Nihuzhuang-Qilidun Fault Detecting Based on Shallow Seismic Exploration and Drilling Joint Geological Profile in Subei Basin
-
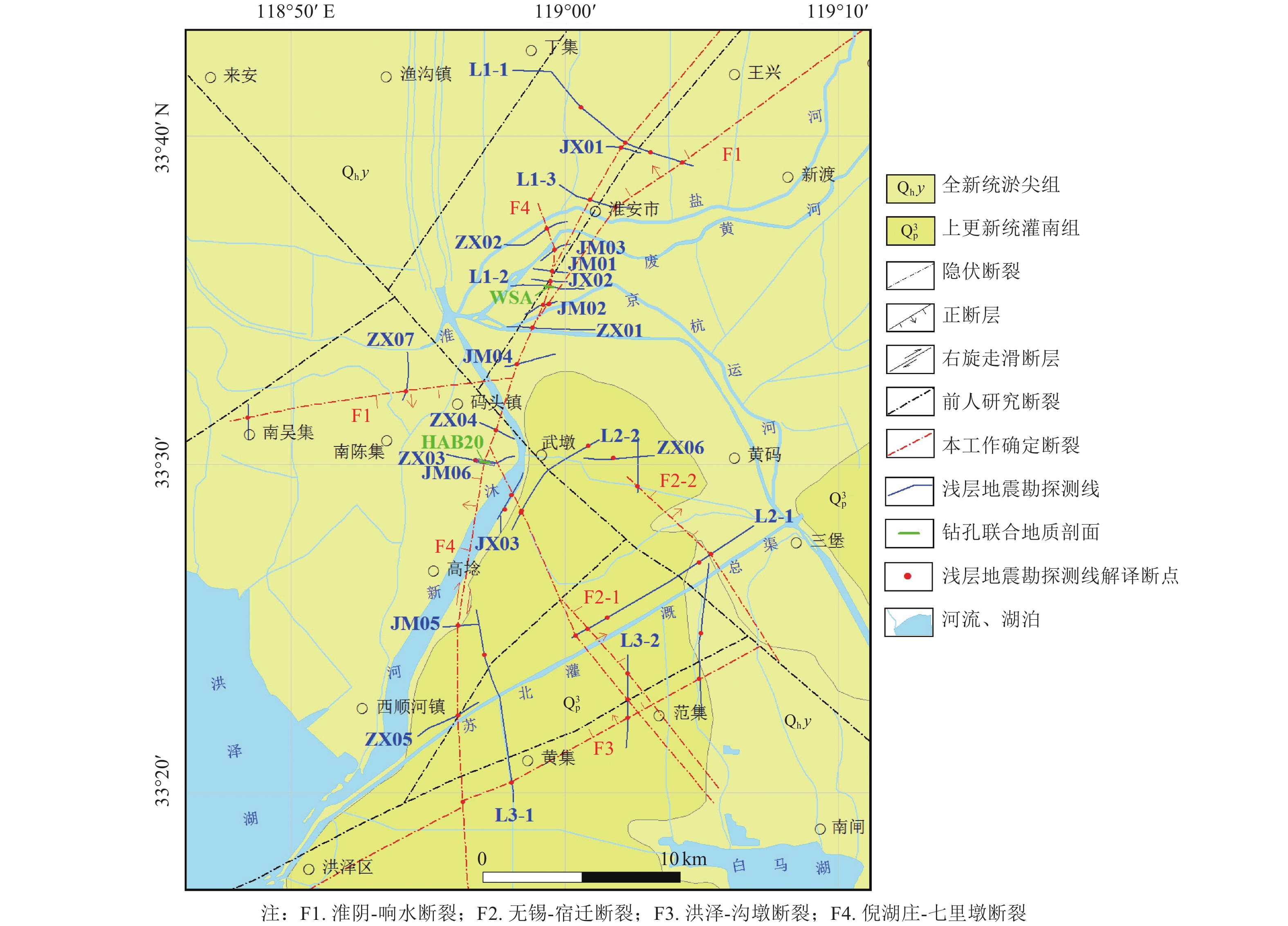
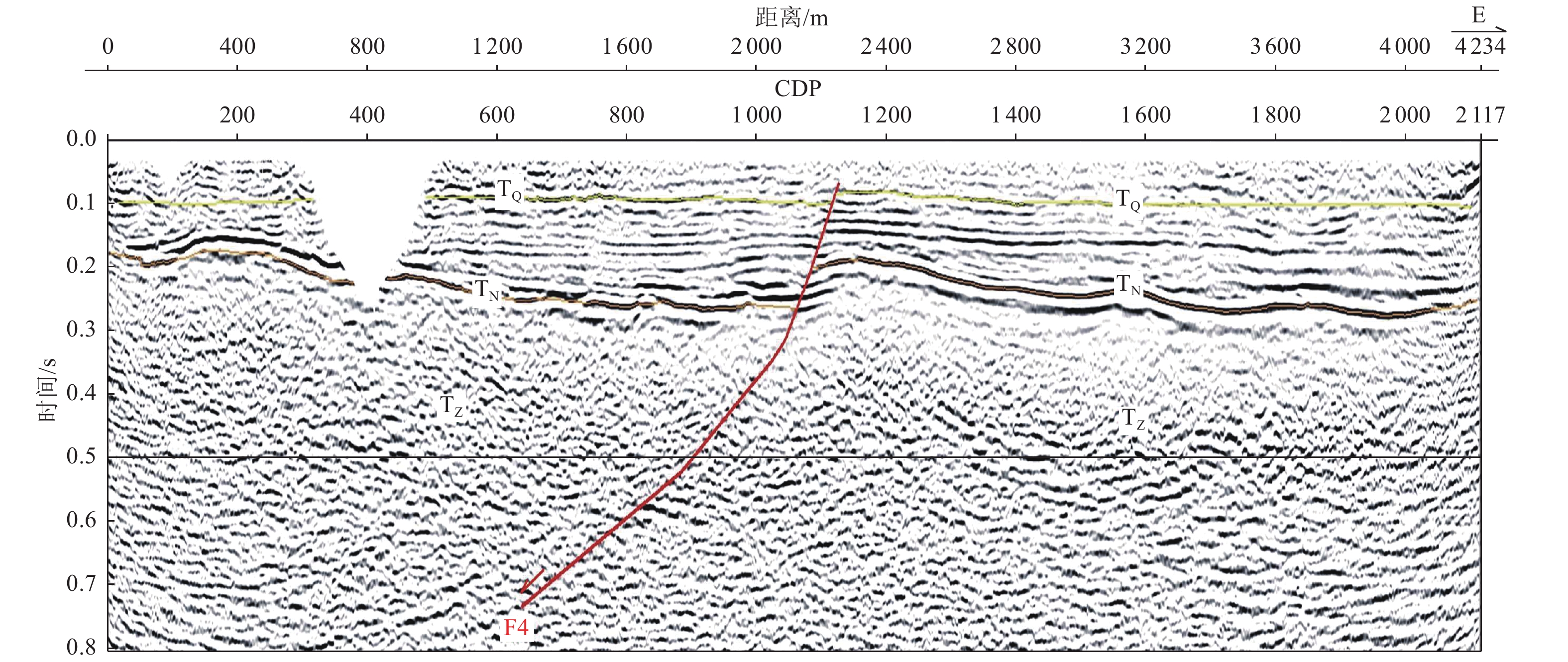
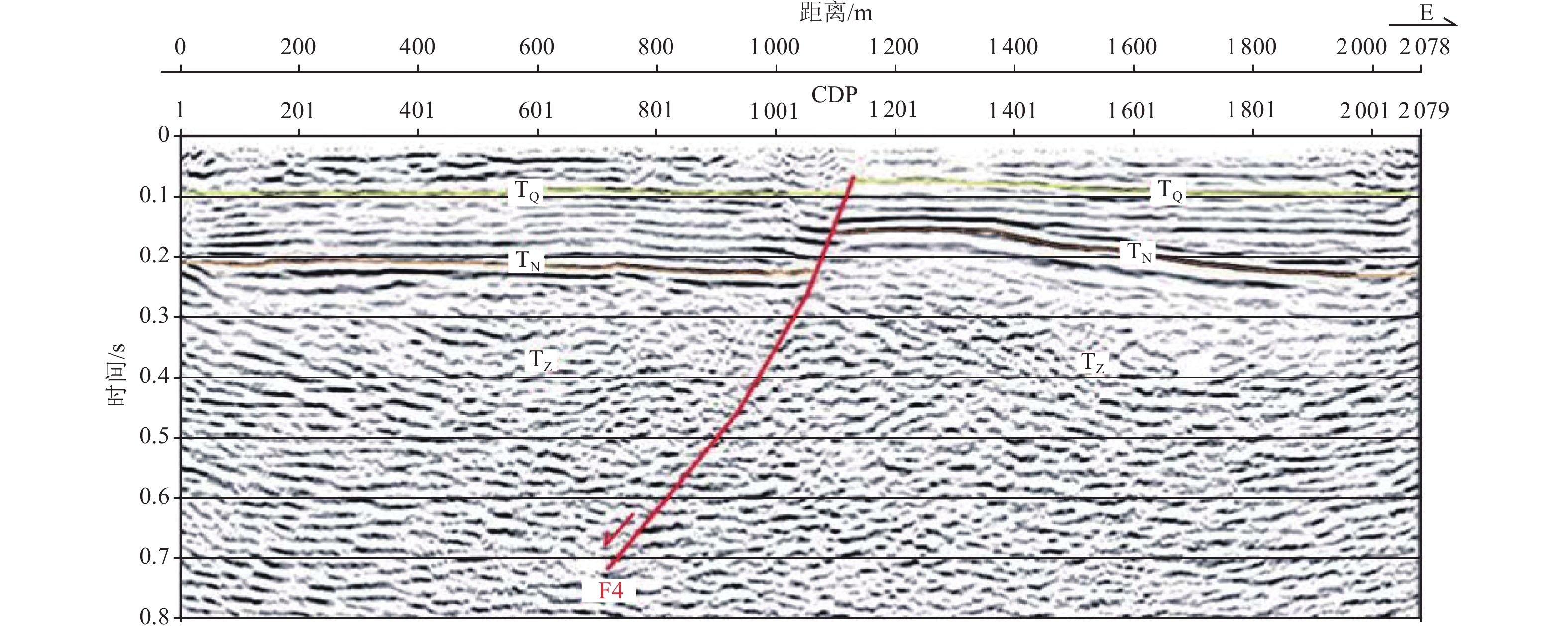
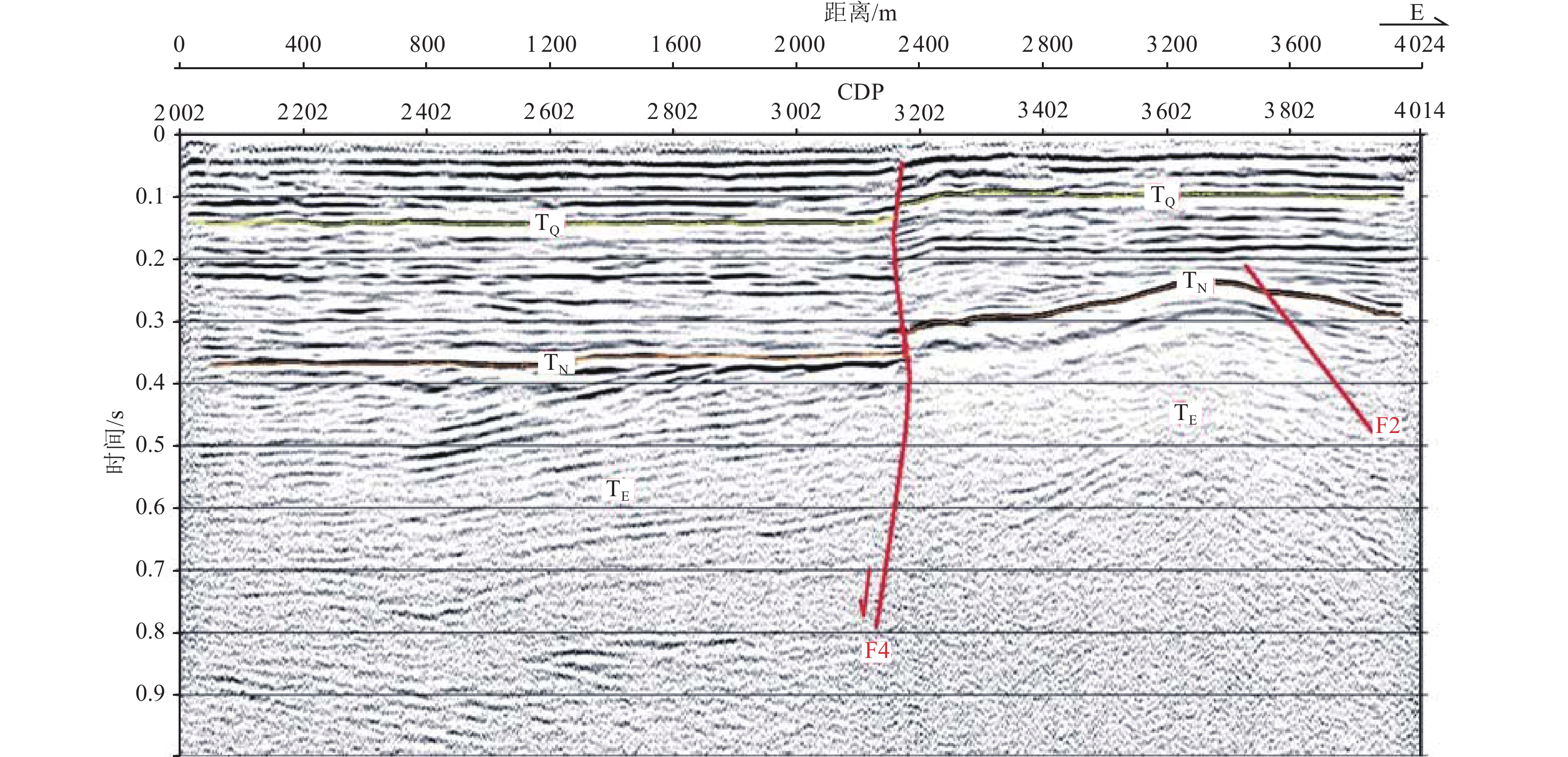
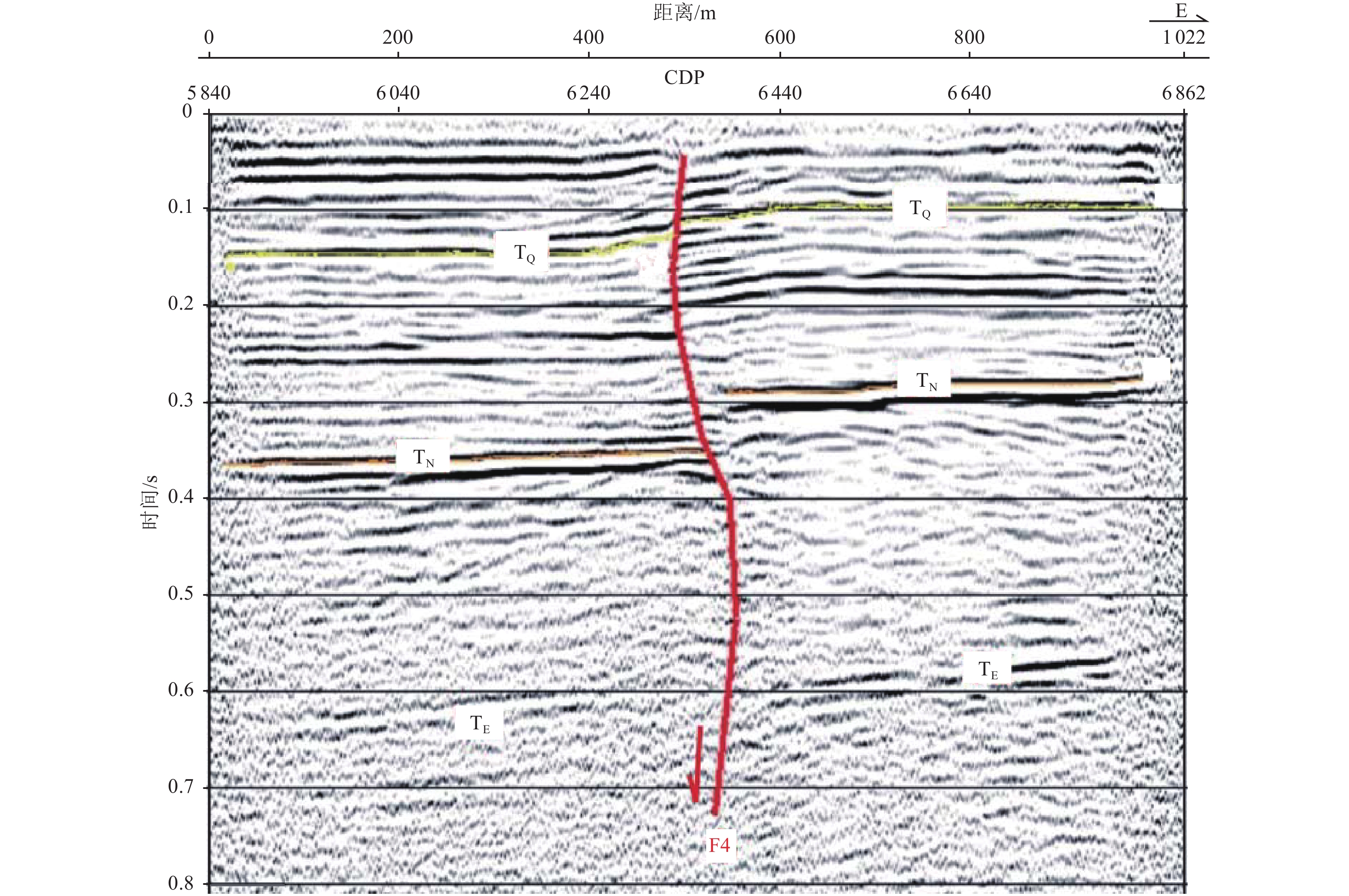
摘要: 浅层地震勘探与钻孔联合地质剖面探测是隐伏断层定位与活动性鉴定的基本手段,需在实际工作中不断总结完善。通过采用浅层地震勘探技术,查明了淮安市区附近隐伏断裂的基本格局,并结合钻孔联合地质剖面探测与第四纪年代学测定,确定了新发现的倪湖庄-七里墩断裂的最新活动时代及活动特征。倪湖庄-七里墩断裂为近南北走向、倾向西的高角度正断层,断层倾角72°~82°,探测断裂长度为43 km。浅层地震勘探揭示其断面具有近直立或呈S形的上下反倾特点,指示具有走滑性质。该断裂错断了北东走向淮阴-响水断裂与北西走向无锡-宿迁断裂,最新活动时代为中更新世中晚期。本次探测工作对技术方法进行了探索,并提出以下建议:针对新发现的隐伏断裂,宜采用从已知点向外逐次探测的方式,即完成上一条测线的设计、施工与解译工作后,根据探测结果布设下一条测线;基于地震时间剖面进行钻探设计时,既要考虑断层两盘反射波组延伸与变形特征,又要考虑物探解译上断点与实际上断点的埋深差异;在河流下游开展钻孔联合地质剖面探测与地层对比时,需充分考虑局部地貌条件差异与第四纪海平面对陆域地表过程的影响。Abstract: It’s a fundamental method for buried fault location and fault activity identification to carry out shallow seismic exploration and drilling joint profile works. Furthermore, the method needs to be constantly summarized and improved in practical work. This paper made a thorough investigation of basic pattern of buried faults in Huaian City urban district by means of shallow seismic exploration, combined with drilling joint geological profile detection and Quaternary chronology test. The latest activity age and characteristics of the newly discovered fault, named Nihuzhuang-Qilidun fault, are defined by then. Nihuzhuang-Qilidun fault is a high-angle normal fault, 43 kilometers investigated, trending nearly South-North and dipping west with dip angle of 72º to 82º. Shallow seismic exploration reveals the up-and-down anti-dip characteristics of the fault plane that is nearly upright or S-shaped. This indicates the strike-slip characteristic of the fault. The fault crosses the NE-trending Huaiyin-Xiangshui fault and the NW-trending Wuxi-Suqian fault. Its latest activity era traces to middle and late Middle Pleistocene. Exploration on the technical method is also carried out in the practical detecting process and the following three suggestions are summarized. It is advisable to take the approach of successive detection from the known point outwards studying newly discovered buried fault. The further survey line should be laid out according to the detection results after completing the design, construction and interpretation of a former survey line. It is necessary to consider not only the extension and deformation characteristics of the reflected wave groups on the two sides of the fault, but also the difference in the burial depth between the breakpoint on the geophysical interpretation and the actual breakpoint while designing drilling plan based on seismic time profiles. The effects of local differences in geomorphological conditions and Quaternary sea level on land surface processes need to be considered when carrying out drilling joint geological profile detection and stratigraphic correlation in the lower reaches of the river.
-
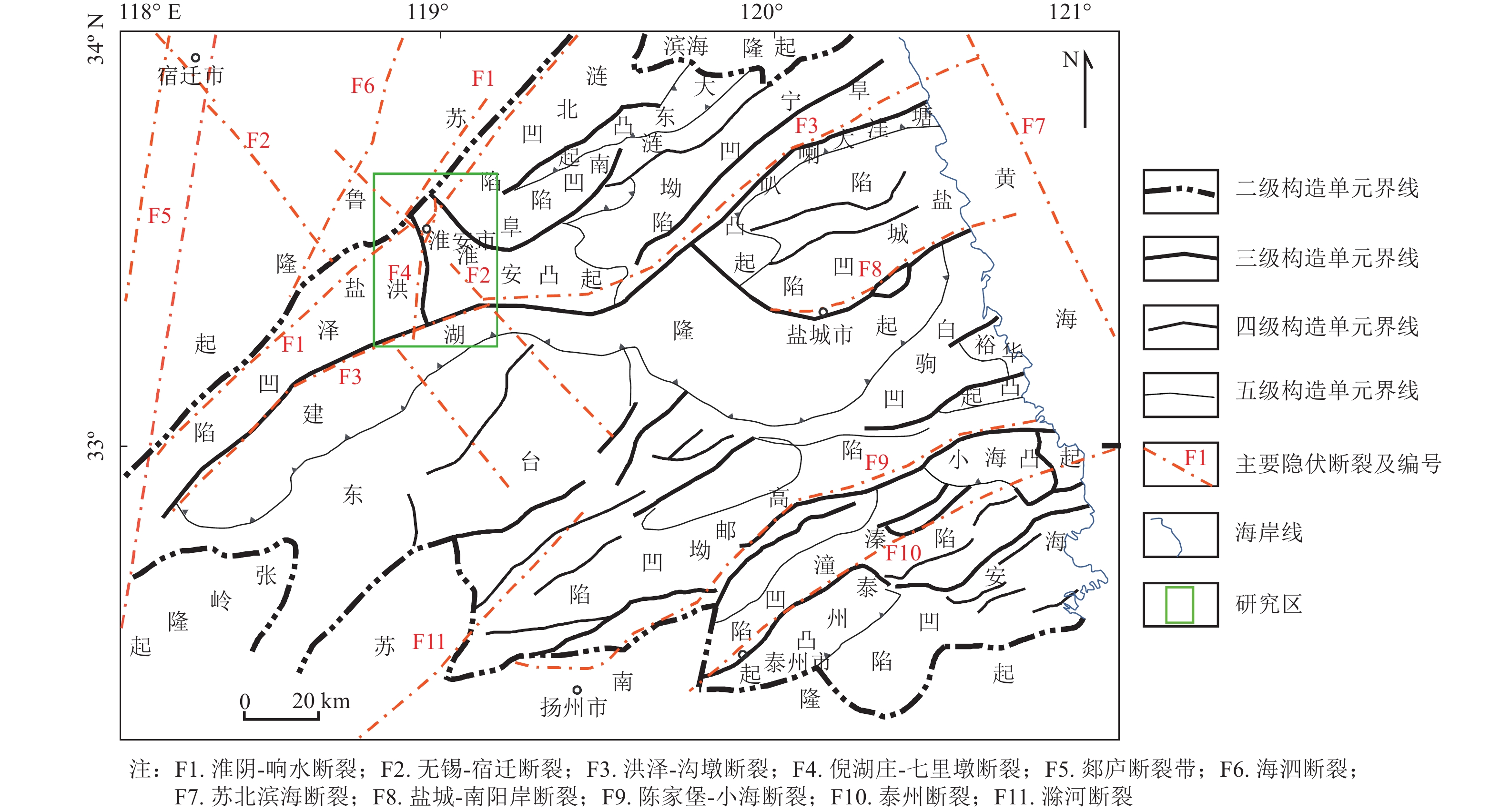
图 1 苏北盆地区域构造(据陈伟等(2020)研究修改)
Figure 1. Regional tectonic map of the Subei basin (Modified after Chen Wei et al., 2020 )
表 1 钻孔联合地质剖面年代样品测试结果
Table 1. Dating results of chronological samples in the drilling joint geological profiles
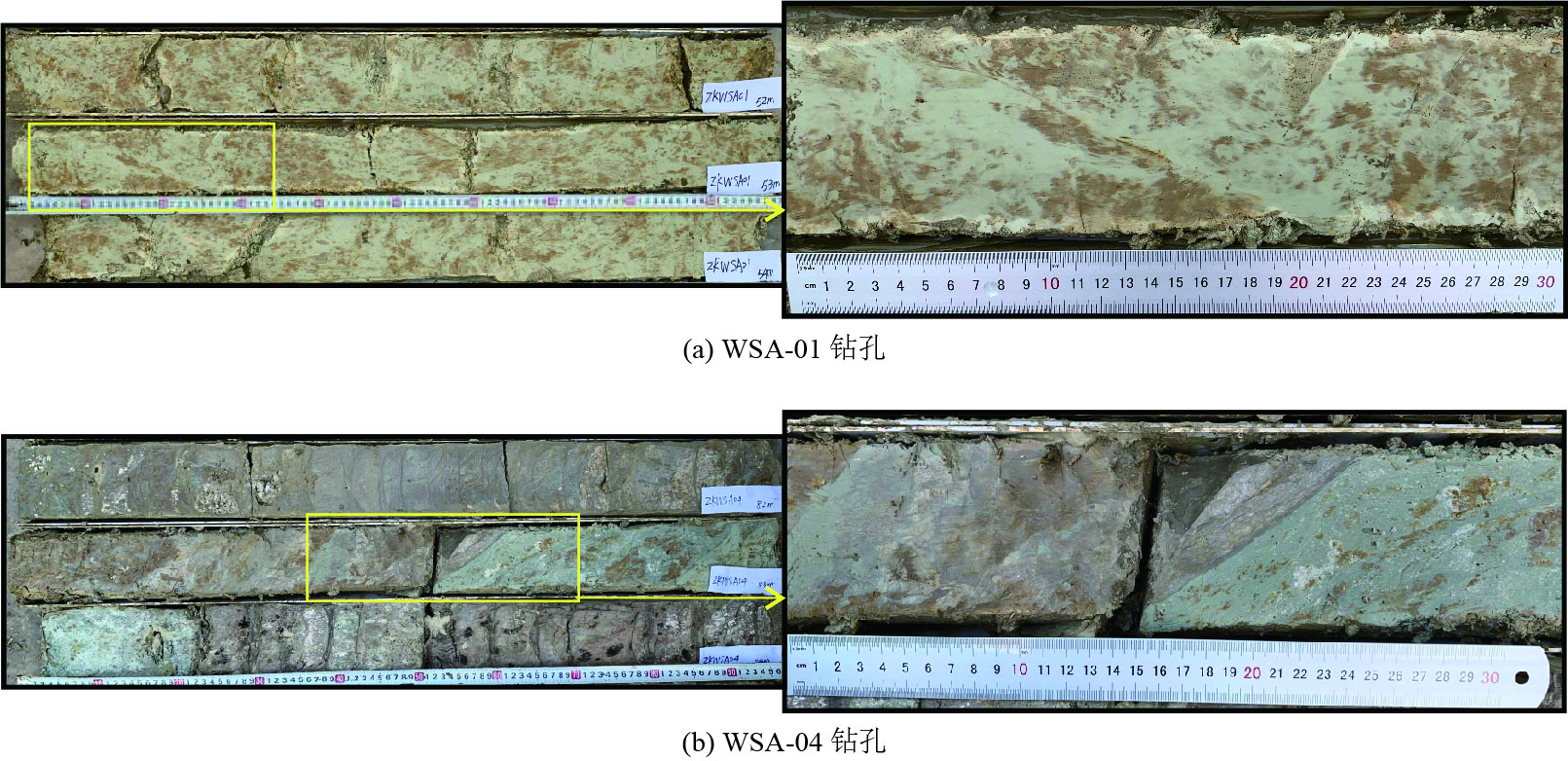
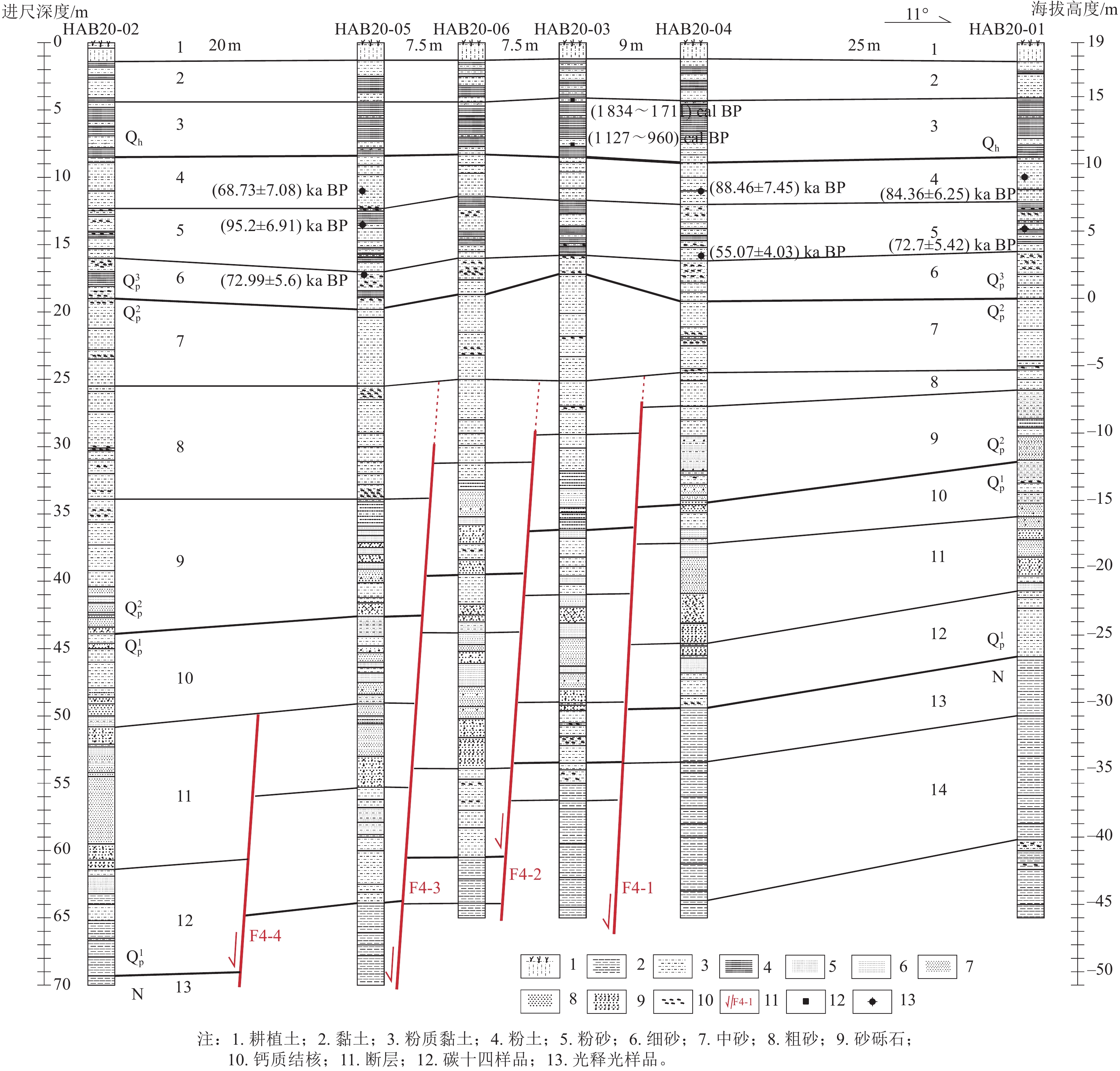
样品编号 钻孔编号 采样深度/m 测年方法 测年结果 WSA05-C03 WSA-05 3.8 碳十四 (5 054~4 865)cal BP WSA05-C06 WSA-05 16.1 碳十四 (4 295~4 090)cal BP WSA05-C08 WSA-05 20.5 碳十四 (5 539~5 477)cal BP WSA05-C09 WSA-05 22.1 碳十四 (4 616~4 421)cal BP WSA05-C10 WSA-05 23.8 碳十四 (9 438~9 252)cal BP WSA05-C12 WSA-05 27.8 碳十四 (11 330~11 210)cal BP WSA05-C13 WSA-05 33.2 碳十四 (9 538~9 467 )cal BP WSA07-06She WSA-07 22.9 碳十四 (2 636~2 283)cal BP WSA07-06Pla WSA-07 22.9 碳十四 (3 572~3 450)cal BP WSA07-07 WSA-07 24.2 碳十四 (10 237~10 129)cal BP WSA05-01 WSA-05 17.6 光释光 (0.89±0.12)ka BP WSA05-02 WSA-05 29.8 光释光 (10.16±0.65)ka BP WSA05-03 WSA-05 32.1 光释光 (8.03±0.51)ka BP WSA05-04 WSA05 41.8 光释光 (117.15±14.91)ka BP WSA05-05 WSA-05 44.0 光释光 (119.37±8.56)ka BP WSA01-01 WSA-01 17.6 光释光 (0.80±0.08)ka BP WSA01-03 WSA-01 25.7 光释光 (10.46±0.68)ka BP WSA01-05 WSA-01 34.55 光释光 (10.09±0.66)ka BP WSA07-01 WSA-07 29.1 光释光 (10.97±0.71)ka BP WSA07-02 WSA-07 33.3 光释光 (107.8±18.22)ka BP WSA07-03 WSA-07 41.8 光释光 (73.5±5.33)ka BP HAB2003-C01 HAB2003 4.1 碳十四 (1 834~1 711)cal BP HAB2003-C02Org HAB2003 7.8 碳十四 (1 127~960)cal BP HAB2003-C02Pla HAB2003 7.7 碳十四 (314~265)cal BP HAB2004-01 HAB2004 11.0 光释光 (88.46±7.45)ka BP HAB2004-02 HAB2004 15.8 光释光 (55.07±4.03)ka BP HAB2001-01 HAB2001 10.0 光释光 (84.36±6.25)ka BP HAB2001-02 HAB2001 13.8 光释光 (72.7±5.42)ka BP HAB2005-01 HAB2005 11.0 光释光 (68.73±7.08)ka BP HAB2005-02 HAB2005 13.6 光释光 (95.2±6.91)ka BP HAB2005-03 HAB2005 17.2 光释光 (72.99±5.6)ka BP -
[1] 柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测——以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地震地质, 28(4): 536—546 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002Chai C. Z. , Meng G. K. , Du P. , et al. , 2006. Comprehensive multi-level exploration of buried active fault: an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 28(4): 536—546. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002 [2] 陈伟, 邱旭明, 2020. 金湖凹陷石港断裂发育特征及其控圈作用. 复杂油气藏, 13(3): 1—5, 17Chen W. , Qiu X. M. , 2020. Development characteristics of Shigang Fault and its trap controlling role in Jinhu Depression. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 13(3): 1—5, 17. (in Chinese) [3] 邓起东, 2002. 城市活动断裂探测和地震危险性评价问题. 地震地质, 24(4): 601—605 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.015Deng Q. D. , 2002. Exploration and seismic hazard assessment of active faults in urban areas. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 601—605. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.015 [4] 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2003. 城市活动断裂探测的方法和技术. 地学前缘, 10(1): 93—104 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012Deng Q. D. , Xu X. W. , Zhang X. K. , et al. , 2003. Methods and techniques for surveying and prospecting active faults in urban areas. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 93—104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012 [5] 方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金等, 2002. 探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法. 地震地质, 24(4): 606—613 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016Fang S. M. , Zhang X. K. , Liu B. J. , et al. , 2002. Geophysical methods for the exporation of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 606—613. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016 [6] 顾勤平, 康清清, 许汉刚等, 2013. 薄覆盖层地区隐伏断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术——以废黄河断层为例. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 1609—1618 doi: 10.6038/cjg20130518Gu Q. P. , Kang Q. Q. , Xu H. G. , et al. , 2013. Seismic exploration methods for buried faults and its up-breakpoint in thin sediment areas-an example of the Feihuanghe fault. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(5): 1609—1618. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20130518 [7] 顾勤平, 许汉刚, 赵启光, 2015. 厚覆盖层地区隐伏活断层探测的地震方法技术—以桥北镇—宿迁断层为例. 物探与化探, 39(2): 408—415Gu Q. P. , Xu H. G. , Zhao Q. G. , 2015. The seismic exploration method for buried active faults in thick sediment area: a case study of Qiaobei-Suqian fault. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 39(2): 408—415. (in Chinese) [8] 何付兵, 徐锡伟, 何振军等, 2020. 利用浅层地震反射剖面探测研究大兴断裂北段新近纪—第四纪的构造特征. 地震地质, 42(4): 893—908 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.04.008He F. B. , Xu X. W. , He Z. J. , et al. , 2020. Research on Neogene-quaternary stratigraphic structure and shallow tectonic features in the north section of Daxing Fault zone based on shallow seismic reflection profiling. Seismology and Geology, 42(4): 893—908. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.04.008 [9] 何仲太, 马保起, 卢海峰等, 2009. 北京东北旺-小汤山断裂存在的证据. 地震地质, 31(2): 233—246 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2009.02.004He Z. T. , Ma B. Q. , Lu H. F. , et al. , 2009. Evidence of the Dongbeiwang-Xiaotangshan fault in Beijing. Seismology and Geology, 31(2): 233—246. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2009.02.004 [10] 雷启云, 柴炽章, 孟广魁等, 2011. 隐伏活断层钻孔联合剖面对折定位方法. 地震地质, 33(1): 45—55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.005Lei Q. Y. , Chai C. Z. , Meng G. K. , et al. , 2011. Method of locating buried active fault by composite drilling section doubling exploration. Seismology and Geology, 33(1): 45—55. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.005 [11] 刘保金, 张先康, 方盛明等, 2002. 城市活断层探测的高分辨率浅层地震数据采集技术. 地震地质, 24(4): 524—532 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006Liu B. J. , Zhang X. K. , Fang S. M. , et al. , 2002. Acquisition technique of high-resolution shallow seismic data for surveying of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 524—532. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006 [12] 刘保金, 张先康, 陈颙等, 2011. 三河-平谷8.0级地震区地壳结构和活动断裂研究——利用单次覆盖深反射和浅层地震剖面. 地球物理学报, 54(5): 1251—1259 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.05.014Liu B. J. , Zhang X. K. , Chen Y. , et al. , 2011. Research on crustal structure and active fault in the Sanhe-Pinggu Earthquake (M8.0) Zone based on single-fold deep seismic reflection and shallow seismic reflection profiling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(5): 1251—1259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.05.014 [13] 潘纪顺, 刘保金, 朱金芳等, 2002. 城市活断层高分辨率地震勘探震源对比试验研究. 地震地质, 24(4): 533—541 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.007Pan J. S. , Liu B. J. , Zhu J. F. , et al. , 2002. Comparative experiment on seismic sources in high-resolution seismic exploration for urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 533—541. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.007 [14] 王银, 孟广魁, 柴炽章等, 2015. 隐伏活断层探测中的精定位技术——以银川盆地芦花台断裂为例. 地震地质, 37(1): 256—268 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.020Wang Y. , Meng G. K. , Chai C. Z. , et al. , 2015. The accurate location methods for buried active fault exploration: an example of Luhuatai Faults in Yinchuan Graben. Seismology and Geology, 37(1): 256—268. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.020 [15] 向宏发, 方仲景, 张晚霞等, 1993. 北京平原区隐伏断裂晚第四纪活动性的初步研究. 地震学报, 15(3): 385—388. [16] 向宏发, 王学潮, 虢顺民等, 2000. 聊城—兰考隐伏断裂第四纪活动性的综合探测研究. 地震地质, 22(4): 351—359 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.04.003Xiang H. F. , Wang X. C. , Guo S. M. , et al. , 2000. Integrated survey and investigation on the quaternary activity of the Liaocheng-Lankao buried fault. Seismology and Geology, 22(4): 351—359. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.04.003 [17] 向宏发, 2003. 隐伏活动构造探测研究的若干问题讨论. 地震地质, 25(3): 460—466 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.03.011Xiang H. F. , 2003. Some problems in the exploration and research of buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 25(3): 460—466. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.03.011 [18] 徐锡伟, 计凤桔, 于贵华等, 2000. 用钻孔地层剖面记录恢复古地震序列: 河北夏垫断裂古地震研究. 地震地质, 22(1): 9—19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.01.002Xu X. W. , Ji F. J. , Yu G. H. , et al. , 2000. Reconstruction of Paleoearthquake(该单词原文章为排版错误, Paleoearthouake该单词应为Paleoearthquake) sequence using stratigraphic records from drill logs: a study at the Xiadian Fault, Beijing. Seismology and Geology, 22(1): 9—19. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.01.002 [19] 杨晓平, 曹景虎, 陈献程, 2012. 夏垫活动断裂两盘岩心氧化铁变化. 地震地质, 34(4): 659—671 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.010Yang X. P. , Cao J. H. , Chen X. C. , 2012. The iron oxide changes in drilling cores from the two walls of Xiadian active fault. Seismology and Geology, 34(4): 659—671. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.010 [20] 张磊, 白凌燕, 蔡向民等, 2014. 北京南口-孙河断裂北西段综合物探剖面定位及其活动性研究. 现代地质, 28(1): 234—242 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.01.027Zhang L. , Bai L. Y. , Cai X. M. , et al. , 2014. Study on the position of north west section of Nankou-Sunhe Fault in Beijing and its activity. Geoscience, 28(1): 234—242. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.01.027 [21] 张世民, 刘旭东, 任俊杰等, 2005. 顺义地裂缝成因与顺义—良乡断裂北段第四纪活动性讨论. 中国地震, 21(1): 84—92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.01.009Zhang S, M. , Liu X. D. , Ren J. J. , et al. , 2005. Quaternary activities of northern segment of the Shunyi-Liangxiang fault. Earthquake Research in China, 21(1): 84—92. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.01.009 [22] 张世民, 王丹丹, 刘旭东等, 2007. 北京南口—孙河断裂带北段晚第四纪活动的层序地层学研究. 地震地质, 29(4): 729—743 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.04.004Zhang S, M. , Wang D. D. , Liu X. D. , et al. , 2007. Sequence stratigraphy study of late quaternary activities of Nankou-Sunhe Fault in its northern segment, Beijing. Seismology and Geology, 29(4): 729—743. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.04.004 [23] 张晓亮, 张磊, 蔡向民等, 2016. 北京平原区黄庄—高丽营断裂北段结构特征及活动特点研究. 中国地质, 43(4): 1258—1265Zhang X. L. , Zhang L. , Cai X. M. , et al. , 2016. A study of structure and activity characteristics of the northern segment of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying Fault in Beijing plain area. Geology in China, 43(4): 1258—1265. (in Chinese) -



 下载:
下载: