Simulation and Experimentation of Rubble Roadbed under Reverse Fault Displacement
-
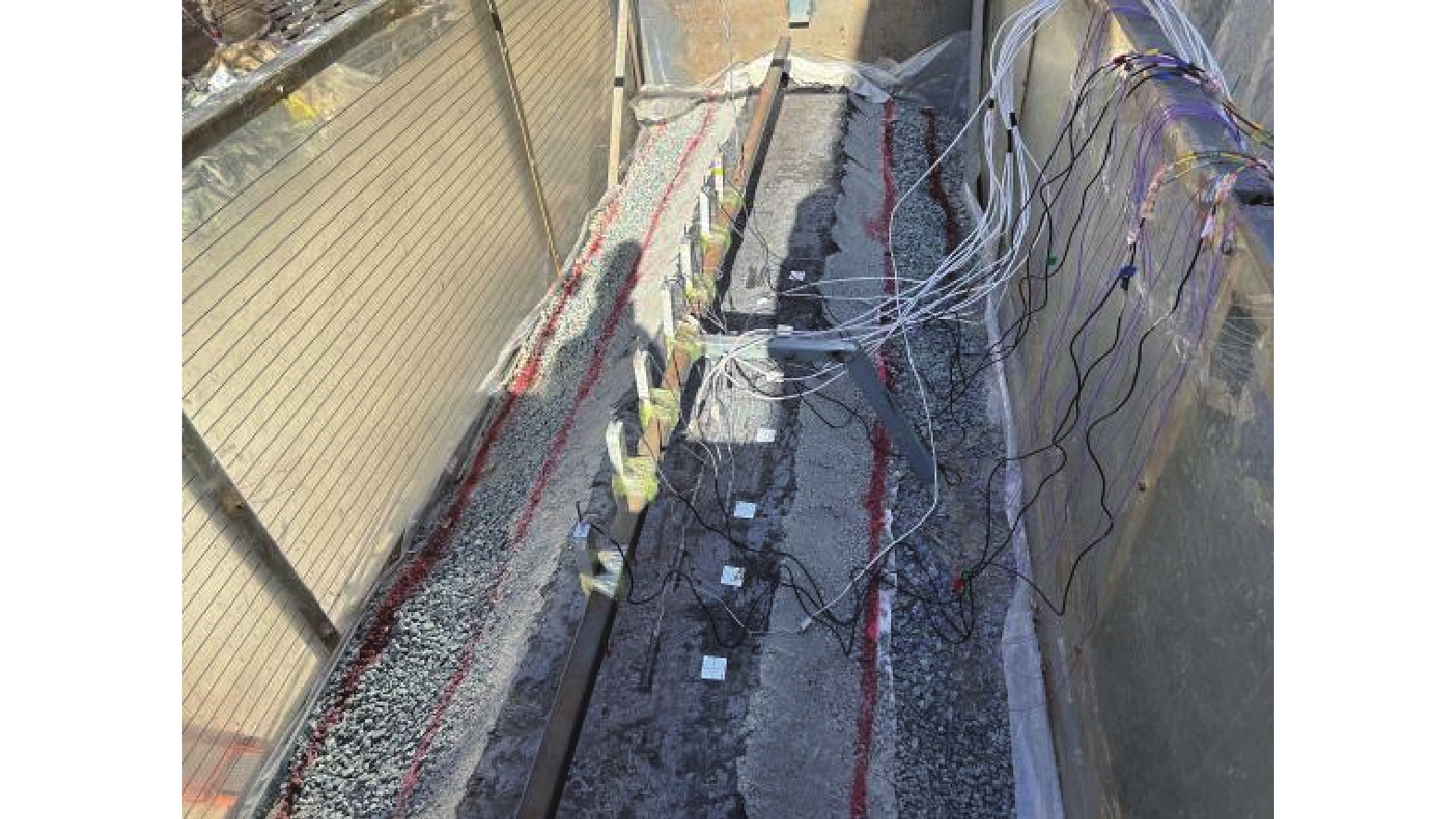
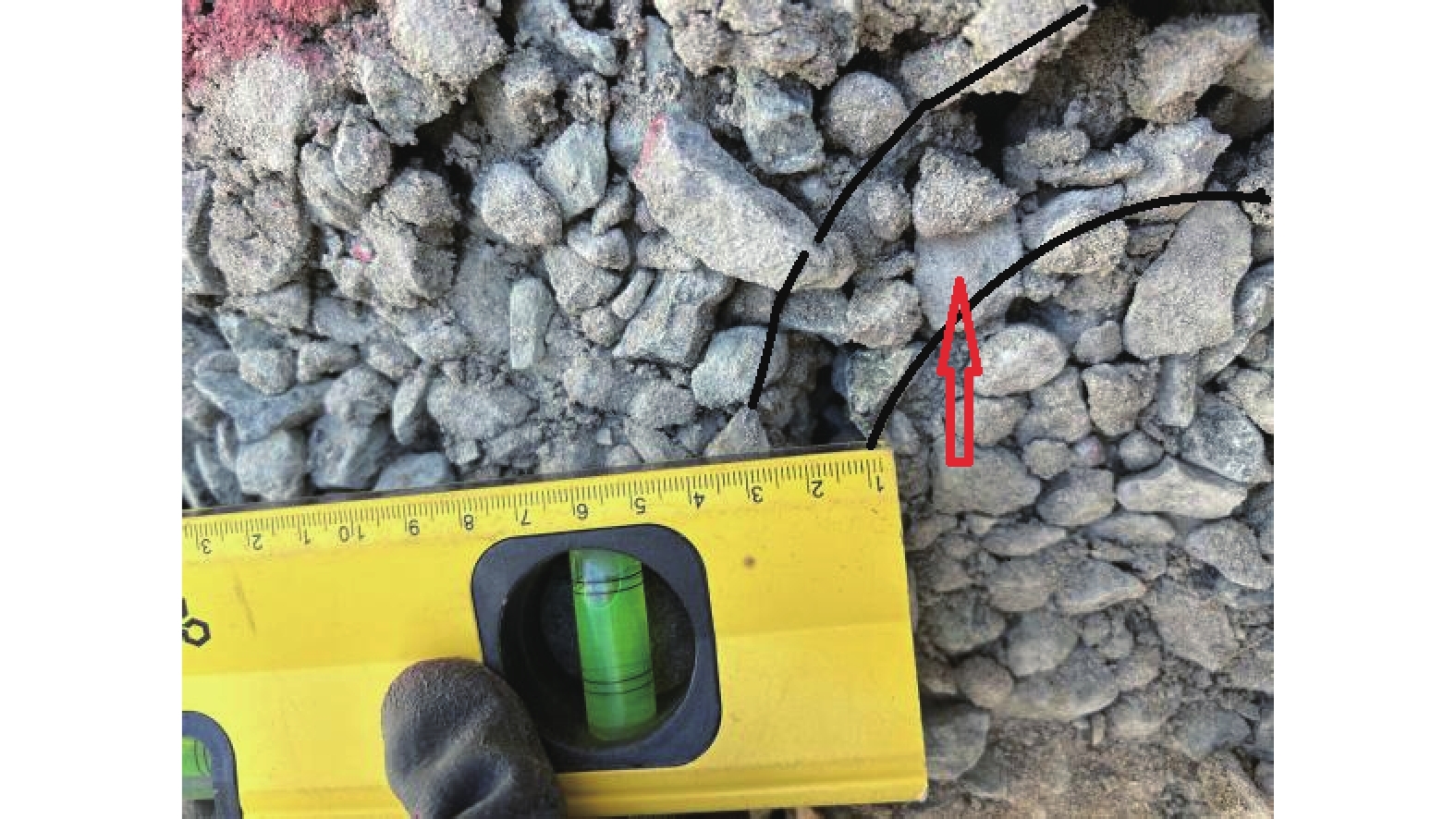
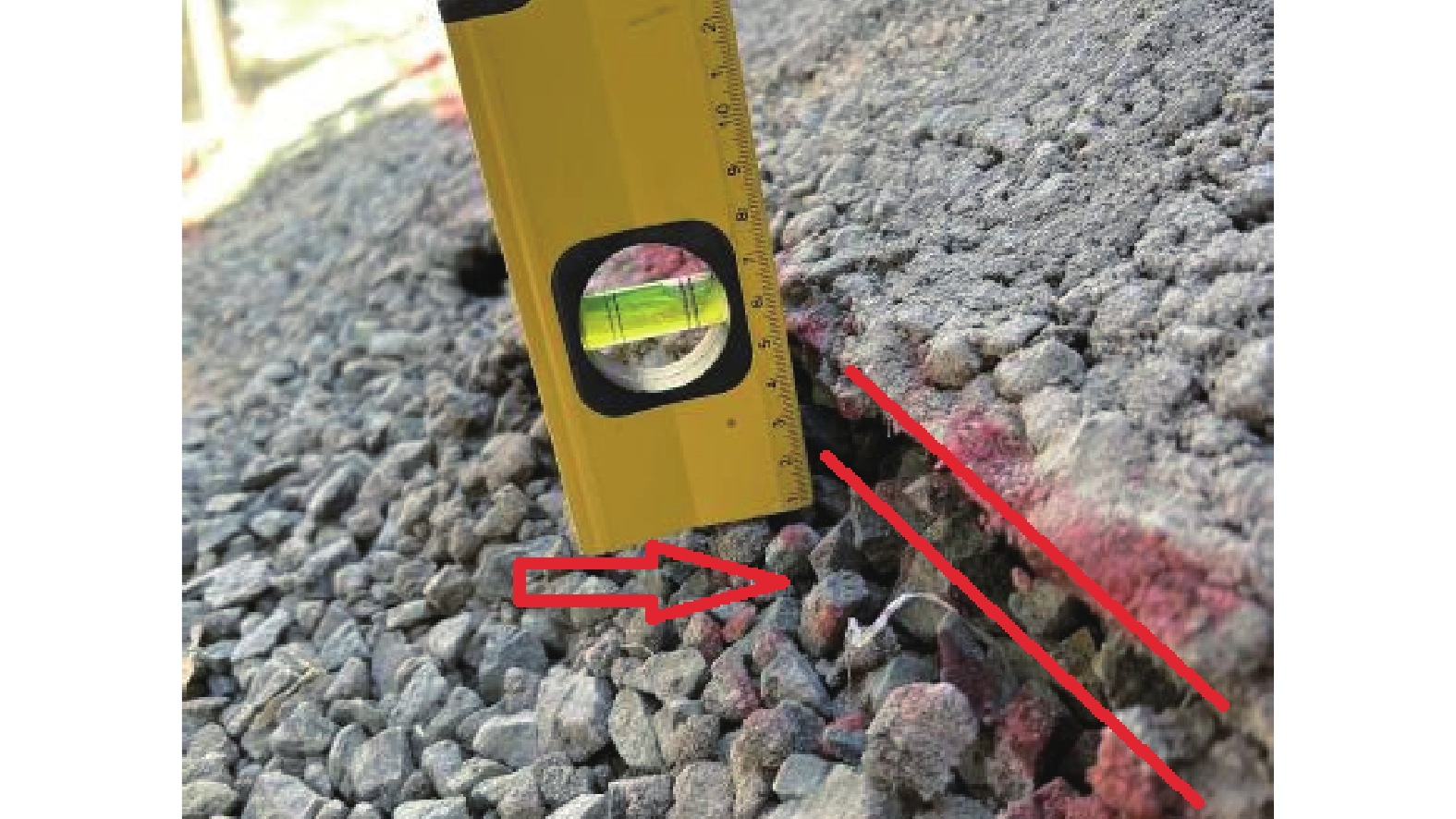
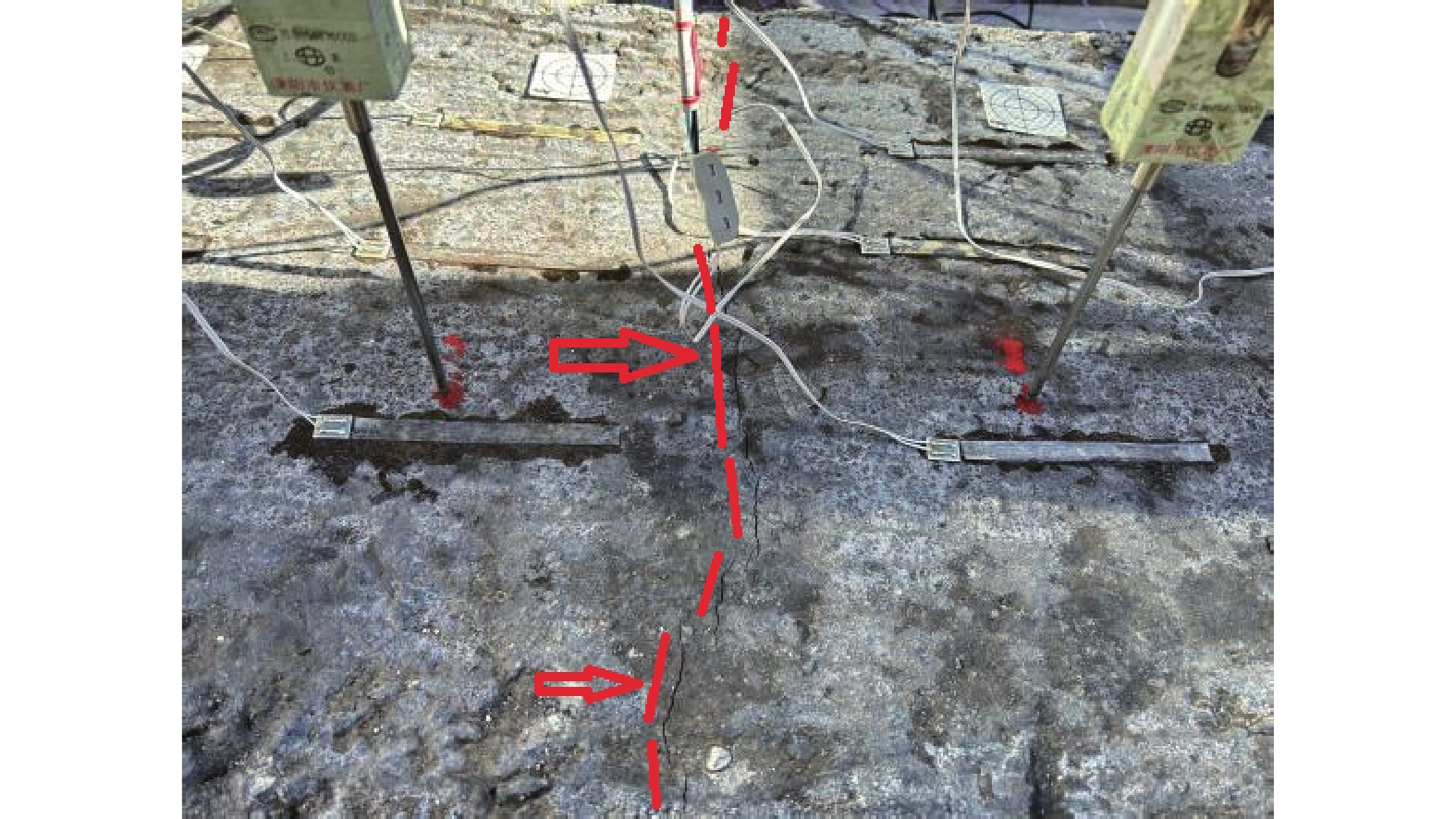
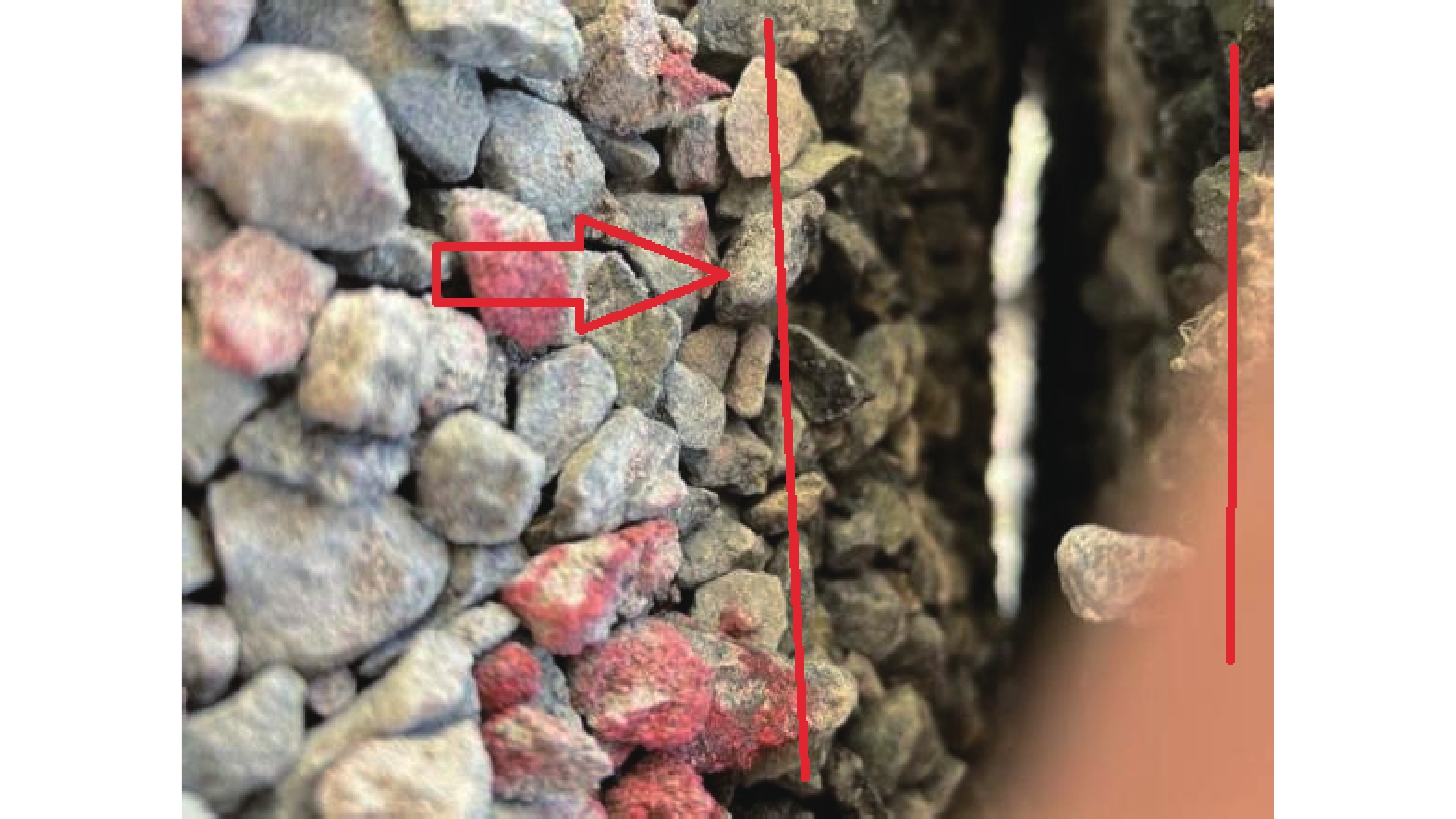
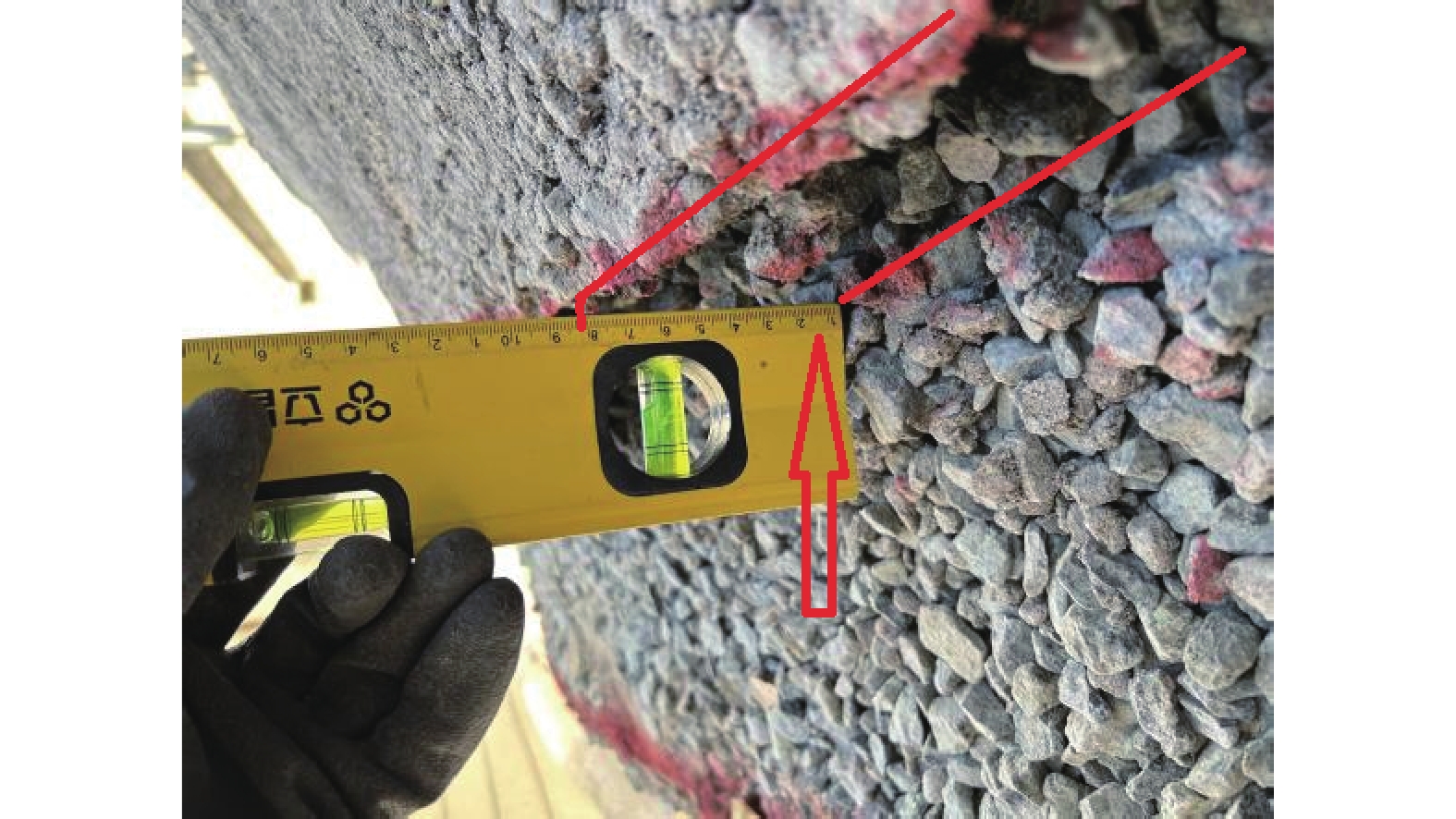
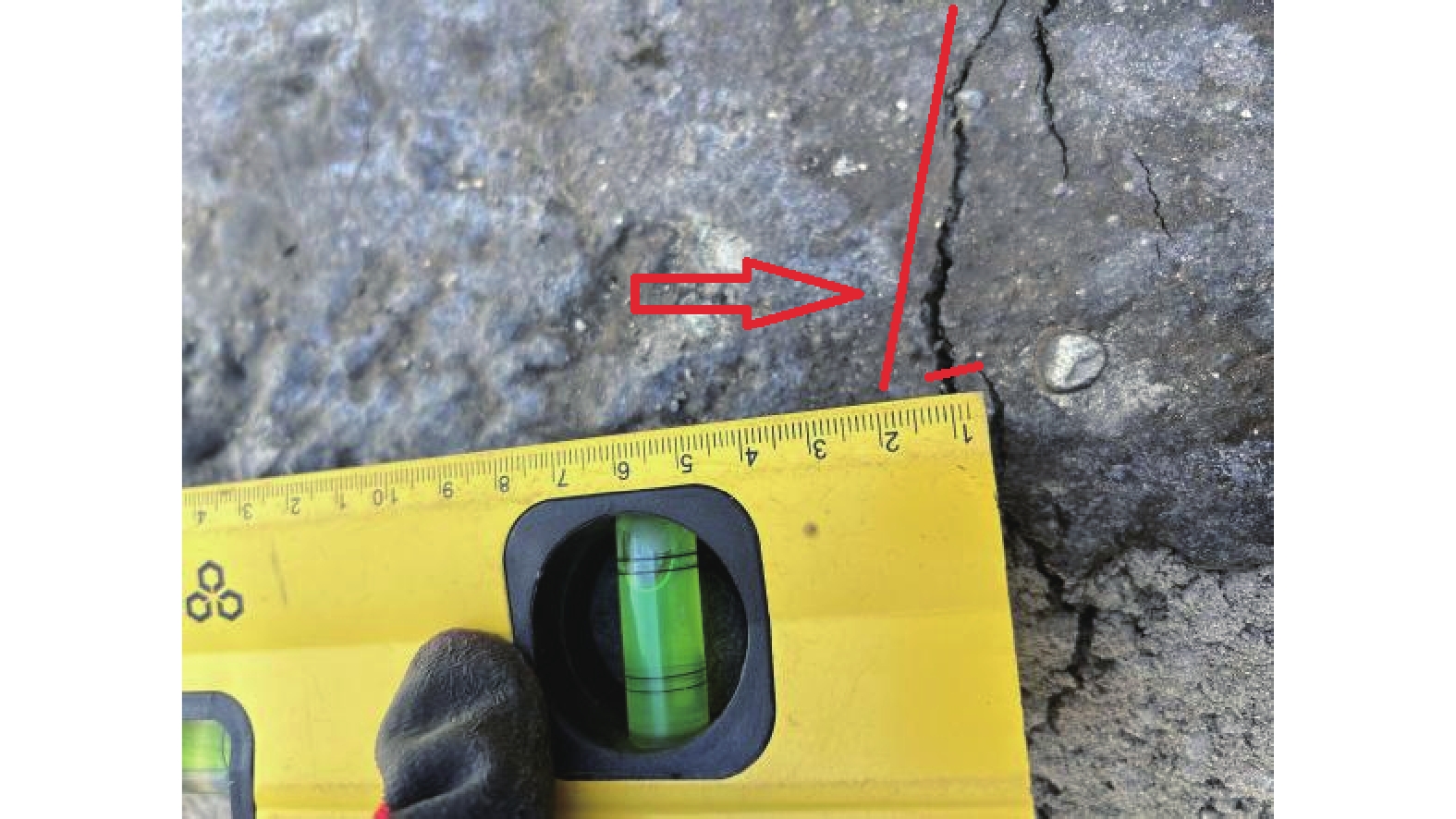
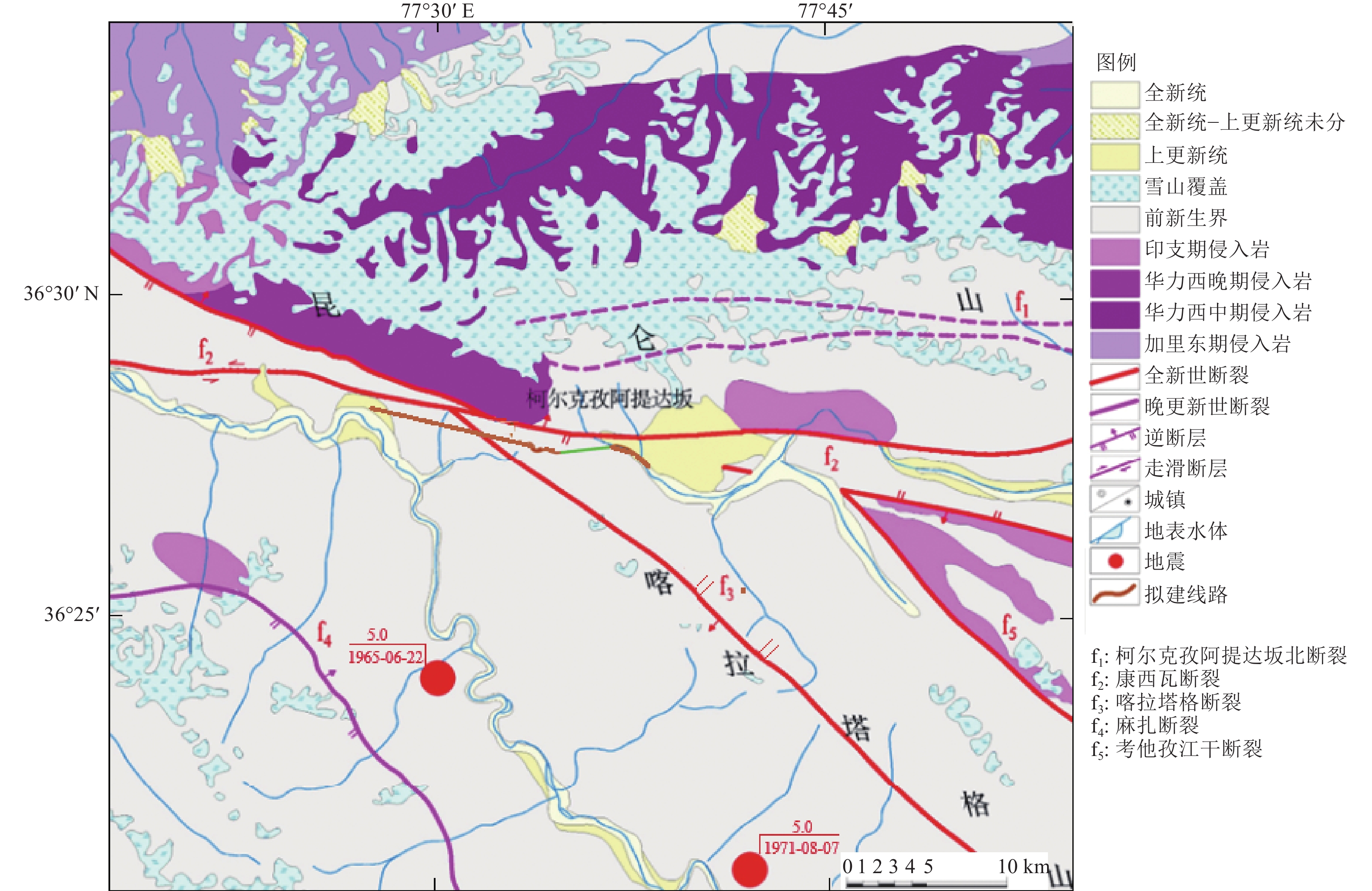
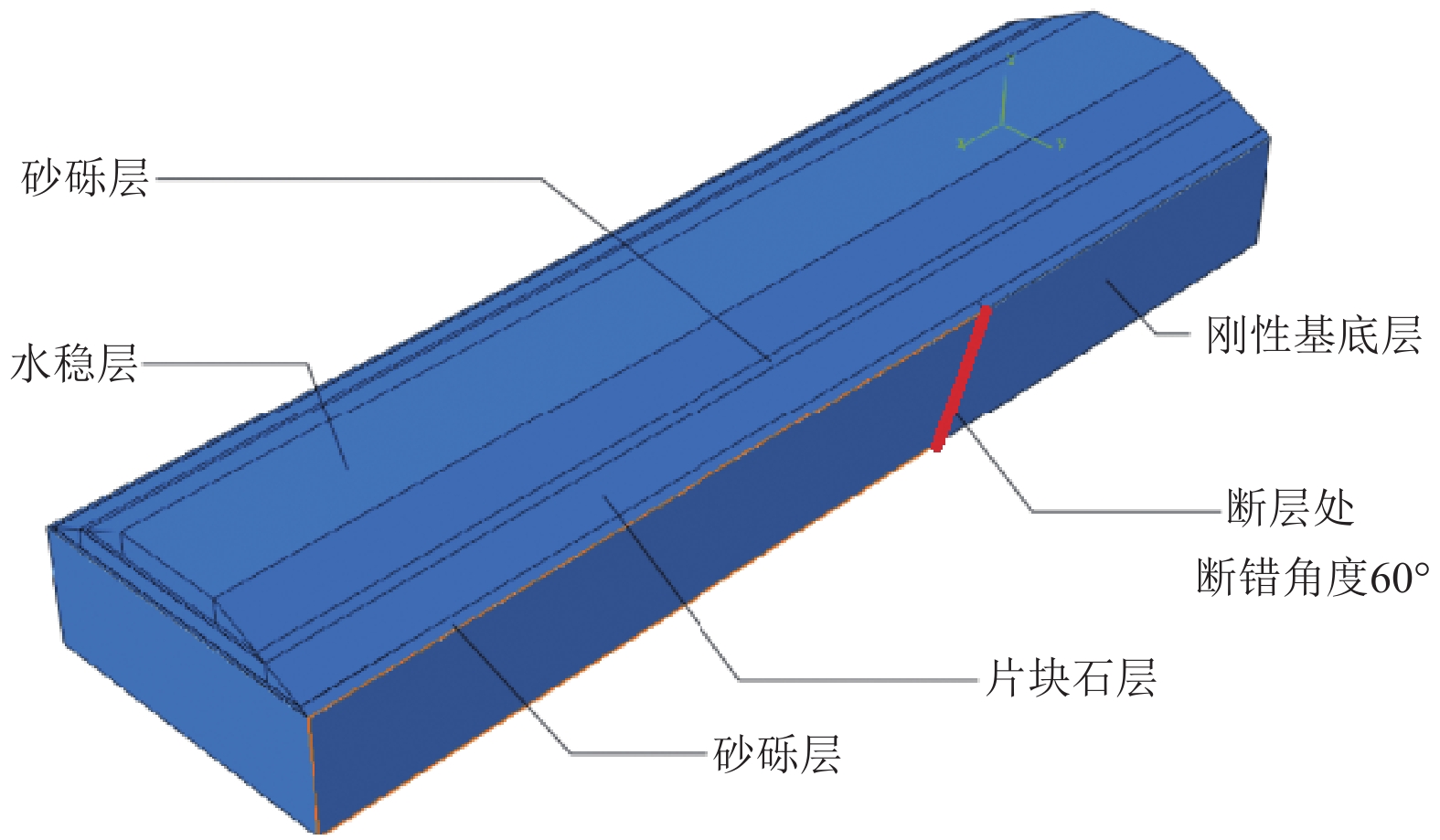
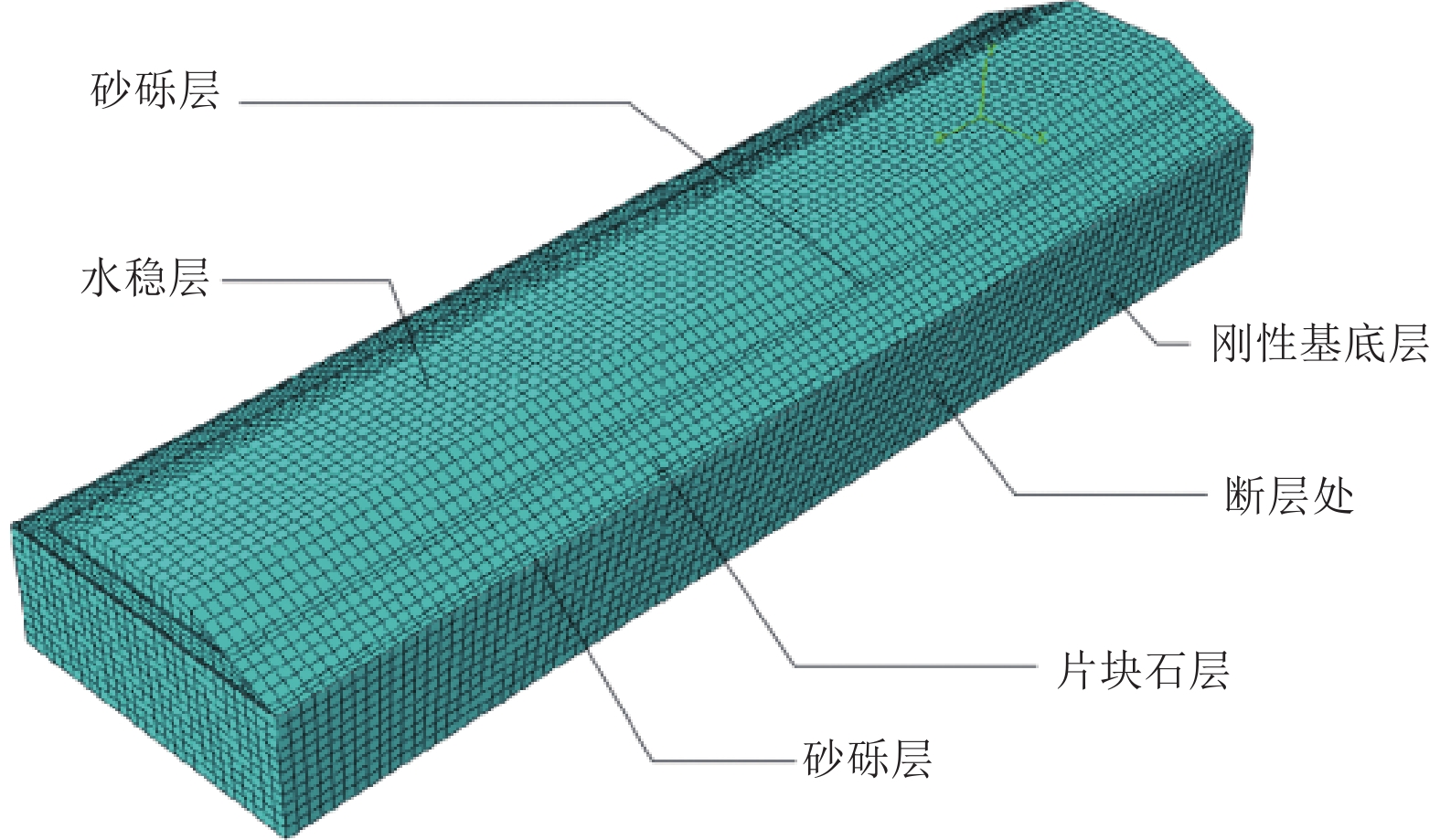
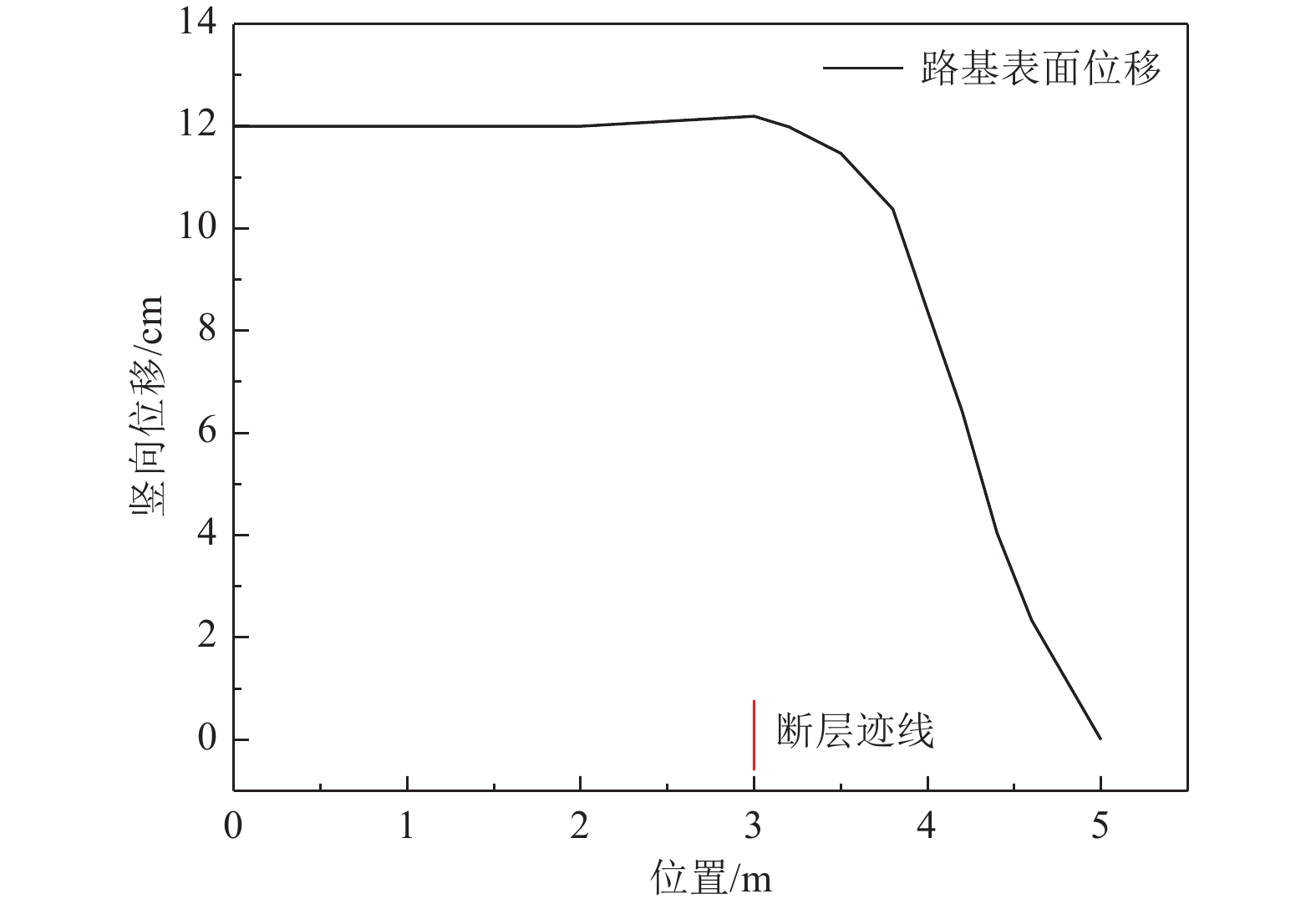
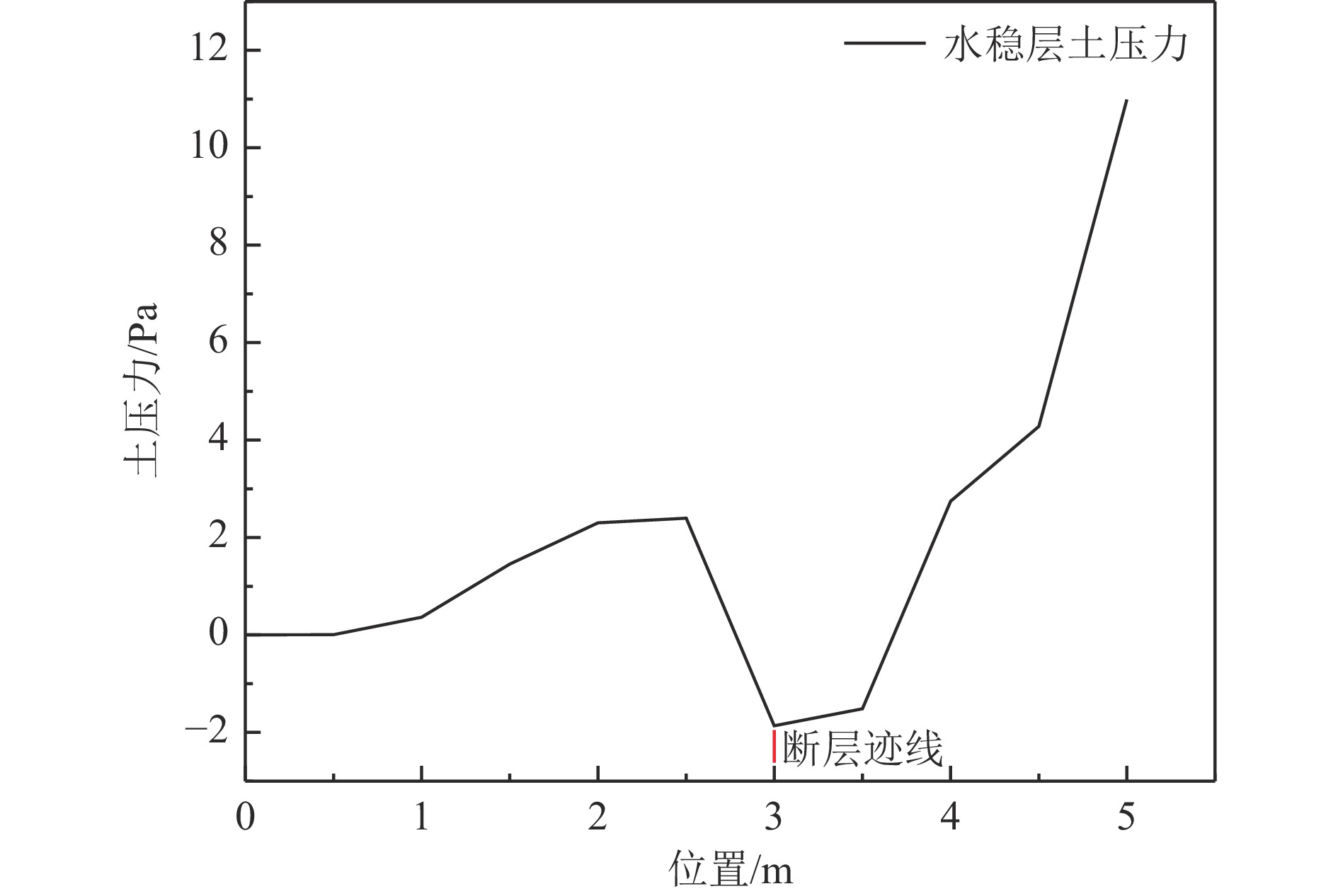
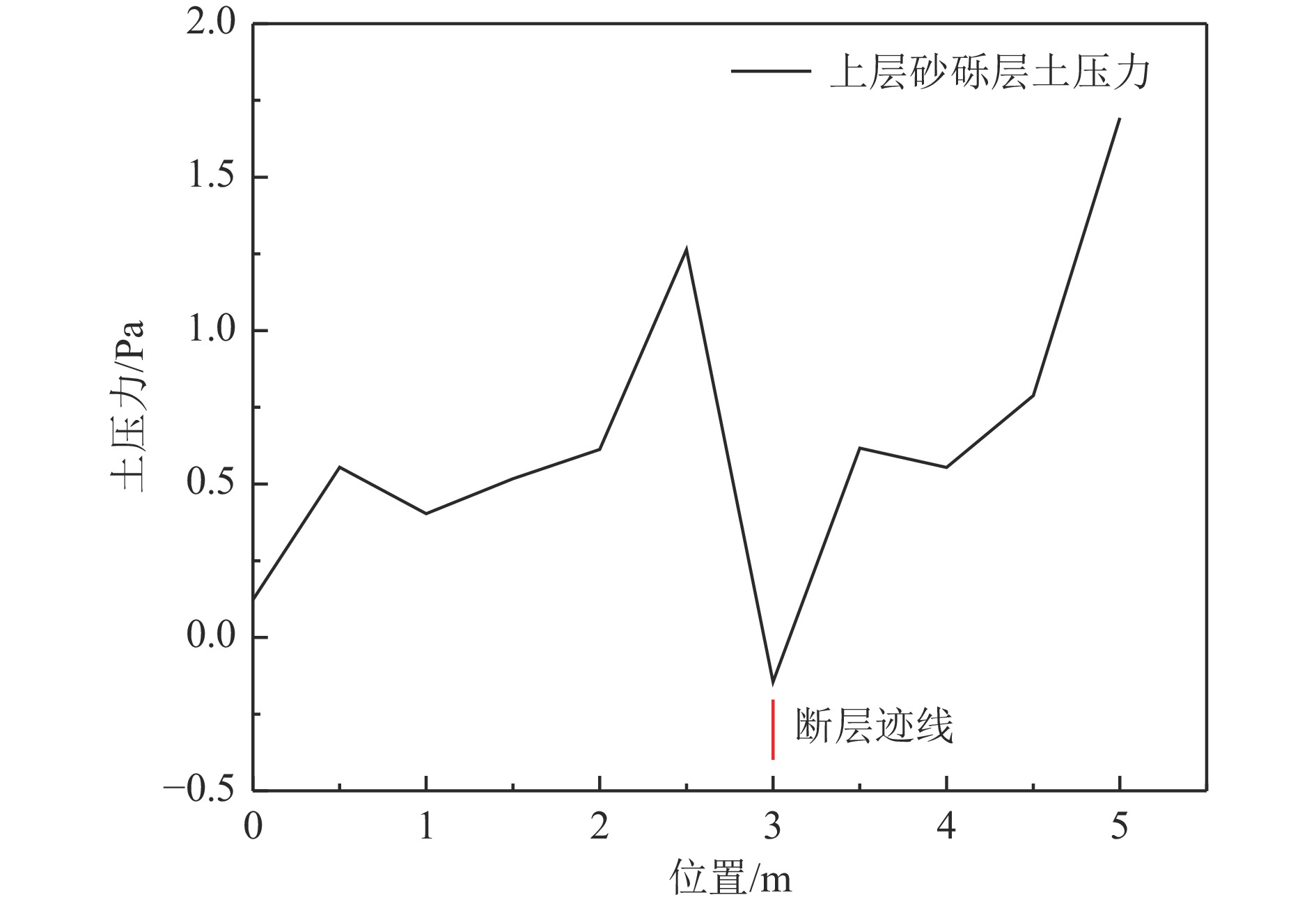
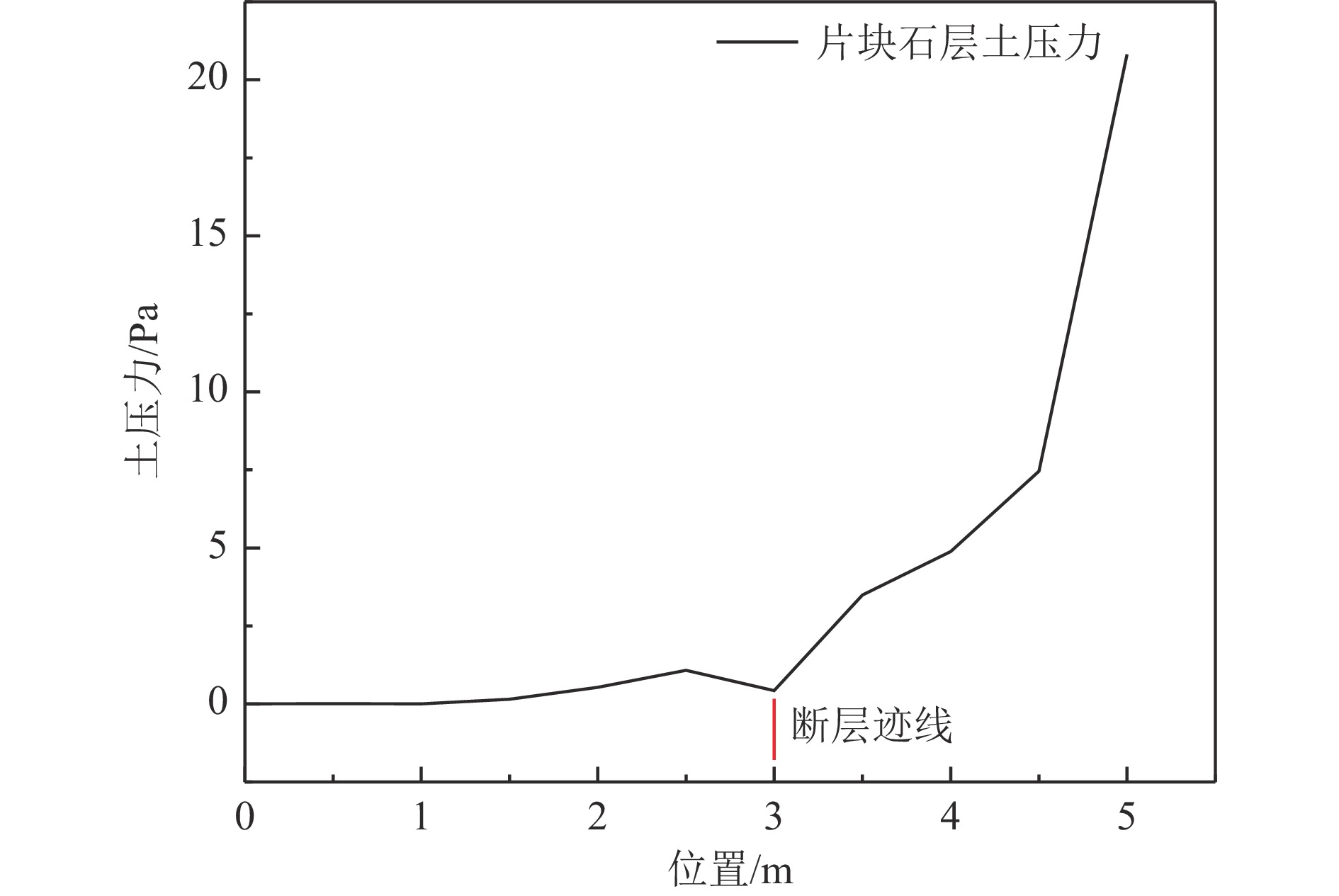
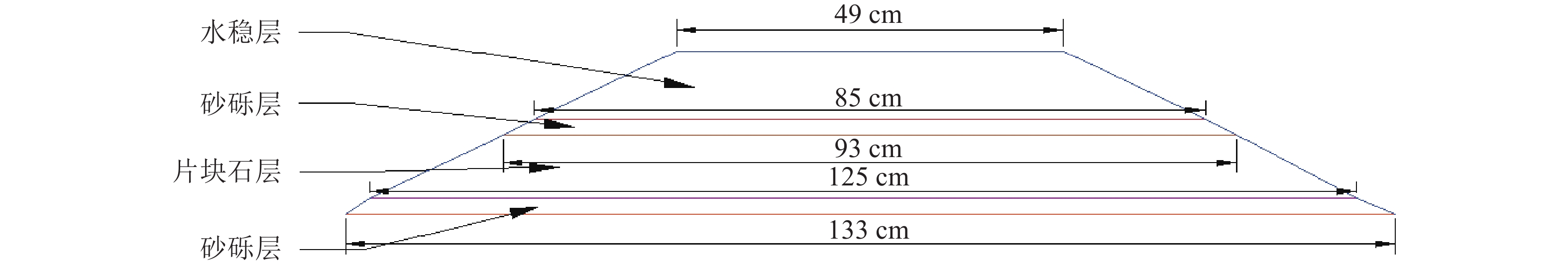
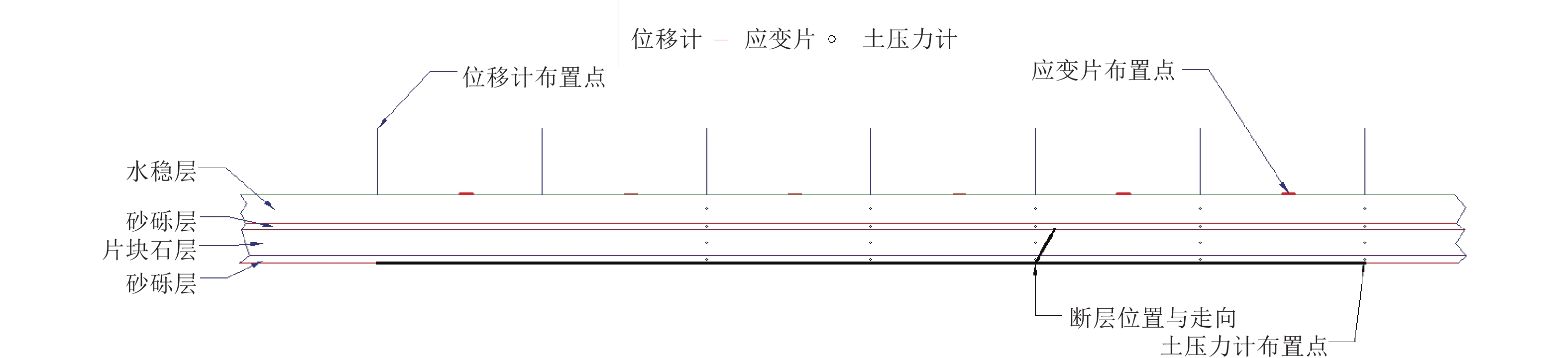
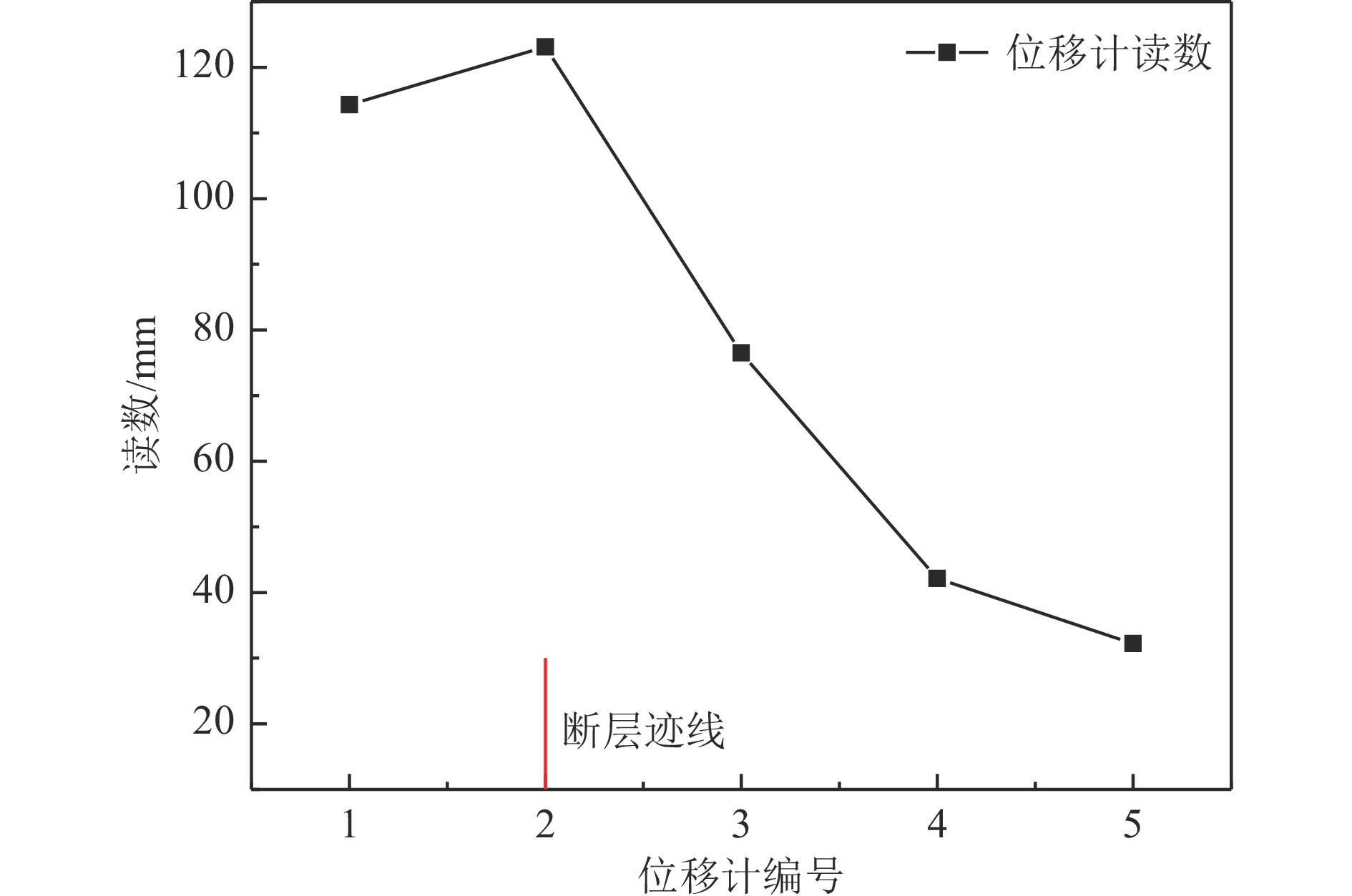
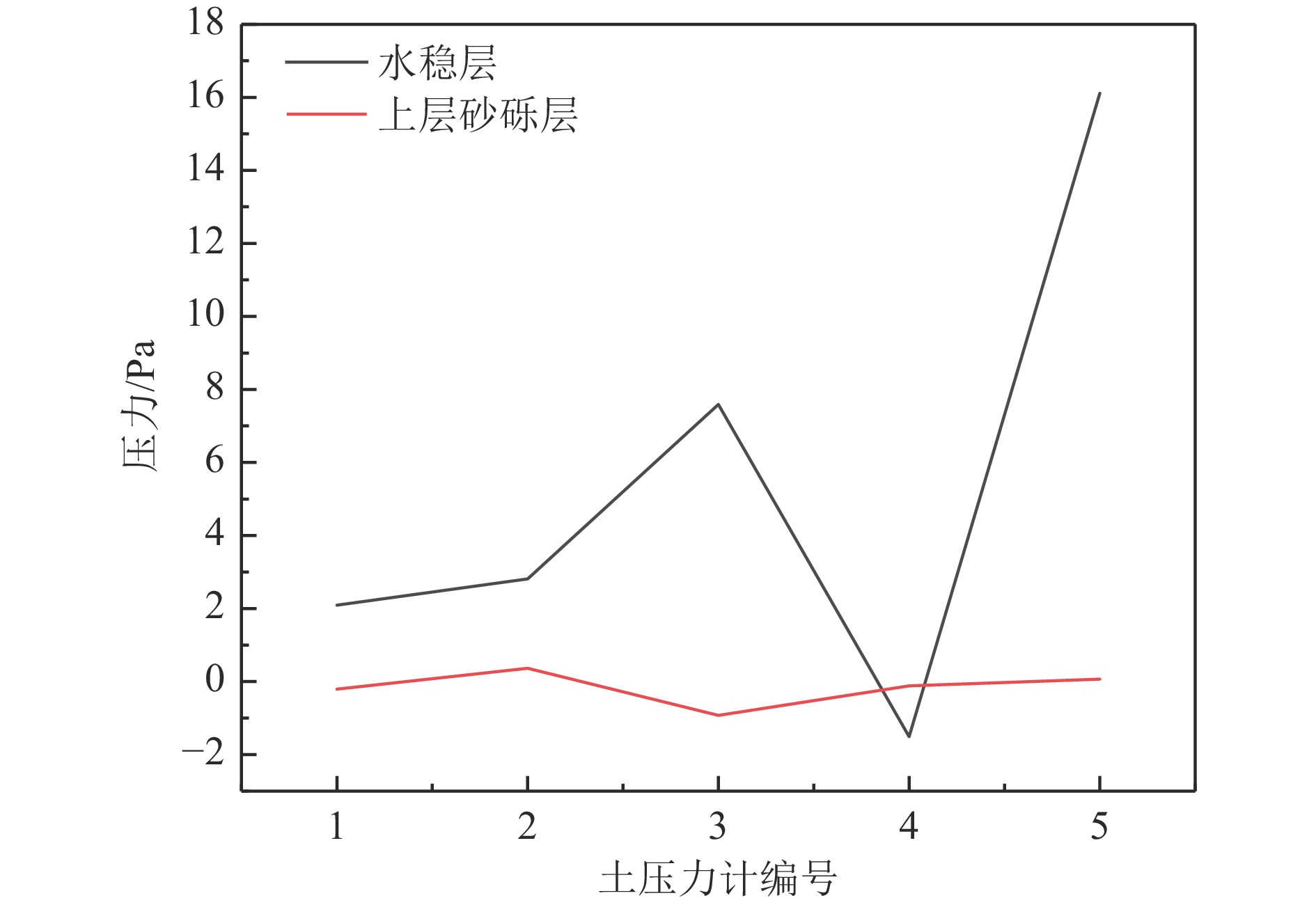
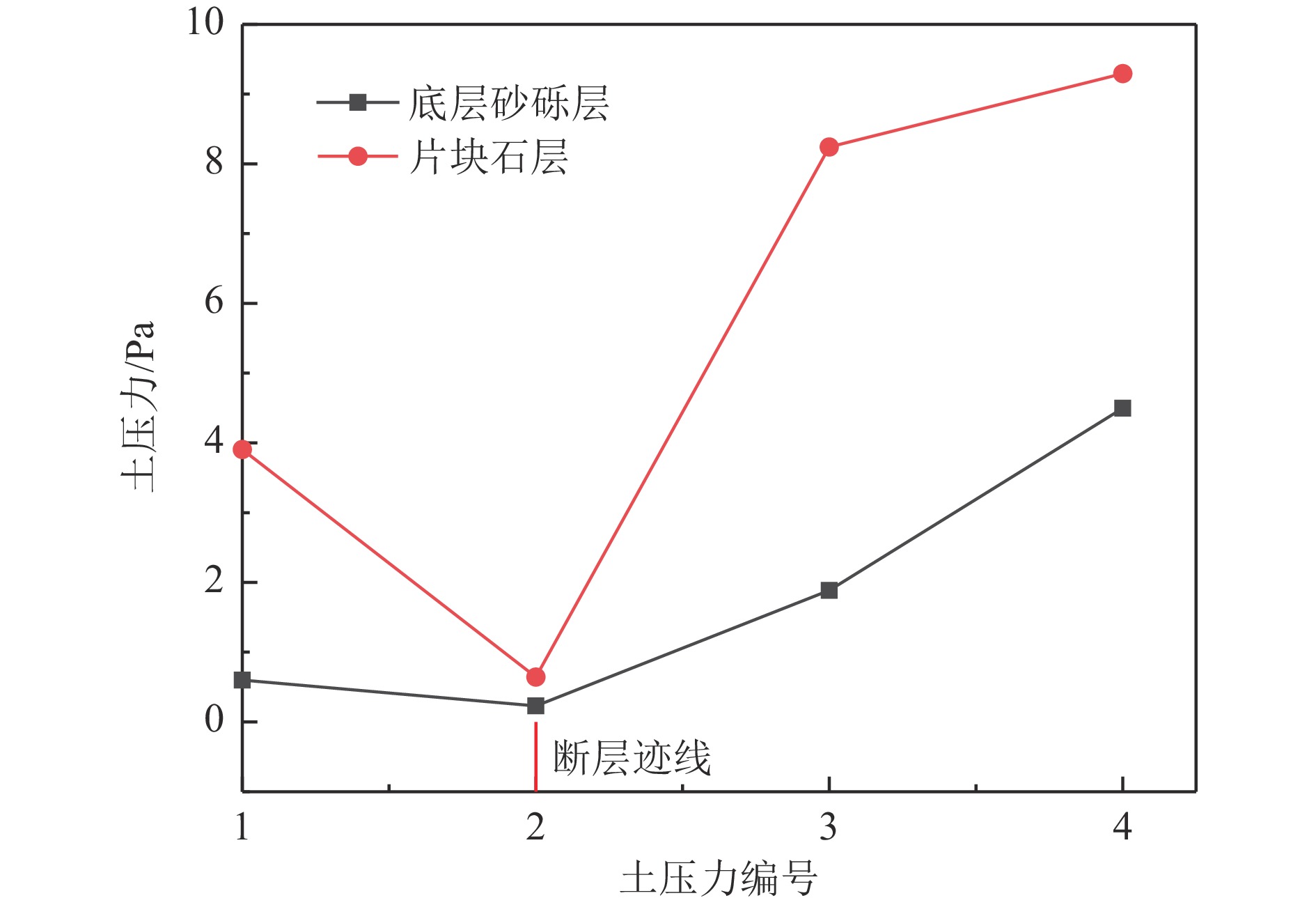
摘要: 以穿越逆断层的新藏公路高寒地区的某片块石路基段为研究对象,通过物理试验和数值模拟,分析了逆断层断错作用下片块石路基的变形与受力特征。物理试验模型按1∶15的比例缩尺建立,试验结果显示:上盘整体抬升,其破坏程度高于下盘,但下盘受断错影响的范围较大。距离断错迹线越近,路基破坏越严重,反之则越轻,最大变形出现在断层迹线处。从破坏形态来看,片块石路基破坏的形式主要有路面隆起、裂缝、水稳层与片块石层脱空、张拉断裂等。数值模拟结果显示:上盘整体抬升,最大变形同样出现在断层迹线处,且断层迹线附近变形急剧变化,距离迹线越远,相对变形逐渐减小。上盘水稳层在远离迹线处受压,靠近迹线处受拉;下盘水稳层在靠近迹线处受拉,远离迹线处受压,下盘端部受压达到最大值;片块石层与砂砾层土的压力基本表现为受压,且压力在迹线处减小。数值模拟中的片块石路基变形和受力特征与试验结果较为吻合,研究结果表明,片块石路基具有较好的抗断效果,这些结论可为跨活动断层片块石路基设计提供科学依据。Abstract: A rubble roadbed section of the Xinjiang–Xizang Highway in a cold region, which crosses a thrust fault, was investigated to analyze its deformation and stress characteristics under fault dislocation through physical experiments and numerical simulations. The physical experiment employed a 1:15 scaled model. Results indicate that the hanging wall experiences overall uplift and suffers more severe damage than the footwall, whereas the footwall is affected over a larger area. Damage severity decreases with increasing distance from the fault trace, with maximum deformation occurring directly at the trace. The primary forms of damage observed include surface uplift, cracks, voids between the water-stable layer and the rubble layer, and tensile fractures. Numerical simulations reveal similar patterns: the hanging wall undergoes overall uplift with maximum deformation near the fault trace, and deformation diminishes with distance from the trace. The water-stable layer on the hanging wall is under tension near the fault trace and compression farther away; on the footwall, it is under tension near the trace and compression at greater distances, with the maximum compressive stress at the end of the footwall. Soil pressures in the rubble and gravel layers are predominantly compressive, decreasing near the fault trace. The deformation and stress distributions from numerical simulations closely match the experimental observations. These findings indicate that rubble roadbeds exhibit considerable resistance to fault-induced dislocation. The results provide valuable scientific guidance for the design and construction of rubble roadbeds across active faults.
-
Key words:
- Segmented stone roadbed /
- Reverse fault /
- Fault displacement /
- Numerical simulation /
- Experimental model
-
表 1 片块石路基数值模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of segmented stone roadbed numerical model
土体 密度/(g·cm−3) 杨氏模量/Pa 泊松比/(°) 屈服强度/MPa 砂砾 1.5 2×107 0.2 1.5 片块石 2 5×108 0.3 30 水稳料 2.2 1.5×109 0.25 10 表 2 缩尺模型相似设计表格
Table 2. Scale model similarity design
比例 1∶1 1∶5 1∶10 1∶15 1∶20 抬升 1.8 m 0.36 m 0.18 m 0.12 m 0.09 m 表 3 片块石路基结构材料与厚度
Table 3. Materials and thickness of block-stone roadbed structure
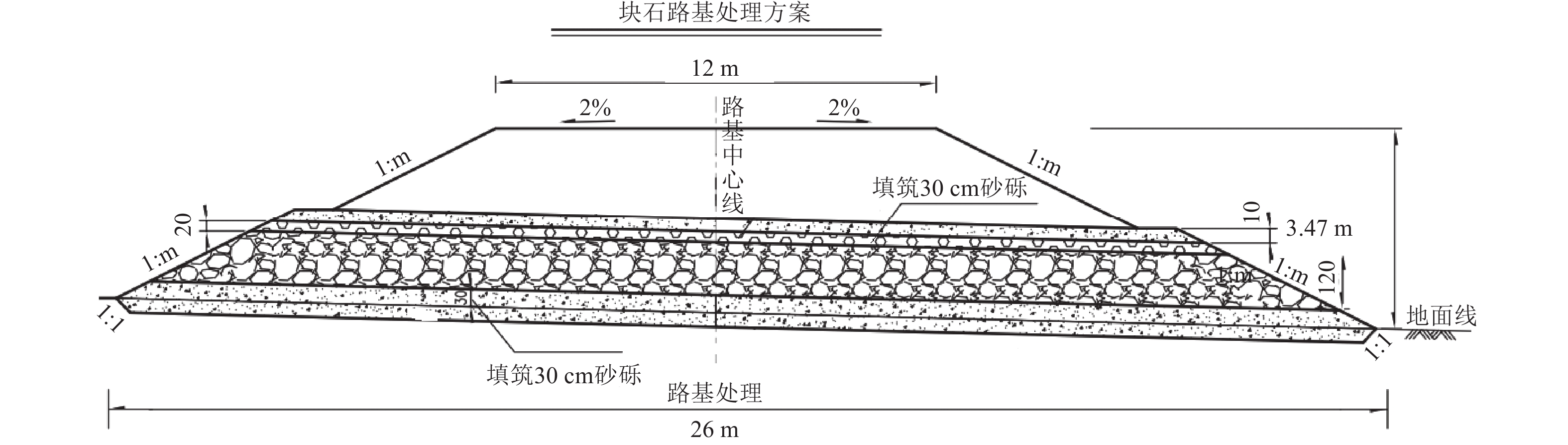
层数 材料属性及厚度 第一层 9 cm水泥稳定层(水泥掺量4.5%) 第二层 2 cm砂砾层 第三层 8 cm片块石层 第四层 2 cm砂砾层 表 4 片块石路基沥青层配合比与水稳层级配
Table 4. Asphalt layer mix proportion and grading of water-stabilized layer for block-stone roadbed
类别 碎石 10~15 mm 碎石 5~10 mm 碎石 3~5 mm 机制砂 0~3 mm 矿粉 水泥含量 沥青 22% 20% 26% 27% 5% 0 水稳料 28.80% 4.30% 8.70% 11.40% 24.60% 4.50% -
陈紫云, 2019. 区域性活动断裂带对高速公路路线方案的影响与控制−以康定新都桥至炉霍高速公路为例. 地质灾害与环境保护, 30(2): 41−51.Chen Z. Y., 2019. The impacts and control of regional active fault on the expressway route plan−Taking the Xingduqiao-Luhuo expressway as an example. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 30(2): 41−51. (in Chinese) 董颂声, 2001. 1999年土耳其伊兹米特地震. 地震学刊, 21(1): 62−65.Dong S. S., 2001. The 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake. Journal of Seismology, 21(1): 62−65. (in Chinese) 董元宏, 邵广军, 张会建等, 2019. 多年冻土区片块石路基尺度效应的数值研究. 路基工程, (6): 24−27. doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.2019.06.05Dong Y. H., Shao G. J., Zhang H. J., et al., 2019. Numerical study on the scale effect of crushed-rock embankment in permafrost regions. Subgrade Engineering, (6): 24−27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.2019.06.05 冯俊文, 运志辉, 苗超等, 2022. 青藏高原多年冻土地区片块石路基修筑技术研究. 交通世界, (24): 143−146. doi: 10.16248/j.cnki.11-3723/u.2022.24.027Feng J. W., Yun Z. H., Miao C., et al., 2022. Research on construction technology of segmented stone roadbed in permafrost regions of the Tibetan plateau. TranspoWorld, (24): 143−146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16248/j.cnki.11-3723/u.2022.24.027 李金平, 王佐, 张娟等, 2015. 多年冻土路基不均匀变形成因分析. 中国公路学报, 28(12): 78−85, 91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.011Li J. P., Wang Z., Zhang J., et al., 2015. Cause analysis on uneven deformation of embankment in permafrost regions. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 28(12): 78−85,91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.011 李小军, 2001. 对近年大震震害现象与工程地震问题研究的思考. 国际地震动态, (8): 26−32.Li X. J., 2001. Comments on phenomena of great earthquake damages and engineering seismological researches. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (8): 26−32. (in Chinese) 舒航, 2021. 热扰动对冻土区片块石路基热状态变化特性的影响研究. 城市道桥与防洪, (5): 265−267. doi: 10.16799/j.cnki.csdqyfh.2021.05.076Shu H., 2021. Research on the influence of thermal disturbance on the thermal state variation characteristics of stone subgrade in frozen soil area. Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control, (5): 265−267. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16799/j.cnki.csdqyfh.2021.05.076 孙宝君, 2011. 浅谈多年冻土地区特殊路基处理措施. 黑龙江交通科技, 32(12): 14, 16. 同济大学. CJJ 194-2013 城市道路路基设计规范[M]. 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013. 王青志, 徐安花, 房建宏, 2018. 高温高含冰量地区片块石路基冻融指数变化分析. 青海交通科技, (5): 56−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6189.2018.05.013Wang Q. Z., Xu A. H., Fang J. H., 2018. Analysis of freeze-thaw index of block-stone embankment in warm and ice-rich permafrost region. Qinghai Transportation Science and Technology, (5): 56−59. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6189.2018.05.013 王青志, 房建宏, 徐安花等, 2019. 高温不稳定多年冻土区片块石路基热状态变化分析. 公路工程, 44(6): 66−70. doi: 10.19782/j.cnki.1674-0610.2019.06.012Wang Q. Z., Fang J. H., Xu A. H., et al., 2019. Analysis of thermal state change of block-stone subgrade in high-temperature unstable permafrost region. Highway Engineering, 44(6): 66−70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19782/j.cnki.1674-0610.2019.06.012 王铁权, 王莉云, 2023. 新疆高山多年冻土区路基结构适用性研究. 甘肃科学学报, 35(2): 124−130. doi: 10.16468/j.cnki.issn1004-0366.2023.02.019Wang T. Q., Wang L. Y., 2023. Study on applicability of subgrade structure in alpine permafrost region of Xinjiang. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 35(2): 124−130. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16468/j.cnki.issn1004-0366.2023.02.019 王治华, 2003. 青藏公路及铁路沿线的活动构造与其次生灾害. 现代地质, 17(3): 227−236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.03.001Wang Z. H., 2003. Active tectonics and its secondary disasters along Qinghai-Tibet line. Geoscience, 17(3): 227−236. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.03.001 魏秉鸿, 2011. 浅谈片、块石通风路基在多年冻土地区路基中的应用. 青海交通科技, (6): 58−59. 奚家米, 张世雷, 陈建兵等, 2015. 多年冻土区封闭条件下片块石路基降温效果数值分析. 路基工程, (5): 1−6, 16. doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.2015.05.01Xi J. M., Zhang S. L., Chen J. B., et al., 2015. Numerical simulation on cooling effect of closed rubble/block stone embankment in Permafrost Areas. Subgrade Engineering, (5): 1−6,16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.2015.05.01 徐平, 2006. 1999年台湾集集地震竖向地面运动研究. 北京: 北京工业大学. 许慧, 2015. 冻土地区高速公路的特殊路基调控研究. 交通建设与管理, (8): 162−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8098.2015.04.057 姚令侃, 冯俊德, 杨明, 2009. 汶川地震路基震害分析及对抗震规范改进的启示. 西南交通大学学报, 44(3): 301−311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.03.001Yao L. K., Feng J. D., Yang M., 2009. Damage analysis of subgrade engineering in Wenchuan earthquake and recommendations for improving seismic design code. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 44(3): 301−311. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.03.001 叶锦华, 王丽群, 许智博等, 2022. 高纬度林区多年冻土片块石路基降温效果及变形特征. 科学技术与工程, 22(20): 8893−8900. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.20.041Ye J. H., Wang L. Q., Xu Z. B., et al., 2022. Cooling effect and deformation characteristics of permafrost rubble subgrade in high latitude forest area. Science Technology and Engineering, 22(20): 8893−8900. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.20.041 俞言祥, 高孟潭, 2001. 台湾集集地震近场地震动的上盘效应. 地震学报, 24(6): 615−621. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2001.06.007Yu Y. X., Gao M. T., 2001. Effects of the hanging wall and footwall on peak acceleration during the Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 24(6): 615−621. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2001.06.007 袁堃, 汪双杰, 牛富俊等, 2016. 多年冻土拓宽路基差异沉降特征分析. 中国公路学报, 29(9): 21−28.Yuan K., Wang S. J., Niu F. J., et al., 2016. Characteristics analysis of differential settlement of widening embankment in permafrost regions. China Journal Highway and Transport, 29(9): 21−28. (in Chinese) 周海涛, 2010. 公路工程抗震减灾技术回顾与展望. 公路交通科技, 27(9): 39−43.Zhou H. T., 2010. Review and prospect of earthquake resistance and disaster mitigation technology of highway engineering. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 27(9): 39−43. (in Chinese) 周尚琪, 2021. 多年冻土地区拓宽路基差异沉降产生机理及变形特征研究. 西安: 长安大学.Zhou S. Q., 2021. Study on differential settlement mechanism and characteristics of widened subgrade in permafrost regions. Xi’an: Chang'an University. (in Chinese) 朱合华, 禹海涛, 韩富强等, 2023. 穿越活动断层隧道抗震韧性设计理念与关键问题. 中国公路学报, 36(11): 193−204. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.11.002Zhu H. H., Yu H. T., Han F. Q., et al., 2023. Seismic resilience design principles and key issues for tunnels crossing active faults. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 36(11): 193−204. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.11.002 宗周红, 林元铮, 林津等, 2023. 跨断层地震动及其对桥梁结构影响研究进展. 中国公路学报, 36(1): 80−96. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.01.008Zong Z. H., Lin Y. Z., Lin J., et al., 2023. Research advances of across-fault ground motions and their effects on bridge structures. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 36(1): 80−96. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.01.008 Hung V. T., Kiyomiya O, An T. X., 2009. Evaluation of seismic resistance for a multi-spans bridge in Vietnam by investigation of earthquake activity and dynamic response analysis. Journal of Structural Engineering, 55A: 537−549. Lutskii S. I., Artiushenko I. A., 2017. Analysis of the bearing capacity of the subsidence base of the roadbed on the permafrost soil. Interactive Science, 10(20): 8−13. (in Russian Petala E., Klimis N. S., 2019. Numerical assessment of distortion and damage induced on a highway embankment due to reverse fault rupture propagation. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 116: 264−277. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.10.029 Regehr J. D., Milligan C. A., Montufar J., et al., 2013. Review of effectiveness and costs of strategies to improve roadbed stability in permafrost regions. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 27(3): 109−131. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000054 Wang L., Kiyomiya O., An T. X., 2009. Comparison of seismic resistance of highway bridge in Yunnan by the specification of China and Japan. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Ser. A1 (Structural Engineering & Earthquake Engineering (SE/EE)), 65(1): 333−344. Yang S., Mavroeidis G. P., Tsopelas P., 2021. Seismic response study of ordinary and isolated bridges crossing strike-slip fault rupture zones. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 50(11): 2841−2862. Zheng S. B., Jiang S. P., 2015. Seismic resistance and damping model test and numerical simulation of highway tunnel. The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 9(1): 673−681. doi: 10.2174/1874149501509010673 -




 下载:
下载: