Comprehensive Study on Activity of the Western Margin Fault and Genesis Analysis of Qinwangchuan Basin
-
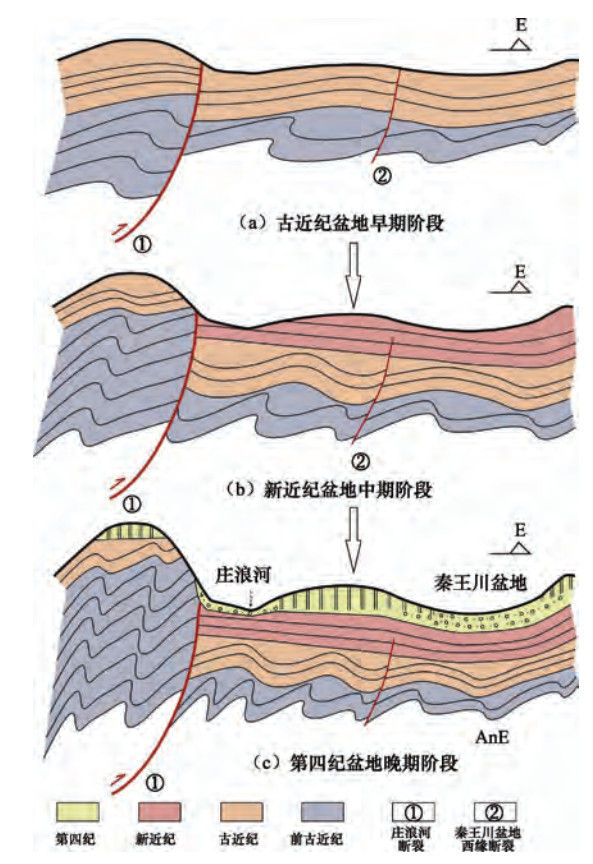
摘要: 秦王川盆地西缘断裂发育于陇中盆地地震构造区内部,本文对其进行了综合研究。浅层人工地震探测表明,该断裂在最小埋深130m处有显示,联合钻探结果表明该深度处为新近纪湖相沉积地层,泥岩层顶面向盆地方向呈斜坡状,槽探未揭露出断层。综合研究表明该断裂发育在新近纪地层内部,并未上穿第四纪沉积物,属于前第四纪隐伏断层。秦王川盆地在古近纪—新近纪山间泛湖盆的基础上,由于区域构造应力不均匀挤压抬升,形成山间负向地形,成为第四纪多变环境下河流堆积的拗陷盆地。秦王川盆地西缘断裂不具有控制中强地震空间分布的作用和形成地表破裂的能力,对盆地的构造稳定性不构成影响,亦不影响兰州新区的规划发展。Abstract: The western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin can be regarded as interior fracture of the seismotectonic province of Longzhong basin.Taking the seismic microzoning of Lanzhou New Area as an opportunity, the authors made a comprehensive research on the western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin.The results showed that in the 130m depth of the upper breakpoint of the fault is fonnd in the Neogene lacustrine strata by shallow seismic exploration and joint drilling, the roof of the mudstone trends in the direction of the Qinwangchuan basin too.The Baojiayao trench reveals no fault eviclerce near surface.Comprehensive research shows that the fault developed in the Neogene strata and did not cut upward the Quaternary sediments through.The western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin is belongs to the buried fault of the former Quaternary.The Qinwangchuan basin was formed on the basic of the negative terrain among the mountains and had become a changeable fluvial-deposited depression basin in the Quaternary period, due to the regional tectonic stress differentiated compression and uplifting after the E-N intermountain Pan-lake Period environment.It could have no the function to control the spatial distribution of mid-strong earthquakes and the ability to form the surface rupture along the western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin.Meanwhile, the tectonic stability of the Qinwangchuan basin and planning and development of Lanzhou New Area are not affected.
-
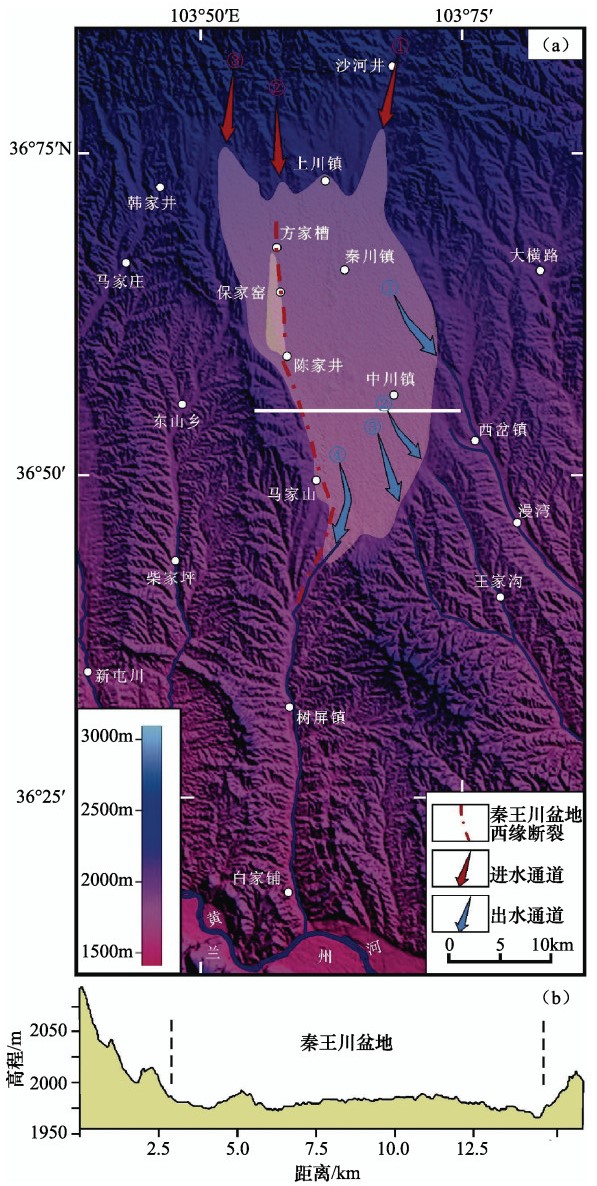
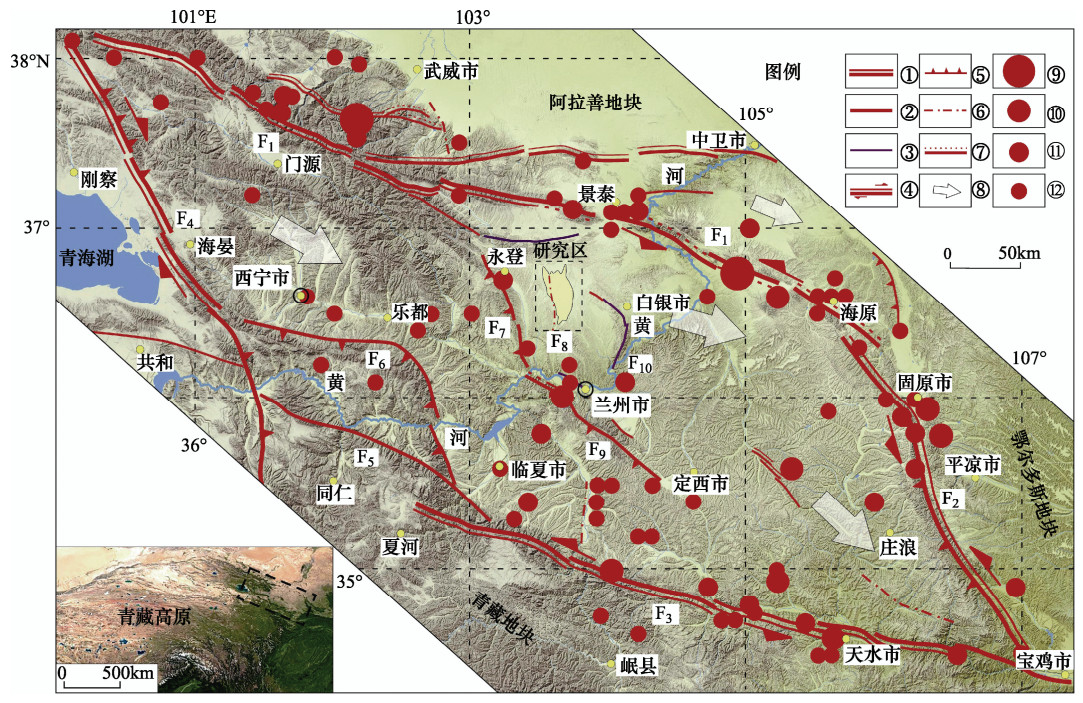
图 1 秦王川盆地及西缘断裂地震构造位置
①全新世断裂;②晚更新世断裂;③早—中更新世断裂;④走滑断裂;⑤逆冲断裂;⑥隐伏断裂;⑦地表破裂带;⑧块体挤出方向(袁道阳等,2004);⑨8.0≤MS ≤8.9;⑩7.0≤MS ≤7.9;⑪ 6.0≤MS ≤6.9;⑫ 4.7≤MS ≤5.9;F1:祁连-海原断裂;F2:六盘山断裂;F3:西秦岭北缘断裂;F4:热水-日月山断裂;F5:青海南山断裂;F6:拉脊山断裂;F7:庄浪河断裂;F8:秦王川盆地西缘断裂;F9:马衔山-兴隆山断裂;F10:白银白杨树沟断裂
Figure 1. Seismo-tectonic background of the western margin fault and Qinwangchuan basin
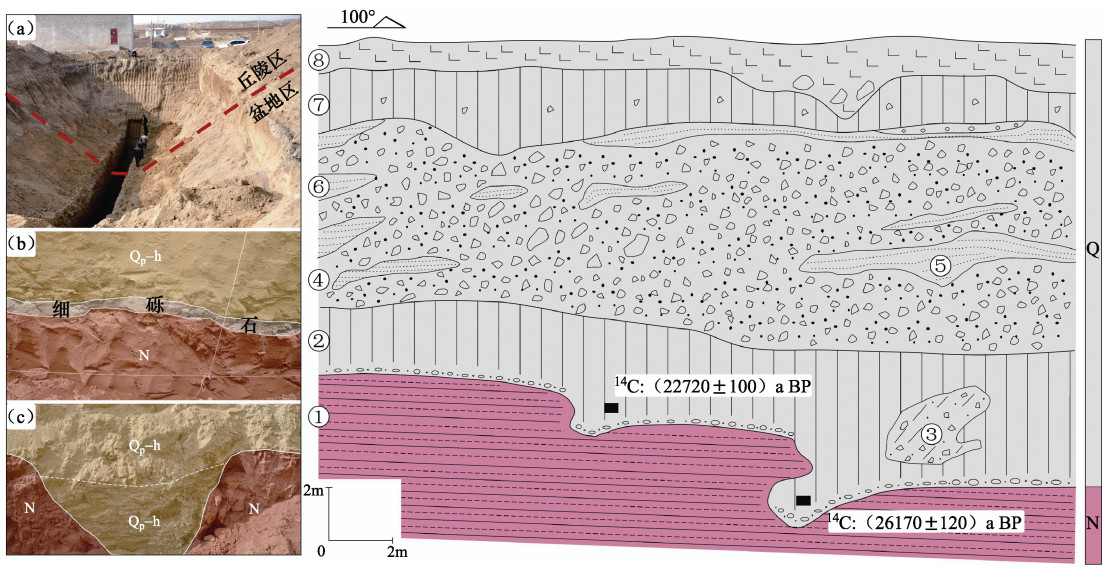
图 7 保家窑探槽南壁素描图
①新近系紫红色泥岩,产状近水平;②浅土黄色粉土,具水成特征;③土黄色泥砾混杂体,未固结,为1次洪水事件产物;④青灰色次棱角状砾石,成份较均一;⑤土黄色粉砂透镜体;⑥褐黄色粉砂透镜体,形态各异;⑦灰色含砾粉土层,沉积较稳定,厚度有变化;⑧砾、土、砂混杂人工耕土层,构成地表
(a)探槽特征,红色短线为DZ6、DZ4、DZ7和ZT2控制的可疑断层F1通过位置;(b)新近系泥岩顶部冲刷面特征,以细砾石薄层为标志;(c)新近系泥岩局部形成的侵蚀凹槽,向下呈尖灭状Figure 7. Sketch profile of southern wall of the Baojiayao trench
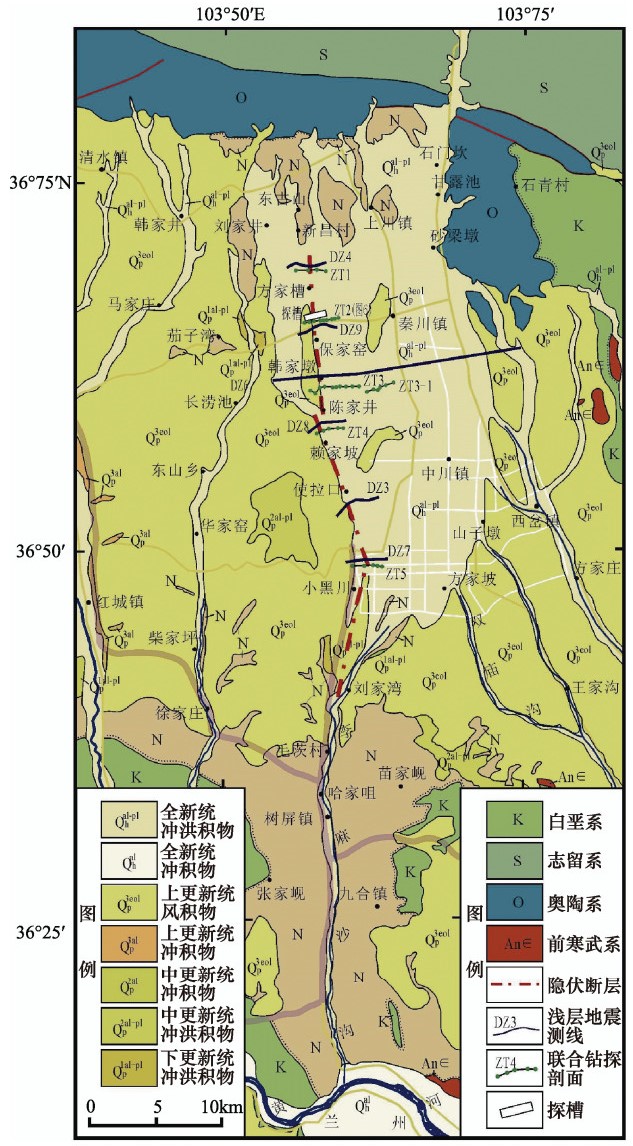
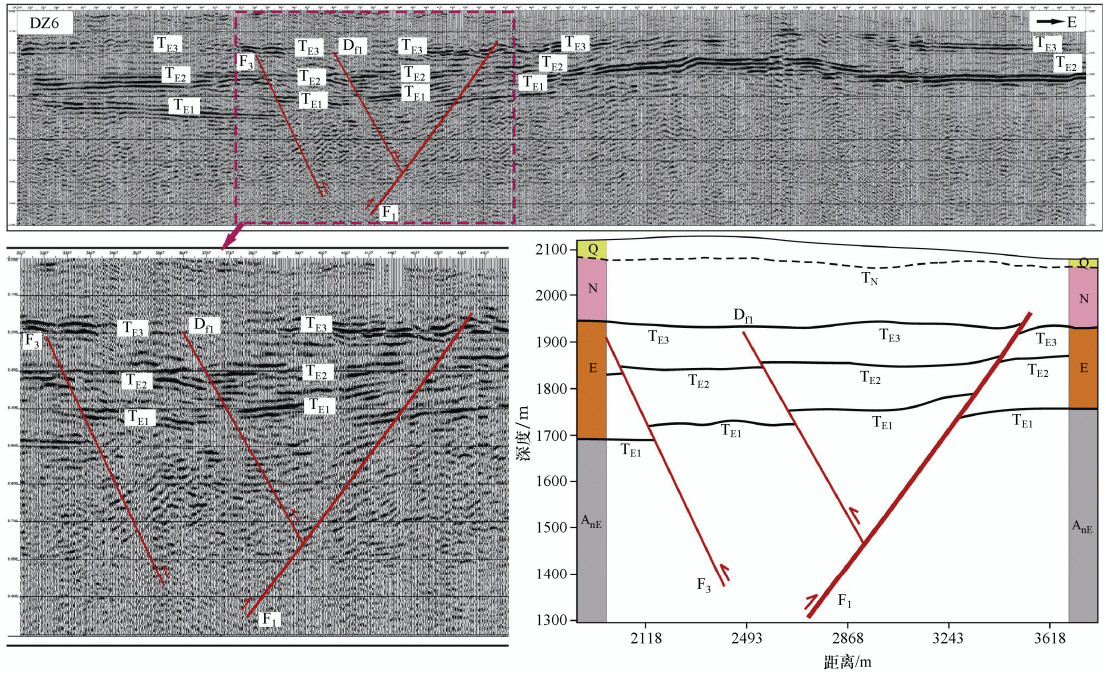
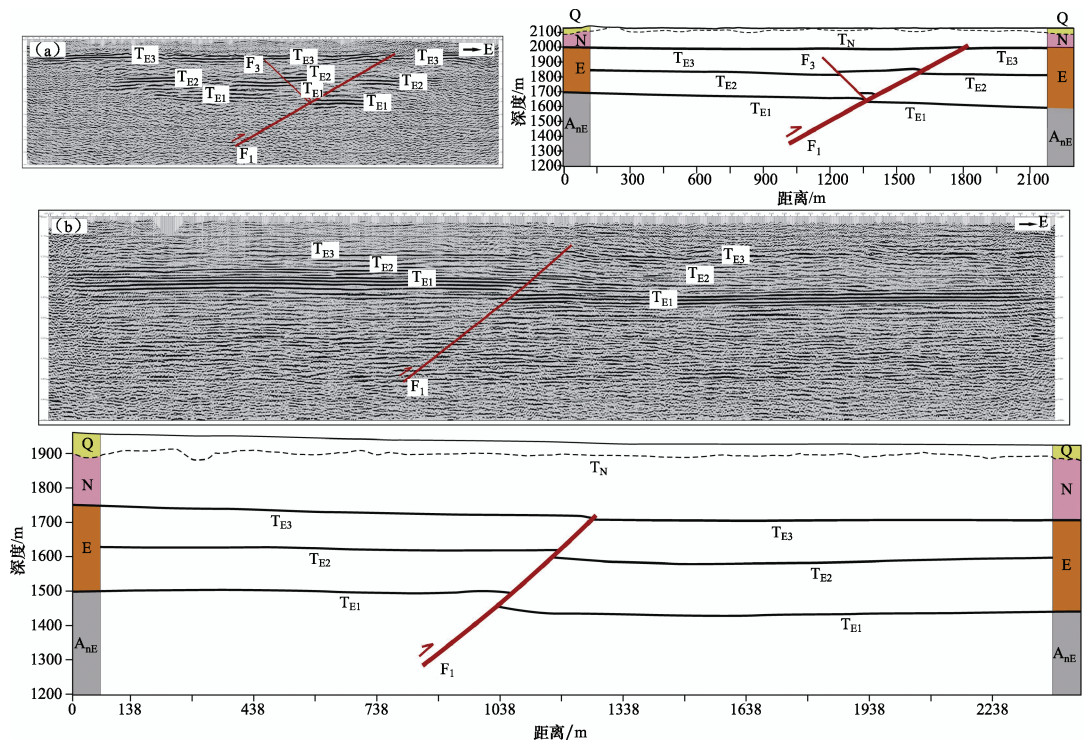
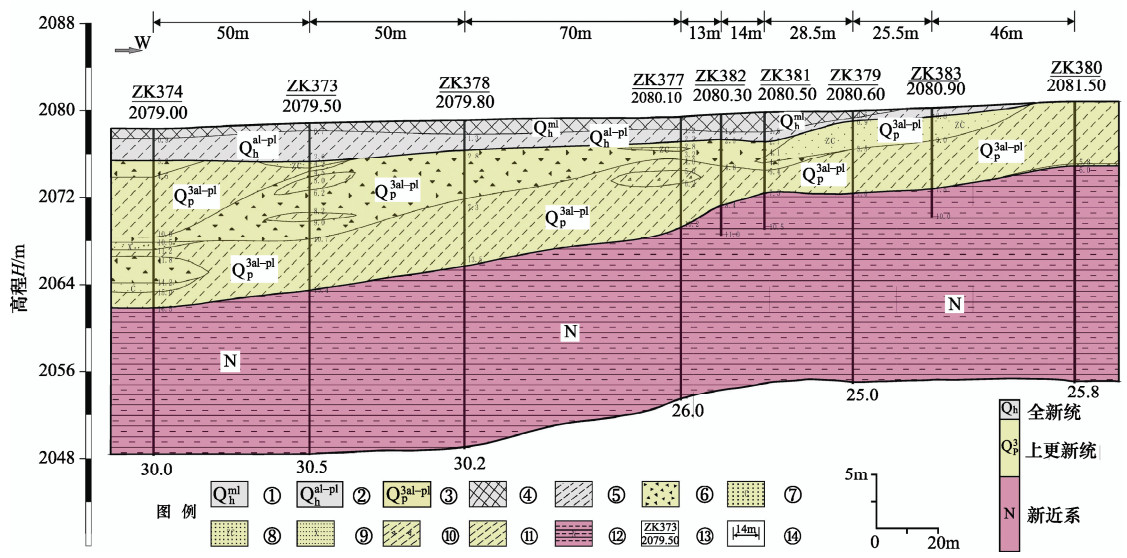
表 1 秦王川盆地西缘断裂浅层地震探测结果表
Table 1. Shallow seismic detection results in the western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin
测线编号 断点 性质 倾向 视倾角/° 断距/m 上断点埋深/m 控制程度 TE3 TE2 TE1 DZ3 F1 逆 W 70 >11 约18 230 可靠 DZ4 F1 逆 W 40 7 20 34 130 可靠 f3 逆 E 55 16 20 195 DZ6 F1 逆 W 40 约4 约18 >20 150 可靠 f3 逆 E 55 约18 >23 185 df1 逆 E 50 约13 约23 185 DZ7 F1 逆 W 60 约4 约25 >45 140 可靠 DZ8 F1 逆 W 45 约5 约14 >30 160 可靠 f3 逆 E 55 约8 >12 215 DZ9 F1 逆 W 45 >4 约10 >10 150 可靠 f3 逆 E 55 约7 >15 180 表 2 秦王川盆地西缘断裂联合钻探结果
Table 2. Cobined drilling results in the western margin fault of Qinwangchuan basin
剖面编号 地点 钻孔/个 长度l/m 孔距d/m 孔深h/m 地面高程/m 揭露地层
厚度/m断层可疑现象 ZT1 新昌村南 4 140.8 40.4—60.0 36.5—40.2 2162.8— 2164.3 Q:11.375 N:27.80 无 ZT2 保家窑
村北9 297.0 13.0—70.0 10.0—30.5 2079.0— 2081.5 Q:10.29 N:11.83 有 ZT3 韩家墩 10 405.0 10.0—9.0 38.0—50.0 2022.5— 2035.0 Q:23.76 N:18.62 无 ZT3—1 货站北路与经一
路交汇处6 138.0 5.0—73.0 25.0—40.3 2024.8— 2025.4 Q:16.35 N:17.59 无 ZT4 陈家井 5 161.0 15.0—66.0 39.6—41.0 2005.8— 2009.3 Q:30.58 N:9.640 无 ZT5 兰州分离科学
研究所5 158.0 12.0—110.0 29.2—30.7 1916.1— 1917.0 Q:9.500 N:20.56 无 -
柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006.隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测——以银川隐伏活动断层为例.地震地质, 28(4):536-546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2003.城市活断层探测的方法和技术.地学前缘, 10(1):150-162. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.038 邓起东, 卢造勋, 杨主恩, 2007.城市活动断层探测和断层活动性评价问题.地震地质, 29(2):189-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.001 高孟潭, 2015.GB 18306-2015《中国地震动参数区划图》宣贯教材.北京:中国质检出版社, 中国标准出版社. 韩飞, 2009.兰州地区晚第三纪沉积序列的磁性地层与古环境意义.兰州:兰州大学. 雷启云, 柴炽章, 孟广魁等, 2008.银川隐伏断层钻孔联合剖面探测.地震地质, 30(1):250-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.018 李吉均, 方小敏, 马海洲等, 1996.晚新生代黄河上游地貌演化与青藏高原隆起.中国科学(D辑), 26(4):316-322. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.04.005 刘池洋, 王建强, 赵红格等, 2015.沉积盆地类型划分及其相关问题讨论.地学前缘, 22(3):1-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201503001 刘小凤, 袁道阳, 刘百篪, 2003.兰州及邻近地区河流阶地变形特征.西北地震学报, 25(2):119-124, 142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2003.02.004 刘兴旺, 袁道阳, 2012.兰州庄浪河阶地差分GPS测量与构造变形分析.西北地震学报, 34(4):393-397, 404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2012.04.0393 宋博文, 徐亚东, 梁银平等, 2014.中国西部新生代沉积盆地演化.地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 39(8):1035-1051. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201408008 袁道阳, 杨斌, 周俊喜等, 2000.兰州秦王川盆地形成和演化特征的初步研究.西北地震学报, 22(3):296-300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2000.03.016 袁道阳, 刘百篪, 张培震等, 2002.兰州庄浪河断裂带的新构造变形与地震活动.地震学报, 24(4):441-444. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2002.04.013 袁道阳, 张培震, 刘百篪等, 2004.青藏高原东北缘晚第四纪活动构造的几何图像与构造转换.地质学报, 78(2):270-278. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2004.02.017 张克信, 王国灿, 骆满生等, 2010.青藏高原新生代构造岩相古地理演化及其对构造隆升的响应.地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 35(5):697-712. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201005001 张鹏, 敖红, 安芷生, 2016.陇中盆地古近纪-新近纪地层学与古气候学研究进展.地球环境学报, 7(2):97-120. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhjxb201602001 张向红, 杨斌, 周俊喜等, 2000.兰州中川民用机场扩建工程场地隐伏活断层探测研究.西北地震学报, 22(4):458-464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2000.04.019 张炎, 孙东怀, 韩飞等, 2010.兰州地区新近纪地层的沉积相与古环境记录.沉积学报, 28(3):611-619. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201003024 中国地震局, 2009. DB/T 15-2009活动断层探测.北京:地震出版社 中华人民共和国国家标准.2005.工程场地地震安全性评价(GB 17741-2005).北京:中国标准出版社. 周本刚, 陈国星, 高战武等, 2013.新地震区划图潜在震源区划分的主要技术特色.震灾防御技术, 8(2):113-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2013.02.001 朱金芳, 黄宗林, 徐锡伟等, 2005.福州市活断层探测与地震危险性评价.中国地震, 21(1):1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.01.001 -



 下载:
下载: