Transverse Seismic Response Analysis of Small and Medium-span Highway Bridges in Service Considering Time-varying Characteristics of Materials
-
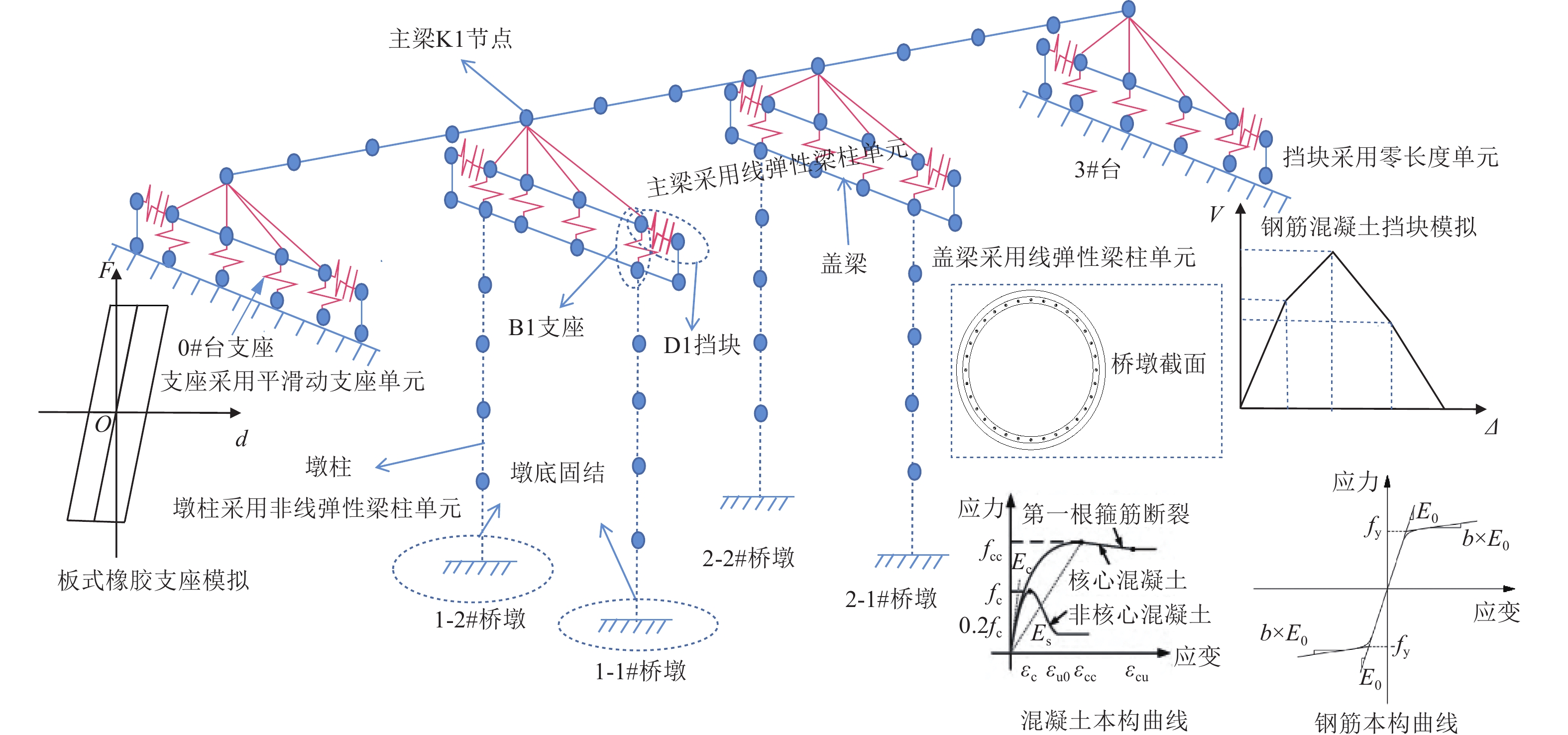
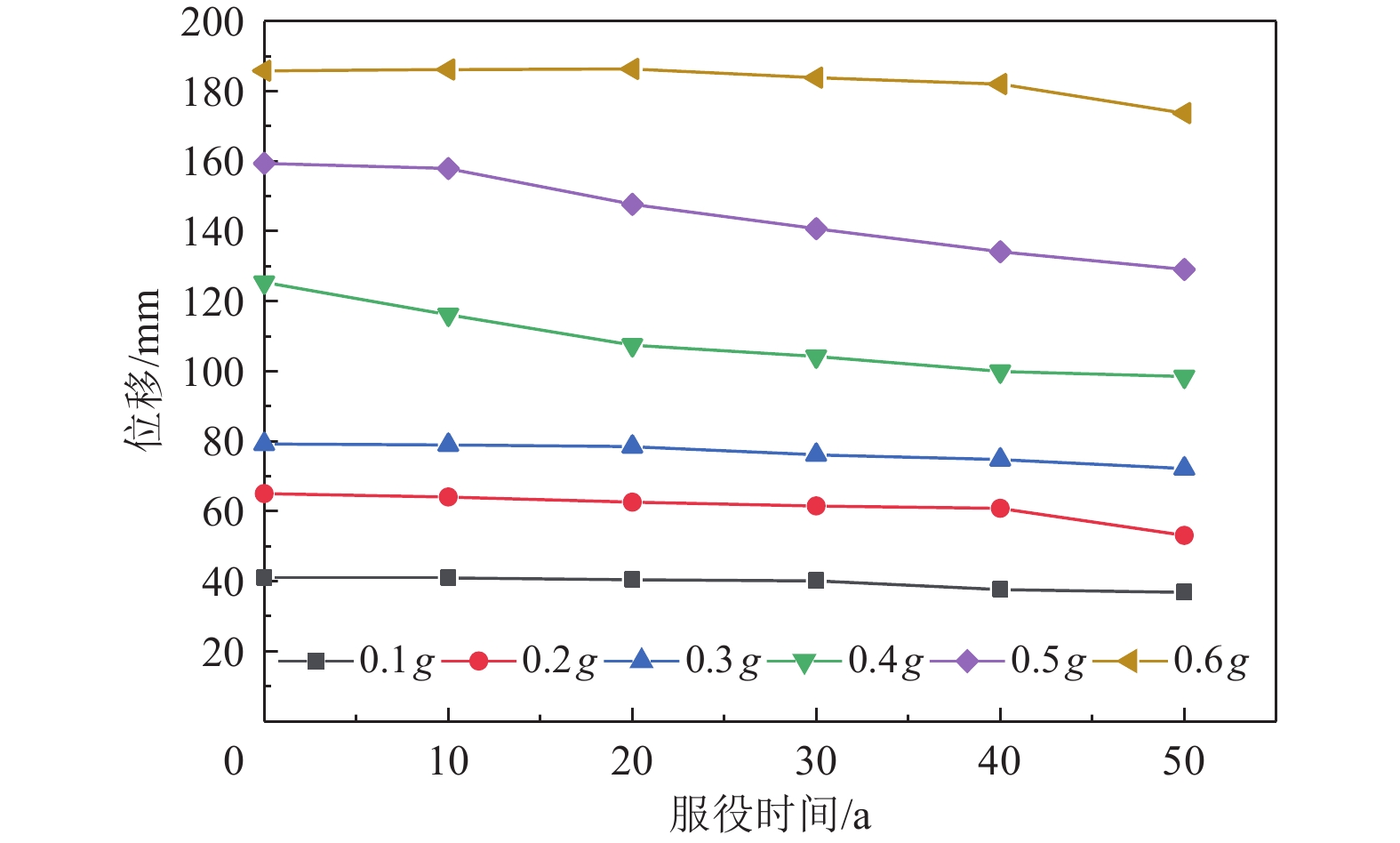
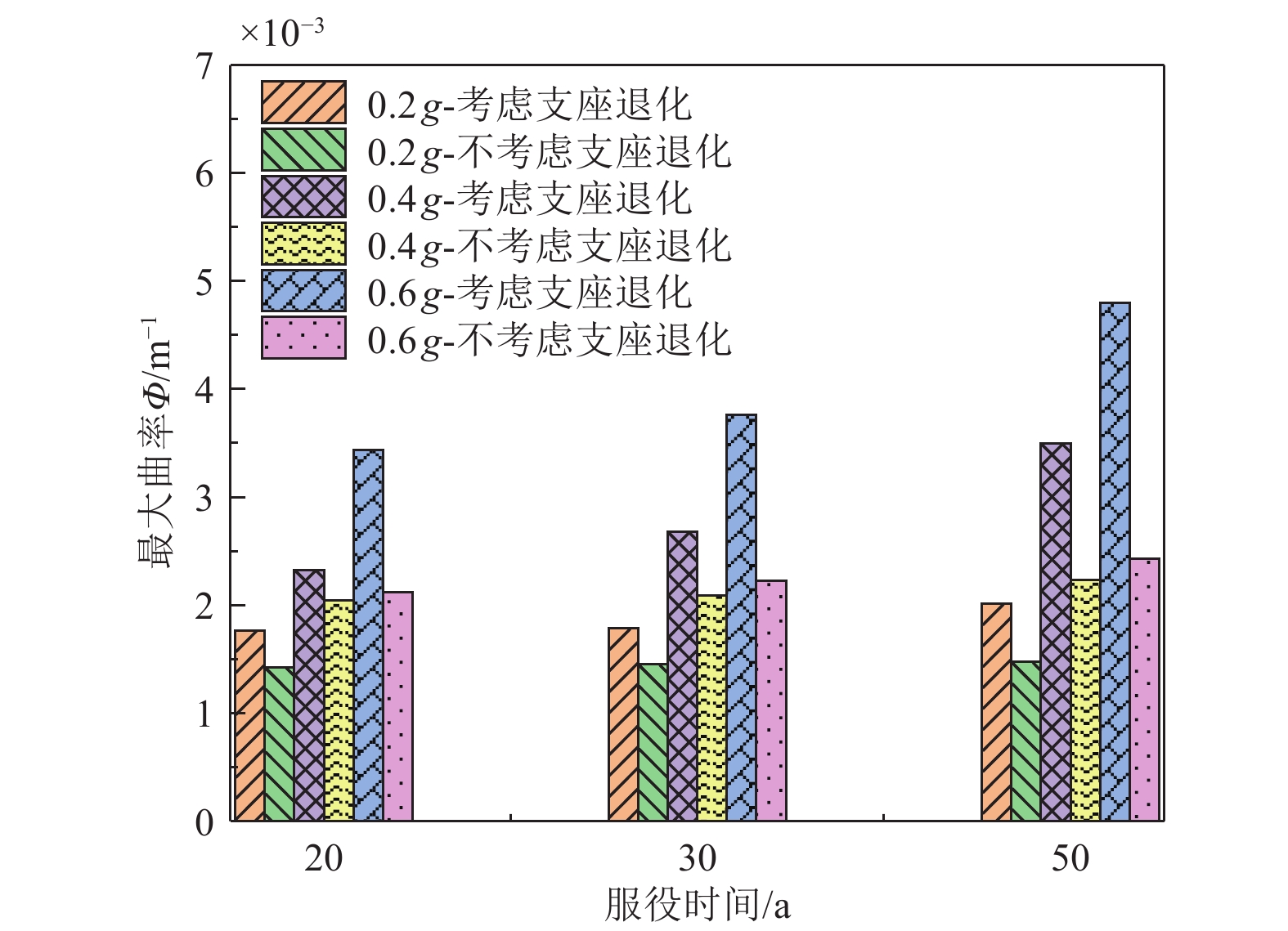
摘要: 构件材料性能会随服役时间的增加而退化,并导致桥梁结构抗震性能存在时变性。为探讨不同服役期下中小跨径桥梁抗震性能变化规律,以3跨预应力混凝土连续桥梁为例,通过分析材料力学性能指标时变性,量化不同服役期构件力学分析模型参数,并考虑桥墩、挡块及支座等构件力学性能退化,采用OpenSees软件建立桥梁有限元分析模型。基于非线性时程分析结果,揭示服役中小跨径桥梁横桥向地震响应时变性。研究结果表明,随着服役时间的增加,材料力学性能发生退化,使中小跨径桥梁各构件抗震能力下降;相同水平地震作用下,中小跨径桥梁主梁及挡块位移响应随服役时间的增加而降低,而桥墩损伤程度加剧,构件震害程度与不考虑构件力学性能时变性时相差较大,其中板式橡胶支座刚度及摩擦系数时变性是关键。因此,在服役中小跨径桥梁抗震分析中,有必要同时考虑桥墩、挡块及支座力学性能退化。Abstract: As the service time of bridge components increases, their material properties degrade, leading to a time-dependent reduction in the seismic performance of the bridge. To investigate the variation in seismic performance of small- and medium-span highway bridges over time, a finite element analysis (FEA) was conducted using a three-span prestressed concrete continuous girder bridge as a case study. This study quantifies the time-varying mechanical properties of components, such as piers, shear keys, and laminated rubber bearings, by incorporating degradation effects into a mechanical analysis model. The bridge FEA model was developed using OpenSees, accounting for the deterioration of key structural elements over time. The analysis reveals that, as service time increases, the degradation of material properties results in a reduced seismic capacity for various components. Under the same seismic event, the displacement response of the main girder and shear key decreases with time, while the damage to the piers becomes more severe. The seismic damage patterns of these components, when accounting for time-varying mechanical properties, differ significantly from those observed without considering such degradation. One critical finding is that the time-dependent variation in stiffness and friction coefficient of laminated rubber bearings plays a crucial role in the overall seismic response. Therefore, in the seismic analysis of small- and medium-span highway bridges, it is essential to consider the concurrent degradation of mechanical properties in piers, shear keys, and laminated rubber bearings to accurately assess their long-term seismic performance.
-
表 1 不同服役时间钢筋及混凝土强度
Table 1. Strength of rebar and concrete with different service time
项目 服役时间T/a 0(初始时间) 20 30 40 50 fy/MPa 335 334 332 329 325 fc/MPa 30.0 23.8 20.7 17.8 16.2 表 2 不同服役时间挡块强度
Table 2. Strength value of shear key with different service time
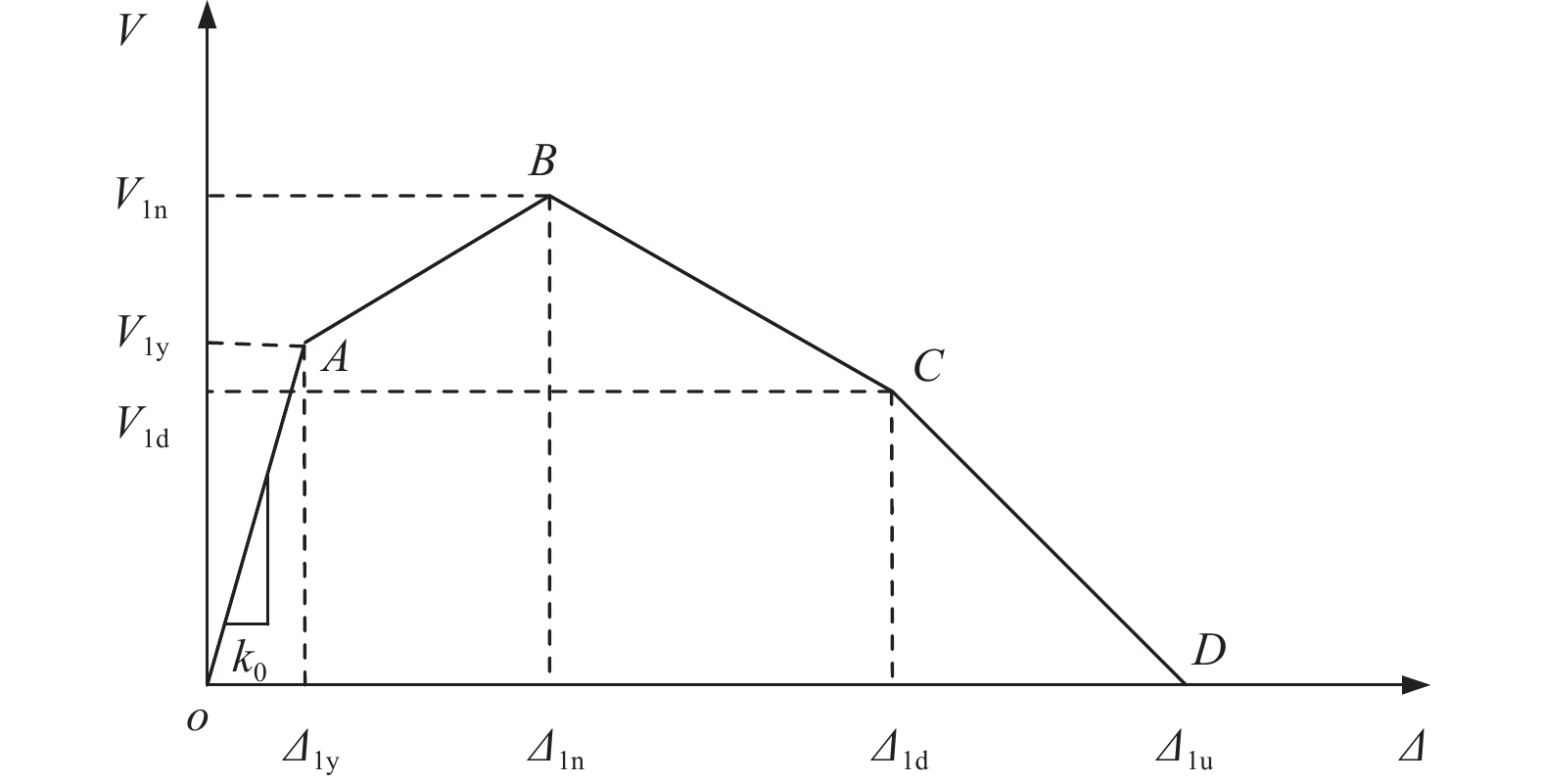
项目 强度/kN 服役0年 服役20年 服役30年 服役40年 服役50年 V1y(A点) 469.91 463.58 458.25 451.65 444.95 V1n(B点) 532.86 519.67 510.56 500.16 491.23 V1d(C点) 423.36 422.10 419.56 415.78 410.44 表 3 不同服役时间挡块位移
Table 3. Displacement value of shear key with different service time
项目 位移/mm 服役0年 服役20年 服役30年 服役40年 服役50年 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{y}}}} $(A点) 7.44 7.42 7.37 7.30 7.21 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{n}}}} $(B点) 17.5 17.5 17.5 17.5 17.5 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{d}}}} $(C点) 70.0 70.0 70.0 70.0 70.0 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{u}}}} $(D点) 117.70 117.70 116.35 115.50 113.75 表 4 不同服时间支座力学性能参数
Table 4. Mechanical property parameters of bearing at different service times
项目 服役时间T/a 0(初始时间) 10 20 30 40 50 剪切模量G/MPa 1.20 1.37 1.49 1.61 1.76 1.88 水平刚度K/MPa 1 293 1 792 2 247 2 914 3 471 3 707 摩擦系数μ 0.2 0.257 0.259 0.259 0.259 0.259 表 5 桥墩损伤状态划分
Table 5. Pier damage status division
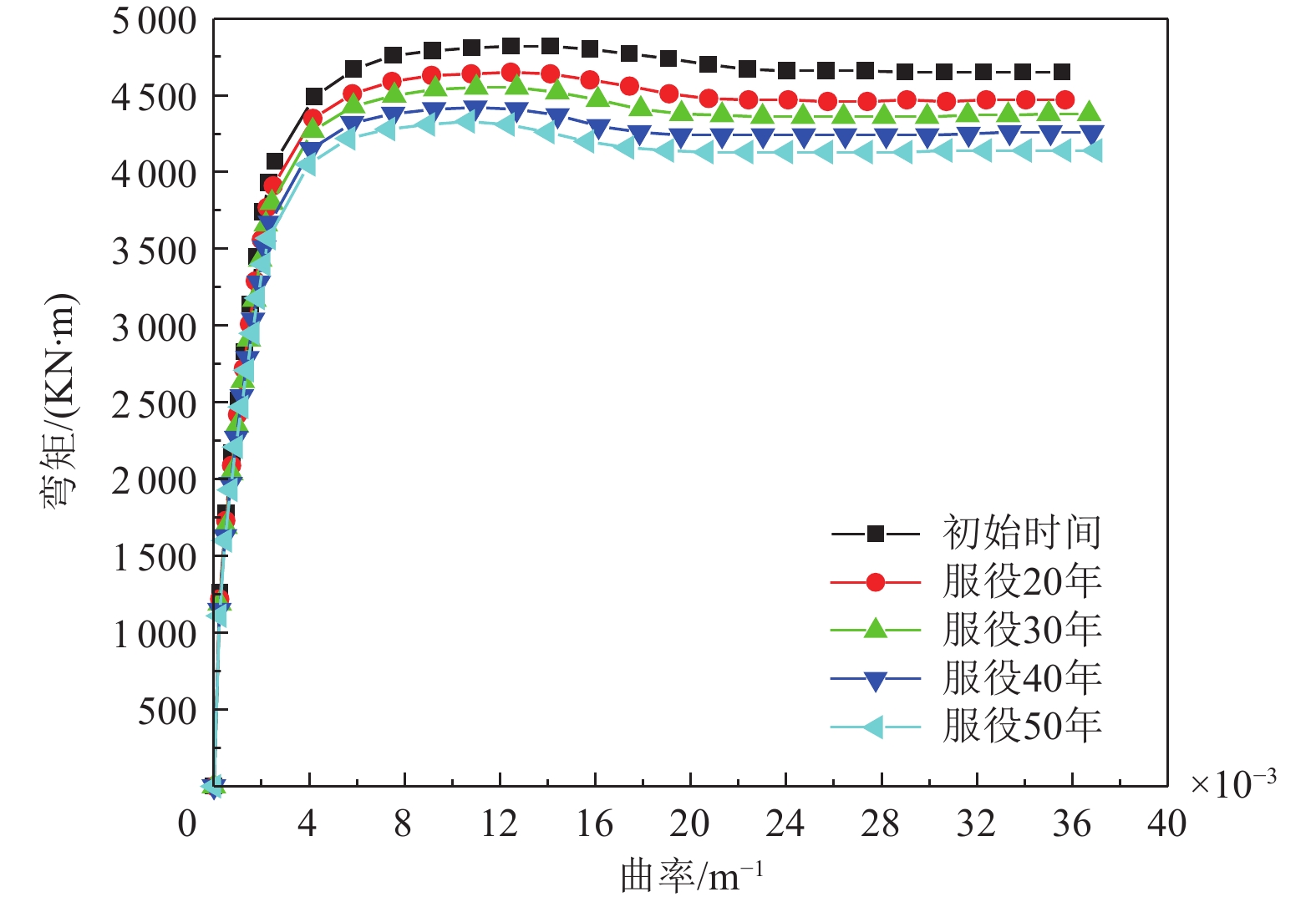
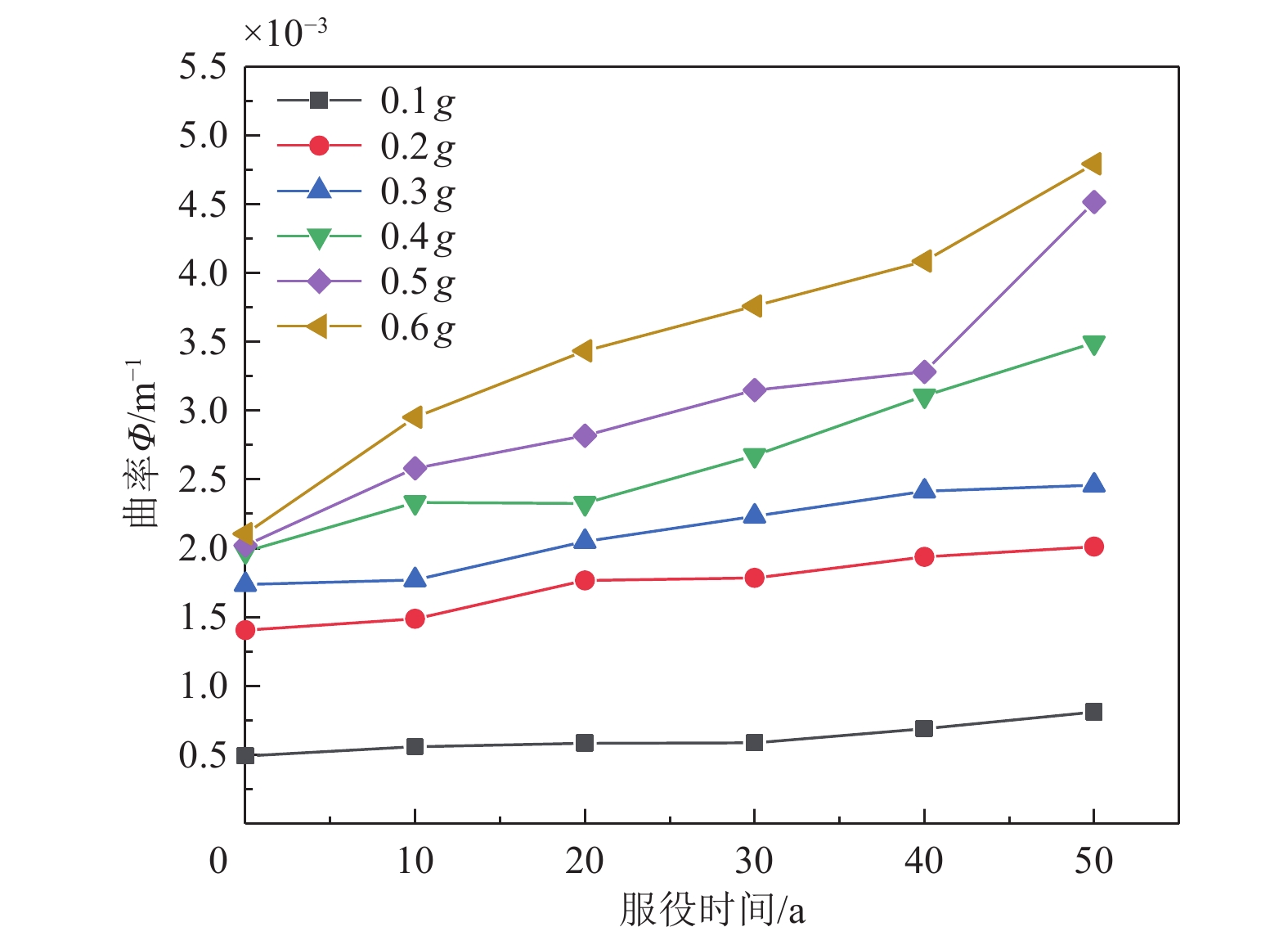
损伤状态 对应曲率/m−1 服役0年 服役20年 服役30年 服役40年 服役50年 无损伤 0≤Φ<1.28×10−3 0≤Φ<1.24×10−3 0≤Φ<1.21×10−3 0≤Φ<1.18×10−3 0≤Φ<1.15×10−3 轻微损伤 1.28×10−3≤Φ<2.14×10−3 1.24×10−3≤Φ<2.07×10−3 1.21×10−3≤Φ<2.03×10−3 1.18×10−3≤Φ<1.98×10−3 1.15×10−3≤Φ<1.95×10−3 中等损伤 2.14×10−3≤Φ<14.12×10−3 2.07×10−3≤Φ<13.24×10−3 2.03×10−3≤Φ<12.71×10−3 1.98×10−3≤Φ<10.96×10−3 1.95×10−3≤Φ<10.64×10−3 严重损伤 14.12×10−3≤Φ<35.58×10−3 13.24×10−3≤Φ<35.69×10−3 12.71×10−3≤Φ<36.72×10−3 10.96×10−3≤Φ<36.84×10−3 10.64×10−3≤Φ<36.95×10−3 完全破坏 Φ≥35.58×10−3 Φ≥35.69×10−3 Φ≥36.72×10−3 Φ≥36.84×10−3 Φ≥36.95×10−3 表 6 钢筋混凝土挡块损伤状态划分及判断准则
Table 6. Criterion for damage status division and judgment of reinforced concrete shear key
判断准则 损伤状态描述 损伤状态 $ \varDelta \leqslant {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{y}}}} $ 钢筋混凝土挡块出现细小裂缝,钢筋不发生屈服。 无损伤 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{y}}}}{\text{ < }}\varDelta \leqslant {\varDelta _{1{\text{n}}}} $ 细小裂缝扩大并连成一线,形成主裂缝,挡块内部部分钢筋发生屈服。 轻微损伤 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{n}}}}{\text{ < }}\varDelta \leqslant {\varDelta _{1{\text{d}}}} $ 主裂缝由上至下贯穿挡块,且裂缝宽度扩大,同时开始产生新的主裂缝。 中等损伤 $ {\varDelta _{1 {\mathrm{d}}}}{\text{ < }}\varDelta \leqslant {\varDelta _{1{\text{u}}}} $ 数条主裂缝贯穿挡块,且宽度较大,部分钢筋暴露,混凝土大面积破坏。 严重损伤 $ \varDelta {\text{ > }}{\varDelta _{1{\text{u}}}} $ 挡块位移明显,钢筋被拉断,挡块甚至完全脱落。 挡块破坏 -
陈嘉佳,马玉宏,黄金等,2020a. 基于天然橡胶支座老化时变规律下近海隔震桥梁时变易损性分析. 科学技术与工程,20(9):3699−3706.Chen J. J., Ma Y. H., Huang J., et al., 2020a. Time-dependent seismic fragility analysis of offshore bridges based on aging time-dependent law of rubber bearings. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(9): 3699−3706. (in Chinese) 陈嘉佳,马玉宏,黄金等,2020b. 基于橡胶隔震支座老化作用的近海隔震桥梁地震响应时变规律. 科学技术与工程,20(13):5247−5254.Chen J. J., Ma Y. H., Huang J., et al., 2020b. Termporal variation in seismic response of offshore isolated bridge due to aging effect of rubber isolation bearing. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(13): 5247−5254. (in Chinese) 董振华,张劲泉,韦韩等,2020. 老化普通板式橡胶支座的剪切性能研究. 工程力学,37(S1):208−216.Dong Z. H., Zhang J. Q., Wei H., et al., 2020. Study on shear performance of common plate rubber bearing in aged situation. Engineering Mechanics, 37(S1): 208−216. (in Chinese) 胡思聪,王连华,李立峰等,2019. 非一致氯离子侵蚀下近海桥梁时变地震易损性研究. 土木工程学报,52(4):62−71,97.Hu S. C., Wang L. H., Li L. F., et al., 2019. Time-dependent seismic fragility assessment of offshore bridges subject to non-uniform chloride-induced corrosion. China Civil Engineering Journal, 52(4): 62−71,97. (in Chinese) 江辉,谷琼,黄磊等,2021. 考虑氯离子侵蚀时变劣化效应的近海斜拉桥地震易损性分析. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),51(1):38−45.Jiang H., Gu Q., Huang L., et al., 2021. Analysis on seismic vulnerability of offshore cable-stayed bridge considering time-dependent deterioration by chloride-induced corrosion. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 51(1): 38−45. (in Chinese) 李超,李宏男,2014. 考虑氯离子腐蚀作用的近海桥梁结构全寿命抗震性能评价. 振动与冲击,33(11):70−77.Li C., Li H. N., 2014. Life-cycle aseismic performance evaluation of offshore bridge structures considering chloride ions corrosion effect. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 33(11): 70−77. (in Chinese) 李立峰,吴文朋,胡思聪等,2016. 考虑氯离子侵蚀的高墩桥梁时变地震易损性分析. 工程力学,33(1):163−170. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0530Li L. F., Wu W. P., Hu S. C., et al., 2016. Time-dependent seismic fragility analysis of high pier bridge based on chloride ion induced corrosion. Engineering Mechanics, 33(1): 163−170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0530 马玉宏,罗佳润,崔杰等,2016. 海洋环境下近海桥梁橡胶隔震支座性能劣化试验. 中国公路学报,29(2):52−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.02.007Ma Y. H., Luo J. R., Cui J., et al., 2016. Performance deterioration tests of rubber isolators for offshore bridges under marine environment. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 29(2): 52−61. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.02.007 孙颖,郑诚斌,卓卫东等,2021. 板式橡胶支座力学模型参数的时变特性研究. 振动与冲击,40(2):91−96.Sun Y., Zheng C. B., Zhuo W. D., et al., 2021. Time-varying properties of the mechanical model parameters of plate rubber bearings. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 40(2): 91−96. (in Chinese) 汤虎,李建中,邵长宇,2016. 中小跨径板式橡胶支座桥梁横向抗震性能. 中国公路学报,29(3):55−65.Tang H., Li J. Z., Shao C. Y., 2016. Seismic performance of small and medium span girder bridges with plate type elastomeric pad bearings in the transverse direction. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 29(3): 55−65. (in Chinese) 徐略勤,李建中,2016. 新型滑移挡块的设计、试验及防震效果研究. 工程力学,33(2):111−118,199. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0547Xu L. Q., Li J. Z., 2016. Design and experimental investigation of a new type sliding retainer and its efficacy in seismic fortification. Engineering Mechanics, 33(2): 111−118,199. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0547 杨国俊,叶苏,李喜梅,2023. 考虑氯离子侵蚀下的RC桥墩时变抗震韧性分析. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),51(8):60−66.Yang G. J., Ye S., Li X. M., 2023. Time-dependent seismic resilience analysis of RC bridge piers considering chloride induced erosion. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 51(8): 60−66. (in Chinese) 叶爱君,管仲国,2011. 桥梁抗震. 2版. 北京:人民交通出版社.Ye A. J., Guan Z. G., 2011. Seismic design of bridges. 2nd ed. Beijing:China Communication Press. (in Chinese) 周敉,张洋,姜永存等,2022. 氯离子侵蚀后桥墩的抗震性能及损伤指标研究. 振动与冲击,41(15):263−272.Zhou M., Zhang Y., Jiang Y. C., et al., 2022. Aseismic performance and damage index of pier after chloride ion erosion. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 41(15): 263−272. (in Chinese) 庄卫林,陈乐生,2013. 汶川地震公路震害分析:桥梁与隧道. 北京:人民交通出版社.Zhuang W. L., Chen L. S., 2013. Analysis of highway's damage in the Wenchuan earthquake:bridge and tunnel. Beijing:China Communications Press. (in Chinese) Coronelli D., Gambarova P., 2004. Structural assessment of corroded reinforced concrete beams: modeling guidelines. Journal of Structural Engineering, 130(8): 1214−1224. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2004)130:8(1214) Du Y. G., Clark L. A., Chan A. H. C., 2005. Residual capacity of corroded reinforcing bars. Magazine of Concrete Research, 57(3): 135−147. doi: 10.1680/macr.2005.57.3.135 Ghosh J., Padgett J. E., 2010. Aging considerations in the development of time-dependent seismic fragility curves. Journal of Structural Engineering, 136(12): 1497−1511. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000260 Itoh Y., Gu H. S., 2009. Prediction of aging characteristics in natural rubber bearings used in bridges. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 14(2): 122−128. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2009)14:2(122) Le Huy M. , Evrard G. , 1998. Methodologies for lifetime predictions of rubber using Arrhenius and WLF models. Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie, 261 −262 (1): 135−142. Li Y. M., Ma Y. H., Zhao G. F., et al., 2020. Experimental study on the effect of alternating ageing and sea corrosion on laminated natural rubber bearing’s tension-shear property. Journal of Rubber Research, 23(3): 151−161. doi: 10.1007/s42464-020-00045-9 Ma Y. H., Li Y. M., Zhao G. F., et al., 2019. Experimental research on the time-varying law of performance for natural rubber laminated bearings subjected to seawater dry-wet cycles. Engineering Structures, 195: 159−171. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.05.101 Zhao G. F., Ma Y. H., Li Y. M., et al., 2017. Development of a modified Mooney-Rivlin constitutive model for rubber to investigate the effects of aging and marine corrosion on seismic isolated bearings. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 16(4): 815−826. doi: 10.1007/s11803-017-0417-6 -




 下载:
下载: