Observation of Nano/micro-scale Structures of Gouges in the Active Fault Zones
-
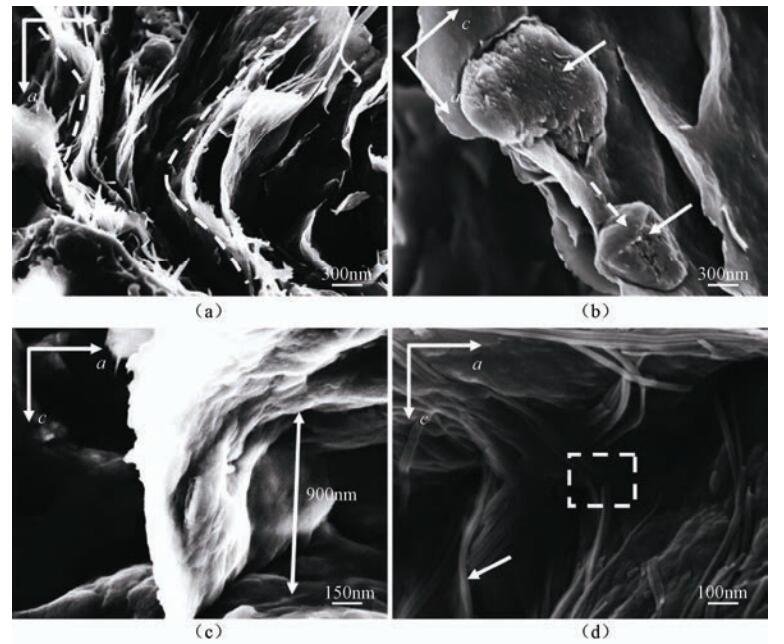
摘要: 断层泥是研究活动断裂带运动性质和活动习性的重要介质。以往,对断层泥的研究主要借助偏光显微镜和低真空扫描电镜进行,观察到的现象有限。借助高真空扫描电镜从纳微米尺度对断层泥进行更精细化的研究,其方法是对野外断层泥进行定向原状样品采集,通过室内样品自然风干、微样制作、表面镀金和扫描电镜观察,从纳微米尺度研究a-b组构面和a-c组构面的各种变形现象。此方法可以帮助确定断层的运动性质、断层滑动面的新老关系,并可鉴别粘滑过程与蠕滑过程;同时,还可以对工程场地中发现的黏土滑动面进行鉴别,区分地震断层和非地震断层。Abstract: Gouges are the common product bydeformation in the shallow crust of the active fault zones. They are made up of unconsolidated clastic, rock grains and clay minerals. Generally, the width of gouges in a fault zone is only a few millimeters to tens of meters, while it formed from one earthquake motion which is just a few millimeters to several centimeters. Gouges record the history and retain all kinds of the active fault zones. Therefore, as an important medium, gouges are useful to study the movement and activity of the active fault zones. In this paper we use high vacuum scanning electron microscope to study of structures of gouges at nano/micro-scale. Firstly, original-state directional samples of gouges in the active fault zones are collected. Secondly, the samples are dried up naturally in laboratory before they are made into micro samples. Thirdly, before observing nano/micro-structures by high vacuum scanning electron microscope, the surfaces of micro samples need to be coated with a layer of gold. Lastly, all kinds of phenomena of deformations on fabric in a-b surface and fabric in a-c surface are analyzed. For example, striations, ridges, grooves, groups of striations in different directions, slickenside, steps and arrangement types of clay minerals can be observed from fabric in a-b surface. Folds, gravels surrounded by clay minerals, rotation, break, clastic particle packed by clay minerals and other phenomena of deformations can be observed from fabric in a-b surface. These phenomena represent different meanings and reflect different mechanical property, which is useful in study of the fault movement, fault age, faulting mode, and faulting type.
-
Key words:
- Active fault zone /
- Gouges /
- Nano/micro-scale structure /
- Observation method
-
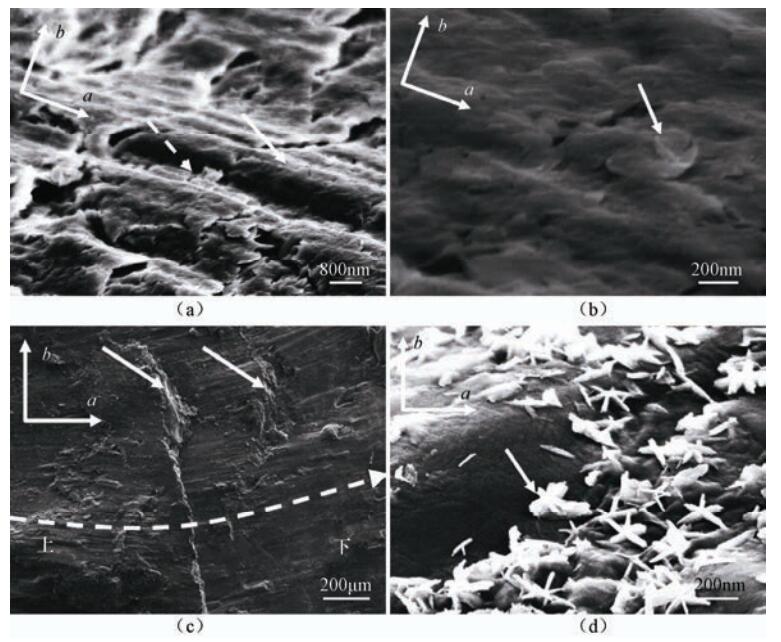
图 1 黏土样品微纳、微米尺度对比观察
(a)自然沉积的黏土,水平方向,片状黏土矿物随机叠加(实箭头);(b)自然沉积的黏土,竖直方向,片状黏土矿物无规则排列;(c)取自钻孔的原状黏土,擦痕明显(实箭头);(d)图 1(c)方框区域局部放大,似“波动”状变形(虚线框区域)
Figure 1. Comparion of clay samples at the nano/micro-scale
-
晁洪太, 1998.第四纪地层中活断层的显微构造标志、隐性活断层及其应用研究.北京:中国地震局地质研究所. 晁洪太, 邓起东, 李家灵等, 2001.第四纪松散沉积物中活断层滑动面的显微构造研究方法.中国地震, 17(4):24-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdz200104003 晁洪太, 孙岩, 王志才等, 2009.发震断裂的纳米级运动学观测一例.自然科学进展, 19(10):1076-1081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.10.008 晁洪太, 孙岩, 王志才等, 2016.同震和无震剪切滑移作用的纳微米级构造观察与分析.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(1):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.01.004 付碧宏, 王萍, 孔屏等, 2008.四川汶川5.12大地震同震滑动断层泥的发现及构造意义.岩石学报, 24(10):2237-2243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200810005 高璐, 尹功明, 刘春茹等, 2011.六盘山东麓断裂断层泥ESR测年研究.核技术, 34(2):121-125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjs201102010 何永年, 林传勇, 史兰斌, 1988.构造岩石学基础.北京:地质出版社, 129-140. 胡玲, 胡道功, 何登发等, 2004.准噶尔盆地南缘霍尔果斯和吐谷鲁断裂带断层泥分形特征与断裂活动关系.地学前缘, 11(4):519-525. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.018 李胜荣, 许虹, 申俊峰等, 2008.结晶学与矿物学.北京:地质出版社, 1-346. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysyjyts201205028 林传勇, 史兰斌, 刘行松等, 1995.断层泥在基岩区断层新活动研究中的意义.中国地震, 11(1):26-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500633724 马浩明, 陈庞龙, 2009.深圳市横岗-罗湖断裂第四纪活动性研究.震灾防御技术, 4(3):266-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2009.03.003 马瑾, Moore D. E., Summers R.等, 1985.温度压力孔隙压力对断层泥强度及滑动性质的影响.地震地质, 7(1):15-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000348599 孙岩, 舒良树, 陆现彩等, 2007.岩石剪切面纳米粒子层的近期研究进展.自然科学进展, 17(10):1331-1337. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2007.10.002 王雷, 2016.活动断裂带断层泥纳微米尺度的特征研究.廊坊: 防灾科技学院. 王醒东, 林中山, 张立永等, 2012.扫描电子显微镜的结构及对样品的制备.广州化工, 40(19):28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2012.19.013 吴大铭, 张裕明, 方仲景等, 1981.论中国郯庐断裂带的活动.地震地质, 3(4):15-26, 93-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000348446 徐叶邦, 1986.海原活动断裂中断层泥的特征、成因及其对断层滑动性能的影响.西北地震学报, 8(1):75-90. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZBDZ198601006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 闫金定, 2015.我国纳米科学技术发展现状及战略思考.科学通报, 60(1):30-37. http://qikan.cqvip.com/article/detail.aspx?id=663726246 杨主恩, 胡碧茹, 洪汉净, 1984.活断层中断层泥的石英碎砾的显微特征及其意义.科学通报, 29(8):484-486. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001997026 杨主恩, 郭芳, 李铁明等, 1999.鲜水河断裂西北段的断层泥特征及其地震地质意义.地震地质, 21(1):21-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.01.003 俞维贤, 安晓文, 李世成等, 2002.澜沧江流域主要断裂断层泥中石英碎砾表面SEM特征及其断裂活动研究.地震研究, 25(3):275-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2002.03.012 袁仁茂, 张秉良, 徐锡伟等, 2014.汶川地震剪切滑动面微-纳米级颗粒的特征、形成机制及地震意义.中国科学:地球科学, 44(8):1821-1832. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JDXK201408020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张秉良, 周永胜, 袁仁茂等, 2014.断层泥伊利石物理化学特征及其意义.震灾防御技术, 9(4):829-837. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140410&journal_id=zzfyjs 周本刚, 沈得秀, 2006.地震安全性评价中若干地震地质问题探讨.震灾防御技术, 1(2):113-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.02.004 Cashman S. M., Baldwin J. N., Cashman K. V., et al., 2007. Microstructures developed by coseismic and aseismic faulting in near-surface sediments, San Andreas fault, California. Geology, 35(7):611-614. doi: 10.1130/G23545A.1 Chao H. T., Wang Z. C., Wang L., et al., 2017. Implication of creep slipping before main shock for earthquake prediction:evidence from nano/micro-scale structure of gouges. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 17(9):6852-6858. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2017.14404 Chou Y. M., Song S. R., Tsao T. M., et al., 2014. Identification and tectonic implications of nano-particle quartz (< 50nm) by synchrotron X-ray diffraction in the Chelungpu fault gouge, Taiwan. Tectonophysics, 619-620:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.07.021 Janssen C., Kanitpanyacharoen W., Wenk H. R., et al., 2012. Clay fabrics in SAFOD core samples. Journal of Structural Geology, 43:118-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.07.004 Kanamori H., Heaton T. H., 2000. Microscopic and Macroscopic physics of earthquakes. In:GeoComplexity and the Physics of Earthquakes. Washington:AGU, 120:147-163. doi: 10.1029/GM120 Laurich B., Urai J. L., Desbois G., et al., 2014. Microstructural evolution of an incipient fault zone in Opalinus Clay:Insights from an optical and electron microscopic study of ion-beam polished samples from the Main Fault in the Mt-Terri Underground Research Laboratory. Journal of Structural Geology, 67:107-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2014.07.014 Ma K. F., Tanaka H., Song S. R., et al., 2006. Slip zone and energetics of a large earthquake from the Taiwan Chelungpu-fault drilling project. Nature, 444(7118):473-476. doi: 10.1038/nature05253 Omori Y., Ikei H., Kugimiya Y., et al., 2015. Nanometre-scale faulting in quartz under an atomic force microscope. Journal of Structural Geology, 79:75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2015.07.008 Schulz S. E., Evans J. P., 2000. Mesoscopic structure of the Punchbowl fault, Southern California and the geologic and geophysical structure of active strike-slip faults. Journal of Structural Geology, 22(7):913-930. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(00)00019-5 Wilson B., Dewers T., Reches Z., et al., 2005. Particle size and energetics of gouge from earthquake rupture zones. Nature, 434(7034):749-752. doi: 10.1038/nature03433 Yuan R. M., Zhang B. L., Xu X. W., et al., 2015. Microstructural and mineral analysis on the fault gouge in the coseismic shear zone of the 2008 Mw7.9 Wenchuan earthquake. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 104(5):1425-1437. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1160-8 -




 下载:
下载: