Vertical Ground Motion Prediction and Validation Using Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Inference MethodA Case Study of the 2022 MW6.7 Menyuan Earthquake in Qinghai, China
-
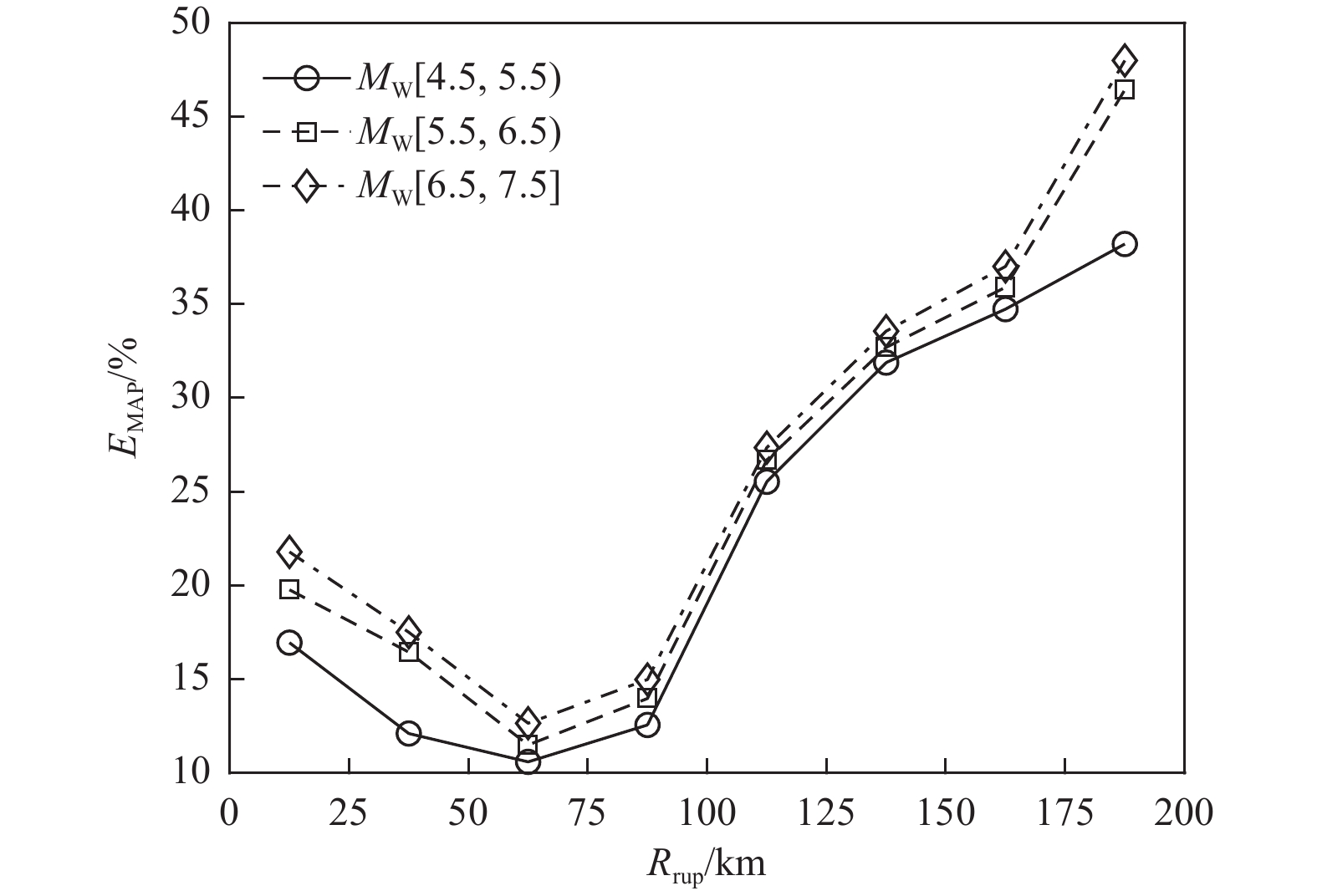
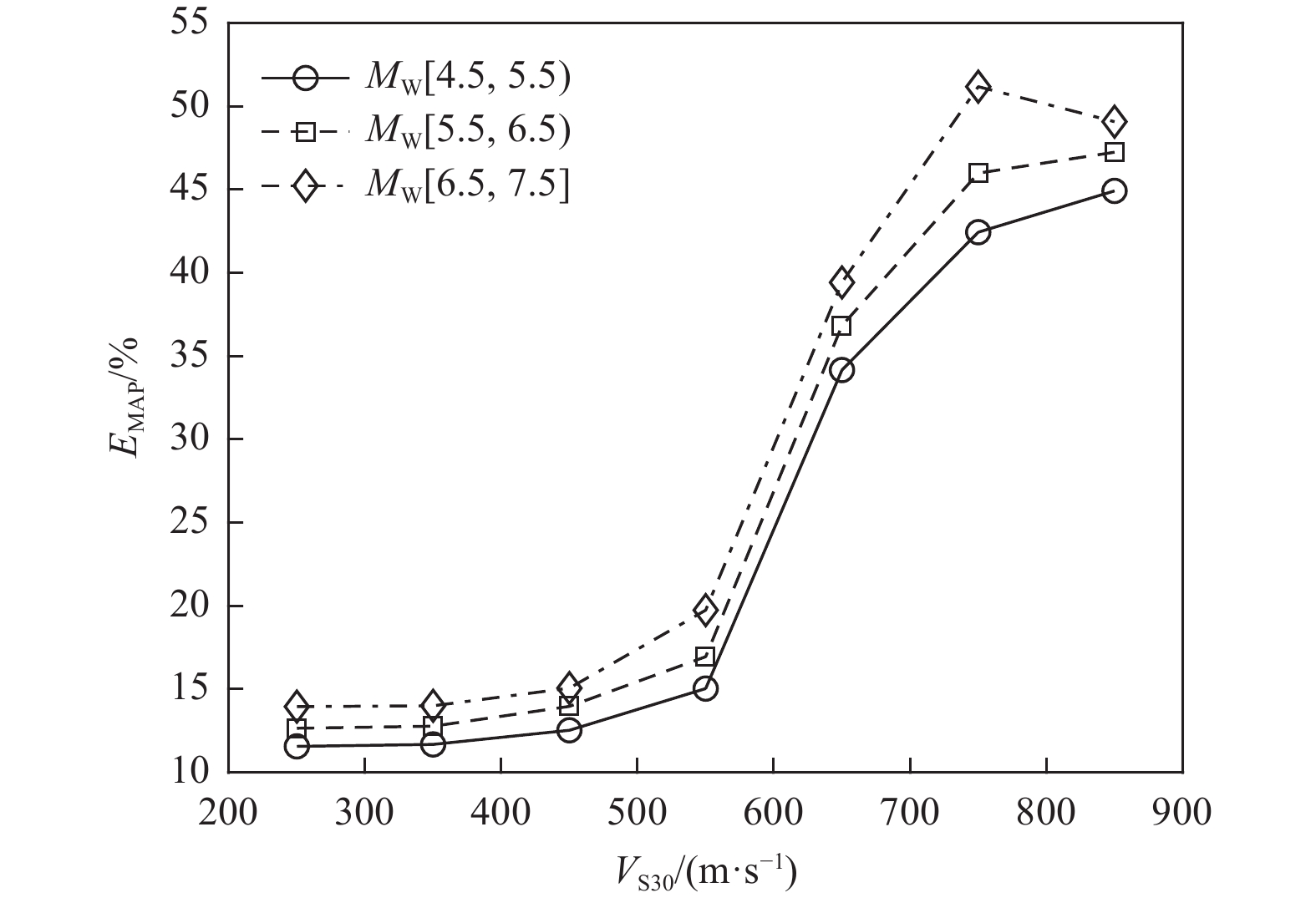
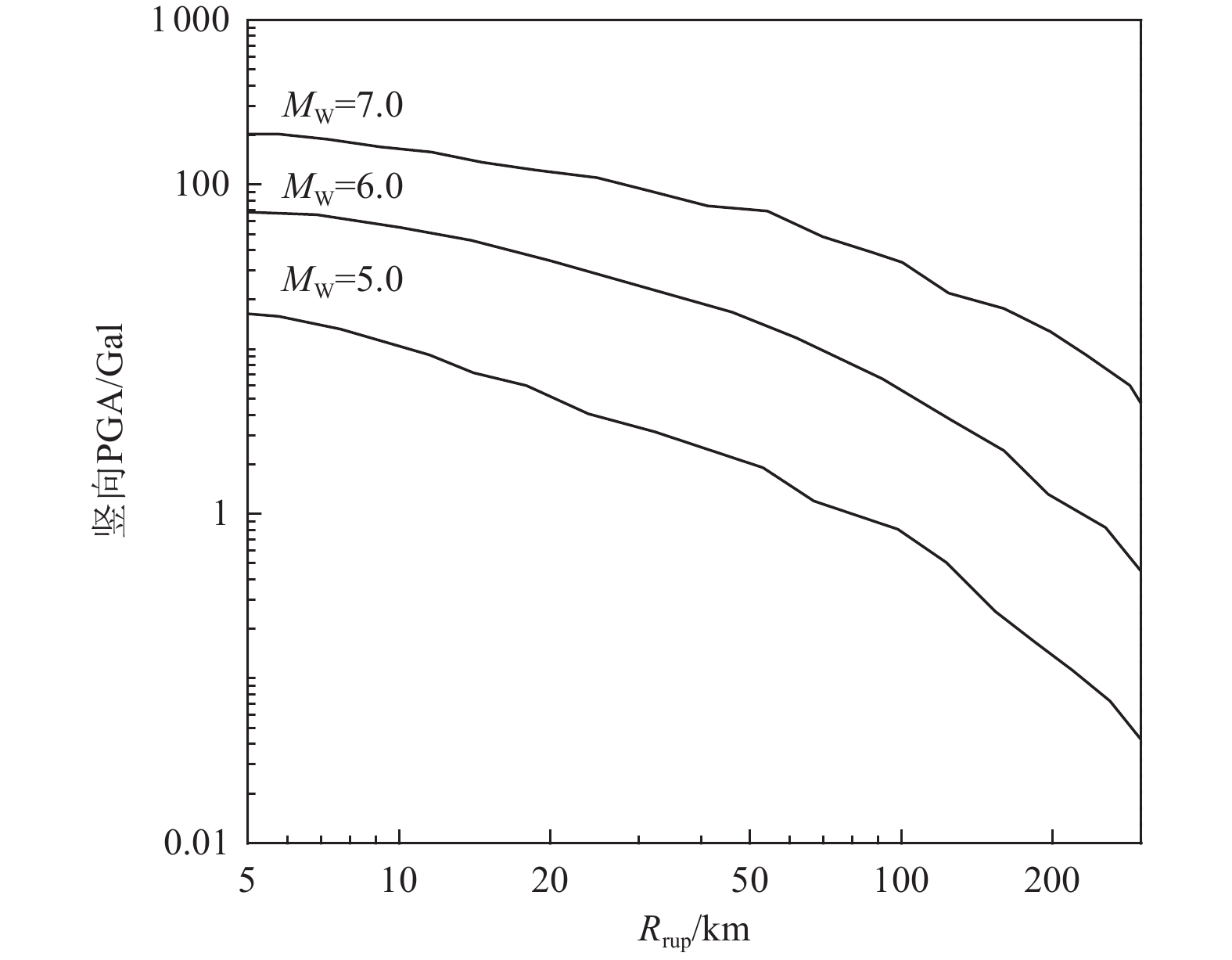
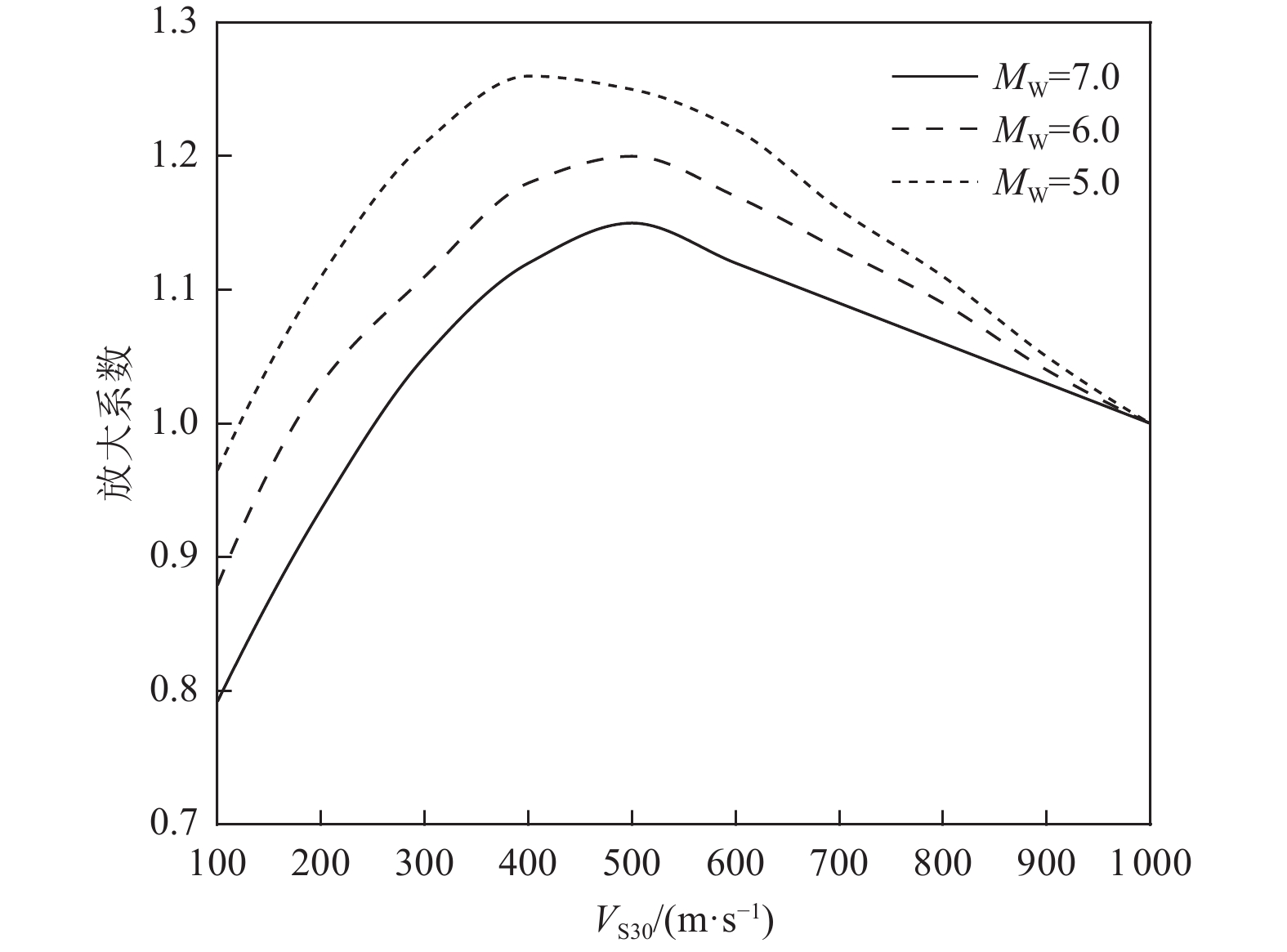
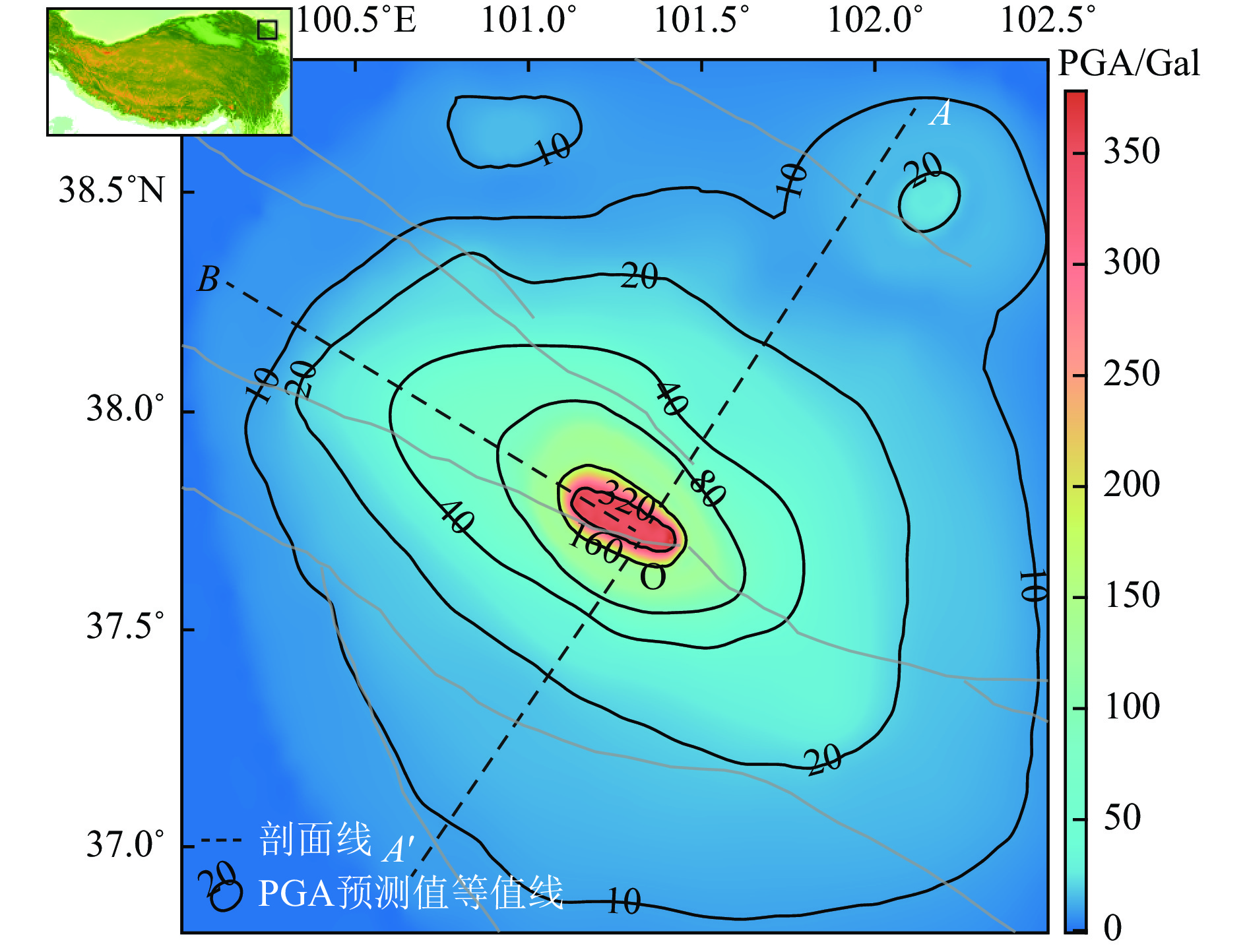
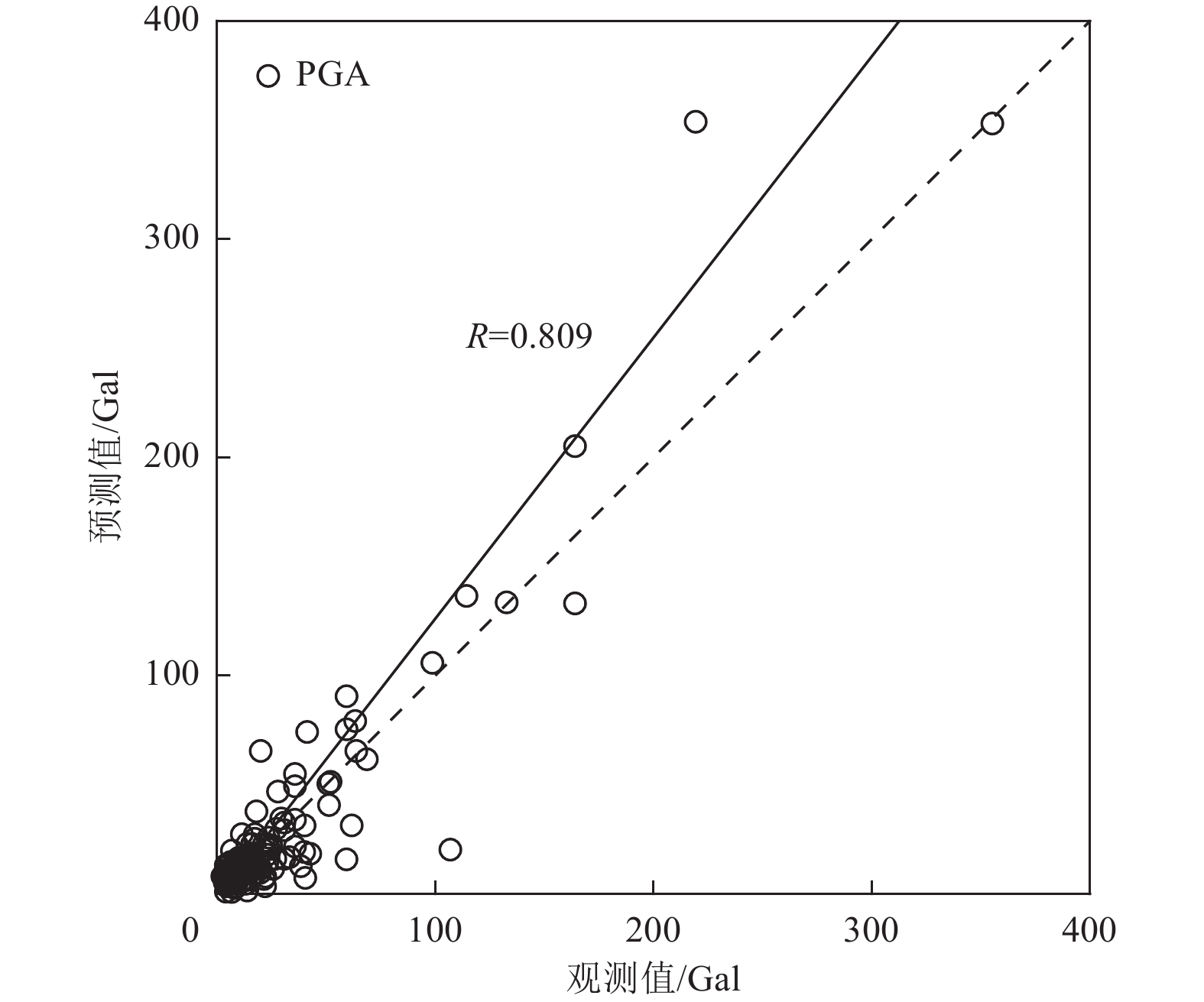
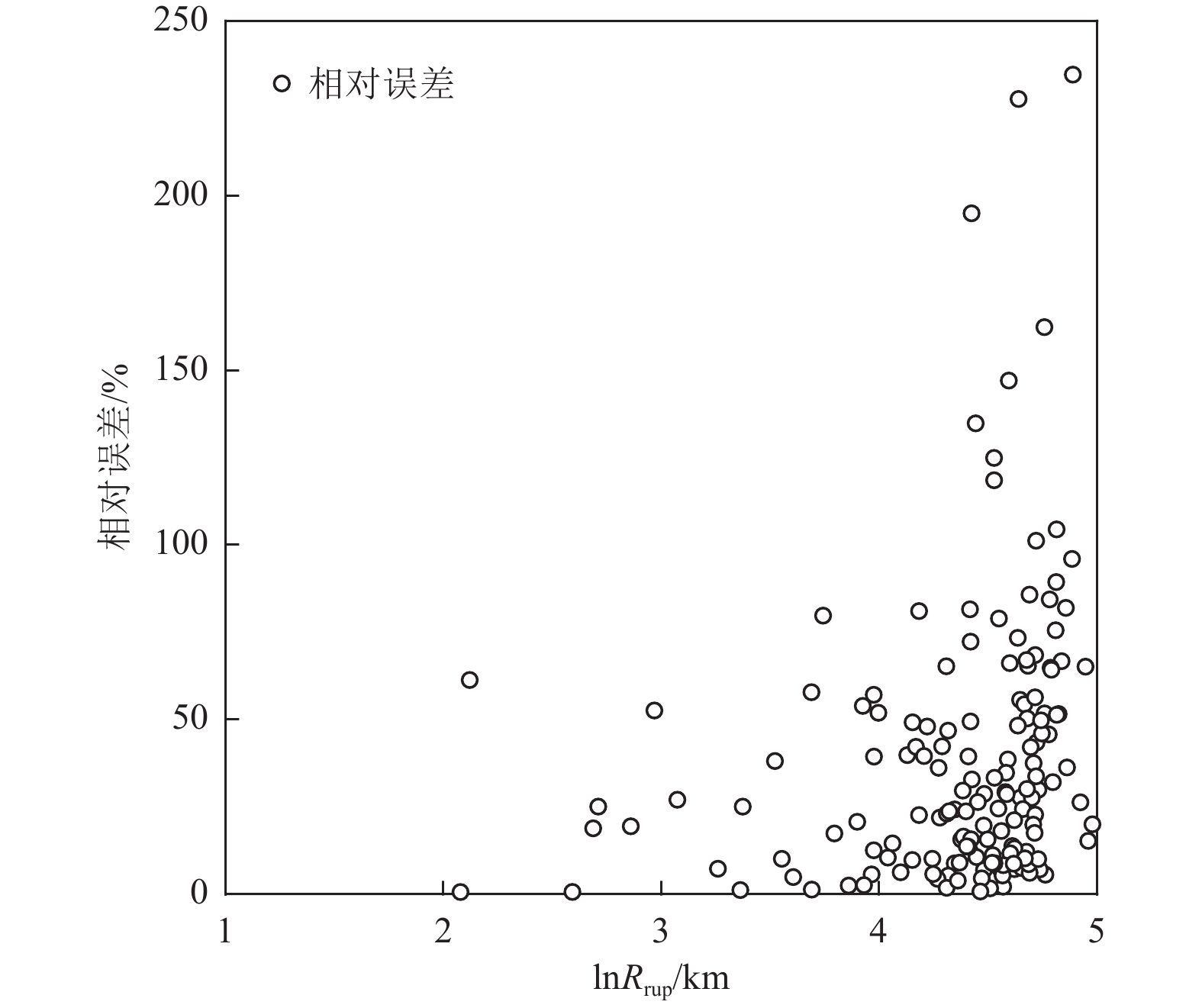
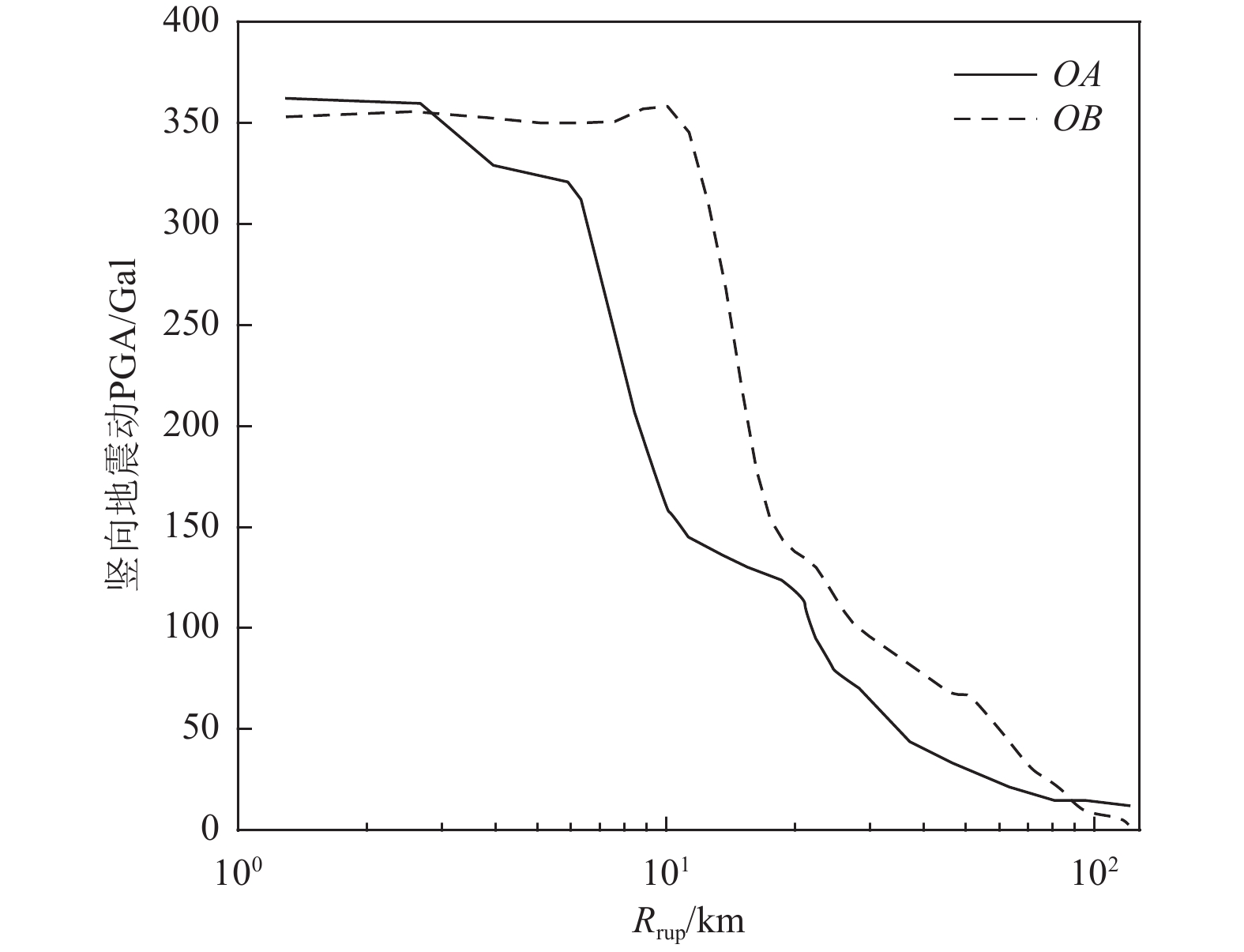
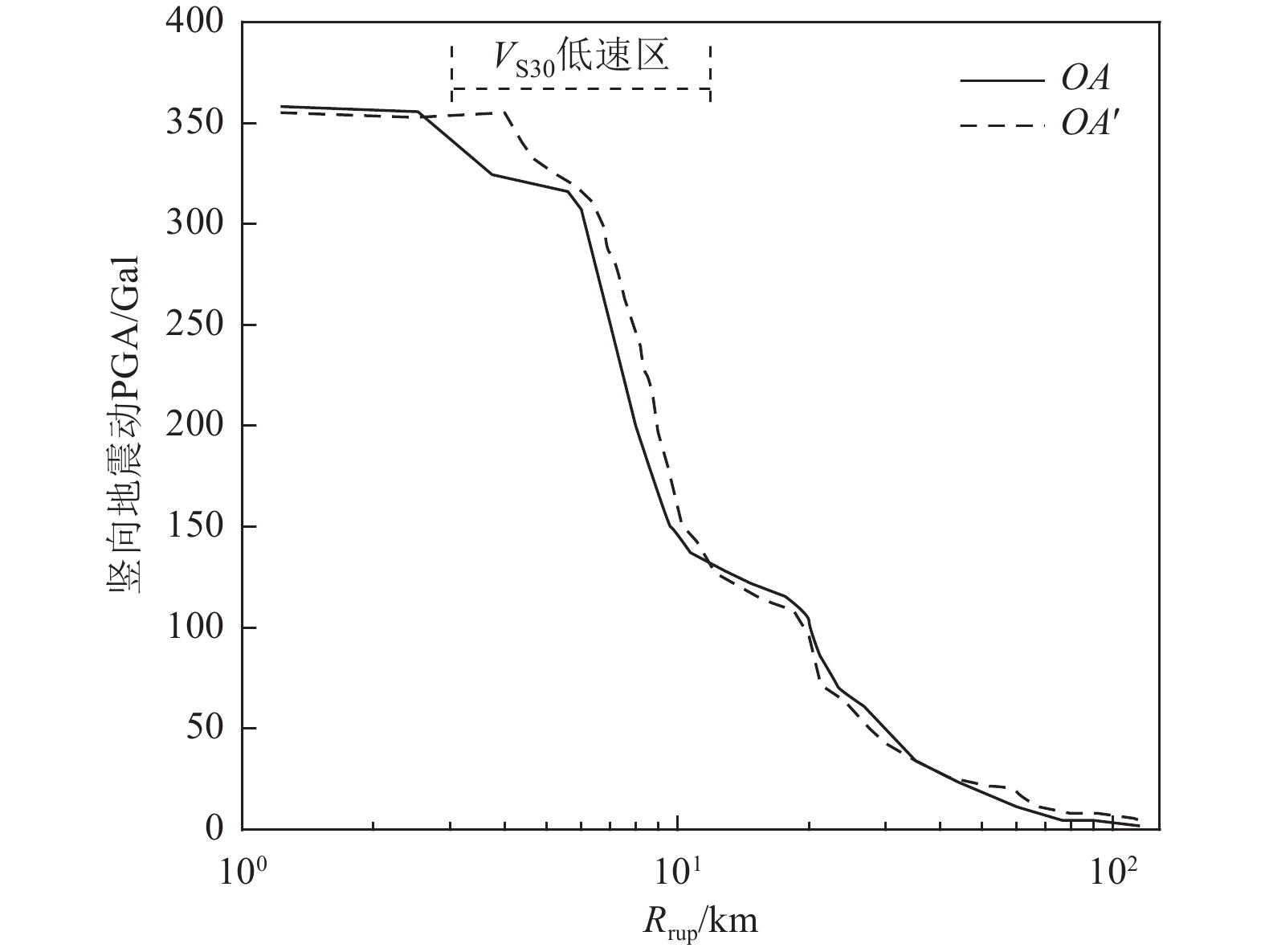
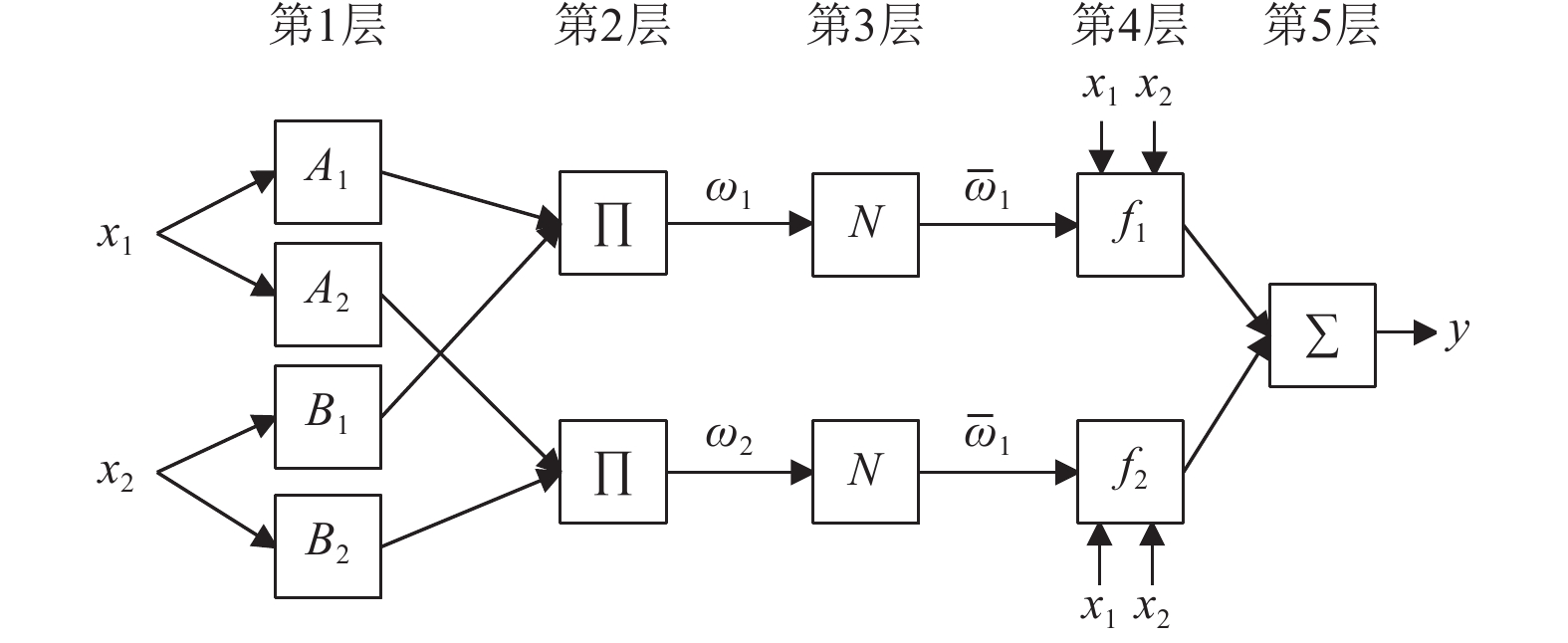
摘要: 为解决竖向地震动预测不确定性较大的问题,利用NGA-West强地震动数据库,基于自适应神经模糊推理方法(ANFIS)建立竖向地震动强度预测模型,计算2022年1月8日青海门源MW6.7地震的竖向地震动峰值加速度分布。在利用国家地震烈度速报与预警工程观测数据开展信度检验的基础上,探讨近场强地震动的方向效应、场地放大效应及其成因机理。研究结果表明:(1)基于ANFIS方法的竖向地震动强度预测模型在门源MW6.7地震竖向PGA预测过程中取得了较好的预测结果,其预测值与观测值相关系数R约为0.809,均方根误差ERMS约为0.046,说明本文预测模型具有较好的可靠性,同时检验了其在我国中强破坏性地震预测中的适用性。(2)门源MW6.7地震的竖向PGA预测值等值线整体上呈椭圆状,其长轴与发震断层走向具有较好的一致性,震中附近竖向PGA极大值约为376.3 Gal。竖向PGA在随断层距增大而不断衰减的同时,呈现出较为显著的方向性效应以及一定程度上的近场大震饱和效应。(3)竖向地震动峰值加速度的场地放大效应相对弱于水平向地震动,随着
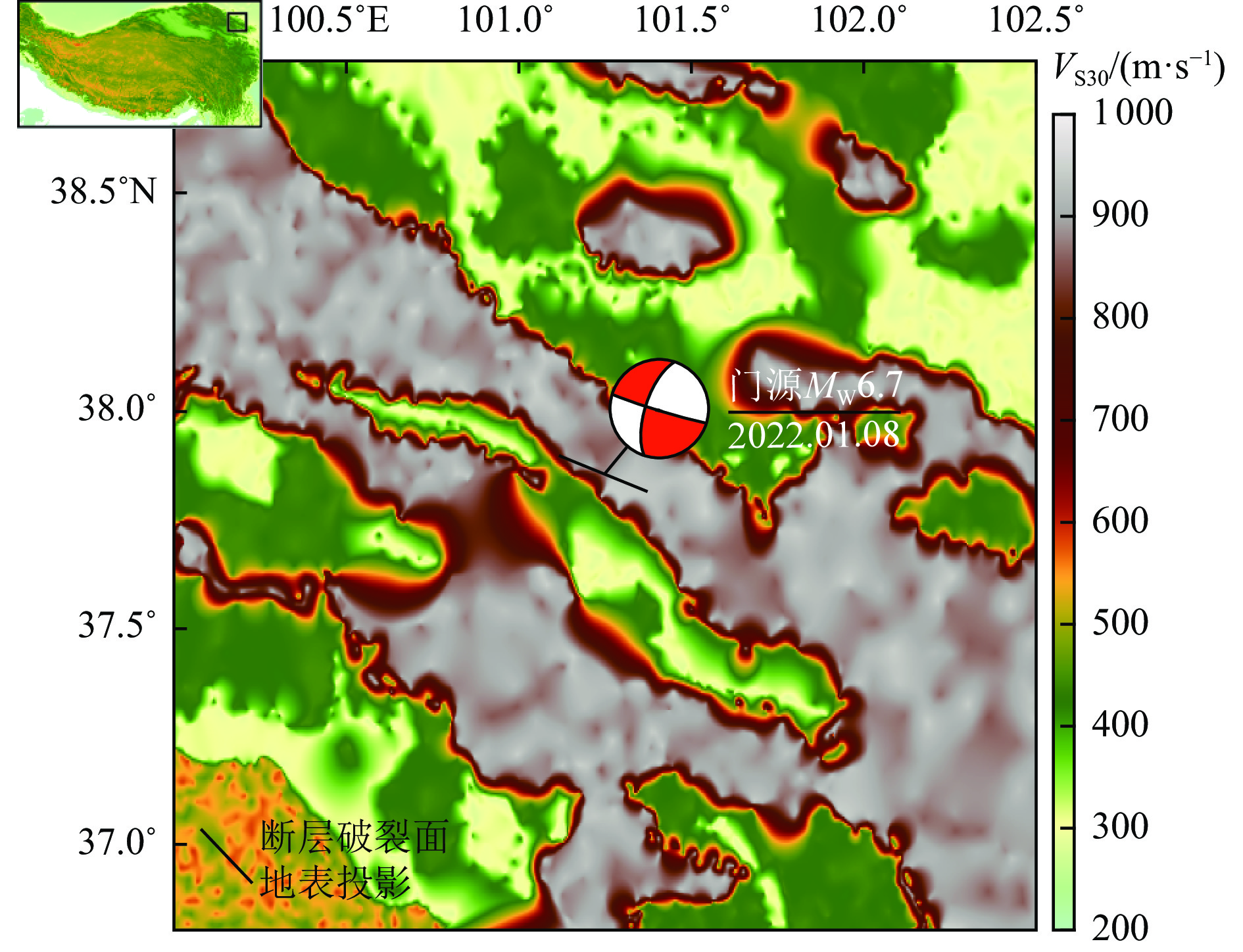
$ {{V}}_{{{\mathrm{S}}30}} $ 的不断降低,竖向PGA相对于基岩场地的PGA最大放大倍数约为1.14~1.27;大震条件(MW=7.0)下软土场地($ {{V}}_{{{\mathrm{S}}30}} $ =100 m/s)处放大系数约为0.79,呈现出一定的软土减震效应。Abstract: To address the large uncertainties associated with estimating vertical ground-motion parameters, this study develops a prediction model for vertical ground shaking during the 8 January 2022 Menyuan MW6.7 earthquake in Qinghai using the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and the NGA-West strong-motion database. Based on validation against observed data from the National Seismic Intensity Rapid Reporting and Early Warning Project, the spatial distribution of peak vertical ground acceleration (PGA) in the Menyuan area is derived to investigate directivity effects, site amplification, and their underlying physical mechanisms. The results show that: (1) the ANFIS-based vertical ground-motion prediction model performs well in reproducing the observed vertical PGA of the Menyuan MW6.7 earthquake, achieving a correlation coefficient (R) of approximately 0.809 and an ERMS of 0.046, demonstrating its reliability and applicability for predicting vertical ground motion in moderate-to-strong damaging earthquakes in China; (2) the predicted vertical PGA contours exhibit an elliptical pattern, with the major axis closely aligned with the strike of the seismogenic fault, and the maximum vertical PGA in the epicentral area reaching about 376.3 Gal. Vertical PGA decreases with increasing fault distance and shows pronounced directivity effects as well as near-field saturation characteristics under strong-motion conditions; (3) the site amplification effect on vertical PGA is generally weaker than that on horizontal motion. As shear-wave velocity decreases, the peak amplification factor of vertical PGA relative to bedrock conditions ranges from 1.14 to 1.27, whereas under strong-motion conditions (MW=7.0), soft-soil sites (VS30=100 m/s) exhibit an amplification coefficient of approximately 0.79, indicating a notable reduction of seismic motion due to soft-soil effects.-
Key words:
- Vertical strong ground motion /
- Fuzzy inference /
- Prediction /
- Site effect /
- Menyuan earthquake
-
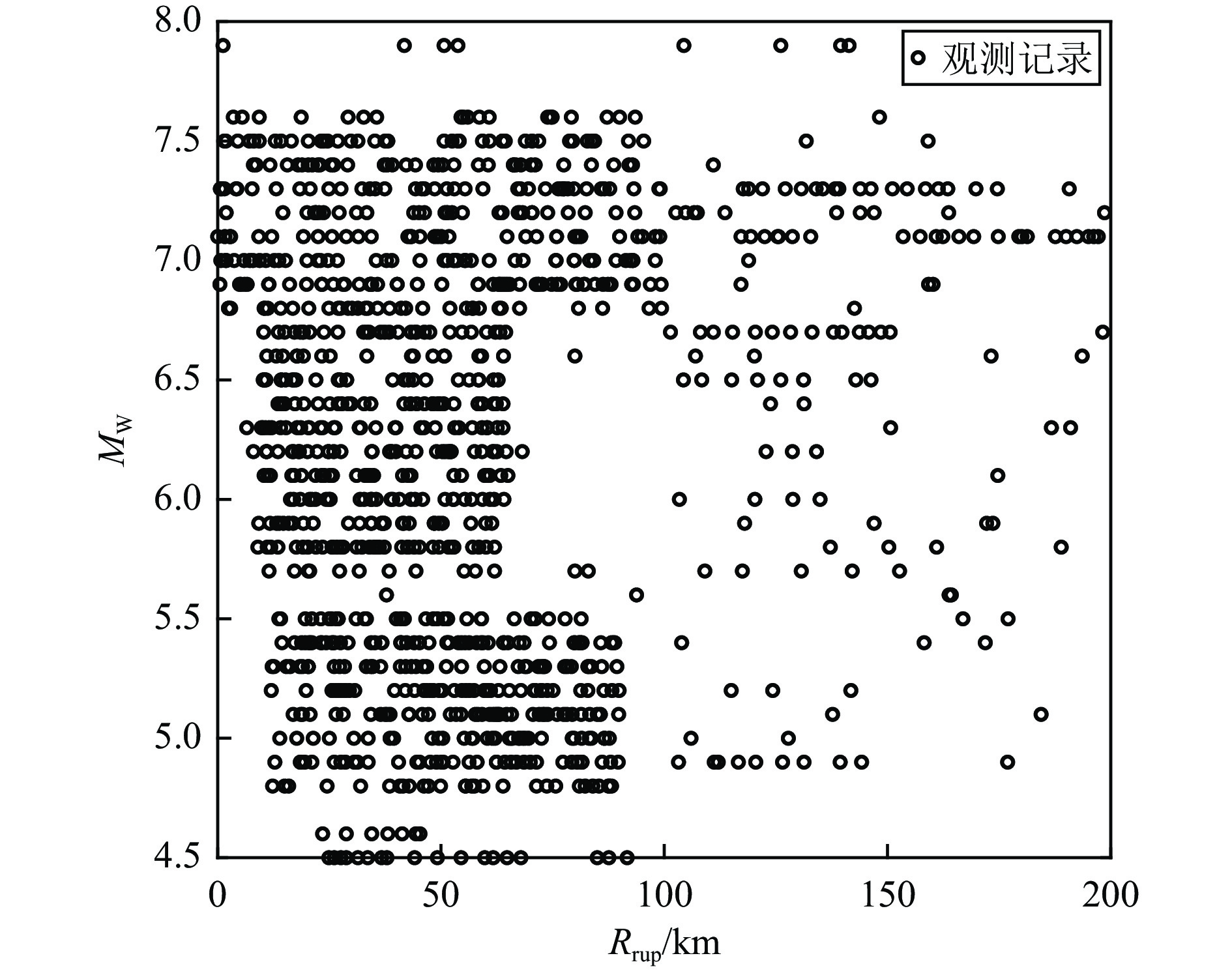
表 1 AS08数据集的总体情况
Table 1. Overview of AS08 dataset
参数 单位 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 MW — 7.9 4.5 6.2 0.5 VS30 $ \text{m/s} $ 1820 210 345 192 $ {{R}}_{\text{rup}} $ $ \text{km} $ 199.8 0.2 68.4 3.7 $ \text{PGA} $ $ \text{g} $ 1.60 0 0.04 0.09 表 2 ANFIS竖向地震动强度预测模型的建模参数
Table 2. Modeling parameters of the ANFIS vertical ground motion intensity prediction model
隶属函数 $ {{M}}_{\text{W}} $ $ {R}_{\text{rup}} $ VS30 a b c a b c a b c 1 0.3190 1.8366 0.0585 0.3298 1.9278 0.2429 0.0019 1.8911 − 0.0027 2 0.3767 1.9284 0.3202 0.3549 1.9172 0.4721 0.0546 1.8450 0.6845 3 0.1409 1.9466 1.1122 0.3415 1.8367 0.8077 0.3525 1.9823 0.8660 表 3 ANFIS竖向地震动预测模型的误差分析
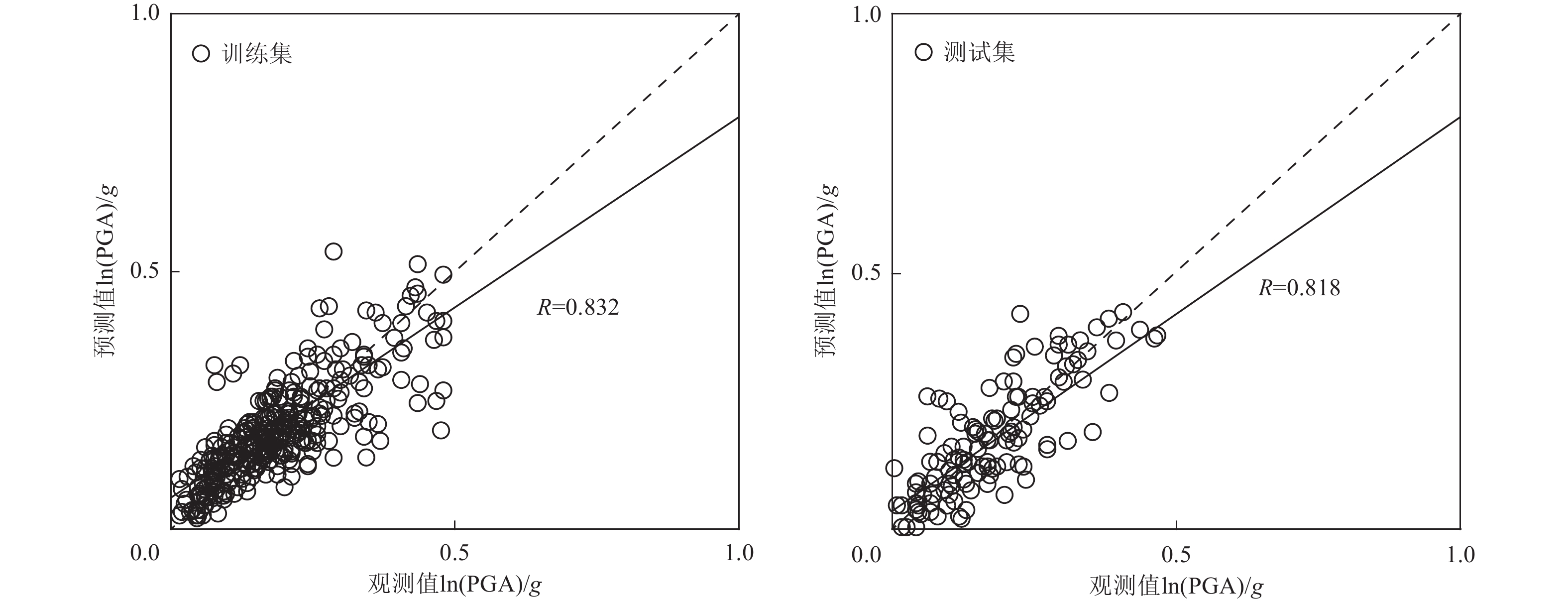
Table 3. Error analysis of ANFIS vertical ground motion prediction model
误差指标 训练集 测试集 2022年门源MW6.7地震 R 0.832 0.818 0.809 EMA 0.013 0.024 0.038 EMAP 0.133 0.156 0.168 ERMS 0.021 0.042 0.046 表 4 不同机器学习预测模型的误差对比
Table 4. Error comparison of different machine learning prediction models
指标 ANFIS ANN-SA GP-OLS R 0.818 0.855 0.811 EMA 0.024 0.460 0.488 表 5 2022年门源MW6.7地震竖向地震动预测的设定条件
Table 5. Setting conditions for vertical ground shaking prediction of the 2022 Menyuan MW6.7 earthquake
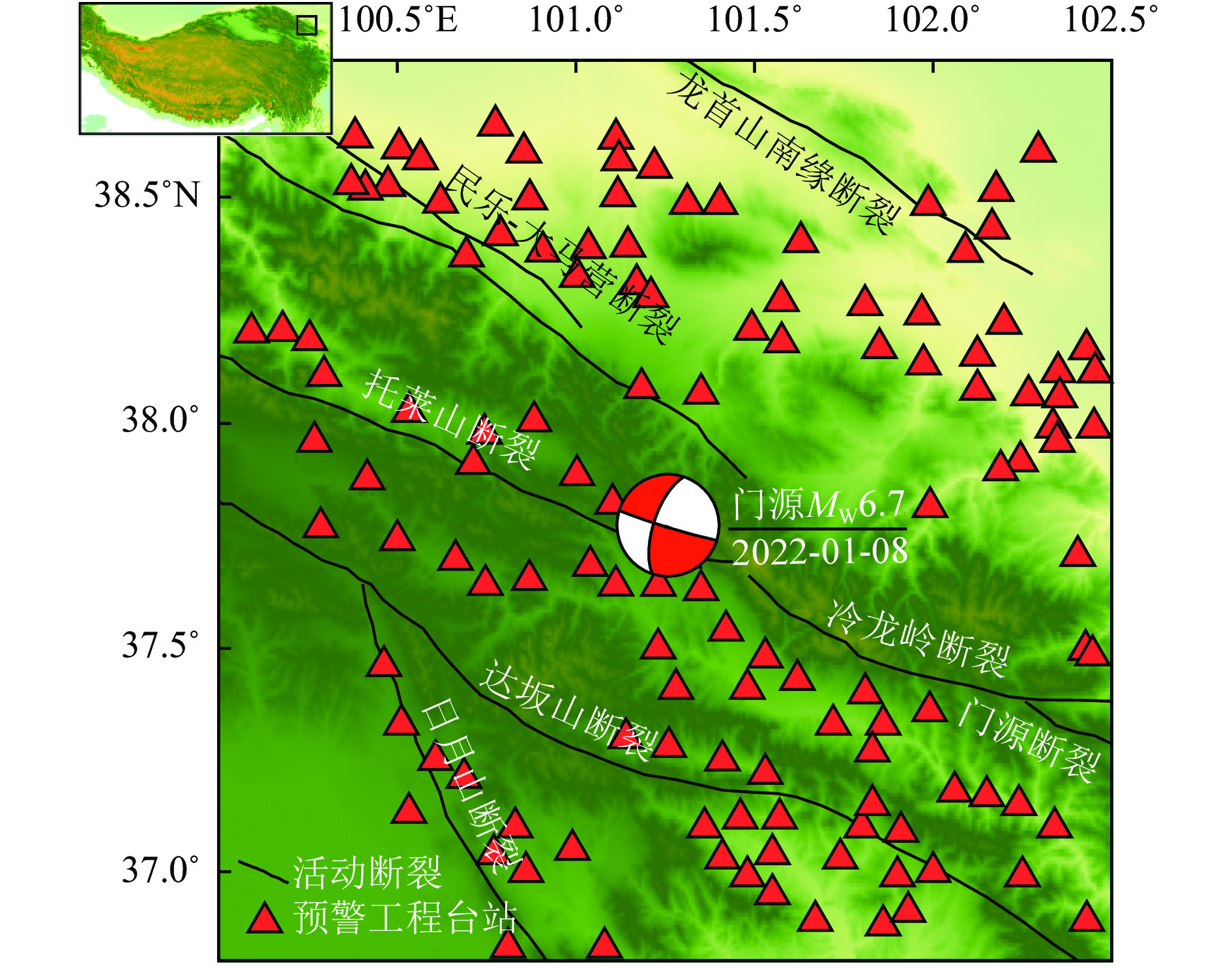
发震日期 地震事件 震级MW 震中位置 发震断层 发震断层走向 震源深度/km 2022-01-08 门源地震 6.7 37.77 °N,101.26 °E 托莱山断裂 NWW-SEE 10 -
白仲航, 项钲, 谭昭芸等, 2024. 自适应神经模糊推理系统优化的快速上肢评估方法. 计算机集成制造系统, 30(5): 1643−1656. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2023.0277Bai Z. H., Xiang Z., Tan Z. Y., et al., 2024. Rapid upper limb assessment method based on adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system optimization. Computer Integrated Manufacturng Systems, 30(5): 1643−1656. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2023.0277 陈凯, 潘华, 2025. 基于机器学习的区域地震动模拟−以2022年泸定MS6.8地震为例. 地震学报, 47(2): 242−253.Chen K., Pan H., 2025. Machine learning-based regional ground seismic motion simulation: a case study of the MS6.8 Luding earthquake in 2022. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 47(2): 242−253. (in Chinese) 陈琨, 王安志, 2024. 卷积神经网络的正则化方法综述. 计算机应用研究, 41(4): 961−969. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.06.0347Chen K., Wang A. Z., 2024. Survey on regularization methods for convolutional neural network. Application Research of Computers, 41(4): 961−969. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.06.0347 邓伟伟, 段朝阳, 闫亮, 2021. 基于自适应神经模糊推理系统的导弹直/气复合控制系统设计. 导航定位与授时, 8(5): 54−60. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.05.008Deng W. W., Duan C. Y., Yan L., 2021. Design of missile direct/air compound control system based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 8(5): 54−60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.05.008 管仲国, 黄勇, 张昊宇等, 2021. 青海玛多7.4级地震桥梁工程震害特性分析. 世界地震工程, 37(3): 38−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2021.03.005Guan Z. G., Huang Y., Zhang H. Y., et al., 2021. Damage characteristics and analysis of bridge engineering in M7.4 Qinghai Maduo earthquake. World Earthquake Engineering, 37(3): 38−45. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2021.03.005 韩建平, 周伟, 2012. 汶川地震竖向地震动特征初步分析. 工程力学, 29(12): 211−219.Han J. P, Zhou W., 2012. Preliminary investigation on characteristics of vertical Ground motion during Wenchuan earthquake. Engineering Mechanics, 29(12): 211−219. (in Chinese) 韩立波, 2022. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震震源机制解. 地震科学进展, 52(2): 49−54. doi: 10.11939/jass.20220008Han L. B., 2022. Focal mechanism of 2022 Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake in Qinghai Province. Progress in Earthquake Sciences, 52(2): 49−54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11939/jass.20220008 洪华嫦, 陈敏杰, 康家馨等, 2023. 基于自适应神经模糊推理系统和简单水质指标预测供水系统三卤甲烷的浓度. 环境科学学报, 43(6): 290−299. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2023.0069Hong H. C., Chen M. J., Kang J. X., et al., 2023. Prediction of trihalomethane levels in tap water based on adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system and simple water quality parameters. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(6): 290−299. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2023.0069 胡进军, 谢礼立, 2011. 地震破裂的方向性效应相关概念综述. 地震工程与工程振动, 31(4): 1−8. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2011.04.001Hu J. J., Xie L. L., 2011. Review of rupture directivity related concepts in seismology. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 31(4): 1−8. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2011.04.001 胡进军, 张辉, 靳超越等, 2021. 基于PCA及PSO智能算法的地震动合成方法−−以中国西部中强地震为例. 工程力学, 38(3): 159−168.Hu J. J., Zhang H., Jin C. Y, et al., 2021. A method to simulate ground motion based on PCA and PSO intelligent algorithms−a case study of moderate magnitude earthquakes in western China. Engineering Mechanics, 38(3): 159−168. (in Chinese) 靳超越, 胡进军, 胡磊等, 2021. 基于机器学习的地震动特征提取与模拟−−以2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震为例. 世界地震工程, 37(4): 73−80.Jin C. Y., Hu J. J., Hu L. et al., 2021. Machine learning-based seismic feature extraction and simulation−−a case study of the 2021 Yangbi M6.4 earthquake. World Earthquake Engineering, 37(4): 73−80. (in Chinese) 刘胜兵, 梅浩华, 黄依莹等, 2024. 玄武岩-聚丙烯混杂纤维轻骨料混凝土强度研究. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 57(12): 1725−1732. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2024-12-007Liu S. B., Mei H. H., Huang Y. Y., et al., 2024. Strength study of basalt-polypropylene hybrid fiber lightweight aggregate concrete. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 57(12): 1725−1732. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2024-12-007 卢滔, 薄景山, 李巨文等, 2009. 汶川大地震汉源县城建筑物震害调查. 地震工程与工程振动, 29(6): 88−95.Lu T., Bo J. S., Li J. W. et al., 2009. Damage to buildings in Hanyuan county town during 2008 MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 29(6): 88−95. (in Chinese) 吕红山, 赵凤新, 2007. 适用于中国场地分类的地震动反应谱放大系数. 地震学报, 29(1): 67−76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2007.01.008Lv H. S., Zhao F. X., 2007. Site coefficients suitable to China site category. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 29(1): 67−76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2007.01.008 潘章容, 周扬, 苗在鹏等, 2023. 2022年1月8日青海门源6.9级地震仪器烈度与宏观烈度对比分析. 高原地震, 35(3): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2023.03.002Pang Z. R., Zhou Y., Miao Z. P., et al., 2023. Comparative analysis on instrument intensaity and macroscopic survey intensity of the Menyuan M6.9 earthquake on January, 8, 2022. Plateau Earthquake Research, 35(3): 8−15. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2023.03.002 彭朝勇, 程振鹏, 郑钰等, 2024. 考虑P波预警参数的震源破裂特征实时持续估测方法. 地球科学, 49(2): 391−402. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2023.167Peng C. Y., Cheng Z. P., Zheng Y., et al., 2024. Real-time continuous estimation of Seismic source rupture characteristics considering P-wave early warning parameters. Earth Science, 49(2): 391−402. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2023.167 齐娟, 罗开海, 杨小卫, 2014. 竖向地震动特性的统计分析. 地震工程与工程振动, 34(S1): 253−260. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2014.S0.253.qij.039Qi J., Luo K. H., Yang X. W., 2014. Statistical analysis on characteristics of vertical ground motions. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 34(S1): 253−260. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2014.S0.253.qij.039 史大成, 温瑞智, 杜春清, 2012. 区域性场地VS30及峰值加速度放大系数估算方法. 地震工程与工程振动, 32(4): 40−46. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2012.04.004Shi D. C., Wen R. Z., Du C. Q., 2012. Study on regional site VS30 and PGA amplification factor. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 32(4): 40−46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2012.04.004 师涵博, 张元生, 2024. 2022年1月8日青海门源6.9级强地震动模拟研究. 地震工程学报, 46(3): 680−691. doi: 10.20000/j.1000-0844.20230920001Shi H. B., Zhang Y. S., 2024. Strong ground motion simulation of the Qinghai M6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 46(3): 680−691. (in Chinese) doi: 10.20000/j.1000-0844.20230920001 石玉成, 陈厚群, 李敏等, 2005. 随机有限断层法合成地震动的研究与应用. 地震工程与工程振动, 25(4): 18−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2005.04.003Shi Y. C., Chen H. Q., Li M., et al., 2005. The study and application of stochastic finite faults method in ground motion synthesizing. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 25(4): 18−23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2005.04.003 宋晋东, 朱景宝, 李水龙等, 2024. 基于机器学习预测模型的现地警报级别地震预警试验−−以2022年9月5日四川泸定6.8级地震为例. 地球物理学报, 67(8): 3004−3016. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0789Song J. D., Zhu J. B., Li S. L., et al., 2024. Test of on-site alert-level earthquake early warning based on machine learning prediction models: A case for the Sichuan Luding M6.8 earthquake on September 5, 2022. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 67(8): 3004−3016. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0789 万永革, 黄少华, 王福昌等, 2023. 2022年门源地震序列揭示的断层几何形状及滑动特性. 地球物理学报, 66(7): 2796−2810. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0345Wan Y. G., Huang S. H., Wang F. C., et al., 2023. Fault geometry and slip characteristics revealed by the 2022 Menyuan earthquake sequence. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 66(7): 2796−2810. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0345 王世进, 尹海权, 张超等, 2024. 基于层次分析法的地震预警设备运行能力综合评价研究. 震灾防御技术, 19(4): 830−836. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20240419Wang S. J., Yin H. Q., Zhang C., et al., 2024. Comprehensive evaluation of operational capability of earthquake warning equipment based on analytic hierarchy process. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 19(4): 830−836. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20240419 谢俊举, 温增平, 高孟潭等, 2010. 2008年汶川地震近断层竖向与水平向地震动特征. 地球物理学报, 53(8): 1796−1805. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.08.005Xie J. J., Wen Z. P., Gao M. T., et al., 2010. Characteristics of near-fault vertical and horizontal ground motion from the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(8): 1796−1805. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.08.005 辛娅云, 2005. 竖向地震作用的重要性. 工程抗震与加固改造, 27(S1): 54−56. doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2005.s1.010Xin Y. Y., 2005. Importance of the vertical seismic effect. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 27(S1): 54−56. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2005.s1.010 徐龙军, 谢礼立, 2007. 竖向地震动加速度反应谱特性. 地震工程与工程振动, 27(6): 17−23. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2007.06.007Xu L. J., Xie L. L., 2007. Characteristics of acceleration response spectra for vertical ground motions. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 27(6): 17−23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2007.06.007 赵德宏, 张帅, 2022. 基于ANFIS算法的天然石材铣削加工条件下的切削载荷预测方法. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 535−542. doi: 10.11717/j.issn:2095-1922.2022.03.19Zhao D. H., Zhang S., 2022. Research on cutting force prediction under the milling condition of natural stone based on ANFIS algorithm. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science), 38(3): 535−542. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11717/j.issn:2095-1922.2022.03.19 郑志, 王勇, 温卫平等, 2025. 基于机器学习的核电厂震后损伤评估及响应预测方法. 工程力学, 42(9): 124−136. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.04.0250Zheng Z., Wang Y., Wen W. P., et al., 2025. A machine learning-based approach to post-earthquake damage assessment and response prediction for nuclear power plants. Engineering Mechanics, 42(9): 124−136. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.04.0250 Abrahamson N., Silva W., 2008. Summary of the Abrahamson & Silva NGA ground-motion relations. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 67−97. doi: 10.1193/1.2924360 Chen S., Hu X. H., Jiang W. P., et al., 2025. Data-physical fusion deep learning for site seismic response using KiK-net records. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 54(3): 993−1008. Giacinto G., Paolucci R., Roli F., 1997. Application of neural networks and statistical pattern recognition algorithms to earthquake risk evaluation. Pattern Recognition Letters, 18(11-13): 1353−1362. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(97)00088-3 Hsu T. Y., Huang C. W., 2021. Onsite early prediction of PGA using CNN with multi-scale and multi-domain P-waves as input. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 626908. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.626908 Jozinović D., Lomax A., Štajduhar I., et al., 2020. Rapid prediction of earthquake ground shaking intensity using raw waveform data and a convolutional neural network. Geophysical Journal International, 222(2): 1379−1389. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggaa233 Segou M., Voulgaris N., 2010. Proschema: A Matlab application for processing strong motion records and estimating earthquake engineering parameters. Computers & Geosciences, 36(7): 977−986. Song C. K. , Chen B., 2024. Heterogeneity effect of elastic properties on piezomagnetic fields associated with dislocation source. Izvestiya. Physics of the Solid Earth, 60(2): 325−332. Wen W. P., Xu T. F., Hu J., et al., 2025. Seismic damage recognition of structural and non-structural components based on convolutional neural networks. Journal of Building Engineering, 102: 112012. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112012 -




 下载:
下载: