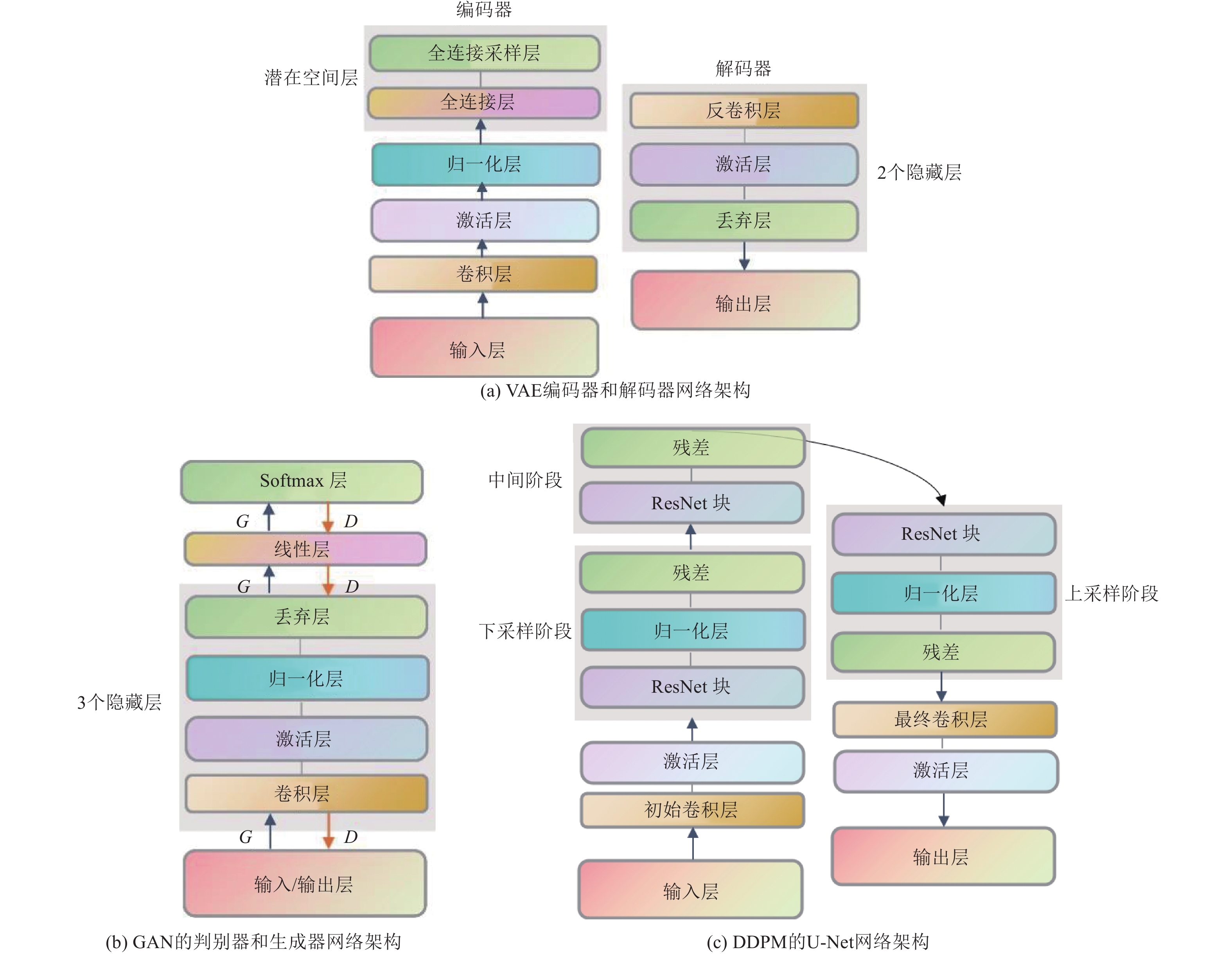
Generative Neural Network-based Strong Ground Motion Simulation
-
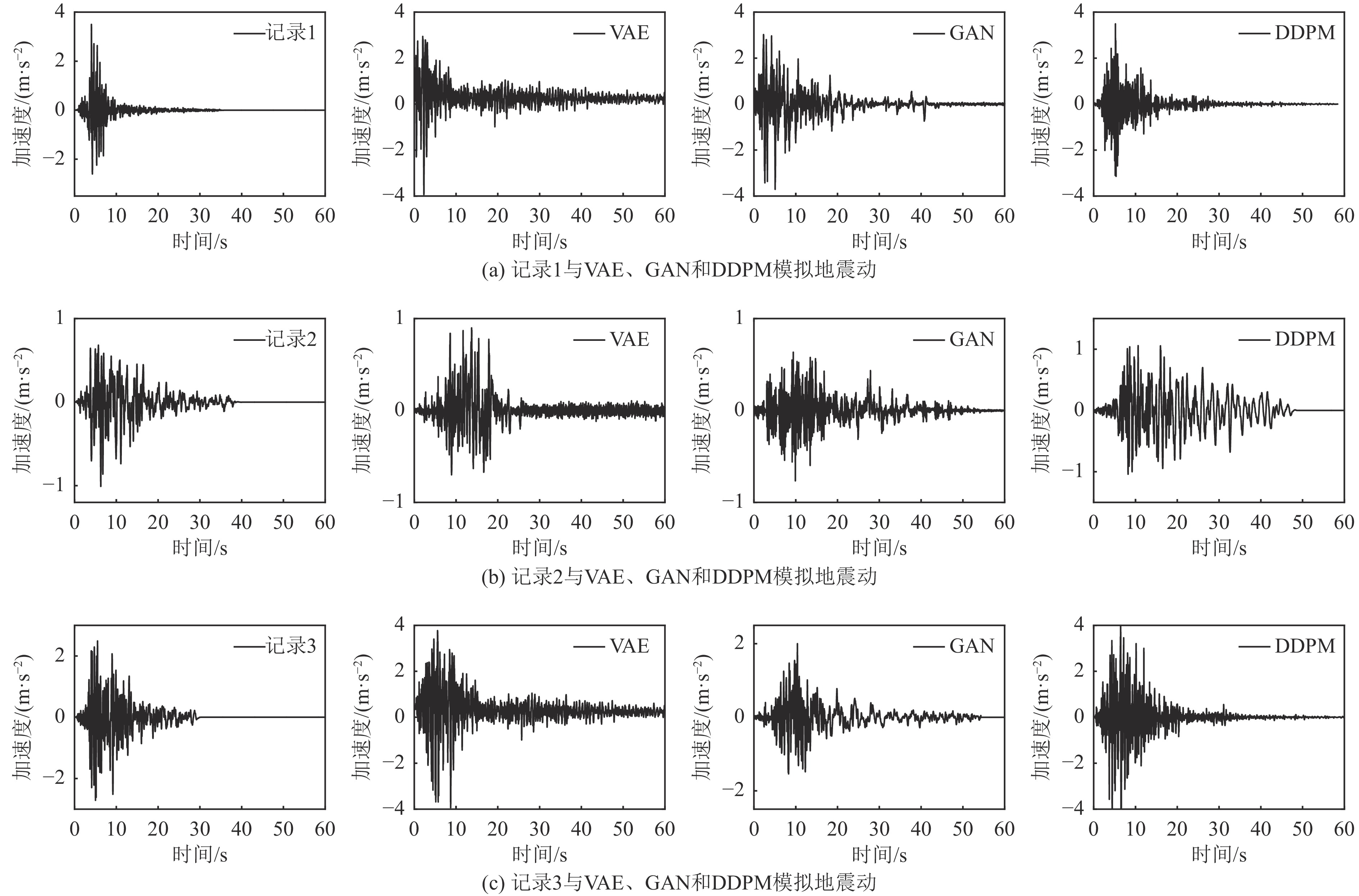
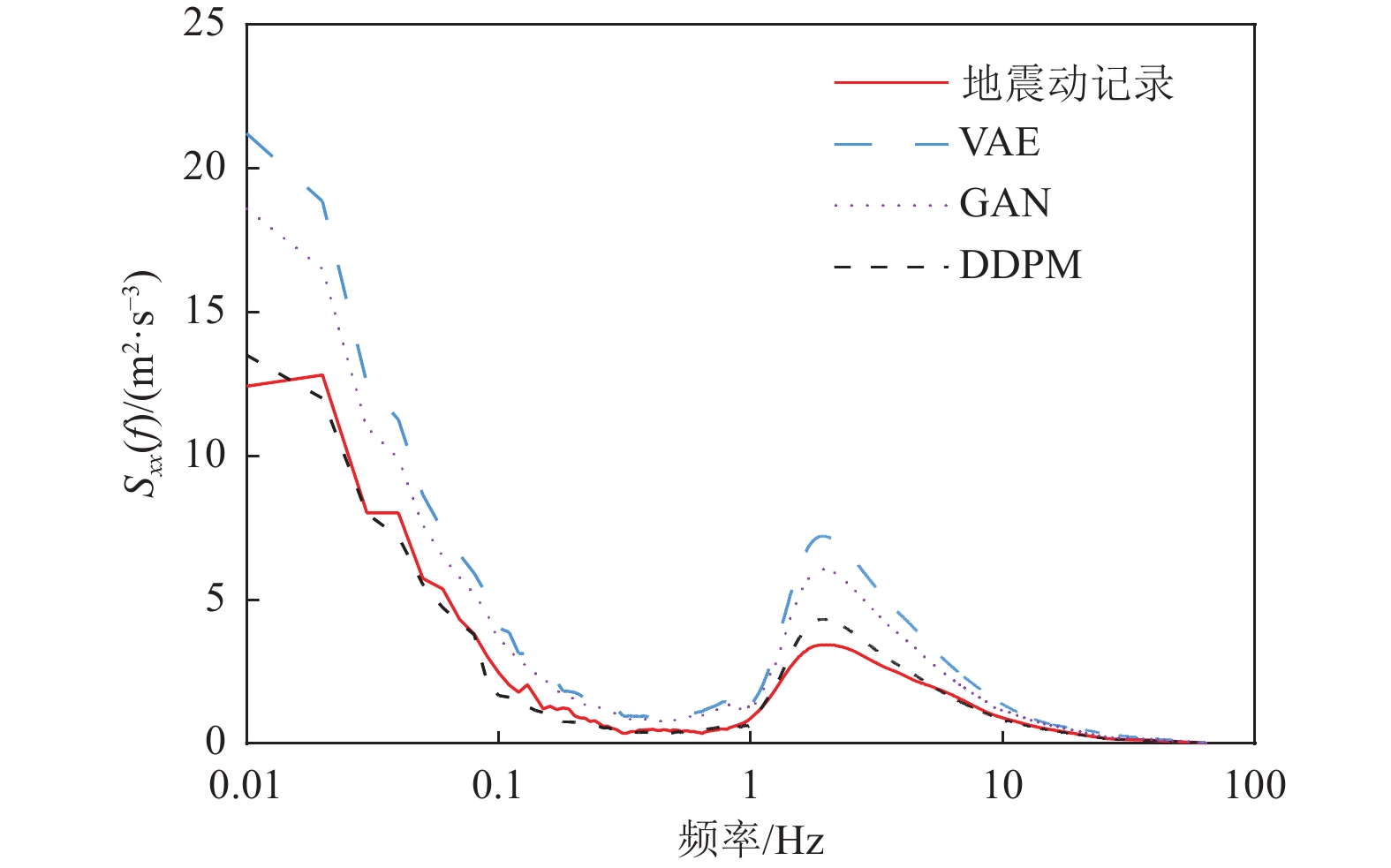
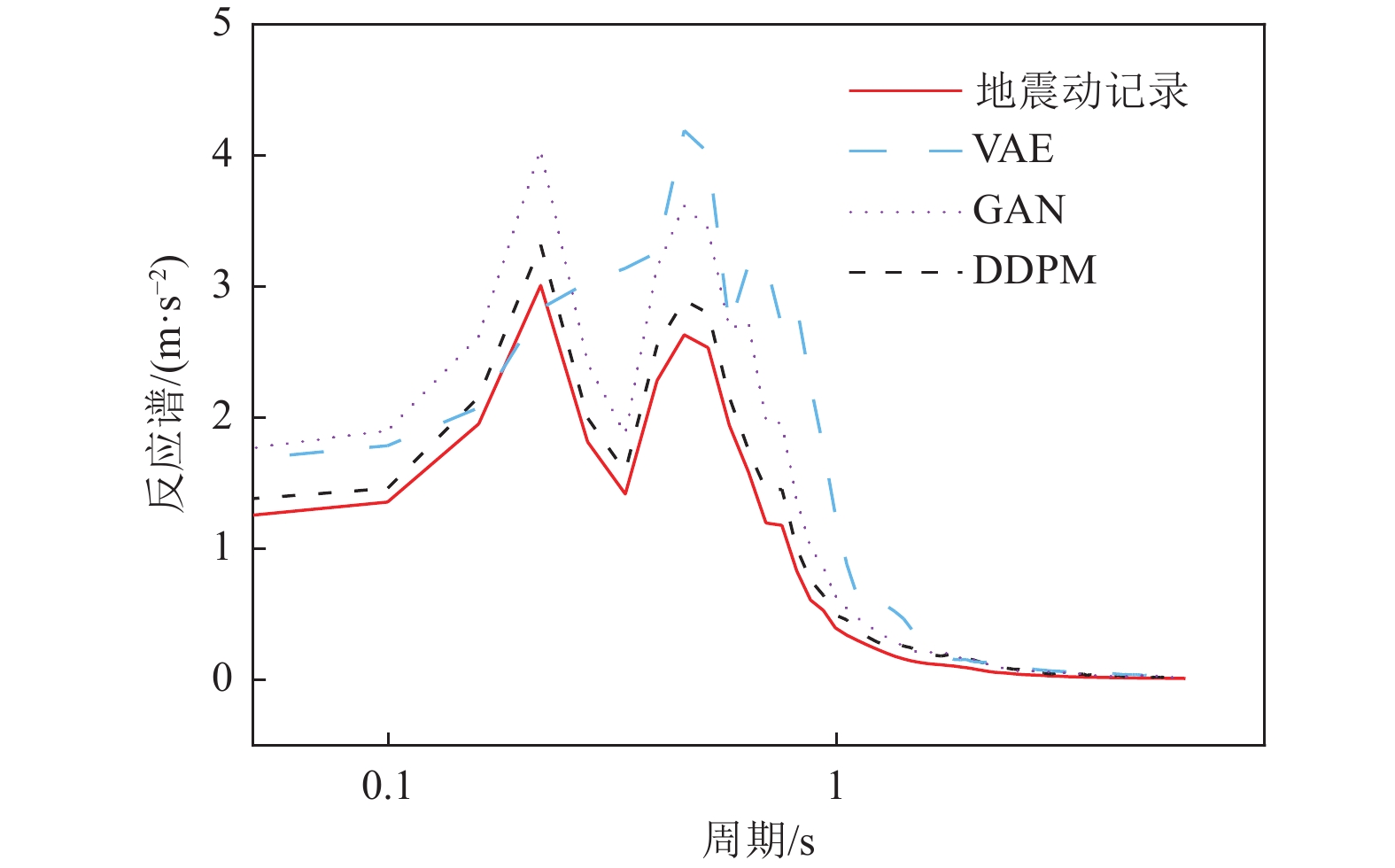
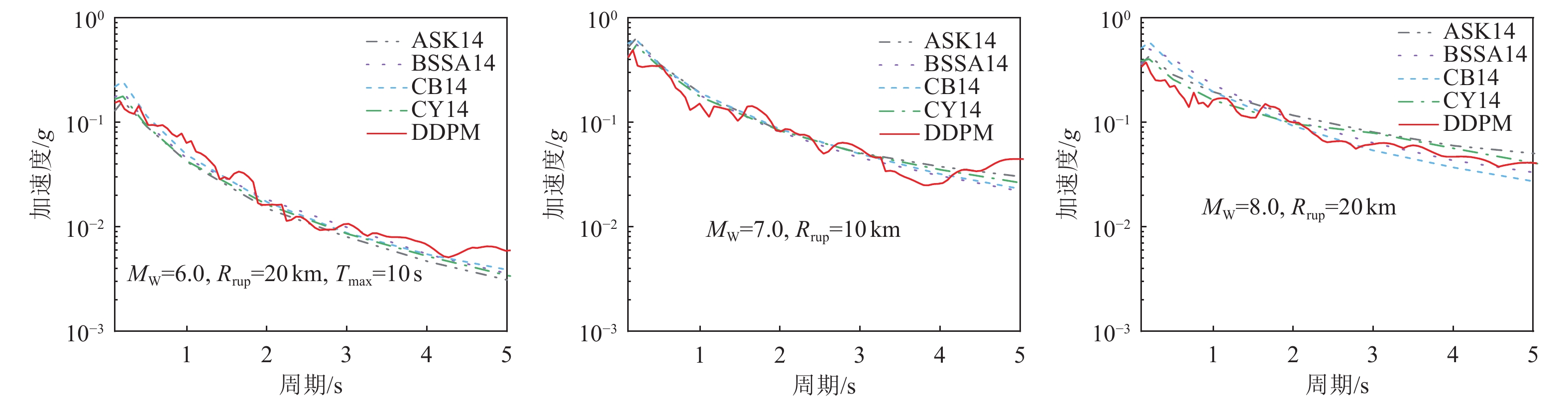
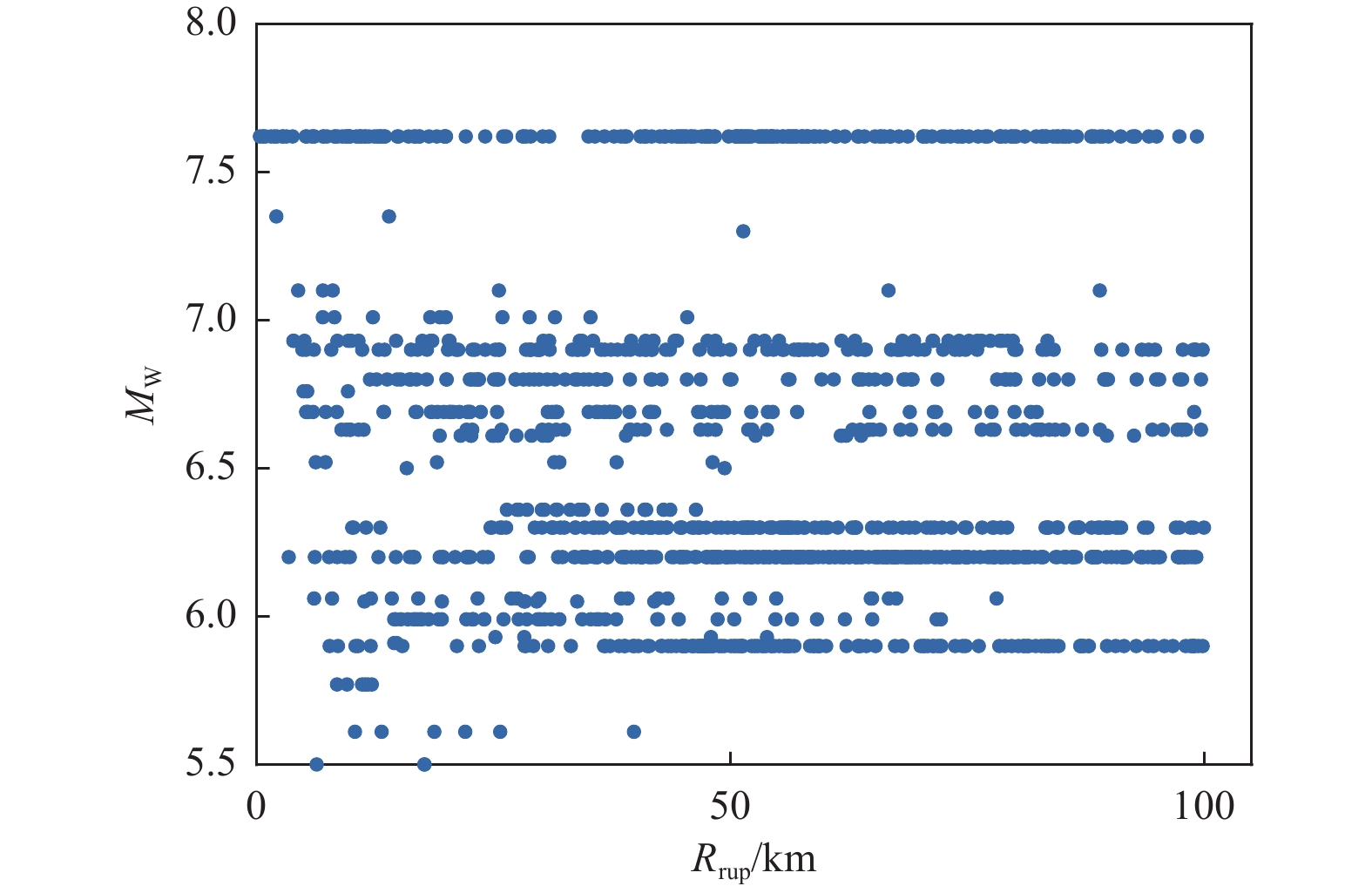
摘要: 基于简单线性关系的分析方法在表征地震动影响因素时,往往导致预测结果与实测数据存在显著偏差。为克服这一局限性,本文基于生成式神经网络无需依赖先验地震学知识即可自动提取特征并生成完整地震动时程的优势,系统评估了3种典型生成式神经网络模型(变分自编码器VAE、生成对抗网络GAN和去噪扩散概率模型DDPM)在地震动模拟中的性能表现。研究采用PEER数据库中的1 451条水平向地震动记录(源自23次独立地震事件)作为训练数据集,对3种模型进行统一训练和对比分析。模拟结果时域和频域的综合评估结果表明,3种模型中DDPM展现出最优的模拟性能,GAN次之,而VAE表现相对欠佳。值得注意的是,GAN模拟结果呈现出显著的长周期成分增强特征,而VAE则表现出明显的持时延长现象。通过与4种经典地震动预测方程的对比研究发现,DDPM模拟结果与GMPEs预测值具有较好的一致性,但存在轻微的系统性低估趋势。Abstract: Analytical approaches based on simple linear relationships often produce substantial discrepancies between predicted and observed ground motions when characterizing their controlling factors. To address this limitation, this study exploits the strengths of generative neural networks, which are capable of automatically extracting features and generating complete ground-motion time histories without requiring prior seismological knowledge. Three representative generative neural network models—the Variational Autoencoder (VAE), Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM)—are systematically evaluated for their performance in ground-motion simulation. A dataset consisting of 1,451 horizontal ground-motion records from 23 independent earthquake events in the PEER database is used for uniform training and comparative analysis of the three models. Comprehensive assessments in both the time and frequency domains indicate that DDPM achieves the best overall simulation performance, followed by GAN, whereas VAE performs relatively poorly. In particular, GAN simulations exhibit a pronounced amplification of long-period components, while VAE results show a notable overestimation of motion duration. Further comparison with four classical ground-motion prediction equations (GMPEs) shows that the DDPM simulations are generally consistent with GMPE estimates, although a slight systematic underestimation is observed.
-
表 1 选定地震记录的信息
Table 1. Selected seismic record information
记录编号 地震名称 站台名称 MW VS30 /(m·s−1) 断层机制 记录1 1980年意大利地震 Tolmezzo 6.50 505.23 逆断层 记录2 1989年洛马普列塔地震 APEEL 10-Skyline 6.93 391.91 逆断层 记录3 1994年北岭地震 Riverside Airport 6.69 389.95 逆断层 -
李平, 范钟元, 周楷等, 2024. 基于强震记录的土层结构放大作用研究−−以SMASS台阵为例. 震灾防御技术, 19(4): 661−674.Li P., Fan Z. Y., Zhou K., et al., 2024. Study of soil structure amplification based on strong earthquake records−−a case study of SMASS array. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 19(4): 661−674. (in Chinese) 孙晓丹, 2010. 强地震动场估计中若干问题的研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学.Sun X. D., 2010. Some issues on estimation of strong ground motion field. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. (in Chinese) 张博涵, 王宏伟, 任叶飞等, 2025. 地震动预测模型评价研究−−以2023年2月6日土耳其地震为例. 震灾防御技术, 20(1): 77−85.Zhang B. H., Wang H. W., Ren Y. F., et al., 2025. Evaluation of ground motion model: a case study of the turkey earthquake on February 6, 2023. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 20(1): 77−85. (in Chinese) Abrahamson N., Silva W., 2008. Summary of the Abrahamson & Silva NGA ground-motion relations. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 67−97. doi: 10.1193/1.2924360 Bengio Y. , Thibodeau-Laufer É. , Alain G. , et al. , 2014. deep generative stochastic networks trainable by backprop. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing: PMLR, 226−234. Boore D. M., Joyner W. B., Fumal T. E., 1997. Equations for estimating horizontal response spectra and peak acceleration from western North American earthquakes: a summary of recent work. Seismological Research Letters, 68(1): 128−153. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.68.1.128 Boore D. M., Atkinson G. M., 2008. Ground-motion prediction equations for the average horizontal component of PGA, PGV, and 5%-damped PSA at spectral periods between 0.01 s and 10.0 s. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 99−138. doi: 10.1193/1.2830434 Campbell K. W., Bozorgnia Y., 2008. NGA ground motion model for the geometric mean horizontal component of PGA, PGV, PGD and 5% damped linear elastic response spectra for periods ranging from 0.01 to 10 s. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 139−171. doi: 10.1193/1.2857546 Chiou B. J., Youngs R. R., 2008. An NGA model for the average horizontal component of peak ground motion and response spectra. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 173−215. doi: 10.1193/1.2894832 Datta A., Wu D. J., Zhu W. Q., et al., 2022. DeepShake: shaking intensity prediction using deep spatiotemporal RNNs for earthquake early warning. Seismological Research Letters, 93(3): 1636−1649. doi: 10.1785/0220210141 Derakhshani A., Foruzan A. H., 2019. Predicting the principal strong ground motion parameters: a deep learning approach. Applied Soft Computing, 80: 192−201. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.03.029 Dhariwal P., Nichol A., 2021. Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. Advances in neural information processing systems, 34: 8780−8794. Gemici M. C. , Rezende D. , Mohamed S. , 2016. Normalizing flows on Riemannian manifolds. (2016-11-09)[2025-09-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02304. Goodfellow I. J. , Pouget-Abadie J. , Mirza M. , et al. , 2014. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal: MIT Press. Heusel M. , Ramsauer H. , Unterthiner T. , et al. , 2017. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: Curran Associates Inc. Ho J. , Jain A. , Abbeel P. , 2020. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver: Curran Associates Inc. , 574. Ho J., Saharia C., Chan W., et al., 2022. Cascaded diffusion models for high fidelity image generation. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 23(1): 47. Jiao P. C., Alavi A. H., 2020. Artificial intelligence in seismology: advent, performance and future trends. Geoscience Frontiers, 11(3): 739−744. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.10.004 Khosravikia F., Clayton P., Nagy Z., 2019. Artificial neural network‐based framework for developing ground‐motion models for natural and induced earthquakes in Oklahoma, Kansas, and Texas. Seismological Research Letters, 90(2A): 604−613. doi: 10.1785/0220180218 Kingma D P, Welling M. , 2018. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. (2018-06-18)[2025-09-20]. https://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~rrtammy/DNN/StudentPresentations/2018/AUTOEN~2.PDF. Liu P., Archuleta R. J., Hartzell S. H., 2006. Prediction of broadband ground-motion time histories: hybrid low/high-frequency method with correlated random source parameters. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 96(6): 2118−2130. doi: 10.1785/0120060036 Miyato T. , Kataoka T. , Koyama M. , et al. , 2018. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver: OpenReview. net. Nichol A. Q. , Dhariwal P. , Ramesh A. , et al. , 2022. GLIDE: towards photorealistic image generation and editing with text-guided diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore: PMLR. Sadigh K., Chang C. Y., Egan J. A., et al., 1997. Attenuation relationships for shallow crustal earthquakes based on California strong motion data. Seismological Research Letters, 68(1): 180−189. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.68.1.180 Salimans T. , Goodfellow I. , Zaremba W. , et al. , 2016. Improved techniques for training GANs. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona: Curran Associates Inc. Song Y. , Ermon S. , 2019. Generative modeling by estimating gradients of the data distribution. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver: Curran Associates Inc. Svozil D., Kvasnicka V., Pospichal J., 1997. Introduction to multi-layer feed-forward neural networks. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 39(1): 43−62. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(97)00061-0 Teräsvirta T., 1994. Specification, estimation, and evaluation of smooth transition autoregressive models. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89(425): 208−218. van den Oord A. , Kalchbrenner N. , Vinyals O. , et al. , 2016a. Conditional image generation with PixelCNN decoders. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona: Curran Associates Inc. Van Den Oord A. , Kalchbrenner N. , Kavukcuoglu K. , 2016b. Pixel recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 1747−1756. Villani C. , 2009. The wasserstein distances. In: Villani C. , ed. , Optimal Transport: Old and New. Berlin: Heidelberg: Springer, 93−111. Wan S., Yen J. Y., 2007. The study of base isolation on the precise machinery system for regional ground motion records with modified back propagation neural network approach. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 14(5): 759−776. doi: 10.1002/stc.177 Wang T. T. , Zhang Z. P. , Li Y. Z. , 2019. EarthquakeGen: earthquake generator using generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts. San Antonio: SEG, 2674−2678. Zhang Y. Q. , Peng B. , Zhou X. Y. , et al. , 2019. A deep convolutional neural network for topology optimization with strong generalization ability. (2019-01-23)[2025-09-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07761 -



 下载:
下载: