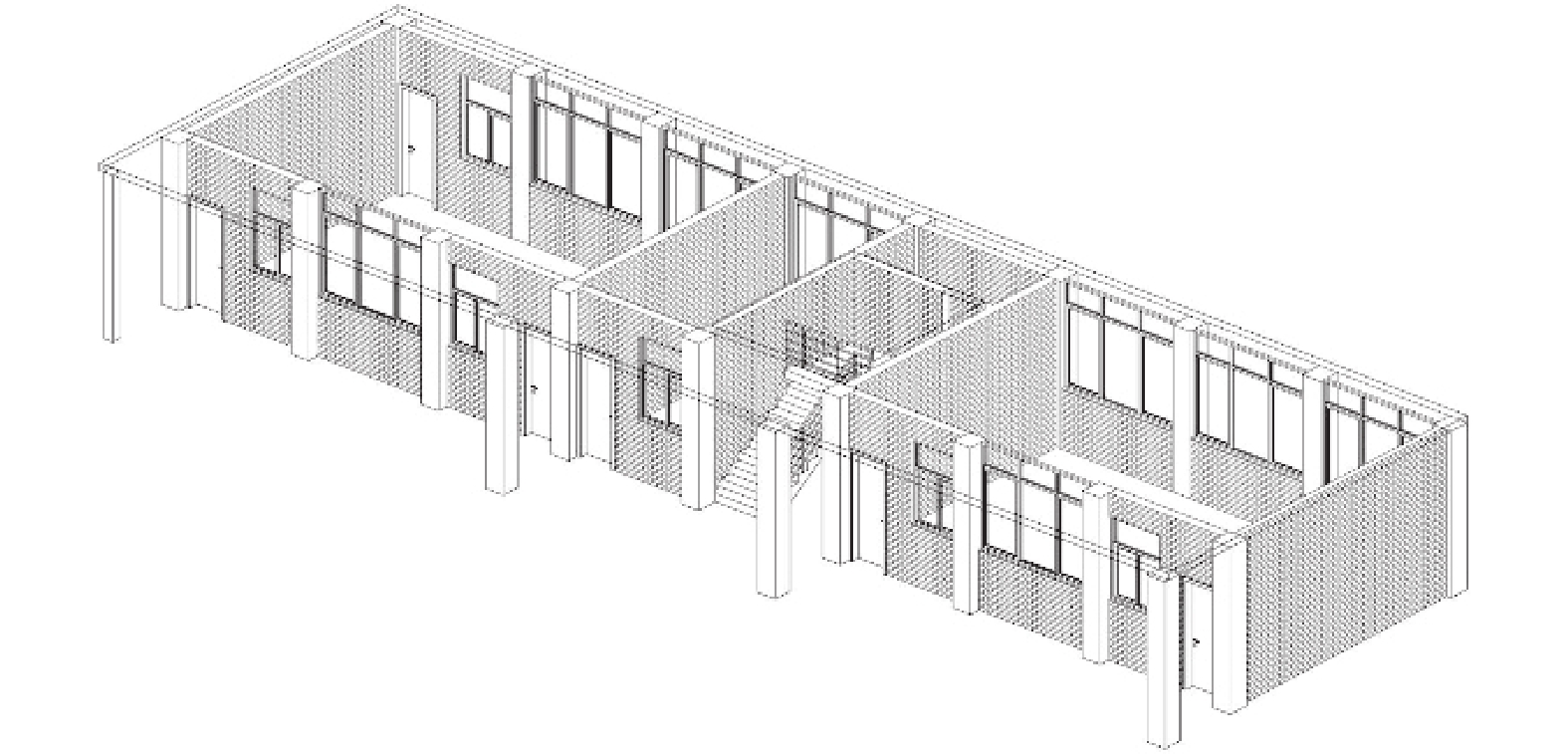
Natural Period Measurement and Analysis of School Buildings with External Corridor
-
摘要: 根据现有的抗震设计方法,结构基本周期是确定设计地震力大小的关键因素。中小学外廊式教学楼在历次地震中均表现出较严重的震害。为研究教学楼实际自振周期与结构设计模型的差异,本文选取4栋典型的外廊式教学楼,采用脉动法测试结构一阶平动和扭转的固有周期,并根据原设计图纸复现了结构计算模型。测试和分析结果表明:实测纵横向自振周期较经验公式估算的周期小,相差范围在8.9%~28.0%,且经验公式估算的周期介于实测值与结构分析软件计算值之间。填充墙的数量和布置形式会对结构3个方向的自振周期产生不同程度的影响,填充墙对横向的刚度作用远大于纵向,同时横墙也使结构抗扭刚度得到极大的提高。不考虑填充墙的计算模型和经验公式均无法同时准确评估3个方向的自振周期。结构整体的抗震性能与填充墙的分布形式和连接方式都有重要的联系,设计中应充分考虑填充墙的布置及参与工作状态,才能准确评估结构抗震设计及结构承载力。Abstract: According to current seismic design methods, the fundamental period of a structure is a critical parameter in determining seismic forces. School corridor buildings in primary and secondary schools have experienced varying degrees of earthquake damage in past seismic events. To investigate discrepancies between the actual natural periods and the design model assumptions for these buildings, four representative corridor school buildings were selected for study. The first-order translational and torsional frequencies were measured using the ambient vibration method. Structural calculation models were then reconstructed based on the original design drawings. The results indicate that the measured natural periods in both longitudinal and transverse directions are consistently shorter than those estimated by empirical formulas, with discrepancies ranging from 8.9% to 28.0%. The empirical formula estimates fall between the measured values and those derived from structural analysis software. Furthermore, the quantity and configuration of infilled walls significantly affect the natural periods in all three directions. Specifically, infilled walls contribute substantially more to lateral stiffness than to longitudinal stiffness, and they markedly enhance the torsional stiffness of the structures. Notably, calculation models and empirical formulas that neglect the presence of infilled walls fail to accurately predict the natural periods simultaneously in all directions. These findings underscore that the seismic response of such structures is strongly influenced by the arrangement and connection details of infilled walls. Therefore, to achieve accurate seismic force estimations and structural capacity evaluations, the configuration and mechanical behavior of infilled walls must be thoroughly incorporated into seismic design considerations.
-
表 1 测试仪器技术指标
Table 1. Technical specification of the test instruments
传感器 放大器 数据采集仪 型号 941B 型号 941型 型号 INV3062-C1(L) 量程 0.125 m/s 积分参数 直通 采样方式 分块平均 灵敏度 23 V·m/s 放大倍数 10 通道数 8 通频带 1~100 Hz 通频带 0.25~25 Hz 采样频率 100 Hz 表 2 结构信息和测试结果
Table 2. Structure information and test results
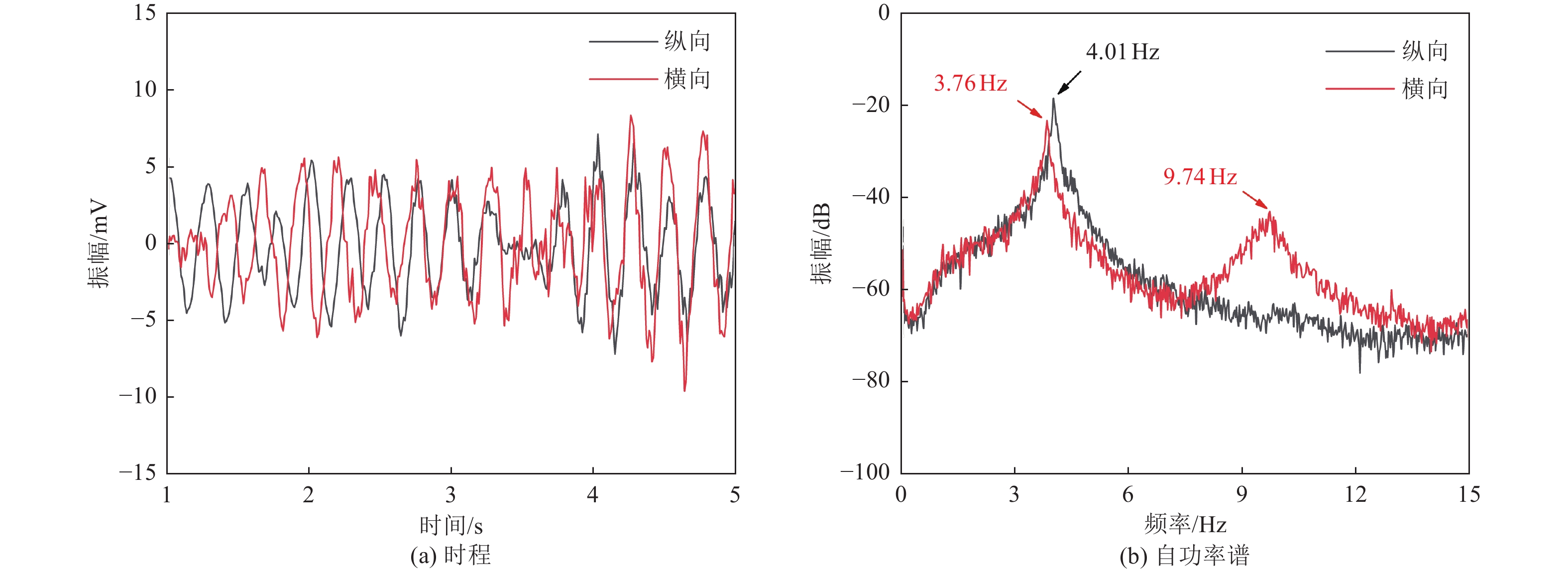
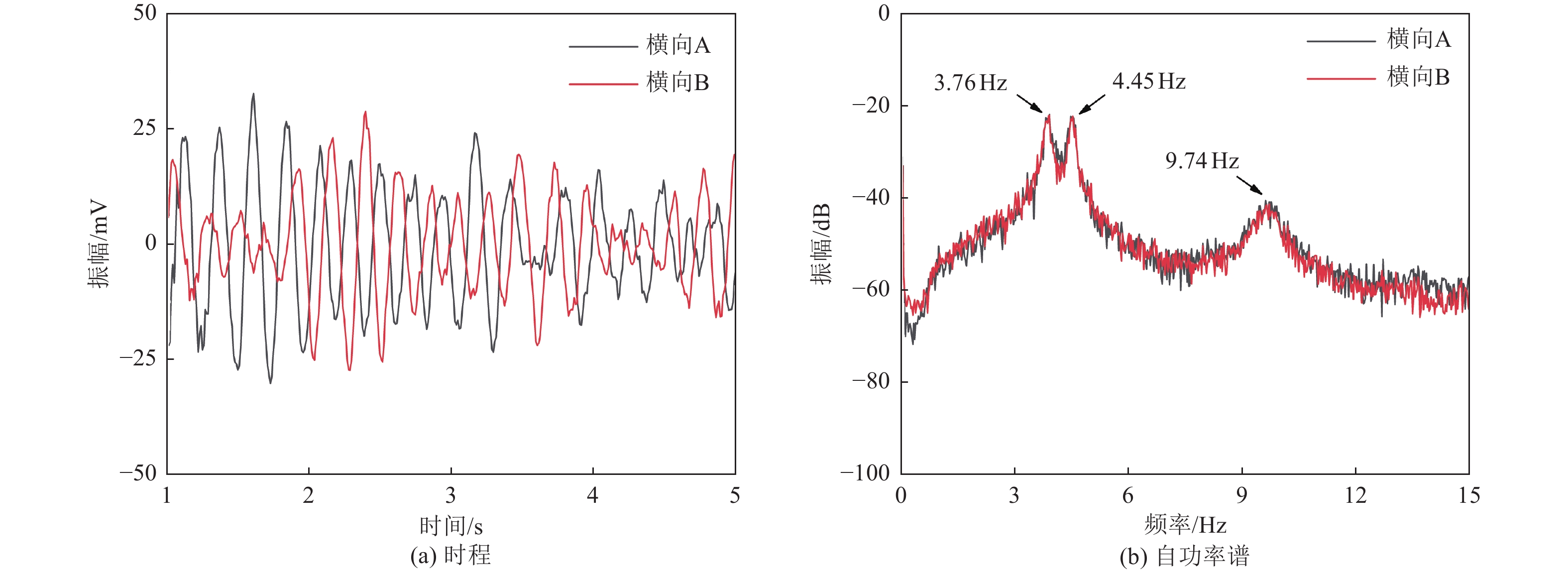
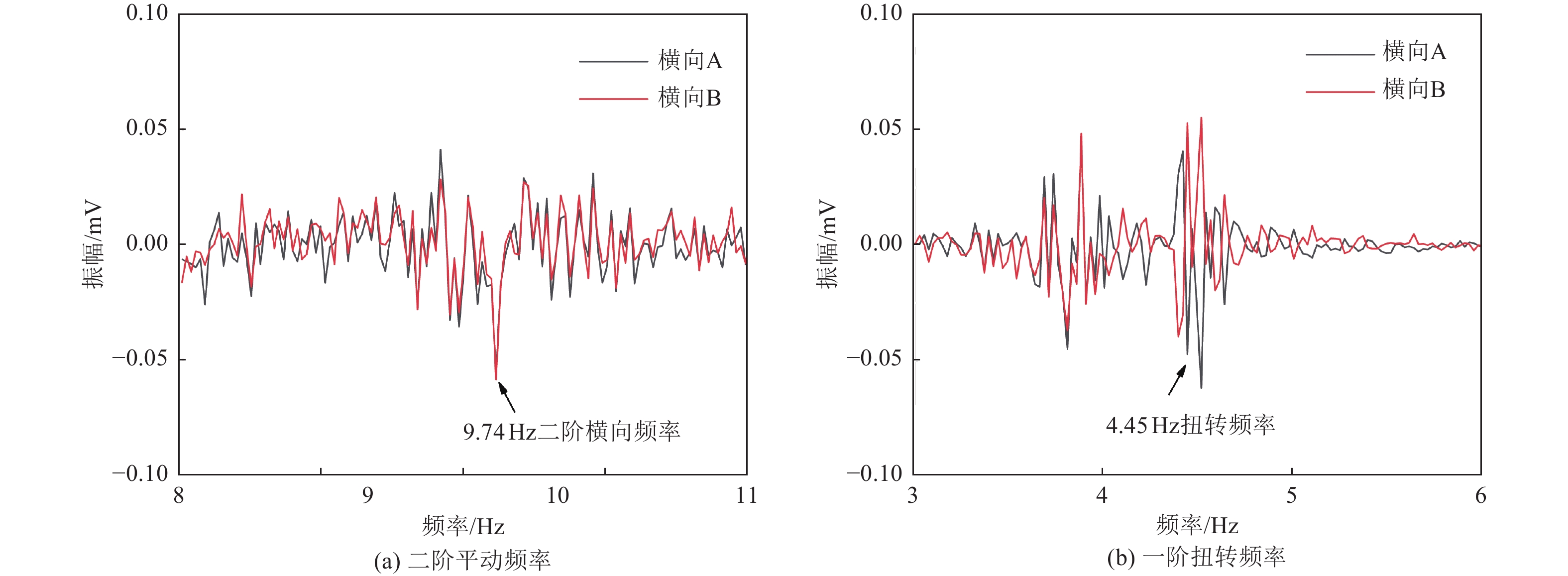
建筑名称 结构形式 形状 层数 长/m 宽/m 高/m 一阶周期/s 纵向 横向 扭转 妥甸小学四层教学楼 框架 矩形 4 40.2 8.7 16.2 0.249 0.266 0.225 法脿小学四层教学楼 框架 矩形 4 26.1 8.1 15.3 0.266 0.240 0.198 程江小学四层教学楼 框架 矩形 4 45.6 9 18.65 0.244 0.244 0.192 程江小学五层教学楼 框架 矩形 5 45.6 9 22.25 0.279 0.279 0.226 表 3 结构自振周期及折减系数
Table 3. Natural periods and reduction factors
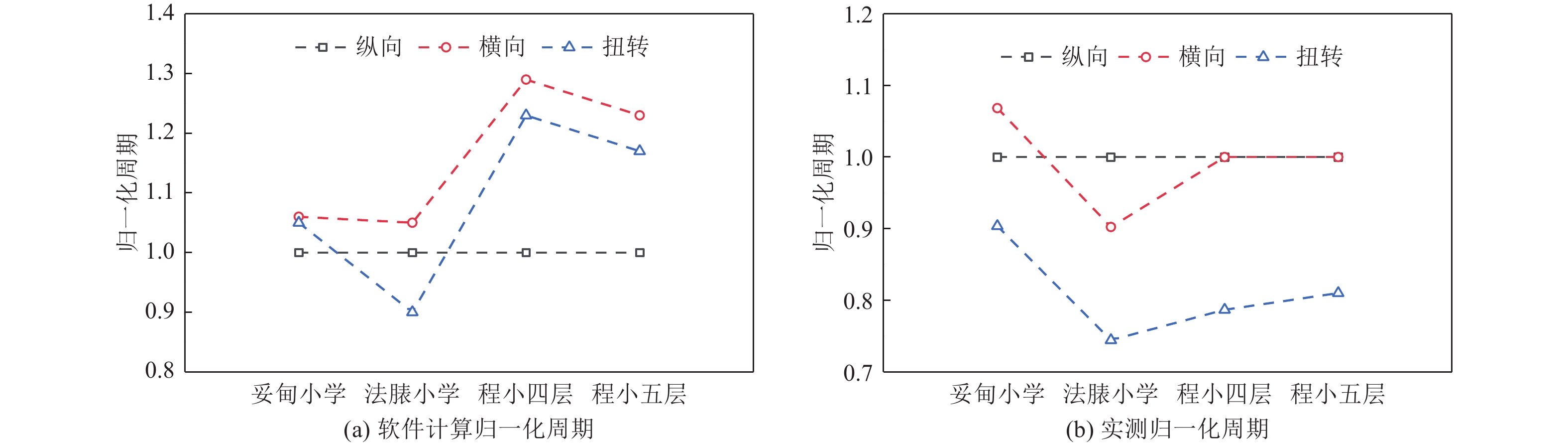
建筑名称 实测一阶周期 软件计算模型一阶周期 折减系数 纵向/s 横向/s 扭转/s 纵向/s 横向/s 扭转/s 纵向 横向 扭转 妥甸小学四层教学楼 0.249 0.266 0.225 0.560 0.592 0.586 0.45 0.45 0.38 法脿小学四层教学楼 0.266 0.240 0.198 0.546 0.572 0.490 0.49 0.42 0.40 程江小学四层楼 0.244 0.244 0.192 0.546 0.705 0.672 0.45 0.35 0.29 程江小学五层楼 0.279 0.279 0.226 0.635 0.784 0.740 0.44 0.36 0.31 表 4 实测与经验公式对比
Table 4. Comparison between measurement and calculation with empirical formula
建筑名称 纵向 横向 实测/s 计算/s 公式/s 误差t/% 误差c/% 实测/s 计算/s 公式/s 误差t/% 误差c/% 妥甸小学 0.249 0.336 0.291 14.4 −15.5 0.266 0.355 0.319 16.6 −11.3 法脿小学 0.266 0.328 0.292 8.9 −12.3 0.240 0.343 0.312 23.1 −9.9 程江小学四层 0.244 0.328 0.302 19.2 −8.6 0.244 0.423 0.339 28.0 −24.8 程江小学五层 0.279 0.382 0.323 13.6 −18.3 0.279 0.470 0.376 25.7 −25.0 注:t为实测周期与经验公式周期的误差,c为计算模型周期与经验公式周期的误差。 -
郭迅,2018. 钢筋混凝土框架结构地震倒塌机理. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,22−25.Guo X. , 2018. Collapse mechanism of RC frame structures suffered from strong earthquake. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 22−25. (in Chinese) 黄群贤,郭子雄,朱雁茹等,2012. 混凝土空心砌块填充墙RC框架抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报,33(2):110−118.Huang Q. X., Guo Z. X., Zhu Y. R., et al., 2012. Experimental study on seismic behavior of RC frames infilled with concrete hollow blocks. Journal of Building Structures, 33(2): 110−118. (in Chinese) 金焕,戴君武,2013. 外廊式RC框架结构教学楼的抗震性能研究. 土木工程学报,46(5):71−77.Jin H., Dai J. W., 2013. Study on seismic behavior of side corridor RC frame school building. China Civil Engineering Journal, 46(5): 71−77. (in Chinese) 刘红彪,郭迅,何福,2010. 9度设防区房屋结构自振周期经验公式研究. 振动与冲击,29(S):101−104.Liu H. B., Guo X., He F., 2010. Study on experimental formulas of natural periods of structures in district of seismic fortification intensity 9. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 29(S): 101−104. (in Chinese) 罗若帆,郭迅,阿拉塔等,2021. 漾濞6.4级地震外廊式教学楼震害调查与分析. 世界地震工程,37(4):53−63.Luo R. F., Guo X., Alata, et al., 2021. Investigation and analysis of seismic damage to side corridor school buildings in M6.4 Yangbi earthquake. World Earthquake Engineering, 37(4): 53−63. (in Chinese) 马玉虎,陆新征,叶列平等,2011. 漩口中学典型框架结构震害模拟与分析. 工程力学,28(5):71−77.Ma Y. H., Lu X. Z., Ye L. P., et al., 2011. Seismic damage simulation and analysis of typical RC frames of Xuankou school. Engineering Mechanics, 28(5): 71−77. (in Chinese) 唐兴荣,周振轶,刘利花等,2012. 多层砌体填充墙框架结构抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报,33(11):72−81.Tang X. R., Zhou Z. Y., Liu L. H., et al., 2012. Experimental study on seismic behavior of multi-story masonry infilled reinforced concrete frame structures. Journal of Building Structures, 33(11): 72−81. (in Chinese) 王波,郭迅,宣越等,2021. 设置半高连续填充墙的RC框架结构地震倒塌振动台试验. 应用基础与工程科学学报,29(3):656−668.Wang B., Guo X., Xuan Y., et al., 2021. Shaking table test on collapse mechanism of RC frame with continuous half-height infilled walls. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 29(3): 656−668. (in Chinese) 温瑞智,胡进军,周正华,2008. 基于环境振动测试的高层钢筋混凝土结构模态参数识别. 地震研究,31(3):268−273.Wen R. Z., Hu J. J., Zhou Z. H., 2008. Mode identification of high-rise reinforced concrete structures based on ambient vibration test. Journal of Seismological Research, 31(3): 268−273. (in Chinese) 阎红霞,杨庆山,秦敬伟等,2012. 各国规范中RC框架自振周期的对比和探讨. 振动与冲击,31(11):108−113.Yan H. X., Yang Q. S., Qin J. W., et al., 2012. Comparison and comment for computing natural vibration period of RC frames in codes of some countries. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 31(11): 108−113. (in Chinese) 闫培雷,孙柏涛,2019. 基于环境激励法的高层钢筋混凝土剪力墙结构自振周期经验公式研究. 工程力学,6(2):87−95.Yan P. L., Sun B. T., 2019. Study on empirical formula of natural vibration period of high-rise reinforced concrete shear wall structure based on environmental motivation method. Engineering Mechanics, 6(2): 87−95. (in Chinese) 杨伟松,陶柱,郭迅等,2022. 填充墙外廊式RC框架结构倒塌振动台试验研究. 建筑结构学报,43(10):160−171.Yang W. S., Tao Z., Guo X., et al., 2022. Shaking table collapse test on exterior corridor RC frame with infill walls. Journal of Building Structures, 43(10): 160−171. (in Chinese) 杨玉成,孙柏涛,2010. 论多层砖砌体住宅楼的抗倒设计−−汶川地震映秀镇漩口中学宿舍楼震害探究. 地震工程与工程振动,30(6):1−12.Yang Y. C., Sun B. T., 2010. On seismic collapse-resistant design of multi-story brick masonry buildings: finding the causes of seismic damage to multi-story hostels of Xuankou middle school in Yingxiu town during Wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 30(6): 1−12. (in Chinese) 张永兵,郭新华,朱腾飞等,2021. 新型砌体填充墙RC框架结构抗震性能研究. 广西大学学报(自然科学版),46(5):1166−1176.Zhang Y. B., Guo X. H., Zhu T. F., et al., 2021. Seismic performance of new masonry-infilled reinforced concrete frame building. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 46(5): 1166−1176. (in Chinese) Al-Chaar G., Lamb G. E., Issa M. A., 2003. Effect of openings on structural performance of unreinforced masonry infilled frames. ACI Symposium Paper, 211: 247−262. Kakaletsis D. J., Karayannis C. G., 2009. Experimental investigation of infilled reinforced concrete frames with openings. ACI Structural Journal, 106(2): 132−141. Mehrabi A. B., Shing P. B., Schuller M. P., et al., 1996. Experimental evaluation of masonry-infilled RC frames. Journal of Structural Engineering, 122(3): 228−237. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1996)122:3(228) Mosalam K. M., White R. N., Gergely P., 1997. Static response of infilled frames using quasi-static experimentation. Journal of Structural Engineering, 123(11): 1462−1469. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1997)123:11(1462) -




 下载:
下载: