Reliminary Research on Quaternary Activity Features of the Northern Section of the Nenjiang Fault Zone
-
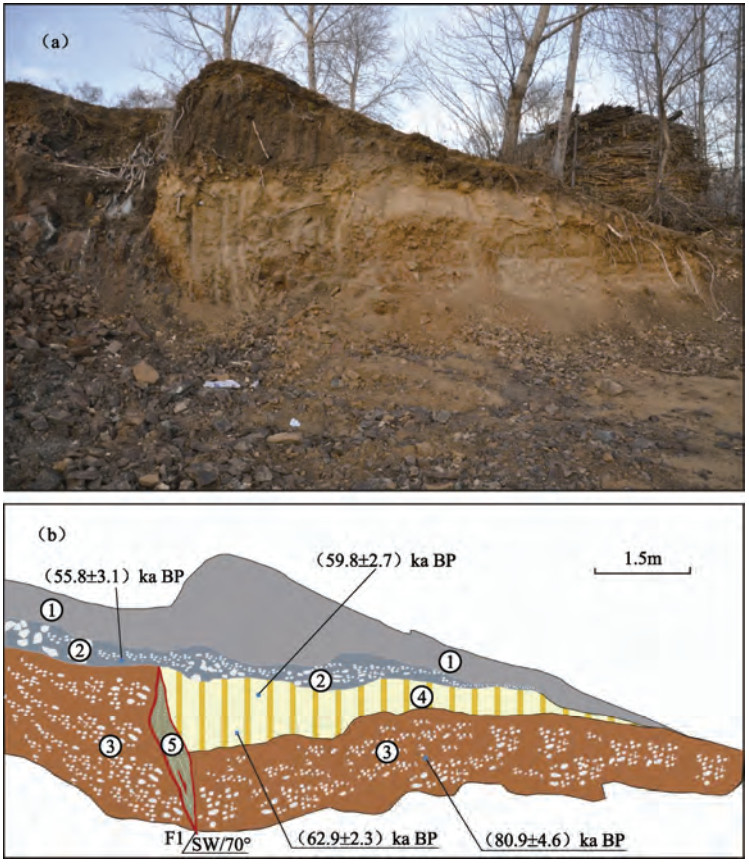
摘要: 嫩江断裂带是松辽盆地的西边界断裂,但受第四系强覆盖等研究条件的限制,前人对该断裂第四纪构造活动的研究较少。本文针对该断裂带北段开展了野外地质调查,并综合大地电磁测深和纵波速度结构等结果,初步研究了嫩江断裂带北段的第四纪活动特征。调查发现,该断裂北段主要发育地貌陡坎、基岩滑坡、地层揉皱变形、近垂直擦痕、基岩崩塌与线性断塞塘等特征。探槽古地震研究揭示断裂带北段在(80.9±4.6)—(62.9±2.3)ka BP曾发生1次古地震事件,运动方式为正断,垂直位移量约1.5m,震级约为MS 7.1—7.3,断裂在晚更新世曾发生过强烈活动。研究结果有助于认识了解该断裂和松辽盆地的第四纪构造变形过程,并为评价该断裂及邻区的地震活动潜势提供参考。Abstract: The Nenjiang fault zone (NJFZ) is the western boundary fault of the Songliao basin, and the Quaternary tectonic deformation of which remains to be understood well because of unfavorable working conditions such as intensive Quaternary coverage. This paper focuses on the Quaternary tectonic activities of the northern section of the NJFZ based on the integrated results of field geological investigation, MT data inversion and P-wave velocity structure. Abundant tectonic evidences are observed along the northern section of the NJFZ such as geomorphic scarps, bedrock landslide, crumple deformation of strata, vertical scratch, and bedrock collapse and linear sag ponds. The trench reveals that at least one normal paleo-event occurred between(80.9±4.6) ka BP and(62.9±2.3)ka BP, which caused 1.5m vertical displacement with an estimated magnitude MS 7.1-7.3, which means that the NFFZ was activated during the late Pleistocene. The results not only help us to understand the Quaternary tectonic deformation process of the NJFZ and the Songliao basin, but also provide references for the assessment of the earthquake potential along the NJFZ and its neighbor areas.
-
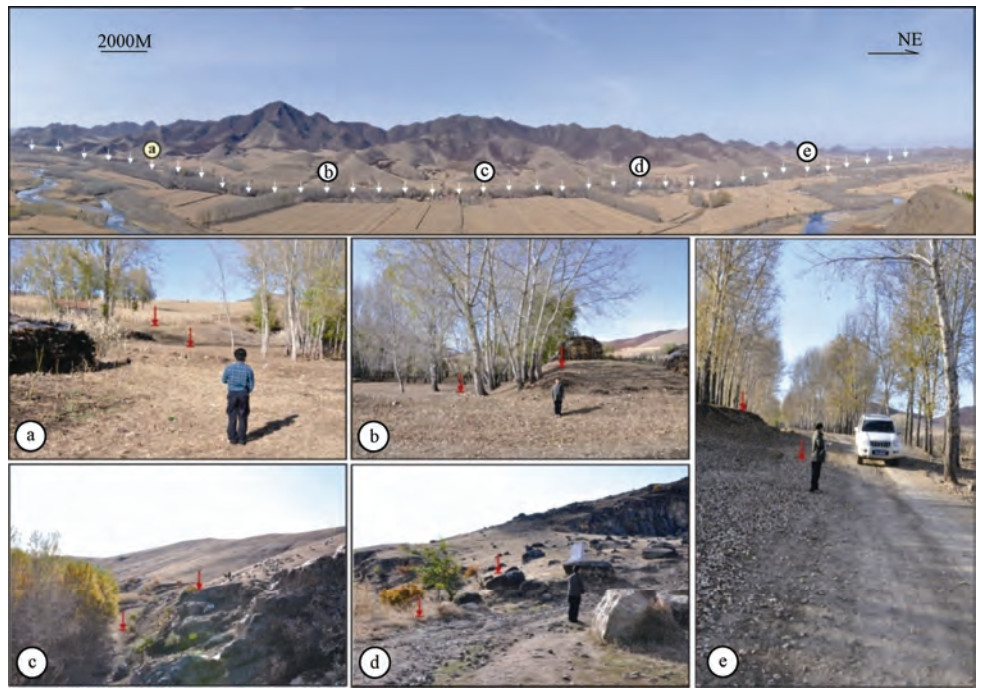
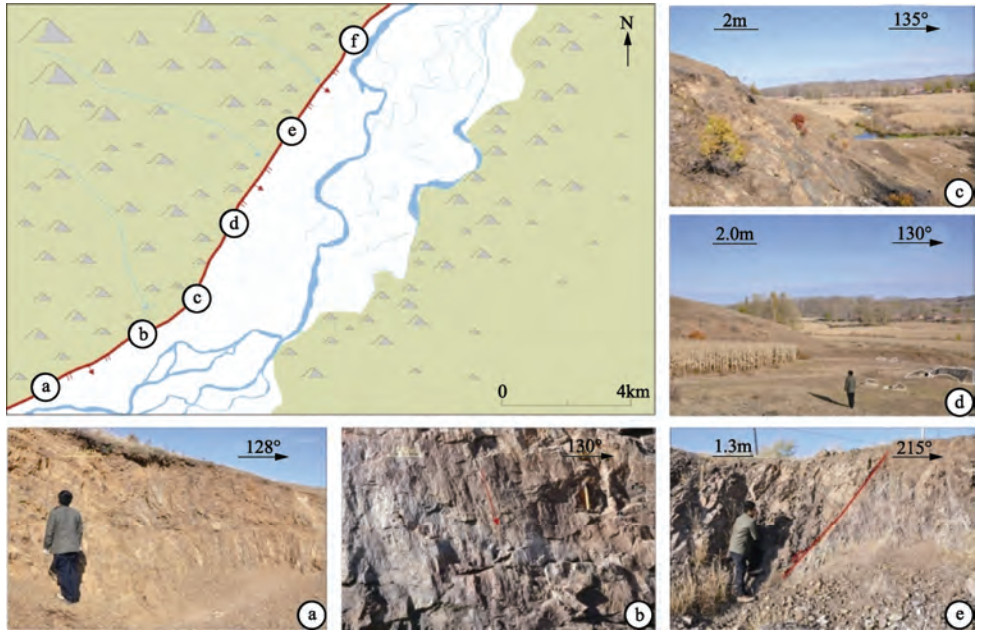
图 1 研究区地震构造(据余中元等,2016;Yu等,2018a)
Figure 1. Seismotectonic map of the research area (Modified from Yu et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2018a)
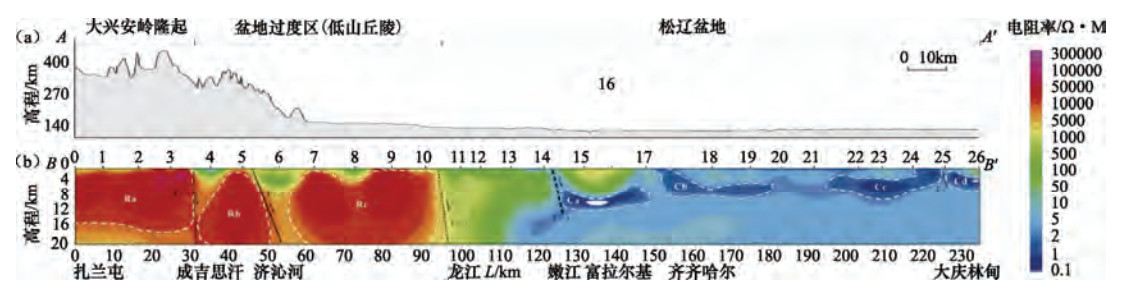
图 3 跨嫩江断裂地形特征(a)与MT 20km反演地质解释结果(b)(据刘殿秘,2008)
Figure 3. The topography and MT 20km inversions across the NJFZ (Modified from Liu, 2008)
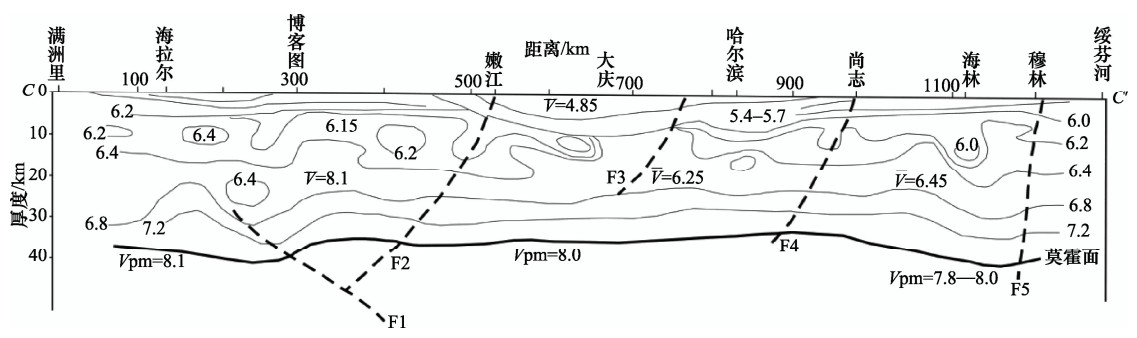
图 4 跨嫩江断裂满洲里-绥芬河地学断面纵波速度结构(据杨宝俊等,1996)
Figure 4. The P-wave velocity structure of Suifenhe-Manzhouli geoscience transect across the NJFZ(Modified from Yang et al., 1996)
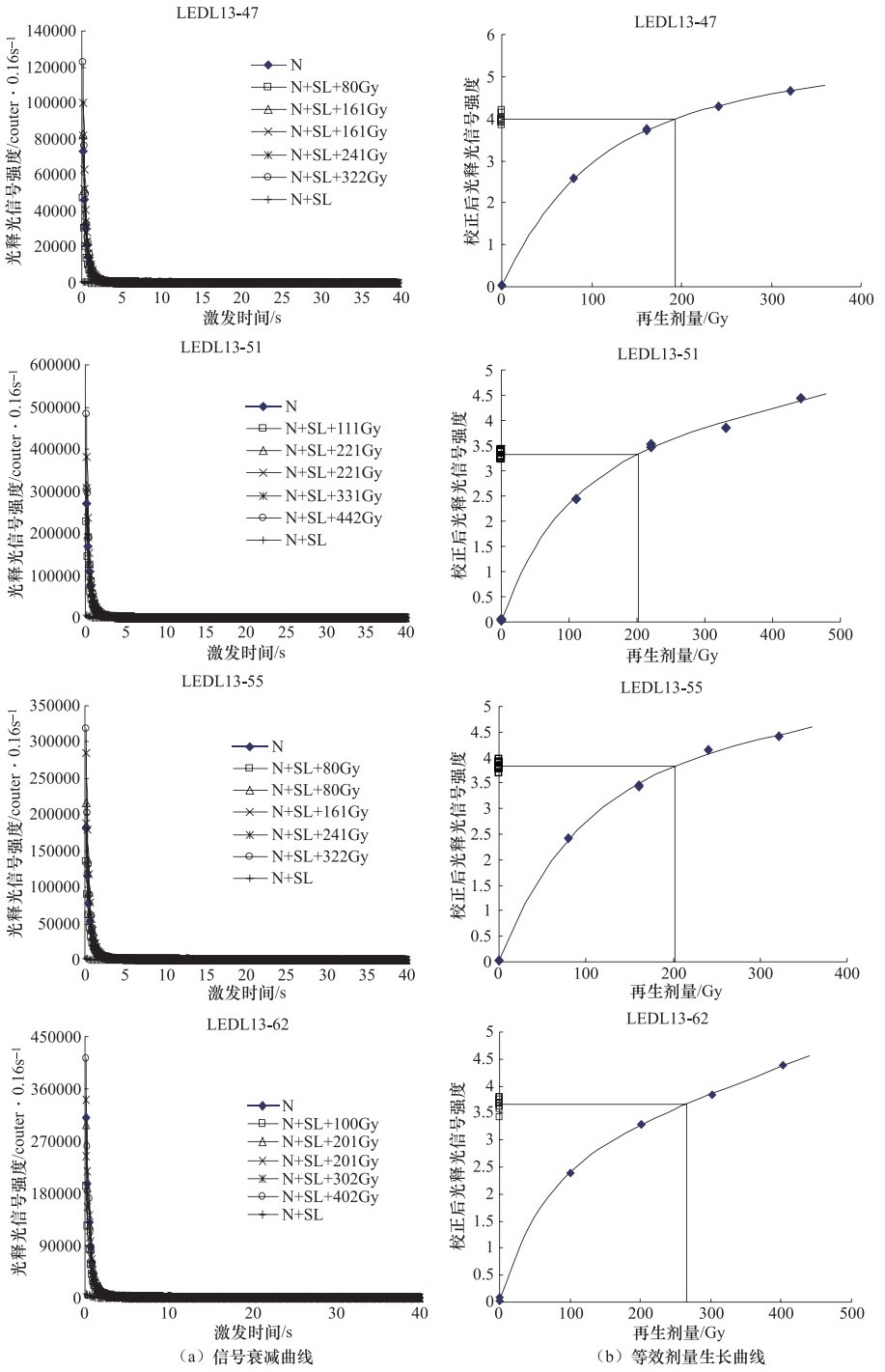
表 1 嫩江断裂北段光释光年代测试结果
Table 1. The OSL dating results of samples from the northern section of the NJFZ
实验号 α计数率
/Counts·ks-1钾元素含量K/% 实际含水量% 环境剂量率
/Gy·ka-1等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka BP LEDL13-47 10.3±0.3 2.1 22 3.5±0.3 192.7±14.7 55.8±3.1 LEDL13-55 10.6±0.3 2.0 23 3.4±0.3 202.1±12.2 59.8±2.7 LEDL13-62 9.3±0.2 2.1 17 3.3±0.3 266.2±22.9 80.9±4.6 LEDL13-51 9.5±0.3 2.1 24 3.2±0.3 202.3±9.7 62.9±2.3 表 2 嫩江断裂北段古地震事件强度估算
Table 2. The estimated magnitude of the paleso-earthquake occurred in northern section of the NJFZ
最新活动时代 陡坎高度 地表破裂长度 估算烈度 估算震级 (80.9±4.6)—(62.9±2.3)ka BP 1.5 m 20 km Ⅸ—Ⅹ度 MS 7.1—7.3 -
陈洪洲, 余中元, 许晓艳等, 2004.嫩江断裂构造及其与地震活动的关系.东北地震研究, 20(4):43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2004.04.007 邓起东, 于贵华, 叶文华, 1992.地震地表破裂参数与震级关系的研究.见: 国家地震局地质研究所编.活动断裂研究(2).北京: 地震出版社, 247-264. 邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平等, 2007.中国活动构造图.北京:地震出版社, 2-3. 刘殿秘, 2008.松辽盆地及其周围典型盆地部分地球物理特征.长春:吉林大学, 12-89. 闵伟, 焦德成, 周本刚等, 2011.依兰-伊通断裂全新世活动的新发现及其意义.地震地质, 33(1):141-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.014 汤兰荣, 吕坚, 曾新福, 2017.赣南及邻区的地震活动特征.华北地震科学, 35(2):82-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2017.02.014 闻学泽, 1995.活动断裂地震潜势的定量评估.北京:地震出版社, 40-93. 徐嘉炜, 马国锋, 1992.郯庐断裂带研究的十年回顾.地质论评, 38(4):316-324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1992.04.004 杨宝俊, 穆石敏, 金旭等, 1996.中国满洲里-绥芬河地学断面地球物理综合研究.地球物理学报, 39(6):772-782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1996.06.007 余中元, 闵伟, 韦庆海等, 2015.松辽盆地北部反转构造的几何特征、变形机制及其地震地质意义——以大安-德都断裂为例.地震地质, 37(1):13-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.002 余中元, 2016.依兰-伊通断裂带的晚第四纪构造变形与分段活动习性.北京:中国地震局地质研究所, 84-130. 余中元, 张培震, 闵伟等, 2016.依兰-伊通断裂带尚志段晚全新世以来的强震复发间隔:来自古地震与历史文献的约束.地震地质, 38(4):844-861. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.04.004 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民等, 2003.中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块.中国科学(D辑), 33(S1):12-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1002 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊等, 2014.东亚大陆新生代构造演化.地震地质, 36(3):574-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003 Liu M., Yang, Y. Q., Shen Z. K., et al., 2007. Active tectonics and intracontinental earthquakes in China: The kinematics and geodynamics. In: Stein S., Mazzotti S., eds., Continental Intraplate Earthquakes: Science, Hazard, and Policy Issues. Boulder: Geological Society of America, 425: 299-318. Min W., Liu Y. G., Jiao D. C., et al., 2013. Evidence for Holocene activity of the Yilan-Yitong fault, northeastern section of the Tan-Lu fault zone in northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 67-68:207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.031 Yin A., 2010. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia:a preliminary synthesis. Tectonophysics, 488(1-4):293-325. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.06.002 Yu Z. Y., Zhang P. Z., Min W., et al., 2015. Late Cenozoic deformation of the Da'an-Dedu Fault Zone and its implications for the earthquake activities in the Songliao basin, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 107:83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.047 Yu Z. Y., Yin N., Shu P., et al., 2018a. Late Quaternary paleoseismicity and seismic potential of the Yilan-Yitong Fault Zone in NE China.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 151:197-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.038 Yu Z. Y., Zhang P. Z., Min W., et al., 2018b. Cenozoic pulsed compression of Da'an-Dedu Fault Zone in Songliao Basin (NE China) and its implications for earthquake potential:Evidence from seismic data. Tectonophysics, 722:383-399. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.11.013 -




 下载:
下载: