Study on Seismic Response of Underground Structure in Saturated Soil Deposit Based on OpenSees
-
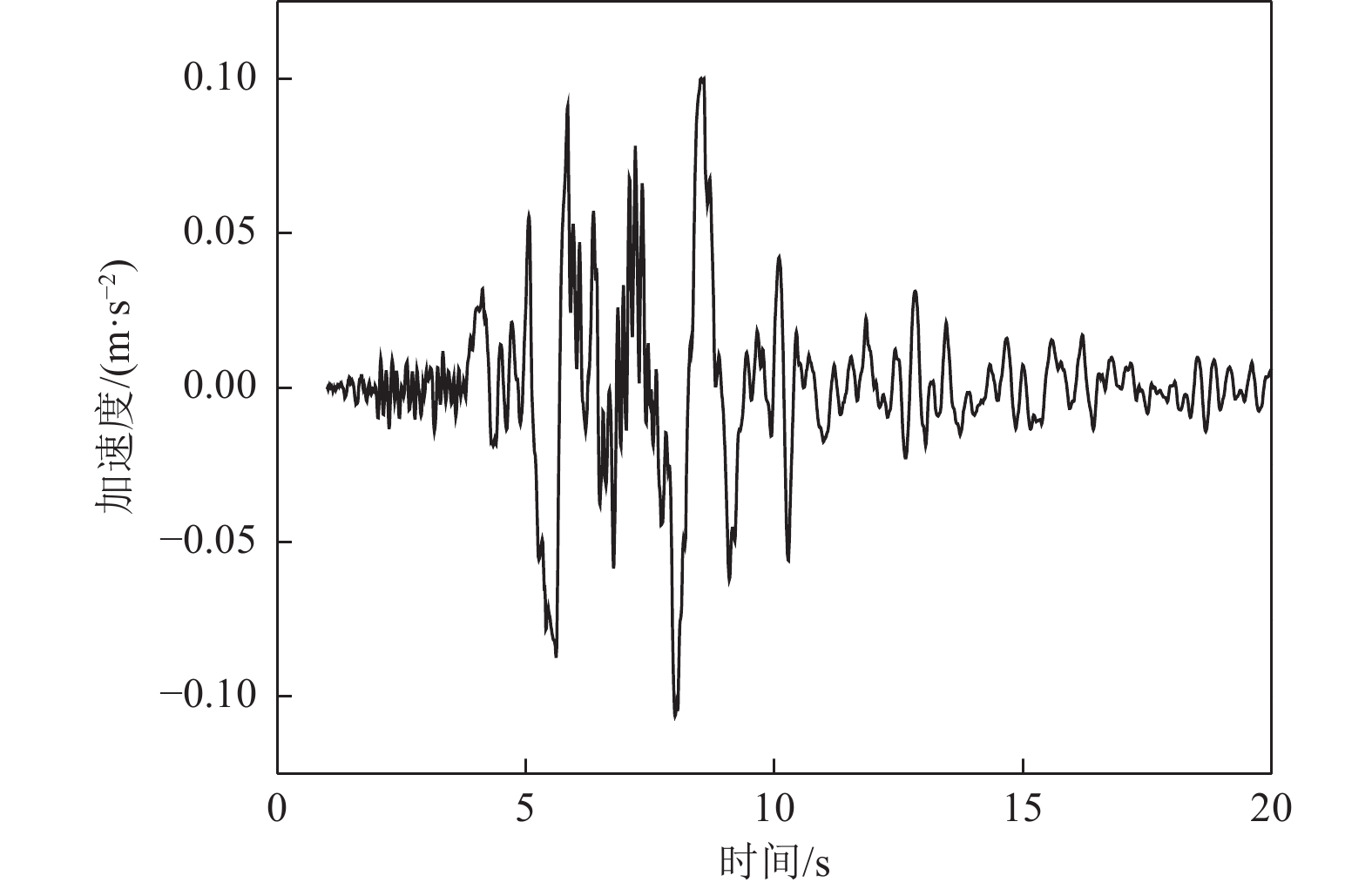
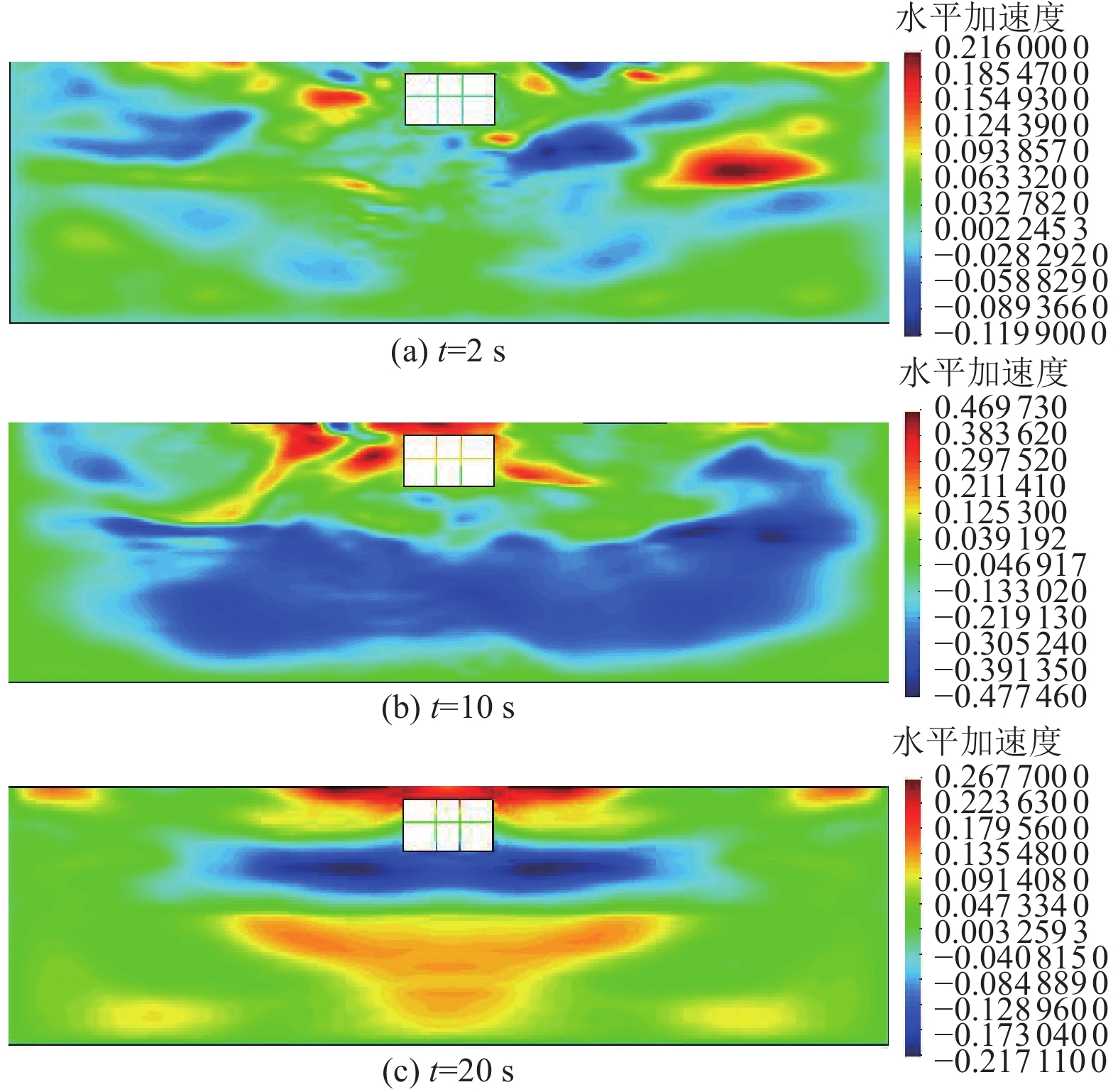
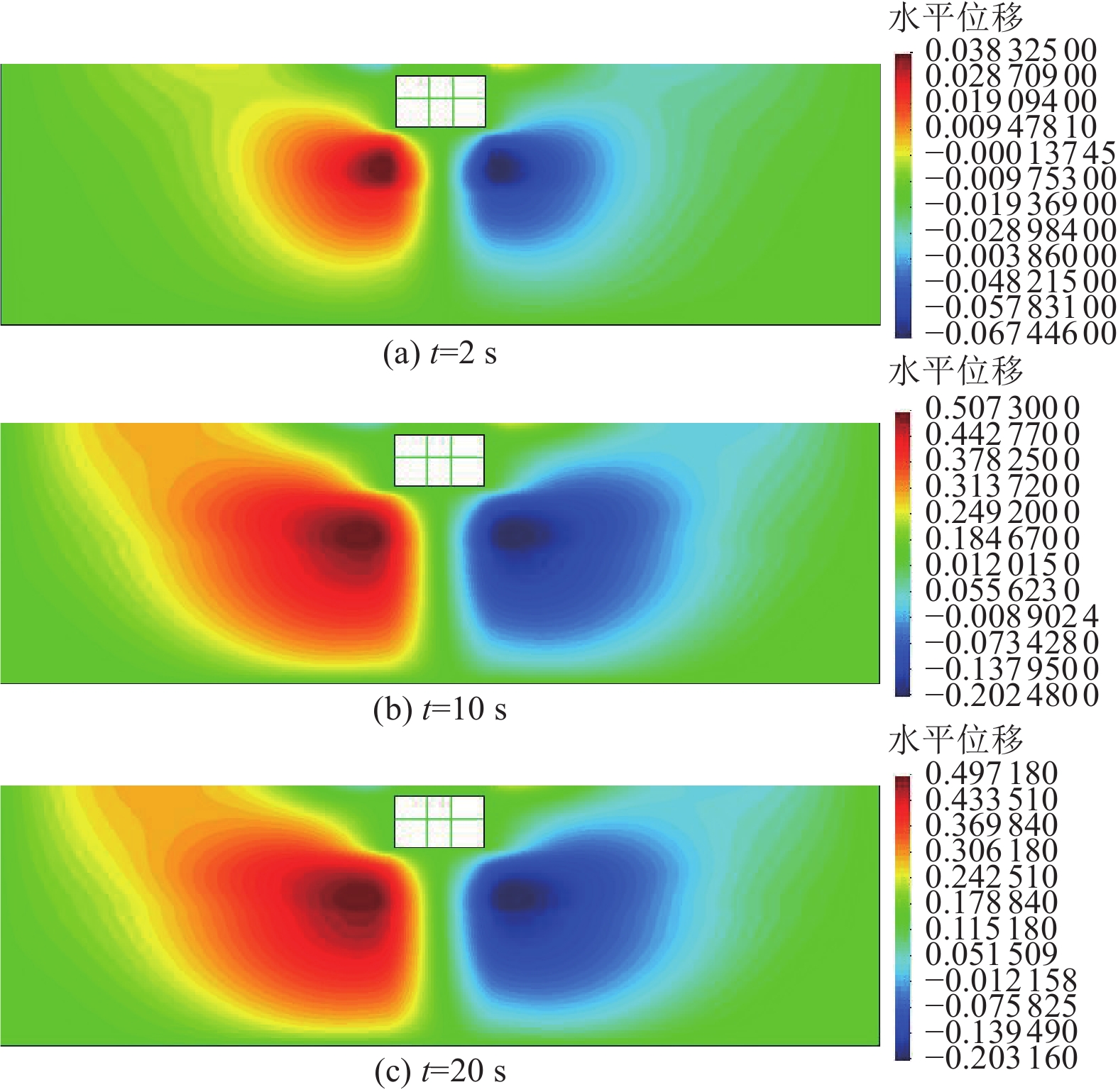
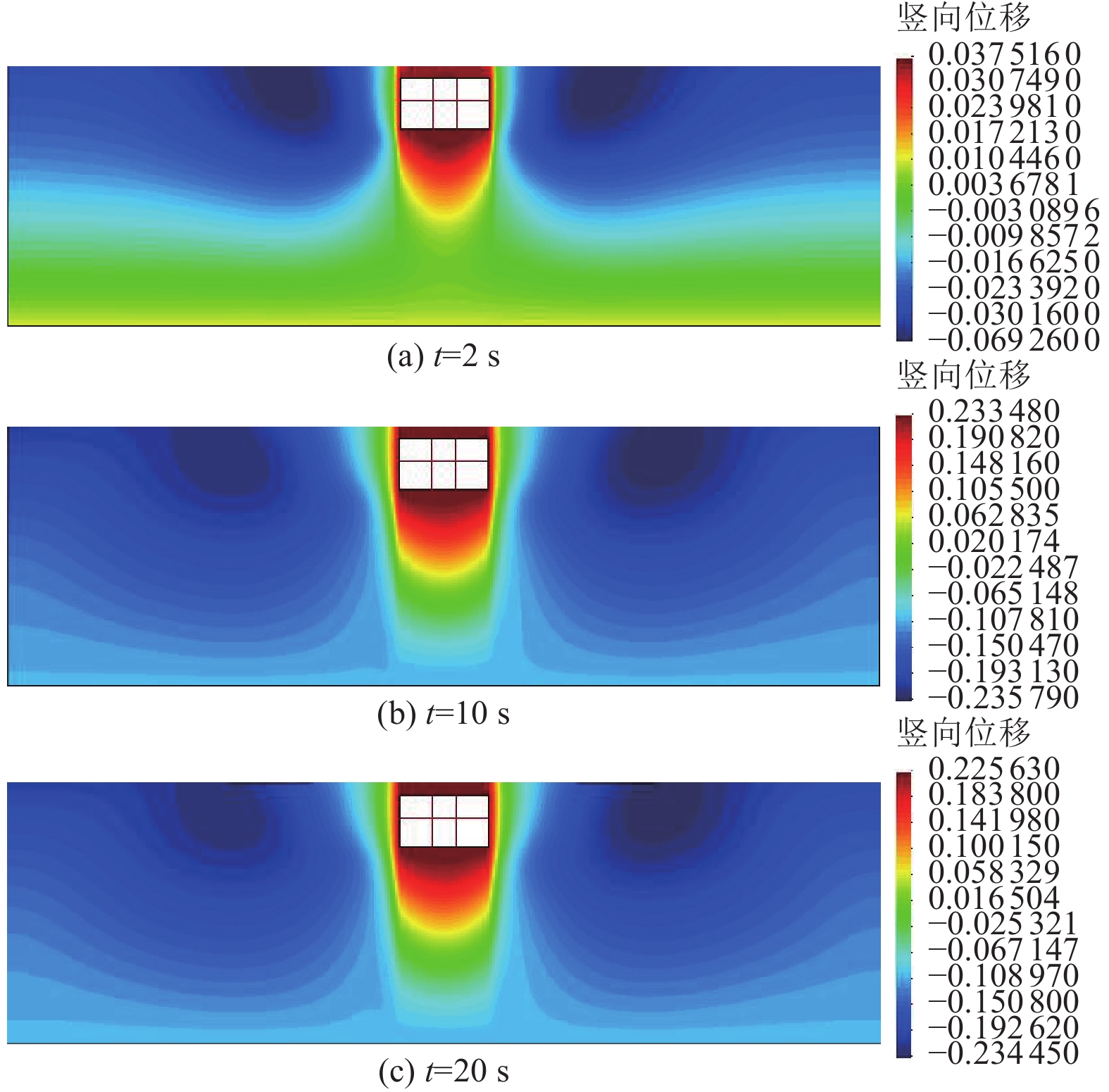
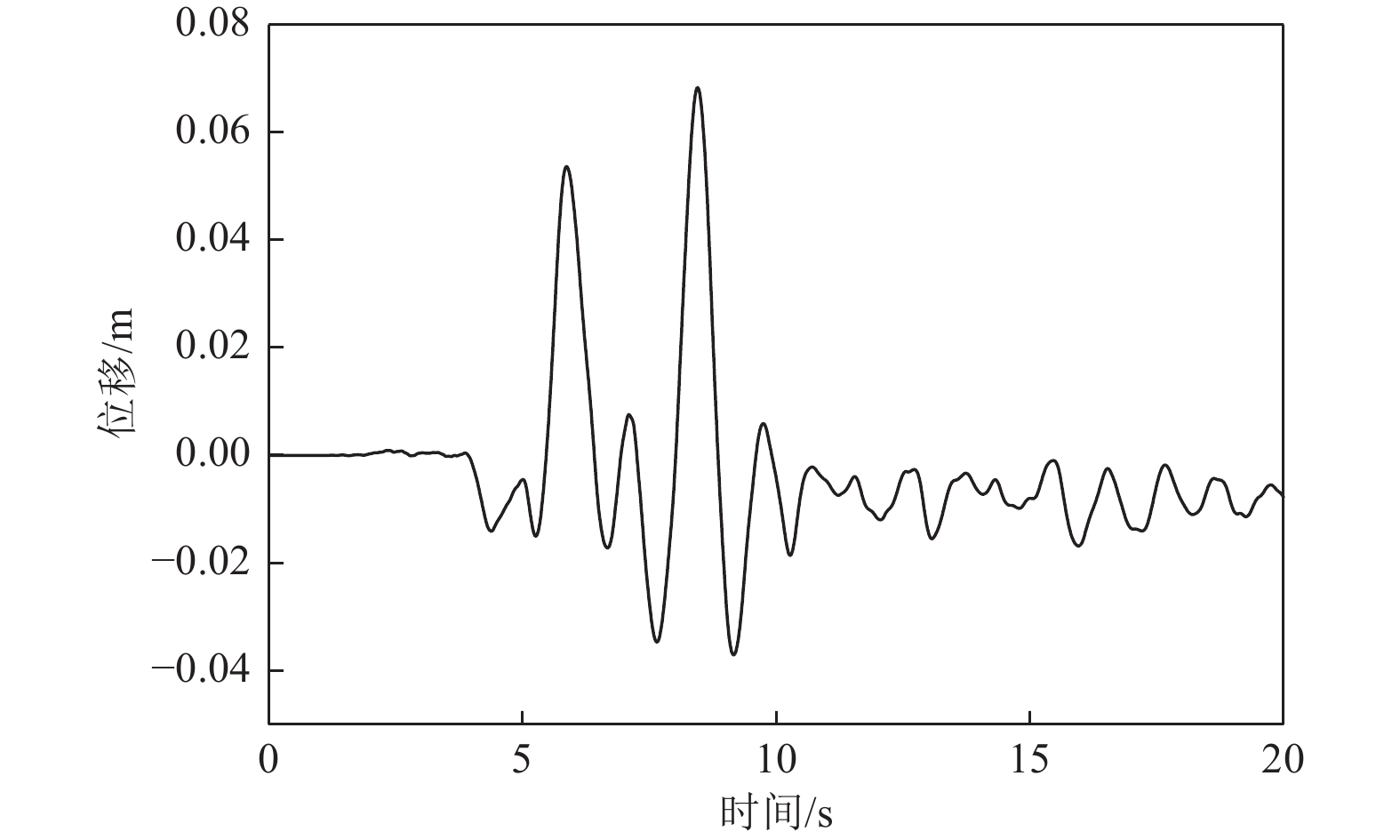
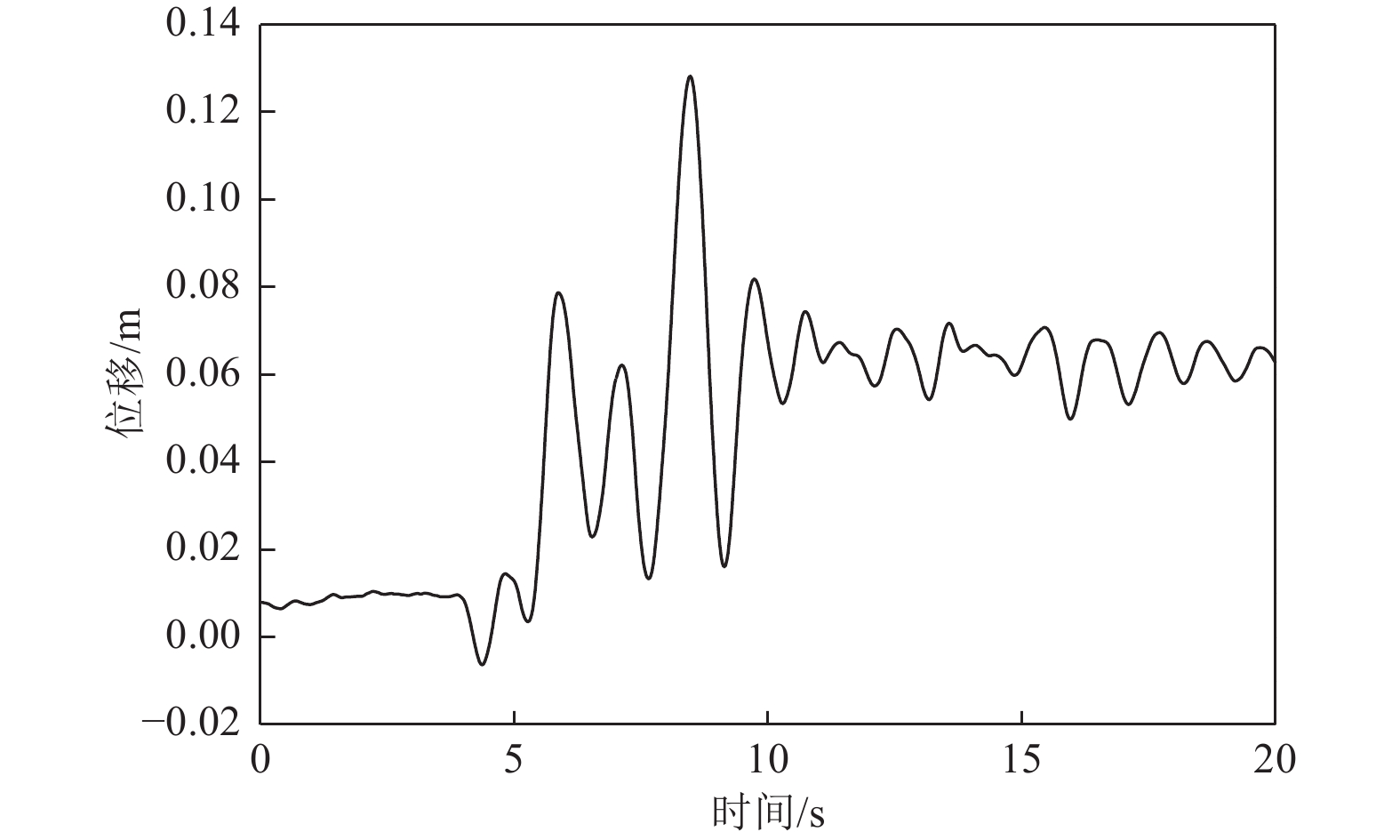
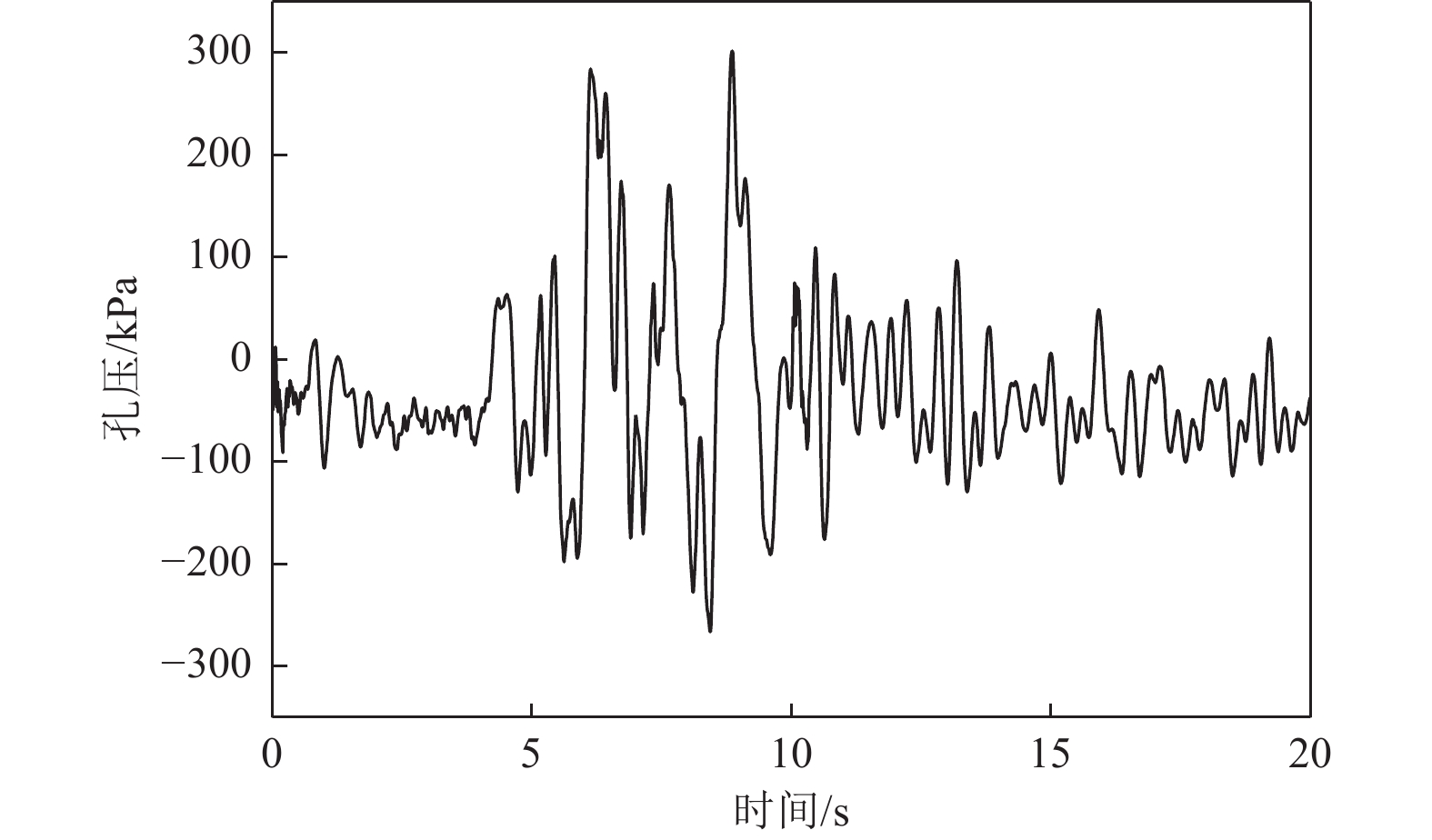
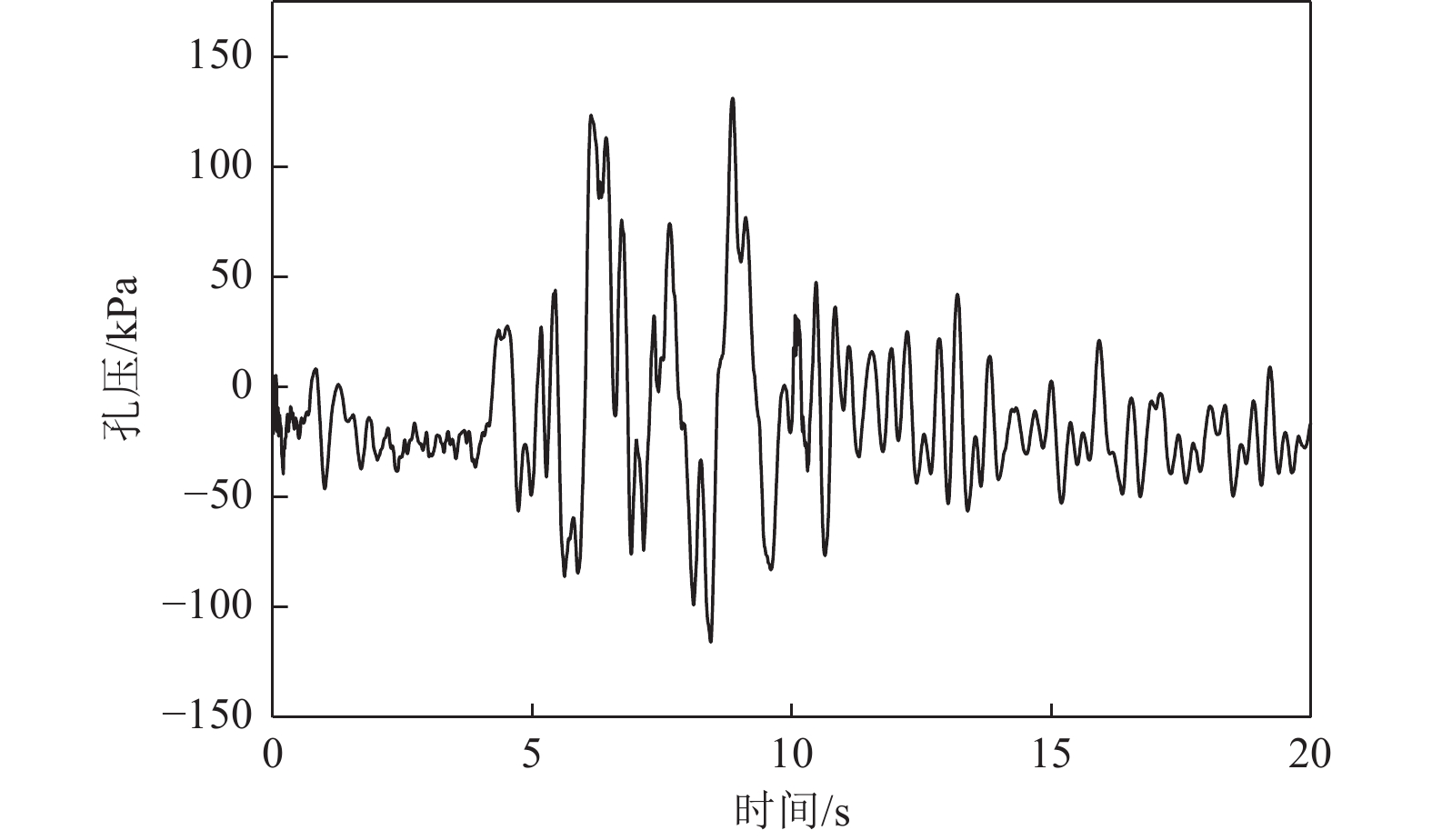
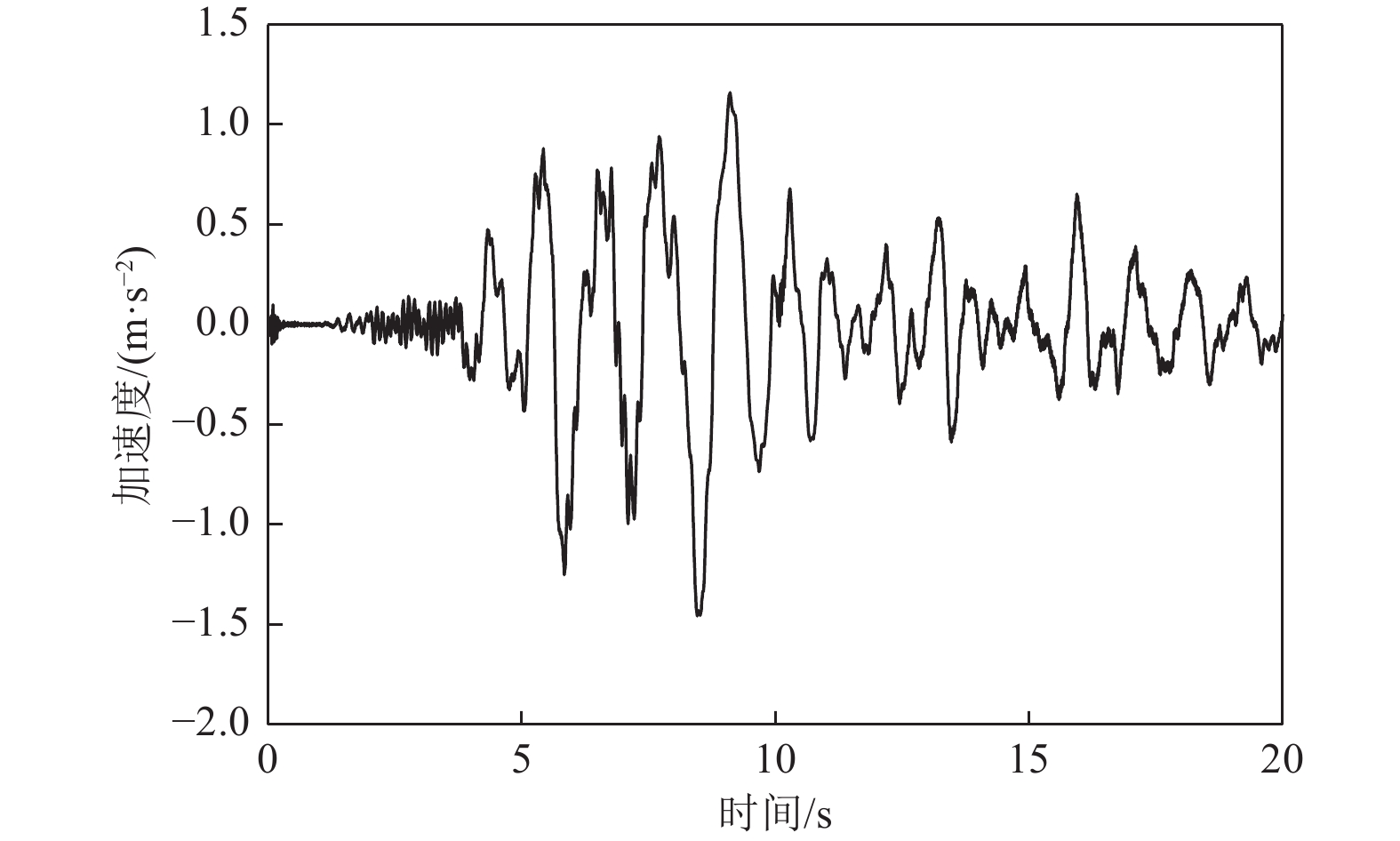
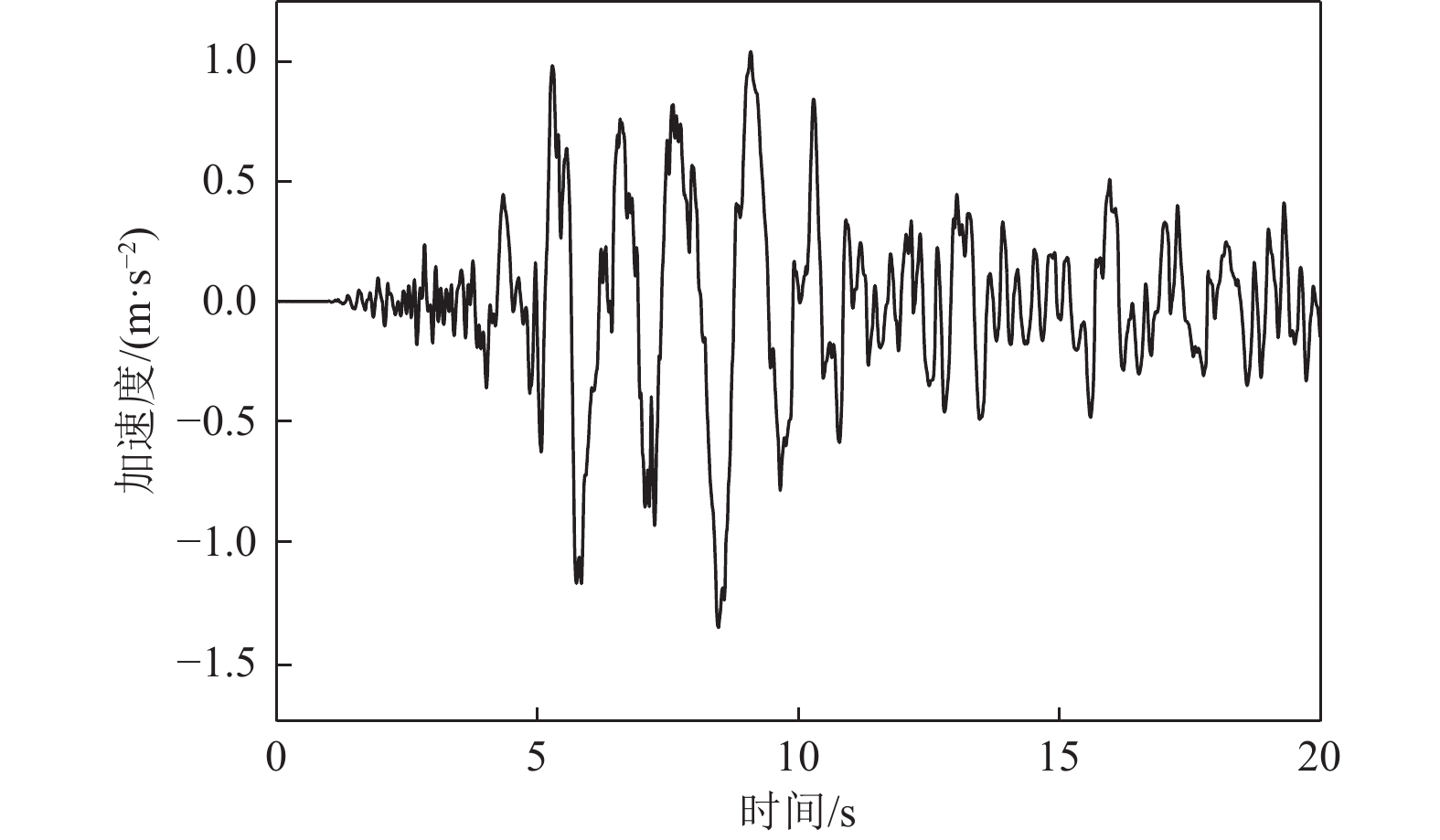
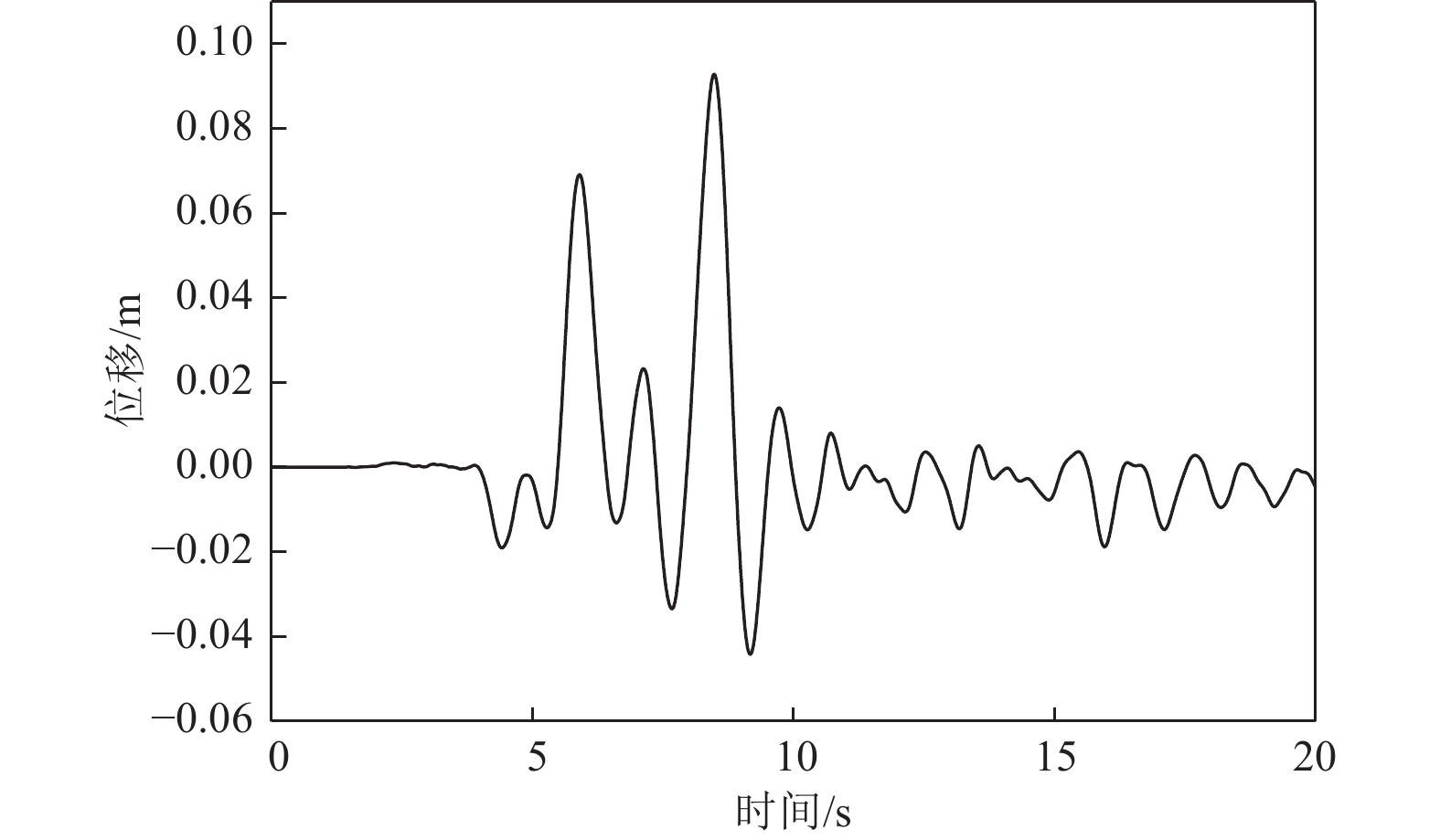
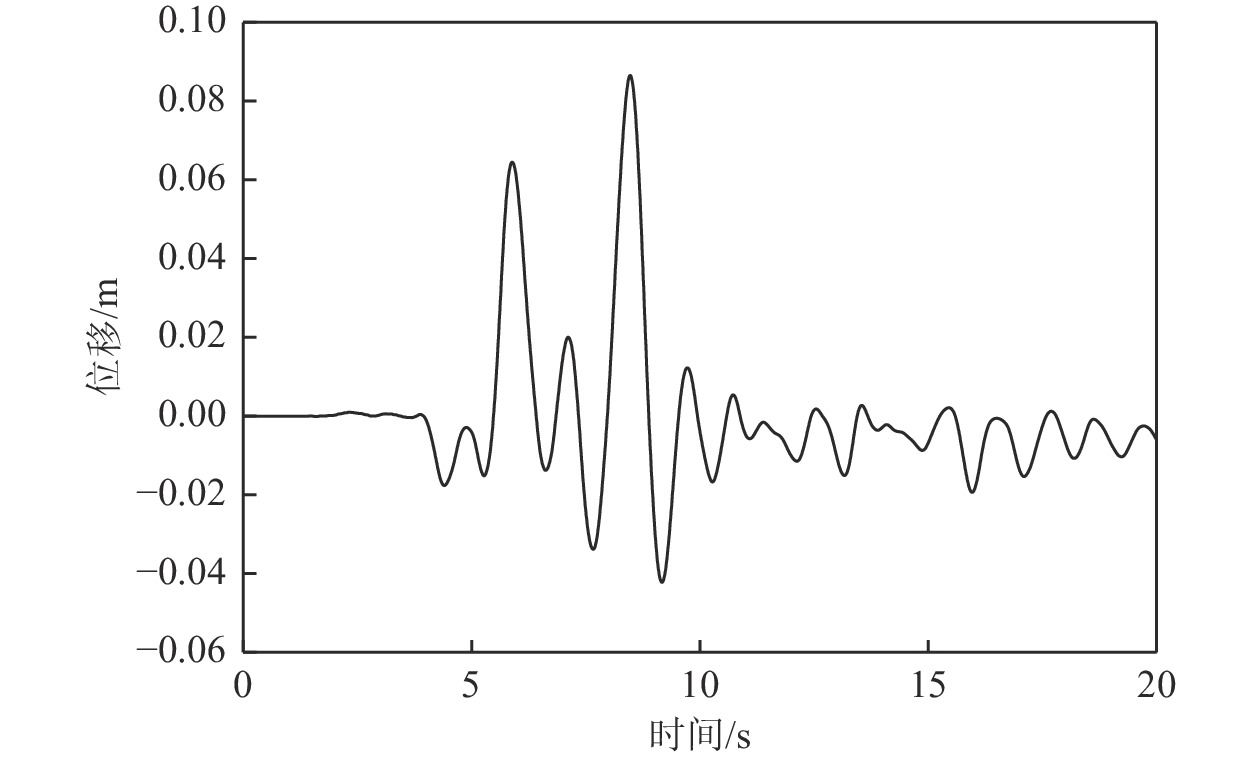
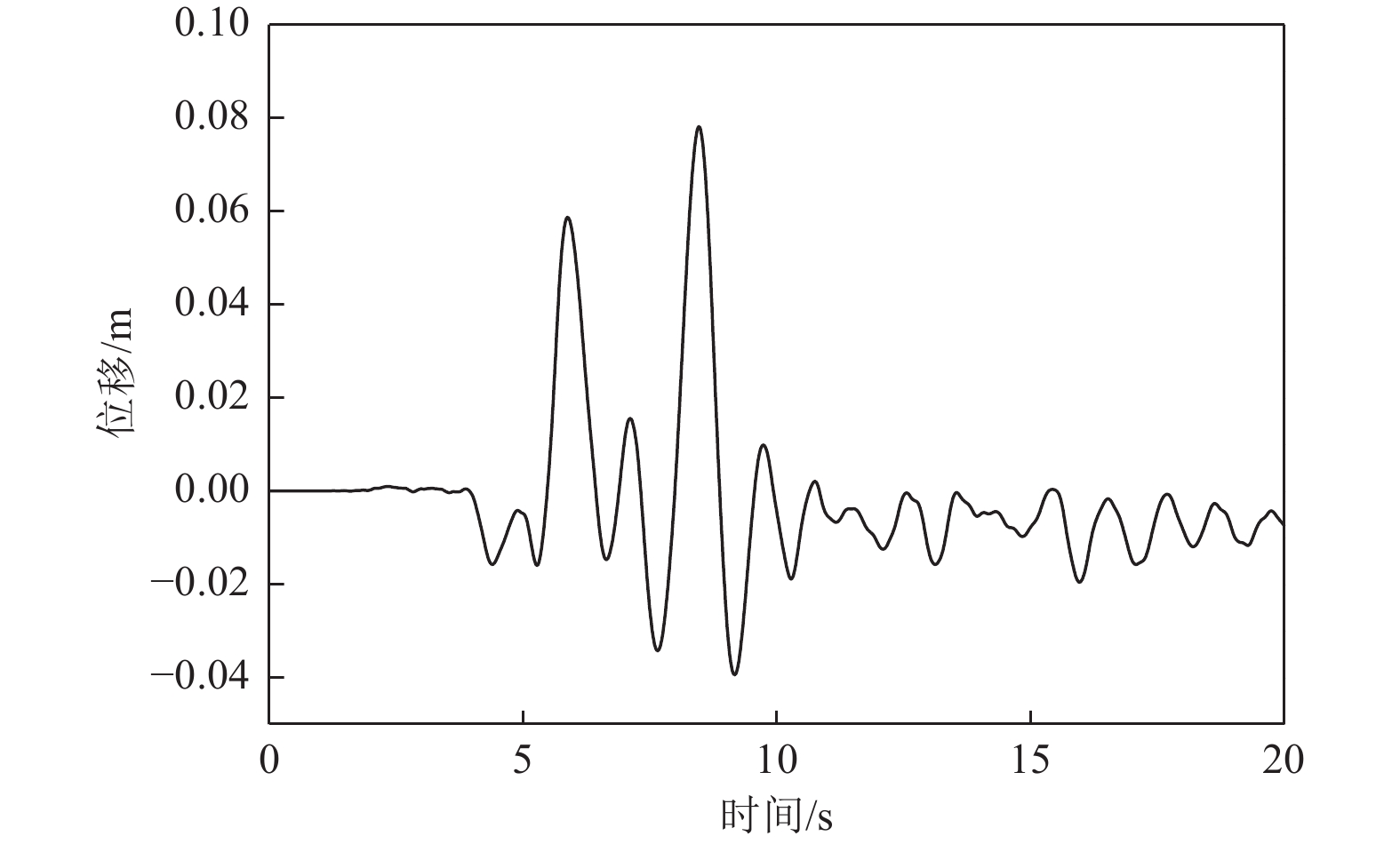
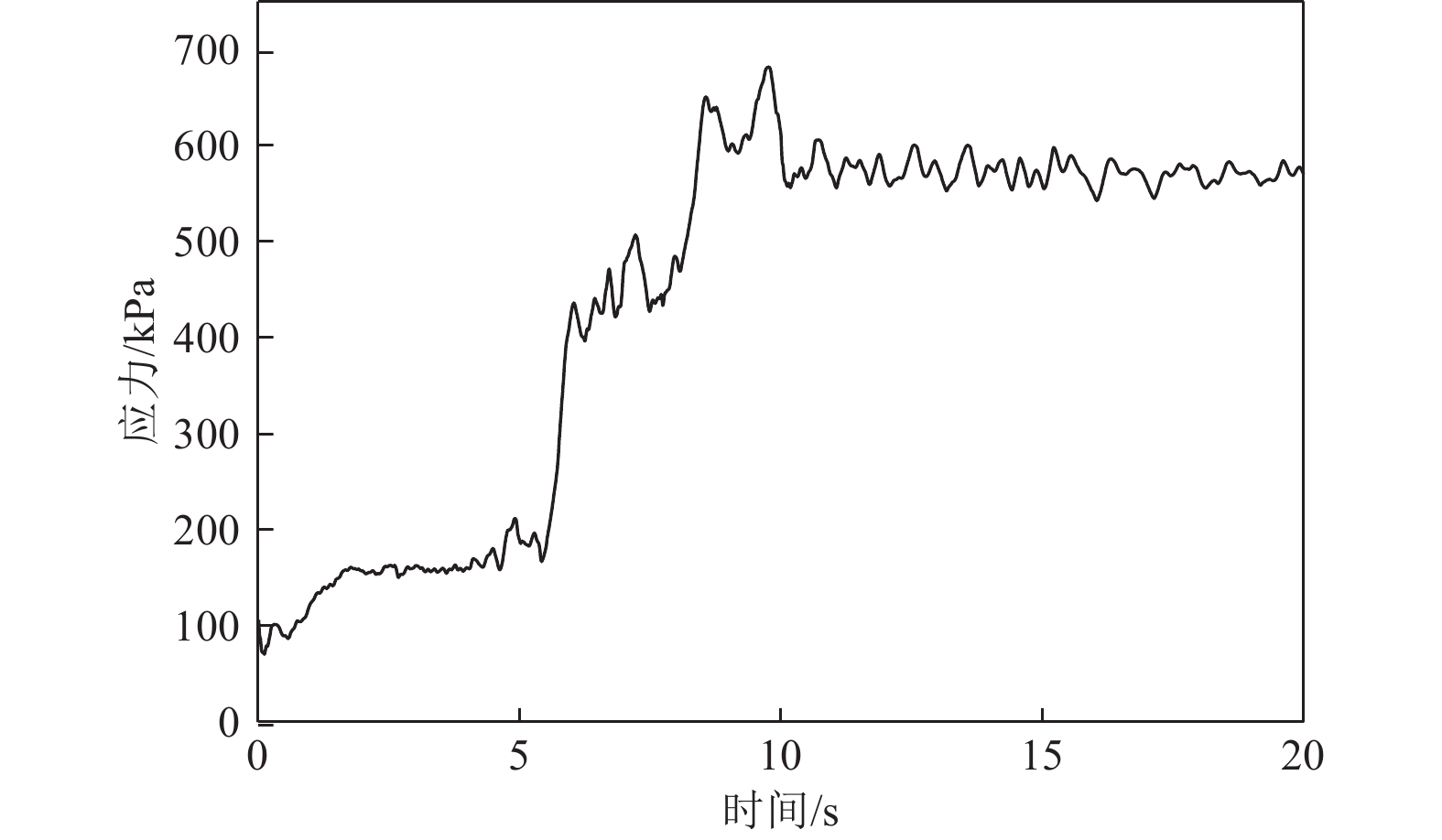
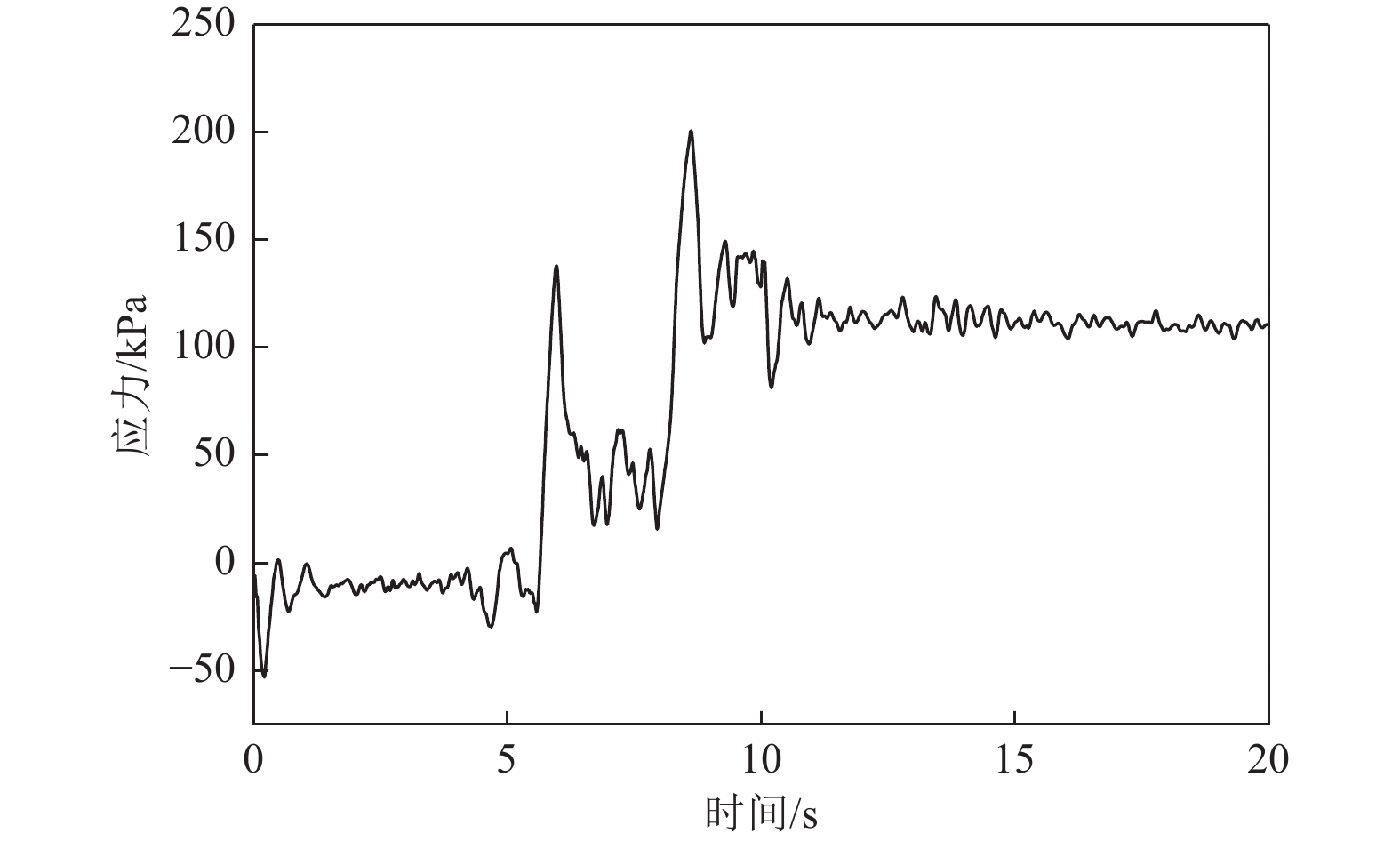
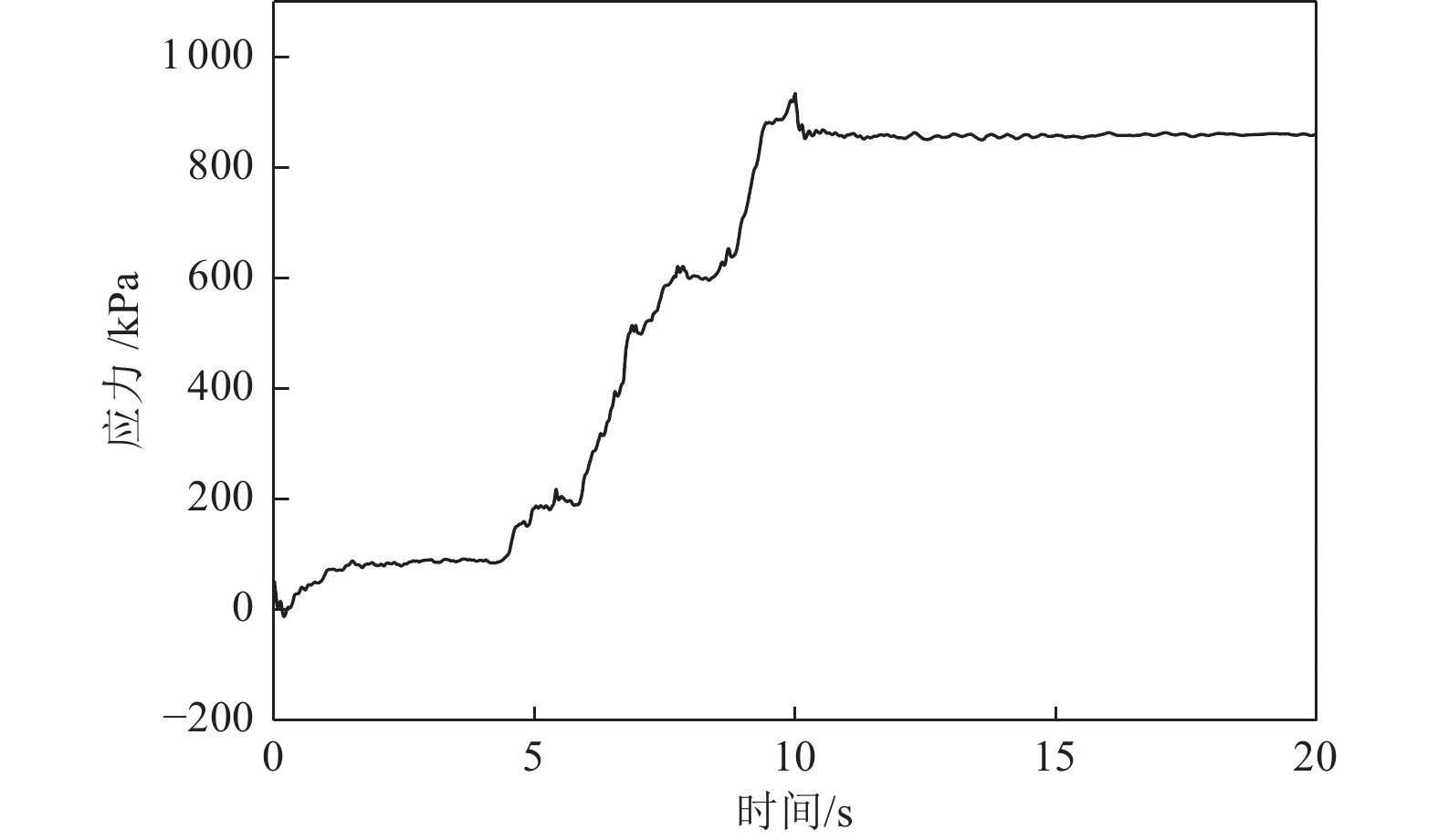
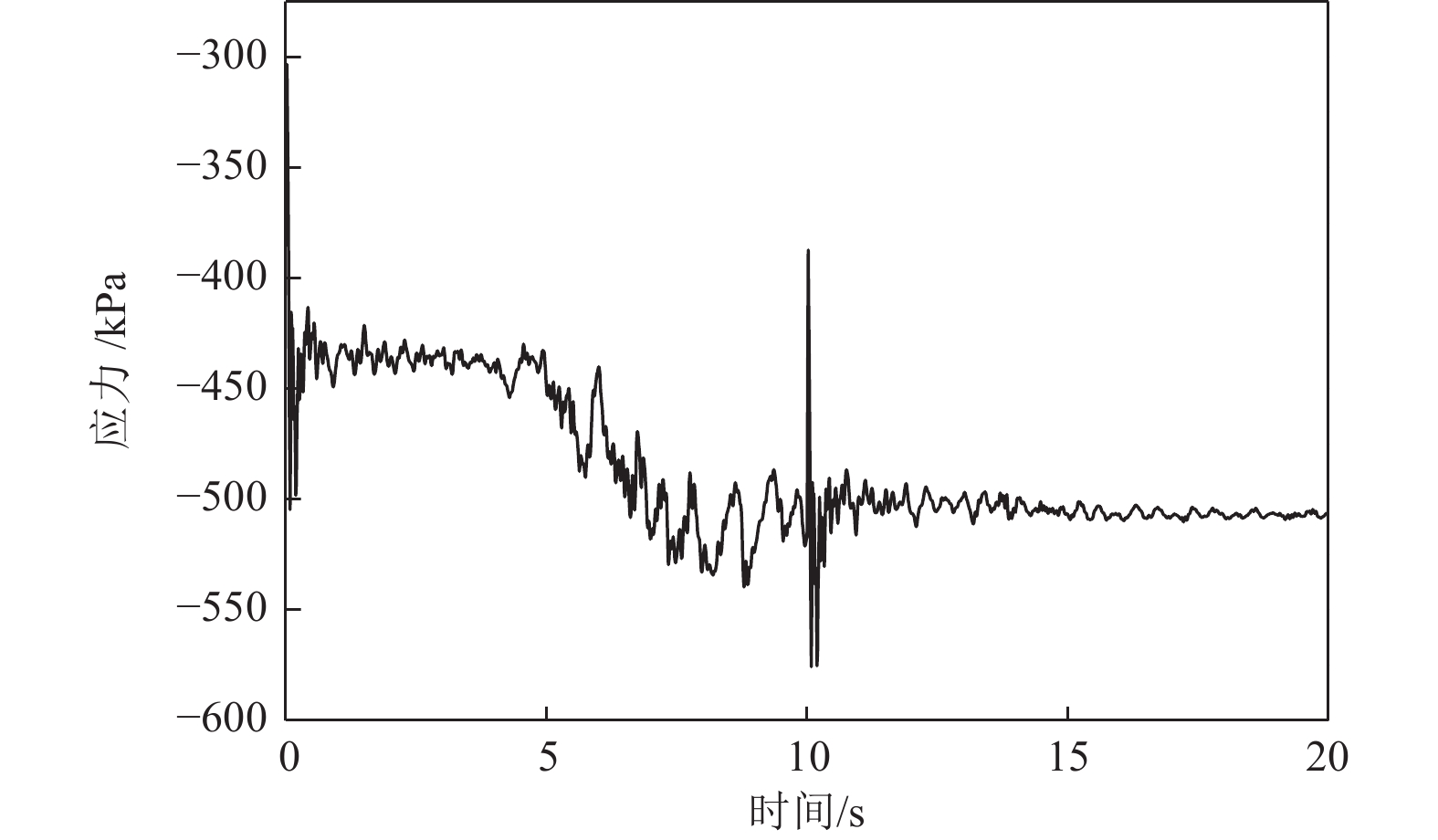
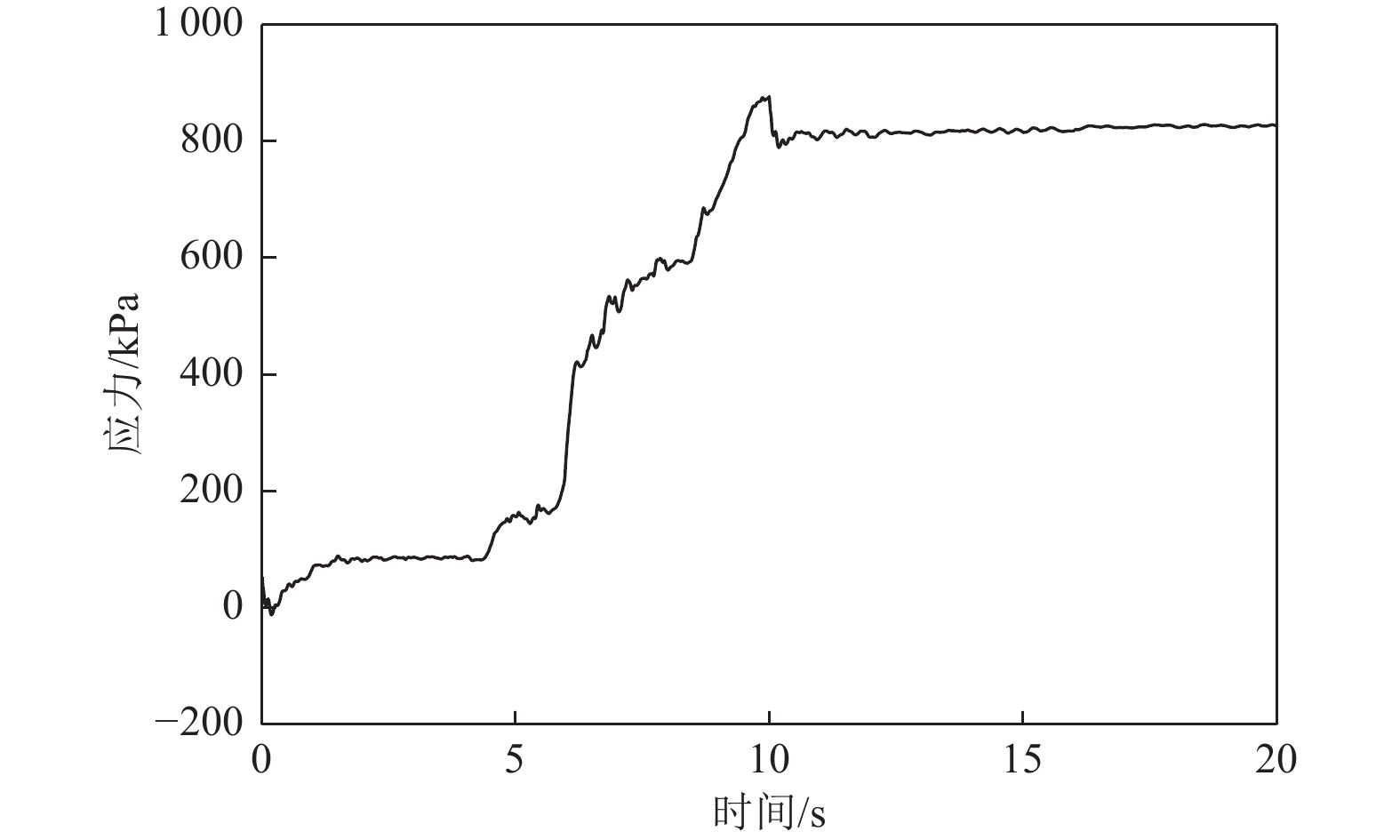
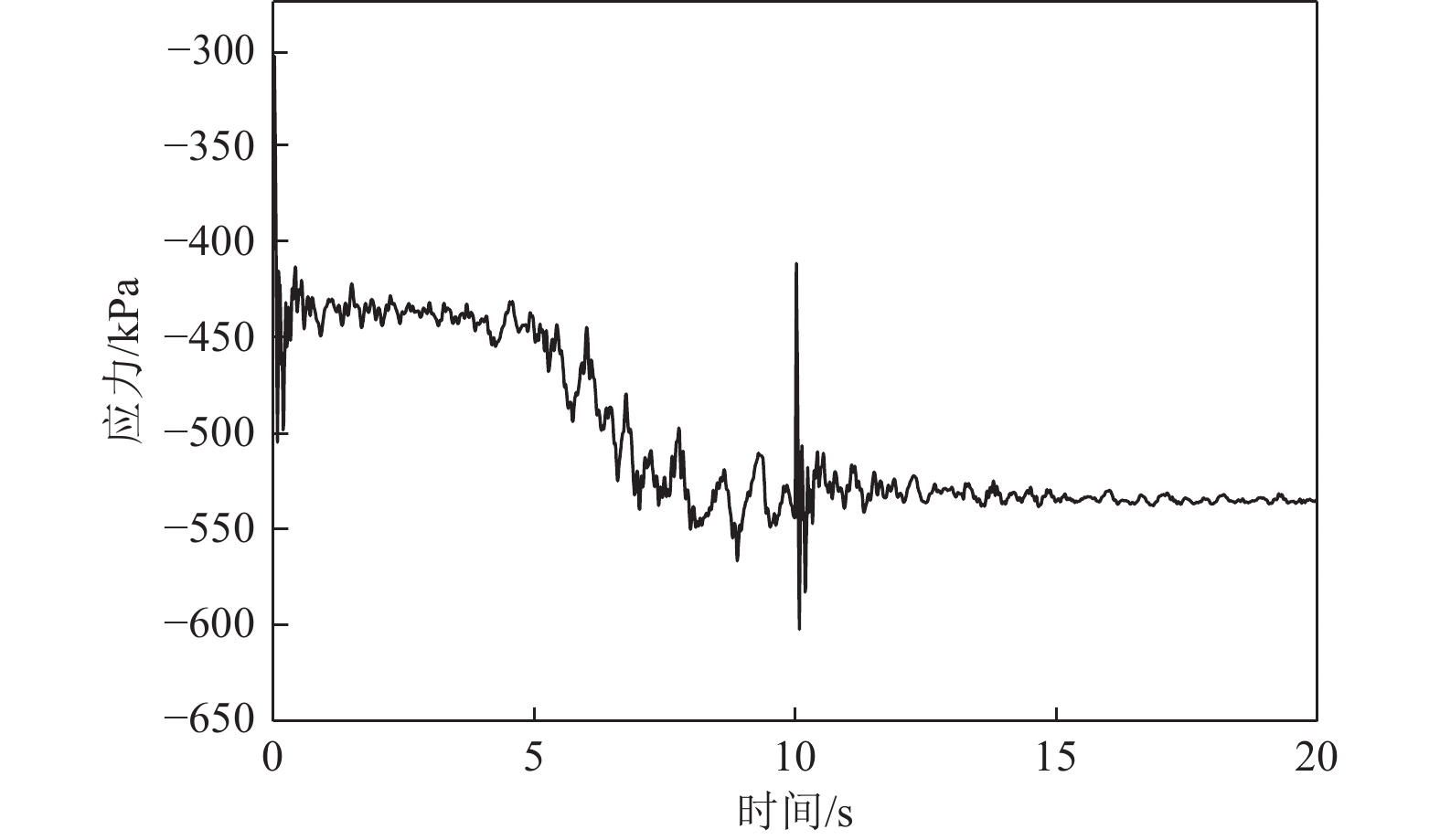
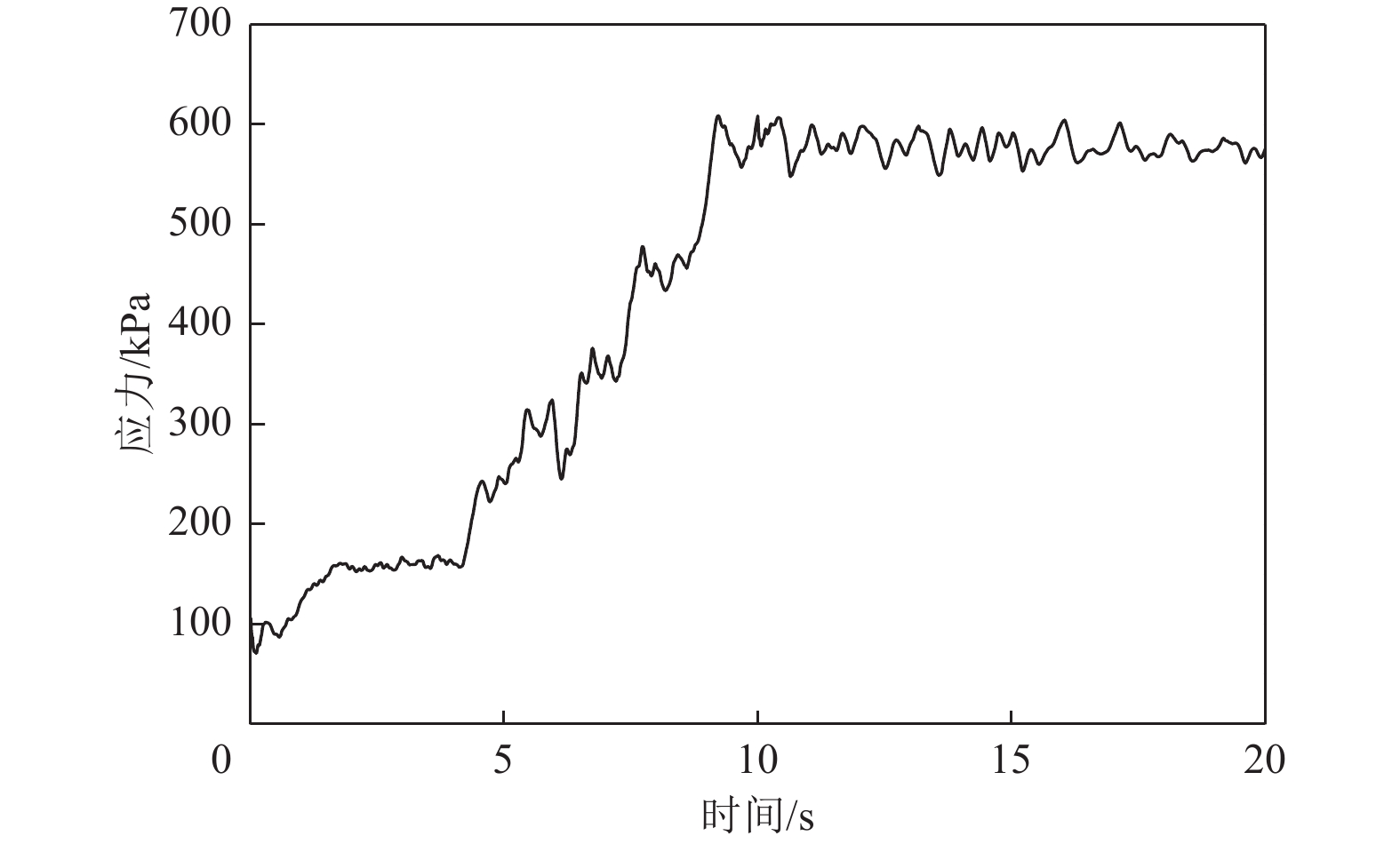
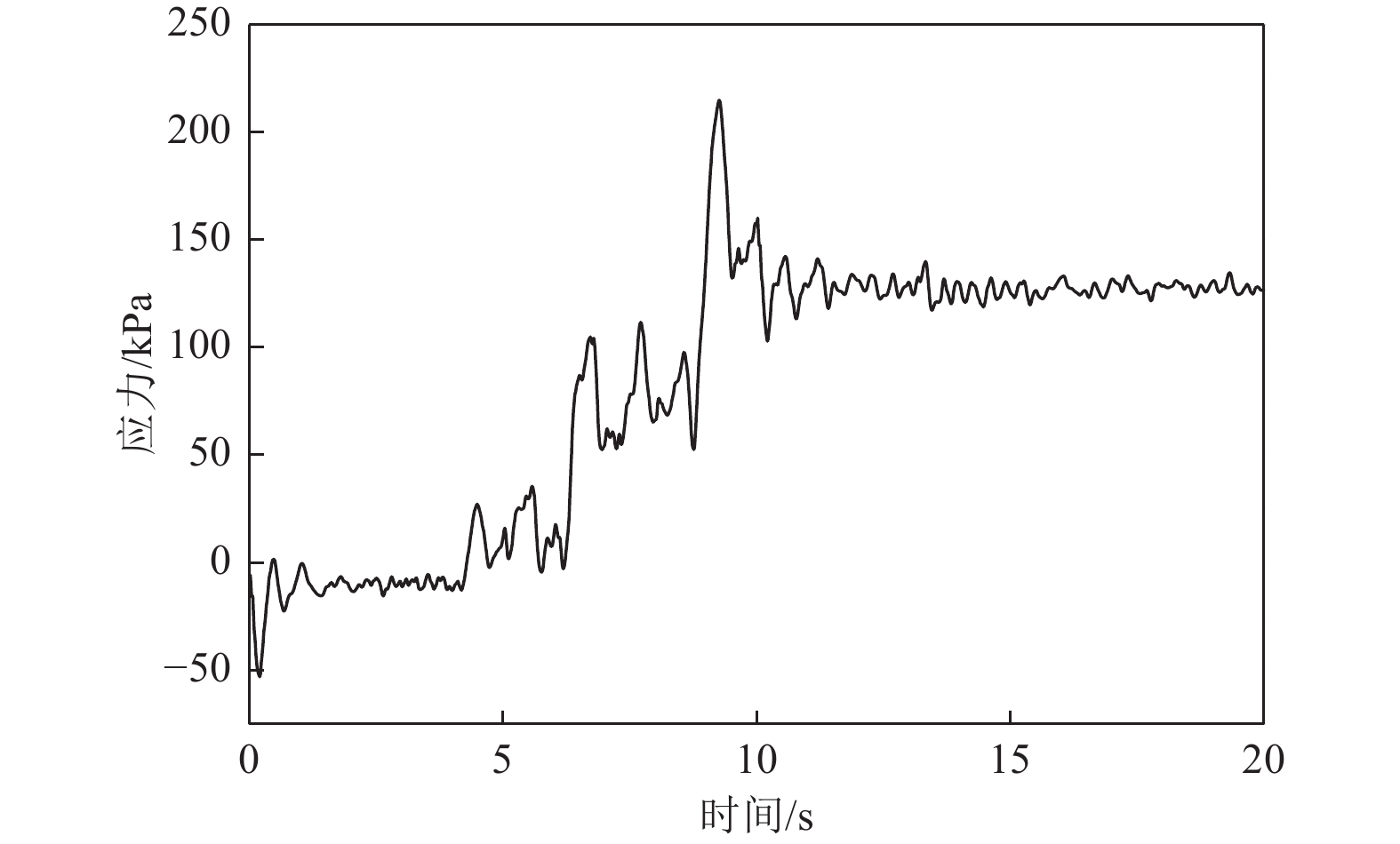
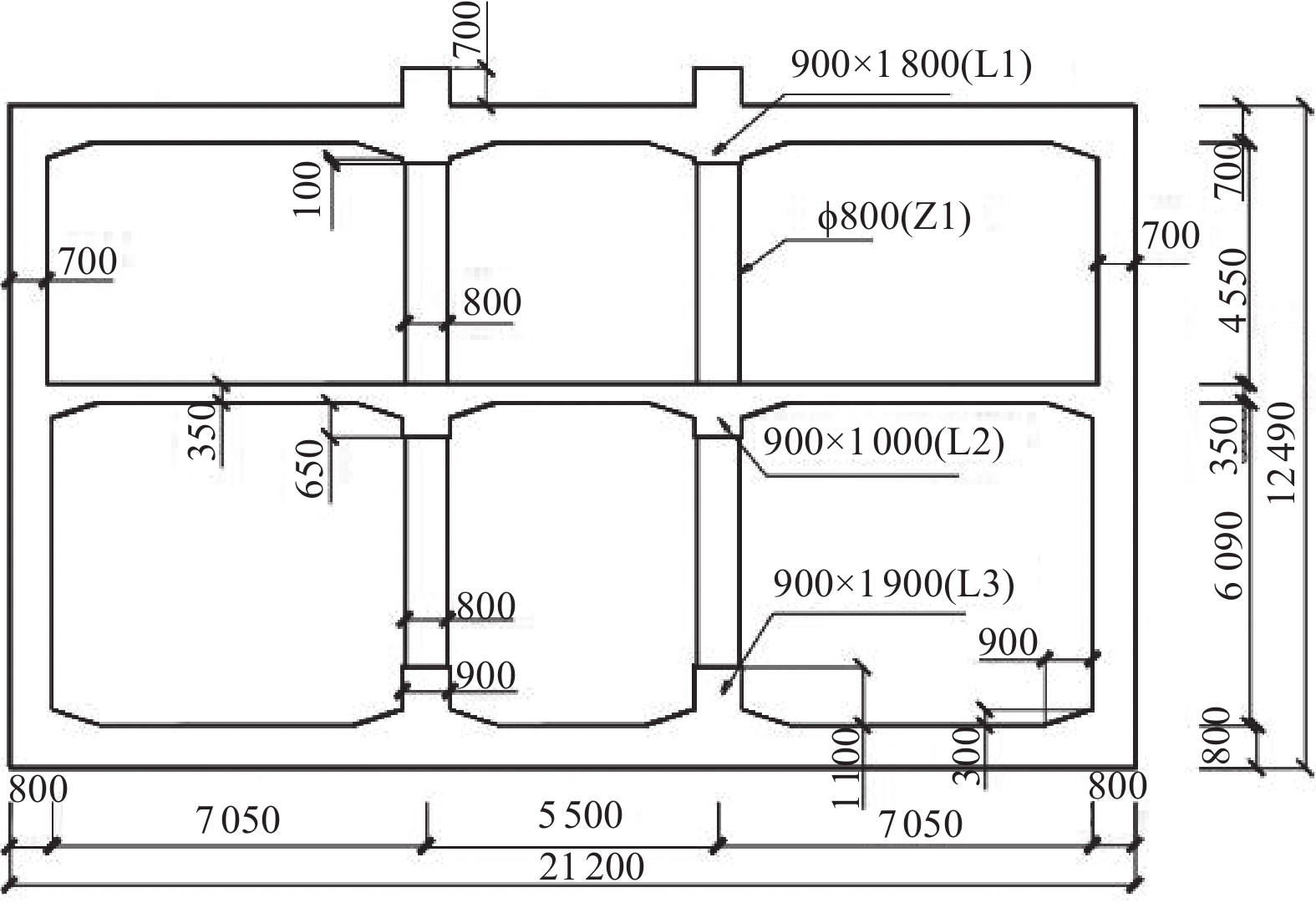
摘要: 应用OpenSees有限元计算程序,选取某地铁车站结构为主要分析对象,构建了饱和土-地下结构体系地震反应运算模型,并利用该模型进行系统的地震反应计算。将现场饱和土动力反应视为饱和两相介质近场波动问题,选取时域显式数值算法进行计算,同时考虑了土体的弹塑性。研究结果显示:(1)因选取弹塑性土体本构,土体-地下结构的位移反应时程和输入地震动的位移时程体现出了显著性差异。(2)对于两层三跨地下结构,在以剪切波形式输入的地震动作用下,顶板的峰值加速度和侧向位移最大,中板次之,底板最小,场地土体对地震波具有放大效应,顶层的层间位移大于底层。(3)在地震动作用下,地下结构不同区域应力时程的改变规律存在非常显著的差异。中柱底部与底板节点处的应力峰值最大。地震动输入结束时,结构存在残余应力。Abstract: Using the finite element calculation software OpenSees, this study focuses on a subway station structure as the primary analysis object while establishing an operational seismic response model for a saturated soil-underground structural system. This model enables a systematic calculation of the seismic response. The study considers the dynamic response of the saturated soil on site as a near-field fluctuation problem of a saturated two-phase medium. A time-domain explicit numerical algorithm is employed for calculations, incorporating the elastic-plastic dynamic response characteristics of the soil. The results of this study indicate several key findings: (1) The elastic-plastic dynamic response characteristics of the site soil are accounted for during the simulation analysis. This consideration reveals a significant difference between the displacement response time histories of the soil and underground structures compared to the displacement time histories of the input ground motion. (2) In the case of a two-story, three-span underground structure subjected to ground motion in the form of shear waves, the roof exhibits the highest peak acceleration and lateral displacement, followed by the middle plate, while the bottom plate shows the smallest values. Additionally, the inter-story displacement of the top layer is greater than that of the bottom layer. (3) Under earthquake loading, there are pronounced differences in the stress time history patterns across various regions of the underground structure. The stress peak at the joint between the bottom of the center column and the bottom plate is the highest observed. Furthermore, when ground motion input ceases, residual stresses remain in the structure.
-
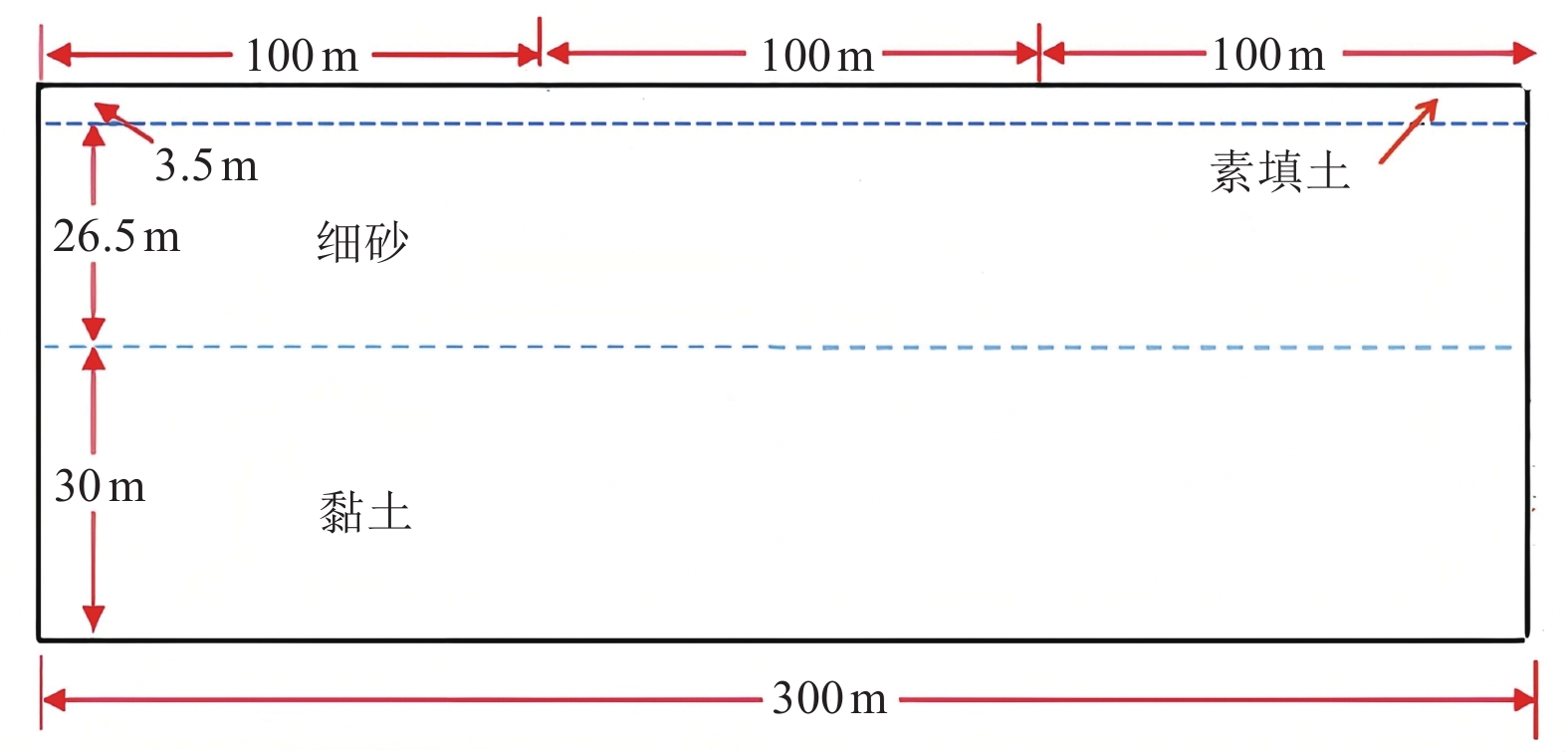
表 1 场地土体物理力学参数
Table 1. Site soil physical and mechanical parameters
土层 重度/(kN·m−3) 内摩擦角/(°) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 孔隙率 素填土 19.0 16 1.0 0.4 — 细砂 19.0 30 7.5 0.3 0.474 黏土 19.3 16 13.2 0.42 — -
陈少林,朱学江,赵宇昕等,2019. 考虑土骨架非线性的饱和土-结构相互作用分析. 地震工程与工程振动,39(1):114−127.Chen S. L., Zhu X. J., Zhao Y. X., et al., 2019. Analysis of saturated soil-structure interaction considering soil skeleton nonlinearity. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 39(1): 114−127. (in Chinese) 程学磊,李文东,海然等,2022. 地震作用下饱和软土场地地下结构动力参数敏感性模拟分析. 广西大学学报(自然科学版),47(1):92−102.Cheng X. L., Li W. D., Hai R., et al., 2022. Parametric sensitivity simulation analyses of subway station structure surrounded by saturated soft soil foundation under earthquake. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 47(1): 92−102. (in Chinese) 崔智谋,2012. 基于流固耦合动力模型的饱和两相介质-地下结构动力相互作用研究. 北京:北京工业大学.Cui Z. M., 2012. Study of dynamic interaction between fluid-saturated porous media of fluid-soild coupling model and underground structure. Beijing:Beijing University of Technology. (in Chinese) 丁伯阳,宋宥整,2019. 饱和土地下源u-P形式解答动力响应计算. 岩土力学,40(2):474−480.Ding B. Y., Song Y. Z., 2019. Dynamic response calculation for u-P solution in saturated soil subjected to an underground point source. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(2): 474−480. (in Chinese) 丁海滨,管凌霄,童立红等,2023. 基于非局部Biot理论的循环荷载下饱和土地基动力特性研究. 工程力学,40(3):141−152.Ding H. B., Guan L. X., Tong L. H., et al., 2023. On investigating the dynamic characteristics of saturated soil foundation subjected to cyclic load based on nonlocal Biot theory. Engineering Mechanics, 40(3): 141−152. (in Chinese) 谷音,庄舒曼,卓卫东等,2015. 考虑饱和土的地铁车站结构非线性地震反应研究. 岩土力学,36(11):3243−3251.Gu Y., Zhuang S. M., Zhuo W. D., et al., 2015. Analysis of nonlinear seismic response of subway station considering saturated soil. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 36(11): 3243−3251. (in Chinese) 李立云,2007. (准)饱和土与地下结构非线性动力相互作用问题研究. 北京:北京工业大学. 刘光磊,宋二祥,刘华北,2007. 可液化地层中地铁隧道地震响应数值模拟及其试验验证. 岩土工程学报,29(12):1815−1822. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.12.012Liu G. L., Song E. X., Liu H. B., 2007. Numerical modeling of subway tunnels in liquefiable soil under earthquakes and verification by centrifuge tests. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 29(12): 1815−1822. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.12.012 刘华北,宋二祥,2005. 可液化土中地铁结构的地震响应. 岩土力学,26(3):381−386,391.Liu H. B., Song E. X., 2005. Earthquake induced liquefaction response of subway structure in liquefiable soil. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 26(3): 381−386,391. (in Chinese) 宋佳,2017. 饱和土场地波动数值模拟方法及其工程应用. 北京:北京工业大学.Song J., 2017. Wave numerical method of saturated site soil and its engineering application. Beijing:Beijing University of Technology. (in Chinese) 王相宝,2014. 基于流固耦合两相介质动力模型的饱和土体-地下结构体系近场波动问题研究. 北京:北京工业大学. 王子辉,2008. 饱和两相与单相土互层场地中地铁车站地震反应分析. 北京:北京交通大学.Wang Z. H., 2008. Seismic analysis of subway station in a site interbedded by saturated two-phase and single-phase soil. Beijing:Beijing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese) 许民泽,崔春义,李静波等,2021. 饱和砂土场地中地铁车站结构地震易损性分析. 工程力学,38(S1):251−258.Xu M. Z., Cui C. Y., Li J. B., et al., 2021. Seismic vulnerability analysis of subway station embedded in saturated sand layers. Engineering Mechanics, 38(S1): 251−258. (in Chinese) 杨军,宋二祥,陈肇元,2003. 饱和土一维简谐响应解析解的求解和应用:Ⅱ应用. 岩土力学,24(5):710−714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.05.008Yang J., Song E. X., Chen Z. Y., 2003. Application of analytical solution of 1-D harmonic response in saturated soil. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 24(5): 710−714. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.05.008 禹海涛,王治坤,刘中宪,2022. SV波入射下均匀饱和地层渗透系数对深埋隧道的影响机制. 岩土工程学报,44(2):201−211.Yu H. T., Wang Z. K., Liu Z. X., 2022. Influence mechanism of permeability coefficient in homogeneously saturated strata on responses of deep tunnels under incidence of SV waves. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 44(2): 201−211. (in Chinese) 袁宗浩,蔡袁强,曾晨,2015. 地铁列车荷载作用下轨道系统及饱和土体动力响应分析. 岩石力学与工程学报,34(7):1470−1479.Yuan Z. H., Cai Y. Q., Zeng C., 2015. Dynamic response of track system and underground railway tunnel in saturated soil subjected to moving train loads. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 34(7): 1470−1479. (in Chinese) 周巧芳,2008. 饱和土中地铁车站的地震响应分析. 北京:北京交通大学. Biot M. A., 1956. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low‐frequency range. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 28(2): 168−178. doi: 10.1121/1.1908239 Li L., Jiao H. Y., Du X. L., et al., 2020. Fully fluid-solid coupling dynamic model for seismic response of underground structures in saturated soils. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 19(2): 257−268. doi: 10.1007/s11803-020-0560-3 Yang Z. H. , Lu J. C. , Elgamal A. , 2008. OpenSees soil models and solid-fluid fully coupled elements user’s manual. San Diego: University of California. Zhu J., Li X. J., Liang J. W., 2020. 3D seismic responses of a long lined tunnel in layered poro-viscoelastic half-space by a hybrid FE-BE method. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 114: 94−113. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2020.02.007 Zienkiewicz O. C., 1982. Basic formulation of static and dynamic behaviours of soil and other porous media. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 3(4): 457−468. doi: 10.1007/BF01908222 -



 下载:
下载: