Quaternary Sedimentary Characteristics and Environmental Evolution in Chizhou Area, Anhui Province
-
摘要: 长江下游河谷地区拥有丰富的第四纪沉积记录,反映了复杂的古环境变化。利用钻孔地层开展沉积特征研究,对于揭示研究区第四纪沉积环境演化有着重要意义。本研究基于池州地区的6个钻孔资料,综合分析了研究区第四纪沉积相及环境演化过程,提供了全面的第四纪沉积环境变化参考模型。研究表明,该地区经历了新构造活动及复杂的气候变化,在河谷区形成“芜湖组+青弋江组”的地层组合;在丘陵地区形成“下蜀组+戚家矶组”的地层组合。第四纪沉积环境经历了早更新世至中更新世中期温暖湿润气候下的高地残坡积物与冲洪积物堆积阶段;中更新世晚期至晚更新世期间全球气候变化明显,总体趋于寒冷干燥,导致河流活动和沉积特征显著变化;全新世以来,受海平面波动影响,形成了具有不同粒级的沉积物堆积阶段。通过对池州地区第四纪河流相、洪积相、风成相等沉积环境的系统研究,发现该区沉积环境由早更新世温暖湿润阶段向中更新世寒冷干燥转变,中晚更新世期间气候波动频繁,以冷干与暖湿交替旋回为特征,直至全新世的温暖、湿润气候。Abstract: The lower Yangtze River Valley preserves abundant Quaternary sedimentary records that offer valuable insights into complex paleoenvironmental changes. Borehole stratigraphy plays a vital role in characterizing these sedimentary sequences and reconstructing the evolution of the Quaternary depositional environment in the region. Drawing upon data from six boreholes in the Chizhou area, this study conducts a comprehensive analysis of Quaternary sedimentary facies and environmental evolution, aiming to establish a reference model for understanding regional Quaternary sedimentary dynamics. The findings suggest that the Chizhou region experienced significant neotectonic activity and climatic fluctuations, which collectively influenced the development of distinct stratigraphic sequences. In the plains, a "Wuhu Formation + Qingyijiang Formation" sequence predominates, while in the hilly areas, the stratigraphy is characterized by the "Xiashu Formation + Qijiaji Formation." During the early to middle Pleistocene, warm and humid climatic conditions favored the formation of high-altitude residual slope deposits and alluvial fan accumulations. In contrast, from the late Middle Pleistocene to the Late Pleistocene, global climatic shifts led to intensified river activity and changes in sedimentary characteristics, with an overall trend toward cooler and drier conditions. The Holocene to the present day is marked by variable sedimentation processes influenced by sea level fluctuations, resulting in the deposition of materials with varying grain sizes. Systematic analysis of fluvial, alluvial, and aeolian facies in the Chizhou area reveals a clear environmental transition: from the warm, humid conditions of the early Pleistocene to the colder, drier environment of the middle Pleistocene. This was followed by frequent alternations between cold-dry and warm-humid phases during the Late Pleistocene. The Holocene is characterized by a return to relatively stable warm and humid climatic conditions.
-
Key words:
- Sedimentary characteristics /
- Sedimentary facies /
- Quaternary /
- Environmental evolution /
- Chizhou area
-
图 1 研究区地理位置与大地构造位置图(张文佑,1983)
Figure 1. Geographical and tectonic location of the study area(Zhang,1983)
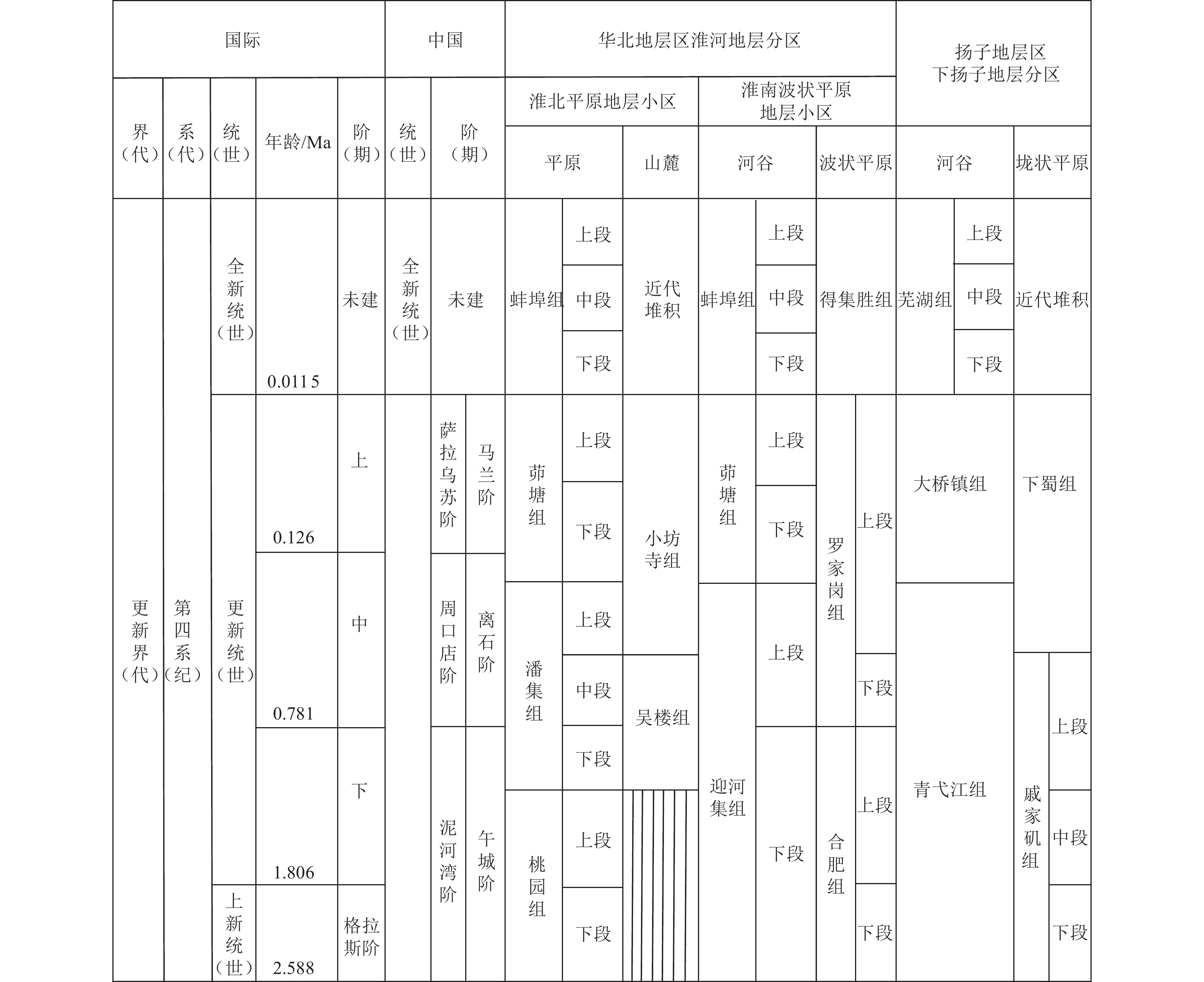
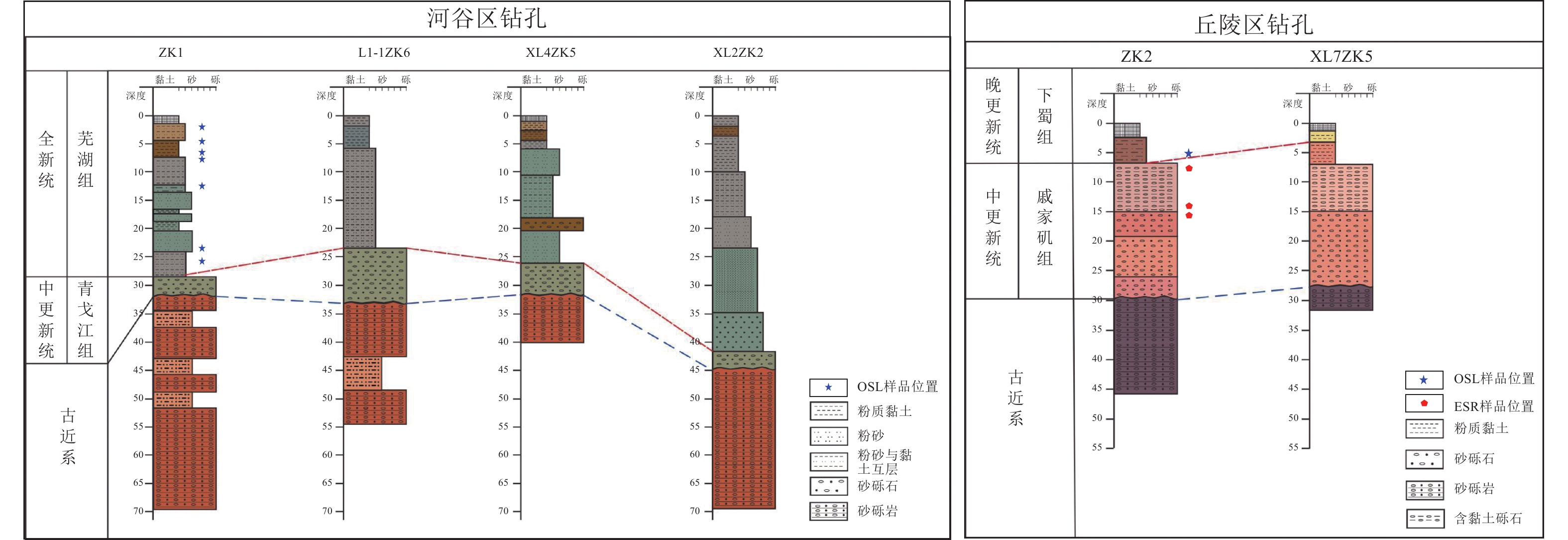
图 2 安徽省第四纪岩石地层与中国和国际地层年代对比(于振江等,2008)
Figure 2. Comparison of Quaternary rock stratigraphy in Anhui province with Chinese and International stratigraphic chronology (Yu et al., 2008)
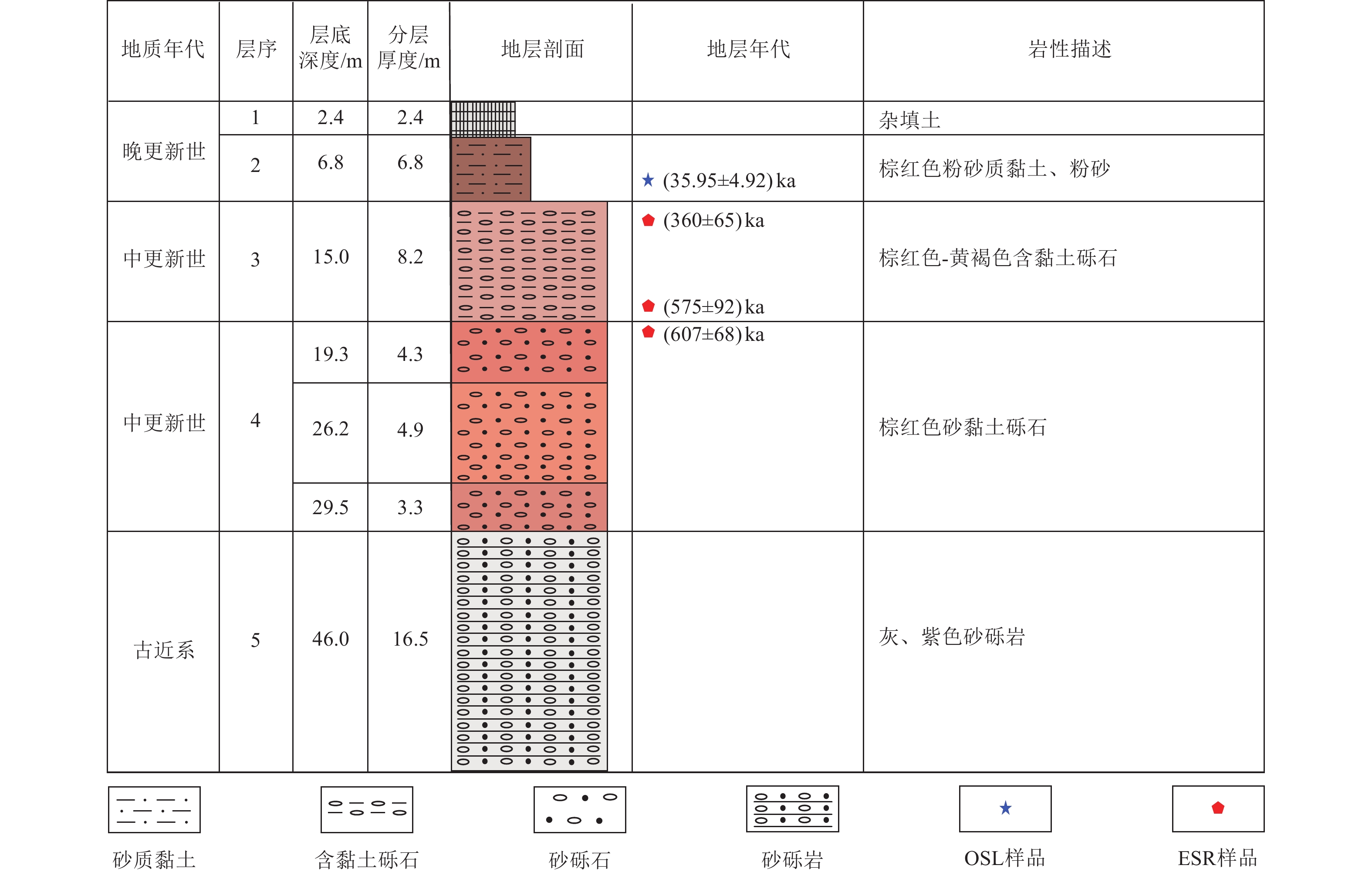
表 2 池州市跨断层钻孔样品ESR 年龄及其参数
Table 2. Electron spin resonance ages and the parameters of cross-fault borehole samples in Chizhou city
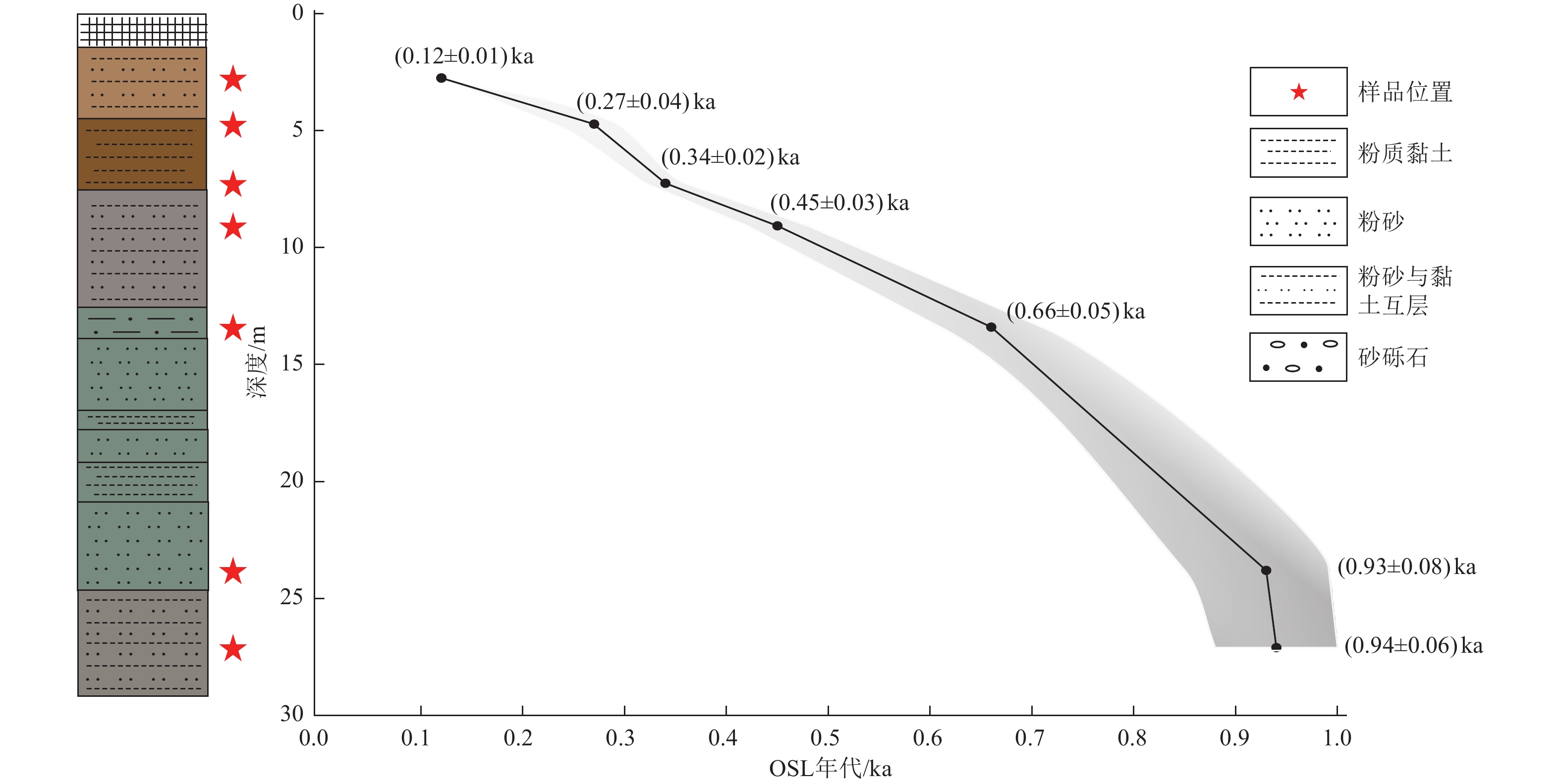
野外编号 样品物质 深度/m 含水量/% 等效剂量/Gy 剂量率/(Gy·ka−1) 年龄/ka ZCZK2-ESR-B2 含黏土砾石 7.05 17±5 930±168 2.58±0. 13 360±65 ZCZK2-OSL-8 含黏土砾石 13.10 21±5 1874±301 3.26±0.16 575±92 ZCZK2-OSL-9 砂黏土砾石 16.70 8±5 2178 ±2433.59±0.18 607±68 -
安徽省地质矿产局,1987. 安徽省区域地质志. 北京:地质出版社.Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Anhui Province,1987. Regional geology of Anhui Province. Beijing:Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) 陈立德,邵长生,2014. 江汉−洞庭盆地下更新统地层划分与对比−−“白沙井砾石层”再研究. 地层学杂志,38(2):208−219.Chen L. D., Shao C. S., 2014. The subdivision and correlation of the Pleistocene in the JiangHan-DongTing Basin: restudy on the “Baishanjjing gravel layer”. Journal of Stratigraphy, 38(2): 208−219. (in Chinese) 程星宇,朱晓雨,蒲阳等,2023. 长江下游地区中更新世下蜀黄土沉积的古气候意义. 热带地理,43(6):1049−1058.Cheng X. Y., Zhu X. Y., Pu Y., et al., 2023. Xiashu Loess deposits in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River and their paleoclimatic significance. Tropical Geography, 43(6): 1049−1058. (in Chinese) 方鸿琪,1959. 长江中下游地区的新构造运动. 地质学报,(3):328−343. 郭炳跃,王毅,张斌等,2020. 安徽池州地区下蜀组沉积环境及成因探讨. 华东地质,41(1):18−26.Guo B. Y., Wang Y., Zhang B., et al., 2020. The sedimentary environment and genesis analysis of the Xiashu formation in the Chizhou area, Anhui Province. East China Geology, 41(1): 18−26. (in Chinese) 郭汝军,魏传义,李长安等,2023. 长江演化百年谜题:回溯与进展. 地震地质,45(1):1−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.01.001Guo R. J., Wei C. Y., Li C. A., et al., 2023. A centennial puzzle of the evolution of the Yangtze River: retrospection and progresses. Seismology and Geology, 45(1): 1−28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.01.001 胡晨琦,胡春生,刘永婷等,2017. 青弋江泾县段最高阶地的ESR年代及其构造气候意义. 山地学报,35(4):469−476.Hu C. Q., Hu C. S., Liu Y. T., et al., 2017. ESR dating and tectonic-climate significance of topmost terrace of Qingyijiang River in Jingxian County. Mountain Research, 35(4): 469−476. (in Chinese) 胡春生,2017. 黄山北麓青弋江河流阶地发育机制与河流演化特征研究. 南京:南京大学.Hu C. S., 2017. Developmental mechanism of river terraces and evolutional characteristics of the Qingyijiang River on the northern fringe of Mt. Huangshan. Nanjing:Nanjing University. (in Chinese) 胡春生,田景梅,何成邦等,2021. 黄山北麓青弋江发育原因及其与长江贯通的关系. 地理科学,41(10):1862−1872.Hu C. S., Tian J. M., He C. B., et al., 2021. Development causes of the Qingyijiang River on the northern piedmont of the Huangshan Mountain and its relationship with the channelization of the Yangtze River. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 41(10): 1862−1872. (in Chinese) 黄恒旭,向芳,王金元等,2018. 三峡及邻区第四纪沉积与地貌特征对古气候的指示. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),45(4):459−467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2018.04.06Huang H. X., Xiang F., Wang J. Y., et al., 2018. Quaternary sedimentary and geomorphic features in the Three Gorges and its adjacent area, implication for paleoclimate. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 45(4): 459−467. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2018.04.06 蒋复初,吴锡浩,肖华国等,1997. 九江地区网纹红土的时代. 地质力学学报,3(4):27−32.Jiang F. C., Wu X. H., Xiao H. G., et al., 1997. Age of the vermiculated red soil in Jiujiang area, central China. Journal of Geomechanics, 3(4): 27−32. (in Chinese) 李从先,陈庆强,范代读等,1999. 末次盛冰期以来长江三角洲地区的沉积相和古地理. 古地理学报,1(4):12−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.1999.04.002Li C. X., Chen Z. Q., Fan D. D., et al., 1999. Palaeogeography and palaeoenvironment in Changjiang Delta since last glaciation. Journal of Palaeogeography, 1(4): 12−25. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.1999.04.002 李徐生,杨达源,鹿化煜,1999. 皖南风尘堆积序列氧化物地球化学特征与古气候记录. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,19(4):75−82.Li X. S., Yang D. Y., Lu H. Y., 1999. Oxide-geochemistry features and paleoclimatic record of the Aeolian-dust depositional sequence in southern Anhui. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 19(4): 75−82. (in Chinese) 李徐生,杨达源,2002. 镇江下蜀黄土-古土壤序列磁化率特征与环境记录. 中国沙漠,22(1):27−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2002.01.006Li X. S., Yang D. Y., 2002. Magnetic susceptibility features and environmental records of the Xiashu Loess in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province. Journal of Desert Research, 22(1): 27−32. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2002.01.006 李增学,2010. 岩相古地理. 北京:地质出版社.Lin Z. Y., Jin X. L., Guan M. L., et al., 2019. Quaternary sedimentary sequence of the southern Yangtze River Delta and its coupling with paleoenvironmental evolution. Science Technology and Engineering,19(13):15−24. (in Chinese) 刘春茹,尹功明,高璐等,2011. 第四纪沉积物ESR年代学研究进展. 地震地质,33(2):490−498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.022Liu C. R., Yin G. M., Gao L., et al., 2011. Research advances in ESR geochronology of Quaternary deposits. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 490−498. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.022 刘华国,李峰,贾启超等,2023. 琼北地区铺前−清澜断裂北段的全新世活动新证据. 煤田地质与勘探,51(12):38−46. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0750Liu H. G., Li F., Jia Q. C., et al., 2023. New evidence for Holocene activity of the northern segment of the Puqian-Qinglan fault in northern Hainan Province. Coal Geology & Exploration, 51(12): 38−46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0750 邵家骥,1999. 苏南及沿江地区柏山组、下蜀组的时代及成因. 江苏地质,23(1):10−16.Shao J. J., 1999. Time and genesis of Baishan and Xiashu formations along the Yangtze River and south Jiangsu. Jiangsu Geology, 23(1): 10−16. (in Chinese) 宋方敏,邓志辉,马晓静等,2008. 长江谷地安庆−马鞍山段新构造和断裂活动特征. 地震地质,30(1):99−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.007Song F. M., Deng Z. H, Ma X. J., et al., 2008. Neotectonics and fault activity in the Anqing-Ma'anshan section of the Changjiang River valley. Seismology and Geology, 30(1): 99−110. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.007 苏晶文,龚建师,李运怀等,2019. 基于地层结构组合的第四纪地质单元划分研究−−以皖江经济带沿江丘陵平原区为例. 中国地质调查,6(5):28−35.Su J. W., Gong J. S., Li Y. H., et al., 2019. Division of Quaternary geological units based on stratigraphic architecture combination: a case study in Wanjiang River economic zone. Geological Survey of China, 6(5): 28−35. (in Chinese) 王旭龙,李晓妮,卢演俦,2004. 红光固体二极管点阵在释光测年中的光照应用. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,24(1):133−137.Wang X. L., Li X. N., Lu Y. C., 2004. Red led and its application to luminescence lighting. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 24(1): 133−137. (in Chinese) 王毅,郭炳跃,郭东峰等,2023. 长江安庆段河谷区第四系沉积特征与古河道演化. 华东地质,44(3):300−312.Wang Y., Guo B. Y., Guo D. F., et al., 2023. Quaternary sedimentary characteristics and paleochannel evolution in the Anqing valley of the Yangtze River. East China Geology, 44(3): 300−312. (in Chinese) 吴利杰,张翼龙,石建省等,2019. 河套盆地第四纪沉积古地理特征及演化. 干旱区资源与环境,33(8):135−145.Wu L. J., Zhang Y. L., Shi J. S., et al., 2019. Quaternary sedimentary paleogeography characteristics and evolution of Hetao Basin. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(8): 135−145. (in Chinese) 向芳,朱利东,王成善等,2005. 长江三峡阶地的年代对比法及其意义. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),32(2):162−166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2005.02.011Xiang F., Zhu L. D., Wang C. S., et al., 2005. Terrace age correlation and its significance in research of Yangtze Three Gorges, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 32(2): 162−166. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2005.02.011 严庠生,杨达源,1991. 安徽沿江地带的新构造运动与地震活动. 地震学刊,11(1):101−107.Yan X. S., Yang D. Y., 1991. On neotectonic movement and earthquakes along the Yangtze River region in Anhui Province. Journal of Seismology, 11(1): 101−107. (in Chinese) 杨立辉,2017. 长江中下游地区第四纪红土沉积特征与成因机制研究. 上海:华东师范大学.Yang L. H., 2017. The study of sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of the Quaternary red clay in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Shanghai:East China Normal University. (in Chinese) 杨献忠,魏乃颐,王强等,2010. 长江三角洲镇江−江都河段古河谷沉积特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,30(5):11−18.Yang X. Z., Wei N. Y., Wang Q., et al., 2010. Sedimentary characteristics of an ancient river channel in Zhenjiang-Jiangdu segment of Yangtze River Delta. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 30(5): 11−18. (in Chinese) 杨勇,2008. 巢湖地区下蜀土沉积环境及气候意义. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉).Yang Y., 2008. The sedimentary environments and climatic significance of Xiashu Loess in Chaohu area. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). (in Chinese) 于振江,黄多成,1996. 安徽省沿江地区网纹红土和下蜀土的形成环境及其年龄. 安徽地质,6(3):48−56.Yu Z. J., Huang D. C., 1996. Formation environment of net veined laterite and Xiashu Loess and their ages in the area along the Yangtze River, Anhui Province. Geology of Anhui, 6(3): 48−56. (in Chinese) 于振江,彭玉怀,2008. 安徽省第四纪岩石地层序列. 地质学报,82(2):254−261. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.02.011Yu Z. J., Peng Y. H., 2008. Quaternary lithostratigraphic sequence in Anhui Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(2): 254−261. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.02.011 张文佑,1983. 中国及邻区海陆大地构造图. 北京:科学出版社. Aitken M. J. , 1998. An introduction to optical dating: the dating of Quaternary sediments by the use of photon-stimulated luminescence. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 39−50. Wu X. W., Wang L., Ta L., et al., 2024. Fluvial landscape change in Anqing through the last glacial cycle: implications for eustatic controls on the Yangtze River's continental-scale incision-aggradation cycles. Quaternary Science Reviews, 333: 108689. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2024.108689 -




 下载:
下载: