Evaluation of Influencing Factors of Earthquake Damage of Multi-storey Brick Building Based on AdaBoost Algorithm
-
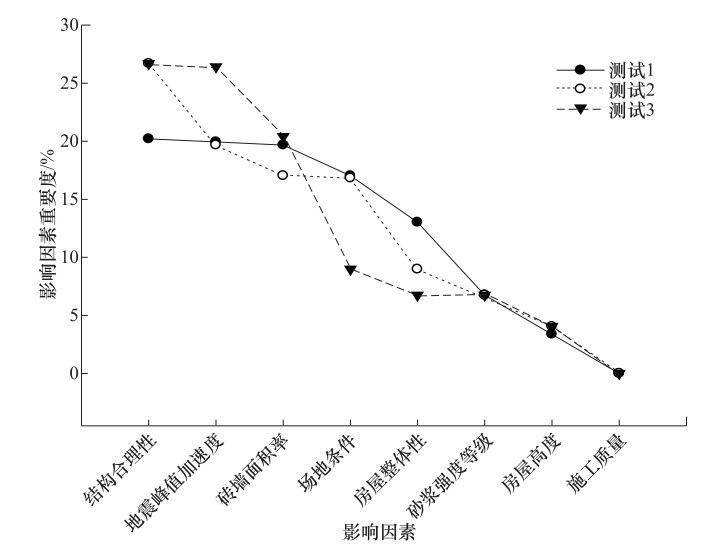
摘要: 多层砖房是最常用的结构形式之一,对其进行震害预测尤为重要,选择合适的影响因素是震害预测中最重要的环节之一。本文基于AdaBoost算法对多层砖房震害影响因素进行评估,给出影响因素重要度排序,并将结果与灰色关联分析法进行比较。研究发现结构合理性、地震峰值加速度、砖墙面积率和场地条件对多层砖房震害影响最大,因此在多层砖房震害预测中应优先考虑这4个因素,并在结构设计建造过程中予以足够重视。
-
关键词:
- 多层砖房 /
- 震害 /
- 影响因素 /
- AdaBoost算法
Abstract: Multi-storey brick houses are one of the most commonly used structural forms, so it is especially important to predict earthquake damage. Choosing the appropriate influencing factors is one of the most important aspects of earthquake damage prediction. Based on the AdaBoost algorithm, this paper evaluates the influencing factors of seismic damage of multi-storey brick buildings, gives the order of importance of factors, and compares the results with the gray correlation analysis method. It is concluded that the structural rationality, the peak acceleration of the earthquake, the area ratio of the brick wall and the site conditions are the most important, so it should be given enough attention in the process of structural design and construction.-
Key words:
- Multi-storey brick houses /
- Earthquake damage /
- Influencing factors /
- AdaBoost algorithm
-
表 1 多层砖房震害影响因素特征及取值
Table 1. Characteristics and influencing factors of seismic damage of multi-storey brick buildings
影响因素 特征 取值 房屋高度 — — 施工质量 其他条件相同时,施工质量越好,破坏程度越低 优 10 中 8 差 6 砂浆等级 — 按实际等级取值 结构合理性 结构合理度越大,破坏程度越低 取结构抗震性能良好隶属度的值(谭克艰等,1997) 砖墙面积率 $砖墙面积率= \frac{砖墙净面积}{建筑面积}$ 按实际计算取值 房屋整体性 整体性越好,破坏程度越低 楼盖 现浇 5 预制 4 木制 3 屋盖 现浇 5 预制 4 木制 3 圈梁 有 1 构造柱 有 1 是否有地下室和筏板基础 是 1 否 0 房屋是否开裂 是 -1 否 0 场地条件 场地条件越好,破坏程度越低 Ⅰ类 10 Ⅱ类 8 Ⅲ类 6 场地条件 场地条件越好,破坏程度越低 Ⅳ类 4 地形地貌是否不利 是 -1 否 0 地下水位是否较高 是 -1 否 0 PGA PGA越大,破坏程度越高 按实际值取值 表 2 数据集
Table 2. Data set
序号 房屋层数 施工质量 砂浆等级/MPa 结构合理性 砖墙面积率/% 房屋整体性 场地条件 PGA/g 破坏程度 1 2 10 25 0.50 8.20 8.00 6 0.20 中等破坏 2 2 10 10 0.40 10.00 8.00 7 0.25 严重破坏 3 3 10 10 0.30 11.50 9.00 8 0.25 中等破坏 4 2 10 35 0.45 9.70 9.50 7 0.15 轻微破坏 5 4 10 25 0.36 7.60 7.50 10 0.20 中等破坏 6 2 10 25 0.55 4.30 10.00 9 0.10 轻微破坏 7 3 10 25 0.43 6.87 8.00 3 0.25 严重破坏 8 3 10 10 0.40 7.52 9.50 7 0.30 中等破坏 9 2 10 35 0.38 8.32 8.50 6 0.20 轻微破坏 10 5 10 10 0.46 11.50 8.00 8 0.25 基本完好 11 2 10 25 0.41 4.65 7.50 9 0.05 轻微破坏 12 3 10 10 0.50 9.42 12.00 8 0.20 基本完好 13 3 10 10 0.47 13.60 9.00 5 0.25 轻微破坏 14 2 10 25 0.52 10.70 8.50 7 0.20 轻微破坏 15 4 10 25 0.48 3.60 7.50 4 0.15 倒塌 16 3 10 25 0.54 6.69 8.00 8 0.25 轻微破坏 17 3 10 10 0.40 8.40 9.50 8 0.20 轻微破坏 18 4 10 25 0.45 8.50 9.46 8 0.30 严重破坏 19 2 10 25 0.47 10.30 7.00 7 0.25 中等破坏 20 4 10 25 0.47 3.23 8.00 8 0.15 轻微破坏 21 2 10 10 0.48 3.50 9.00 8 0.10 轻微破坏 22 3 10 5 0.35 8.64 8.00 7 0.20 严重破坏 23 3 10 10 0.37 6.00 8.00 7 0.20 严重破坏 24 3 10 10 0.34 9.00 10.00 7 0.25 严重破坏 25 3 10 10 0.40 9.00 7.00 7 0.30 倒塌 26 3 10 10 0.44 6.00 9.00 7 0.15 中等破坏 27 3 10 25 0.40 10.00 10.00 8 0.30 倒塌 28 3 10 25 0.40 9.00 10.00 7 0.25 倒塌 29 2 10 10 0.50 9.00 12.00 10 0.20 基本完好 30 4 10 10 0.50 9.00 9.00 9 0.15 轻微破坏 表 3 影响因素重要度排序及与灰色关联分析法结果的对比
Table 3. Ranking of factors of influence factors and comparison with results of grey correlation analysis method
影响因素 重要度(AdaBoost结果) 灰色关联分析法中的排名 结构合理性 0.266878512 4 PGA 0.196731755 1 砖墙面积率 0.170314083 2 场地条件 0.168439716 5 房屋整体性 0.089834515 8 砂浆等级 0.067375887 6 房屋高度 0.040425532 7 施工质量 0.000000000 3 -
贾晗曦, 林均岐, 刘金龙, 2019.建筑结构地震易损性分析研究综述.震灾防御技术, 14(1):42—51. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190105&flag=1 姜伟, 马令勇, 刘功良, 2011.基于MATLAB神经网络方法的多层砖房震害预测.西北地震学报, 33(2):155—158. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb201102009 刘本玉, 叶燎原, 江见鲸, 2002.用模糊人工神经网络方法预测多层砖房震害.清华大学学报(自然科学版), 42(6):843—846. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhdxxb200206036 刘章军, 叶燎原, 2007.基于模糊概率的多层砖房震害预测.地震研究, 30(1):99—105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzyj200701019 欧盛, 2011.砖砌体房屋震害预测方法研究.哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所. 谭克艰, 曹晖, 毛沂, 1997.建筑体型抗震性能模糊评判专家系统.重庆建筑大学学报, 19(06):108—112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JIAN706.018.htm 汤皓, 陈国兴, 2006.基于灰关联与人工神经网络综合评价模型的多层砖房震害预测.世界地震工程, 22(4):133—139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdzgc200604025 杨秀萍, 程运平, 陈克珩等, 2013.基于ACCRBF网络的多层砖房震害预测.震灾防御技术, 8(1):90—96. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130110&flag=1 尹之潜, 李树桢, 赵直等, 1991.地震灾害预测与地震灾害等级.中国地震, 7(1):11—21. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=661030 于天洋, 郭恩栋, 李倩等, 2018.清水池震害综合预测方法.震灾防御技术, 13(2):353—362. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180210&flag=1 Asim K. M., Idris A., Iqbal T., et al., 2018. Seismic indicators based earthquake predictor system using Genetic Programming and AdaBoost classification. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 111: 1—7. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.04.020 Jia H. X., Lin J. Q., Liu J. L., 2019. An earthquake fatalities assessment method based on feature importance with deep learning and random forest models. Sustainability, 11(10): 2727. doi: 10.3390/su11102727 Provost F., Hibert C., Malet J. P., 2017. Automatic classification of endogenous landslide seismicity using the Random Forest supervised classifier:Seismic sources automatic classification. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(1): 113—120. doi: 10.1002/2016GL070709 Shin Y., Kim D. W., Kim J. Y., et al., 2009. Application of AdaBoost to the Retaining Wall Method Selection in Construction. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 23(3): 188—192. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000001 -



 下载:
下载: