Damage Analysis of Girder Bridge Under Near-fault Pulse-like Earthquake Motion Considering Wave Propagation Effect
-
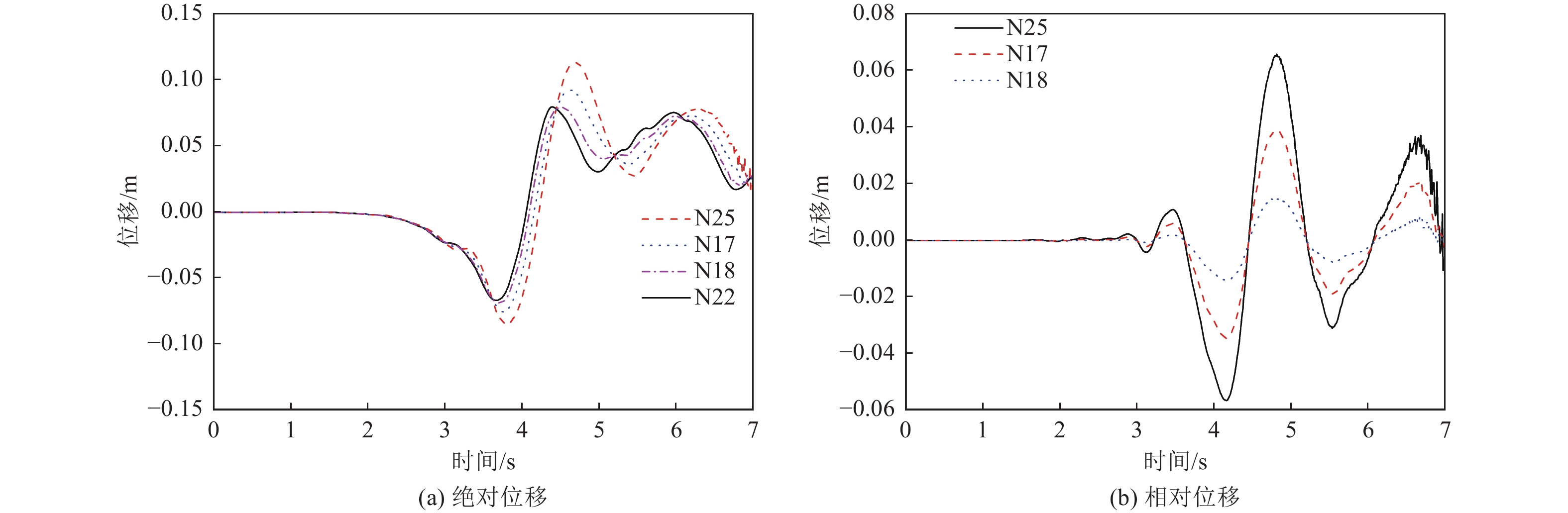
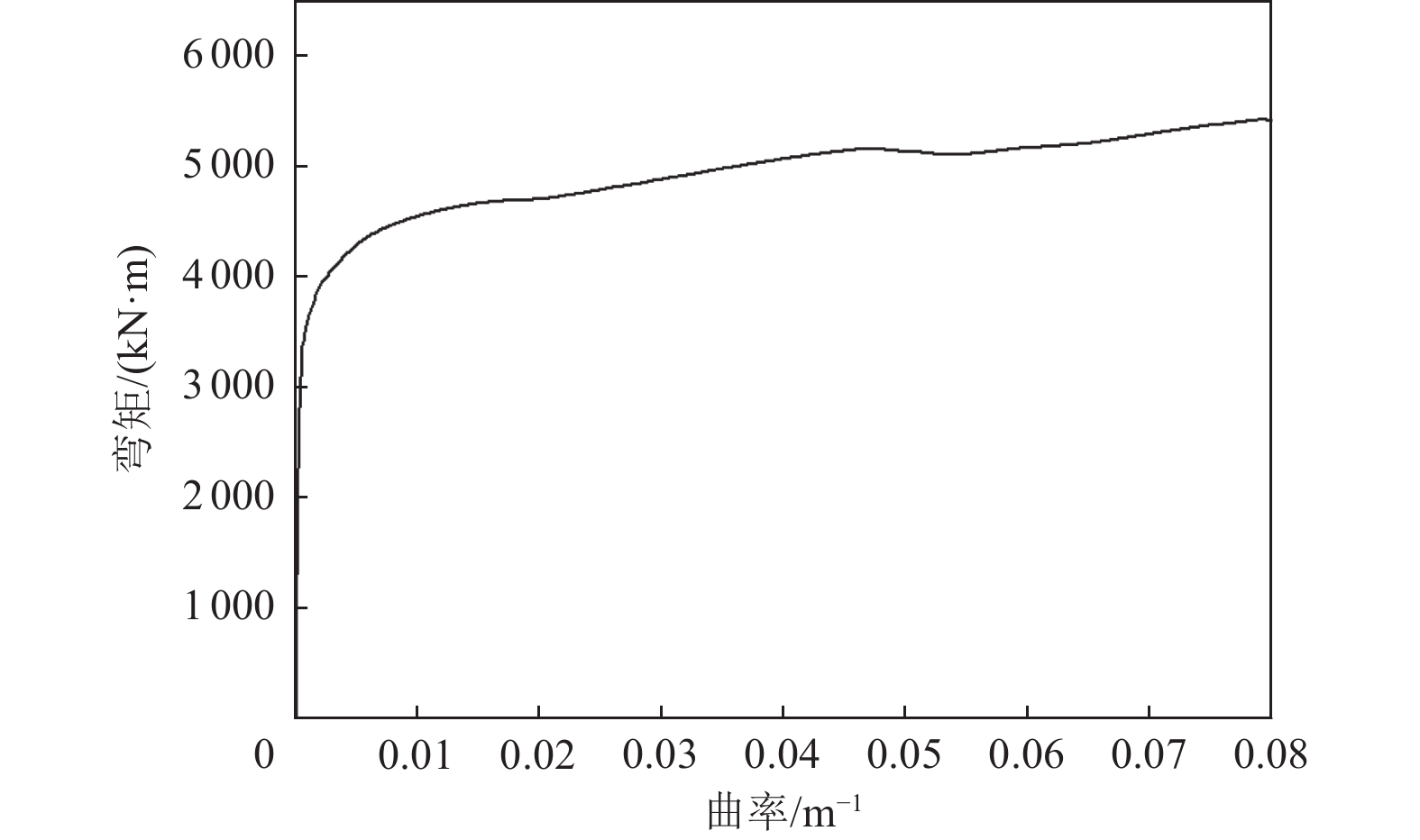
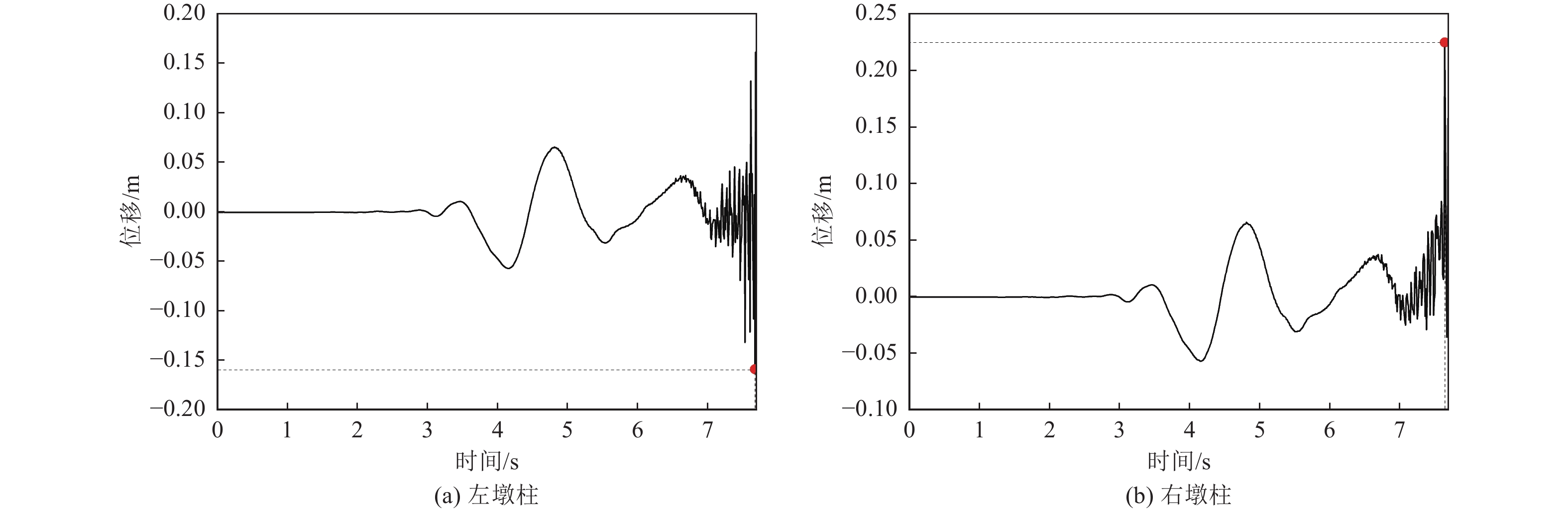
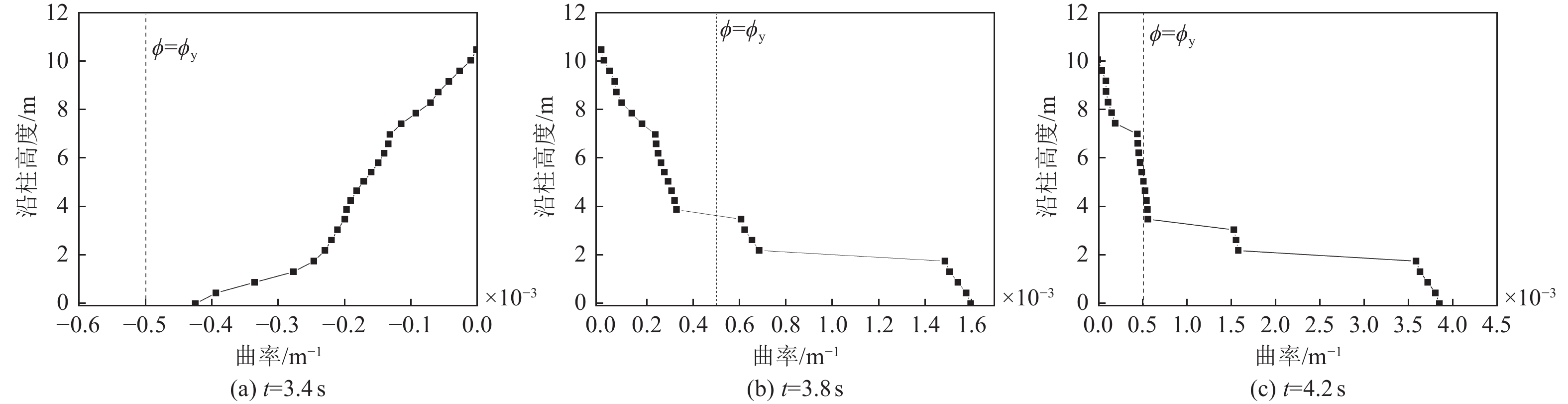
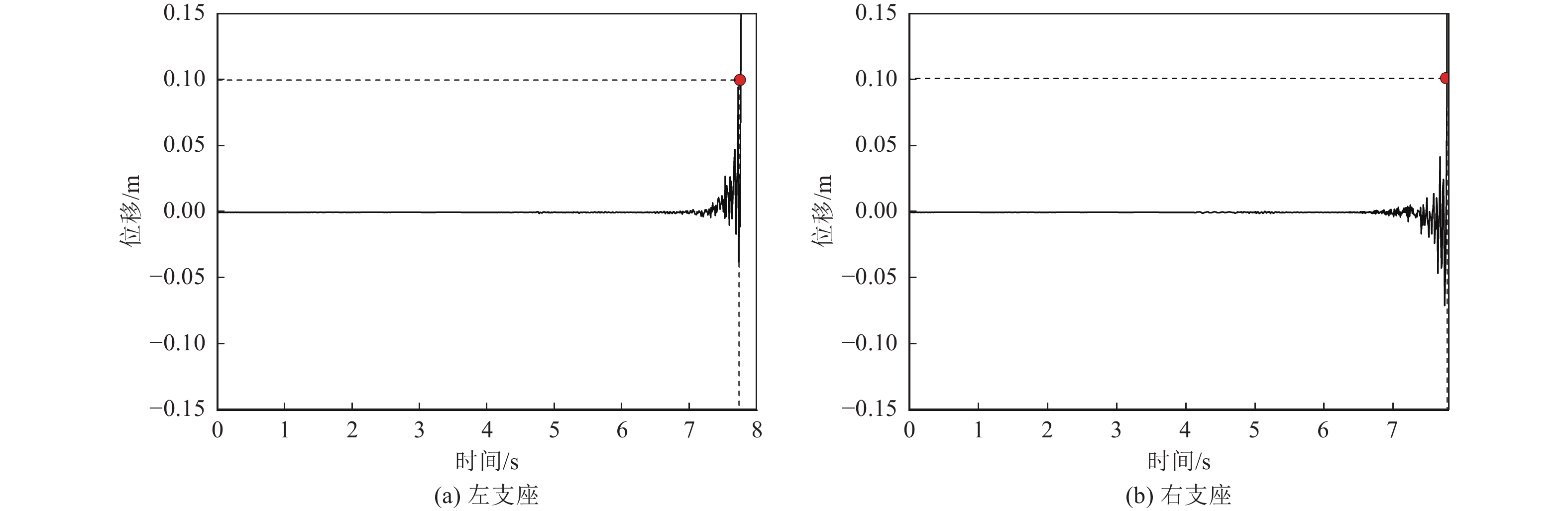
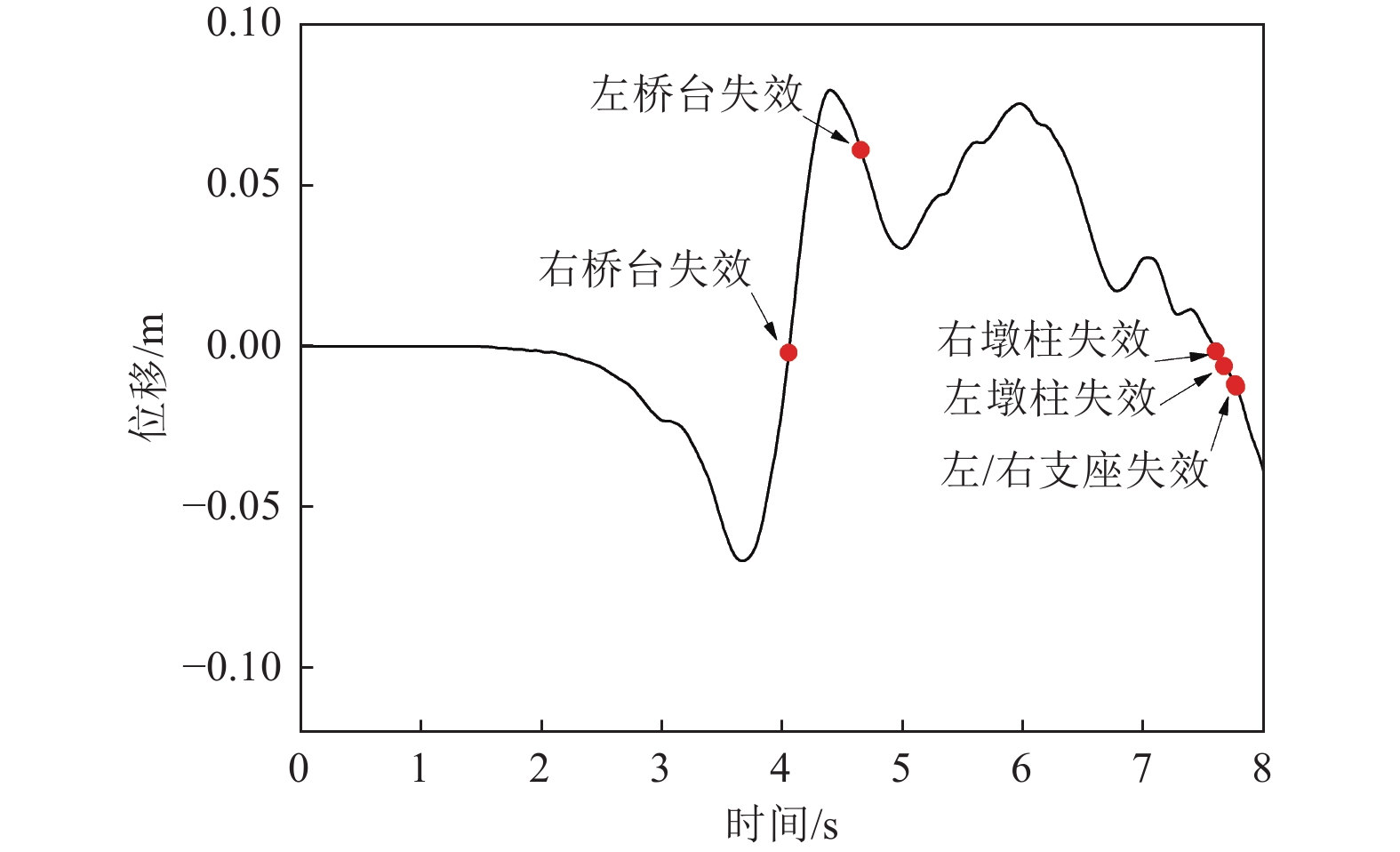
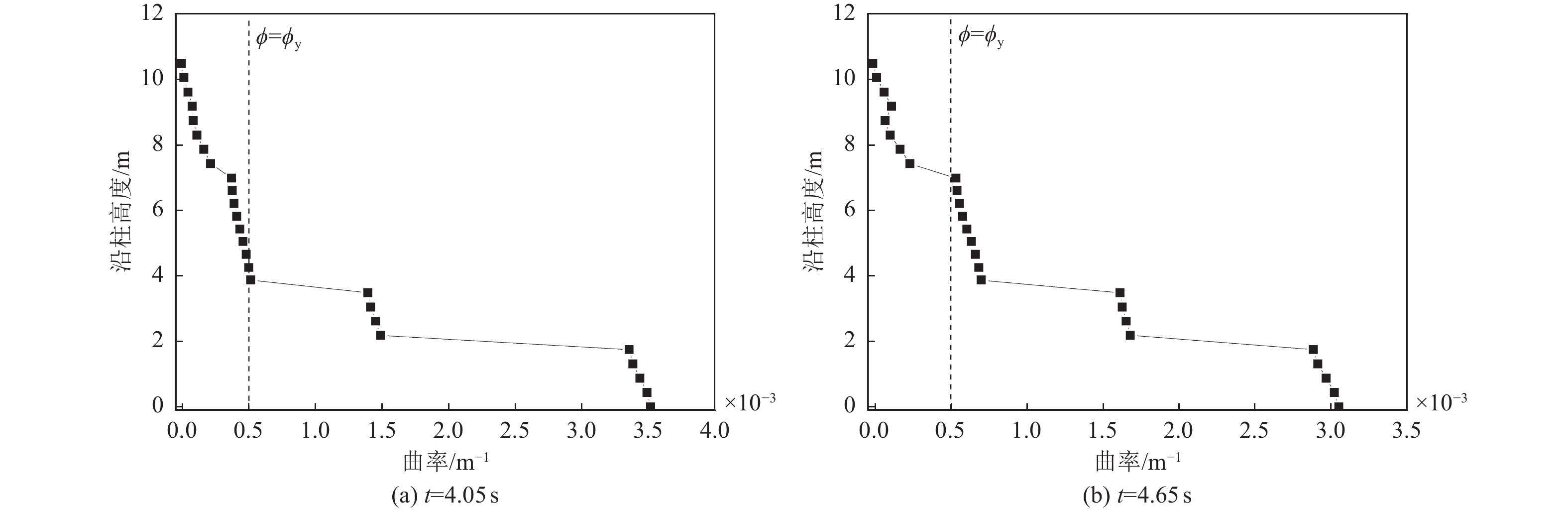
摘要: 在近断层地震动激励的初始阶段,输入地震动从结构底部以波动形式向上传播,然而波动效应对近断层脉冲型地震动作用下梁桥结构地震破坏过程的影响特征尚不明确。为此,利用数值分析方法对某三跨梁桥在近断层脉冲型地震动作用下考虑波动效应的破坏过程、破坏机理开展研究。研究结果表明,在近断层脉冲型地震动作用下,墩柱底部截面曲率发展较合理,梁桥墩顶支座抗震能力较强,梁桥桥台处容许剪切位移是桥梁结构的抗震弱点,因此,在近断层地区的梁桥桥台抗震措施设计中应保证具有充足的容许剪切位移。Abstract: During the initial phase of near-fault seismic excitation, the input ground motion propagates inside the structure from bottom to top in the form of waves, but the influence of the wave propagation effect on the seismic damage process of girder bridge structures under the action of near-fault pulse-type ground motion is not clear. In this paper, numerical analysis method is utilized to study the failure process and failure mechanism of a three-span girder bridge under the action of near-fault pulse-type earthquake considering the wave propagation effect. The results show that the development of the curvature of the bridge pier section is reasonable enough during the seismic excitation process. The bearing at the pier top shows great aseismic capability, the allowable shear displacement of the abutment is the weak point of the whole girder bridge system. Thus, it is important to guarantee a reasonable allowable shear displacement for the abutment of girder bridges located in the near-fault region. Our results provide a reference value for the seismic design of girder bridges in near-fault regions.
-
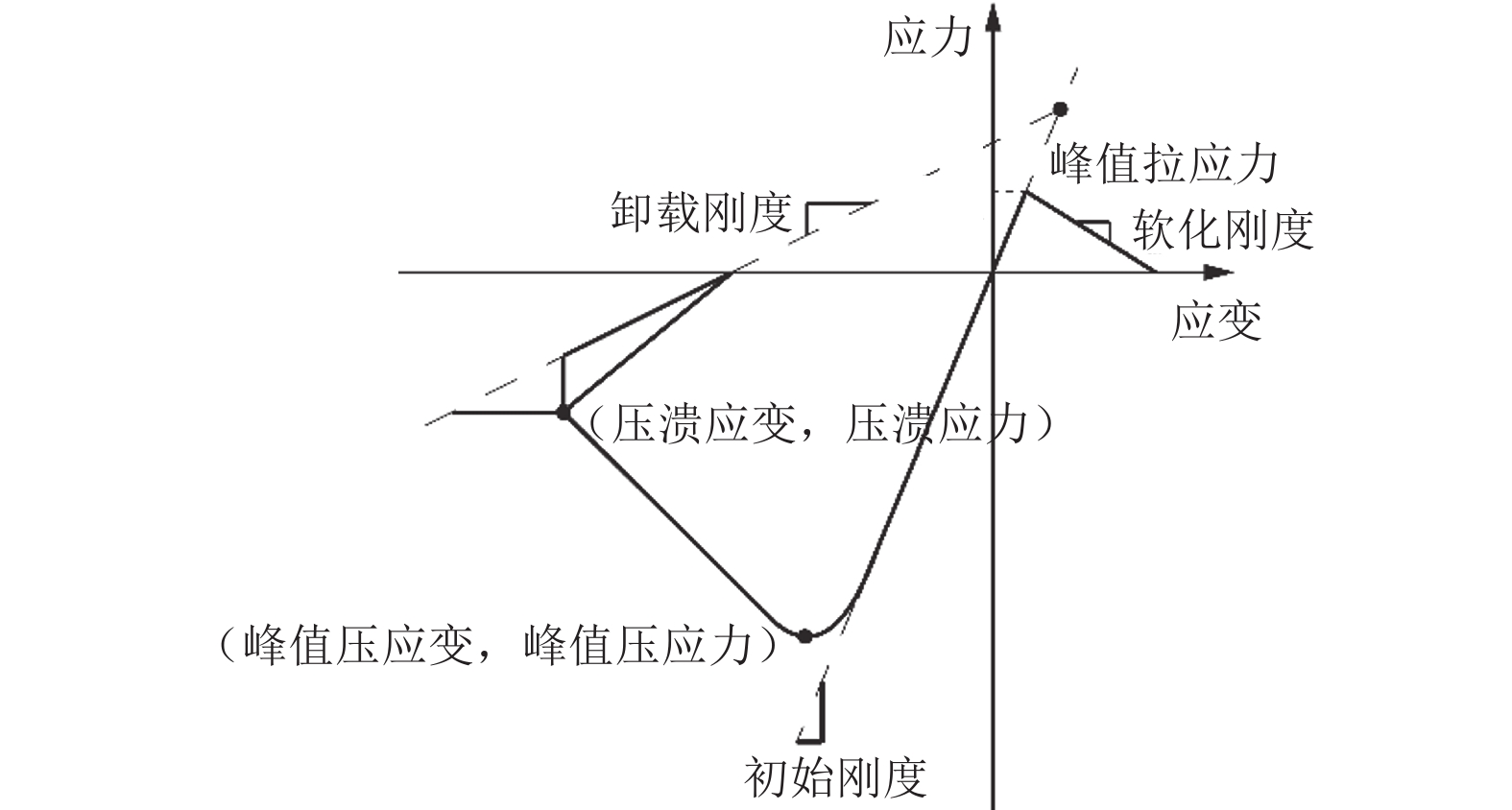
表 1 混凝土材料本构参数
Table 1. Parameters for the core and cover concrete material
材料参数 峰值压应力$ /\mathrm{M}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 峰值压应变$ {\varepsilon }_{0} $ $ \mathrm{压}\mathrm{溃}\mathrm{应}\mathrm{力}/\mathrm{M}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 压溃应变${\varepsilon }_{{\rm{u}}}$ 峰值拉应力$ /\mathrm{M}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 软化刚度$ /\mathrm{G}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 核心层 −30.85 −0.002 1 −6.2 −0.012 2.16 300 保护层 −30.00 −0.002 0 −6.0 −0.005 2.10 300 表 2 不同国家规范给出的等效塑性铰长度计算公式
Table 2. Computing formula for the equivalent length of pier plastic hinge in China, USA, Europe and Japan
规范名称 等效塑性铰长度$ {L}_{\mathrm{p}} $计算公式 按规范公式计算
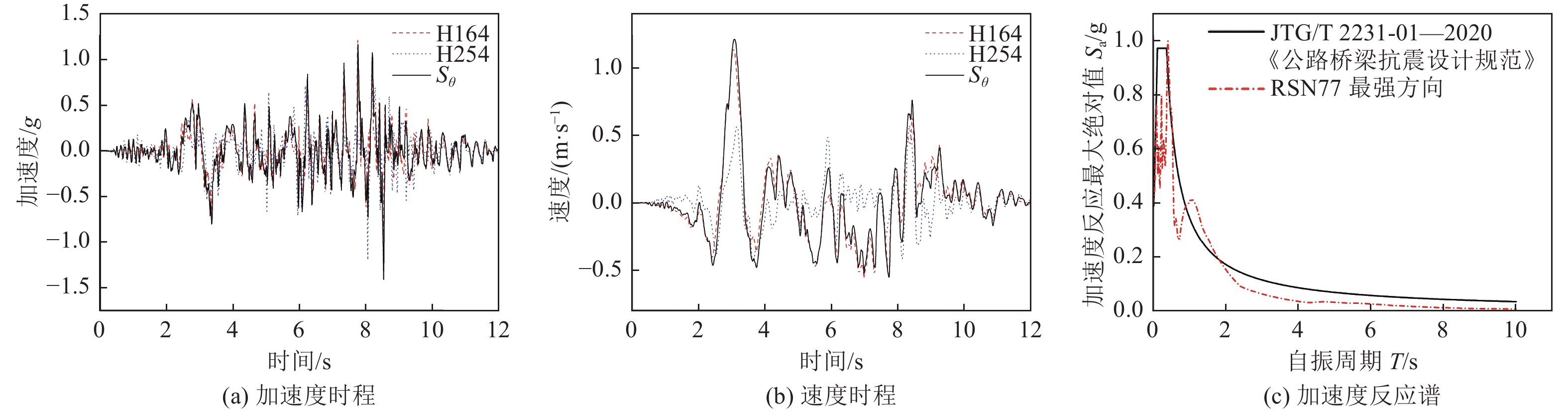
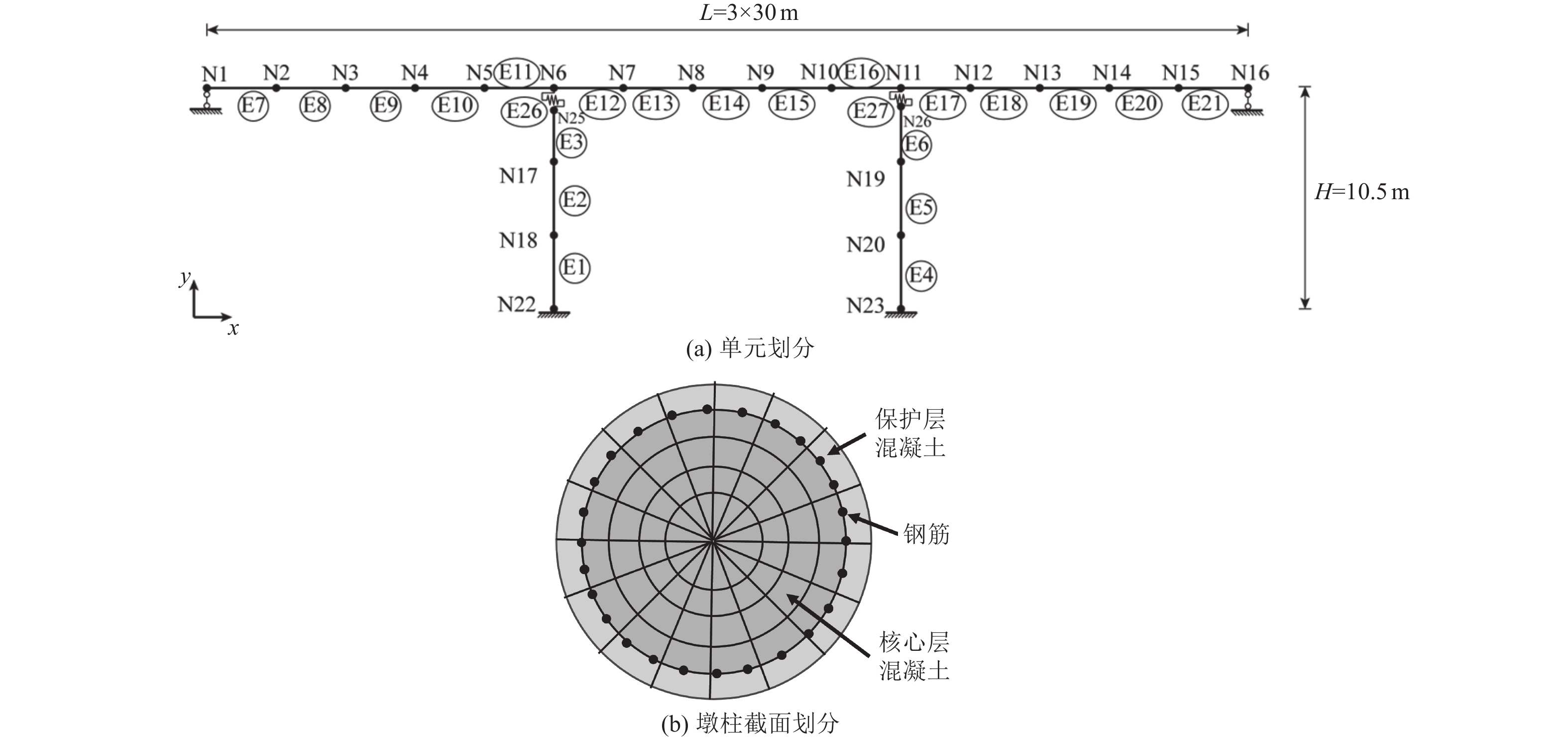
得到的$ {L}_{\mathrm{p}} $/m美国Version 1.7《Seismic design criteria》 $0.08 L+0.022{f}_{{\rm{s}}}{d}_{{\rm{s}}}$ 0.86 中国JTG/T 2231-01—2020《公路桥梁抗震设计规范》 $0.08 L+0.022{f}_{{\rm{s}}}{d}_{{\rm{s}}}\geqslant \mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(0.044{f}_{{\rm{s}}}{d}_{{\rm{s}}},2/3 h\right)$ 0.86 欧洲BS EN 1998-2: 2005+A2:2011《Eurocode 8-Design of structures for earthquake resistance-part 2: bridges》 $0.1 L+0.015{f}_{{\rm{s}}}{d}_{{\rm{s}}}$ 1.18 日本《Specifications for highway bridges-part V seismic design》 $0.2 L-0.1 h;0.1 h\leqslant{L}_{{\rm{p}}}\leqslant 0.5 h$ 0.75 -
姜迎春, 2013. 结构地震响应波动分析的被研究块体方法. 大连: 大连理工大学.Jiang Y. C. , 2013. Investigated lump method for wave propagation analysis of earthquake response of structure. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese) 罗韧, 许慧荣, 李鸿晶等, 2010. 汶川地震中百花大桥倒塌模拟分析. 土木建筑与环境工程, 32(S2): 49—51. 吕大刚, 王光远, 2001. 基于损伤性能的抗震结构最优设防水准的决策方法. 土木工程学报, 34(1): 44—49Lü D. G. , Wang G. Y. , 2001. Decision-making method of optimal fortification level for aseismic structures based on damage performance. China Civil Engineering Journal, 34(1): 44—49. (in Chinese) 邵光强, 刘开, 蒋丽忠等, 2017. 高速铁路桥墩等效塑性铰长度研究. 铁道工程学报, 34(7): 53—59Shao G. Q. , Liu K. , Jiang L. Z. , et al. , 2017. Study of plastic hinge length in high-speed railway bridge piers. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 34(7): 53—59. (in Chinese) 王伟军, 虞庐松, 李子奇等, 2022. 近断层地震特性对隔震曲线连续梁桥地震响应的影响. 地震工程学报, 44(1): 86—92, 127Wang W. J. , Yu L. S. , Li Z. Q. , et al. , 2022. Influence of near-fault ground motion characteristics on the seismic response of isolated continuous curved girder bridges. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 44(1): 86—92, 127. (in Chinese) 夏春旭, 2020. 近断层地震动脉冲识别及考虑波动效应的桥梁地震破坏分析. 大连: 大连理工大学.Xia C. X. , 2020. Pulse identification of near-fault earthquake ground motion and analysis of the seismic damage of bridge considering wave-propagation effect. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese) 杨伟, 欧进萍, 2009. 基于能量原理的Park & Ang损伤模型简化计算方法. 地震工程与工程振动, 29(2): 159—165Yang W. , Ou J. P. , 2009. A simplified method for computing Park & Ang damage model based on energy concept. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 29(2): 159—165. (in Chinese) 曾永平, 董俊, 陈克坚等, 2020. 近断层高铁简支梁桥抗震性能分析研究. 铁道工程学报, 37(12): 70—76Zeng Y. P. , Dong J. , Chen K. J. , et al. , 2020. Research on the seismic performance of simply supported beam bridge of near-fault high-speed railway. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 37(12): 70—76. (in Chinese) 张海燕, 樊燕燕, 李江龙, 2022. 铁路梁式桥地震灾害损失评估. 世界地震工程, 38(1): 139—147Zhang H. Y. , Fan Y. Y. , Li J. L. , 2022. Earthquake disaster loss assessment of railway beam bridge. World Earthquake Engineering, 38(1): 139—147. (in Chinese) 张鹏, 2018. 跨断层简支梁桥的概率性地震损伤特性研究. 北京: 北京交通大学.Zhang P. , 2018. Study on the probabilistic seismic damage character of simply supported girder bridge under fault-crossing earthquakes. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese) Beolchini G. C., Galeota D., Giammatteo M. M., et al., 2000. Seismic behavior of high strength RC columns. In: Proceedings of the 12 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Auckland: WCEE, 1—8. Bi K. M. , Ren W. X. , Cheng P. F. , et al. , 2015. Domino-type progressive collapse analysis of a multi-span simply-supported bridge: a case study. Engineering Structures, 90: 172—182. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.02.023 Priestley M. J. N. , Park R. , 1987. Strength and ductility of concrete bridge columns under seismic loading. ACI Structural Journal, 84(1): 61—76. Salem H. M. , Helmy H. M. , 2014. Numerical investigation of collapse of the Minnesota I-35 W bridge. Engineering Structures, 59: 635—645. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.11.022 Xia C. X. , Liu C. G. , 2018. Explicit fiber element and its application to piers under multipulse near-fault earthquake motion. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 27(18): e1547. doi: 10.1002/tal.1547 Xia C. X. , Liu C. G. , 2019. Identification and representation of multi-pulse near-fault strong ground motion using adaptive wavelet transform. Applied Sciences, 9(2): 259. doi: 10.3390/app9020259 Xu Z. , Lu X. Z. , Guan H. , et al. , 2013. Progressive-collapse simulation and critical region identification of a stone arch bridge. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 27(1): 43—52. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000329 Ye L. P. , Otani S. , 1999. Maximum seismic displacement of inelastic systems based on energy concept. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 28(12): 1483—1499. Zhou R. , Zong Z. H. , Huang X. Y. , et al. , 2014. Seismic response study on a multi-span cable-stayed bridge scale model under multi-support excitations. Part II: numerical analysis. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A, 15(6): 405—418. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1300340 Zong Z. H. , Xia Z. H. , Liu H. H. , et al. , 2016. Collapse failure of prestressed concrete continuous rigid-frame bridge under strong earthquake excitation: testing and simulation. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 21(9): 04016047. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000912 -



 下载:
下载: