A Review of Research Progress on the Late Quaternary Activities of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone
-
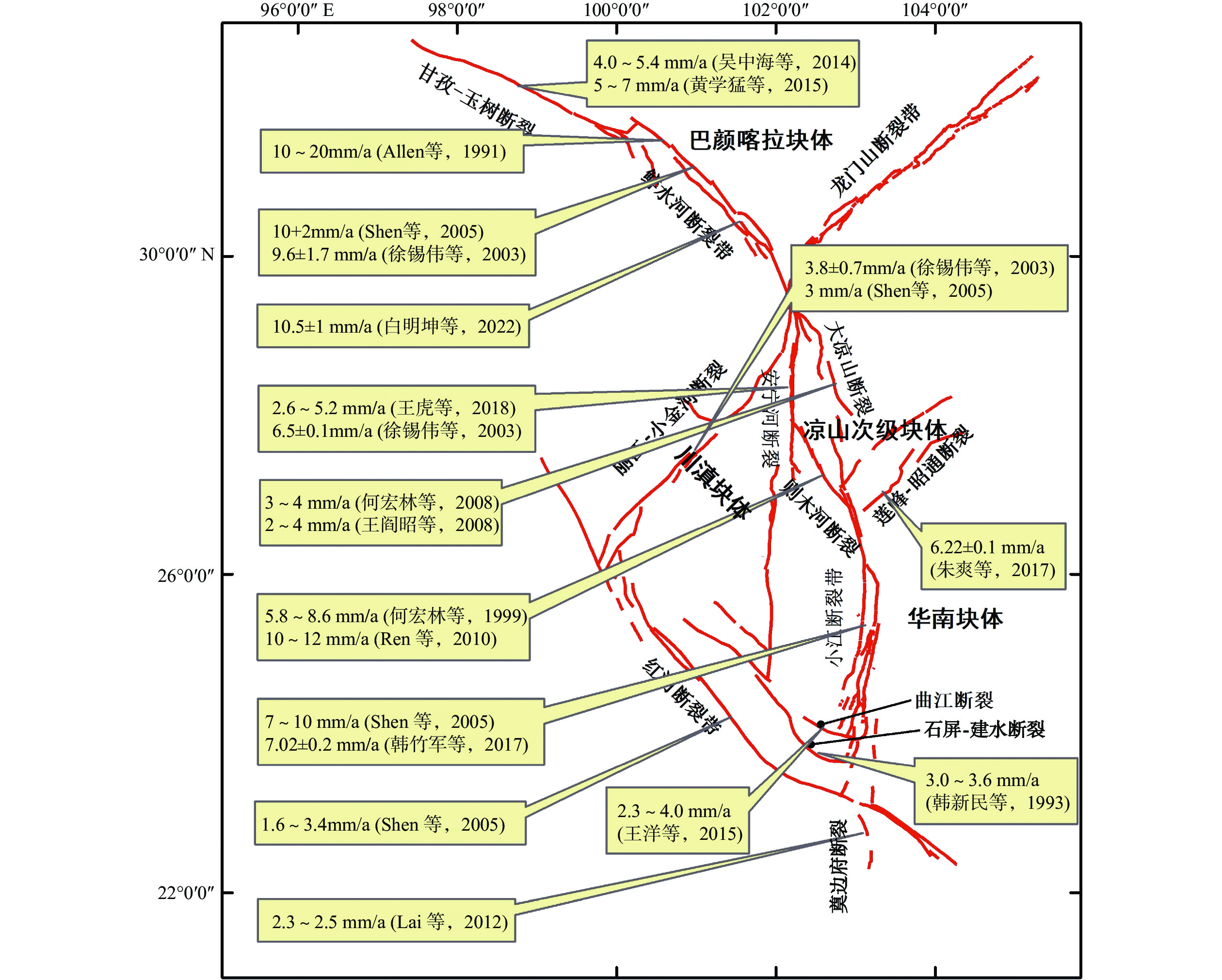
摘要: 小江断裂带是川滇菱形块体的东南边界断裂,是大型左旋走滑断裂。在总结已有研究成果的基础上,概述了小江断裂带空间展布、滑动速率、地震活动特征、强震地表破裂特征、地震危险性等方面的研究进展。已有研究结果表明,小江断裂带可分为北段、中段、南段,其中中段又可分为东支和西支。整条断裂带全新世的滑动速率为10 mm/a左右,其中北段和中段滑动速率为8~12 mm/a,南段滑动速率小于8 mm/a。小江断裂带沿线及周边地区地震频发,北段、中段地震活动性明显高于南段,强震活动具有明显的时空不均匀性,南段和巧家-东川段为地震空区,具有较高的强震危险性。通过对小江断裂带的论述,认为小江断裂带南段穿过红河断裂并向南延伸,但小江断裂带向南延伸模式及小江断裂带南段速度亏损是否由曲江断裂、石屏-建水断裂和红河断裂吸收,小江断裂带古地震是否与曲江断裂、石屏-建水断裂古地震相互影响,“Y”字形构造带吸收和调节模式还需进一步研究。Abstract: The Xiaojiang fault zone is the southeastern boundary fault of the Sichuan-Yunnan diamond block, and is a large left-lateral strike-slip fault. On the basis of summarizing the previous research results, this paper summarizes the research progress of the Xiaojiang fault zone in terms of spatial distribution, slip rate, seismic activity characteristics, surface rupture characteristics of strong earthquakes, and earthquake risk. The results of previous studies have shown that the Xiaojiang fault zone can be divided into three segments: the northern segment, the middle segment and the southern segment, and the middle segment can be further divided into the eastern branch and the western branch. The Holocene slip rate of the entire fault is about 10 mm/a, of which the slip rate of the northern and middle segments is 8-12 mm/a, and the slip rate of the southern segment is less than 8mm/a; earthquakes occur frequently along the Xiaojiang fault zone and the surrounding areas, The seismic activity of the northern and middle segments is significantly higher than that of the southern segment, and the strong earthquake activity has obvious spatial and temporal inhomogeneity. The southern segment of the Xiaojiang Fault and the Qiaojia-Dongchuan segment are seismic void zones with high risk of strong earthquakes.Through the discussion of the Xiaojiang fault zone, it is concluded that the southern section of the Xiaojiang fault extends southward through the Red River Fault, but the southward extension pattern of the Xiaojiang fault zone, whether the velocity loss of the southern section of the Xiaojiang fault zone is absorbed by the Qujiang fault, the Shiping-Jianshui fault and the Red River Fault, whether the paleoseismicity of the Xiaojiang fault zone interacts with that of the Qujiang fault and the Shiping-Jianshui fault, and the "Y " pattern of absorption and modulation in the tectonic zone needs further study.
-
Key words:
- Xiaojiang fault zone /
- Slip rate /
- Seismic activity /
- Surface rupture /
- Seismic hazard
-
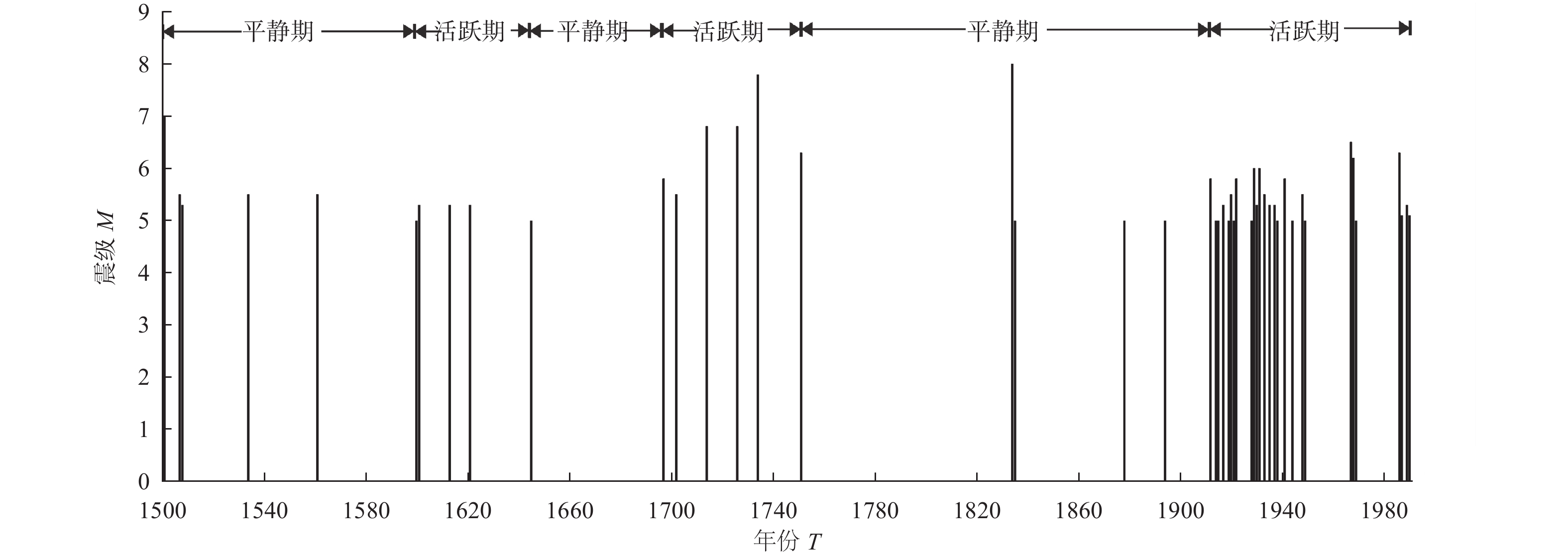
图 2 小江断裂带沿线M≥5地震M-T关系图(修改自宋方敏等(1998))
Figure 2. M-T map of M≥5 earthquakes along the Xiaojiang fault zone (According to Song et al(1998))
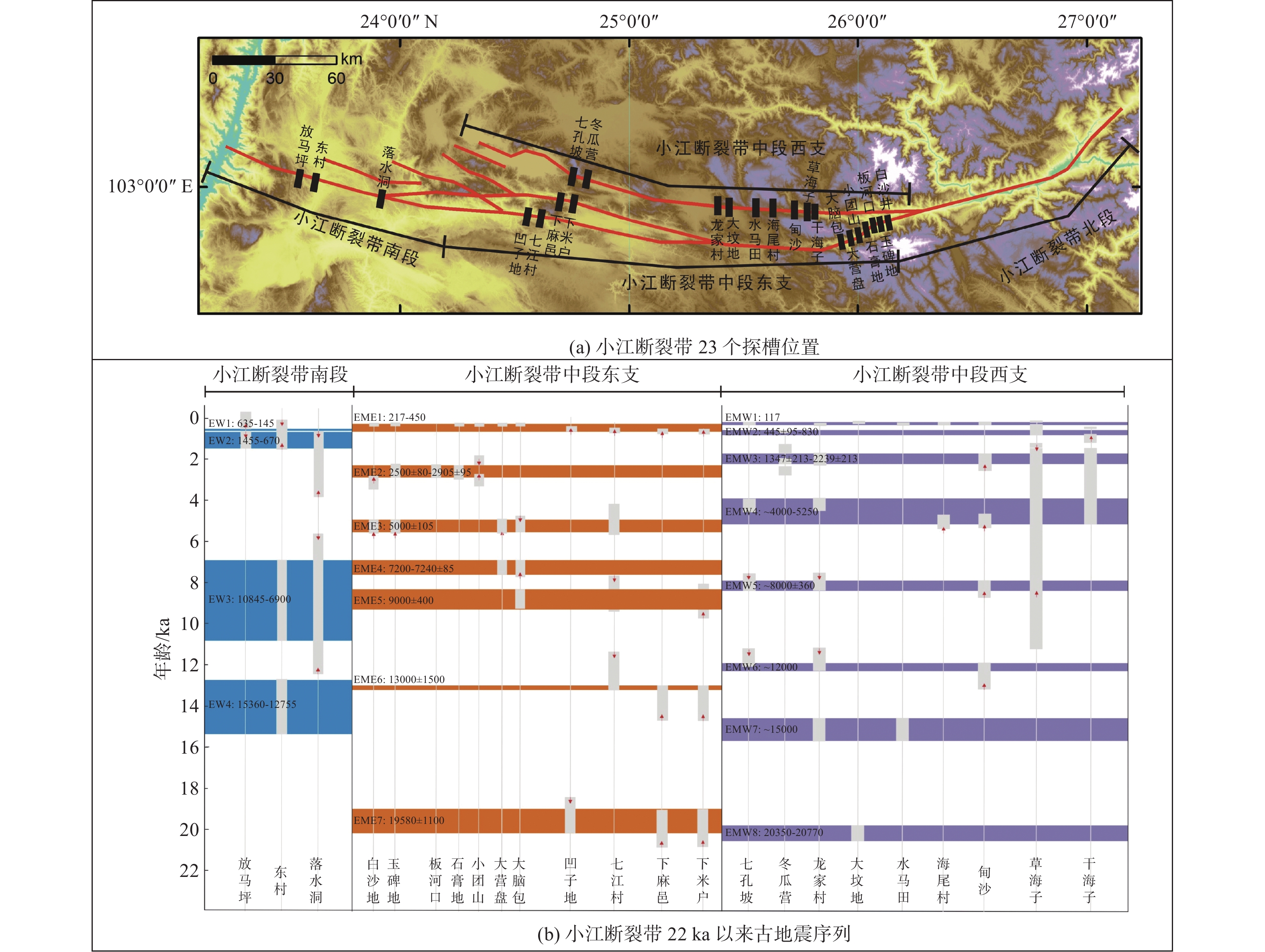
表 1 小江断裂带晚第四纪各段滑动速率
Table 1. List of the Late Quaternary slip rates of each segment of the Xiaojiang fault zone
序号 分段 滑动速率/(mm·a–1) 参考文献 1
北段15±2 何宏林等(2002) 2 10.0 闻学泽等(2011) 3 10.4 魏文薪等(2012) 4 5.97 王伶俐等(2016) 5 10~13 胡萌萌等(2023) 6 中段 中段西支 7.0~9.0 何宏林等(1993) 7 中段东支 6.0~7.5 何宏林等(1993) 8 中段西支 6.5~7.4 陈睿等(1988) 9 中段东支 4.8~9.6 朱成男等(1983) 10 中段西支 7.5~8.6 宋方敏等(1998) 11 中段东支 4.5~5.1 宋方敏等(1998) 12
整段8.0~9.0 闻学泽等(2011) 13 11.4 魏文薪等(2012) 14 7.19 王伶俐等(2016) 15 南段 1.66 何宏林等(1993) 16 2.5~4.8 宋方敏等(1998) 17 4.0 闻学泽等(2011) 18 11.3 魏文薪等(2012) 19 5.30 王伶俐等(2016) 20 6.5 程佳等(2012) 21 7.02±0.2 韩竹军等(2017) 22
全段7±2 Shen等(2005) 23 10.1±2.0 王阎昭等(2008) 24 10.0 程佳等(2012) 表 2 小江断裂带沿线及周边主要地震(M≥6)事件(1500—1990年)
Table 2. Major earthquake events (M≥6) along and around the Xiaojiang fault zone (From AD1500 to AD1990)
编号 日期/(年-月-日) 震中位置 震级M 震中烈度/度 地点 纬度 经度 1 1500-01-13 24.9°N 103.1°E ≥7 ≥8 云南宜良 2 1571-09-19 24.1°N 102.8°E 6¼ 7 云南通海 3 1606-11-30 23.6°N 102.8°E 6¾ 8 云南建水 4 1713-02-26 25.6°N 103.3°E 6¾ 9 云南寻甸 5 1725-01-08 25.1°N 103.1°E 6¾ 9 云南宜良、嵩明间 6 1733-08-02 26.3°N 103.1°E 7¾ 10 云南东川 7 1750-09-15 24.7°N 102.9°E 6¼ 8 云南澄江 8 1763-12-30 24.2°N 102.8°E 6½ ≥7 云南江川、通海间 9 1789-06-07 24.2°N 102.9°E 7 8 云南华宁 10 1833-09-06 25.0°N 103.0°E 8 ≥10 云南嵩明 11 1909-05-11 24.4°N 103.0°E 6 7 云南华宁、弥勒间 12 1909-05-11 24.4°N 103.0°E 6½ 7 云南华宁、弥勒间 13 1927-03-15 26.0°N 103.0°E 6 8 云南寻甸 14 1930-05-15 26.8°N 103.0°E 6 7~8 云南巧家南 15 1966-02-05 26.1°N 103.1°E 6½ 9 云南东川 16 1966-02-13 26.1°N 103.1°E 6.2 7~8 云南东川 17 1985-04-18 25.9°N 102.9°E 6.3 8 云南禄劝 表 3 小江断裂带各段的古地震复发周期
Table 3. Paleoseismic recurrence periods in various sections of the Xiaojiang fault zone
-
白明坤, Marie-Luce C. , 李海兵等, 2022. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段晚第四纪走滑速率及区域强震危险性研究. 地质学报, 96(7): 2312—2332 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.005Bai M. K. , Marie-Luce C. , Li H. B. , et al. , 2022. Late Quaternary slip rate and earthquake hazard along the Qianning segment, Xianshuihe fault. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(7): 2312—2332. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.005 常玉巧, 陈立春, 李西等, 2021. 小江断裂带宜良盆地西缘断裂晚第四纪活动的地质地貌证据. 地震研究, 44(2): 152—161Chang Y. Q. , Chen L. C. , Li X. , et al. , 2021. The Late Quaternary activity of the fault along the western Margin of the Yiliang Basin of the Xiaojiang fault zone. Journal of Seismological Research, 44(2): 152—161. (in Chinese) 常祖峰, 周荣军, 安晓文等, 2014. 昭通-鲁甸断裂晚第四纪活动及其构造意义. 地震地质, 36(4): 1260—1279Chang Z. F. , Zhou R. J. , An X. W. , et al. , 2014. Late-Quaternary activity of the Zhaotong-Ludian Fault Zone and its tectonic implication. Seismology and Geology, 36(4): 1260—1279. (in Chinese) 陈君贤, 韩竹军, 程捷, 2021. 小江断裂带南段新寨盆地新构造运动特征. 华南地震, 41(3): 82—91Chen J. X. , Han Z. J. , Cheng J. , 2021. Characteristics of Neotectonic movement in Xinzhai Basin in the southern Section of Xiaojiang fault zone. South China Journal of Seismology, 41(3): 82—91. (in Chinese) 陈睿, 李玶, 1988. 小江西支断裂的滑动速率与强震重复周期. 地震地质, 10(2): 1—13Chen R. , Li P. , 1988. Slip rates and earthquake recurrence intervals of the western branch of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Seismology and Geology, 10(2): 1—13. (in Chinese) 程佳, 刘杰, 甘卫军等, 2011. 川滇菱形块体东边界各断层段强震演化特征研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(9): 1311—1326.Cheng J. , Liu J. , Gan W. J. , et al. , 2011. Characteristics of strong earthquake evolution around the eastern boundary faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan rhombic block. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(11): 1716—1729. 程佳, 徐锡伟, 甘卫军等, 2012. 青藏高原东南缘地震活动与地壳运动所反映的块体特征及其动力来源. 地球物理学报, 55(4): 1198—1212Cheng J. , Xu X. W. , Gan W. J. , et al. , 2012. Block model and dynamic implication from the earthquake activities and crustal motion in the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(4): 1198—1212. (in Chinese) 程佳, 刘杰, 徐锡伟等, 2014. 大凉山次级块体内强震发生的构造特征与2014年鲁甸6.5级地震对周边断层的影响. 地震地质, 36(4): 1228—1243Cheng J. , Liu J. , Xu X. W. , et al. , 2014. Tectonic characteristics of strong earthquakes in Daliangshan sub-block and impact of the MS6.5 Ludian earthquake in 2014 on the surrounding faults. Seismology and Geology, 36(4): 1228—1243. (in Chinese) 崔笃信, 王庆良, 胡亚轩等, 2009. 用GPS数据反演海原断裂带断层滑动速率和闭锁深度. 地震学报, 31(5): 516—525Cui D. X. , Wang Q. L. , Hu Y. X. , et al. , 2009. Inversion of GPS data for slip rates and locking depths of the Haiyuan fault. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 31(5): 516—525. (in Chinese) 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康等, 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 66—73Deng Q. D. , Zhang P. Z. , Ran Y. K. , et al. , 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 66—73. (in Chinese) 邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平等, 2007. 中国活动构造图. 北京: 地震出版社.Deng Q. D. , Ran Y. K. , Yang X. P. , et al. , 2007. Map of active tectonics in China. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) 邓起东, 闻学泽, 2008. 活动构造研究——历史、进展与建议. 地震地质, 30(1): 1—30Deng Q. D. , Wen X. Z. , 2008. A review on the research of active tectonics—history, progress and suggestions. Seismology and Geology, 30(1): 1—30. (in Chinese) 国家地震局震害防御司, 1995. 中国历史强震目录: 公元前23世纪—公元1911年. 北京: 地震出版社, 1—514. 韩新民, 毛玉平, 1993. 石屏——建水断裂带未来三十年内七级以上大地震危险性分析. 地震研究, 16(1): 52—59Han X. M. , Mao Y. P. , 1993. Seismic risk analysis to Shiping-Jianshui Fault Zone in the next 30 years. Journal of Seismological Research, 16(1): 52—59. (in Chinese) 韩竹军, 董绍鹏, 毛泽斌等, 2017. 小江断裂带南段全新世活动的地质地貌证据与滑动速率. 地震地质, 39(1): 1—19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.01.001Han Z. J. , Dong S. P. , Mao Z. B. , et al, 2017. The Holocene activity and strike-slip rate of the southern segment of Xiaojiang Fault in the southeastern Yunnan region, China. Seismology and Geology, 39(1): 1—19. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.01.001 何宏林, 李玶, 方仲景, 1992. 滇东南楔形构造区发震构造背景探讨. 地震地质, 14(3): 217—226He H. L. , Li P. , Fang Z. J. , 1992. Analysis of seismogenic conditions in the wedge tectonic region of southeast Yunnan Province. Seismology and Geology, 14(3): 217—226. (in Chinese) 何宏林, 方仲景, 李玶, 1993. 小江断裂带西支断裂南段新活动初探. 地震研究, 16(3): 291—298He H. L. , Fang Z. J. , Li P. , 1993. A preliminary approach to the fault activity of southern segment on Xiaojiang West Branch Fault. Journal of Seismological Research, 16(3): 291—298. (in Chinese) 何宏林, 池田安隆, 宋方敏, 等, 2002. 小江断裂带第四纪晚期左旋走滑速率及其构造意义. 地震地质, 24(1): 14—26He H. L. , Ikeda Y. , Song F. M. , et al. , 2002. Late Quaternary slip rate of the Xiaojiang Fault and its implication. Seismology and Geology, 24(1): 14—26. (in Chinese) 何宏林, 池田安隆, 何玉林等, 2008. 新生的大凉山断裂带——鲜水河-小江断裂系中段的裁弯取直. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(5): 564—574.He H. L. , Ikeda Y. , He Y. L. , et al. , 2008. Newly-generated Daliangshan fault zone — Shortcutting on the central section of Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault system. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1248—1258. 胡萌萌, 吴中海, 黄小龙等, 2020. 云南1588年通海-曲江7.0级地震的发震断层厘定及小江断裂带南端的未来强震危险性问题. 地质学报, 94(10): 3090—3105 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.020Hu M. M. , Wu Z. H. , Huang X. L. , et al. , 2020. Definition of seismogenic fault for the 1588 Tonghai-Qujiang M7.0 earthquake in the Yunnan Province and future strong earthquake risk at the southern end of Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(10): 3090—3105. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.020 胡萌萌, 吴中海, 李家存等, 2023. 小江断裂带巧家段晚第四纪走滑速率研究. 地质学报, 97(1): 16—29Hu M. M. , Wu Z. H. , Li J. C. , et al. , 2023. The Late Quaternary strike-slip rate of the Qiaojia segment of the Xiaojiang fault zone. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(1): 16—29. (in Chinese) 呼楠, 韩竹军, 2013. 滇东南弧形构造带现今活动性质的地震学研究. 地震地质, 35(1): 1—21Hu N. , Han Z. J. , 2013. Seismological study on behaviors of present-day movement of arcuate tectonic belt in southeast Yunnan. Seismology and Geology, 35(1): 1—21. (in Chinese) 黄学猛, 田坤, 杜义等, 2015. 玉树巴塘断裂晚第四纪滑动速率及其构造意义. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 51(1): 65—78Huang X. M. , Tian K. , Du Y. , et al, 2015. Late Quaternary slip rate of the Yushu Batang fault and its tectonic significance. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 51(1): 65—78. (in Chinese) 阚荣举, 张四昌, 晏凤桐等, 1977. 我国西南地区现代构造应力场与现代构造活动特征的探讨. 地球物理学报, 20(2): 96—109Kan R. J. , Zhang S. C, Yan F. T. , et al. , 1977. Present tectonic stress field and its relation to the characteristics of recent tectonic activity in southwestern China. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 20(2): 96—109. (in Chinese) 李凯, 李家存, 马晓雪等, 2020. 多源遥感影像在活动断裂研究中的应用——以小江断裂带为例. 城市地质, 15(3): 342—350Li K. , Li J. C. , Ma X. X. , et al. , 2020. The application of multi-source remote sensing image in the study of active faults - Taking Xiaojiang Fault Zone as an example. Urban Geology, 15(3): 342—350. (in Chinese) 李玶, 汪良谋, 1975. 云南川西地区地震地质基本特征的探讨. 地质科学, 10(4): 308—326Li P. , Wang L. M. , 1975. Exploration of the seismo-geological features of the Yunnan-West Sichuan region. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 10(4): 308—326. (in Chinese) 李玶, 1993. 鲜水河-小江断裂带. 北京: 地震出版社. 李西, 2015. 川滇地块云南地区不同发育阶段边界断裂破裂特征研究. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Li X. , 2015. Study on boundary fault rupture characterics of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block at different development stages in Yunnan province. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 李煜航, 郝明, 季灵运等, 2014. 青藏高原东缘中南部主要活动断裂滑动速率及其地震矩亏损. 地球物理学报, 57(4): 1062—1078Li Y. H. , Hao M. , Ji L. Y. , et al. , 2014. Fault slip rate and seismic moment deficit on major active faults in mid and South part of the eastern margin of Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(4): 1062—1078. (in Chinese) 毛燕, 刘自凤, 叶建庆等, 2016. 小江断裂带强震危险性分析. 地震研究, 39(2): 213—217Mao Y. , Liu Z. F. , Ye J. Q. , et al. , 2016. Analysis on strong earthquake risk of Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Journal of Seismological Research, 39(2): 213—217. (in Chinese) 毛泽斌, 2017. 小江断裂带南段晚第四纪活动性研究. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).Mao Z. B. , 2017. The activity of the south segment of Xiaojiang fault in Late Quaternary. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Beijing). (in Chinese). 孟昭彤, 刘静伟, 谢卓娟等, 2021. b值的时空分布特征与地震危险性的关联分析. 地球物理学进展, 36(1): 30—38Meng Z. T. , Liu J. W. , Xie Z. J. , et al. , 2021. Analysis of the correlation between the temporal-spatial distribution of b-value and seismic hazard: a review. Progress in Geophysics, 36(1): 30—38. (in Chinese) 钱晓东, 秦嘉政, 2008. 小江断裂带及周边地区强震危险性分析. 地震研究, 31(4): 354—361Qian X. D. , Qin J. Z. , 2008. Strong earthquake risk analysis of Xiaojiang Fault Zone and surrounding areas. Journal of Seismological Research, 31(4): 354—361. (in Chinese) 冉勇康, 王虎, 李彦宝等, 2012. 中国大陆古地震研究的关键技术与案例解析(1)——走滑活动断裂的探槽地点、布设与事件识别标志. 地震地质, 34(2): 197—210Ran Y. K. , Wang H. , Li Y. B. , et al. , 2012. Key techniques and several cases analysis in paleoseismic studies in mainland China (1): trenching sites, layouts and paleoseismic indicators on active strike-slip faults. Seismology and Geology, 34(2): 197—210. (in Chinese) 沈军, 汪一鹏, 宋方敏等, 1997. 小江断裂带中段的北东向断裂与断块结构. 地震地质, 19(3): 203—210Shen J. , Wang Y. P. , Song F. M. , et al. , 1997. The ne-trending faults and block structure in the central section of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Seismology and Geology, 19(3): 203—210. (in Chinese) 沈军, 汪一鹏, 宋方敏等, 1998. 相对蠕滑速率与特征地震复发间隔的估计——以小江断裂带为例. 地震地质, 20(4): 328—331Shen J. , Wang Y. P. , Song F. M. , et al. , 1998. Relative creep rate and characteristic earthquake recurrence interval-Example from the Xiaojiang Fault Zone in Yunnan, China. Seismology and Geology, 20(4): 328—331. (in Chinese) 宋方敏, 汪一鹏, 俞维贤等, 1998. 小江活动断裂带. 北京: 地震出版社, 1—237. 宋剑, 杨少敏, 王伟等, 2016. 安宁河-则木河-小江断裂带闭锁特征研究. 大地测量与地球动力学, 36(6): 490—494Song J. , Yang S. M. , Wang W. , et al. , 2016. Study on the locking characteristics of Anninghe-Zemuhe-Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 36(6): 490—494. (in Chinese) 孙云梅, 2018. 基于GPS观测资料的红河断裂带及周边地区地壳形变特征研究. 昆明: 云南师范大学.Sun Y. M. , 2018. Crustal deformation characteristics in the Red River fault zone andsurrounding areas based on GPS observations. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University. (in Chinese) 滕德贞, 1978. 云南省小江断裂带中段地震地质基本特征. 地震研究, (2): 55—64. 王虎, 冉勇康, 陈立春等, 2018. 安宁河断裂带南段滑动速率估计. 地震地质, 40(5): 967—979Wang H. , Ran Y. K. , Chen L. C. , et al. , 2018. Determination of slip rate on the southern segment of the Anninghe Fault. Seismology and Geology, 40(5): 967—979. (in Chinese) 王伶俐, 王青华, 张勇等, 2016. 基于GPS的云南地区主要断裂带现今运动特征分析. 防灾科技学院学报, 18(1): 1—8Wang L. L. , Wang Q. H. , Zhang Y. , et al. , 2016. Analysis of current activity of main Faults in Yunnan region based on GPS. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 18(1): 1—8. (in Chinese) 王洋, 张波, 侯建军等, 2015. 曲江断裂晚第四纪活动特征及滑动速率分析. 地震地质, 37(4): 1177—1192Wang Y. , Zhang B. , Hou J. J. , et al. , 2015. Late Quaternary activity of the Qujiang Fault and analysis of the slip rate. Seismology and Geology, 37(4): 1177—1192. (in Chinese) 王阎昭, 王恩宁, 沈正康等, 2008. 基于GPS资料约束反演川滇地区主要断裂现今活动速率. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(5): 582—597.Wang Y. Z. , Wang E. N. , Shen Z. K. , et al. , 2008. GPS-constrained inversion of present-day slip rates along major faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1267—1283. 魏文薪, 江在森, 武艳强等, 2012. 小江断裂带的运动及应变积累特征研究. 大地测量与地球动力学, 32(2): 11—15Wei W. X. , Jiang Z. S. , Wu Y. Q. , et al. , 2012. Study on Motion characteristics and strain accumulation of Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 32(2): 11—15. (in Chinese) 闻学泽, 1993. 小江断裂带的破裂分段与地震潜势概率估计. 地震学报, 15(3): 322—330. 闻学泽, 杜方, 龙锋等, 2011. 小江和曲江-石屏两断裂系统的构造动力学与强震序列的关联性. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(5): 713—724.Wen X. Z. , Du F. , Long F. , et al. , 2011. Tectonic dynamics and correlation of major earthquake sequences of the Xiaojiang and Qujiang-Shiping fault systems, Yunnan, China. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(10): 1563—1575. 闻学泽, 杜方, 易桂喜等, 2013. 川滇交界东段昭通、莲峰断裂带的地震危险背景. 地球物理学报, 56(10): 3361—3372Wen X. Z. , Du F. , Yi G. X. , et al. , 2013. Earthquake potential of the Zhaotong and Lianfeng fault zones of the eastern Sichuan-Yunnan border region. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(10): 3361—3372. (in Chinese) 吴中海, 周春景, 冯卉等, 2014. 青海玉树地区活动断裂与地震. 地质通报, 33(4): 419—469Wu Z. H. , Zhou C. J. , Feng H. , et al. , 2014. Active faults and earthquake around Yushu in eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(4): 419—469. (in Chinese) 吴中海, 龙长兴, 范桃园等, 2015. 青藏高原东南缘弧形旋扭活动构造体系及其动力学特征与机制. 地质通报, 34(1): 1—31Wu Z. H. , Long C. X. , Fan T. Y. , et al. , 2015. The arc rotational-shear active tectonic system on the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic characteristics and mechanism. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 1—31. (in Chinese) 谢张迪, 2019. 鲜水河-小江断裂系和红河断裂带交切关系的地震学研究. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Xie Z. D. , 2019. Seismological study on the relationship between the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault system and the Honghe fault zone. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 郑荣章等, 2003. 川滇地区活动块体最新构造变动样式及其动力来源. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 151—162.Xu X. W. , Wen X. Z. , Zheng R. Z. , et al. , 2003. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 210—226. 徐锡伟, 韩竹军, 杨晓平等, 2016. 中国及邻近地区地震构造图. 北京: 地震出版社. 易桂喜, 闻学泽, 范军等, 2004. 由地震活动参数分析安宁河-则木河断裂带的现今活动习性及地震危险性. 地震学报, 26(3): 294—303Yi G. X. , Wen X. Z. , Fan J. , et al. , 2004. Assessing current faulting behaviors and seismic risk of the Anninghe-Zemuhe fault zone from seismicity parameters. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(3): 294—303. (in Chinese) 易桂喜, 闻学泽, 2007. 多地震活动性参数在断裂带现今活动习性与地震危险性评价中的应用与问题. 地震地质, 29(2): 254—271Yi G. X. , Wen X. Z. , 2007. The Application and limitation of multiple seismicity parameters to assessing current Faulting behavior and seismic potential of active fault zones. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 254—271. (in Chinese) 易桂喜, 闻学泽, 苏有锦, 2008. 川滇活动地块东边界强震危险性研究. 地球物理学报, 51(6): 1719—1725Yi G. X. , Wen X. Z. , Su Y. J. , 2008. Study on the potential strong-earthquake risk for the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan active faulted-block, China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(6): 1719—1725. (in Chinese) 俞维贤, 汪一鹏, 王彬等, 2004. 云南小江西支断裂古地震及现今地震危险性研究. 地震研究, 27(S1): 29—32Yu W. X. , Wang Y. P. , Wang B. , et al. , 2004. Palaeo-earthquake and the current risk study on the west branch of the Xiaojiang Fault in Yunnan. Journal of Seismological Research, 27(S1): 29—32. (in Chinese) 云南省地震局, 1988. 云南省地震资料汇编. 北京: 地震出版社. 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民等, 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12—20.Zhang P. Z. , Deng Q. D. , Zhang G. M. , et al. , 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 13—24. 张培震, 2008. 青藏高原东缘川西地区的现今构造变形、应变分配与深部动力过程. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(9): 1041—1056.Zhang P. Z. , 2008. Present-day crustal movement and tectonic deformation in China continent. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 45(10): 865—874. 张赛鹏, 2019. GPS约束下川滇地区断层活动性研究. 武汉: 中国地震局地震研究所.Zhang S. P. , 2019. Research on block fault activity in Sichuan-Yunnan region under the constraints of GPS results. Wuhan: Institute of Seismology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 张世民, 谢富仁, 2001. 鲜水河—小江断裂带7级以上强震构造区的划分及其构造地貌特征. 地震学报, 23(1): 36—44Zhang S. M. , Xie F. R. , 2001. Seismo tectonic divisions of strong earthquakes (MS≥7.0) and their tectonic geomorphology along Xianshuihe Xiaojiang fault zone. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 23(1): 36—44. (in Chinese) 张伟恒, 李文巧, 田勤俭等, 2018. 基于牛栏江宽谷面的变形讨论莲峰、昭通断裂带第四纪活动特征. 地震, 38(4): 22—36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2018.04.003Zhang W. H. , Li W. Q. , Tian Q. J. , et al. , 2018. Quaternary activity characteristics of the Lianfeng and Zhaotong fault zones based on deformation of the broad valley surfaces of the Niulan River. Earthquake, 38(4): 22—36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2018.04.003 张效亮, 2009. 利用GPS观测数据评估川滇南部地区活动断裂地震危险性. 北京: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所.Zhang X. L. , 2009. Seismic hazard assessment of the active faults in Southern Sichuan-Yunnan region using GPS observations. Beijing: Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 赵静, 江在森, 牛安福等, 2015. 川滇菱形块体东边界断层闭锁程度与滑动亏损动态特征研究. 地球物理学报, 58(3): 872—885Zhao J. , Jiang Z. S. , Niu A. F. , et al. , 2015. Study on dynamic characteristics of fault locking and fault slip deficit in the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan rhombic block. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(3): 872—885. (in Chinese) 郑立龙, 孔凡全, 黄赞慧等, 2019. 小江断裂带中段西支沧溪-清水海断层更新世活动性. 科学技术与工程, 19(14): 39—45Zheng L. L. , Kong F. Q. , Huang Z. H. , et al. , 2019. The Pleistocene activity of Cangxi-Qingshuihai Fault of the West branch in the middle segment of Xiaojiang Fault. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(14): 39—45. (in Chinese) 中国地震局震害防御司, 1999. 中国近代地震目录: 公元1912年~1990年, MS≥4.7. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社. 中国地震学会地震地质专业委员会, 1994. 中国活动断层研究. 北京: 地震出版社. 朱成男, 滕德贞, 段家乐等, 1983. 云南小江断裂带水平错距的测定. 云南地质, 2(4): 319—326. 朱爽, 杨国华, 刘辛中等, 2017. 川滇地区近期地壳变形动态特征研究. 武汉大学学报•信息科学版, 42(12): 1765—1772Zhu S. , Yang G. H. , Liu X. Z. , et al. , 2017. The deformation characteristics of Sichuan-Yunnan region in recent period. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 42(12): 1765—1772. (in Chinese) Allen C. R. , Luo Z. L. , Qian H. , et al. , 1991. Field study of a highly active fault zone: the Xianshuihe fault of southwestern China. GSA Bulletin, 103(9): 1178—1199. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1991)103<1178:FSOAHA>2.3.CO;2 Burchfiel B. C. , Wang E. , 2003. Northwest-trending, middle Cenozoic, left-lateral faults in southern Yunnan, China, and their tectonic significance. Journal of Structural Geology, 25(5): 781—792. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00065-2 Copley A. , 2008. Kinematics and dynamics of the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Geophysical Journal International, 174(3): 1081—1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03853.x England P. , Molnar P. , 1990. Right-lateral shear and rotation as the explanation for strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet. Nature, 344(6262): 140—142. doi: 10.1038/344140a0 England P. , Molnar P. , 2005. Late Quaternary to decadal velocity fields in Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110(B12): B12401. Guo P. , Han Z. J. , Dong S. P. , et al. , 2021. Latest Quaternary active faulting and paleoearthquakes on the southern segment of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, SE Tibetan Plateau. Lithosphere, 2021(1): 7866379. doi: 10.2113/2021/7866379 He H. L. , Song F. M. , Li C. Y. , 1999. Topographic survey of micro faulted landform and estimation of strike slip rate for the Zemuhe Fault, Sichuan province. Seismology and Geology, 21(4): 361—369. Hu Y. X. , Deng R. S. , 1988. A palaeoseismic profile at Dongguaying village, Yangzhong Lake, Yunnan province. Journal of Seismological Research, 11(3): 309—324. Lai K. Y., Chen Y. G., Lâm D. Đ., 2012. Pliocene-to-present morphotectonics of the Dien Bien Phu fault in Northwest Vietnam. Geomorphology, 173—174: 52—68. Li X. , Ran Y. K. , Chen L. C. , et al. , 2015. Late quaternary large earthquakes on the western Branch of the Xiaojiang Fault and their Tectonic Implications. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 89(5): 1516—1530. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12561 Molnar P. , Lyon-Caent H. , 1989. Fault plane solutions of earthquakes and active tectonics of the Tibetan Plateau and its margins. Geophysical Journal International, 99(1): 123—153. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1989.tb02020.x Ren Z. K. , Lin A. M. , Rao G. , 2010. Late Pleistocene–Holocene activity of the Zemuhe Fault on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics, 495(3—4): 324—336. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.09.039 Royden L. H. , Burchfiel B. C. , King R. W. , et al. , 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science, 276(5313): 788—790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788 Schoenbohm L. M. , Burchfiel B. C. , Chen L. Z. , 2006. Propagation of surface uplift, lower crustal flow, and Cenozoic tectonics of the southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Geology, 34(10): 813—816. doi: 10.1130/G22679.1 Shen J. , Wang Y. P. , Song F. M. , 2003. Characteristics of the active Xiaojiang fault zone in Yunnan, China: a slip boundary for the southeastward escaping Sichuan-Yunnan Block of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21(10): 1085—1096. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00185-2 Shen Z. K. , Lü J. N. , Wang M. , et al. , 2005. Contemporary crustal deformation around the Southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110(B11): B11409. Wang E., Burchfiel B. C., Royden L. H., et al., 1998. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red River, and Dali fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China. Boulder: Geological Society of America, 108. Wang Y. , Zhang B. , Hou J. J. , et al. , 2014. Structure and tectonic geomorphology of the Qujiang fault at the intersection of the Ailao Shan-Red River fault and the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault system, China. Tectonophysics, 634: 156—170. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.07.031 Wen X. Z. , Ma S. L. , Xu X. W. , et al. , 2008. Historical pattern and behavior of earthquake ruptures along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan faulted-block, southwestern China. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 168(1—2): 16—36. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2008.04.013 Wiemer S., Wyss M., 1997. Mapping the frequency-magnitude distribution in asperities: An improved technique to calculate recurrence times? Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B7): 15115—15128. Xu X. W. , Deng Q. D. , 1996. Nonlinear characteristics of paleoseismicity in China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 101(B3): 6209—6231. doi: 10.1029/95JB01238 Zhang P. Z. , Shen Z. K. , Wang M. , et al. , 2004. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology, 32(9): 809—812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1 Zhang P. Z. , 2013. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics, 584: 7—22. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.02.021 -




 下载:
下载: