Study on Mechanical Behavior of Large Steering Curved Tunnel under Combined Action of Earthquake and Fault Dislocation
-
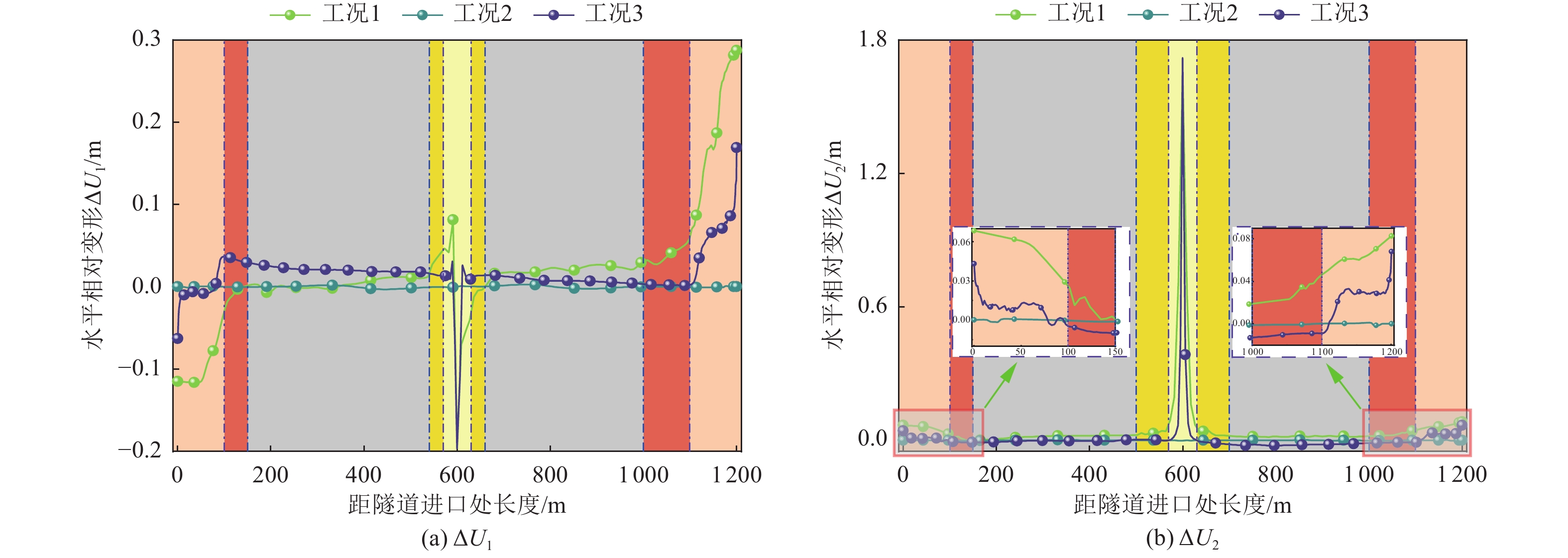
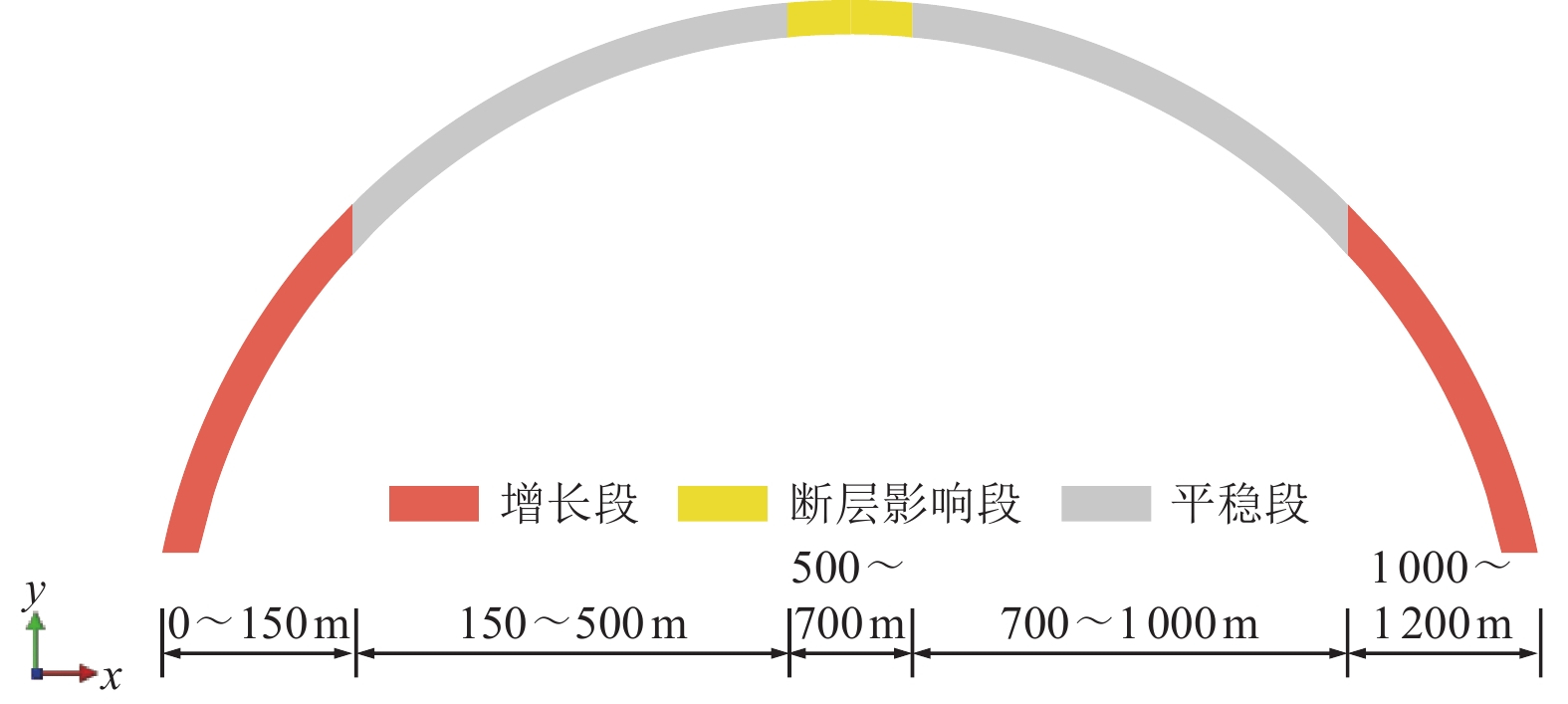
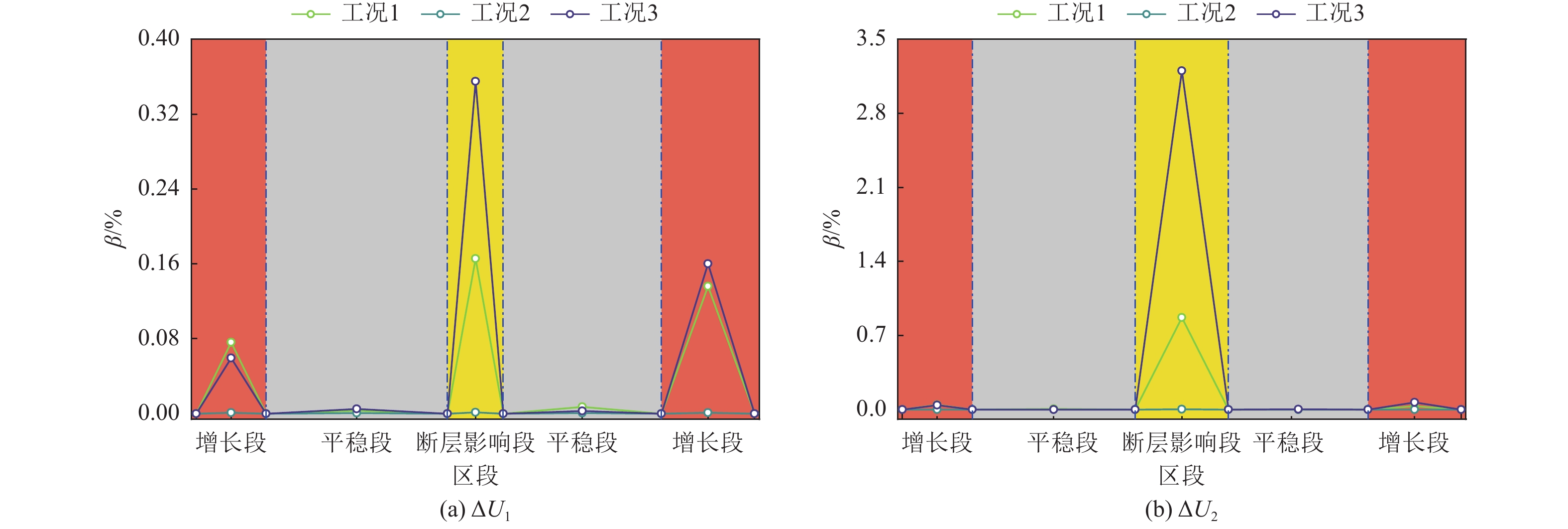
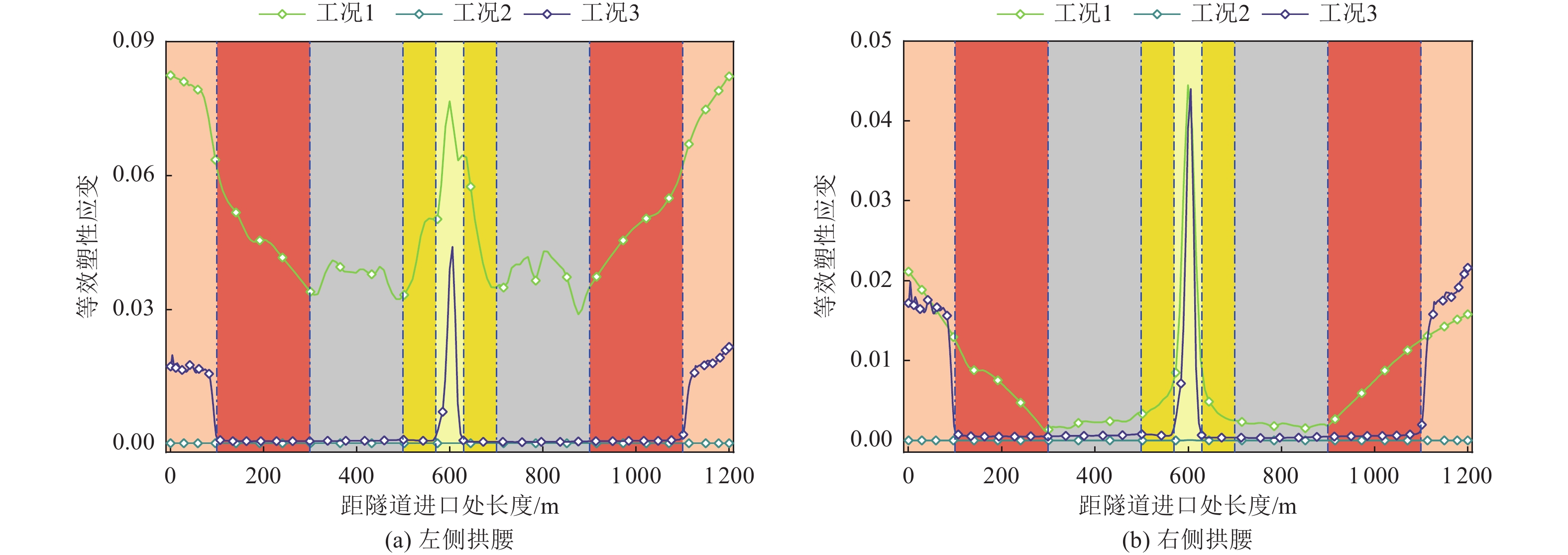
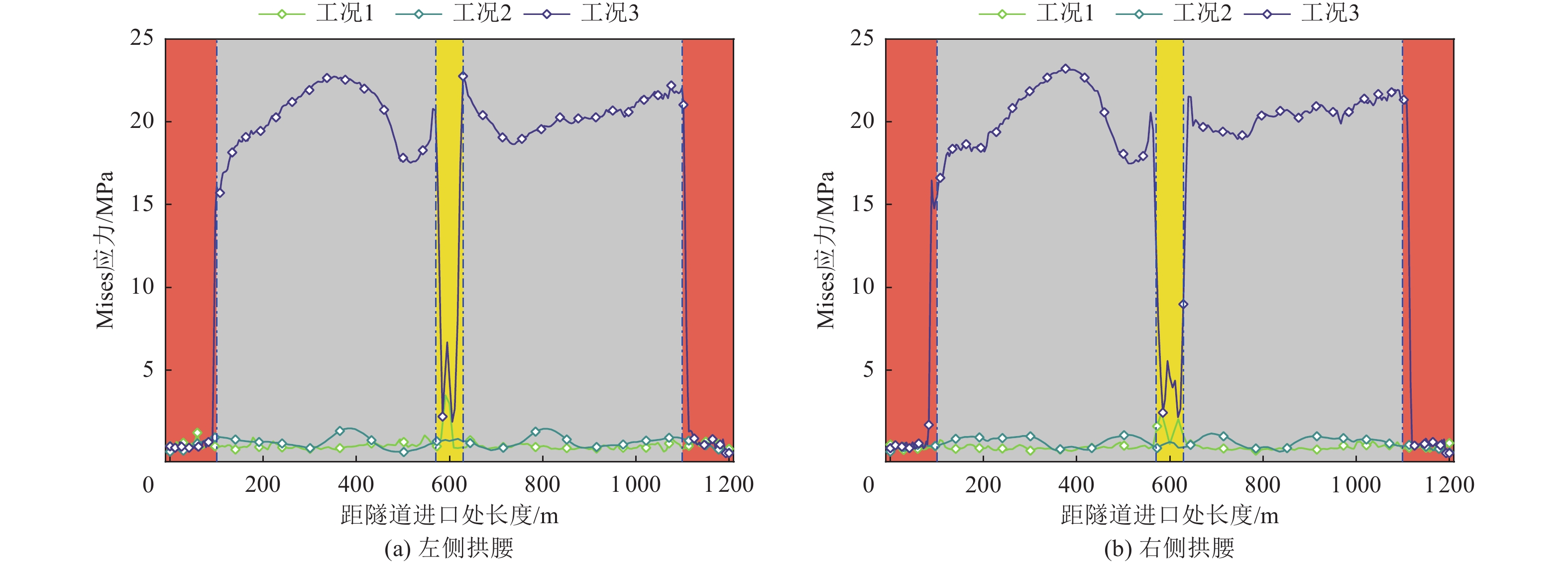
摘要: 针对现有研究较少涉及极高烈度区地震和断层错动共同作用下曲线隧道力学行为的问题,依托跑马山隧道极高烈度地震区和大转向曲线隧道工程特点,通过ABAQUS软件建立大转向曲线隧道在地震和断层错动共同作用下的数值模型,探明截面相对变形、塑性应变及应力纵向分布情况。研究结果表明,曲线隧道在地震和断层错动共同作用下,其截面相对变形最值与变形区域均有较大增长,其中,最值与变形区域较上述二者单独作用分别增长20%、50%;曲线隧道在地震和断层错动共同作用下,其塑性应变极值及影响范围均较地震或断层错动单独作用下高,分别为单独作用下的2、3倍,比二者单独作用下的塑性应变极值和影响范围线性相加大,表明在地震和断层错动共同作用下,其对曲线隧道的影响并非简单的线性相加;根据截面相对变形、等效塑性应变及应力纵向分布情况,可将曲线隧道分为3个区段,分别为增长段、平稳段及断层影响段,对应的长度分别为隧道跨度的50%、33%、17%,增长段主要为断层错动和地震作用的共同结果,而断层影响段主要与断层错动有关。Abstract: IThis study addresses the limited research on the mechanical behavior of curved tunnels subjected to the combined effects of high-intensity earthquakes and fault dislocations. Using the Paomashan Tunnel, located in a high-intensity seismic zone with a large steering curve, as a case study, a numerical model was developed in ABAQUS to analyze the longitudinal distribution of relative cross-sectional deformation, plastic strain, and stress under the combined action of seismic forces and fault dislocation. The results indicate that, under the combined effects of seismic and fault dislocation, the maximum relative cross-sectional deformation and the deformation zones of the curved tunnel increase significantly. Specifically, the maximum deformation increases by 20%, and the deformation zone expands by 50%, compared to the effects of seismic or fault dislocation alone. Additionally, the peak plastic strain and its affected range under the combined action are much higher than those under either seismic or fault dislocation separately, being 2 and 3 times greater, respectively. This demonstrates that the combined impact of seismic and fault dislocation is not simply a linear superposition. Based on the relative cross-sectional deformation, equivalent plastic strain, and longitudinal stress distribution, the curved tunnel can be divided into three sections: the growth section (50% of the tunnel span), the stable section (33%), and the fault-affected section (17%). The growth section is primarily influenced by the combined effects of seismic and fault dislocation, while the fault-affected section is mainly dominated by fault dislocation.
-
Key words:
- Curved tunnel /
- Extremely high intensity area /
- Earthquake /
- Fault dislocation /
- Numerical simulation
-
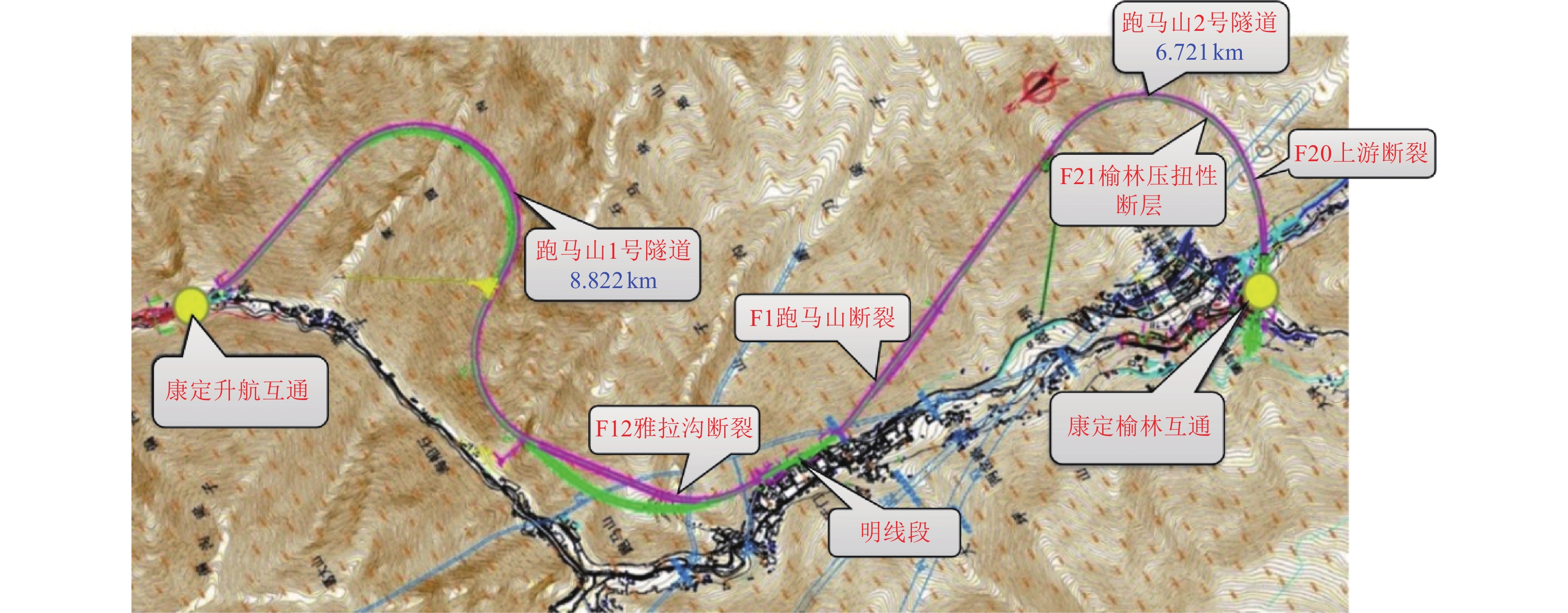
表 1 跑马山隧道平面线型
Table 1. Summary of plane line types of Paomashan tunnel
隧道名称 交点号 转角/(°) 半径/m 跨度/m 跑马山1号隧道 JD1 50.2 950 806.0 JD2 26.1 1 360 614.2 JD3 118.4 1 030 1 769.5 JD4 33.9 2 050 1 195.3 跑马山2号隧道 JD5 28.7 1 150 570.0 JD6 166.9 980 1 947.2 JD7 95.3 1 000 1 478.1 表 2 模型材料参数
Table 2. The parameters of materials
名称 V级围岩 C30 重度/(kN·m−3) 18 25 弹性模量/MPa 1 000 30 000 内摩擦角/(°) 32 — 泊松比 0.4 0.2 黏聚力/MPa 0.135 — 表 3 工况设计
Table 3. The case design
工况编号 作用形式 工况1 地震、断层错动共同作用 工况2 地震作用 工况3 断层错动作用 -
陈峻博,王天强,耿萍等,2025. 蠕滑-强震叠加作用下跨断层隧道动力响应分析研究. 铁道标准设计,69(1):129−138.Chen J. B., Wang T. Q., Geng P., et al., 2025. Dynamic response analysis on a cross-fault tunnel subjected to action of strong earthquake after fault creep-slip. Railway Standard Design, 69(1): 129−138. (in Chinese) 陈熹,2017. 活动断层错动下跨断层隧道动力响应及破坏机理研究. 成都:西南交通大学.Chen X. ,2017. Study on dynamic response and failure mechanism of the crossing-fault tunnel under the action of active fault. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University. (in Chinese) 杜修力,赵密,王进廷,2006. 近场波动模拟的人工应力边界条件. 力学学报,38(1):49−56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2006.01.007Du X. L., Zhao M., Wang J. T., 2006. A stress artificial boundary in FEA for near-field wave problem. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 38(1): 49−56. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2006.01.007 高波,王峥峥,袁松等,2009. 汶川地震公路隧道震害启示. 西南交通大学学报,44(3):336−341,374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.03.005Gao B., Wang Z. Z., Yuan S., et al., 2009. Lessons learnt from damage of highway tunnels in Wenchuan Earthquake. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 44(3): 336−341,374. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.03.005 郭翔宇,曾冠雄,王琦等,2021a. Ⅴ级围岩-断层条件下修正地震系数法对铁路隧道适用范围研究. 铁道学报,43(12):130−137.Guo X. Y., Zeng G. X., Wang Q., et al., 2021a. Study on applicability of modified seismic coefficient method to railway tunnels under condition of grade V surrounding rock and fault. Journal of the China Railway Society, 43(12): 130−137. (in Chinese) 郭翔宇,耿萍,丁梯等,2021b. 逆断层黏滑作用下隧道力学行为研究. 振动与冲击,40(17):249−258.Guo X. Y., Geng P., Ding T., et al., 2021b. Mechanical behavior of tunnel under stick-slip action of reverse fault. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 40(17): 249−258. (in Chinese) 李金都,陈书涛,1999. 南水北调西线调水区地质条件与关键工程地质问题分析. 人民黄河,21(2):22−24. 廖振鹏,刘晶波,1986. 离散网格中的弹性波动(Ⅰ). 地震工程与工程振动,(2):1−16.Liao Z. P., Liu J. B., 1986. Elastic wave motion in discrete grids (I). Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, (2): 1−16. (in Chinese) 刘涛,赵冯兵,罗建强,2020. 特大断面公路隧道浅埋段抗减震技术研究. 现代隧道技术,57(S1):596−602.Liu T., Zhao F. B., Luo J. Q., 2020. Research on aseismic technology for shallow-buried section of super-large diameter highway tunnel. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 57(S1): 596−602. (in Chinese) 彭述权,刘贤,樊玲等,2023. 地震动和断层错动联合作用下隧道纵向响应解析解. 震灾防御技术,18(2):215−225. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20230202Peng S. Q., Liu X., Fan L., et al., 2023. Analytical solution for the longitudinal response of tunnels under combined seismic-fault misalignment. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 18(2): 215−225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20230202 苏茹,2019. 基于裂缝缺陷的隧道二次衬砌地震动力响应分析. 西安:西安建筑科技大学.Su R., 2019. Analysis and research on the dynamic response of tunnel secondary lining layer with crack defection. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology. (in Chinese) 汪振,钟紫蓝,黄景琦等,2020a. 走滑断层错动下山岭隧道关键断面变形及损伤演化. 建筑结构学报,41(S1):425−433.Wang Z., Zhong Z. L., Huang J. Q., et al., 2020a. Deformation and damage evolution of critical cross section of mountain tunnels under strike-slip fault movement. Journal of Building Structures, 41(S1): 425−433. (in Chinese) 汪振,钟紫蓝,赵密等,2020b. 正断型断裂模拟及其对山岭隧道影响研究. 岩土工程学报,42(10):1876−1884.Wang Z., Zhong Z. L., Zhao M., et al., 2020b. Simulation of normal fault rupture and its impact on mountain tunnels. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 42(10): 1876−1884. (in Chinese) 闫高明,申玉生,信春雷等,2019. 衬砌背后空洞对隧道地震响应影响的振动台试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报,38(12):2491−2501.Yan G. M., Shen Y. S., Xin C. L., et al., 2019. Shaking table test research of the influence of voids on seismic responses of tunnel structures. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 38(12): 2491−2501. (in Chinese) 赵大能,王毅,任志华,2023. 考虑断层错动-地震动共同作用的隧道结构力学响应分析. 现代隧道技术,60(4):95−105.Zhao D. N., Wang Y., Ren Z. H., 2023. Mechanical response analysis for tunnel structure considering the interaction of fault dislocation and seismic motion. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 60(4): 95−105. (in Chinese) 周佳媚,程毅,邹仕伟等,2019. 断层错动及地震作用下隧道力学特性研究. 铁道标准设计,63(11):138−144.Zhou J. M., Cheng Y., Zou S. W., et al., 2019. Research on mechanical characteristics of tunnel under fault movement and seismic. Railway Standard Design, 63(11): 138−144. (in Chinese) 周彦良,戴俊,张晓君,2013. 地震波输入方向对曲线隧道地震响应的影响分析. 铁道建筑,(8):65−67. Cui Z., Sheng Q., Zhang G. M., et al., 2022. Response and mechanism of a tunnel subjected to combined fault rupture deformation and subsequent seismic excitation. Transportation Geotechnics, 34 :100749. Fabozzi S., Bilotta E., Yu H., et al., 2018. Effects of the asynchronism of ground motion on the longitudinal behaviour of a circular tunnel. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 82: 529−541. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.09.005 Fan L., Chen J. L., Peng S. Q., et al., 2020. Seismic response of tunnel under normal fault slips by shaking table test technique. Journal of Central South University, 27(4): 1306−1319. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4368-0 Somerville P., Irikura K., Graves R., et al., 1999. Characterizing crustal earthquake slip models for the prediction of strong ground motion. Seismological Research Letters, 70(1): 59−80. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.70.1.59 Wells D. L., Coppersmith K. J., 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 974−1002. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0840040974 Yan G. M., Shen Y. S., Gao B., et al., 2020. Damage evolution of tunnel lining with steel reinforced rubber joints under normal faulting: an experimental and numerical investigation. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 97: 103223. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.103223 Yu H. T., Li X. X., Li P., 2022. Analytical solution for vibrations of a curved tunnel on viscoelastic foundation excited by arbitrary dynamic loads. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 120: 104307. -



 下载:
下载: