Characteristics of Measured In-situ Stress Field in A Tunnel Site in Central Tianshan Mountains and Its Significance to Regional Crustal Stability
-
摘要: 新疆中天山地质及构造条件复杂,某隧址埋深最大接近
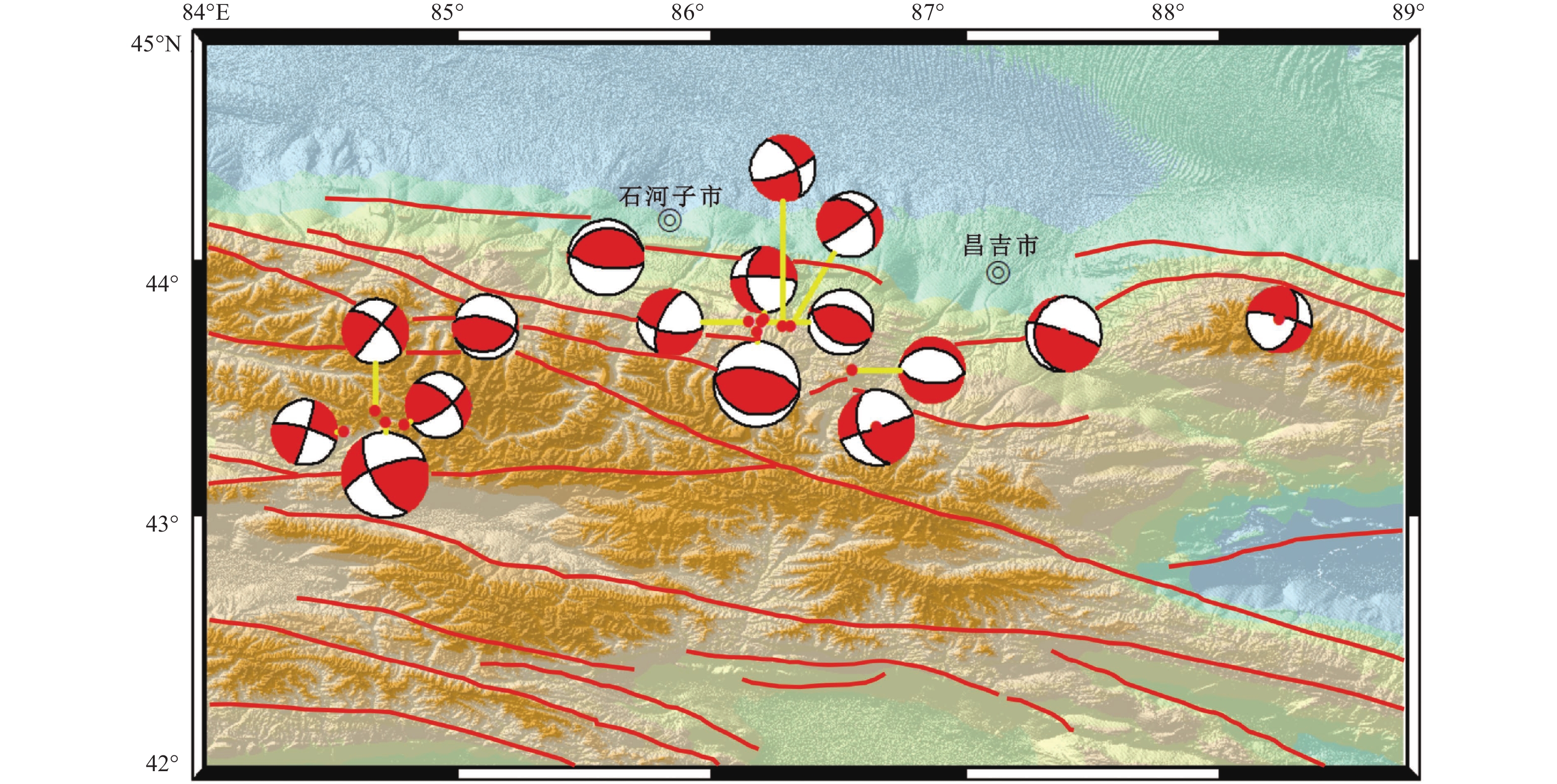
1336 m,探明隧址区地应力场特征和断层摩擦系数对隧址区稳定性评价具有重要工程及理论价值。本文基于隧址区内9个钻孔获得的37条实测地应力数据,通过统计及拟合数据,引入断层摩擦系数μ、地壳应力积累指标μm,并结合区域地震分布和震源机制等进行分析。研究表明,中天山隧址区最大水平主应力优势方向为N37°E,与区域构造应力场NNE方向相符;浅部地壳以水平构造应力为主,最大、最小水平主应力随深度线性增长梯度分别为0.024和0.017,应力状态以逆冲型为主,局部兼有走滑型。隧址区内断层摩擦系数μ分析揭示,其主要分布范围为0.15~0.3,表明大部分断层处于低强度状态,而F6断裂μ值达到0.39,明显高于其他断层,同时区内地壳应力积累指标μm近80%,应力积累不高,未达到临界滑动值0.5,但F6断裂处应力积累程度均高于0.5,说明F6断裂相较其他断层的应力积累更大,更具有活动性。结合NWW向断层附近地震频发及近年小震震源机制解特征,表明隧址区断层更易沿北西西向形成滑动。Abstract: The geological and tectonic conditions of the central Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang are highly complex. The tunnel site in this region reaches a maximum burial depth of nearly 1 336 m. Investigating the in-situ stress field characteristics and fault friction coefficients at the site is of considerable engineering and theoretical importance for assessing tunnel stability. Based on 37 in-situ stress measurements from nine boreholes, this study conducts statistical and regression analyses, introduces the fault friction coefficient (μ) and crustal stress accumulation index (μm), and integrates these with regional seismic distribution and focal mechanism data. The results indicate that the dominant orientation of maximum horizontal principal stress is N37°E, consistent with the NNE-directed regional tectonic stress field. Horizontal tectonic stress is dominant in the shallow crust, with maximum and minimum horizontal principal stresses increasing linearly with depth at gradients of 0.024 and 0.017, respectively. The stress regime is primarily thrust-type, with local strike-slip characteristics. Analysis of the fault friction coefficient shows that most values fall within 0.15~0.3, suggesting low-intensity faults; however, the F6 fault exhibits a higher μ value of 0.39, significantly above the regional average. Similarly, while nearly 80% of μm values remain below the critical sliding threshold of 0.5, the F6 fault exceeds this level, indicating greater stress accumulation and higher activity. Combined with the frequent seismicity along NWW-trending faults and focal mechanism solutions, these findings suggest that faults in the tunnel site area are more susceptible to sliding in the NWW direction. -
表 1 隧址区内其余断层性质
Table 1. Properties of other faults in tunnel site area
断裂编号 产状 断裂性质 走向/(°) 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) Fw-1 117 207 76 逆断层 Fw-2 108 18 40~80 右行平移断层 Fw-3 128 38 73 — Fw-4 81 351 60~80 — Fw-5 94 4 61 逆断层 Fw-6 114 204 86 逆断层 Fw-7 121 211 68 逆断层 Fw-8 42 312 86 正断层 Fw-9 105 — — — Fw-10 113 23 78 正断层 Fw-11 113 205 80 — Fw-12 115 203 80 — Fw-13 90 190 81 逆断层 Fw-14 100 190 83 逆断层 表 2 隧址区实测地应力数据
Table 2. In-situ stress data measured in tunnel site area
编号 测号段 深度/m 钻孔岩性 应力值/MPa 地应力累计指数μs 线性相关系数R σH σh σv ZK1 1 195.1 花岗闪长岩 16.8 9.3 4.9 0.63 0.63 2 278.3 花岗闪长岩 22.6 13.2 7.0 0.62 0.60 3 306.1 炭质板岩 23.3 14.7 7.7 0.60 0.55 4 333.7 炭质板岩 22.2 13.5 8.3 0.56 0.63 5 361.5 炭质板岩 25.7 15.4 9.0 0.58 0.62 6 383.1 炭质板岩 25.0 16.8 9.6 0.55 0.53 ZK2 1 119.8 片麻状花岗闪长岩 12.1 7.4 3.2 0.65 0.53 2 210.8 片麻状花岗闪长岩 15.1 9.8 5.7 0.54 0.56 3 301.8 片麻状花岗闪长岩 18.2 11.2 8.1 0.48 0.69 4 365.5 片麻状花岗闪长岩 20.3 12.5 9.9 0.44 0.75 5 447.4 片麻状花岗闪长岩 22.2 14.4 12.1 0.39 0.77 6 492.9 片麻状花岗闪长岩 21.8 15.5 13.3 0.33 0.74 7 547.5 片麻状花岗闪长岩 26.3 17.2 14.8 0.37 0.79 8 583.9 片麻状花岗闪长岩 28.1 18.5 15.8 0.37 0.78
ZK31 111.0 大理岩 7.1 5.2 3.0 0.46 0.46 2 156.5 大理岩 8.0 5.3 4.2 0.38 0.71 3 192.9 大理岩 9.5 6.5 5.2 0.36 0.70 4 220.2 大理岩 11.8 8.3 5.9 0.41 0.59 5 256.6 大理岩 14.5 9.9 6.9 0.44 0.61 6 302.1 大理岩 17.3 11.2 8.2 0.44 0.67 7 347.6 大理岩 18.5 11.1 9.4 0.42 0.81 8 429.5 大理岩 20.7 12.8 11.6 0.37 0.87 9 456.8 大理岩 21.4 14.3 12.3 0.36 0.78 10 484.1 大理岩 22.1 14.8 13.1 0.34 0.81 11 511.4 大理岩 23.0 14.3 13.8 0.33 0.95 ZK4 1 243.5 花岗闪长岩 9.9 6.8 5.9 0.35 0.77 2 511.2 石英片岩 16.3 11.4 12.3 0.26 0.83 ZK5 1 229.5 石英片岩 9.8 6.2 5.5 0.37 0.84 2 585.8 片麻岩 16.9 12.9 14.1 0.21 0.72 ZK6 1 350.0 花岗岩 11.5 8.7 8.6 0.21 0.98 2 776.0 花岗闪长岩 21.8 15.7 19.0 0.27 0.46 ZK7 1 231.8 片麻状闪长岩 8.4 5.7 5.6 0.27 0.94 2 761.8 片麻状闪长岩 20.2 12.7 18.3 0.41 0.26 ZK8 1 208.5 砂质板岩 9.5 6.1 5.0 0.41 0.75 2 352.8 大理岩 12.3 8.5 8.5 0.26 0.98 ZK9 1 235.4 砂质板岩 10.8 7.5 5.7 0.41 0.65 2 371.9 大理岩 13.6 9.6 8.9 0.28 0.87 表 3 ZK9钻孔k值的拟合值与实测值误差分析
Table 3. Error analysis of ZK9 borehole k value fitting result to the measured result
深度/m 拟合 实测 误差/% kH,max kh,min kH,max kh,min kH,max kh,min 235.4 1.94 1.29 1.91 1.32 1 2 371.9 1.83 1.18 1.54 1.07 18 10 表 4 深度400 m处钻孔的k、μ值
Table 4. k and μ values of boreholes at depth of 400 m
钻孔 kH,max kh,min σ'/MPa τ μ ZK1 2.69 1.72 18.34 7.11 0.39 ZK2 1.95 1.26 14.65 4.50 0.31 ZK3 1.82 1.17 13.50 3.87 0.29 ZK4 1.75 0.95 9.05 1.82 0.20 ZK5 1.83 1.19 8.70 1.59 0.18 ZK6 1.84 1.20 8.28 1.34 0.16 ZK7 1.79 1.18 7.74 1.18 0.15 ZK8 1.76 1.22 8.64 1.55 0.18 ZK9 1.78 1.16 9.23 1.89 0.21 -
崔光耀, 王明年, 于丽等, 2013. 汶川地震断层破碎带段隧道结构震害分析及震害机理研究. 土木工程学报, 46(11): 122−127.Cui G. Y., Wang M. N., Yu L., et al., 2013. Study on the characteristics and mechanism of seismic damage for tunnel structures on fault rupture zone in Wenchuan seismic disastrous area. China Civil Engineering Journal, 46(11): 122−127. (in Chinese) 黄禄渊, 杨树新, 崔效锋等, 2013. 华北地区实测应力特征与断层稳定性分析. 岩土力学, 34(S1): 204−213.Huang L. Y., Yang S. X., Cui X. F., et al., 2013. Analysis of characteristics of measured stress and stability of faults in North China. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 34(S1): 204−213. (in Chinese) 李艳永, 王成虎, 朱皓清等, 2020. 北天山地区震源机制与构造应力场特征. 地震, 40(2): 117−129. doi: 10.12196/j.issn.1000-3274.2020.02.009Li Y. Y., Wang C. H., Zhu H. Q., et al., 2020. The focal mechanism and stress field inversion in northern Tianshan mountain. Earthquake, 40(2): 117−129. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12196/j.issn.1000-3274.2020.02.009 刘卓岩, 王成虎, 徐鑫等, 2017. 基于地应力实测数据分析郯庐断裂带中段滑动趋势. 现代地质, 31(4): 869−876. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.021Liu Z. Y., Wang C. H., Xu X., et al., 2017. Slip tendency analysis of the Mid-segment of Tan-Lu fault belt based on stress measurements. Geoscience, 31(4): 869−876. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.021 牛安福, 张凌空, 闫伟等, 2011. 中国钻孔应变观测能力及在地震预报中的应用. 大地测量与地球动力学, 31(2): 48−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2011.02.011Niu A. F., Zhang L. K., Yan W., et al., 2011. Borehole strain measurement and application to earthquake prediction in China. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 31(2): 48−52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2011.02.011 王成虎, 丁立丰, 李方全等, 2012. 川西北跨度23a的原地应力实测数据特征及其地壳动力学意义分析. 岩石力学与工程学报, 31(11): 2171−2181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.11.004Wang C. H., Ding L. F., Li F. Q., et al., 2012. Characteristics of in-situ stress measurement in northwest Sichuan basin with timespan of 23 years and its crustal dynamics significance. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 31(11): 2171−2181. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.11.004 王成虎, 宋成科, 郭启良等, 2014. 利用原地应力实测资料分析芦山地震震前浅部地壳应力积累. 地球物理学报, 57(1): 102−114. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140110Wang C. H., Song C. K., Guo Q. L., et al., 2014. Stress build-up in the shallow crust before the Lushan earthquake based on the in-situ stress measurements. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(1): 102−114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20140110 王洪, 王成虎, 高桂云等, 2021. 青海共和盆地地应力状态与断层稳定性分析. 震灾防御技术, 16(1): 123−133. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210113Wang H., Wang C. H., Gao G. Y., et al., 2021. The state of the in-situ stress and fault slide evaluation of Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(1): 123−133. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210113 王渝生, 2008. 李四光的地质力学与地震成因理论. 科技导报, 26(11): 98. 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛等, 2004. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区. 地球物理学报, 47(4): 654−662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016Xie F. R., Cui X. F., Zhao J. T., et al., 2004. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 654−662. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016 阎渊, 2023. 青海门源MS6.9地震同震破裂的隧道破坏效应与启示. 地质力学学报, 29(6): 869−878. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023027Yan Y., 2023. The tunnel damage effects and implications of the coseismic rupture of the Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake in Qinghai, China. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(6): 869−878. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023027 张杰, 王成虎, 贾晋等, 2018. 基于实测应力数据的北天山西部区域断层滑动趋势分析. 地震工程学报, 40(1): 73−78, 91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.01.073Zhang J., Wang C. H., Jia J., et al., 2018. Fault slip tendency in the western area of North Tianshan based on measured in-situ stress data. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 40(1): 73−78,91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.01.073 张志斌, 赵晓成, 任林, 2020. 新疆天山中段的震源机制解与构造应力场特征分析. 地震地质, 42(3): 595−611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.004Zhang Z. B., Zhao X. C., Ren L., 2020. Focal mechanism solution and tectonic stress field characteristics of the middle Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 595−611. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.004 Anderson E. M., 1905. The dynamics of faulting. Transactions of the Edinburgh Geological Society, 8(3): 387−402. doi: 10.1144/transed.8.3.387 Brodsky E. E., Mori J. J., Anderson L., et al., 2020. The state of stress on the fault before, during, and after a major earthquake. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 48: 49−74. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-053018-060507 Byerlee J., 1978. Friction of rocks. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 116(4-5): 615−626. doi: 10.1007/BF00876528 Haimson B. C., Cornet F. H., 2003. ISRM Suggested Methods for rock stress estimation-Part 3: hydraulic fracturing (HF) and/or hydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures (HTPF). International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 40(7-8): 1011−1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.08.002 Raleigh C. B., Healy J. H., Bredehoeft J. D., 1976. An experiment in earthquake control at Rangely, colorado. Science, 191(4233): 1230−1237. doi: 10.1126/science.191.4233.1230 Sheorey P. R., 1994. A theory for in situ stresses in isotropic and transverseley isotropic rock. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 31(1): 23−34. Wang W. L., Wang T. T., Su J. J., et al., 2001. Assessment of damage in mountain tunnels due to the Taiwan Chi-Chi earthquake. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 16(3): 133−150. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(01)00047-5 Zoback M. D., Healy J. H., Roller J. C., et al., 1978. Normal faulting and in situ stress in the South Carolina coastal plain near Charleston. Geology, 6(3): 147−152. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1978)6<147:NFAISS>2.0.CO;2 Zoback M. D. , 2007. Reservoir geomechanics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. -




 下载:
下载: