New Finding of Earthquake Surface Rupture on Zhongdian-Daju Fault
-
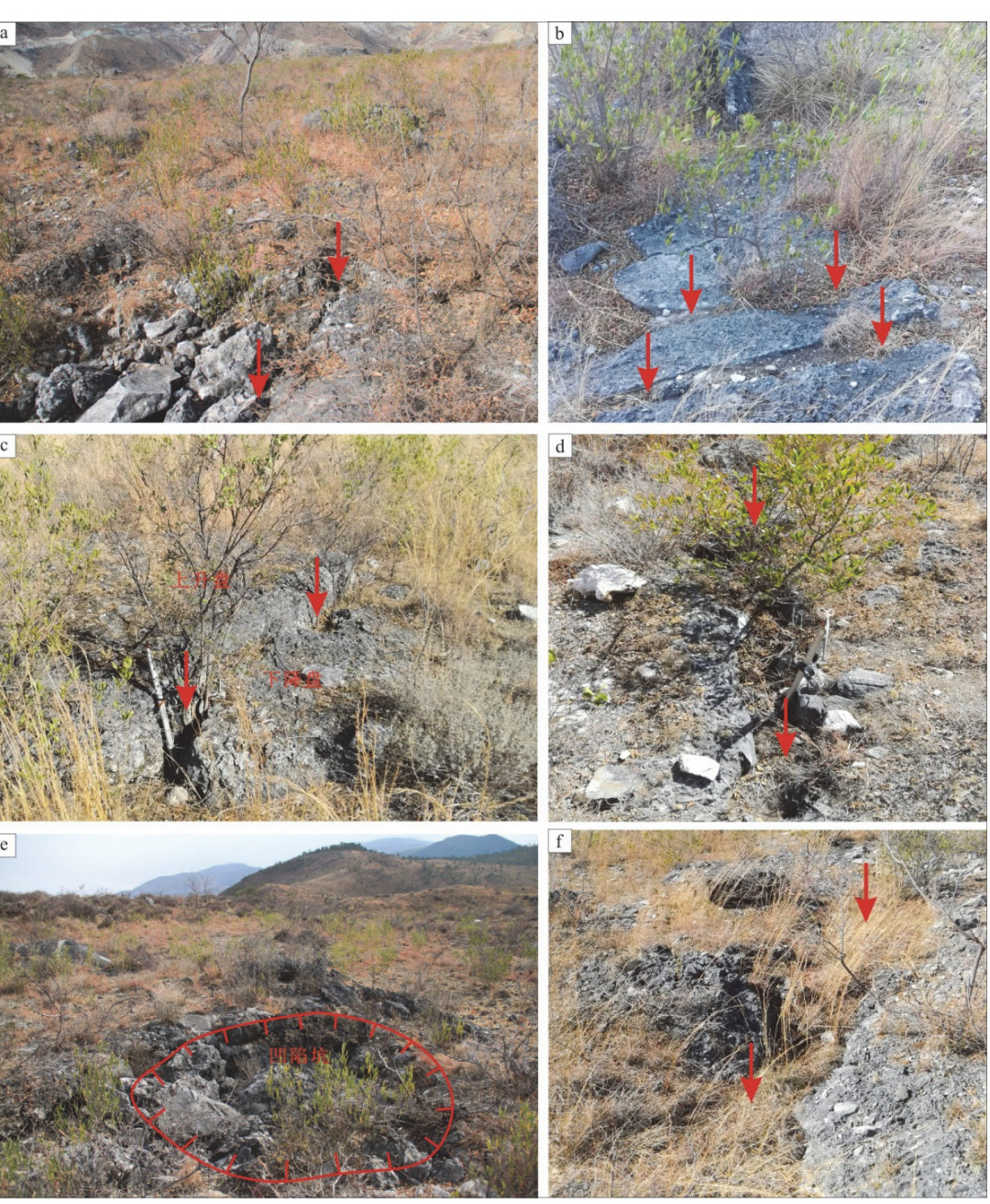
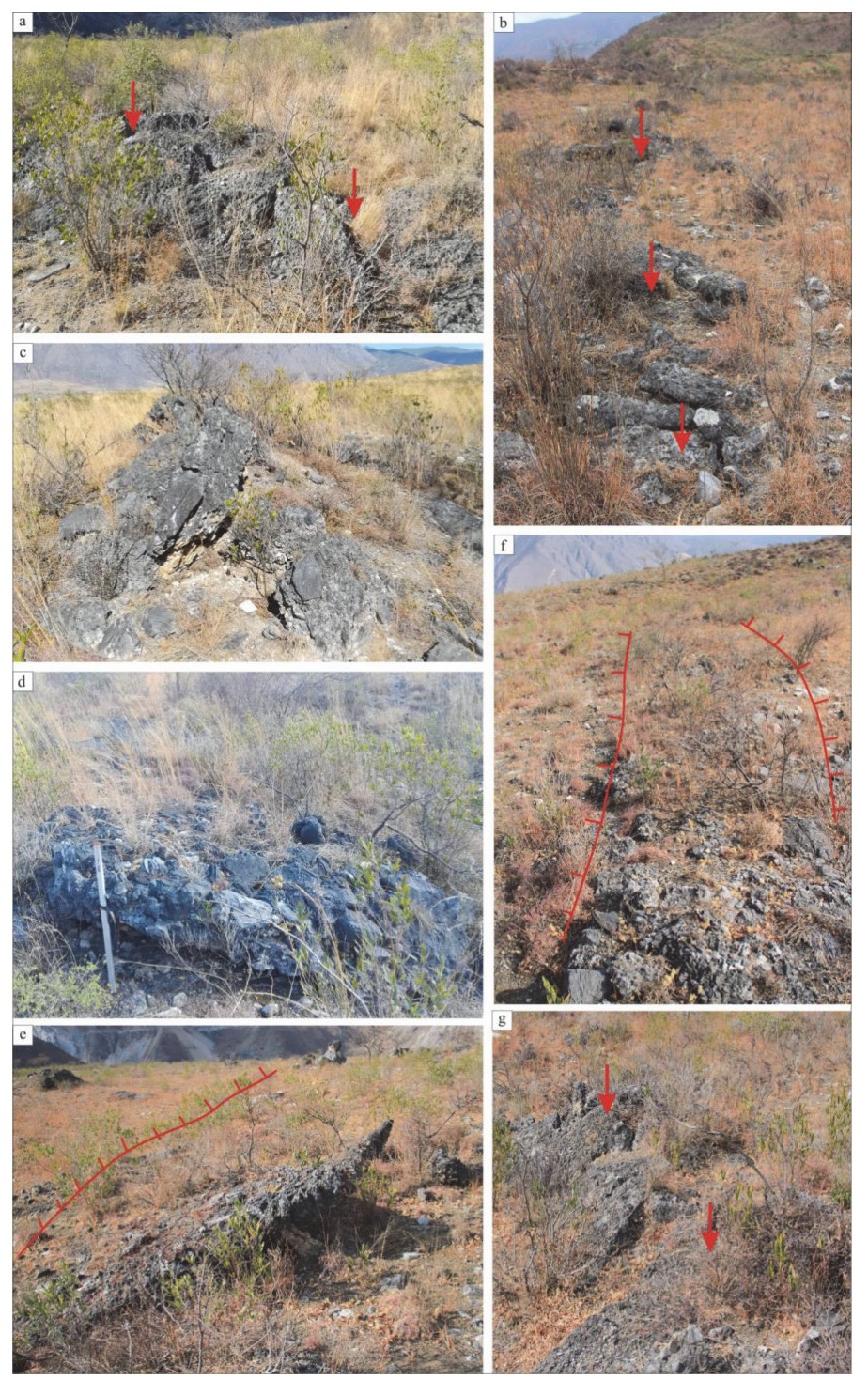
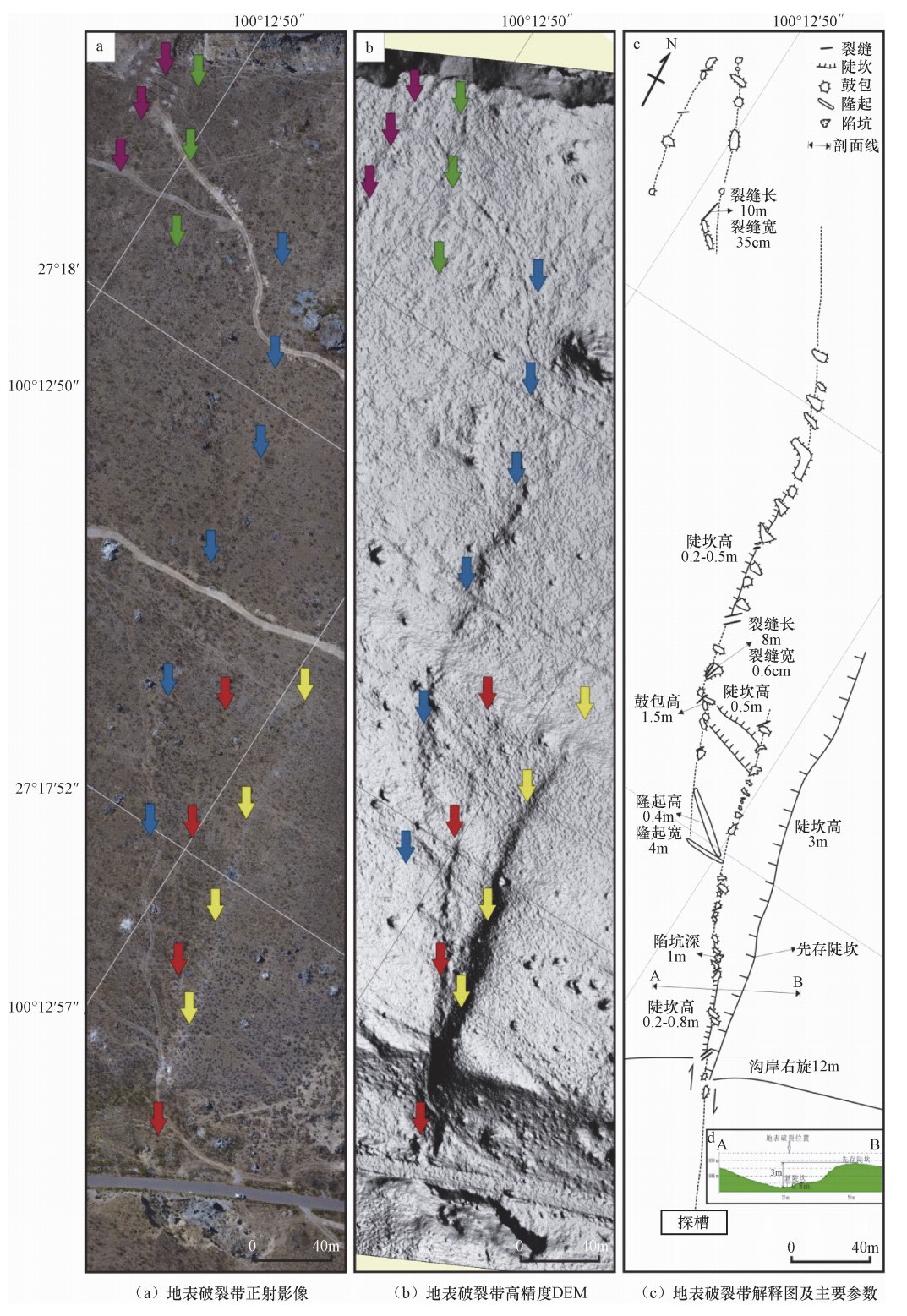
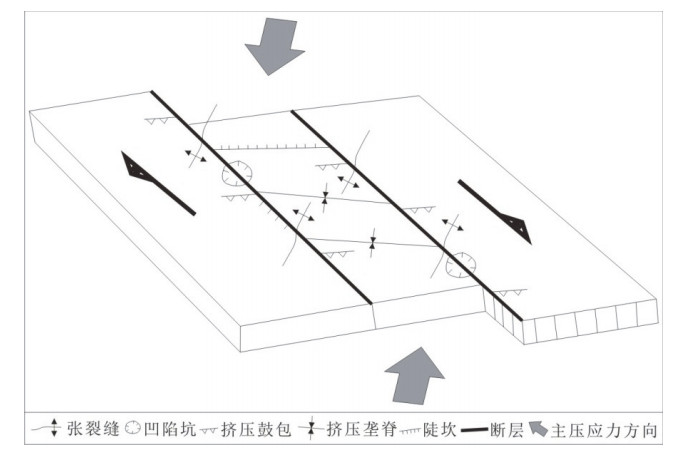
摘要: 中甸-大具断裂是川滇菱形块体的西南边界,总体走向310°—320°。近年来我们对该断裂进行了1:50000条带状地质填图,发现了断裂活动的地质地貌证据。其中,在丽江大具盆地内(金沙江右岸)沿断裂新发现一处典型地震地表破裂带,长约600m,宽120m左右,主要表现为地表挤压鼓包、挤压垄脊、张裂缝、挤压阶区等,呈NW走向,与中甸-大具断裂走向基本一致。野外工作中,我们详细记录和测量了地表破裂的破裂样式、破裂规模和相关定量数据,利用旋翼无人机测绘了地表破裂带的形态和展布,获得了高精度DEM,分析了地表破裂表现出的运动性质。在已有资料的基础上讨论了地表破裂的形成时代、归属、震级大小,简要分析了其发震断层。新地震地表破裂带的发现为进一步研究中甸-大具断裂活动特征、古地震及地震危险性提供了基础资料。Abstract: The Daju fault is the south segment of the Deqin-Zhongdian-Daju fault zone,with an overall trend of 310°-320°. In recent years,the fracture has been scaled by 1:50000,and the geomorphological evidence of the fault activity has been discovered. A typical earthquake surface rupture zone was newly found along the fault in the Daju Basin (the right bank of Jinsha River) in the Majiacun-Dadong segment,about 600 meters long and about 120 meters wide,mainly represented by mole track,uplifts,transtensional crack,and extrusion-apart. The trend of the rupture is basically the same as that of Daju fault in NW direction; the right-lateral dislocation of the left bank of the ancient gully trench was found 12m on the southeast side of the rupture zone. The trenche excavated nearby revealed that the latest activity of the fault was broken to the near surface,and the age of the undistorted strata was (50±5) aB.P. Comprehensive analysis of the rupture characteristics of the surface rupture and the ruptureintensity distribution and focal mechanism of the Lijiang earthquake in 1996 are carried out.. It is believed that the surface rupture zone of the earthquake may not be directly related to the Lijiang earthquake,but it should be a new one. The rupture event represents an undiscovered ancient earthquake event. Based on the existing data,the formation age,coseismic displacement and magnitude of surface rupture are discussed. The discovery of the surface rupture zone of the new earthquake provides basic data for further study of the characteristics of large fault activities,paleo-earthquakes and seismic hazards.
-
Key words:
- Zhongdian-Daju Fault /
- surface rupture /
- mole track /
- right-lateral slip
-
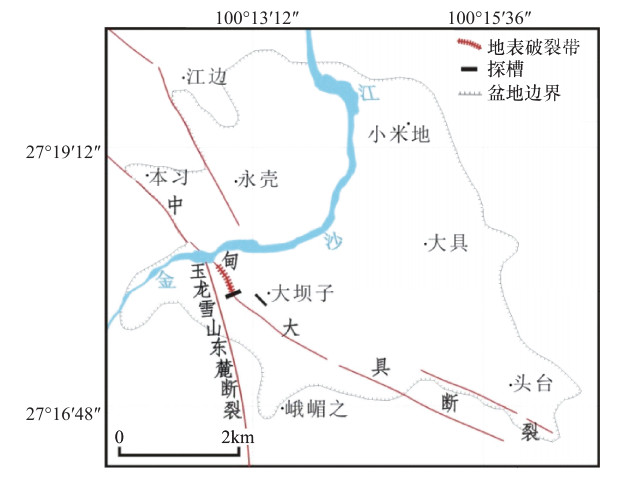
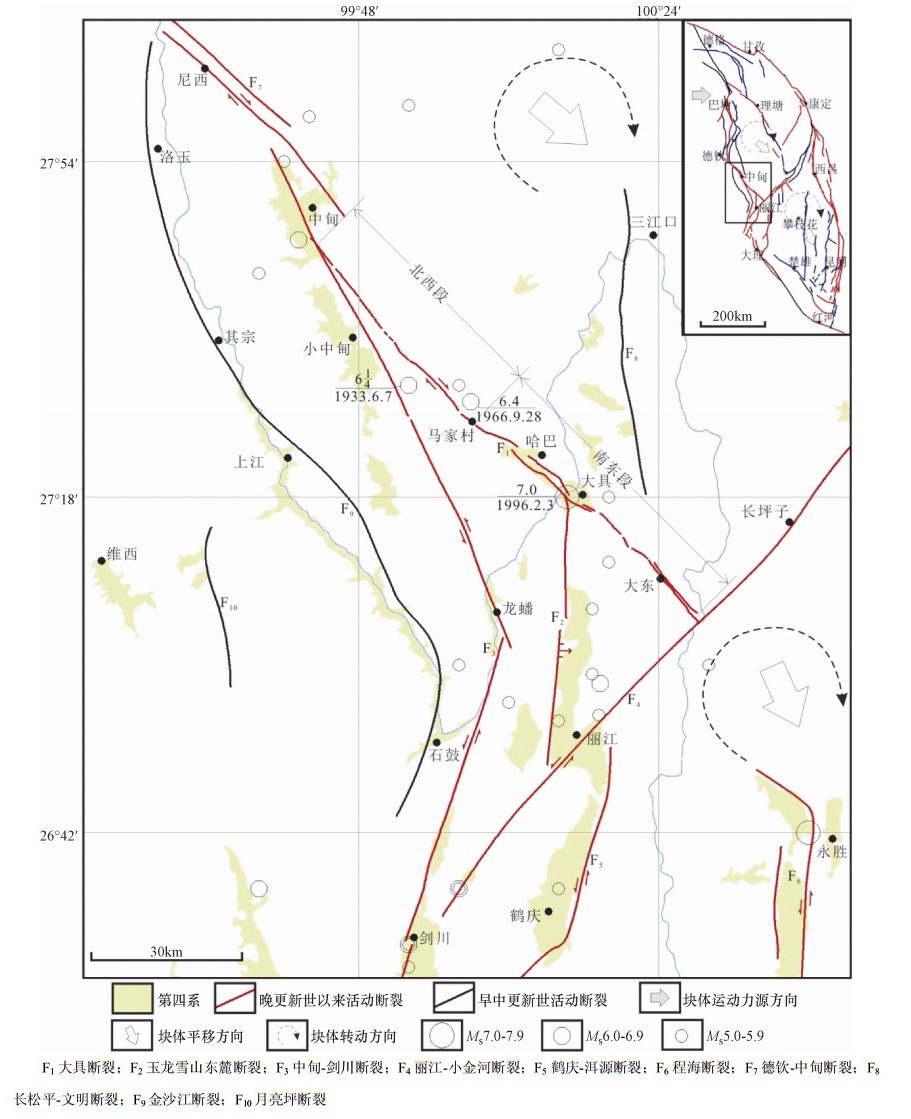
图 1 云南大具盆地及其邻区主要活动断裂与强震震中分布图(部分内容据徐锡伟等,2003)
F1大具断裂;F2玉龙雪山东麓断裂;F3中甸-剑川断裂;F4丽江-小金河断裂;F5鹤庆-洱源断裂;F6程海断裂;F7德钦-中甸断裂;F8长松平-文明断裂;F9金沙江断裂;F10月亮坪断裂
Figure 1. Major active faults and epicentral distribution of strong earthquakas in Daju basin and its adjacent areas(Part of the content auovding to Xu Xiwei et al, 2003)
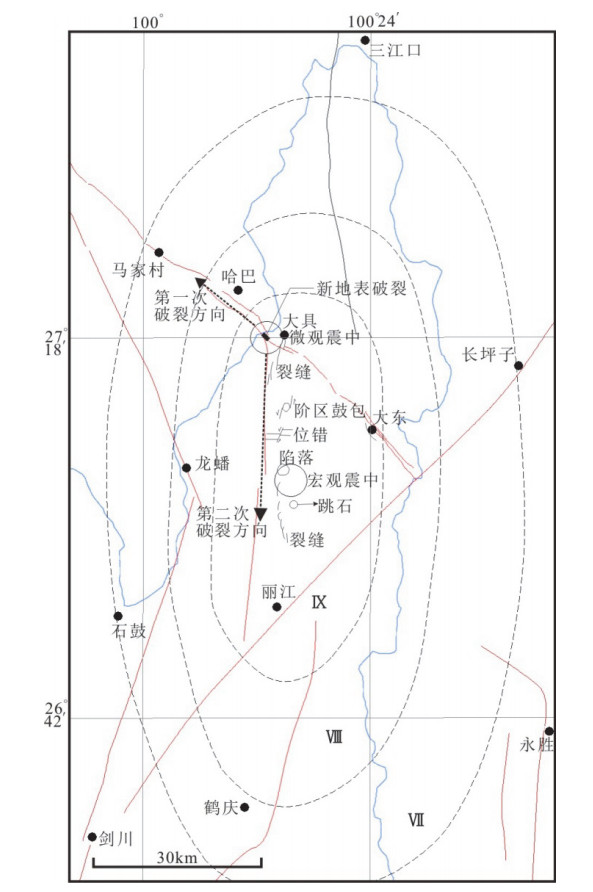
图 7 丽江地震地表破裂、烈度及破裂方向简图(据王绍晋等,1997;周光全等,1997;韩新民等,1997)
Figure 7. Simplified map of surface rupture, intensity andrupture direction of Lijiang earthquake(according to Wang Shaojin et al, 1997;Zhou Guangquan et al, 1997;Han Xinmin et al, 1997)
-
常祖峰, 2015.2013年云南奔子栏M5.9地震发生的地震地质背景.地震地质, 37(1):192-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.015 常祖峰, 张艳凤, 李鉴林等, 2014.德钦-中甸-大具断裂晚第四纪活动的地质与地貌表现.地震研究, 37(1):46-52. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/dzyj201401007 韩新民, 周瑞琦, 1997.丽江7.0级地震的烈度分布.地震研究, 20(1):35-46. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2562025 韩竹军, 虢顺民, 向宏发等, 2004.1996年2月3日云南丽江7.0级地震发生的构造环境.地震学报, (4):410-418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2004.04.010 皇甫岗, 1997.1996年2月3日云南丽江7.0级地震.地震研究, 20(1):1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhen200404010 国家地震局地质研究所, 云南省地震局, 1990.滇西北地区活动断裂.北京: 地震出版社. 国家地震局震害防御司, 1995.中国历史强震目录: 公元前23世纪-公元1911年.北京: 地震出版社. 虢顺民, 向宏发, 1996.红河断裂带第四纪右旋走滑与尾端拉张转换关系研究.地震地质, 18(4):301-309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600061846 李光涛, 程理, 李峰等, 2019.中甸-大具断裂南东段第四纪活动的地质地貌证据.地震地质, 41(3):545-560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.03.001 冉勇康, 王景钵, 尤惠川等, 1990.云南大理上关-潘曲一带存在历史地震破裂遗迹.地震地质, 12(3):272-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDZ199003012.htm 沈军, 汪一鹏, 任金卫, 2001.中国云南德钦-中甸-大具断裂带第四纪右旋走滑运动.青藏高原岩石圈现今变动与动力学.北京: 地震出版社. 石许华, 王二七, 王刚等, 2008.青藏高原东南缘玉龙雪山(5596m)晚新生代隆生的侵蚀与构造控制.控制第四纪研究, 28(2):222-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200802004 苏生瑞, 王运生, 王士天, 2004.丽江地震区应力场研究.地质评论, 50(1):57-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200401008 王明明, 刘韶, 史丙新等, 2017.2013年香格里拉-德荣Ms 5.9级地震震中区地质地貌调查.华南地震, 37(1):80-88. https://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_south-china-journal-seismology_thesis/0201264615057.html 王绍晋, 龙晓帆, 罗淑进, 1997.丽江地震序列的震源机制、发震应力场和破裂特征.地震研究, 20(1):26-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZYJ701.004.htm 王运生, 王士天, 李渝生, 2000.滇西北玉龙雪山隆升机制.山地学报, 18(4):313-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2000.04.005 吴中海, 胡道功, 吴珍汉, 2004.青藏铁路邻侧昆仑山2001年Ms8.1级地震地表破裂特征分析.地球学报, 25(4):411-414. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200404004 吴中海, 张永双, 胡道功等, 2008.滇西北哈巴-玉龙雪山东麓断裂的晚第四纪正断层作用及其动力学机制探讨.中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 38(11):1361-1375. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200811004 徐锡伟, 陈文彬, 于贵华等, 2002.2001年11月14日昆仑山库赛湖地震(Ms8.1)地表破裂带的基本特征.地震地质, 24(1):1-17. 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 郑荣章等, 2003.川滇地区活动块体最新构造变动样式及其动力来源.中国科学(D辑), 33(增刊):151-162. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1017 徐扬, 菊地正幸, 苏有锦, 1998.1996年2月3日云南丽江地震震源过程的体波反演.地震学报, 20(2):113-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.1998.02.001 尹功明, 苏刚, 丁锐等, 2017.云南玉龙雪山东麓断层的运动性质及其地貌意义.第四纪研究, 37(2):250-259. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201702004 俞维贤, 王彬, 谢英情等, 2004.玉龙雪山周缘主要断裂的断层泥中石英碎砾表面SEM特征与丽江地震.地震研究, 27(1):81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2004.01.013 张建国, 周瑞琦, 吴伯黔等, 1997.丽江7.0级地震地表破裂与形变特征.地震研究, 20(1):58-65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhen200302006 张西娟, 曾庆利, 马寅生, 2006.玉龙-哈巴雪山断块差异隆升的基本特征及其地质灾害效应.中国地质, 33(5):1075-1082. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.05.017 赵希涛, 张永双, 胡道功等, 2006.云南丽江地区大具盆地早更新世金沙江砾石层的发现及其意义.地质通报, 25(12):1381-1386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.005 周光全, 张建国, 周瑞琦等, 1997.丽江7.0级地震的地震地质构造背景分析.地震研究, 20(1):92-100. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2562031 Allen, C. R., Gillespie, A. R., Han, Y., et al, 1984. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China:Quaternary geology, slip rates, and seismic hazard[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 95 (6):686-700. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95<686:RRAAFY>2.0.CO;2 Allen, C. R., Luo, Z., Qian, H., et al, 1991. Field study of a highly active fault zone:The Xianshuihe fault of southwestern China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 103(9):1178-1199. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1991)103<1178:FSOAHA>2.3.CO;2 Gan W. J., Zhang P. Z., Shen Z. K., et al, 2007. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan Plateau inferred from GPS measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(B8):B04816. doi: 10.1029-2005JB004120/ Kong P., Na C. G., Fink D., et al, 2009. Moraine dam related to late Quaternary glaciation in the Yulong Mountains, southwest China, and impacts on the Jinsha River. Quaternary Science Reviews, 28(27):3224-3235. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1d49432b8b3ae55a58a8fa953fc6e492 Tapponnier, P., Peltzer, G., Armijo, R., 1986. On the mechanics of the collision between India and Asia. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 19 (1):113-157. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.07 Wang, E., Burchfiel, B. C., 1997. Interpretation of Cenozoic Tectonics in the Right-Lateral Accommodation Zone Between the Ailao Shan Shear Zone and the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. International Geology Review, 39(3):191-219. doi: 10.1080/00206819709465267 Wang, E., Burchfiel, B. C., Royden, L. H., et al, 1998. Late cenozoic Xianshuihe/Xiaojiang and Red River fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China. Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, 327:1-108. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2f9d9fcd1d57fe2555b8597858941f6b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn -



 下载:
下载: