The study on extraction of seismic damage of buildings from remote sensing image based on fully convolutional neural network
-
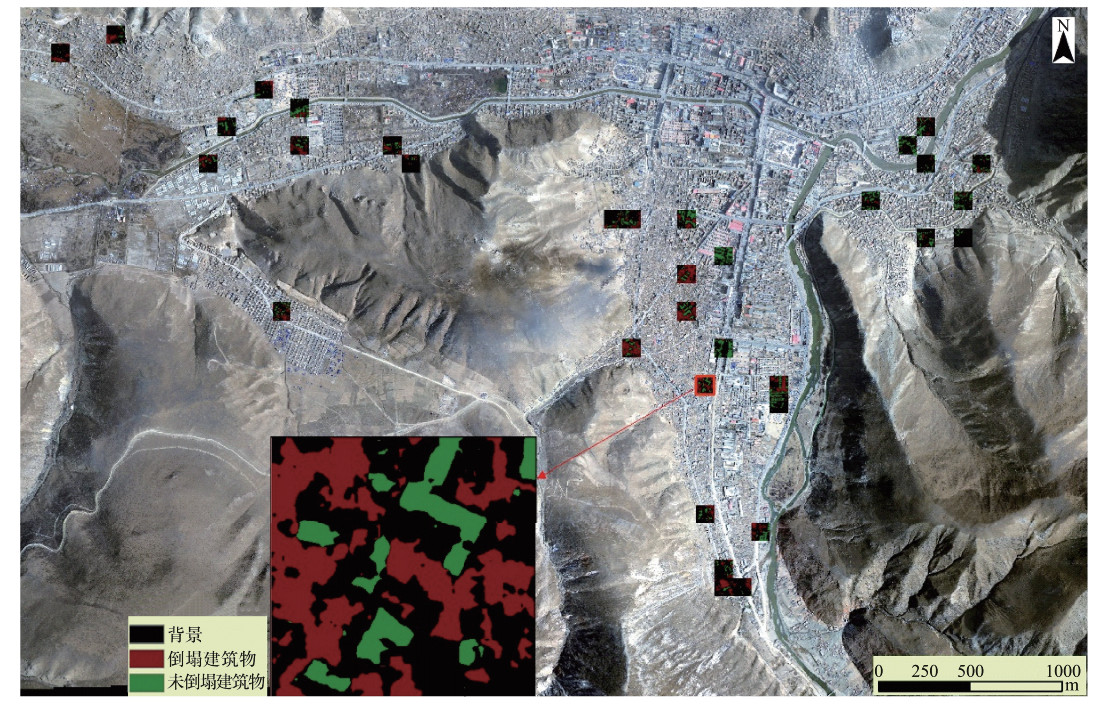
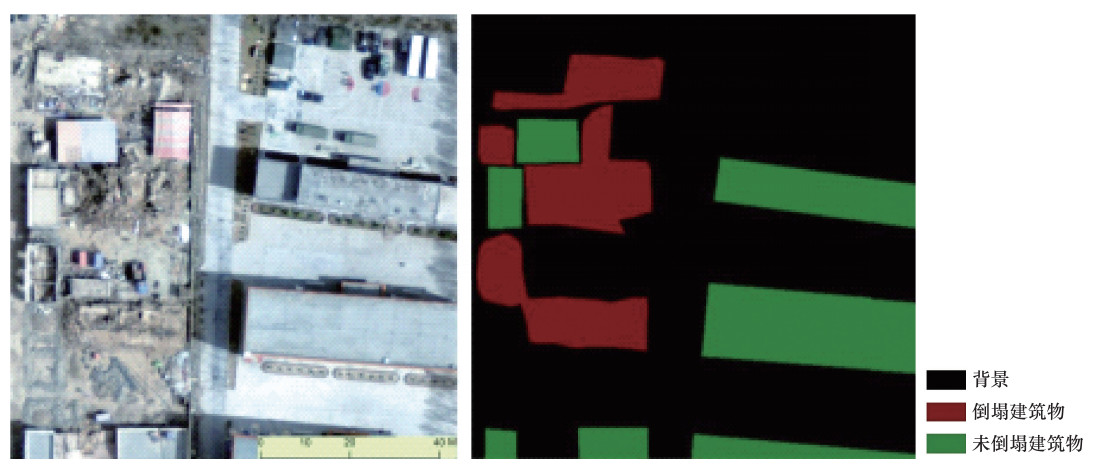
摘要: 为解决建筑物震害信息提取自动化程度不高的问题,本文将全卷积神经网络应用于建筑物震害遥感信息提取。以玉树地震后获取的玉树县城区0.2m分辨率航空影像作为建筑物震害信息提取试验数据源,将试验区地物划分为倒塌建筑物、未倒塌建筑物和背景3类。对427个500×500像素的子影像进行人工分类与标注,选取393个组成训练样本集,34个用于验证。利用训练样本集对全卷积神经网络进行训练,采用训练后的网络对验证样本进行建筑物震害信息提取及精度评价。研究结果表明:建筑物震害遥感信息提取总体分类精度为82.3%,全卷积神经网络方法能提高信息提取自动化程度,具有较好的建筑物震害信息提取能力。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that the automation degree of extracting damaged Buildings caused by earthquake is not very high,in this paper a fully convolutional neural network is applied to extract the remote sensing information of earthquake damage to buildings. The 0.2m-resolution aerial image of the Yushu County urban area obtained after the Yushu earthquake was used as the data source to test the result of convolutional neural network. The objects in the test area were classified into collapsed buildings,uncollapsed buildings,and background. Classify and label 427 sub-images of 500×500 pixels manually,393 of them were selected as training sample set,and others as verification sample set. The training sample set is used to train the full convolutional neural network and the trained network is used to extract the building seismic damage information and evaluate the accuracy based on the verification sample. The result shows that the overall classification accuracy is 82.3%,and the fully convolutional neural network can improve the automation of information extraction and has a better ability to extract building seismic damage information.
-
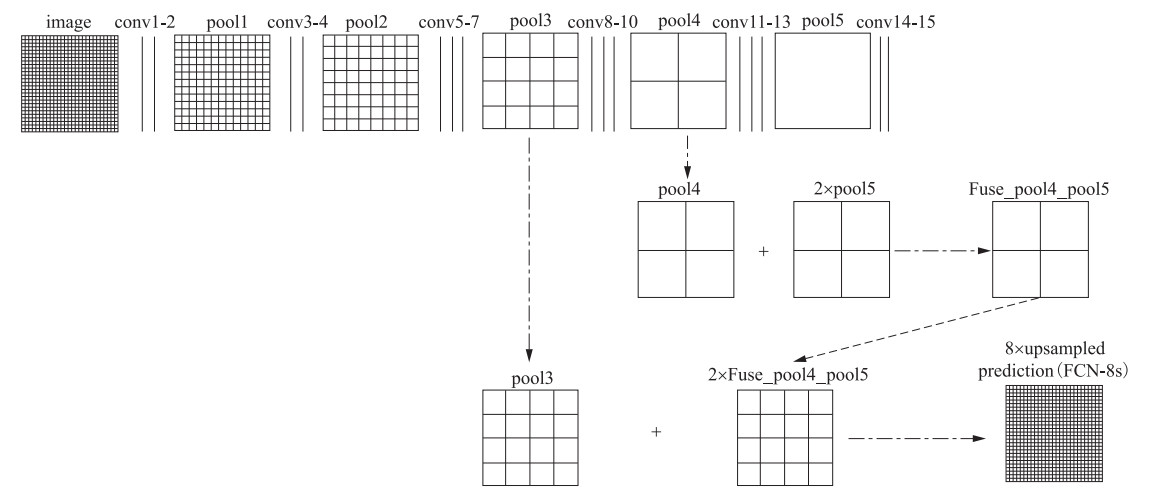
图 1 全卷积神经网络结构图(Long等,2015)
Figure 1. Structure diagram of skip-layers of fully convolutional neural network(Long等, 2015)
表 1 基于全卷积神经网络的建筑物震害提取结果混淆矩阵
Table 1. The obfuscation matrix of building damage extraction results based on full convolutional neural network

背景 倒塌建筑物 未倒塌建筑物 合计 正确率 背景 5098760 309868 299996 5708624 0.893 倒塌建筑物 550951 1042364 19899 1613214 0.646 未倒塌建筑物 308373 19246 850543 1178162 0.722 合计 5958084 1371478 1170438 8500000 表 2 基于cart监督分类的建筑物震害提取结果混淆矩阵
Table 2. confusion matrix of building damage extraction results based on cart supervised classification

背景 倒塌建筑物 未倒塌建筑物 合计 正确率 背景 3400364 1744432 563828 5708624 0.596 倒塌建筑物 206370 1366026 40818 1613214 0.847 未倒塌建筑物 366833 234979 576350 1178162 0.490 合计 3973567 3345437 1180996 8500000 -
常亮, 邓小明, 周明全等, 2016.图像理解中的卷积神经网络.自动化学报, 42(9):1300-1312. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdhxb201609002 陈文凯, 何少林, 张景发等, 2008.利用遥感技术提取震害信息方法的研究进展.西北地震学报, 30(1):88-93. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdzxb200801018 董燕生, 潘耀忠, 方伟华等, 2011.基于面向对象技术的建筑物震害识别方法研究.地震研究, 34(3):372-377, 403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2011.03.020 金永涛, 杨秀峰, 高涛等, 2018.基于面向对象与深度学习的典型地物提取.国土资源遥感, 30(1):22-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201801004 刘文涛, 李世华, 覃驭楚, 2018.基于全卷积神经网络的建筑物屋顶自动提取.地球信息科学学报, 20(11):1562-1570. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180159 王晓青, 窦爱霞, 王龙等, 2015.2013年四川芦山7.0级地震烈度遥感评估.地球物理学报, 58(1):163-171. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201501014 王晓青, 魏成阶, 苗崇刚等, 2003.震害遥感快速提取研究——以2003年2月24日巴楚-伽师6.8级地震为例.地学前缘, (S1):285-291. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy2003z1039 王岩, 王晓青, 窦爱霞, 2009.面向对象遥感分类方法在汶川地震震害提取中的应用.地震, 29(3):54-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/diz200903007 文翔, 周斌, 阎春恒, 2014.遥感分类方法在建筑物震害提取中的应用(以玉树地震为例).地震地磁观测与研究, 35(5):134-143. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdcgcyyj201405025 吴剑, 陈鹏, 刘耀林等, 2013.震害损毁建筑物高分辨率遥感信息提取方法.地理与地理信息科学, 29(3):35-38, 47, 2. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxygtyj201303008 杨春, 2015.面向对象的高分辨率遥感影像建筑物倒损信息提取.北京: 中国地质大学(北京). Bottou L., 2012. Stochastic gradient descent tricks[M]//Neural networks: Tricks of the trade. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 421-436. Carreira J., Sminchisescu C., 2011. CPMC:Automatic object segmentation using constrained parametric min-cuts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 34(7):1312-1328. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xlyj200906002 Erhan D., Szegedy C., Toshev A., et al., 2014. Scalable object detection using deep neural networks. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH. Fulkerson B., Vedaldi A., Soatto S., et al., 2009. Class segmentation and object localization with superpixel neighborhoods. 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan. Girshick R., Donahue J., Darrell T., et al., 2014. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH. Girshick R., 2015. Fast R-CNN. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago. Janalipour M., Mohammadzadeh A., 2016. Building damage detection using object-based image analysis and ANFIS from high-resolution image (Case study:BAM Earthquake, Iran). IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 9 (5):1937-1945. He K., Zhang X., Ren S., et al., 2015. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Hinton G. E., 2012. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 25(2):1097-1105. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1dc5d01904d2c274eaec2181a93aa339&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Lecun Y., Bottou L., Bengio Y., et al., 1998. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86 (11):2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 Liu W., Anguelov D., Erhan D., et al., 2016.SSD: Single shot multibox detector. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin, Germany: Springer Verlag. Long J., Shelhamer E., Darrell T., 2015. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA. Mnih V., 2013. Machine learning for aerial image labeling. Toronto: University of Toronto. Ren S. Q., He K. M., Girshick R., et al., 2017. Faster R-CNN:Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39 (6):1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 Sermanet P., Eigen D., Zhang X., et al., 2013.OverFeat: Integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks.International Conference on Learning Representations. Shotton J., Johnson M., Cipolla R., 2008. Semantic texton forests for image categorization and segmentation. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Anchorage, AK, USA. Shotton J., Winn J., Rother C., et al., 2009. Textonboost for image understanding:Multi-class object recognition and segmentation by jointly modeling texture, layout, and context. International Journal of Computer Vision, 81 (1):2-23. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=84f14846bf7b58db99c982392291faa9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Simonyan K., Zisserman A., 2014. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Szegedy C., Liu W., Jia Y., et al., 2015. Going deeper with convolutions.2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA. -



 下载:
下载: