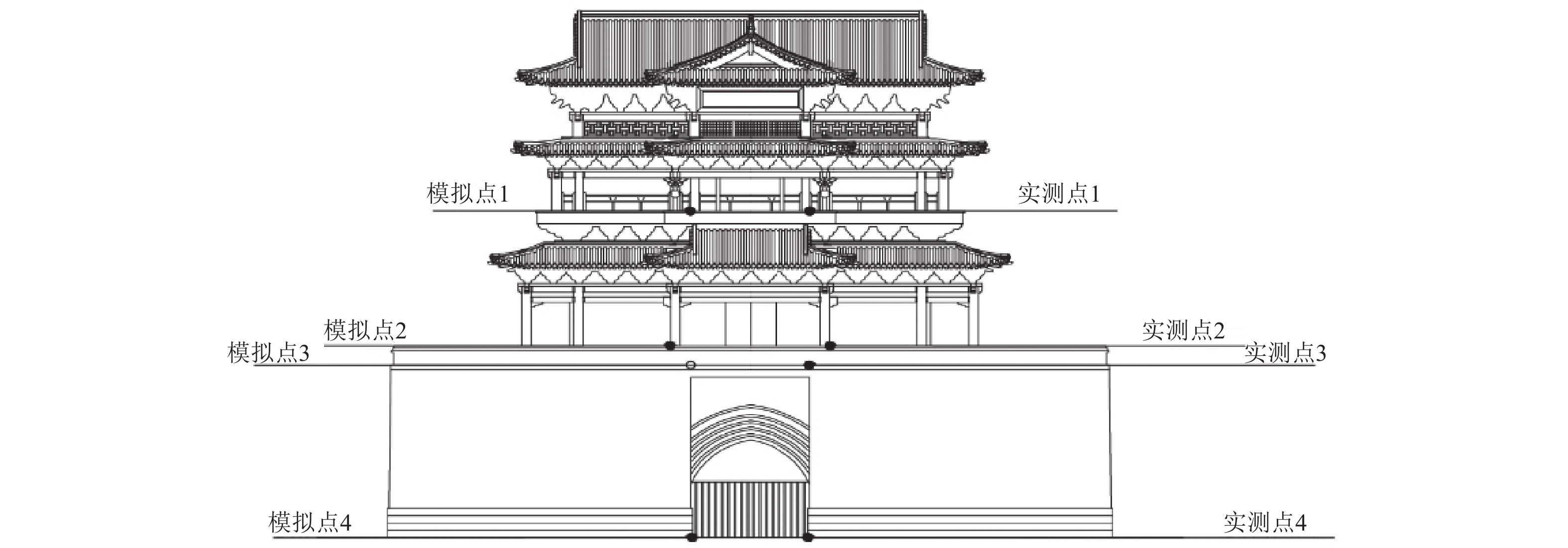
FSWT Technique in the Impact of Traffic Vibration on Qingyuan Building
-
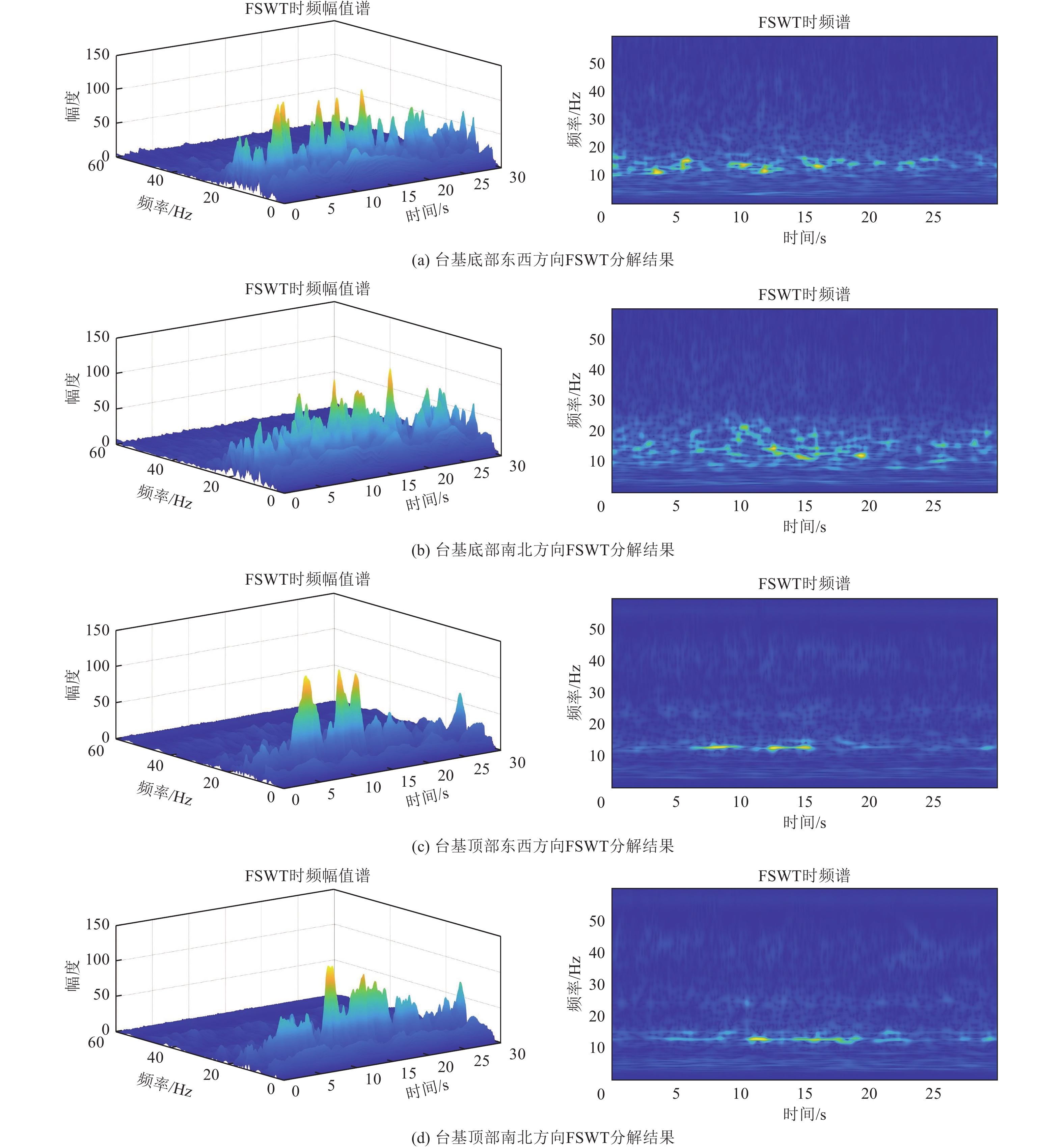
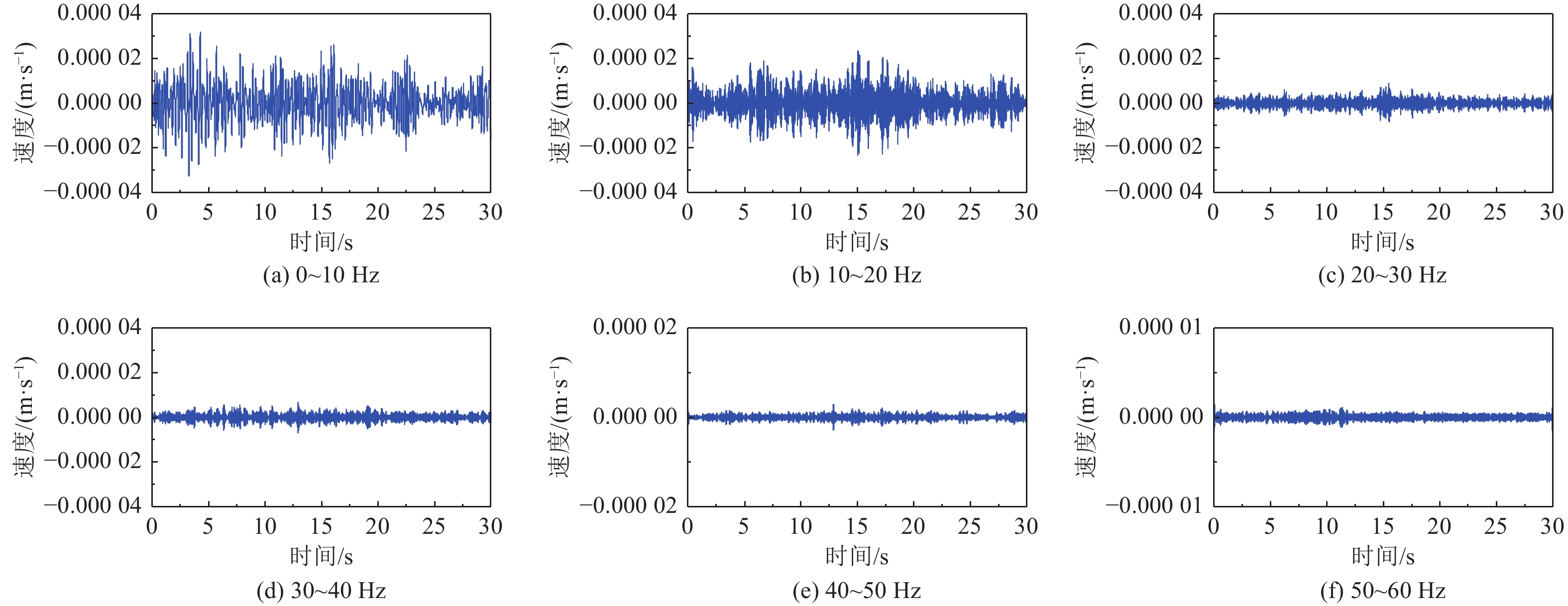
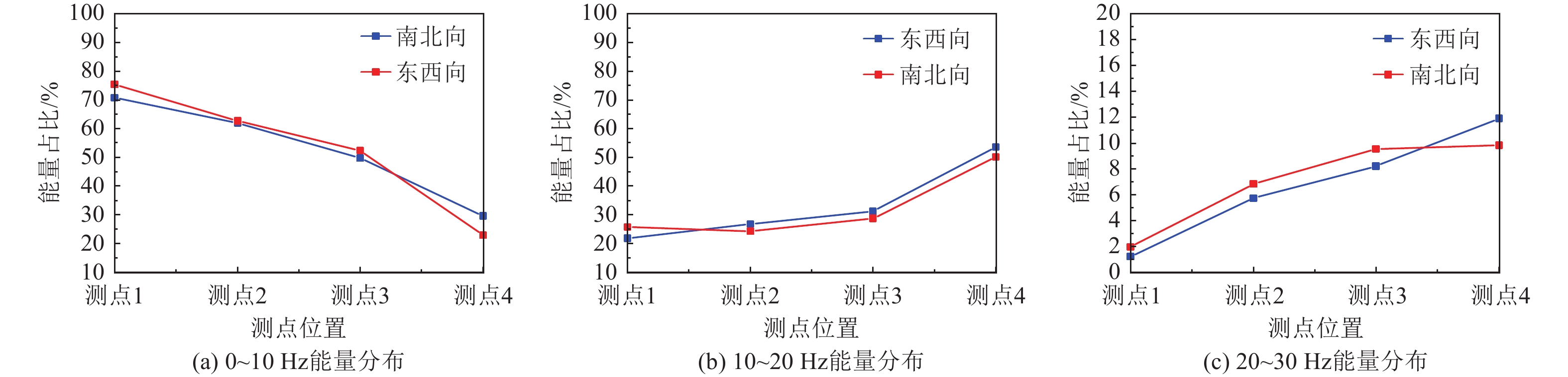
摘要: 交通振动对古建筑的结构健康和长期稳定性构成了潜在威胁,尤其在现代城市环境中,交通荷载频繁且多样化,因此引入了一种结合时域分析的频率切片小波变换(Frequency Slice Wavelet Transform, FSWT)分析法,系统的研究交通振动对古建筑的影响。首先,对清远楼进行了现场振动测试,采用时域分析对交通振动信号进行初步处理,获取振动响应的基本特性;通过FSWT分析法对信号进行详细的时频分析,揭示振动信号的频率特性及其随时间变化的规律,分解出各个频率成分在不同时间段的能量分布;最后,建立有限元模型,进一步验证其方法的可靠性。研究结果显示:以时频能量为参考值更能反映出振动信号的实际变化规律及结构最易受影响的位置,即交通振动在古建筑中的传播具有明显的层次特征,0~10 Hz频段的振动能量随着高度增加而逐渐增大,在10~20 Hz频段,振动能量主要集中在台基结构,且随着频率的升高,能量逐渐集中于台基底部。此外,分析结果还揭示了木结构与台基在动态响应中的差异,为交通振动对古建筑的影响分析及易损部位的识别提供了科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 交通振动 /
- 古建筑 /
- 时域分析 /
- 频率切片小波变换(FSWT) /
- 时频分析
Abstract: Traffic-induced vibrations present a potential risk to the structural health and long-term stability of ancient buildings, particularly in modern urban environments with frequent and variable traffic loads. In this study, a frequency slice wavelet transform (FSWT) method, combined with time-domain analysis, is employed to systematically investigate the effects of traffic vibrations on ancient structures. Vibration tests were first conducted on Qingyuan Tower, with time-domain analysis used to preprocess traffic vibration signals and extract the fundamental characteristics of the structural responses. FSWT was then applied for detailed time-frequency analysis, revealing the frequency content, time-varying behavior, and energy distribution of each frequency component over time. A finite element model was subsequently established to validate the reliability of the method. The results indicate that time-frequency energy provides a more accurate reflection of vibration variations and identifies regions most affected by traffic-induced vibrations. Specifically, the propagation of traffic vibrations exhibits a hierarchical pattern: energy in the 0~10 Hz range increases with height, while energy in the 10~20 Hz range is primarily concentrated in the base, and at higher frequencies, vibration energy becomes increasingly focused at the base. Moreover, the analysis highlights differences in dynamic responses between the wooden superstructure and the foundation, offering a scientific basis for assessing the impact of traffic vibrations on ancient buildings and identifying structurally vulnerable areas. -
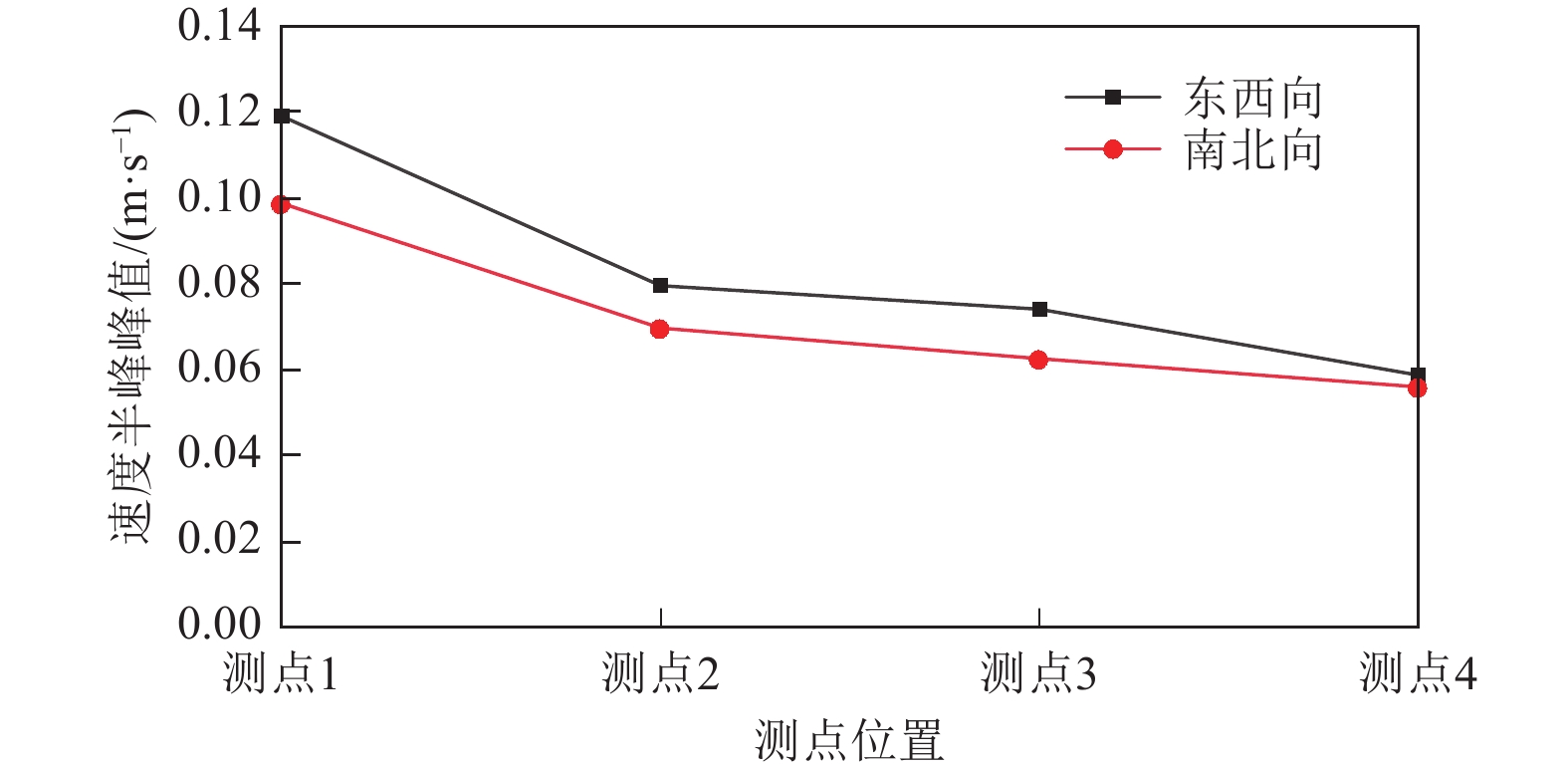
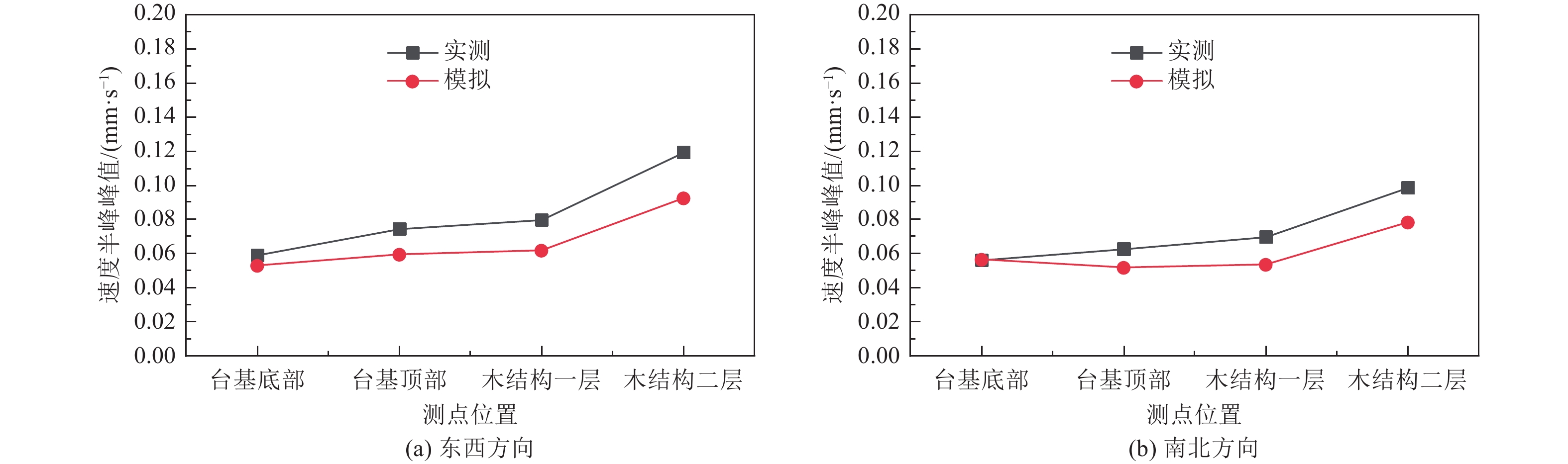
表 1 各测点振动速度半峰峰值
Table 1. Vibration velocity half-peak units at each measurement point
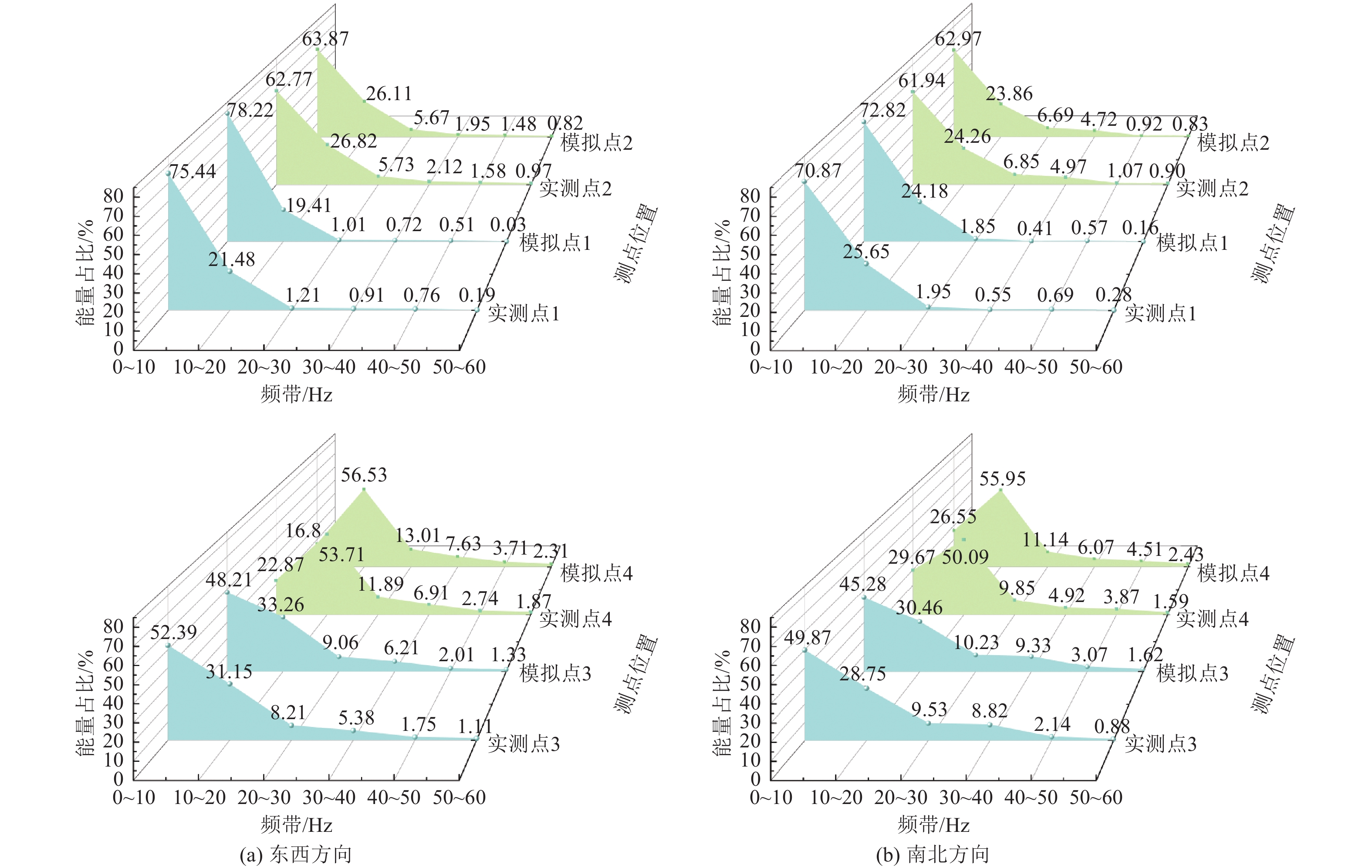
测点位置 速度半峰峰值(mm·s−1) 东西方向 南北方向 测点1 0.1192 0.0987 测点2 0.0794 0.0698 测点3 0.0742 0.0625 测点4 0.0589 0.0558 表 2 不同测点不同频带内能量分布比重对比(单位:百分比)
Table 2. Comparison of the weights of energy distribution in different frequency bands at different measurement points(Unit:%)
频带/Hz 测点1 测点2 测点3 测点4 东西 南北 东西 南北 东西 南北 东西 南北 0~10 75.44 70.87 62.77 61.94 52.39 49.87 22.87 29.67 10~20 21.48 25.65 26.82 24.26 31.15 28.75 53.71 50.09 20~30 1.21 1.95 5.73 6.85 8.21 9.53 11.89 9.85 30~40 0.91 0.55 2.12 4.97 5.38 8.82 6.91 4.92 40~50 0.76 0.69 1.58 1.07 1.75 2.14 2.74 3.87 50~60 0.19 0.28 0.97 0.90 1.11 0.88 1.87 1.59 表 3 清远楼木材参数设置
Table 3. Material parameter settings for Qingyuan building's timber
EL/MPa ER/MPa ET/MPa GRT/MPa GLR/MPa GLR/MPa μRT μLR μLT 12000 1200 800 600 800 400 0.4 0.35 0.3 注:EL 、ER 、ET分别是顺纹、径向和弦向的弹性模量;GRT、GLR、GLR分别是弦切面内、顺纹面内和径切面内的剪切模量;μRT、μLR、μLT分别是弦切面内、径切面内和顺纹面内的泊松比。利用ABAQUS中的ENGINEERING CONSTANT定义不同方向的弹性模量和泊松比。 表 4 清远楼台基参数设置
Table 4. Parameter settings for Qingyuan building's pedestal
材料 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 夯土 2720 80 0.2 表 5 榫卯、斗拱节点参数设置
Table 5. Parameter settings of mortise and tenon joints and bracket sets
节点类型 kx/(kN·m−1) ky/(kN·m−1) kz/(kN·m−1) kθ/(kN·m·rad−1) 榫卯 ∞ 1.26×109 1.26×109 7 362 ×109斗拱 2 197.3 2 197.3 127 950 296.71 注:kx、ky、kz分别为x、 y、z轴方向拉伸弹簧的刚度系数;kθ为弯曲弹簧的刚度系数。 表 6 土体参数设置
Table 6. Parameter settings for soil
土层 厚度/m 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/(kg·m−3) 泊松比 黏聚力/Pa 摩擦角/(°) 填土层 3 1900 12 0.29 21.2 22 粉土层 6 1660 15 0.25 15.5 22.1 圆砾层 6 1890 80 0.2 23 38 粉砂层 10 1790 14 0.25 25 28 卵石层 7 1940 90 0.2 0 40 黏土层 8 1930 25.4 0.3 30 18.5 表 7 清远楼前4阶频率及周期
Table 7. The first four order frequencies and periods of Qingyuan building
振型阶数 频率/Hz 圆频率/(rad·s−1) 周期/s 1 0.8618 5.412 1.160 2 1.0135 6.365 0.987 3 1.3058 8.200 0.766 4 2.7554 17.304 0.363 -
巴振宁, 符瞻远, 付继赛等. 2023. 地铁列车振动对颐和园北宫门古建筑木结构影响的实测与分析. 振动工程学报, 36(6): 1602−1612.Ba Z. N., Fu Z. Y., Fu J. S., et al., 2023. Measurement and analysis of the influence of metro train vibration on the ancient wooden structures of North Palace Gate of the Summer Palace. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 36(6): 1602−1612. (in Chinese) 杜昕然, 吴筱荣, 2018. 浅析宣化清远楼建筑艺术特征. 中国民族博览, (22): 186−187. 高润东, 蒋利学, 王春江等, 2015. 基于等效斜压杆理论的RC框架填充墙承载力计算方法研究. 结构工程师, 31(5): 37−41. doi: 10.15935/j.cnki.jggcs.2015.05.007Gao R. D., Jiang L. X., Wang C. J., et al., 2015. Development capacity calculation method for RC frames with infilled walls based on the equivalent diagonal strut theory. Structural Engineers, 31(5): 37−41. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15935/j.cnki.jggcs.2015.05.007 郭涛, 方向, 谢全民等, 2013. 频率切片小波变换在爆破振动信号时频特征精确提取中应用. 振动与冲击, 32(22): 73−78.Guo T., Fang X., Xie Q. M., et al., 2023. Application of FSWT in accurate extraction of time-frequency features for blasting vibration signals. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 32(22): 73−78. (in Chinese) 李广振, 宗刚, 张斌等, 2015. 地铁与地面车辆引发振动的时频特征比较研究. 土木工程, 4(1): 8−17. doi: 10.12677/HJCE.2015.41002Li G. Z., Zong G, Zhang B., et al., 2015. Comparative study on time-frequency characteristic of the vibration induced by underground subway and road vehicle. Hans Journal of Civil Engineering, 4(1): 8−17. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12677/HJCE.2015.41002 刘喜武, 张宁, 勾永峰等, 2008. 地震勘探信号时频分析方法对比与应用分析. 地球物理学进展, 23(3): 743−753.Liu X. W., Zhang N., Gou Y. F., et al., 2008. The comparison and application of time-frequency analysis methods to seismic signal. Progress in Geophysics, 23(3): 743−753. (in Chinese) 刘玉桥, 邓红卫, 吴路波等, 2020. 基于VMD联合小波阈值去噪法的微震监测信号去噪研究. 矿业研究与开发, 40(2): 98−103. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2020.02.018Liu Y. Q., Deng H. W., Wu L. B., et al., 2020. Study on signal denoising of microseismic monitoring based on combined variational mode decomposition and wavelet threshold method. Mining Research and Development, 40(2): 98−103. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2020.02.018 倪伟杰, 潘志宏, 2020. 基于等效弹簧斜撑的填充墙RCS组合框架结构抗震性能研究. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版), 34(1): 111−118.Ni W. J., Pan Z. H, 2020. Research on seismic performance of infilled wall RCS composite structure based on equivalent spring struts. Journal of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 34(1): 111−118. (in Chinese) 王坤, 李凌均, 郝旺身等, 2023. 全矢FSWT方法在轴承故障诊断中的应用. 机械设计与制造, (12): 205−208.Wang K., L L. J., Hao W. S., et al., 2023. Application of full vector frequency slice wavelet transform method in bearing fault diagnosis. Machinery Design & Manufacture, (12): 205−208. (in Chinese) 袁玉卿, 张弦, 樊兴伟, 2022. 道路交通振动对开封城墙的影响. 噪声与振动控制, 42(6): 192−197, 246.Yuan Y. Q., Zhang X., Fan X. W., 2022. Influence of traffic vibration on Kaifeng ancient wall. Noise and Vibration Control, 42(6): 192−197,246. (in Chinese) 查文华, 洪宝宁, 徐毅, 2007. 交通荷载下路面振动响应信号的时频特征分析. 工程抗震与加固改造, 29(4): 105−109. doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2007.04.003Zha W. H., Hong B. N., Xu Y., 2007. Time-frequency characteristic analysis of pavement vibration response signals under traffic loadings. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 29(4): 105−109. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2007.04.003 赵国彦, 邓青林, 马举, 2015. 基于FSWT时频分析的矿山微震信号分析与识别. 岩土工程学报, 37(2): 306−312.Zhao G. Y., Deng Q. L., Ma J., 2015. Recognition of mine microseismic signals based on FSWT time-frequency analysis. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 37(2): 306−312. (in Chinese) 朱利明, 王成龙, 蓝天等, 2018. 地铁运行引起的南京鼓楼振动测试与分析. 建筑结构学报, 39(S1): 291−296. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2018.S1.038Zhu L. M., Wang C. L., Lan T., et al., 2018. Vibration test and analysis of Nanjing drum tower caused by metro operation. Journal of Building Structures, 39(S1): 291−296. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2018.S1.038 Biswal B., Mishra S., 2014. Power signal disturbance identification and classification using a modified frequency slice wavelet transform. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 8(2): 353−362. Liu X. L., Jiang Z. W., Yan Z. H., 2012. Improvement of accuracy in damage localization using frequency slice wavelet transform. Shock and Vibration, 19(4): 585−596. doi: 10.1155/2012/174563 Sheng Z. P., Xu Y. G., Zhang K., 2021. Applications in bearing fault diagnosis of an improved Kurtogram algorithm based on flexible frequency slice wavelet transform filter bank. Measurement, 174: 108975. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.108975 Yan Z. H., Miyamoto A., Jiang Z. W., 2009. Frequency slice wavelet transform for transient vibration response analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 23(5): 1474−1489. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2009.01.008 Yan Z. H., Miyamoto A., Jiang Z W., et al., 2010. An overall theoretical description of frequency slice wavelet transform. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 24(2): 491−507. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2009.07.002 -




 下载:
下载: