A New Discovered Buried Active Fault Zone in the Wulashan Piedmont Basin—Sanhu Fault Zone
-
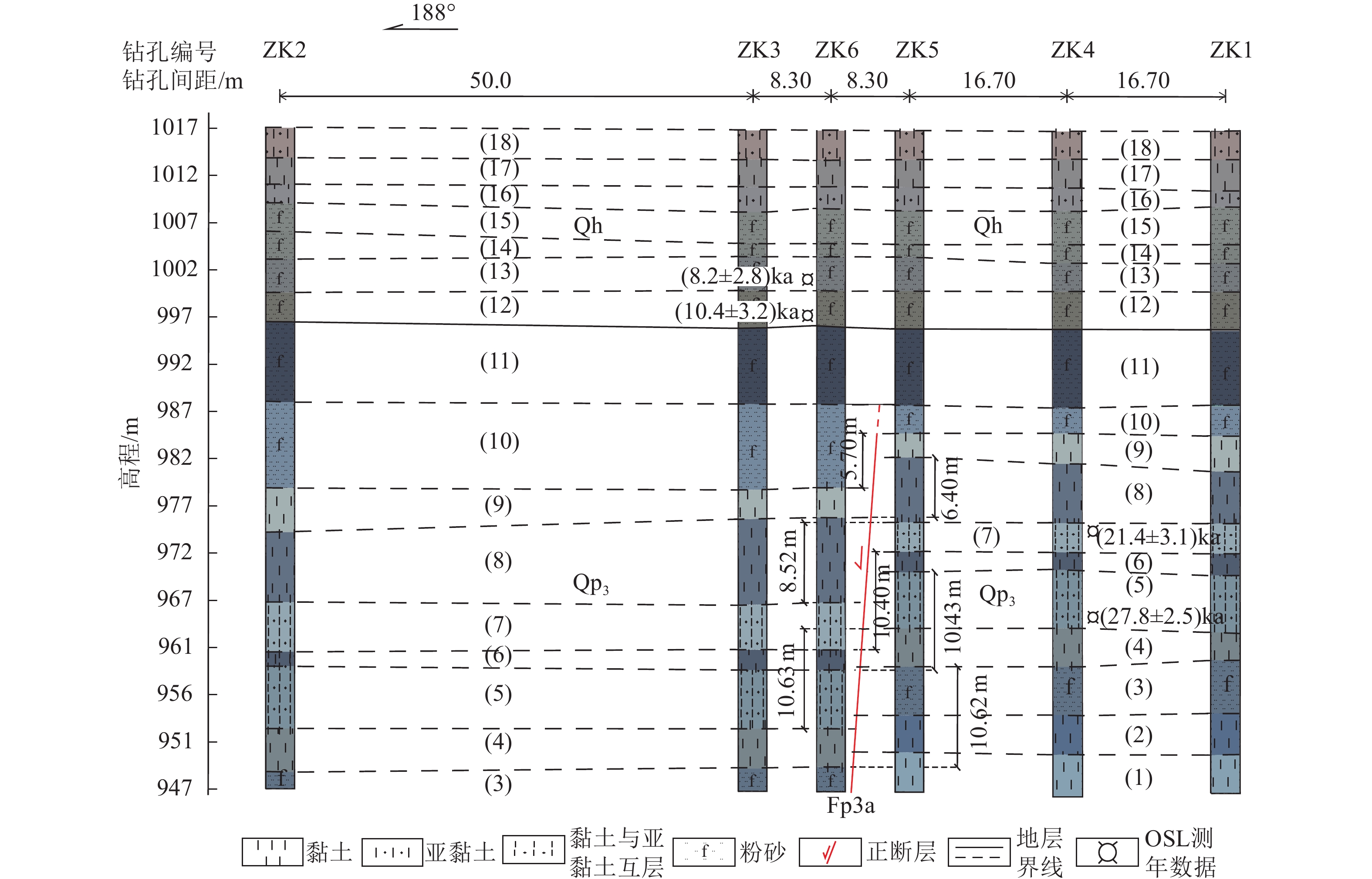
摘要: 乌拉山山前盆地是河套断陷带的重要组成部分。探明乌拉山山前盆地内隐伏活动断裂的分布和晚第四纪活动特征,对于认识乌拉山山前盆地构造特征和震害防御具有重要意义。浅层地震勘探在乌拉山山前盆地内新发现1条隐伏活动断裂带——三湖断裂带,该断裂带由Fp3、Fp4、Fp5、Fp6断层组成,视倾向南,皆为正断层,其中,Fp3、Fp4、Fp6断层为晚更新世断裂,Fp5断层为中更新世断裂。选取三湖断裂带中经浅层地震勘探确定的上断点埋深最浅的 Fp3 断层上断点,开展钻孔联合地质剖面探测工作,并将Fp3断层修正为Fp3a断层。结果表明:(1)Fp3a断层的上断点埋深为29.0 m,结合光释光年龄数据,断错的最新地层形成于晚更新世晚期,证明该断裂为1条活动断裂;(2)Fp3a断层在晚更新世晚期发生了4次古地震事件,按照由老至新排序,事件Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ的垂直断距分别为1.88、2.12、0.70、5.70 m,说明Fp3a断层在晚更新世晚期活动频度较高,活动强度大。Abstract: The Wulashan piedmont basin represents a key structural unit within the Hetao fault-depression zone. Determining the distribution of buried active faults and their activity during the late Quaternary is essential for understanding the tectonic framework of the basin and for guiding seismic hazard mitigation. Through shallow seismic exploration, a previously unidentified buried active fault system—the Sanhu fault zone—has been revealed within the basin. This zone consists of the Fp3, Fp4, Fp5, and Fp6 faults, all southward-dipping normal faults. Among them, Fp3, Fp4, and Fp6 are late Pleistocene faults, whereas Fp5 is a middle Pleistocene fault. The Fp3 fault, identified as having the shallowest burial depth of the upper breakpoint in the zone, was selected for a joint drilling and geological profile survey and subsequently revised as the Fp3a fault. The results show that: (1) The burial depth of the uppermost breakpoint of the Fp3a fault is 29.0 m. Combined with optically stimulated luminescence dating, the youngest faulted strata were formed in the late stage of the late Pleistocene, confirming the Fp3a fault as an active fault. (2) Four paleoearthquake events were identified on the Fp3a fault during this period. The vertical displacements of events I–IV, from oldest to youngest, are 1.88 m, 2.12 m, 0.70 m, and 5.70 m, respectively, indicating that the Fp3a fault experienced relatively frequent and intense activity during the late stage of the late Pleistocene.
-
表 1 浅层地震勘探解译断点参数表
Table 1. Parameters of the uppermost point interpreted by shallow seismic exploration
断层编号 上断点埋深/m 垂直断距/m 上断点距离/m 视倾向 断层性质 Fp1 137 2~6 10527 S 正断层 Fp2 150 2~6 9321 S 正断层 Fp3 60 2~6 3272 S 正断层 Fp4 72 5~8 2628 S 正断层 Fp5 232 3~5 1990 S 正断层 Fp6 85 2~4 1696 S 正断层 表 2 三湖钻孔联合地质剖面岩性描述
Table 2. Lithological description of the Sanhu joint drilling geologic section
层号 岩性特征描述 地质时代 (1) 黏土,灰黑色,可塑,见水平层理,见青灰黏土条带。 Qp3 (2) 黏土,灰黑色,混含少量青灰黏土团块,上部夹青灰粉砂薄层。 (3) 粉砂,浅黑灰色、青灰色,局部夹亚黏土薄层。 (4) 黏土,浅青灰色,见水平层理,局部与灰色、浅黄灰色亚黏土互层。 (5) 黏土与亚黏土互层,青灰色,黑色,见水平层理,有机质含量高。 (6) 黏土,灰黑色、青灰色,水平层理发育,局部有机质含量高。 (7) 黏土与亚黏土互层,浅青灰色,夹黑色黏土薄层,见水平层理。 (8) 黏土,灰黑色,夹青灰色黏土薄层,略有腥味,局部见水平纹层。 (9) 黏土,青灰色,局部夹灰褐色粉砂薄层。 (10) 粉砂,青灰色,松散,较纯净。 (11) 粉砂,灰黑色,较松散,夹青灰、灰黑色黏土薄层,略有腥味。 (12) 粉砂,浅褐黄色,略显黄绿色,较松散,局部混杂褐灰色黏土团块。 Qh (13) 粉砂,浅青灰、褐灰色,较松散,手搓见云母薄片。 (14) 粉砂,浅青灰色,略显灰绿色,较松散,局部混含青灰黏土团块。 (15) 粉砂,褐灰色,较松散,局部含浅褐灰黏土团块。 (16) 亚黏土,褐灰色,可塑,切面光滑,手搓略有粉感。 (17) 黏土,褐灰色,局部可见黑灰色铁锰斑,可塑,切面光滑。 (18) 亚黏土,浅黄褐色,上部见植物根系,下部混含砖红色黏土团块。 表 3 三湖钻孔联合地质剖面光释光年龄样品测试结果
Table 3. OSL dating results of samples from the Sanhu joint drilling geological section
样品编号 埋深/m U/ppm Th/ppm K/% 实测含水量/% 环境剂量率/(Gy·ka-1) 等效剂量/Gy 释光年龄/ka SHZK6-OSL3 15.50 4.3 12.5 2.0 23.9 4.0±0.4 32.9±11.3 8.2±2.8 SHZK6-OSL4 20.30 3.6 11.2 2.0 21.2 3.8±0.3 39.5±9.5 10.4±3.2 SHZK4-OSL9 42.35 9.4 8.3 1.2 35.3 4.0±0.4 85.7±12.2 21.4±3.1 SHZK4-OSL11 51.45 6.7 12.6 1.9 30.5 4.2±0.4 120.5±10.5 27.8±2.5 注:光释光样品由山东省地震工程研究院完成测试。 表 4 三湖钻孔联合地质剖面主要标志层断距
Table 4. Fault displacements of marker layers in the Sanhu joint drilling geological section
层号 地层岩性 上盘(下降盘) 下盘(上升盘) 垂直断距/m 层底界埋深/m 层厚度/m 层底界埋深/m 层厚度/m (10) 粉砂 37.81 8.80 32.11 3.10 5.70 (9) 青灰色黏土 40.98 3.17 34.58 2.47 6.40 (8) 灰黑色黏土 49.98 9.00 41.46 6.88 8.52 (7) 浅青灰色黏土与亚黏土互层 54.98 5.00 44.58 3.12 10.40 (6) 灰黑色黏土 57.10 2.12 46.67 2.09 10.43 (5) 青灰色黏土与亚黏土互层 63.31 6.21 52.68 6.01 10.63 (4) 浅青灰色黏土 67.37 4.06 56.75 4.07 10.62 表 5 Fp3a断层的古地震矩震级
Table 5. The moment magnitude pf paleo-earthquake along the Fp3a fault
序号 古地震事件 同震位移/m 估算的矩震级/MW 1 Ⅰ 1.88 6.80±0.34 2 Ⅱ 2.12 6.84±0.34 3 Ⅲ 0.70 6.50±0.34 4 Ⅳ 5.70 7.15±0.34 -
柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测−−以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地震地质, 28(4): 536−546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002Chai C. Z., Meng G. K., Du P., et al., 2006. Comprehensive multi-level exploration of buried active fault: an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 28(4): 536−546. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002 陈立春, 2002. 河套断陷带的古地震、强震复发规律和未来可能强震地点. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Chen L. C., 2002. Paleoearthquakes, the law of strong earthquake recurrence and potential sites for the occurrence of future strong earthquakes in the Hetao fault-depression zone. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese) 邓起东, 尤惠川, 1985. 鄂尔多斯周缘断陷盆地带的构造活动特征及其形成机制. 见: 国家地震局地质研究所编, 现代地壳运动研究(1). 北京: 地震出版社, 58−78. 国家地震局《鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系》课题组, 1988. 鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系. 北京: 地震出版社, 39−61. 贺为民, 2025. 钻孔联合地质剖面探测施工中若干问题探讨. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文), 56(2): 157−166.He W. M., 2025. Discussion on several problems in the construction of joint drilling geological section surveys. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 56(2): 157−166. (in Chinese) 雷启云, 柴炽章, 孟广魁等, 2011. 隐伏活断层钻孔联合剖面对折定位方法. 地震地质, 33(1): 45−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.005Lei Q. Y., Chai C. Z., Meng G. K., et al., 2011. Method of locating buried active fault by composite drilling section doubling exploration. Seismology and Geology, 33(1): 45−55. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.005 李建彪, 2006. 河套盆地晚第四纪成湖环境变化与构造活动研究. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Li J. B., 2006. A study on the lake forming environment and tectonic activity during the late quaternary in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia autonomous region, China. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese) 李建彪, 冉勇康, 郭文生, 2007. 呼包盆地第四纪地层与环境演化. 第四纪研究, 27(4): 632−644. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.04.020Li J. B., Ran Y. K., Guo W. S., 2007. Division of quaternary beds and environment evolution in Hubao basin in China. Quaternary Sciences, 27(4): 632−644. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.04.020 李彦宝, 冉勇康, 陈立春等, 2015. 河套断陷带主要活动断裂最新地表破裂事件与历史大地震. 地震地质, 37(1): 110−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.009Li Y. B., Ran Y. K., Chen L. C., et al., 2015. The latest surface rupture events on the major active faults and great historical earthquakes in Hetao fault-depression zone. Seismology and Geology, 37(1): 110−125. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.009 刘哲, 赵华, 杨劲松等, 2022. 晚更新世以来内蒙古哈素海钻孔地层记录及其年龄. 地质通报, 41(2-3): 271−281. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.2-3.007Liu Z., Zhao H., Yang J. S., et al., 2022. Stratigraphy and chronology of a Late Pleistocene sediment core from Hasuhai Lake in Inner Mongolia. Geological Bulletin of China, 41(2-3): 271−281. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.2-3.007 马保起, 盛小青, 张守仁等, 1998. 乌拉山山前断裂晚第四纪活动研究. 见: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所编, 地壳构造与地壳应力文集(11). 北京: 地震出版社, 22−27. 马保起, 李德文, 郭文生, 2004. 晚更新世晚期呼包盆地环境演化与地貌响应. 第四纪研究, 24(6): 630−637. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.004Ma B. Q., Li D. W., Guo W. S., 2004. Geomorphological response to environmental changes during the late stage of late pleistocene in Hubao basin. Quaternary Sciences, 24(6): 630−637. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.004 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局, 1991. 内蒙古自治区区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社, 331−343.Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Nei Mongol, 1991. Regional geology of Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia) autonomous region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 331−343. (in Chinese) 冉勇康, 陈立春, 杨晓平等, 2003. 鄂尔多斯地块北缘主要活动断裂晚第四纪强震复发特征. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33 (增刊): 135−143.Ran Y. K., Chen L. C., Yang X. P., et al., 2003. Recurrence characteristics of late-quaternary strong earthquakes on the major active faults along the northern border of Ordos block. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 189−200. (in Chinese) 王新亮, 2006. 内蒙古呼−包盆地第四纪沉积、构造特征研究. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).Wang X. L., 2006. Quaternary sedimentary and structure features of the Hohhot-Baotou basin, Inner Mongolia. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese) 吴利杰, 张翼龙, 石建省等, 2019. 河套盆地第四纪岩石地层区划及沉积序列. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(10): 91−101.Wu L. J., Zhang Y. L., Shi J. S., et al., 2019. Quaternary lithostratigraphic regionalization and sedimentary sequence of Hetao Basin. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(10): 91−101. (in Chinese) 徐卫红, 刘雅彬, 赵金玲等, 2012a. 内蒙古自治区鄂尔多斯市杭锦旗七星湖旅游区地热普查报告. 鄂尔多斯: 内蒙古自治区第二水文地质工程地质勘查院. 徐卫红, 王存良, 赵金玲等, 2012b. 内蒙古自治区达拉特旗吉隆生态区(一区)N热4地热井勘查. 内蒙古自治区第二水文地质工程地质勘查院. 尤惠川, 1985. 河套断陷盆地带地质构造特征及其成因机制的讨论. 见: 国家地震局地质研究所编, 现代地壳运动研究(1). 北京: 地震出版社, 88−97. He Z. T., Ma B. Q., Hao Y. J., et al., 2020. Surface rupture geomorphology and vertical slip rates constrained by terraces along the Wulashan piedmont fault in the Hetao Basin, China. Geomorphology, 358: 107116. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107116 Wells D. L., Coppersmith K. J., 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 974−1002. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0840040974 -




 下载:
下载: