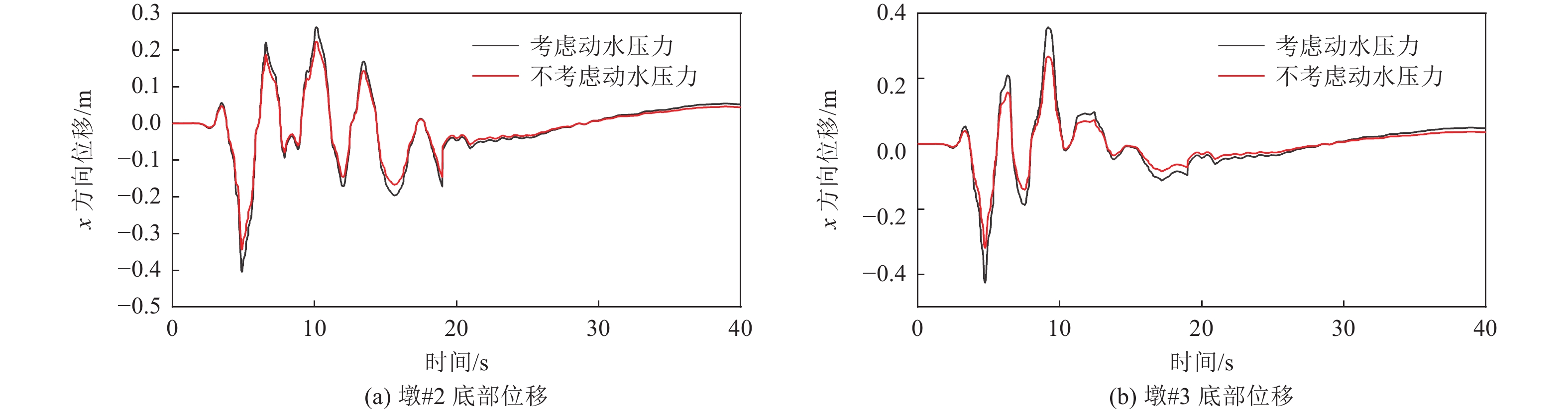
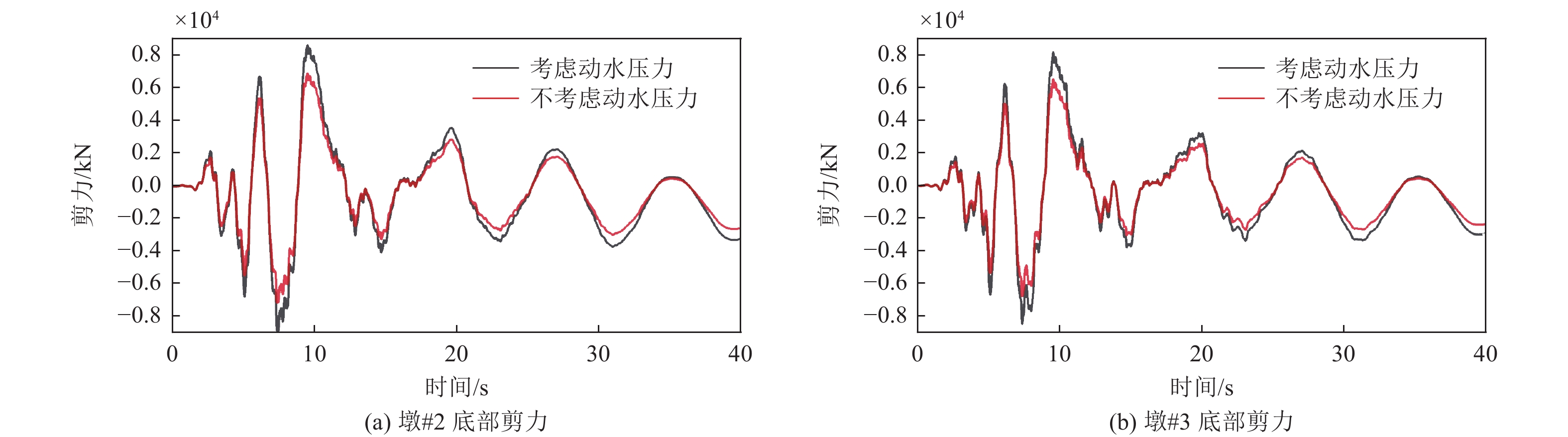
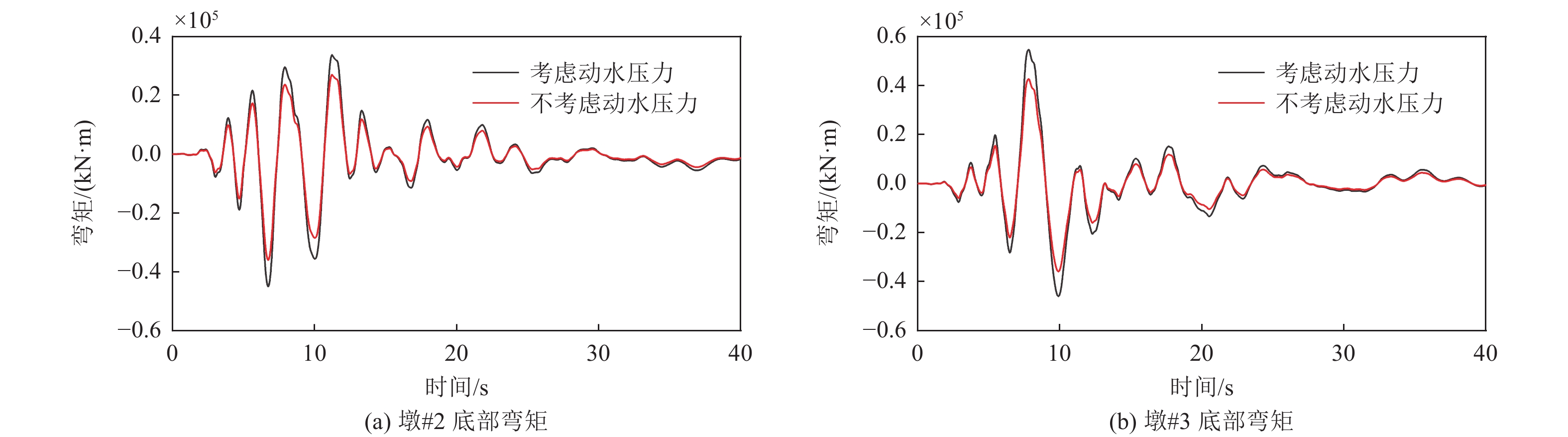
|
何颖, 于琴, 刘中宪, 2019. 考虑散射效应沉积河谷空间相关多点地震动模拟. 岩土力学, 40(7): 2739—2747, 2788He Y. , Yu Q. , Liu Z. X. , 2019. Simulation of multi-point spatially correlated earthquake ground motions of sedimentary valleys considering scattering effect. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(7): 2739—2747, 2788. (in Chinese)
|
|
黄磊, 刘中宪, 张雪等, 2020. 含流体层的河谷场地对地震波散射的间接边界元法模拟. 地震学报, 42(6): 657—668Huang L. , Liu Z. X. , Zhang X. , et al. , 2020. IBEM simulation of seismic wave scattering by valley topography with fluid layer. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 42(6): 657—668. (in Chinese)
|
|
李丽, 赵国峰, 李吉等, 2020. 一致激励与多点激励对悬索桥地震响应影响分析. 震灾防御技术, 15(2): 252—259Li L. , Zhao G. F. , Li J. , et al. , 2020. Analysis of the influence of uniform excitation and multi-point excitation on the seismic response of suspension bridge. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(2): 252—259. (in Chinese)
|
|
李平, 薄景山, 肖瑞杰等, 2018. 地震动河谷场地效应研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(2): 331—341Li P. , Bo J. S. , Xiao R. J. , et al. , 2018. The study of effect by the valley site on ground motion. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(2): 331—341. (in Chinese)
|
|
李伟华, 赵成刚, 2008. 平面SV波在饱和土半空间中圆柱形孔洞周边的散射. 地震工程与工程振动, 28(6): 1—7Li W. H. , Zhao C. G. , 2008. An analytical solution for the scattering of plane SV-waves around cylindrical cavity in a fluid-saturated porous media half space. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 28(6): 1—7. (in Chinese)
|
|
李忠献, 李笑穹, 李宁, 2014. 空间相关多点多维地震动的模拟. 地震工程与工程振动, 34(4): 64—72Li Z. X. , Li X. Q. , Li N. , 2014. Simulation of multi-point and multi-dimension spatially correlated earthquake ground motions. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 34(4): 64—72. (in Chinese)
|
|
梁建文, 吴孟桃, 巴振宁, 2021. 流体饱和半空间二维地形三分量弹性波散射间接边界元模拟. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2766—2779Liang J. W. , Wu M. T. , Ba Z. N. , 2021. IBEM simulation of three-component scattering of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated half-space with 2 D topography. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(8): 2766—2779. (in Chinese)
|
|
闫磊, 李青宁, 岳克锋等, 2019. 多维多点激励下考虑支座摩擦滑移及结构碰撞的非规则桥梁抗震性能研究. 世界地震工程, 35(2): 68—77Yan L. , Li Q. N. , Yue K. F. , et al. , 2019. Seismic behavior of irregular bridges under multi-dimensional and multi-point excitation considering friction slip of bearings and structural pounding. World Earthquake Engineering, 35(2): 68—77. (in Chinese)
|
|
Bi K. M. , Hao H. , 2012. Modelling and simulation of spatially varying earthquake ground motions at sites with varying conditions. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 29: 92—104. doi: 10.1016/j.probengmech.2011.09.002
|
|
Huang H. C. , Chiu H. C. , 1995. The effect of canyon topography on strong ground motion at Feitsui damsite: quantitative results. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 24(7): 977—990.
|
|
Li X. Q. , Li Z. X. , Crewe A. J. , 2018. Nonlinear seismic analysis of a high-pier, long-span, continuous RC frame bridge under spatially variable ground motions. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 114: 298—312. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.07.032
|
|
Liu Z. X. , Li W. X. , Jin L. G. , et al. , 2023 a. Efficient simulation of stochastic seismic response of long-span bridges in river valleys using hybrid BEM-FEM. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 165: 107690. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107690
|
|
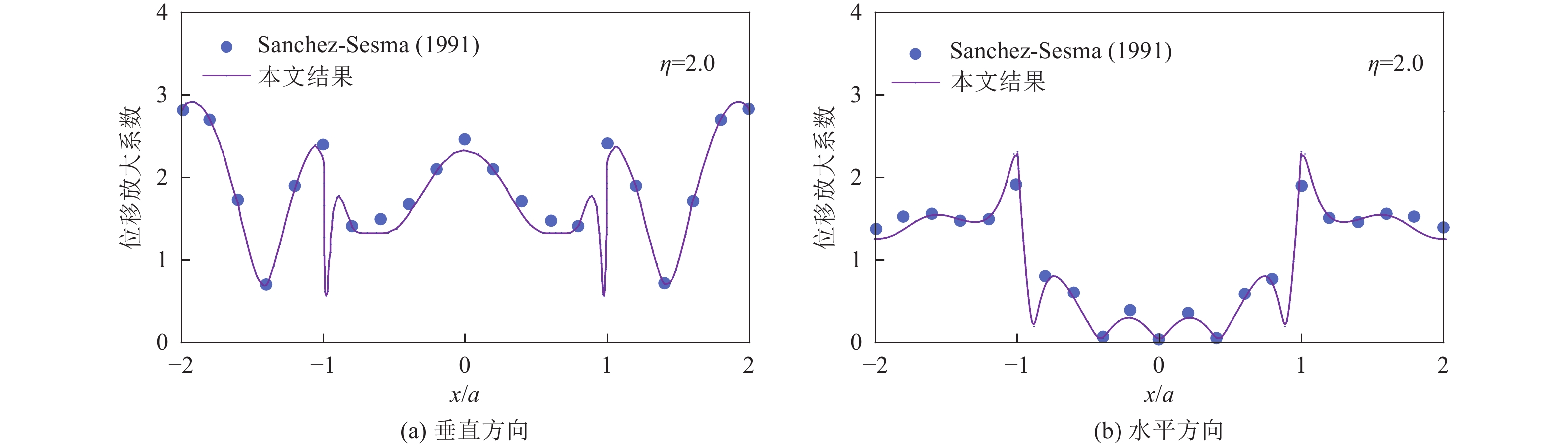
Sánchez-Sesma F. J. , Campillo M. , 1991. Diffraction of P, SV, and Rayleigh waves by topographic features: a boundary integral formulation. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 81(6): 2234—2253.
|
|
Wang P. G. , Zhao M. , Du X. L. , 2019. Simplified formula for earthquake-induced hydrodynamic pressure on round-ended and rectangular cylinders surrounded by water. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 145(2): 04018137. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001567
|
|
Wu Y. X. , Gao Y. F. , Zhang N. , et al. , 2016. Simulation of spatially varying ground motions in V-shaped symmetric canyons. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 20(6): 992—1010. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2015.1010049
|
|
Zanardo G. , Hao H. , Modena C. , 2002. Seismic response of multi-span simply supported bridges to a spatially varying earthquake ground motion. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 31(6): 1325—1345.
|



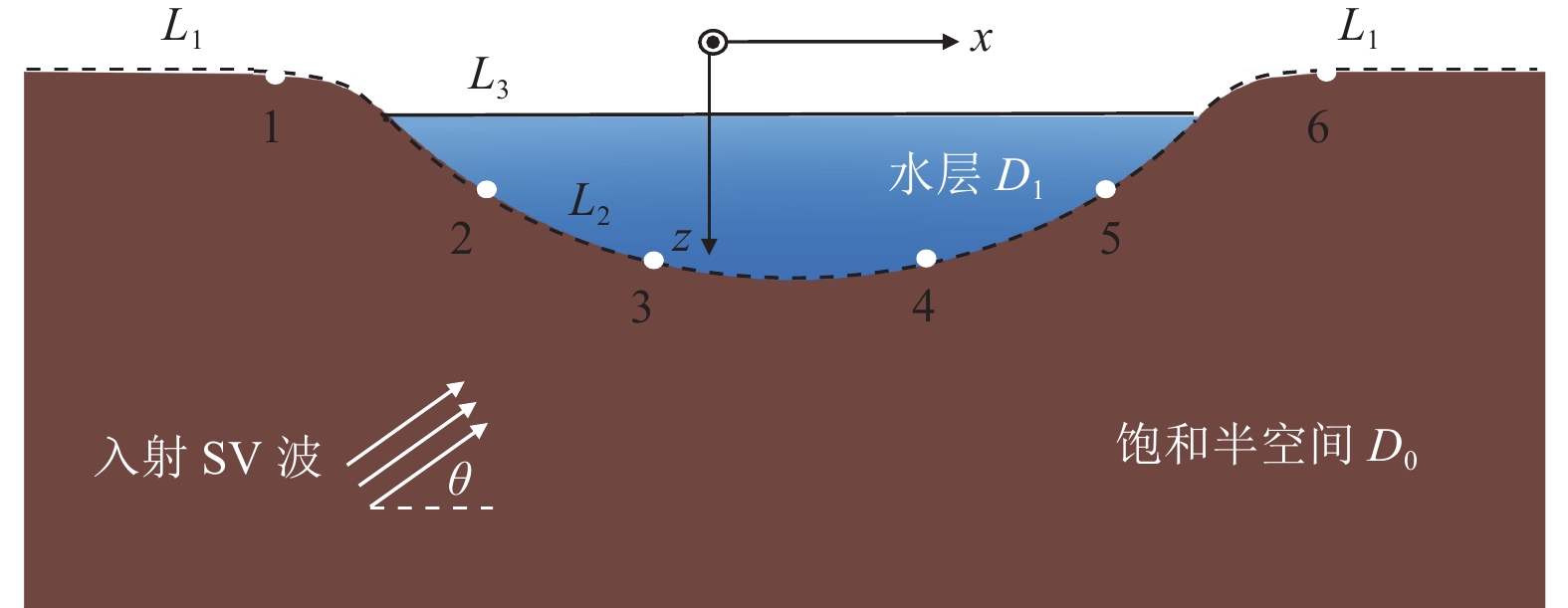
 下载:
下载: