Experimental Study on the Effect of Cyclic Loading Frequency on the Bearing Capacity of Sand
-
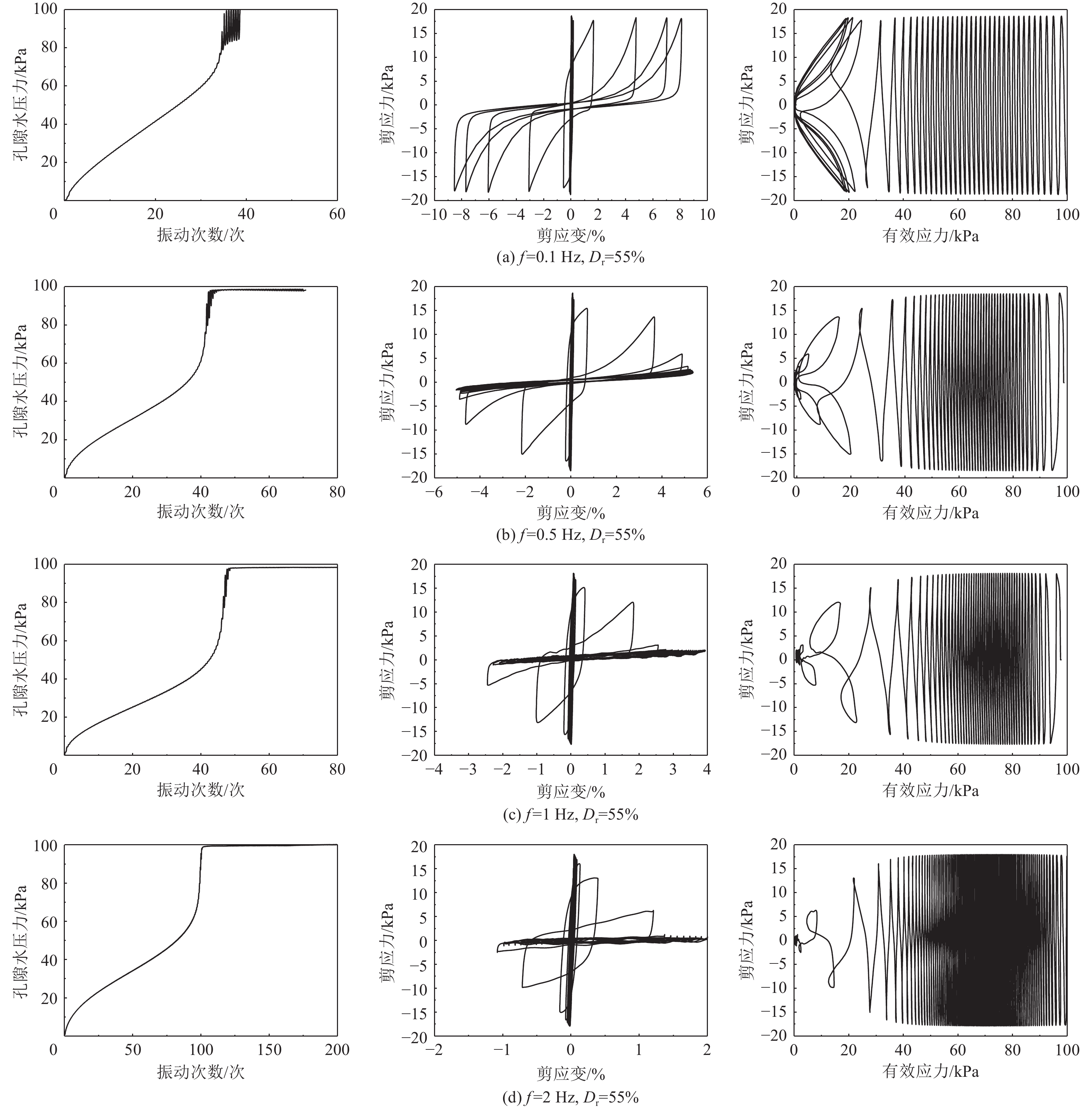
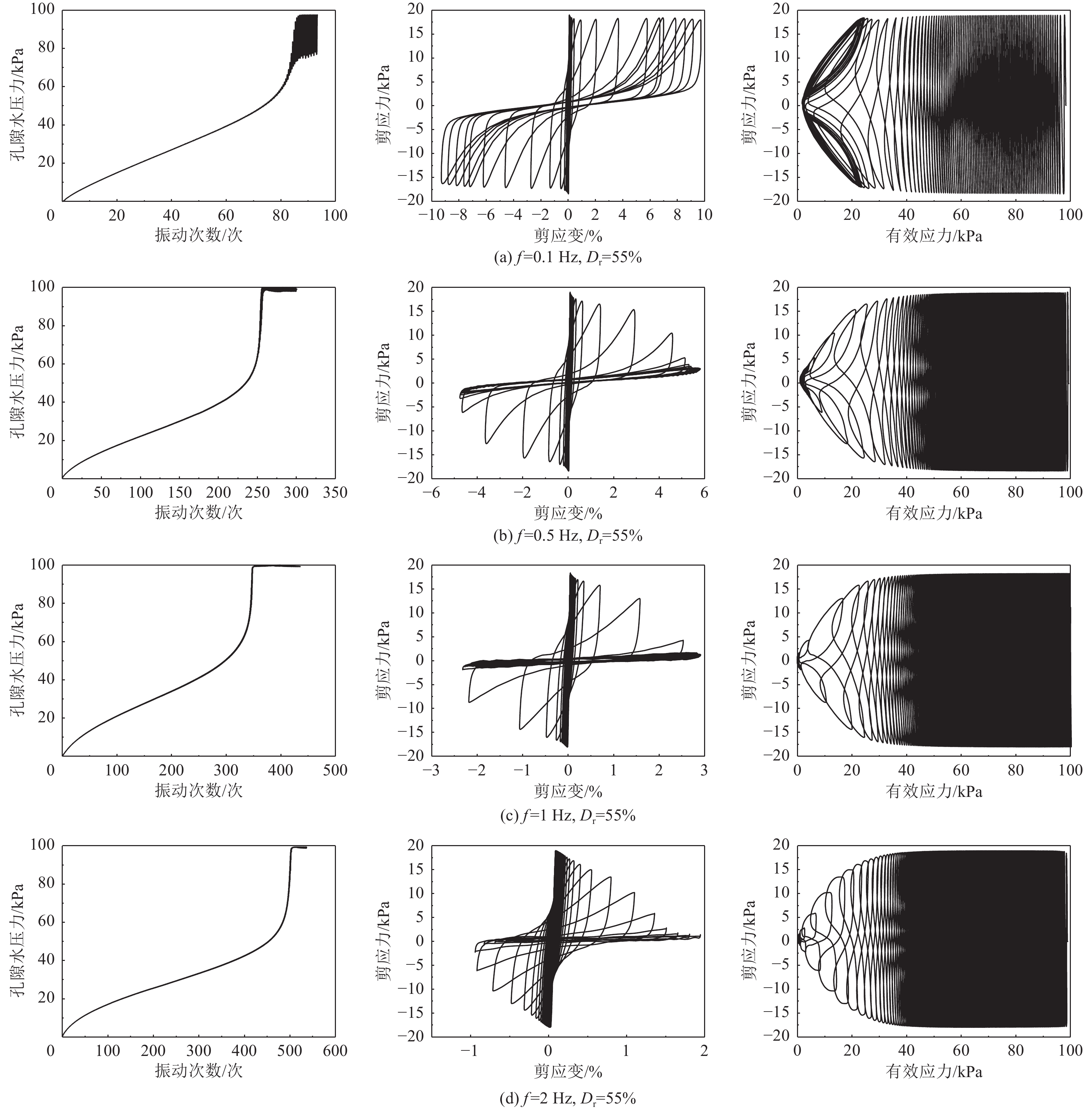
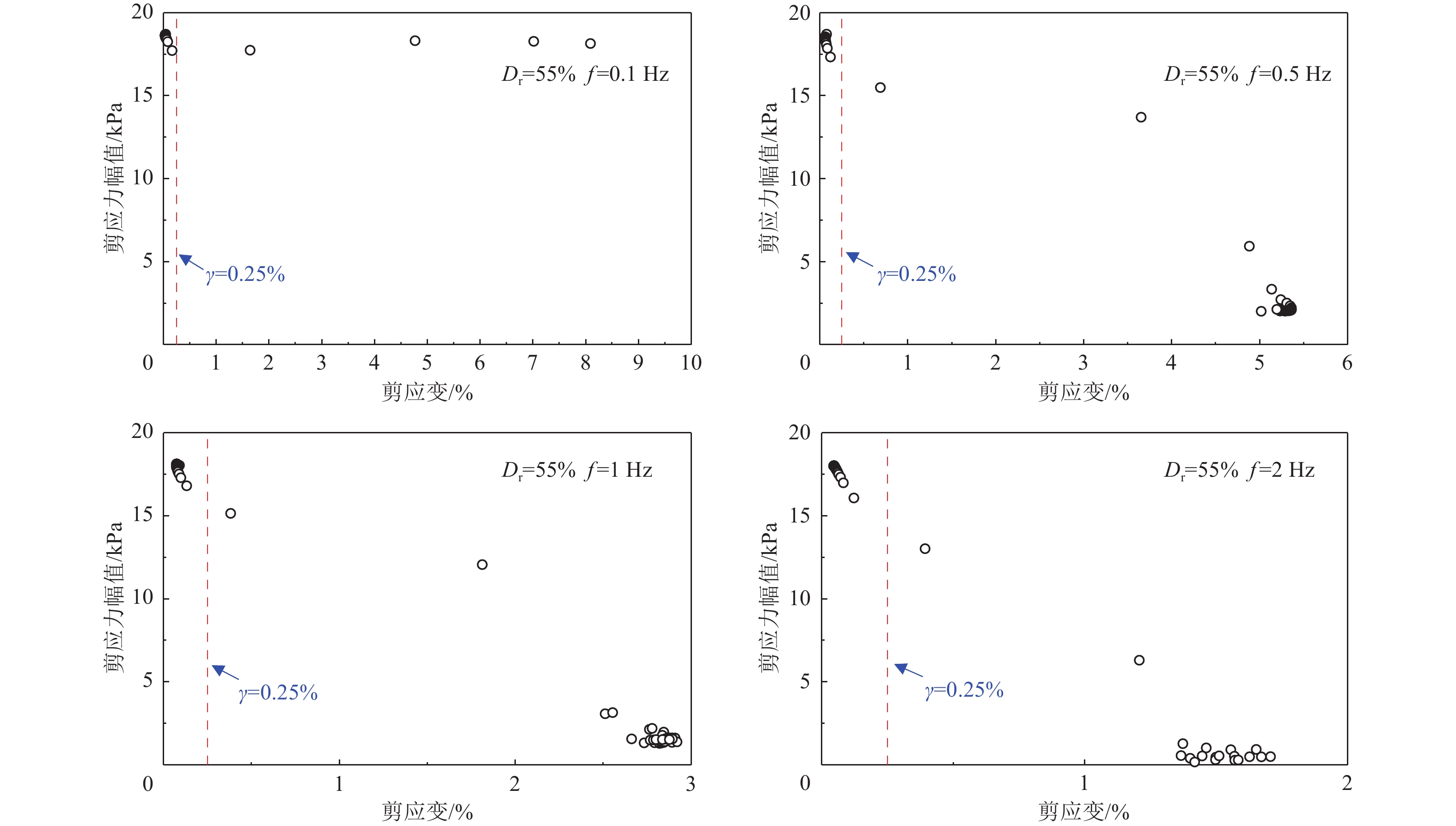
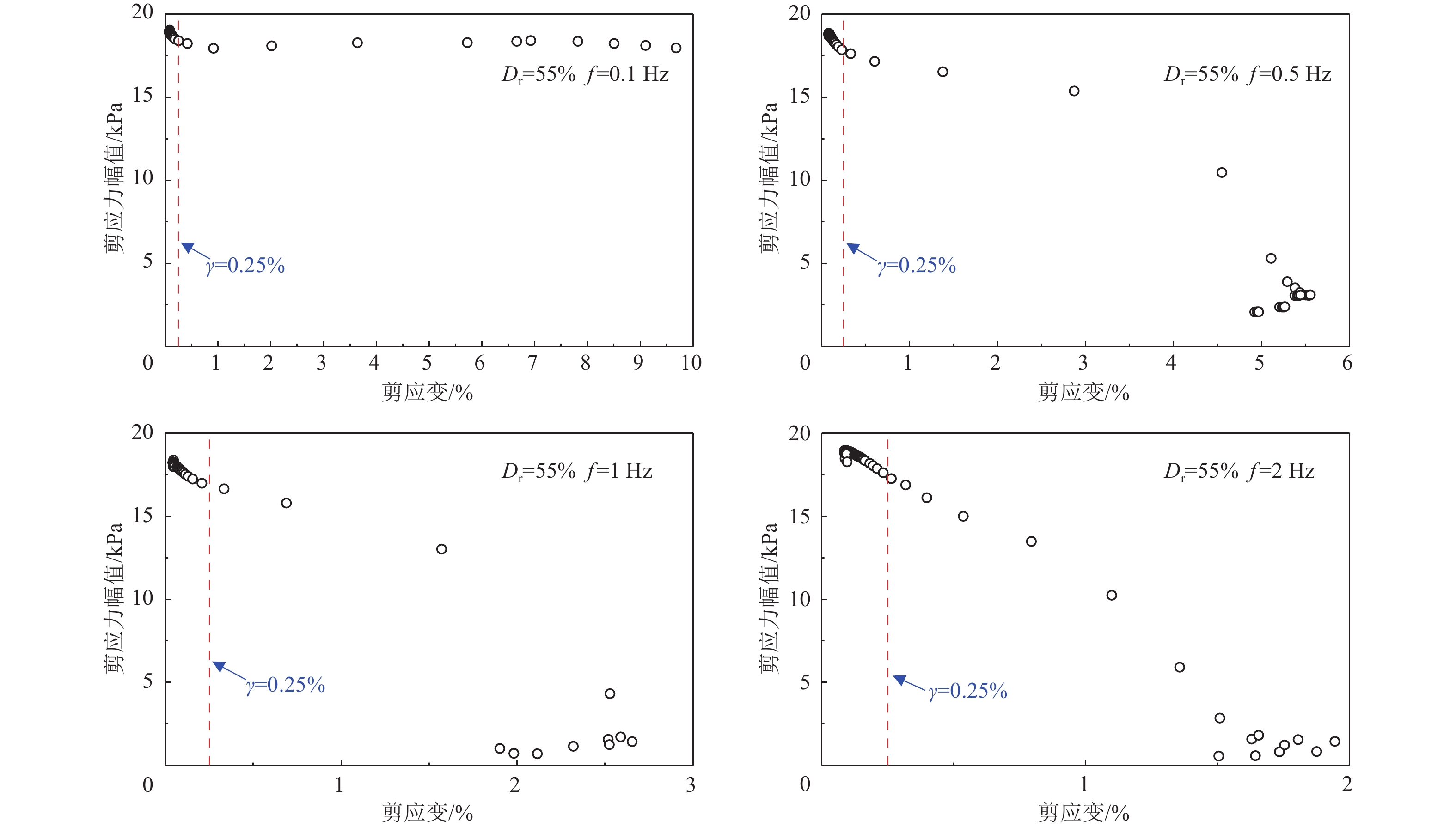
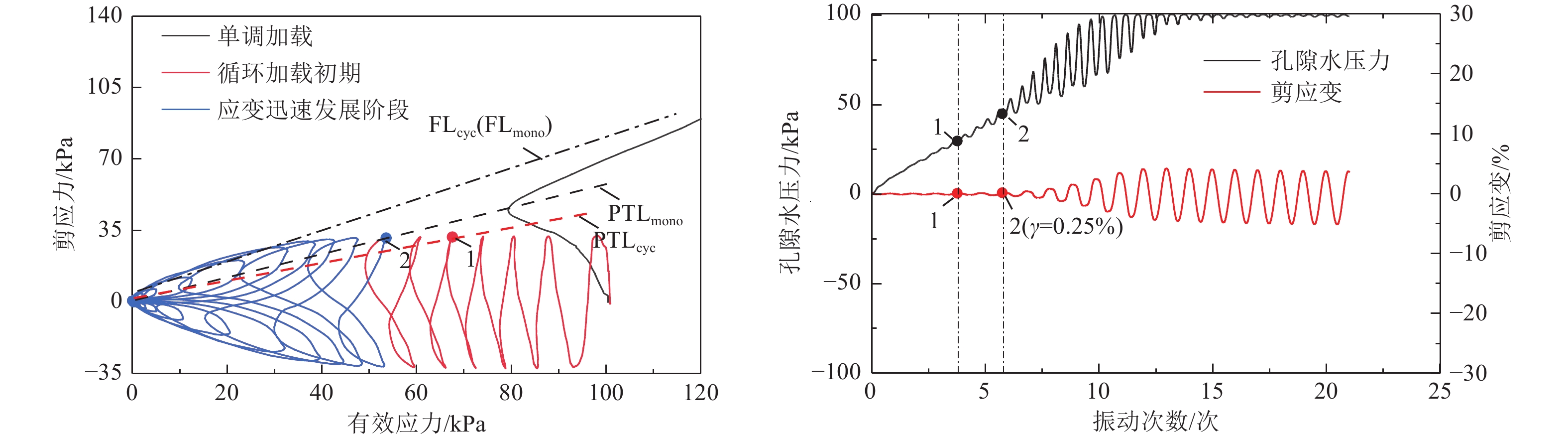
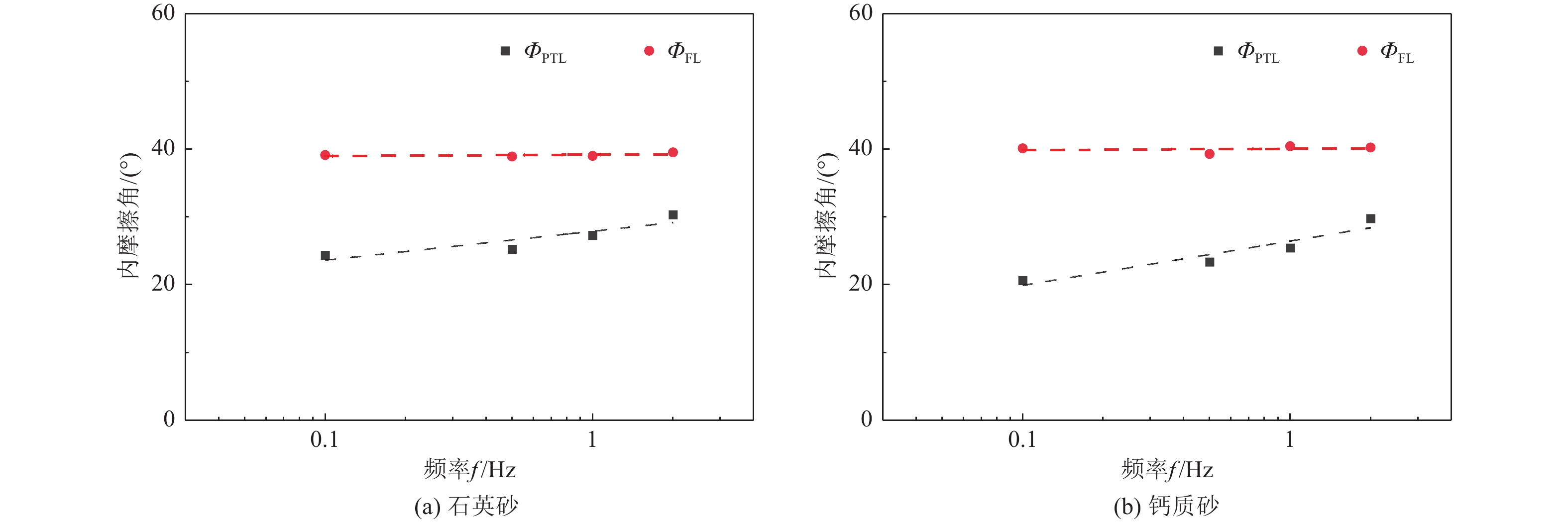
摘要: 本文针对相对密实度为35%、55%、75%的钙质砂和石英砂,开展了系列不排水单调和循环扭剪试验,重点探讨了循环加载频率为0.1、0.5、1、2 Hz作用下的砂土抗剪能力差异和静动力剪切特性的相关性。试验表明,无论是石英砂还是钙质砂,循环加载频率对其动应力-应变的影响十分显著,高频作用下,砂土液化后呈现抗剪能力衰减特性。低频荷载作用下,应重点关注砂土变形失稳问题,高频荷载作用下,则应重点考虑砂土抗剪能力失稳问题;循环荷载和单调加载下的相变应力比不同,当有效剪应力比(q/p')超过单调加载下的相变应力比时,砂土呈现变形快速发展特征;不同循环加载频率下,砂土的循环加载破坏线和单调加载破坏线基本相近。Abstract: A series of undrained monotonic and cyclic torsional shear tests were conducted on calcareous sand and quartz sand at relative densities of 35%, 55%, and 75% to investigate the bearing capacity differences and the relationship between static and dynamic shear behavior under varying cyclic loading frequencies (0.1Hz, 0.5Hz, 1Hz, and 2Hz). The experimental results reveal that the dynamic stress–strain responses of both quartz sand and calcareous sand are significantly influenced by the loading frequency. Specifically, under high-frequency cyclic loading, the post-liquefaction strength of the sand is notably reduced, indicating attenuation of bearing capacity. In contrast, under low-frequency loading conditions, deformation instability becomes the dominant concern. This distinction highlights the need to differentiate between deformation-driven and strength-driven instability mechanisms depending on the loading frequency. Furthermore, the results indicate that the phase transformation stress ratios differ between cyclic and monotonic loading conditions. When the effective shear stress ratio (q/p′) surpasses the monotonic phase transformation threshold, the sand exhibits rapid strain development, signaling the onset of significant deformation. Notably, irrespective of the cyclic loading frequency, the failure envelope under cyclic loading closely aligns with that observed under monotonic loading, suggesting a consistent ultimate strength criterion across loading modes.
-
表 1 试验方案
Table 1. Test condition
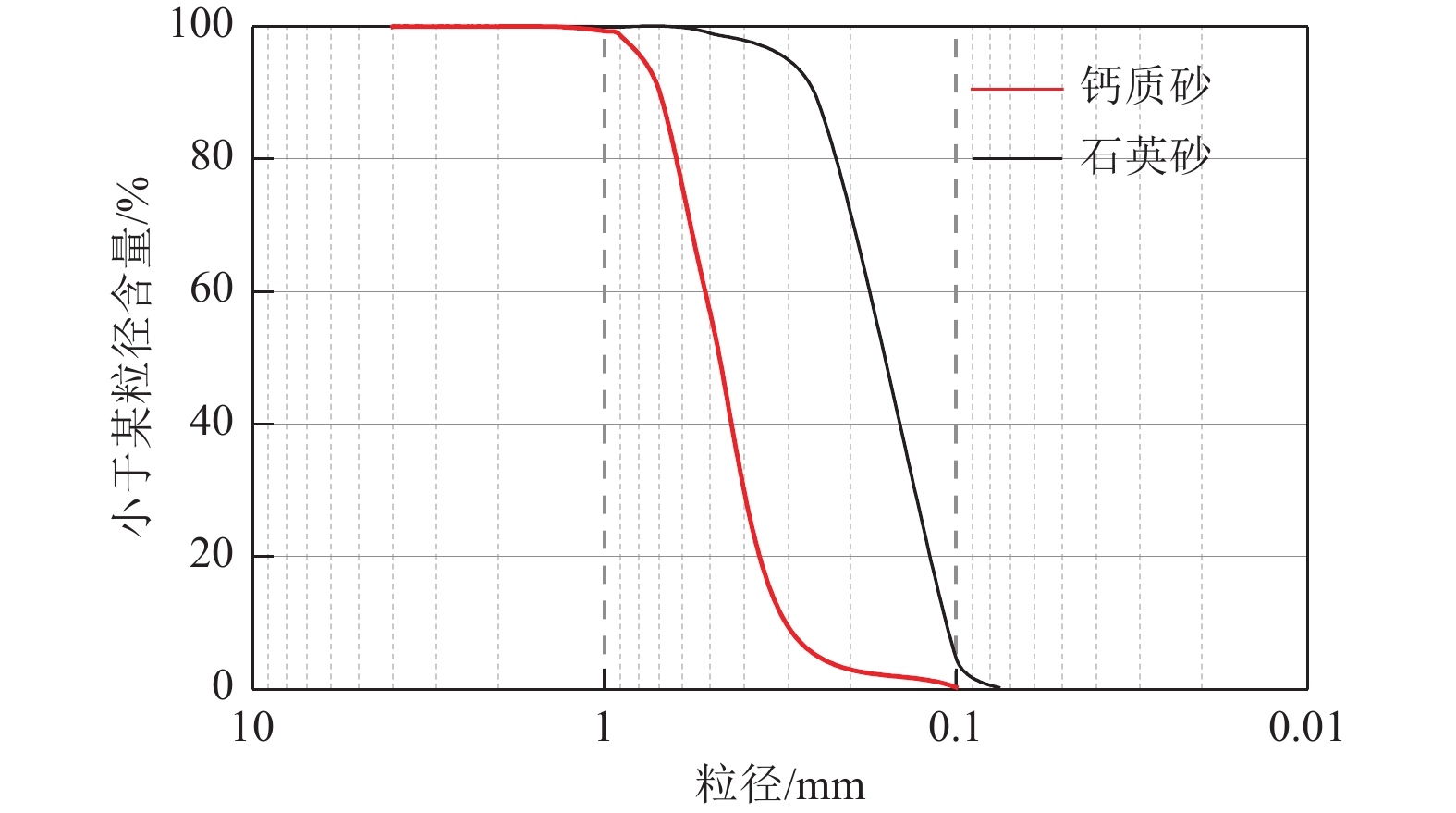
试验类型 试验材料 相对密实度Dr 加载速率s或频率f 循环应力比CSR 单调扭剪 石英砂 35%、55%、75% 5 kPa/min — 钙质砂 循环扭剪 石英砂 35% 0.5、2 Hz 0.15 55% 0.1、0.5、1、2 Hz 0.20 75% 0.35 钙质砂 35% 0.1、0.5、1、2 Hz 0.25 55% 0.20 75% 0.35 -
陈龙伟,刘昊儒,任叶飞等,2024. 2023年2月6日土耳其双强震场地液化及其震害特征现场调查分析. 岩土工程学报,46(7):1541−1548. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230333Chen L. W., Liu H. R., Ren Y. F., et al., 2024. In-situ investigation of site liquefaction and liquefaction-induced damages triggered by two strong Türkiye earthquakes on Feb. 6th, 2023. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 46(7): 1541−1548. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230333 董林,王兰民,夏坤等,2017. 基于台湾集集地震数据的CPT与SPT液化判别方法比较. 岩土力学,38(12):3643−3648.Dong L., Wang L. M., Xia K., et al., 2017. Comparison of CPT-based and SPT-based liquefaction discrimination methods by Taiwan Chi-Chi earthquake data. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 38(12): 3643−3648. (in Chinese) 丰土根,张礼明,2013. 振动频率对饱和松砂动力特性影响试验研究. 水利与建筑工程学报,11(3):11−14,76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2013.03.005Feng T. G., Zhang L. M., 2013. Experimental study on effect of vibration frequency on dynamic behaviors of saturated loose sands. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 11(3): 11−14,76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2013.03.005 郭莹,2003. 复杂应力条件下饱和松砂的不排水动力特性试验研究. 大连:大连理工大学.Guo Y., 2003. Experimental studies on undrained cyclic behavior of loose sands under complex stress conditions considering static and cyclic coupling effect. Dalian:Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese) 郭莹,贺林,2009. 振动频率对饱和砂土液化强度的影响. 防灾减灾工程学报,29(6):618−623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2132.2009.06.004Guo Y., He L., 2009. The influences of the vibration frequencies on liquefaction strength of saturated sands. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 29(6): 618−623. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2132.2009.06.004 李建国,2005. 波浪荷载作用下饱和钙质砂动力特性的试验研究. 武汉:中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所).Li J. G., 2005. Experimental research on dynamic behavior of saturated calcareous sand under wave loading. Wuhan: Chinese Academy of Sciences, P.R. China (Institute of Rock & Soil Mechanics). (in Chinese) 刘鑫,李飒,刘小龙等,2019. 南海钙质砂的动剪切模量与阻尼比试验研究. 岩土工程学报,41(9):1773−1780. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201909024Liu X., Li S., Liu X. L., et al., 2019. Experimental study on dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of calcareous sands in the South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 41(9): 1773−1780. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201909024 栾茂田,许成顺,何杨等,2006. 复杂应力条件下饱和松砂单调与循环剪切特性的比较研究. 地震工程与工程振动,26(1):181−187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2006.01.030Luan M. T., Xu C. S., He Y., et al., 2006. A comparative study on monotonic and cyclic shear behavior of saturated loose sand under complex stress condition. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 26(1): 181−187. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2006.01.030 栾茂田,张振东,许成顺等,2008. 许成顺等. K0固结条件下砂土的循环剪切特性试验研究. 岩土力学,29(9):2323−2328.Luan M. T., Zhang Z. D., Xu C. S., et al., 2008. Experimental studies of cyclic shear characteristic of sand under K0 consolidation condition. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 29(9): 2323−2328. (in Chinese) 王立朝,侯圣山,董英等,2024. 甘肃积石山Ms 6.2级地震的同震地质灾害基本特征及风险防控建议. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,35(3):108−118.Wang L. C., Hou S. S., Dong Y., et al., 2024. Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and suggestions for their risk control. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 35(3): 108−118. (in Chinese) 吴世明,徐攸在,1998. 土动力学现状与发展. 岩土工程学报,20(3):125−131. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.03.030Wu S. M., Xu Y. Z., 1998. State-of-art and development of soil dynamics. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 20(3): 125−131. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.03.030 谢定义,1992. 饱和砂土体液化的若干问题. 岩土工程学报,14(3):90−98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1992.03.014 许成顺,刘晨,刘海强等,2013. 竖向-扭转双向耦合剪切仪功能分析及应用. 北京工业大学学报,39(2):233−238. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2013020233Xu C. S., Liu C., Liu H. Q., et al., 2013. Function analysis and application of vertical-torsional coupling shear apparatus. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 39(2): 233−238. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2013020233 许成顺,王冰,杜修力等,2021. 循环加载频率对砂土液化模式的影响试验研究. 土木工程学报,54(11):109−118.Xu C. S., Wang B., Du X. L., et al., 2021. Experimental study on effect of cyclic loading frequency on liquefaction mode of sand. China Civil Engineering Journal, 54(11): 109−118. (in Chinese) 虞海珍,2006. 复杂应力条件下饱和钙质砂动力特性的试验研究. 武汉:华中科技大学.Yu H. Z., 2006. Experimental research on dynamic behavior of saturated calcareous sand under complex stress conditions. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology. (in Chinese) 袁晓铭,曹振中,孙锐等,2009. 汶川8.0级地震液化特征初步研究. 岩石力学与工程学报,28(6):1288−1296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.026Yuan X. M., Cao Z. Z., Sun Y., et al., 2009. Preliminary research on liquefaction characteristics of Wenchuan 8.0 earthquake. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 28(6): 1288−1296. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.026 Airey D. W., Fahey M., 1991. Cyclic response of calcareous soil from the North-West Shelf of Australia. Géotechnique, 41(1): 101−121. Green R. A. , Olson S. M. , Cox B. R. , et al. , 2011. Geotechnical aspects of failures at Port-au-Prince Seaport during the 12 January 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Earthquake Spectra, 27(1 Suppl1): 43−65. Hyodd M., Hyde A. F. L., Aramaki N., 1998. Liquefaction of crushable soils. Géotechnique, 48(4): 527−543. Hyodo M., Aramaki N., Itoh M., et al., 1996. Cyclic strength and deformation of crushable carbonate sand. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 15(5): 331−336. doi: 10.1016/0267-7261(96)00003-6 Ishihara K., Koga Y., 1981. Case studies of liquefaction in the 1964 Niigata earthquake. Soils and Foundations, 21(3): 35−52. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.21.3_35 Lee K. L., Focht J. A., 1976. Cyclic testing of soil for ocean wave loading problems. Marine Geotechnology, 1(4): 305−325. doi: 10.1080/10641197609388171 Mejia L. H. , Yeung M. R. , 1995. Liquefaction of coralline soils during the 1993 Guam earthquake. In: Kramer S. , Siddharthan R. , eds. , Earthquake-Induced Movements and Seismic Remediation of Existing Foundations and Abutments. San Diego: ASCE, 33−48. Mulilis J. P. , Chan C. K. , Seed H. B. , 1975. The effects of method of sample preparation on the cyclic stress-strain behavior of sands. Berkeley: Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California, 75. Salem M., Elmamlouk H., Agaiby S., 2013. Static and cyclic behavior of North Coast calcareous sand in Egypt. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 55: 83−91. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.09.001 Shahnazari H., Jafarian Y., Tutunchian M. A., et al., 2016. Undrained cyclic and monotonic behavior of Hormuz calcareous sand using hollow cylinder simple shear tests. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 14(4): 209−219. doi: 10.1007/s40999-016-0021-6 Silva W. , 1988. Soil response to earthquake ground motion: final report. Walnut Creek: Woodward-Clyde Consultants. Yoshimi Y., Oh-Oka H., 1975. Influence of degree of shear stress reversal on the liquefaction potential of saturated sand. Soils and Foundations, 15(3): 27−40. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.15.3_27 -




 下载:
下载: