In-situ Stress Measurement of Qushan Island in Hangzhou Bay and Its Crustal Dynamic Significance
-
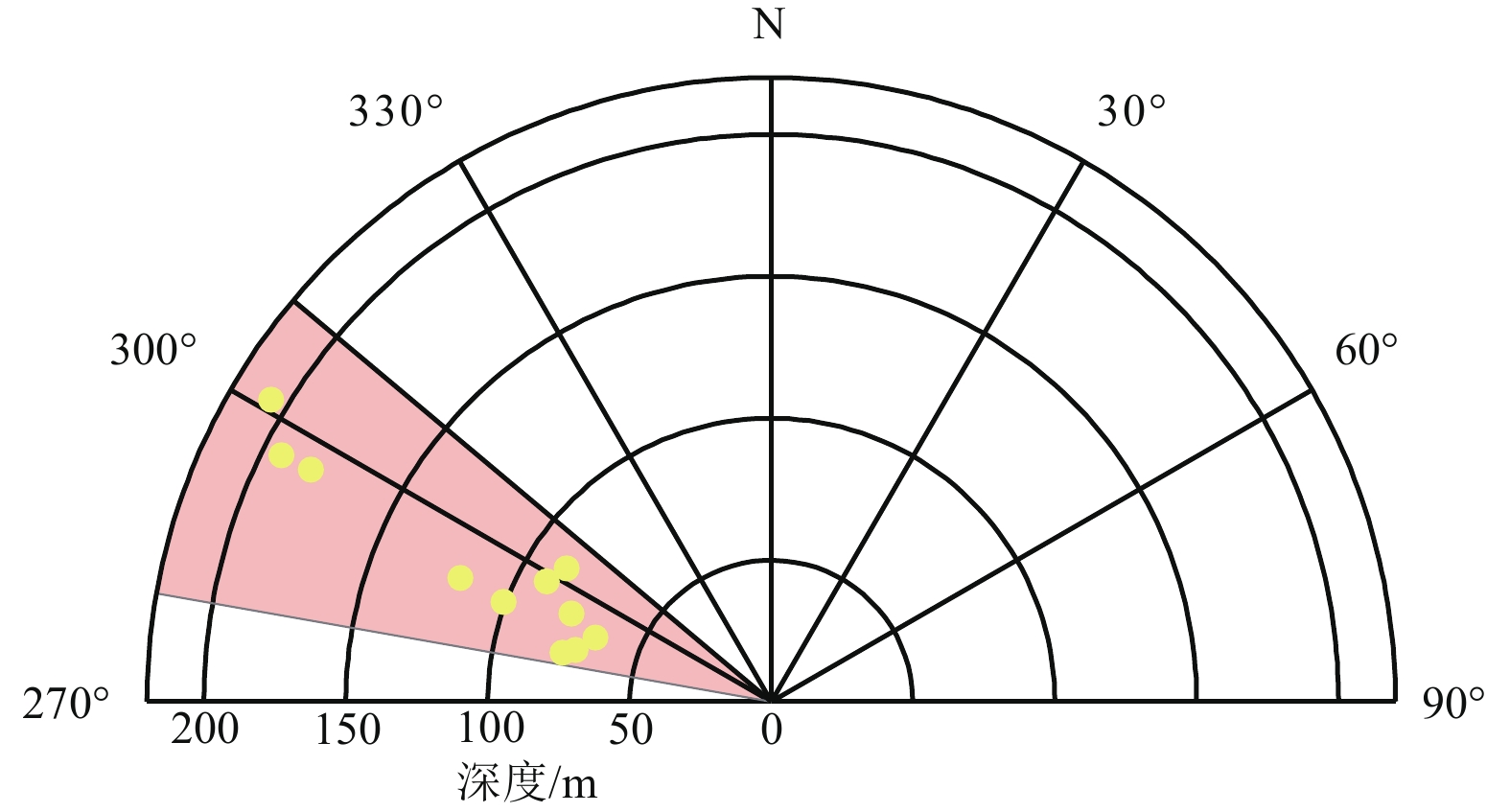
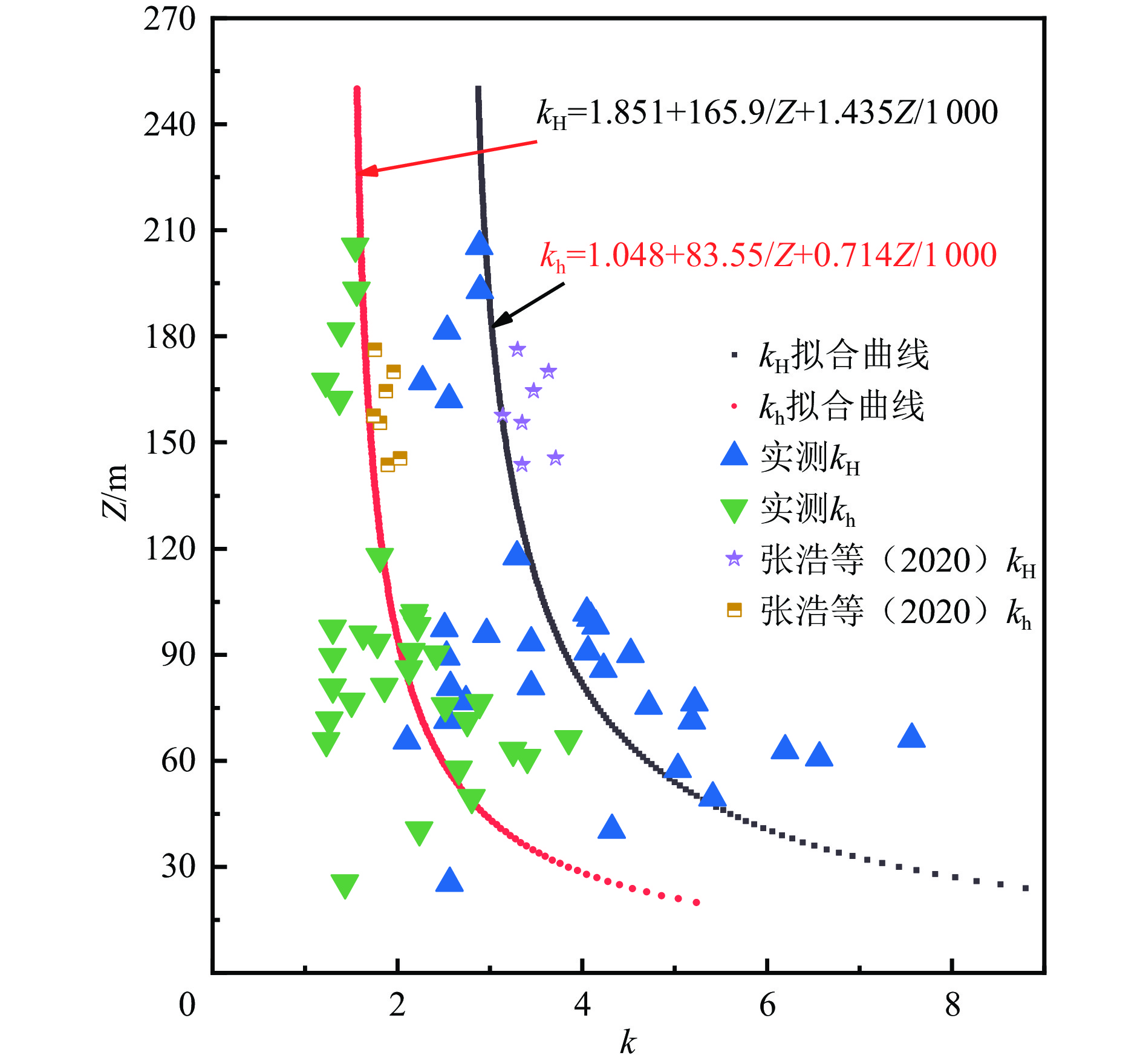
摘要: 杭州湾衢山岛屿位于中国大陆华北、华南活动地块和华北、华南地应力分区的边界地带,该区域的地应力研究工作对于理解该区域地壳应力状态和地壳动力学行为意义重大。研究区小衢山岛大地构造位于华南地槽褶皱系的浙东南褶皱带东北部,距上海芦潮港30海里。基于小衢山岛上3个钻孔的水压致裂原地应力测试数据综合分析,研究区最大水平主应力方向范围为N56.9°W~ N76.9°W,说明该区域主要受太平洋板块和菲律宾海板块向北西西、北西向俯冲推挤力源的影响。最大、最小水平主应力量值基本随深度增加而增大,最大水平主应力量值一般为7.39~15.74 MPa,最小水平主应力量值一般为3.99~8.41 MPa,最大、最小侧压力系数范围分别为2.11≤kH≤7.56,1.23≤kh≤3.85。利用实测数据计算的剪应力积累因子μ的范围是0.36~0.77,平均值为0.55,剪应力积累程度较高。研究结果为认识中国大陆东部华北、华南活动地块的分界分区问题提供了新的地应力证据。Abstract: Qushan Island, located in Hangzhou Bay, lies at the boundary zone between the North China and South China active blocks, within the North China–South China in-situ stress zone. Investigating the in-situ stress state in this region is crucial for understanding the crustal stress distribution and tectonic dynamics. The Xiaoqushan Island tectonic structure, situated in the northeastern part of the South Zhejiang fold belt within the geosynclinal fold system of South China, is approximately 30 km from Luchao Port, Shanghai. Based on a comprehensive analysis of in-situ stress measurements from three boreholes on Xiaoqushan Island, the orientation of the maximum horizontal principal stress ranges from N56.9°W to N76.9°W, indicating that the region is primarily influenced by NWW- and NW-directed compressive forces associated with the subduction and push of the Pacific and Philippine Sea plates. Both the maximum and minimum horizontal principal stress values generally increase with depth. Maximum horizontal principal stress values range from 7.39 to 15.74 MPa, while minimum horizontal principal stress values range from 3.99 to 8.41 MPa. The corresponding maximum and minimum lateral pressure coefficients are 2.11~7.56 and 1.23~3.85, respectively. Analysis of the measured data indicates that the shear stress accumulation factor (μ) ranges from 0.36 to 0.77, with an average value of 0.55, suggesting a high degree of shear stress accumulation in the study area.
-
Key words:
- Qushan Island /
- In-situ stress measurement /
- Tectonic stress field /
- Crustal dynamics
-
表 1 3个钻孔水压致裂原地应力数据及特征值分析汇总表
Table 1. Summary of hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress data and characteristic value analysis for three drilling holes
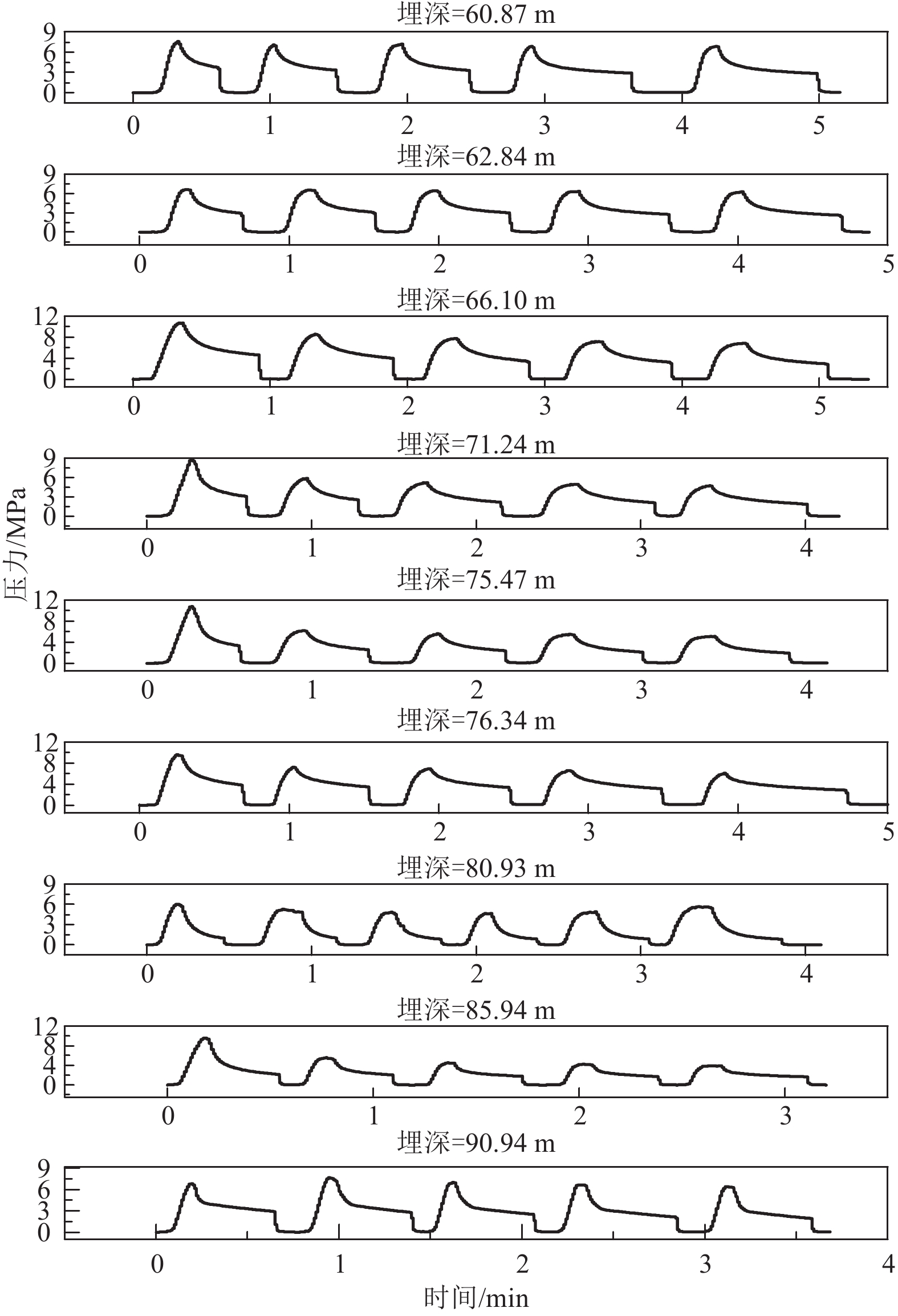
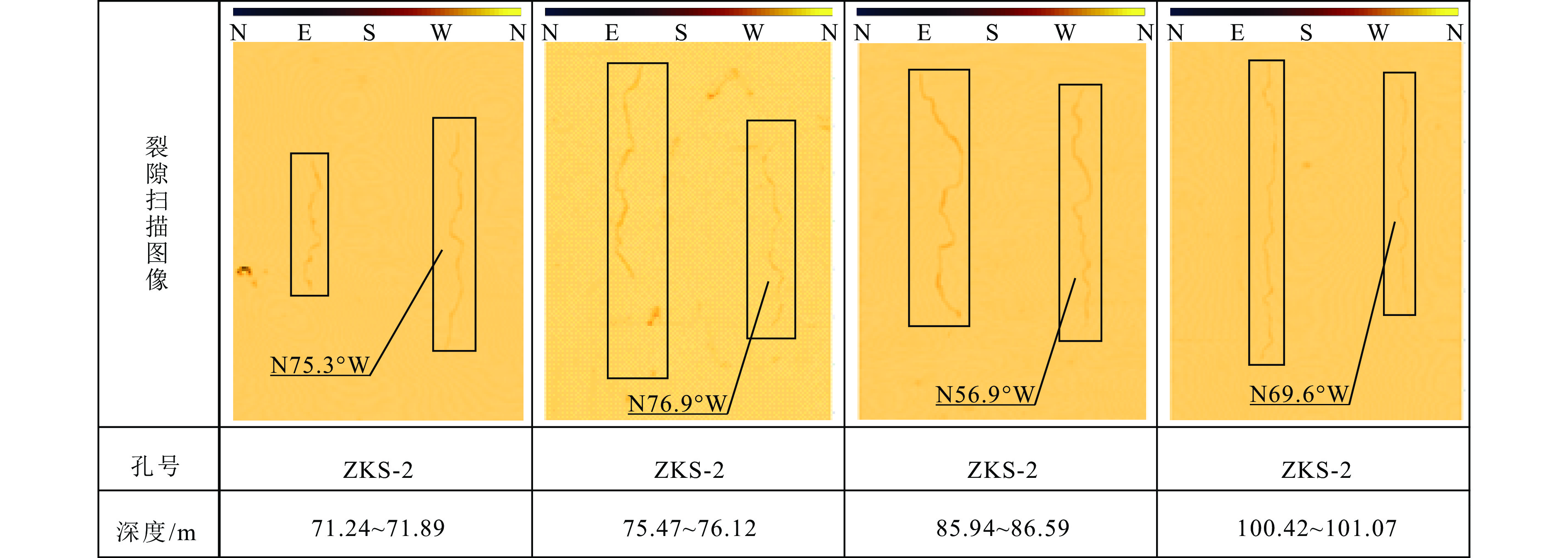
钻孔编号 深度/m SH/MPa Sh/MPa Sv/MPa kH kh μ R 最大主应力方向 ZKS-1 71.54 4.83 2.40 1.90 2.55 1.27 0.44 0.17 — 80.86 5.52 2.79 2.14 2.58 1.30 0.44 0.19 — 89.47 6.00 3.08 2.37 2.53 1.30 0.43 0.19 N61.9°W 93.42 8.54 4.42 2.48 3.45 1.78 0.55 0.32 — ZKS-1 97.38 6.48 3.35 2.58 2.51 1.30 0.43 0.20 — 162.21 11.02 5.89 4.30 2.56 1.37 0.44 0.24 — 167.27 10.07 5.44 4.43 2.27 1.23 0.39 0.18 — 181.49 12.20 6.68 4.81 2.54 1.39 0.43 0.25 N63.3°W 192.96 14.82 7.99 5.11 2.90 1.56 0.49 0.30 N63.3°W 205.54 15.74 8.41 5.45 2.89 1.54 0.49 0.29 N58.9°W ZKS-2 60.87 10.60 5.50 1.61 6.57 3.41 0.74 0.43 — 62.84 10.32 5.42 1.67 6.19 3.25 0.72 0.43 — 66.1 13.25 6.75 1.75 7.56 3.85 0.77 0.43 — 71.24 9.80 5.20 1.89 5.19 2.75 0.68 0.42 N75.3°W 75.47 9.44 5.04 2.00 4.72 2.52 0.65 0.41 N76.9°W 76.34 10.55 5.85 2.02 5.21 2.89 0.68 0.45 — 80.93 7.39 3.99 2.14 3.45 1.86 0.55 0.35 — 85.94 9.64 4.84 2.28 4.23 2.13 0.62 0.35 N56.9°W 90.94 9.79 5.19 2.41 4.06 2.15 0.60 0.38 — 95.86 7.54 4.14 2.54 2.97 1.63 0.50 0.32 — 100.42 10.88 5.78 2.66 4.09 2.17 0.61 0.38 N69.6°W ZKS-3 65.70 3.67 2.14 1.74 2.11 1.23 0.36 0.21 N70.1°W 76.72 5.58 3.05 2.03 2.74 1.50 0.47 0.29 N66.3°W 90.07 10.81 5.78 2.39 4.53 2.42 0.64 0.40 — 98.16 10.79 5.76 2.60 4.15 2.22 0.61 0.39 — 101.74 10.92 5.90 2.70 4.05 2.19 0.60 0.39 — 117.76 10.28 5.65 3.12 3.29 1.81 0.53 0.35 N68.3°W 均值 3.77 2.00 0.55 0.32 N67.0°W 注:侧压力系数kH=SH/SV、kh=Sh/SV; 剪应力积累因子μ=(SH−SV)/(Sh−SV); 应力型因子R=(SH−Sh) /(SH−SV)。 -
陈婧, 杨彦明, 肖爽等, 2019. 基于非线性拟合的上海及周边地区地震烈度衰减关系研究. 高原地震, 31(3): 6−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2019.03.002Chen J., Yang Y. M., Xiao S., et al., 2019. Study on seismic intensity attenuation in shanghai and its adjacent regions based on nonlinear fitting. Plateau Earthquake Research, 31(3): 6−12. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2019.03.002 陈涛, 宋方敏, 陈献程等, 2019. 2017年临安4.2级地震震中附近断裂活动性研究. 华南地震, 39(1): 115−128.Chen T., Song F. M., Chen X. C., et al., 2019. Study on the activity of faults near the epicenter of the Lin'an M4.2 earthquake in 2017. South China Journal of Seismology, 39(1): 115−128. (in Chinese) 高敏, 王鑫, 张景发, 2015. 利用遥感、重磁数据研究昌化−普陀断裂的空间展布特征. 科学技术与工程, 15(4): 1−4, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.04.001Gao M., Wang X., Zhang J. F., 2015. The space distribution characteristics research of changhua−putuo fracture based on remote sensing, gravity and magnetic data. Science Technology and Engineering, 15(4): 1−4,16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.04.001 韩竹军, 徐杰, 冉勇康等, 2003. 华北地区活动地块与强震活动. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 108−118. Han Z. J., Xu J., Yan Y. K., et al., 2003. Active blocks and strong seismic activity in North China region. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 153−167. 胡峰, 姚华建, 余厚云等, 2024. 分形应力对设定地震构建的影响−−以郯庐断裂带为例. 中国科学: 地球科学, 54(5): 1714−1724.Hu F., Yao H. J., Yu H. Y., et al., 2024. Influence of self-similar stresses on scenario earthquake construction: an example along the Tanlu Fault. Science China Earth Sciences, 67(5): 1687−1697. (in Chinese) 基姆弗兰克林, 张受天, 1988. 国际岩石力学学会试验方法委员会确定岩石应力的建议方法. 岩石力学与工程学报, 7(4): 357−388. 李宏, 安其美, 谢富仁, 2005. 福建沿海边缘陆域的原地应力测量研究. 地震学报, 27(5): 508−514.Li H., An Q. M., Xie F. R., 2005. Study on in-situ stress measurement around coastal marginal land in fujian. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27(5): 508−514. (in Chinese) 李伟, 李嘉, 吴宛秋等, 2024. 郯庐断裂带辽东湾段新生代右旋走滑时限的探讨. 地球科学, 49(6): 2071−2084. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.480Li W., Li J., Wu W. Q., et al., 2024. Time limit of dextral strike-slip in cenozoic of Liaodong bay section of Tan-Lu fault zone. Earth Science, 49(6): 2071−2084. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.480 刘昌森, 吕美丽, 1998. 上海地区地震放大效应的初步探讨. 上海地质, (1): 7−13.Liu C. S., Lü M. L., 1998. Preliminary analysis of the seismic amplification effect in Shanghai. Shanghai Land & Resources, (1): 7−13. (in Chinese) 曲国胜, 郝重涛, 陈国光等, 1992. 镇海−温州断裂分段性及新生代构造应力场研究. 地震学刊, 12(2): 11−20.Qu G. S., Hao C. T., Chen G. G., et al., 1992. A study on the segmentation and tectonic stress field of the zhenhai-wenzhou extending faults in cenozoic. Journal of Seismology, 12(2): 11−20. (in Chinese) 任烨, 夏波, 刘菲, 2018. 孔底解除法在上海综合深井钻孔原地应力测量中的应用. 华南地震, 38(1): 71−76. doi: 10.13512/j.hndz.2018.01.009Ren Y., Xia B., Liu F., 2018. Application of hole-bottom relief method in stress measurement of in-situ bored hole in Shanghai. South China Journal of Seismology, 38(1): 71−76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13512/j.hndz.2018.01.009 王成虎, 郭啟良, 丁立丰等, 2009. 工程区高地应力判据研究及实例分析. 岩土力学, 30(8): 2359−2364. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.08.029Wang C. H., Guo Q. L., Ding L. F., et al., 2009. High in-situ stress criteria for engineering area and a case analysis. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 30(8): 2359−2364. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.08.029 王成虎, 2014. 地应力主要测试和估算方法回顾与展望. 地质论评, 60(5): 971−996. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2014.05.005Wang C. H., 2014. Brief review and outlook of main estimate and measurement methods for in-situ stresses in rock mass. Geological Review, 60(5): 971−996. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2014.05.005 王辉, 张国民, 汪素云等, 2004. 应用地震学方法研究中国大陆活动地块应力应变场. 地球物理学报, 47(6): 1035−1043.Wang H., Zhang G. M., Wang S. Y., et al., 2004. Stress and strain fields of active tectonic blocks in the China mainland deduced by seismological methods. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(6): 1035−1043. (in Chinese) 吴义, 胡志生, 刘冬等, 2021. 温州市突发性地质灾害发育特征及防治对策. 地质论评, 67(S1): 5−6.Wu Y., Hu Z. S., Liu D., et al., 2021. Development characteristics and prevention countermeasures of sudden geological disasters in Wenzhou. Geological Review, 67(S1): 5−6. (in Chinese) 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛等, 2004. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区. 地球物理学报, 47(4): 654−662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016Xie F. R., Cui X. F., Zhao J. T., et al., 2004. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 654−662. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016 徐纪人, 赵志新, 石川有三, 2008. 中国大陆地壳应力场与构造运动区域特征研究. 地球物理学报, 51(3): 770−781.Xu J. R., Zhao Z. X., Yuzo, I., 2008. Regional characteristics of crustal stress field and tectonic motions in and around Chinese mainland. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(3): 770−781. (in Chinese) 徐杰, 周本刚, 计凤桔等, 2012. 中国东部海域及其邻区现代构造应力场研究. 地学前缘, 19(4): 1−7.Xu J., Zhou B. G., Ji F. J., et al., 2012. The recent tectonic stress field of offshore of China mainland and adjacent areas. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(4): 1−7. (in Chinese) 徐峣, 张永谦, 严加永等, 2019. 华南东南部上地幔远震P波速度结构及意义. 中国地质, 46(4): 737−749. doi: 10.12029/gc20190405Xu Y., Zhang Y. Q., Yan J. Y., et al., 2019. Teleseismic P-wave velocity structure of upper mantle beneath the southeastern part of South China and its implications. Geology in China, 46(4): 737−749. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12029/gc20190405 严兆彬, 2018. 浙西早寒武世地震事件沉积特征与地质意义研究. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京).Yan Z. B., 2018. Sedimentary features resulting from seismic events of the early cambrian in the western Zhejiang province and its geological significance. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing. (in Chinese) 叶建亭, 周舟, 2019. 浙江青田县东源辉绿岩矿矿体特征及覆盖层分布. 世界有色金属, 44(8): 258−259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.08.151Ye J. T., Zhou Z., 2019. Ore body characteristics and cover layer distribution of Dongyuan diabase in Qingtian County, Zhejiang Province. World Nonferrous Metals, 44(8): 258−259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.08.151 于海英, 魏薇, 王鹏等, 2022.2021年11月17日江苏省盐城市大丰区海域MS5.0地震快速测定与应急产品产出. 地震地磁观测与研究, 43(3): 172−177.Yu H. Y. , Wei W. , Wang P. , et al. , 2021. Fast detection and emergency products output of the MS5.0 earthquake in Dafeng sea area, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province on November 17, 2021. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 43(3): 172−177. (in Chinese) 苑伟娜, 石富强, 吴静, 2021. 华北地区应力累积变化及其对现今地震活动的指示. 大地测量与地球动力学, 41(9): 939−944.Yuan W. N., Shi F. Q., Wu J., 2021. Cumulated stress changes and its implications for current seismic activities in North China. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 41(9): 939−944. (in Chinese) 张国民, 马宏生, 王辉等, 2005. 中国大陆活动地块边界带与强震活动. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 602−610. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.693Zhang G. M., Ma H. S., Wang H., et al., 2005. Boundaries between active_tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the China mainland. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(3): 602−610. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1002/cjg2.693 张浩, 施刚, 巫虹等, 2020. 上海地区浅部地应力测量及其构造地质意义分析. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 583−594. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.051Zhang H., Shi G., Wu H., et al., 2020. In-situ stress measurement in the shallow basement of the Shanghai area and its structural geological significance. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 583−594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.051 张培震, 王琪, 马宗晋, 2002. 中国大陆现今构造运动的GPS速度场与活动地块. 地学前缘, 9(2): 430−441. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.02.022Zhang P. Z., Wang Q., Ma Z. J., 2002. GPS velocity field and active crustal blocks of contemporary tectonic deformation in continental china. Earth Science Frontiers, 9(2): 430−441. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.02.022 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民等, 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12−20. Zhang P. Z., Deng Q. D., Zhang G. M., et al., 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 13−24. Zhang Y. X., Song C. S., Zhao J. H., 2015. Study on hydraulic fracturing method for in situ stress measurement in deep boreholes. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 741: 567−571. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.741.567 Zoback M. D., Barton C. A., Brudy M., et al., 2003. Determination of stress orientation and magnitude in deep wells. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 40(7-8): 1049−1076. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.07.001 -




 下载:
下载: