凸起的影响可忽略。(4)与SV波入射下均匀半空间半圆形凸起地形的地震响应相比,无论是单个半圆形凸起还是相邻2个半圆形凸起,在$ \left|x/a\right| $ ≤1.0范围内,层状半空间地表位移谱放大系数明显大于均匀半空间地表位移谱放大系数;在$ \left|x/a\right| $ ≥1.0范围内,偶尔会出现层状半空间地表位移谱放大系数小于均匀半空间地表位移谱放大系数的情形。Abstract: In this paper, the seismic response of two adjacent semi-cylindrical hills in layered half space for incident SV wave is calculated by finite element method. The interaction between adjacent hills is compared and analyzed, and the conclusions are as follows: (1) When the dimensionless frequency$\eta $ is small, the effect of the hill distance L on the spectral amplification coefficient$\beta $ is significantly greater than that of high frequencies. In addition, the smaller the hill distance is, the greater the influence of the right hill on the left hill. And the influence of the left hill on the right hill is also affected by the incident angle. (2) When$\eta $ >1.0, for the same incident wave frequency and incident angle, the larger the hill distance, the smaller the influence on the spectral amplification coefficients$\beta $ . (3) When the input wave wavelength is greater than the width of the hill, the interaction between adjacent hill could be ignored. (4) Compared with the seismic response of the semi-cylindrical hill in the half space, whether it is a single hill or two adjacent hills, in the range of$| x /a | $ ≤1.0, the surface displacement spectrum amplification coefficient of the layered half space is obviously larger than that of the uniform half-space. In the range of$| x /a | $ ≥1.0, occasionally the amplification coefficient of the surface displacement spectrum of the layered half-space is smaller than that of the uniform half-space. -
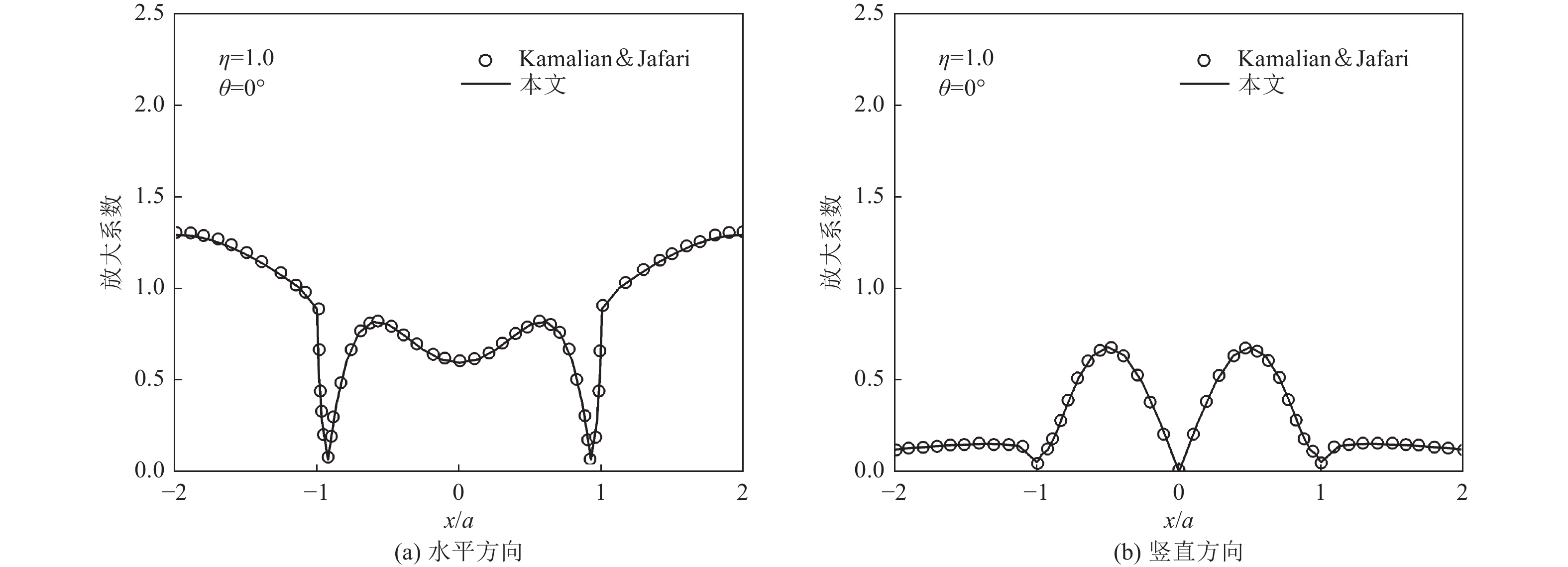
图 4 本文计算结果与文献(Kamalian等,2006)
Figure 4. Comparison of results from this paper and reference(Kamalian et al.,2006)
表 1 无量纲频率对应的实际频率
Table 1. Actual frequency corresponding to the dimensionless frequency
$ \eta $ 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 2 4 $ f $/Hz 1.25 2.5 3.75 5 10 20 -
巴振宁, 梁建文, 2015. Rayleigh波斜入射下层状场地中凸起地形的三维响应分析. 中国科学: 技术科学, 45(8): 874—888 doi: 10.1360/N092014-00045Ba Z. N. , Liang J. W. , 2015. Three dimensional responses of a hill in a layered half-space for obliquely incident Rayleigh waves. Scientia Sinica: Technologica, 45(8): 874—888. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N092014-00045 巴振宁, 黄棣旸, 梁建文等, 2017. 层状半空间中周期分布凸起地形对平面SH波的散射. 地球物理学报, 60(3): 1039—1052 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170317Ba Z. N. , Huang D. Y. , Liang J. W. , et al. , 2017. Scattering and diffraction of plane SH-waves by periodically distributed hill topographies. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(3): 1039—1052. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20170317 巴振宁, 彭琳, 梁建文等, 2018. 任意多个凸起地形对平面P波的散射. 工程力学, 35(7): 7—17, 23Ba Z. N. , Peng L. , Liang J. W. , et al. , 2018. Scatter and diffraction of arbitrary number of hills for incident plane P-waves. Engineering Mechanics, 35(7): 7—17, 23. (in Chinese) 丁海平, 朱重洋, 于彦彦, 2017. P, SV波斜入射下凹陷地形地震动分布特征. 振动与冲击, 36(12): 88—92, 98Ding H. P. , Zhu C. Y. , Yu Y. Y. , 2017. Characteristic of ground motions of a canyon topography under inclined P and SV waves. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 36(12): 88—92, 98. (in Chinese) 杜永军, 赵启成, 刘殿魁等, 2005. 半圆形凸起地形对SH波的散射与地震动—有多个浅埋圆孔情形. 自然灾害学报, 14(3): 155—161 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2005.03.028Du Y. J. , Zhao Q. C. , Liu D. K. , et al. , 2005. Scattering of SH-waves by a semi-cylindrical hill above multiple subsurface cavities. Journal of Natural Disasters, 14(3): 155—161. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2005.03.028 郝明辉, 张郁山, 2015. 相邻地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 中国地震, 31(4): 656—667 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2015.04.006Hao M. H. , Zhang Y. S. , 2015. Analysis of the adjacent terrain effect on the properties of ground motion. Earthquake Research in China, 31(4): 656—667. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2015.04.006 郝明辉, 张郁山, 2018. SV波斜入射下凸起地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 震灾防御技术, 13(3): 552—561 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180306Hao M. H. , Zhang Y. S. , 2018. Analysis of terrain effect on the properties of ground motion due to inclined SV wave. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 552—561. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180306 胡聿贤, 孙平善, 章在墉等, 1980. 场地条件对震害和地震动的影响. 地震工程与工程振动, (试刊1): 34—41. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.1980.00.003 梁建文, 张彦帅, Lee V. W. , 2006. 平面SV波入射下半圆形凸起地形地表运动解析解. 地震学报, 28(3): 238—249 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2006.03.003Liang J. W. , Zhang Y. S. , Lee V. W. , 2006. Surface motion of a semi-cylindrical hill for incident plane SV waves: analytical solution. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 28(3): 238—249. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2006.03.003 梁建文, 巴振宁, 2008. 弹性层状半空间中凸起地形对入射平面SH波的放大作用. 地震工程与工程振动, 28(1): 1—10Liang J. W. , Ba Z. N. , 2008. Surface motion of a hill in layered half-space subjected to incident plane SH waves. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 28(1): 1—10. (in Chinese) 廖振鹏, 2002. 工程波动理论导引. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社. 刘晶波, 1996. 局部不规则地形对地震地面运动的影响. 地震学报, 18(2): 239—245. 刘晶波, 王振宇, 杜修力等, 2005. 波动问题中的三维时域粘弹性人工边界. 工程力学, 22(6): 46—51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2005.06.008Liu J. B. , Wang Z. Y. , Du X. L. , et al. , 2005. Three-dimensional visco-elastic artificial boundaries in time domain for wave motion problems. Engineering Mechanics, 22(6): 46—51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2005.06.008 刘中宪, 张雪, 孙帅杰等, 2018. 邻近山体地形地震动力相互作用边界元法模拟. 应用力学学报, 35(4): 722—729Liu Z. X. , Zhang X. , Sun S. J. , et al. , 2018. Boundary element method simulation for seismic dynamic interaction of adjacent mountain terrain. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 35(4): 722—729. (in Chinese) 盛志强, 卢育霞, 石玉成等, 2013. 河谷地形的地震反应分析. 地震工程学报, 35(1): 126—132, 202 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.01.0126Sheng Z. Q. , Lu Y. X. , Shi Y. C. , et al. , 2013. Seismic response analysis of valley topography. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 35(1): 126—132, 202. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.01.0126 孙平善, 陈达生, 左惠强等, 1991. 澜沧-耿马地震震害分布与场地影响. 见: 陈达生主编, 云南澜沧-耿马地震震害论文集. 北京: 科学出版社. 唐晖, 李小军, 李亚琦, 2012. 自贡西山公园山脊地形场地效应分析. 振动与冲击, 31(8): 74—79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.08.015Tang H. , Li X. J. , Li Y. Q. , 2012. Site effect of topograghy on ground motions of Xishan Park of Zigong City. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 31(8): 74—79. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.08.015 袁一凡, 田启文, 2012. 工程地震学. 北京: 地震出版社. 周国良, 李小军, 侯春林等, 2012. SV波入射下河谷地形地震动分布特征分析. 岩土力学, 33(4): 1161—1166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.029Zhou G. L. , Li X. J. , Hou C. L. , et al. , 2012. Characteristic analysis of ground motions of canyon topography under incident SV seismic waves. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 33(4): 1161—1166. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.029 Athanasopoulos G. A. , Pelekis P. C. , Leonidou E. A. , 1999. Effects of surface topography on seismic ground response in the Egion (Greece) 15 June 1995 earthquake. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 18(2): 135—149. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(98)00041-4 Çelebi M. , 1987. Topographical and geological amplifications determined from strong-motion and aftershock records of the 3 March 1985 Chile earthquake. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 77(4): 1147—1167. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0770041147 Çelebi M. , Bazzurro P. , Chiaraluce L. , et al. , 2010. Recorded motions of the 6 April 2009 Mw 6.3 L'Aquila, Italy, earthquake and implications for building structural damage: overview. Earthquake Spectra, 26(3): 651—684. doi: 10.1193/1.3450317 Dai D. H. , Zhang N. , Lee V. W. , et al. , 2019. Scattering and amplification of SV waves by a semi-cylindrical hill in a half-space by a wavefunction-based meshless method using mapping and point-matching strategies. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 106: 252—263. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.05.016 Kamalian M. , Jafari M. K. , Sohrabi-Bidar A. , et al. , 2006. Time-domain two-dimensional site response analysis of non-homogeneous topographic structures by a hybrid BE/FE method. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 26(8): 753—765. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2005.12.008 Kumar N. , Narayan J. P. , Kumar V. , et al. , 2021. Effects of shape and complexity of ridge topography on the comparative amplification scenario for the SH- and SV-waves. Journal of Earth System Science, 130(1): 36. doi: 10.1007/s12040-020-01525-7 Paolucci R. , 2002. Amplification of earthquake ground motion by steep topographic irregularities. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 31(10): 1831—1853. Spudich P. , Hellweg M. , Lee W. H. K. , 1996. Directional topographic site response at Tarzana observed in aftershocks of the 1994 Northridge, California, earthquake: implications for mainshock motions. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 86(1 B): S193—S208. doi: 10.1785/BSSA08601BS193 Trifunac M. D. , Hudson D. E, 1971. Analysis of the Pacoima dam accelerogram—San Fernando, California, earthquake of 1971. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 61(5): 1393—1411. -











 下载:
下载: