Deep Learning Approach for Seismic Geohazard DetectionA Case Study in Jiuzhaigou M7.0 Earthquake, Sichuan, 2017
-
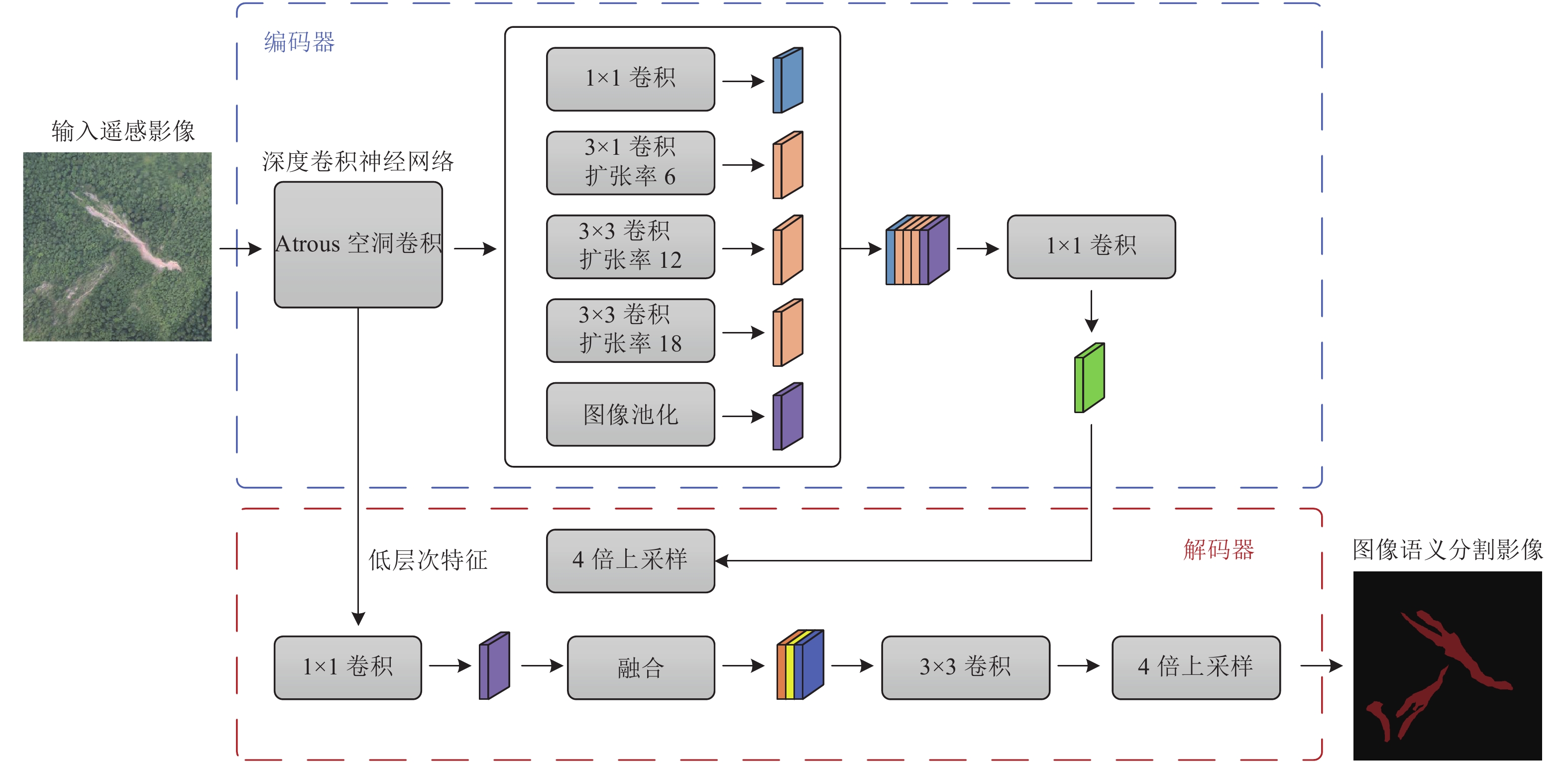
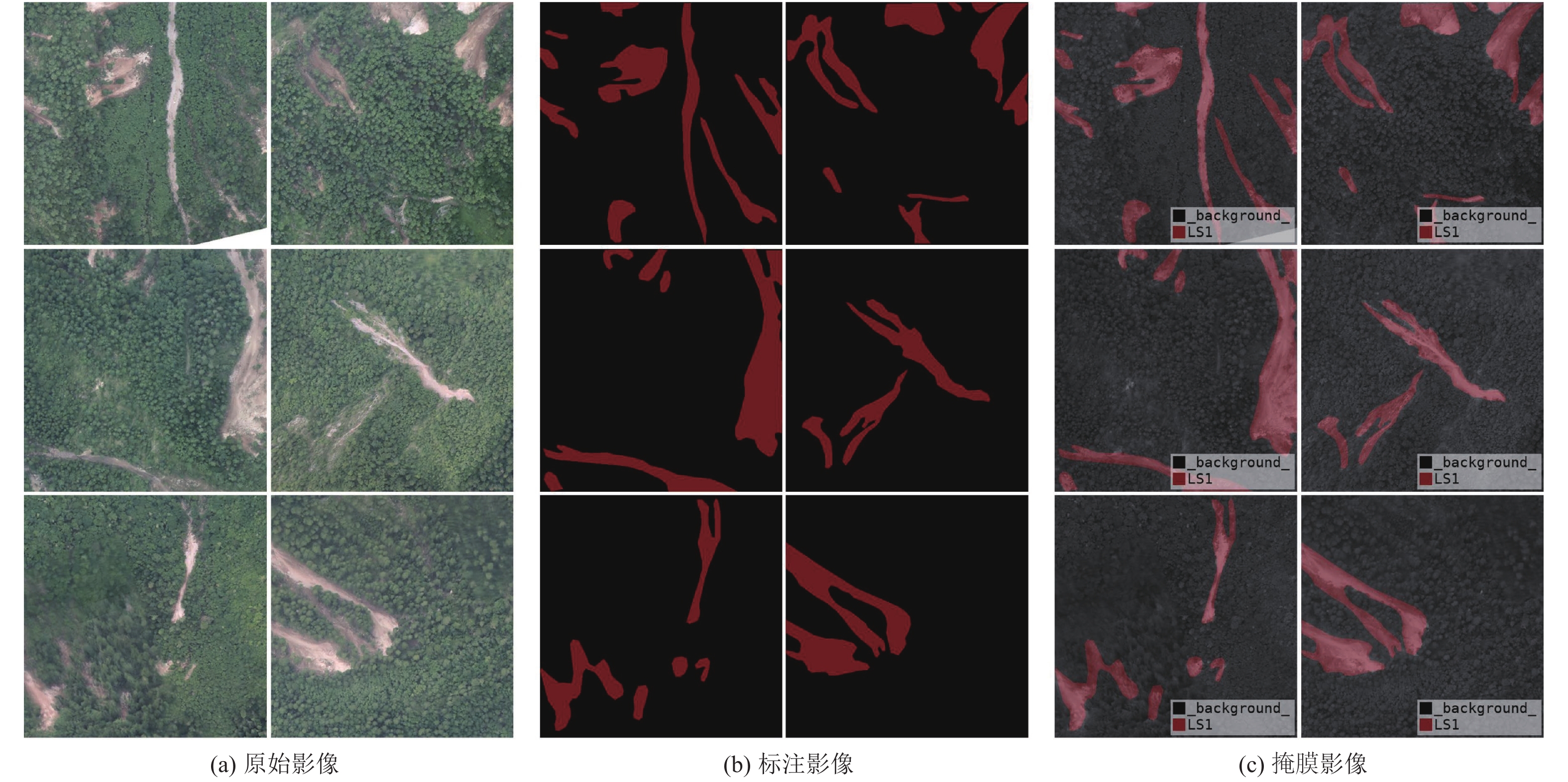
摘要: 遥感影像识别方法是破坏性地震震后地质灾害快速、准确获取的重要方法之一,传统的遥感影像识别方法主要以人工目视识别方法和半自动识别方法为主,需投入大量的人力和时间。针对破坏性地震震后地质灾害解译时间长、投入人力多等问题,以2017年8月8日四川九寨沟7.0级地震震后高分辨率无人机遥感影像为研究样本,提出基于深度学习网络的地震地质灾害识别方法。首先结合震后遥感影像解译资料和现场调查资料,提取九寨沟地震地质灾害无人机遥感影像特征,并构建研究区地震地质灾害解译指标和分类数据集;然后采用DeepLabv3+网络结构及softmax损失函数,建立基于深度学习网络的地震地质灾害遥感影像图像语义分割模型方法;最后采用半监督学习方法进行结果验证。研究结果表明,基于深度学习网络的地震地质灾害识别方法可有效识别九寨沟地震地质灾害分布信息,整体分类识别准确率为94.22%,F1分数值为0.77,结果具有较好的一致性和准确性,可提升地震现场灾情获取和重点地震隐患识别等工作效率及服务能力。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习网络 /
- 地质灾害 /
- DeepLabv3+ /
- 图像语义分割 /
- 九寨沟7.0级地震
Abstract: Remote sensing image recognition method is one of the important methods for rapid and accurate acquisition of seismic geohazards after destructive earthquakes. Traditional remote sensing image recognition methods are mainly artificial visual recognition method and semi-automatic recognition method, which need a lot of manpower and time. Aiming at the problems of long time and large investment in the interpretation of geohazards after destructive earthquakes, this paper takes the high-resolution UAV remote sensing images after the Jiuzhaigou M7.0 earthquake in Sichuan on August 8,2017 as the research sample, and proposes a seismic geohazard identification method based on deep learning network. In this study, firstly, the characteristics of UAV remote sensing images of seismic geohazards in Jiuzhaigou were extracted by combining the interpretation data of remote sensing images after the earthquake and the field investigation data, and the interpretation indexes and classification data sets of seismic geohazards in the study area were constructed. Then, the DeepLabv3+ network structure and softmax loss function were used to establish the semantic segmentation model of remote sensing images of seismic geohazards based on deep learning. Finally, the semi-supervised learning method was used to verify the results. The results show that the seismic geohazards identification method based on deep learning can effectively identify the distribution information of Jiuzhaigou seismic geohazards. The overall classification and identification accuracy is 94.22%, and the F1 score is 0.77, indicating that the results have good consistency and accuracy, which can improve the efficiency and service ability of seismic geohazard acquisition and key seismic hazard identification in the earthquake site. -
表 1 深度学习网络识别结果的混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix of deep learning network recognition results
混淆矩阵 预测像素值 背景/个 地质灾害/个 实际像素值 背景/个 7522390 173619 地质灾害/个 341392 875495 -
[1] 陈梦, 2019. 基于深度学习的建筑物震害遥感识别研究. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所.Chen M., 2019. Research on identification of building damage information from remote sensing image based on deep learning. Beijing: Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, CEA. (in Chinese) [2] 邓飞, 窦爱霞, 吴玮莹等, 2018. 基于无人机遥感的四川九寨沟地震极灾区灾情快速调查. 灾害学, 33(3): 210—215 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2018.03.039Deng F. , Dou A. X. , Wu W. Y. , et al. , 2018. Rapid investigation of disaster situation in extreme disaster area of Jiuzhaigou earthquake in Sichuan based on UAV remote sensing. Journal of Catastrophology, 33(3): 210—215. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2018.03.039 [3] 董秀军, 许强, 佘金星等, 2020. 九寨沟核心景区多源遥感数据地质灾害解译初探. 武汉大学学报▪信息科学版, 45(3): 432—441 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190076Dong X. J. , Xu Q. , She J. X. , et al. , 2020. Preliminary study on interpretation of geological hazards in Jiuzhaigou based on multi⁃source remote sensing data. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 45(3): 432—441. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190076 [4] 彭龙康, 刘励聪, 陈学泓等, 2021. 遥感影像云检测网络泛化性能研究: 以DeepLabv3+为例. 遥感学报, 25(5): 1169—1186 doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210061Peng L. K. , Liu L. C. , Chen X. H. , et al. , 2021. Generalization ability of cloud detection network for satellite imagery based on DeepLabv3+. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25(5): 1169—1186. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210061 [5] 佘金星, 程多祥, 刘飞等, 2018. 机载激光雷达技术在地质灾害调查中的应用——以四川九寨沟7.0级地震为例. 中国地震, 34(3): 435—444 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2018.03.005She J. X. , Cheng D. X. , Liu F. , et al. , 2018. Application of airborne LiDAR technology in geological disaster investigation—taking the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake in Sichuan province as an example. Earthquake Research in China, 34(3): 435—444. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2018.03.005 [6] 王港, 陈金勇, 高峰等, 2018. 基于深度学习的遥感影像基础设施目标检测研究. 无线电工程, 48(3): 219—224 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2018.03.11Wang G. , Chen J. Y. , Gao F. , et al. , 2018. Research on the infrastructure target detection of remote sensing image based on deep learning. Radio Engineering, 48(3): 219—224. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2018.03.11 [7] 吴浩霖, 2020. 基于无人机影像和深度学习技术的建筑物分类和统计——服务于震前预评估的建筑物快速调查. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Wu H. L., 2020. Classification and statistics of buildings based on UAV images and deep learning technology: rapid building survey for pre-evaluation before earthquake. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese) [8] 吴玮莹, 王晓青, 邓飞, 2017. 基于高分卫星遥感影像的地震应急滑坡编目与分布特征探讨——以2017年8月8日九寨沟7.0级地震为例. 震灾防御技术, 12(4): 815—825 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170410Wu W. Y. , Wang X. Q. , Deng F. , 2017. Compilation and spatial analysis of co-seismic landslide inventory by using high-resolution remote sensing images in earthquake emergency response—An example of the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake on August 8, 2017. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(4): 815—825. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170410 [9] 许冲, 王世元, 徐锡伟等, 2018.2017年8月8日四川省九寨沟MS7.0地震触发滑坡全景. 地震地质, 40(1): 232—260 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.017Xu C. , Wang S. Y. , Xu X. W. , et al. , 2018. A panorama of landslides triggered by the 8 August 2017 Jiuzhaigou, Sichuan MS7.0 earthquake. Seismology and Geology, 40(1): 232—260. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.017 [10] 朱祺夫, 赵俊三, 陈磊士等, 2018. 基于深度学习的遥感影像城市建筑用地提取. 软件导刊, 17(10): 18—21 doi: 10.11907/rjdk.181278Zhu Q. F. , Zhao J. S. , Chen L. S. , et al. , 2018. Urban construction land extraction of the remote sensing image based on depth learning. Software Guide, 17(10): 18—21. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11907/rjdk.181278 [11] Chen L. C., Zhu Y. K., Papandreou G., et al., 2018. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer. [12] Choi S. S. , Cha S. H. , Tappert C. C. , 2010. A survey of binary similarity and distance measures. Journal of Systemics, 8(1): 43—48. [13] Russakovsky O. , Deng J. , Su H. , et al. , 2015. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 115(3): 211—252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [14] Yang W. , Zhang J. L. , Xu Z. Y. , et al. , 2019. Real-time DeepLabv3+ for pedestrian segmentation. Journal of Optical Technology, 86(9): 570—578. doi: 10.1364/JOT.86.000570 [15] Yao X. X. , Guo J. , Hu J. , et al. , 2019. Using deep learning in semantic classification for point cloud data. IEEE Access, 7: 37121—37130. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905546 -




 下载:
下载: