Study of Dynamic Interaction of Pile Foundation Frame Structures in Sloping Sites
-
摘要: 为研究缓倾斜坡场地中桩基框架结构间结构-土-结构动力相互作用特性,使用ABAQUS软件建立系列结构-土-结构二维有限元分析模型,考虑土-结构非线性特性,在0°~15°设置6种坡度条件,对缓倾斜坡场地中的建筑开展非线性有限元数值分析。结果表明:(1)相较于相邻建筑物,斜坡坡角对结构间峰值加速度的影响更大;(2)斜坡在放大坡上结构地震动响应的同时缩小了坡下结构的地震动响应;(3)相邻建筑物对基础各单桩顶的峰值剪力响应有较大影响,而对桩顶总剪力的影响不大,在水平或缓倾斜坡场地中SSSI效应均导致了结构桩顶剪力重分布现象。本研究可为实际工程中普遍存在的斜坡场地下结构的抗震设计提供理论参考。
-
关键词:
- 缓倾斜坡场地 /
- 相邻建筑物 /
- 结构-土-结构相互作用 /
- 有限元分析 /
- 非线性特性
Abstract: To investigate the dynamic interaction characteristics of structure–soil–structure systems between pile-supported frame structures on gently sloping sites, a series of two-dimensional finite element models were developed using ABAQUS. These models incorporated the nonlinear behavior of both soil and structures and were analyzed under six slope conditions ranging from 0° to 15°. The nonlinear finite element analyses yielded the following key findings: (1) slope angle has a significant impact on the peak acceleration experienced between adjacent structures; (2) slopes amplify the ground motion response of structures located on the slope while reducing the response of structures situated at the slope base; (3) neighboring buildings notably affect the peak shear response at individual pile tops but have minimal influence on the total shear force of the piles. On horizontal or gently inclined slopes, the structure–soil–structure interaction (SSSI) effect leads to a redistribution of shear forces at pile tops. These results provide a theoretical basis for the seismic design of structures on sloped sites, which are common in practical engineering applications. -
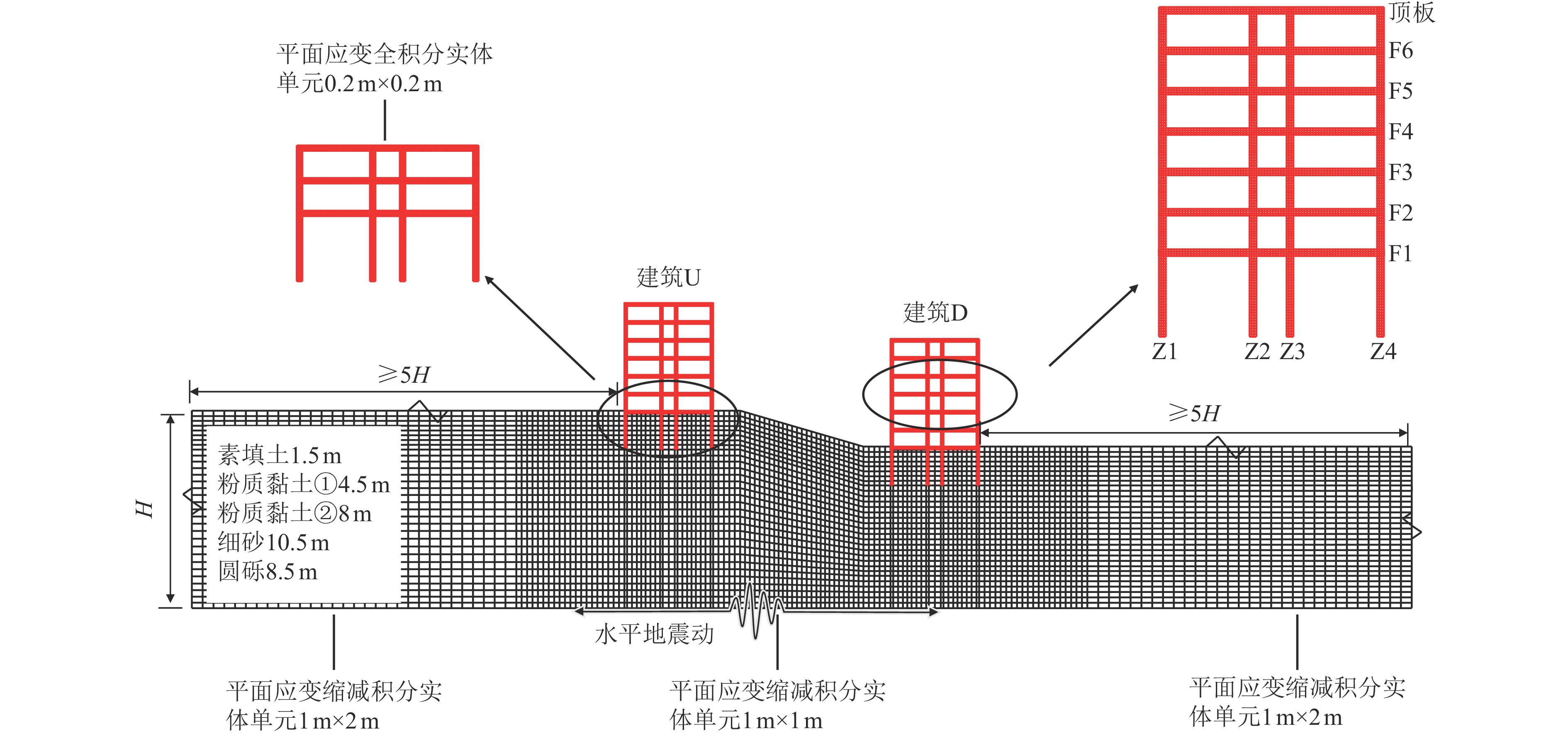
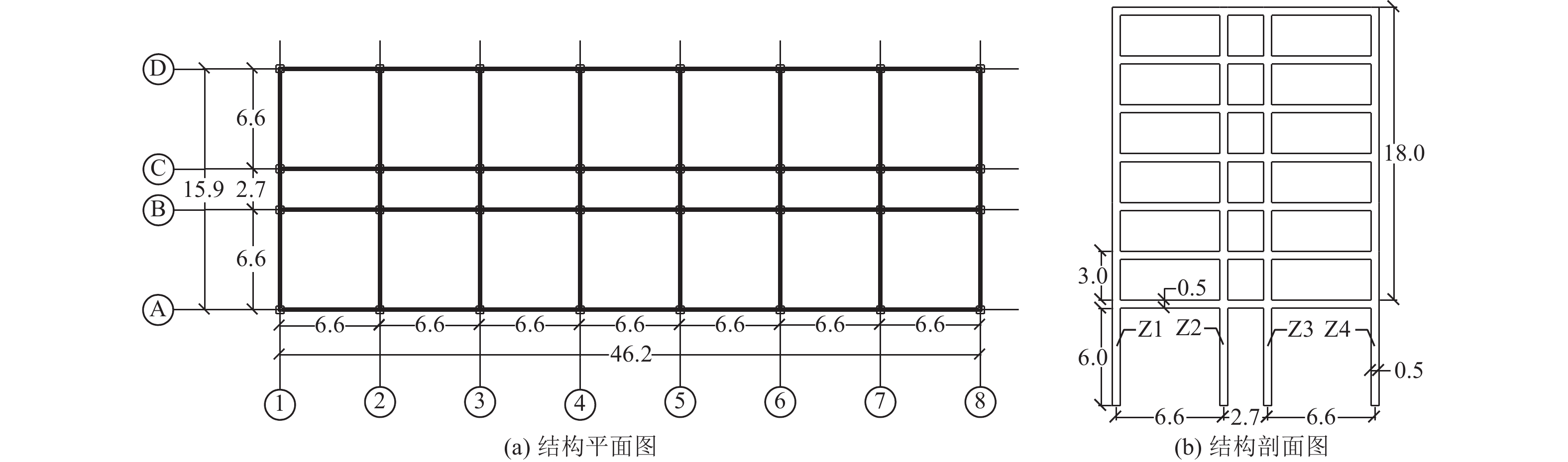
表 1 场地土模型信息
Table 1. Site soil model information
土体名称 厚度/m 密度ρ/(t·m−3) 剪切波速VS/(m·s−1) 内摩擦角φ/(o) 动态泊松比μ 素填土 1.5 1.88 130 8 0.49 粉质黏土① 4.5 1.92 218 13 0.49 粉质黏土② 8 1.97 220 17 0.49 细砂 10.5 1.98 400 25 0.49 圆砾 8.5 2.15 478 35 0.49 表 2 工况布置
Table 2. Working condition arrangement
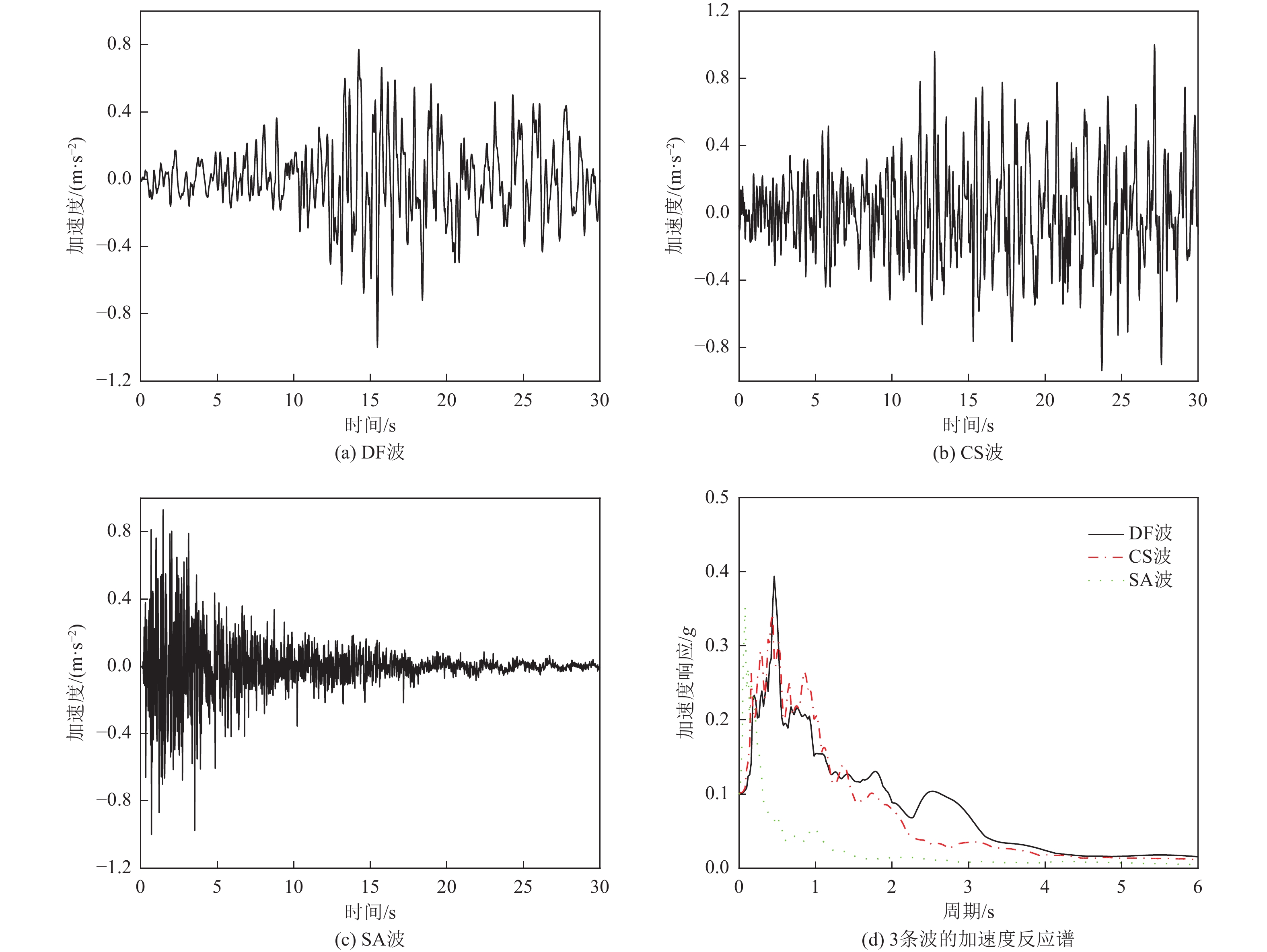
序号 斜坡坡度 相邻建筑物 地震波类型 1 (0°,A) (0°,U)(0°,D) DF 波
CS 波
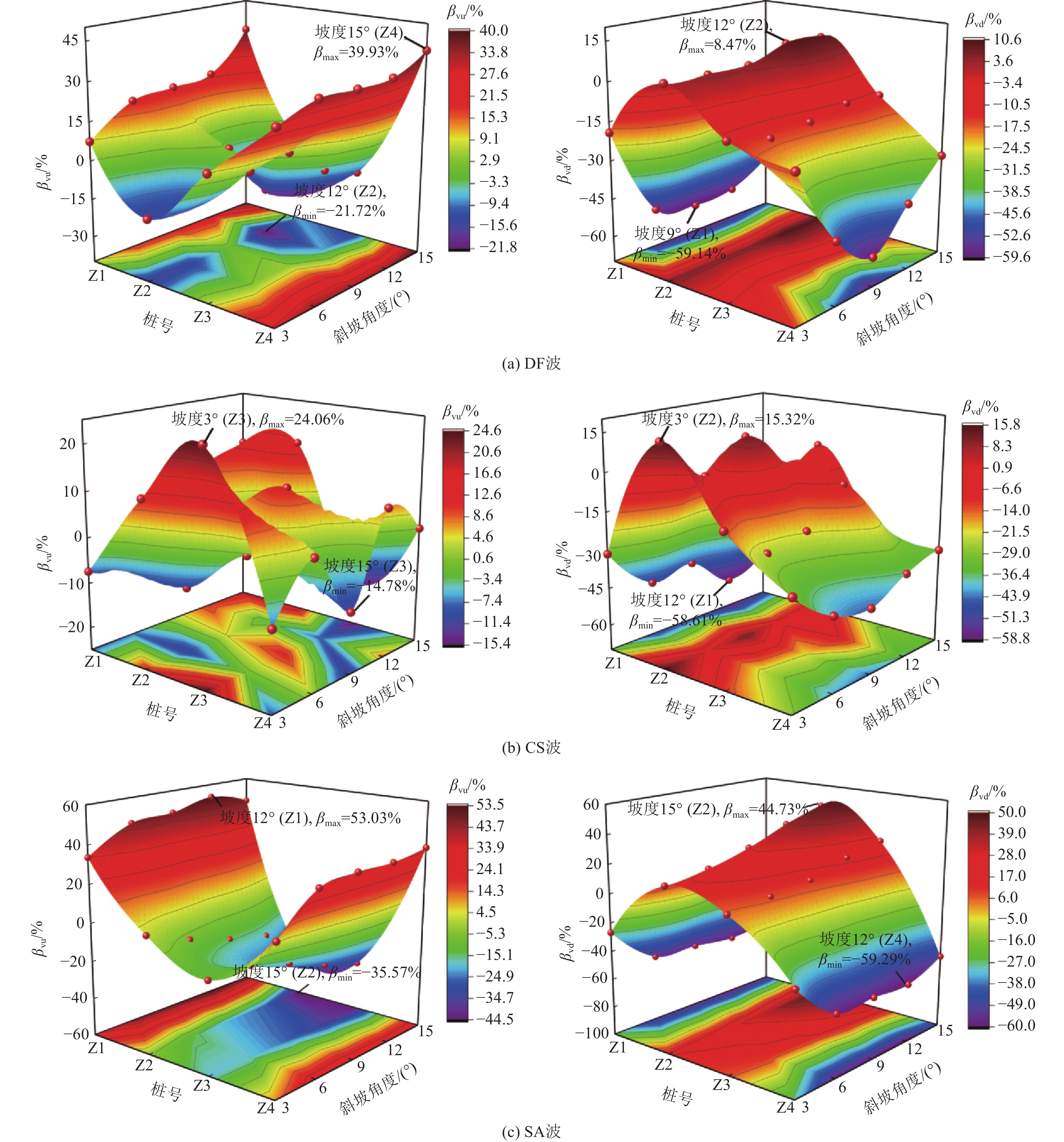
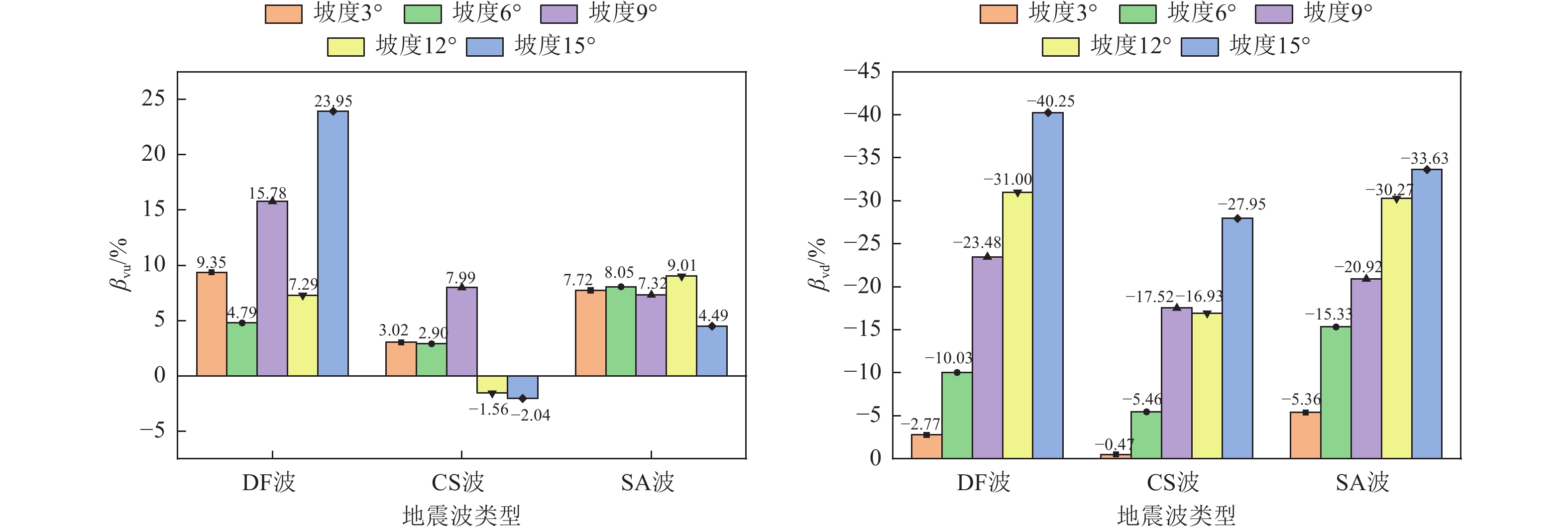
SA 波2 (3°,A) (3°,U)(3°,D) 3 (6°,A) (6°,U)(7°,D) 4 (9°,A) (9°,U)(9°,D) 5 (12°,A) (12°,U)(12°,D) 6 (15°,A) (15°,U)(15°,D) 表 3 相邻建筑物对坡上结构峰值加速度影响系数JAU(单位:百分比)
Table 3. Influence coefficient(JAU)of adjacent buildings on peak acceleration of structure located up the slope(Unit: %)
位置 DF波 CS波 SA波 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 顶板 −1.672 −0.888 −1.003 −0.165 −0.785 −0.218 −0.849 0.339 0.191 0.226 −0.479 −0.268 −0.765 0.017 −0.349 −0.795 0.486 −1.229 F6 −0.991 −1.003 −0.667 −0.119 −0.467 −0.144 −1.448 0.454 0.682 0.428 −0.306 −0.003 −0.871 −0.305 −0.794 −0.719 −0.565 −0.520 F5 −0.791 −0.820 −0.385 −0.649 −0.901 −0.236 −0.031 −0.638 −0.975 0.380 −0.113 1.051 −0.372 −3.889 −1.212 0.541 −1.274 −1.146 F4 0.661 0.965 0.666 1.457 1.502 −0.394 −0.890 −0.822 −1.193 −1.016 −0.507 0.813 −0.011 −0.118 0.075 −0.789 0.484 −0.640 F3 0.275 0.284 −0.362 0.826 1.048 0.630 −2.490 −0.999 −0.971 −2.161 −0.810 1.417 −0.956 −0.283 0.411 −0.313 −1.487 −0.017 F2 −3.330 −0.703 −1.717 −1.740 −0.686 0.882 −3.508 −0.919 −1.841 −1.227 −1.886 −1.507 −1.161 −0.888 1.871 1.196 −1.677 0.839 F1 −5.233 −1.200 2.238 −1.054 2.682 −5.450 −2.663 −0.690 −2.674 −2.915 −4.082 −4.143 −0.284 2.890 1.699 1.094 2.302 4.850 表 4 相邻建筑物对坡下结构峰值加速度影响系数JAD(单位:百分比)
Table 4. Influence coefficient(JAD) of adjacent buildings on peak acceleration of structure located down the slope(Unit: %)
位置 DF波 CS 波 SA 波 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 顶板 −1.796 −0.380 −0.409 −0.396 0.329 0.193 0.319 0.911 1.202 1.030 1.051 2.468 −0.601 0.908 −1.926 −0.953 2.000 3.600 F6 −0.693 −0.485 −0.624 −0.217 −0.066 −0.019 −0.687 0.664 1.589 0.114 1.157 0.807 −0.879 −0.996 −3.260 −1.835 −1.483 −0.632 F5 −0.747 −0.106 −1.102 0.117 0.063 0.268 0.778 −0.690 −0.546 −0.181 0.034 −0.833 −0.291 1.919 −1.005 −0.995 −2.117 −3.170 F4 1.059 −0.624 0.543 0.744 1.894 3.208 −0.321 −0.147 −0.624 0.308 0.564 −0.105 0.344 −0.490 −0.664 0.258 −0.116 0.991 F3 0.212 −0.827 0.467 0.135 −0.455 −0.519 −1.431 −0.845 −0.006 0.749 −0.082 0.768 0.312 −0.690 −2.966 −0.997 −1.524 −0.294 F2 −3.451 −4.506 −2.373 −3.422 −4.963 −6.466 −3.148 −2.856 −1.912 −2.713 −3.202 −2.411 −0.863 −0.594 −2.189 2.825 −1.416 0.014 F1 −0.321 −2.736 −0.007 1.385 3.860 3.309 −2.087 −2.494 −2.889 −0.173 −1.428 −2.522 −0.457 −0.219 −2.358 2.880 0.875 3.841 表 5 相邻建筑物对坡上结构峰值剪力影响系数JVU(单位:百分比)
Table 5. Influence coefficient(JVU)of adjacent buildings on peak shear force of structure located up the slope(Unit: %)
位置 DF波 CS 波 SA 波 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° Z1 9.293 −9.893 0.187 −3.022 −2.480 −0.522 13.372 −11.191 −12.749 −6.188 14.220 1.069 −15.442 6.558 0.736 1.127 3.566 1.940 Z2 15.357 −14.251 −18.560 −5.993 −15.259 11.422 8.316 −5.002 −14.643 −9.715 0.178 22.125 −3.664 2.100 −5.038 1.180 4.789 −2.649 Z3 −1.515 5.288 3.729 −2.249 16.191 0.164 3.362 18.227 −16.165 −11.074 5.764 −6.920 7.180 0.787 3.629 2.443 −0.497 −0.117 Z4 −8.920 14.472 6.384 −1.509 −1.557 −5.450 6.595 −0.882 3.087 −7.289 13.180 3.232 8.343 1.113 4.630 −1.605 −0.491 1.511 总计 −8.051 3.285 −9.665 2.263 −5.432 2.741 2.517 0.615 −0.588 −1.309 −2.912 −12.041 −0.068 1.267 0.299 0.579 3.090 2.295 表 6 相邻建筑物对坡下结构峰值剪力影响系数JVD(单位:百分比)
Table 6. Influence coefficient(JVD)of adjacent buildings on peak shear force of structure located down the slope(Unit: %)
位置 DF波 CS 波 SA 波 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° 0° 3° 6° 9° 12° 15° Z1 14.010 6.448 7.421 12.248 −8.277 −4.301 −3.768 −11.889 −13.958 6.236 −2.025 0.883 4.059 6.249 16.873 15.062 18.175 −7.537 Z2 1.710 −3.765 5.212 0.909 4.831 2.246 6.226 27.548 0.993 20.724 −3.814 −0.485 −1.070 5.207 8.598 1.418 4.259 5.101 Z3 −0.395 0.098 5.456 1.891 2.744 −1.641 −2.674 −6.232 −14.057 7.613 3.320 −10.918 2.906 −3.345 0.603 0.547 2.428 0.398 Z4 −0.117 −0.278 1.881 −1.450 −7.489 −1.400 −1.506 −15.916 2.740 0.086 5.069 −7.276 18.656 4.024 5.777 13.110 −0.415 −2.774 总计 0.590 −8.556 2.509 −1.826 −1.540 −0.619 0.272 6.385 −0.244 −0.624 12.004 5.931 3.469 −4.861 3.805 3.504 0.639 2.739 -
庄海洋, 陈国兴, 2009. 对土体动力黏塑性记忆型嵌套面模型的改进. 岩土力学, 30(1): 118−122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.019Zhuang H. Y., Chen G. X., 2009. Improvement of dynamic viscoplastic memorial nested yield surface model of soil. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 30(1): 118−122. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.019 Alitalesh M., Shahnazari H., Baziar M. H., 2018. Parametric study on seismic topography–soil–structure interaction; topographic effect. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 36(4): 2649−2666. doi: 10.1007/s10706-018-0489-8 Ba Z. N., Pei Y. F., Yu F. X., et al., 2024. A semi-analytical approach for site-city interaction under oblique incident SH waves. Structures, 68: 107057 doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2024.107057 Bararpour M., Janalizade A., Tavakoli H. R., 2016. The effect of 2D slope and valley on seismic site response. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(2): 93. doi: 10.1007/s12517-015-2039-5 Brennan A. J., Madabhushi S. P. G., 2009. Amplification of seismic accelerations at slope crests. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 46(5): 585−594. doi: 10.1139/T09-006 Chen S. P., Zhai C. H., Liu Q. F., et al., 2023. Assessing the influence of nonlinear soil behaviour on site-city interaction. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 171: 107973. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.107973 Erfani A., Ghanbari A., Massumi A., 2021. Seismic behaviour of structures adjacent to slope by considering SSI effects in cemented soil mediums. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 15(1): 2−14. doi: 10.1080/19386362.2019.1681817 Fatahi B., Huang B. H., Yeganeh N., et al., 2020. Three-dimensional simulation of seismic slope–foundation–structure interaction for buildings near shallow slopes. International Journal of Geomechanics, 20(1): 04019140. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001529 Lee J., Fenves G. L., 1998. Plastic-damage model for cyclic loading of concrete structures. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 124(8): 892−900. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1998)124:8(892) Long H., Wang Z. C., Zhang C. S., et al., 2021. Nonlinear study on the structure-soil-structure interaction of seismic response among high-rise buildings. Engineering Structures, 242: 112550. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112550 Madany M., Guo P. J., 2021. Structure–soil–structure interaction analysis for lateral seismic earth pressure of deeply buried structure in layered ground. International Journal of Geomechanics, 21(11): 04021217. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002189 Shabani M. J., Shamsi M., Ghanbari A., 2021a. Dynamic response of three-dimensional midrise buildings adjacent to slope under seismic excitation in the direction perpendicular to the slope. International Journal of Geomechanics, 21(11): 04021204. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002158 Shabani M. J., Shamsi M., Ghanbari A., 2021b. Seismic response of RC moment frame including topography–soil–structure interaction. Practice Periodical on Structural Design and Construction, 26(4): 04021046. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SC.1943-5576.0000625 Shamsi M., Shabani M. J., Zakerinejad M., et al., 2022. Slope topographic effects on the nonlinear seismic behavior of groups of similar buildings. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 51(10): 2292−2314. Sucasaca J., Sáez E., 2021. Topographical and structure-soil-structure interaction effects on dynamic behavior of shear-wall buildings on coastal scarp. Engineering Structures, 247: 113113. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113113 Wang H. F., Lou M. L., Chen X., et al., 2013. Structure–soil–structure interaction between underground structure and ground structure. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 54: 31−38. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.07.015 Yamamoto Y., Baker J. W., 2013. Stochastic model for earthquake ground motion using wavelet packets. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 103(6): 3044−3056. doi: 10.1785/0120120312 Yan L., Long H., Liu S. W., et al., 2020. Analysis on influence of adjacent buildings on mutual seismic acceleration response. E3S Web of Conferences, 165: 04055. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202016504055 Zhang N., Gao Y. F., Yang J., et al., 2015. An analytical solution to the scattering of cylindrical SH waves by a partially filled semi-circular alluvial valley: near-source site effects. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 14(2): 189−201. doi: 10.1007/s11803-015-0016-3 -



 下载:
下载: