Intelligent Analysis of Structure Reinforcement Strategies Based on Random Forest
-
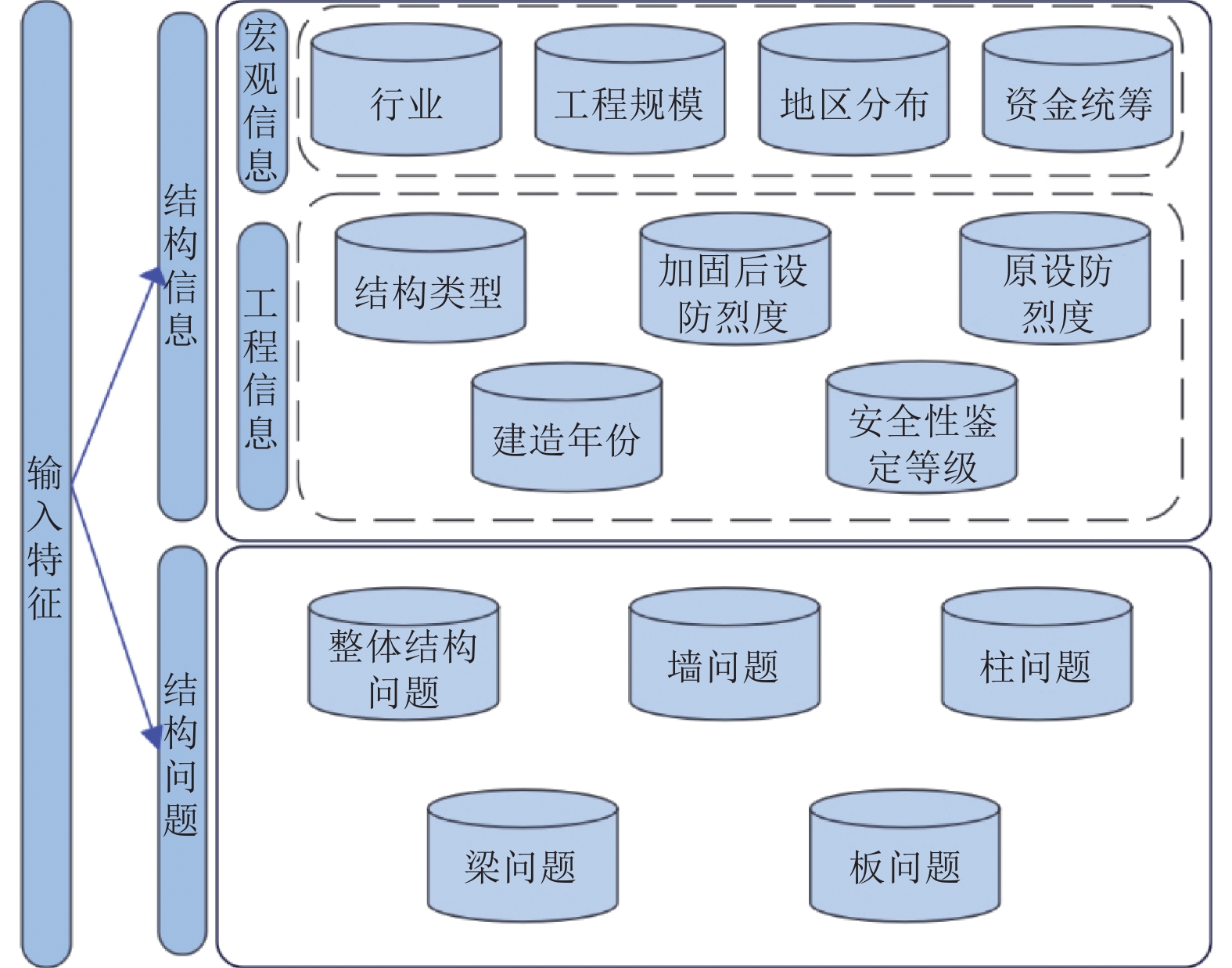
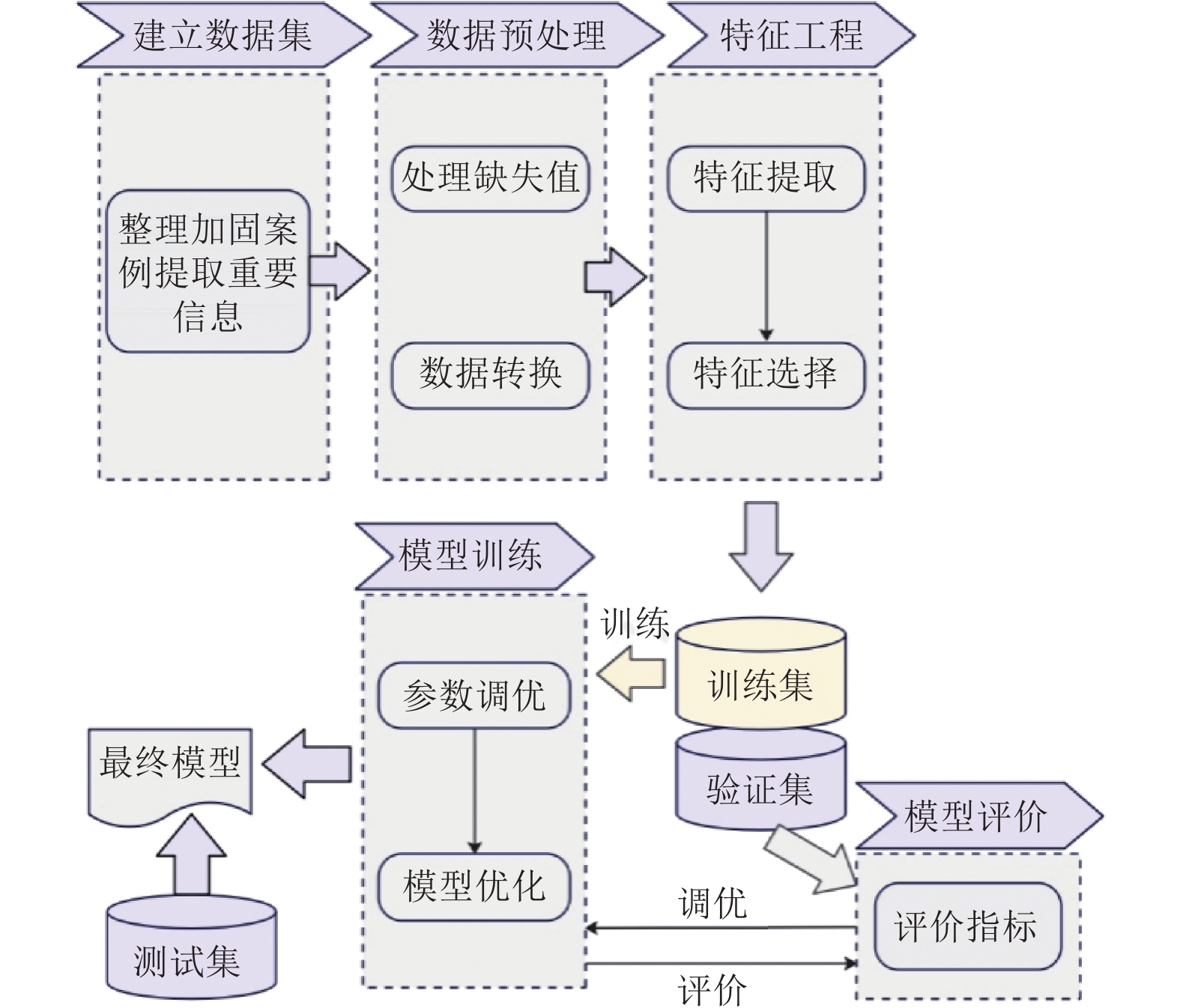
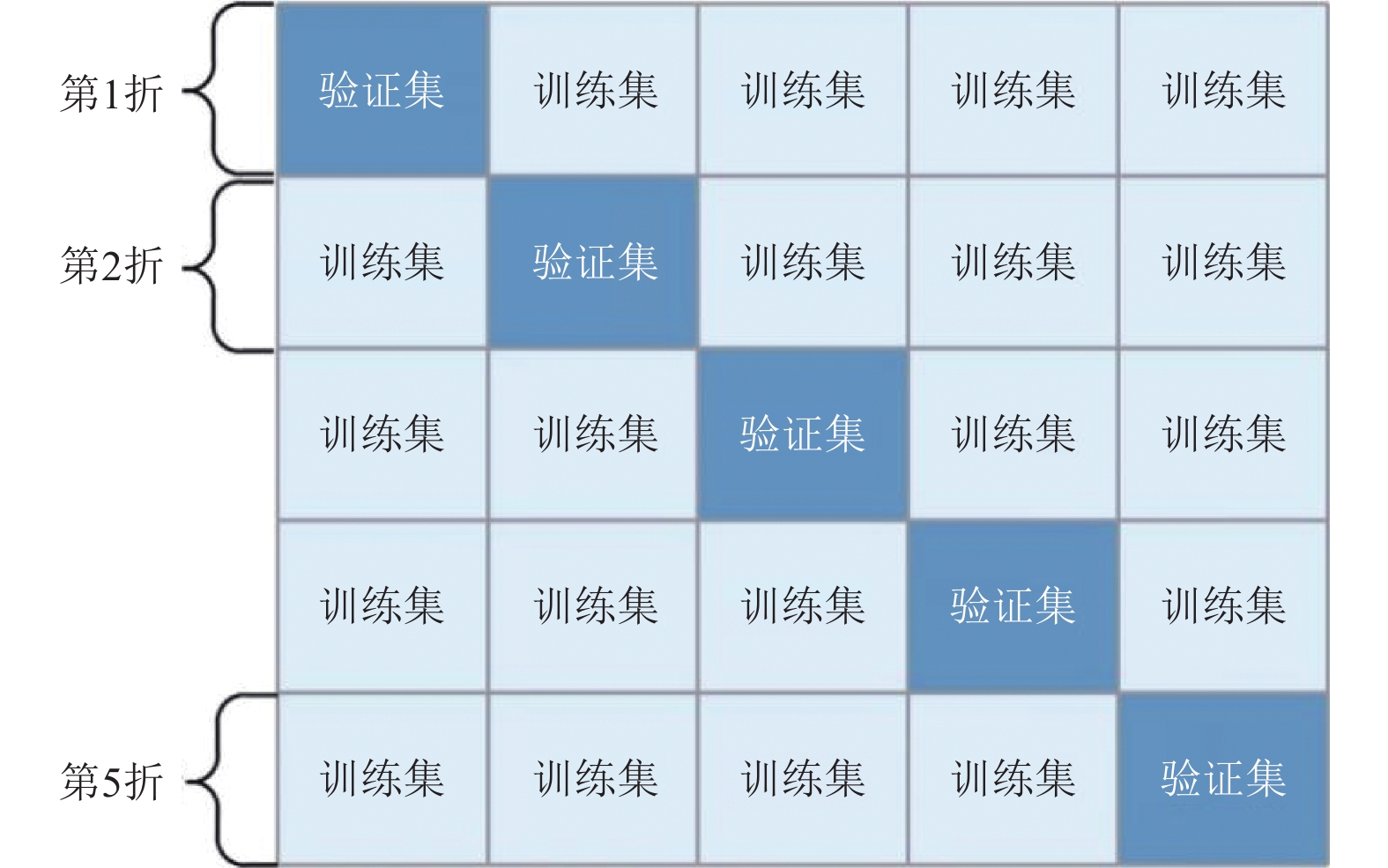
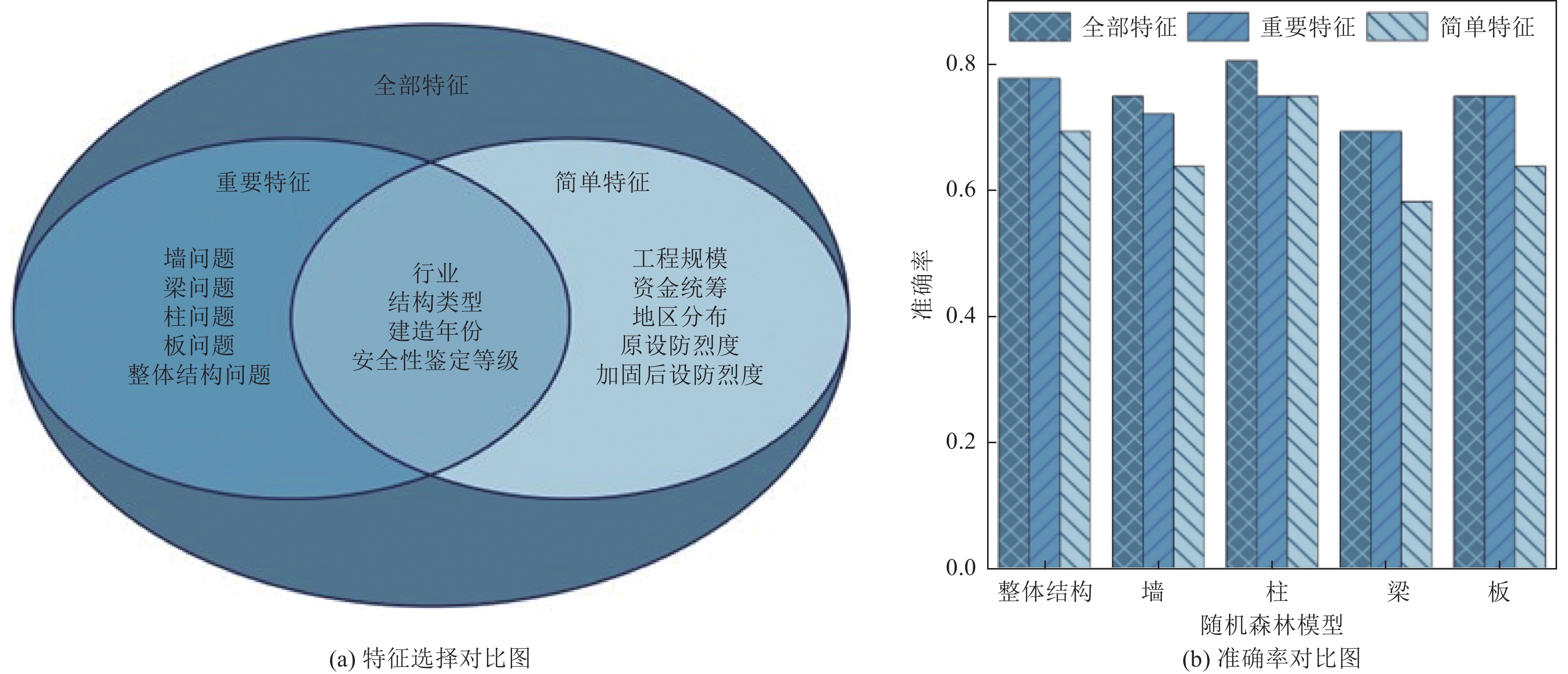
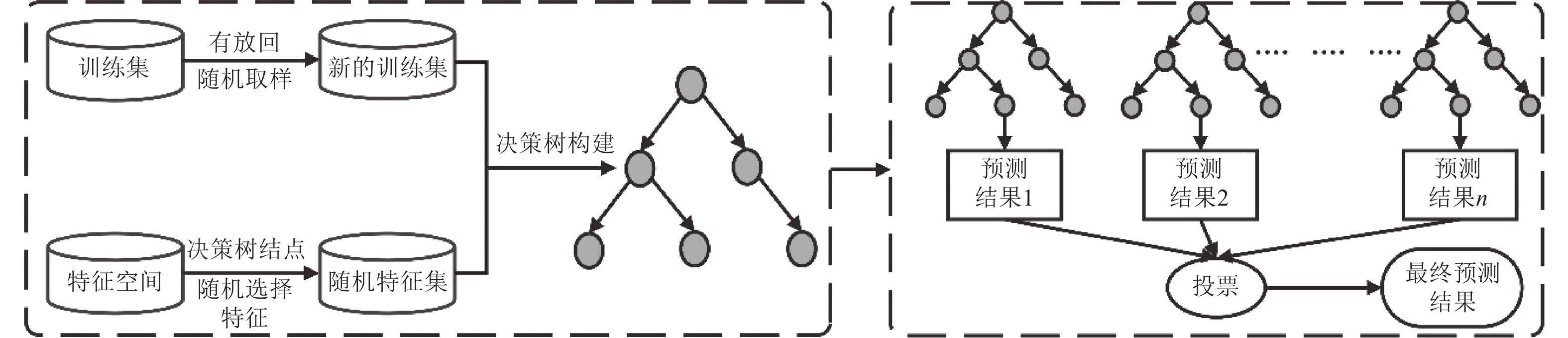
摘要: 工程结构加固是指为满足新的功能需求、安全标准或抗震设防要求,对既有结构进行的加固补强。加固方案的选择往往依托技术人员的专业技术水平和工程经验,具有一定的主观性。本研究采用机器学习中的随机森林算法作为数据分析工具,选取结构信息和结构问题两方面共14个影响因素作为输入特征,结构整体加固与局部加固方案作为输出特征。通过构建结构加固策略智能分析模型,有效应对加固方案复杂、组合情况多样而难以建模的问题。本研究以122个实际工程案例为样本构建数据集,通过5个独立随机森林模型(整体结构、墙、柱、梁、板)的构建与整合实现了结构整体加固和局部加固方案的预测,分析了全部特征、重要特征和简单特征3种不同输入特征组合的随机森林模型预测结果,以探究不同输入特征对模型准确率的影响。结果表明,基于全部特征和基于重要特征的机器学习模型准确率相近,5个模型的准确率均可达到69%以上,其中部分模型可以达到80%左右;而基于简单特征的随机森林模型准确率较低。由此可见,选取的重要特征与随机森林模型的预测准确率相关性高,而简单特征难以构建可靠的预测模型。研究成果可为结构加固领域的智能化决策和分析提供参考。Abstract: Engineering structure reinforcement involves upgrading existing structures to satisfy new functional requirements, safety standards, or seismic performance criteria. Traditionally, the selection of reinforcement strategies relies heavily on engineers’ technical expertise and experience, introducing subjectivity into the decision-making process. This study applies the Random Forest (RF) algorithm from machine learning as a data-driven analysis tool, using 14 factors related to structural information and performance issues as input features, and overall and component-level reinforcement strategies as output features. The proposed intelligent analysis model effectively addresses the complexity and combinatorial diversity inherent in structural reinforcement schemes. A dataset comprising 122 real engineering cases is constructed, and five independent RF models are trained to predict reinforcement strategies for the overall structure, walls, columns, beams, and slabs. Model performance is evaluated under three input feature configurations: all features, important features, and simple features. The results show that models using all features or selected important features achieve comparable accuracy, with all five models reaching over 69% and some approaching 80%, whereas models based on simple features exhibit lower accuracy. These findings indicate a strong correlation between the selected important features and the predictive performance of the RF models, while simple features are insufficient to construct reliable predictions. The study provides a practical reference for intelligent decision-making and analysis in structural reinforcement, supporting more systematic and data-driven strategy selection.
-
表 1 输入特征信息表:结构信息
Table 1. Input properties information table: structure information
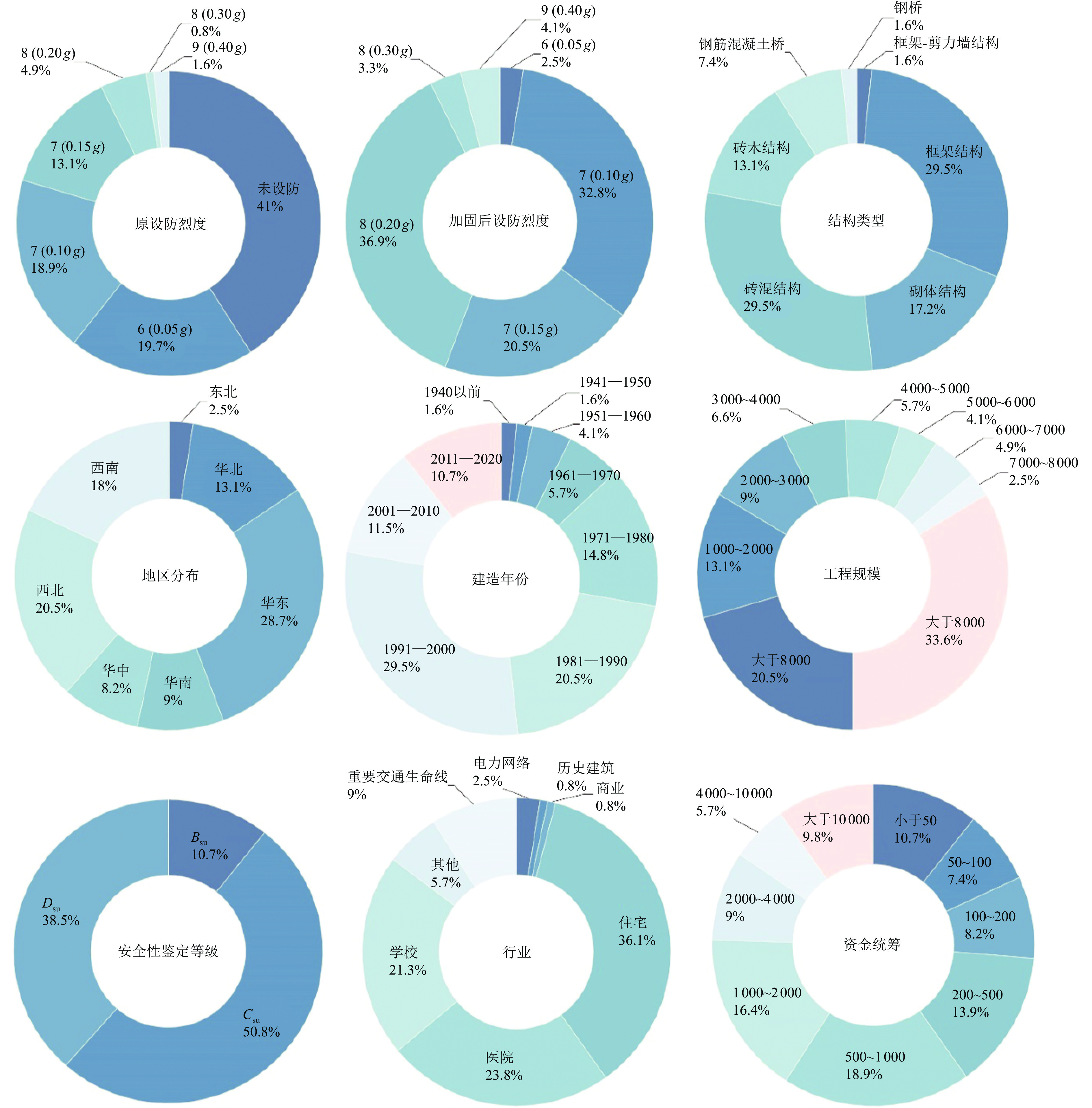
编号 行业 原设防烈度 加固后设防烈度 结构类型 建造年份 地区分布 工程规模/m2 资金统筹/万元 安全性鉴定等级 1 医院 8(0.20 g) 8(0.20 g) 砌体结构 1960 华北 3 065.85 3 000 Dsu 2 商业 8(0.20 g) 8(0.20 g) 框架结构 2009 华北 74 000 大于10 000 Bsu ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 73 住宅 未设防 7(0.15 g) 砌体结构 1990 华中 76 655 1 182.4 Csu ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 121 电力网络 8(0.20 g) 8(0.20 g) 砖混结构 1973 西北 3 931.45 2 014 Dsu 122 电力网络 7(0.10 g) 8(0.20 g) 砖混结构 1982 西北 500 96.68 Dsu 表 2 输入特征信息表:结构问题
Table 2. Input properties information table: structure issues
编号 整体结构问题 墙问题 柱问题 梁问题 板问题 1 功能改造,抗震能力不足 出现裂缝 无 无 开裂 2 功能改造,抗震能力不足 无 承载力不足 承载力不足 承载力不足 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 73 结构整体性差缺少抗震构造措施 出现裂缝 无 无 无 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 121 老化,抗震能力不足 砂浆强度不足 无 承载力不足 承载力不足 122 结构整体性差缺少抗震构造措施 出现裂缝 无 配筋不足 产生较大变形 表 3 5个子加固方案的输出特征信息表
Table 3. Output feature information for the five sub-reinforcement schemes
编号 整体结构加固方案 墙加固方案 柱加固方案 梁加固方案 板加固方案 1 增设剪力墙 钢筋混凝土板墙 无 无 粘贴碳纤维 2 屈曲约束支撑 无 粘钢和增大截面 增大截面及粘钢 粘贴碳纤维 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 73 无 高延性混凝土 无 无 无 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 121 无 钢筋混凝土板墙 无 外包钢 粘贴碳纤维 122 增设圈梁和构造柱 无 无 粘钢 粘贴碳纤维 表 4 特征-代码对照表
Table 4. Character-to-code reference
特征值 特征分类 分类代码 行业 电力网络/历史建筑/商业/住宅/医院/学校/其他/重要交通生命线 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 原设防烈度 未设防/5/6(0.05 g)/7(0.10 g)/7(0.15 g)/8(0.20 g)/8(0.30 g)/9(0.40 g) 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 加固后的设防烈度 6(0.05 g)/7(0.10 g)/7(0.15 g)/8(0.20 g)/8(0.30 g)/9(0.40 g) 1/2/3/4/5/6 结构类型 剪力墙结构/框架-剪力墙结构/框架结构/砌体结构/砖混结构/砖木结构/钢筋混凝土桥/钢桥 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 建造年份 1940以前/1941—1950/1951—1960/1961—1970/1971—1980/1981—1990/1991—2000/2001—2010/
2011—20201/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9 地区分布 东北/华北/华东/华南/华中/西北/西南 1/2/3/4/5/6/7 工程规模/m2 小于50/50~100/100~200/200~500/500~1 000/1 000~2 000/2 000~4 000/4 000~10 000/大于10 000 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9 资金统筹/万元 小于50/50~100/100~200/200~500/500~1 000/1 000~2 000/2 000~4 000/4 000~10 000/大于10 000 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9 安全性鉴定等级 Bsu/Csu/Dsu 1/2/3 整体结构问题 其他/不满足现行规范的设防烈度要求/地震后房屋受损/功能改造,抗震能力不足/结构整体性差,缺少抗震构造措施/老化,抗震能力不足/遭遇水灾,结构受损 0/1/2/3/4/5/6 墙问题 其他/出现裂缝/墙体钢筋裸露/砂浆强度不足/无明显开裂,承载力不足 0/1/2/3/4 柱问题 其他/承载力不足/轴压比不足 0/1/2 梁问题 其他/承载力不足/钢筋锈胀、保护层脱落/较大范围锈蚀/开裂/配筋不满足要求 0/1/2/3/4/5 板问题 其他/产生较大变形/承载力不足/钢筋锈胀、保护层脱落/开裂/配筋不满足要求 0/1/2/3/4/5 整体结构
加固方案隔振加固/内部结构置换/普通支撑/屈曲约束支撑/屈曲约束支撑和黏滞阻尼器/外加子结构/增设剪力
墙/增设圈梁和构造柱/无/重建/1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9/10 墙加固方案 钢板加固/钢筋混凝土板墙/钢筋网高强度聚合物砂浆/钢筋网水泥砂浆/高延性混凝土/植筋/无/重建 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 柱加固方案 外包钢/增大截面/增大截面和外包钢/粘钢/粘钢和增大截面/无/重建 1/2/3/4/5/6/7 梁加固方案 外包钢/增大截面/增大截面及粘钢/粘钢/粘贴碳纤维/无/重建 1/2/3/4/5/6/7 板加固方案 增浇叠合层/粘钢/粘贴碳纤维/无/重建 1/2/3/4/5 表 5 不同特征组合下5个随机森林模型的参数配置
Table 5. Parameter configurations for five Random Forest models under different feature combinations
模型类型 基于全部特征模型 基于重要特征模型 基于简单特征模型 整体结构 墙 柱 梁 板 整体结构 墙 柱 梁 板 整体结构 墙 柱 梁 板 NumTrees 40 40 20 31 34 40 32 24 24 30 39 24 33 30 25 NumPredictorsToSample 4 9 4 8 5 4 4 5 3 5 4 5 4 8 5 MaxNumSplits 21 17 18 18 20 21 19 19 18 18 18 19 19 19 20 MinLeafSize 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 表 6 模型运行结果
Table 6. Results of model operation
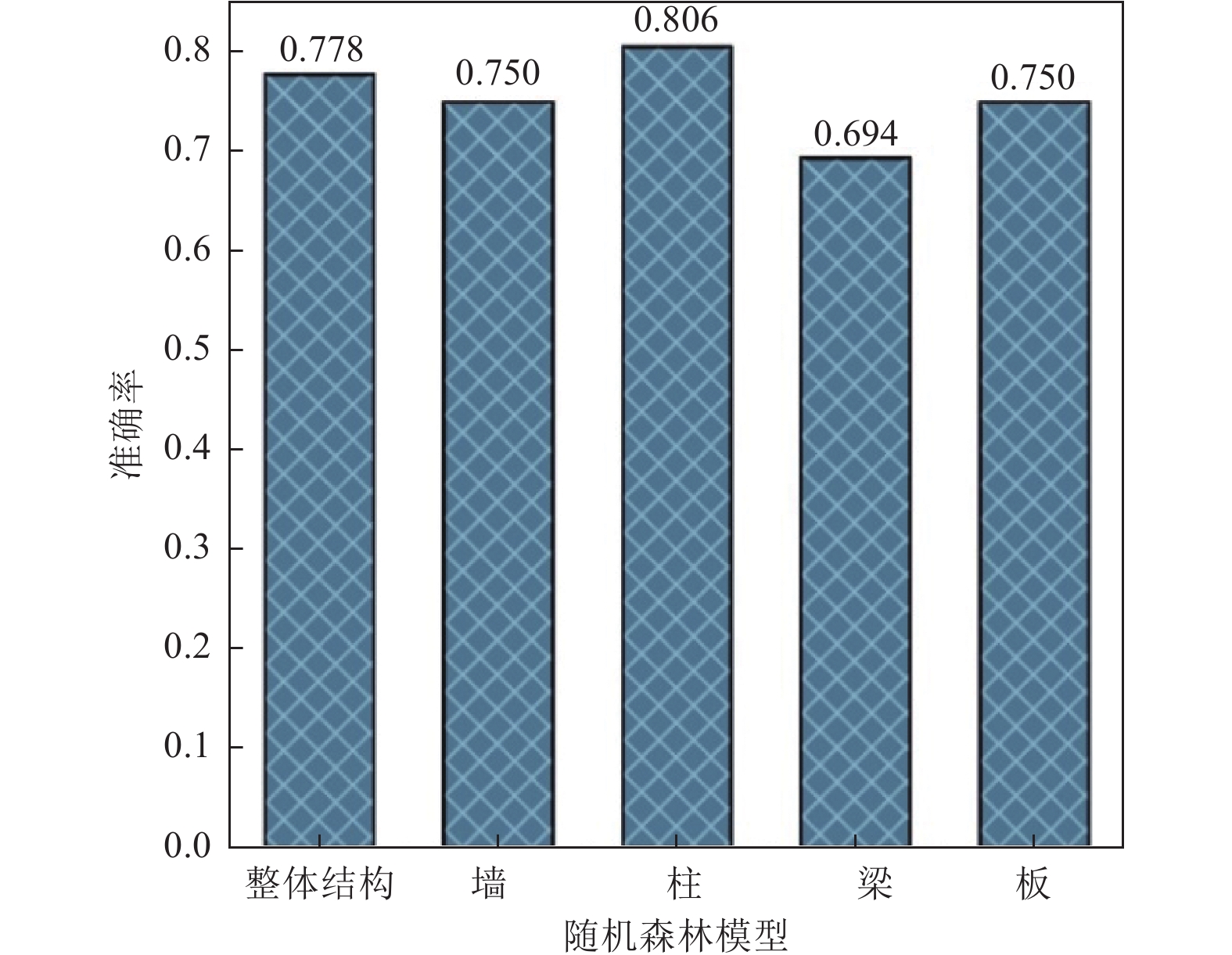
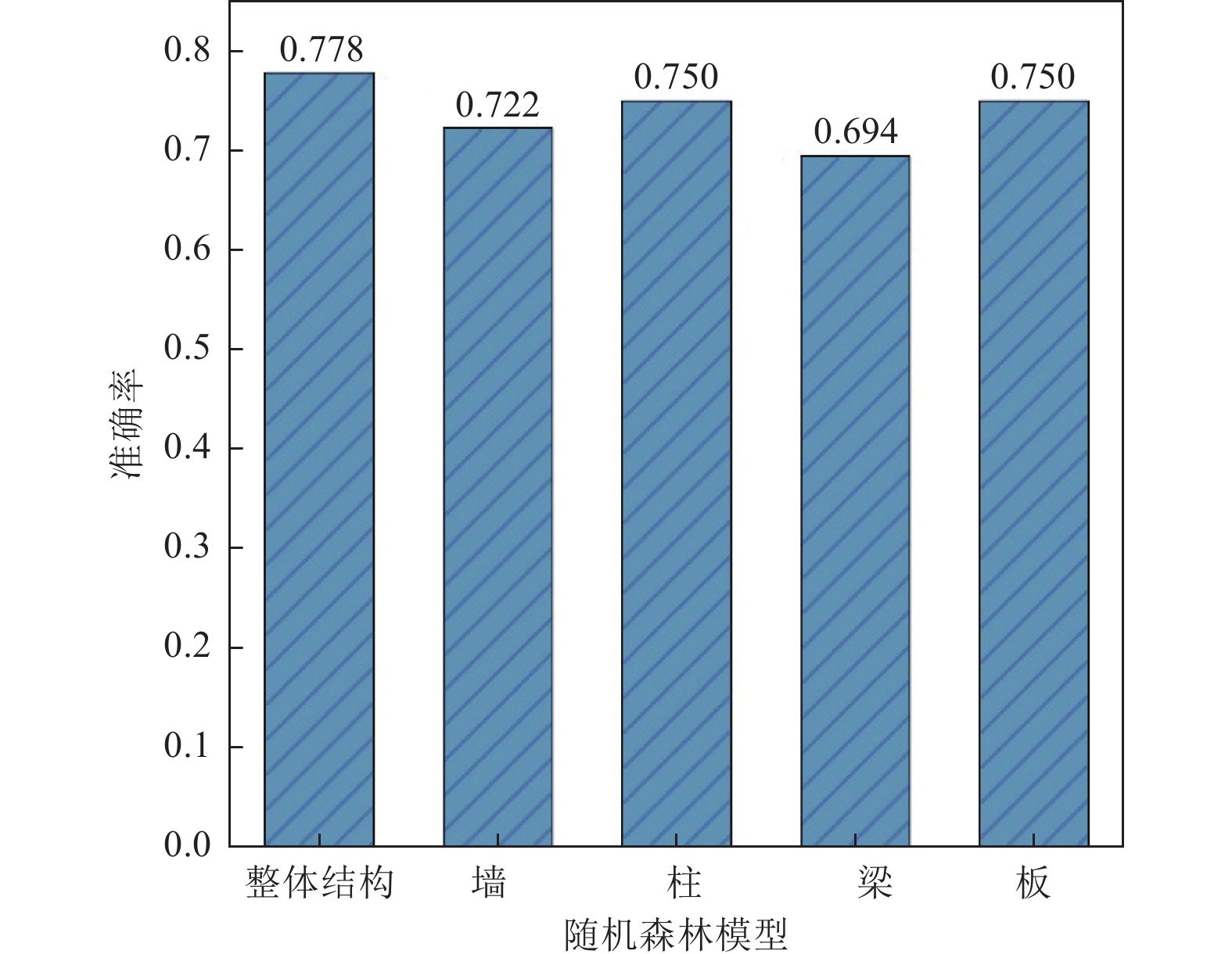
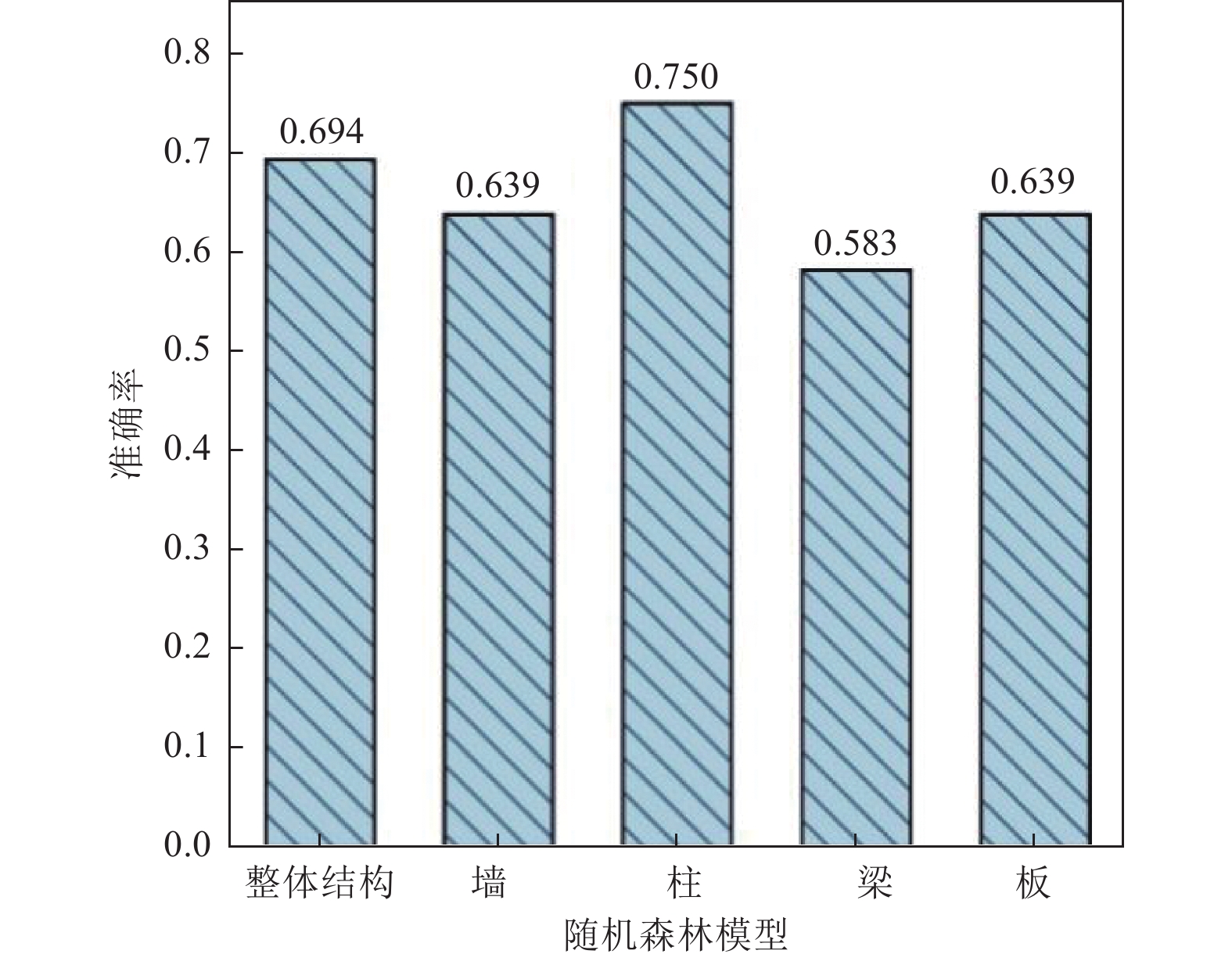
模型类型 特征来源 特征个数 准确率 整体 墙 柱 梁 板 平均值 标准差 基于全部特征 直接获得+分类总结 14 0.778 0.750 0.806 0.694 0.750 0.756 0.037 基于重要特征 根据随机森林模型特征重要性选取 9 0.778 0.722 0.750 0.694 0.750 0.739 0.029 基于简单特征 加固资料中直接获得 9 0.694 0.639 0.750 0.583 0.639 0.661 0.057 表 7 模型输入:结构信息
Table 7. Model input: structure information
行业 原设防烈度 加固后设防烈度 结构类型 建造年份 地区分布 工程规模/m2 资金统筹/万元 安全性鉴定等级 住宅 未设防 7(0.10 g) 砖混结构 1980 华南 960 373 Bsu 表 8 模型输入:结构问题
Table 8. Model input: structure issues
整体结构问题 墙问题 柱问题 梁问题 板问题 结构整体性差缺少抗震构造措施 砂浆强度不足 无 较大范围锈蚀 钢筋锈胀、保护层脱落 表 9 模型输出:预测加固方案
Table 9. Model output: predicted reinforcement schemes
整体结构 墙 柱 梁 板 全部特征模型预测 无 钢筋网高强度聚合物砂浆 无 粘贴碳纤维 粘贴碳纤维 重要特征模型预测 无 钢筋网高强度聚合物砂浆 无 粘贴碳纤维 粘贴碳纤维 简单特征模型预测 无 高延性混凝土 无 无 无 实际加固方案 无 钢筋网高强度聚合物砂浆 无 粘贴碳纤维 粘贴碳纤维 -
丁威, 俞珂, 舒江鹏, 2021. 基于深度学习和无人机的混凝土结构裂缝检测方法. 土木工程学报, 54(S1): 1−12. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.s1.016Ding W., Yu K., Shu J. P., 2021. Method for detecting cracks in concrete structures based on deep learning and UAV. China Civil Engineering Journal, 54(S1): 1−12. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.s1.016 范向前, 刘决丁, 史晨雨等, 2023. 基于人工神经网络方法的FRP增强混凝土断裂研究新思路. 防灾减灾工程学报, 43(3): 626−636. doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.20210429003Fan X. Q., Liu J. D., Shi C. Y., et al., 2023. Innovative idea on fracture analysis of FRP reinforced concrete using artificial neural network. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 43(3): 626−636. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.20210429003 胡少伟, 李原昊, 单常喜等, 2023. 基于改进的PSO-BP神经网络的边坡稳定性研究. 防灾减灾工程学报, 43(4): 854−861.Hu S. W., Li Y. H., Shan C. X., et al., 2023. Research on slope stability based on improved PSO-BP neural network. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 43(4): 854−861. (in Chinese) 江宝得, 李秀春, 罗海燕等, 2023. 异质集成学习在滑坡易发性评价中的对比研究. 土木工程学报, 56(10): 170−179. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.22060553Jiang B. D., Li X. C., Luo H. Y., et al., 2023. A comparative analysis of heterogeneous ensemble learning methods for landslide susceptibility assessment. China Civil Engineering Journal, 56(10): 170−179. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.22060553 刘宇飞, 樊健生, 聂建国等, 2021. 结构表面裂缝数字图像法识别研究综述与前景展望. 土木工程学报, 54(6): 79−98. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.06.008Liu Y. F., Fan J. S., Nie J. G., et al., 2021. Review and prospect of digital-image-based crack detection of structure surface. China Civil Engineering Journal, 54(6): 79−98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.06.008 骆勇鹏, 王林堃, 廖飞宇等, 2021. 基于一维卷积神经网络的结构损伤识别. 地震工程与工程振动, 41(4): 145−156. doi: 10.13197/j.eeed.2024.0306Luo Y. P., Wang L. K., Liao F. Y., et al., 2021. Vibration-based structural damage identification by 1-dimensional convolutional neural network. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 41(4): 145−156. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeed.2024.0306 孙平定, 蔡润, 谢成阳等, 2019. 基于遗传优化神经网络的边坡稳定性评价. 现代电子技术, 42(5): 75−78. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2019.05.018Sun P. D., Cai R., Xie C. Y., et al., 2019. Slope stability evaluation based on genetic optimization neural network. Modern Electronics Technique, 42(5): 75−78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2019.05.018 王俊杰, 焦柯, 彭子祥, 2022. 基于神经网络的建筑结构安全评估模型研究. 建筑科学与工程学报, 39(4): 174−182. doi: 10.19815/j.jace.2021.09065Wang J. J., Jiao K., Peng Z. X., 2022. Research on safety assessment model of building structure based on neural network. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 39(4): 174−182. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19815/j.jace.2021.09065 王全才, 2011. 随机森林特征选择. 大连: 大连理工大学.Wang Q. C., 2011. Random forest feature selection. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese) 汪学清, 刘爽, 李秋燕等, 2021. 基于K折交叉验证的SVM隧道围岩分级判别. 矿冶工程, 41(6): 126−128, 133.Wang X. Q., Liu S., Li Q. Y., et al., 2021. Classification and discrimination of surrounding rock of tunnel based on SVM of K-fold cross validation. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 41(6): 126−128,133. (in Chinese) 肖坚, 2013. 基于随机森林的不平衡数据分类方法研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学.Xiao J., 2013. Research on imbalanced data classification method based on random forest algorithm. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. (in Chinese) 徐镇凯, 袁志军, 胡济群, 2006. 建筑结构检测与加固方法. 工程力学, 23(S2): 117−130.Xu Z. K., Yuan Z. J., Hu J. Q., 2006. The inspection and strengthening methods on building structures. Engineering Mechanics, 23(S2): 117−130. (in Chinese) 张健飞, 蔡东成, 2022. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的结构损伤识别研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 42(1): 132−142. doi: 10.13197/j.eeed.2022.0113Zhang J. F., Cai D. C., 2022. Research on structural damage identification based on multi-scale convolutional neural networks. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 42(1): 132−142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeed.2022.0113 张梦涵, 魏进, 卞海丁, 2022. 基于机器学习的边坡稳定性分析方法−−以国内618个边坡为例. 地球科学与环境学报, 44(6): 1083−1095. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2022.09019Zhang M. H., Wei J., Bian H. D., 2022. Slope stability analysis method based on machine learning−taking 618 slopes in China as examples. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 44(6): 1083−1095. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2022.09019 张书颖, 陈适之, 韩万水等, 2022. 基于集成学习的FRP加固混凝土梁抗弯承载力预测研究. 工程力学, 39(8): 245−256.Zhang S. Y., Chen S. Z., Han W. S., et al., 2022. Study on prediction of FRP strengthened reinforced concrete beam’s moment bearing capacity based on ensemble learning algorithm. Engineering Mechanics, 39(8): 245−256. (in Chinese) 张鑫, 李安起, 赵考重, 2011. 建筑结构鉴定与加固改造技术的进展. 工程力学, 28(1): 1−11.Zhang X., Li A. Q., Zhao K. Z., 2011. Advances in assessment and retrofitting of building structures. Engineering Mechanics, 28(1): 1−11. (in Chinese) 张鑫, 岳庆霞, 2021. 既有结构评估、加固改造理论及关键技术研究进展. 山东建筑大学学报, 36(5): 76−82.Zhang X., Yue Q. X., 2021. Development on theory and technology on the evaluation, strengthening and retrofitting of existing structures. Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 36(5): 76−82. (in Chinese) 张鑫, 盛业谱, 邓祥文等, 2022. 基于优化支持向量机的强夯有效加固深度研究. 山东建筑大学学报, 37(1): 118−124.Zhang X., Sheng Y. P., Deng X. W., et al., 2022. Study on the effective reinforcement depth of dynamic consolidation based on optimized support vector machine. Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 37(1): 118−124. (in Chinese) Belgiu M., Drăguţ L., 2016. Random forest in remote sensing: a review of applications and future directions. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 114: 24−31. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.01.011 Johansson U., Boström H., Löfström T, et al., 2014. Regression conformal prediction with random forests. Machine Learning, 97(1): 155−176. Kostinakis K., Morfidis K., Demertzis K., et al., 2023. Classification of buildings' potential for seismic damage using a machine learning model with auto hyperparameter tuning. Engineering Structures, 290: 116359. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116359 Ma D. Y., Li X. D., Lin B. R., et al., 2023. An intelligent retrofit decision-making model for building program planning considering tacit knowledge and multiple objectives. Energy, 263: 125704. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125704 -



 下载:
下载: