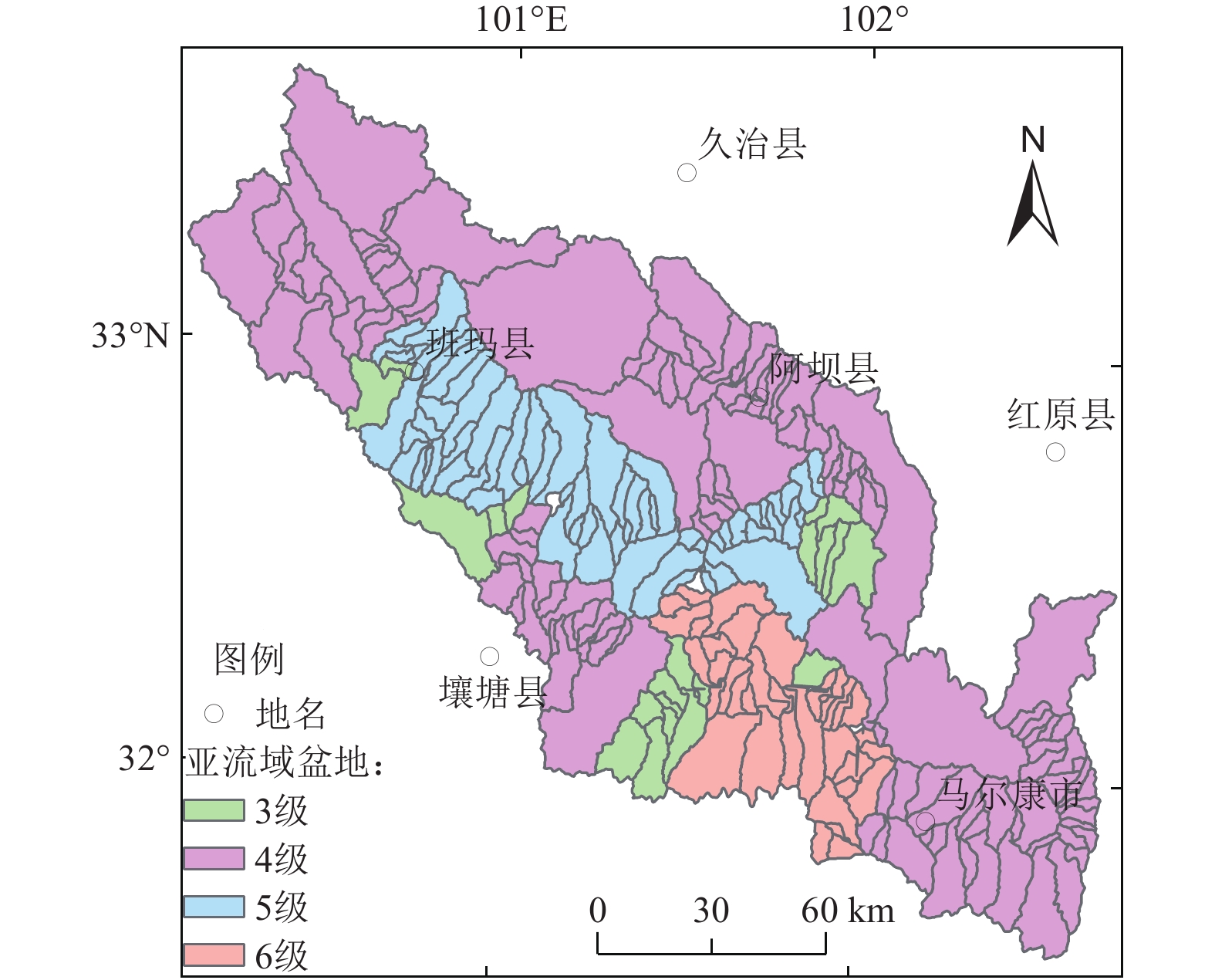
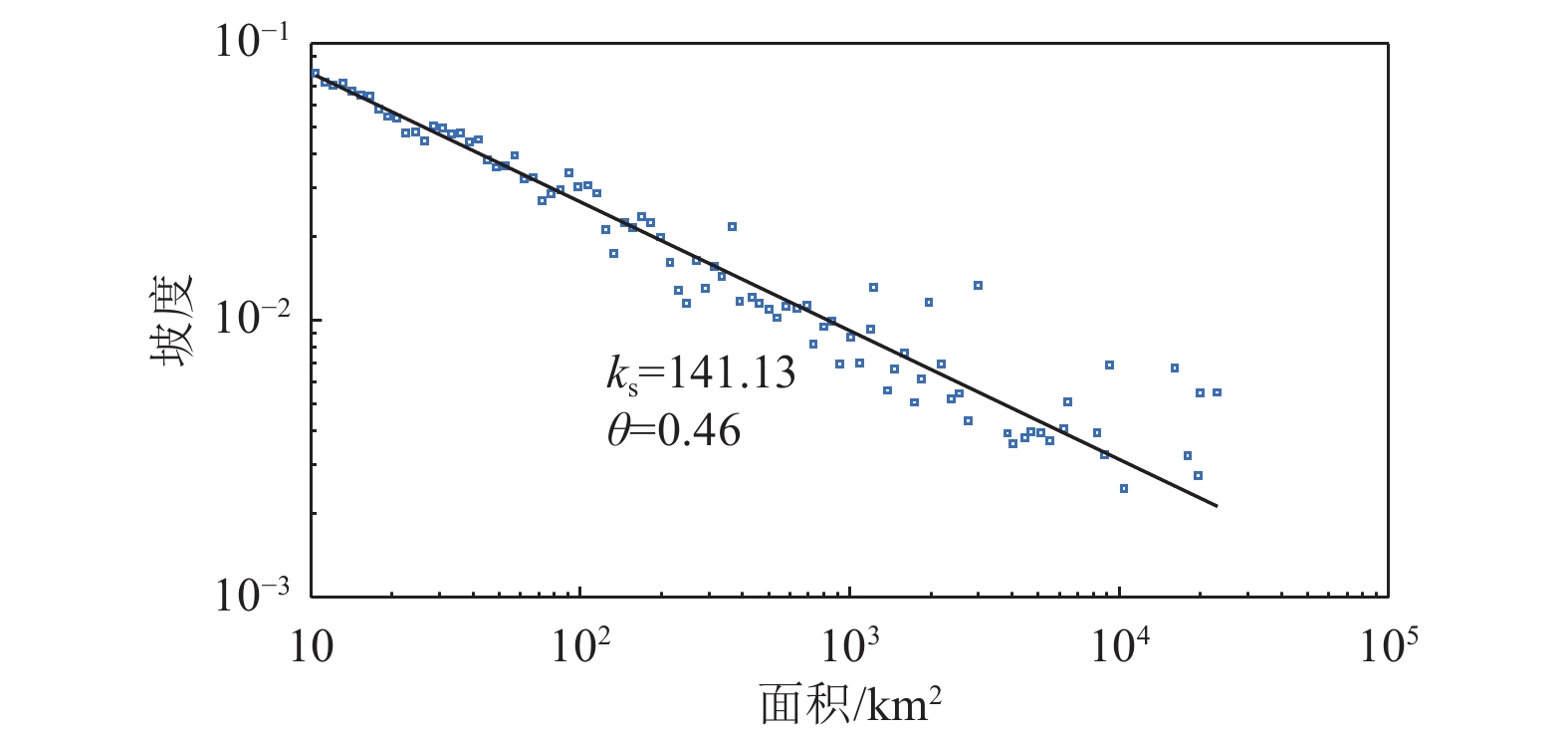
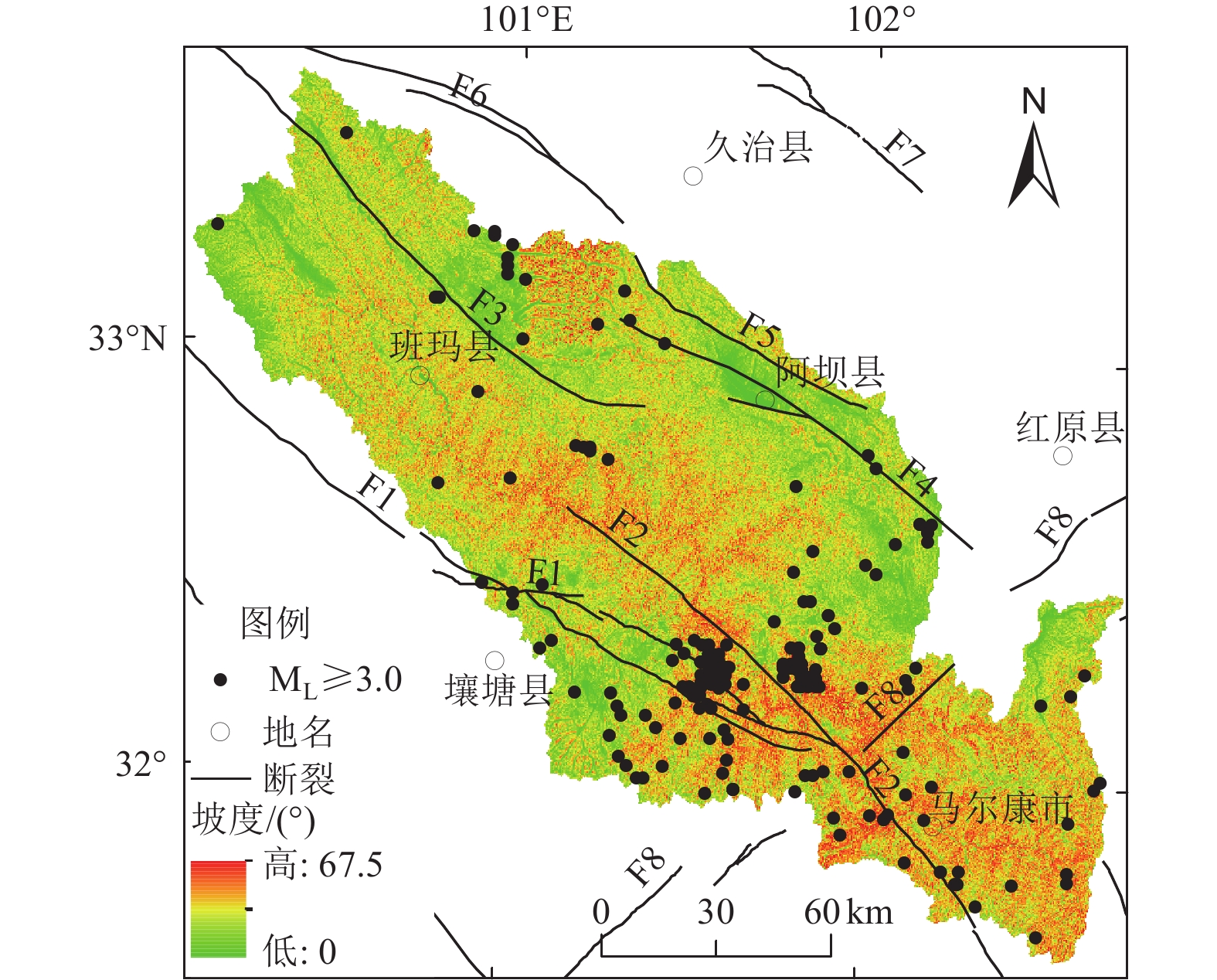
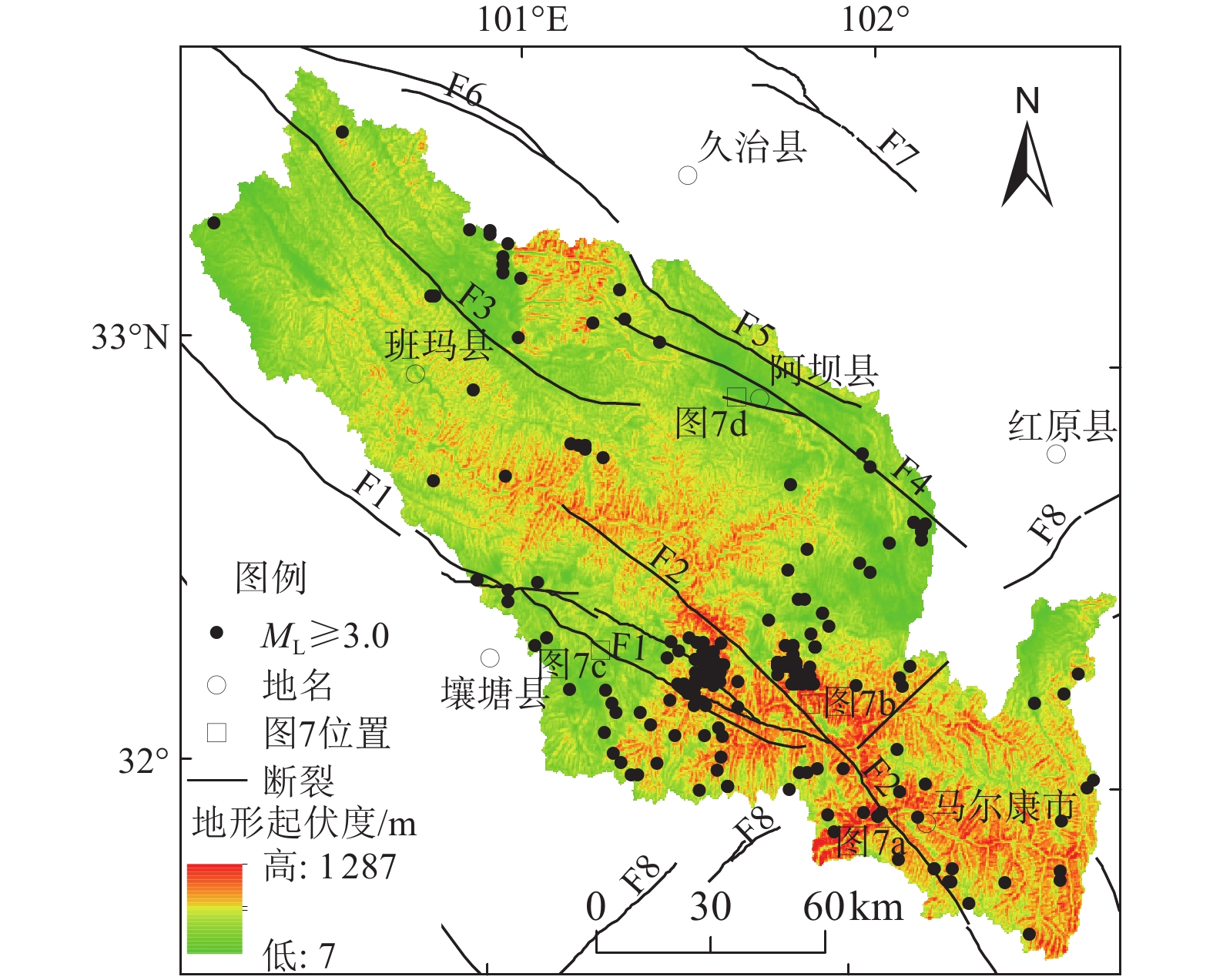
|
常直杨, 王建, 白世彪等, 2015. 面积高程积分值计算方法的比较. 干旱区资源与环境, 29(3): 171—175Chang Z. Y. , Wang J. , Bai S. B. , et al. , 2015. Comparison of hypsometric integral methods. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 29(3): 171—175. (in Chinese)
|
|
陈长云, 任金卫, 孟国杰等, 2013. 巴颜喀拉块体东部活动块体的划分、形变特征及构造意义. 地球物理学报, 56(12): 4125—4141Chen C. Y. , Ren J. W. , Meng G. J. , et al. , 2013. Division, deformation and tectonic implication of active blocks in the eastern segment of Bayan Har block. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(12): 4125—4141. (in Chinese)
|
|
陈彦杰, 郑光佑, 宋国城, 2005. 面积尺度与空间分布对流域面积高度积分及其地质意义的影响. 地理学报, (39): 53—69Chen Y. J. , Zheng G. Y. , Song G. C. , 2005. Influence of area and space dependence for hypsometric integral and its geological implications. Journal of Geographical Science, (39): 53—69. (in Chinese)
|
|
高青, 李奋生, 邵崇建, 2018. 汶川地震驱动的剥蚀作用及对龙门山地貌演化的影响. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 45(3): 386—392Gao Q. , Li F. S. , Shao C. J. , 2018. The erosion driven by Wenchuan earthquake and its impact on the geomorphic evolution of Longmenshan, Sichuan, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 45(3): 386—392. (in Chinese)
|
|
韩海辉, 高婷, 易欢等, 2012. 基于变点分析法提取地势起伏度——以青藏高原为例. 地理科学, 32(1): 101—104Han H. H. , Gao T. , Yi H. , et al. , 2012. Extraction of relief amplitude based on Change Point Method——A case study on the Tibetan Plateau. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 32(1): 101—104. (in Chinese)
|
|
何建军, 任俊杰, 丁锐等, 2016. 青藏高原东缘龙日坝断裂带南段晚第四纪活动及其构造意义. 震灾防御技术, 11(4): 707—721He J. J. , Ren J. J. , Ding R. , et al. , 2016. Late quaternary activity of the Southern Segment of Longriba fault zone in Eastern Tibet and its tectonic implications. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 11(4): 707—721. (in Chinese)
|
|
洪艳, 赵银兵, 王运生等, 2019. 利用面积高程积分方法研究龙门山断裂带地貌隆升特征. 科学技术与工程, 19(30): 43—51Hong Y. , Zhao Y. B. , Wang Y. S. , et al. , 2019. Study on the geomorphic uplift characteristics of the Longmenshan fault zone using hypsometric integral method. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(30): 43—51. (in Chinese)
|
|
贾营营, 付碧宏, 王岩等, 2010. 青藏高原东缘龙门山断裂带晚新生代构造地貌生长及水系响应. 第四纪研究, 30(4): 825—836Jia Y. Y. , Fu B. H. , Wang Y. , et al. , 2010. Late Cenozoic tectono-geomorphic growth and drainage response in the Longmen Shan fault zone, east margin of Tibet. Quaternary Sciences, 30(4): 825—836. (in Chinese)
|
|
李奋生, 赵国华, 李勇等, 2015. 龙门山地区水系发育特征及其对青藏高原东缘隆升的指示. 地质论评, 61(2): 345—355Li F. S. , Zhao G. H. , Li Y. , et al. , 2015. The characteristics of drainage development in Longmen Mountains Area and its indication to the uplift of eastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Geological Review, 61(2): 345—355. (in Chinese)
|
|
李明, 张世民, 姜大伟等, 2019. 龙门山中北段流域地貌特征及其构造意义. 震灾防御技术, 14(3): 640—651Li M. , Zhang S. M. , Jiang D. W. , et al. , 2019. Geomorphic features and tectonic significance of the middle and North Section of Longmenshan. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(3): 640—651. (in Chinese)
|
|
李伟, 谢超, 程宏宾等, 2021. 利用水系方位角和GPS数据研究龙门山后山断裂运动模式. 四川地震, (2): 7—10Li W. , Xie C. , Cheng H. B. , et al. , 2021. Study on the fault movement model of the backmountain of Longmen Mountain based on the azimuth angle and GPS data. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (2): 7—10. (in Chinese)
|
|
李勇, 周荣军, 赵国华等, 2015. 汶川地震驱动的隆升、剥蚀作用与龙门山地貌生长——以映秀红椿沟为例. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 42(1): 5—17Li Y. , Zhou R. J. , Zhao G. H. , et al. , 2015. Uplift and erosion driven by Wenchuan earthquake and their effects on geomorphic growth of Longmen Mountains——A case study of Hongchun gully in Yingxiu, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 42(1): 5—17. (in Chinese).
|
|
梁明剑, 周荣军, 闫亮等, 2014. 青海达日断裂中段构造活动与地貌发育的响应关系探讨. 地震地质, 36(1): 28—38Liang M. J. , Zhou R. J. , Yan L. , et al. , 2014. The relationships between neotectonic activity of the middle segment of Dari Fault and its geomorphological response, Qinghai Province, China. Seismology and Geology, 36(1): 28—38. (in Chinese)
|
|
梁明剑, 杨耀, 杜方等, 2020. 青海达日断裂中段晚第四纪活动性与1947年M7¾地震地表破裂带再研究. 地震地质, 42(3): 703—714Liang M. J. , Yang Y. , Du F. , et al. , 2020. Late Quaternary activity of the central segment of the Dari Fault and restudy of the surface rupture zone of the 1974 M7¾ Dari earthquake, Qinghai Province. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 703—714. (in Chinese)
|
|
梁欧博, 任俊杰, 吕延武, 2018. 涪江流域河流地貌特征对虎牙断裂带活动性的响应. 地震地质, 40(1): 42—56Liang O. B. , Ren J. J. , Lü Y. W. , 2018. The response of fluvial geomorphologic characteristics of the Fujiang drainge basin to activity of the Huya fault zone. Seismology and Geology, 40(1): 42—56. (in Chinese)
|
|
刘静, 曾令森, 丁林等, 2009. 青藏高原东南缘构造地貌、活动构造和下地壳流动假说. 地质科学, 44(4): 1227—1255Liu J. , Zeng L. S. , Ding L. , et al. , 2009. Tectonic geomorphology, active tectonics and lower crustal channel flow hypothesis of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Geology, 44(4): 1227—1255. (in Chinese)
|
|
苏琦, 2015. 青藏高原东北缘典型流域地貌参数分析与构造变形探讨. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所.Su Q. , 2015. Study on typical drainage basins along northeastern Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic deformation. Lanzhou: China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology. (in Chinese)
|
|
孙东, 王道永, 吴德超等, 2010. 马尔康巴拉水电站近场区主要断裂活动性及对工程的影响. 工程地质学报, 18(6): 940—949Sun D. , Wang D. Y. , Wu D. C. , et al. , 2010. Activity and effect of main faults in near field of Bala Hydropower station in Maerkang. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(6): 940—949. (in Chinese)
|
|
熊仁伟, 任金卫, 张军龙等, 2010. 玛多—甘德断裂甘德段晚第四纪活动特征. 地震, 30(4): 65—73Xiong R. W. , Ren J. W. , Zhang J. L. , et al. , 2010. Late Quaternary active characteristics of the Gande Segment in the Maduo-Gande Fault zone. Earthquake, 30(4): 65—73. (in Chinese)
|
|
徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 陈桂华等, 2008. 巴颜喀拉地块东部龙日坝断裂带的发现及其大地构造意义. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(5): 529—542.Xu X. W. , Wen X. Z. , Chen G. H. , et al. , 2008. Discovery of the Longriba fault zone in eastern Bayan Har block, China and its tectonic implication. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1209—1223.
|
|
闫亮, 李勇, 赵国华等, 2018. 青藏高原东缘龙门山构造带晚第四纪构造隆升作用的河流地貌响应. 第四纪研究, 38(1): 232—246Yan L. , Li Y. , Zhao G. H. , et al. , 2018. The uplift process and the geomorphological features of the rivers system in the Longmen Shan since Late Quaternary. Quaternary Sciences, 38(1): 232—246. (in Chinese)
|
|
詹艳, 梁明剑, 孙翔宇等, 2021.2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震深部环境及发震构造模式. 地球物理学报, 64(7): 2232—2252Zhan Y. , Liang M. J. , Sun X. Y. , et al. , 2021. Deep structure and seismogenic pattern of the 2021.5. 22 Madoi (Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake.Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(7):2232—2252.(in Chinese)
|
|
张会平, 2006. 青藏高原东缘、东北缘典型地区晚新生代地貌过程研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.Zhang H. P. , 2006. Study on late Cenozoic geomorphic processes of typical regions along the eastern and northeastern Tibetan margins. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese)
|
|
张培震, 闻学泽, 徐锡伟等, 2009.2008年汶川8.0级特大地震孕育和发生的多单元组合模式. 科学通报, 54(7): 944—953 doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-7-944Zhang P. Z. , Wen X. Z. , Xu X. W. , et al. , 2009. Tectonic model of the great Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(7): 944—953. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-7-944
|
|
张岳桥, 杨农, 施炜等, 2008. 青藏高原东缘新构造及其对汶川地震的控制作用. 地质学报, 82(12): 1668—1678Zhang Y. Q. , Yang N. , Shi W. , et al. , 2008. Neotectonics of eastern Tibet and its control on the Wenchuan Earthquake. Acta Geologica sinica, 82(12): 1668—1678. (in Chinese)
|
|
郑立龙, 2015. 汶川地震后绵远河流域地表隆升与侵蚀过程研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.Zheng L. L. , 2015. The research of surface uplift and erosion process of Mianyuan river drainage basin after the Wenchuan Earthquake. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese)
|
|
周文英, 梁明剑, 左洪等, 2022. 濑溪河流域地貌对泸县MS6.0地震发震构造变形的响应及其指示作用. 地震学报, 44(2): 250—259Zhou W. Y. , Liang M. J. , Zuo H. , et al. , 2022. Response of the topography of Laixihe drainage to the structural deformation induced by MS6.0 Luxian earthquake and its indication. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 44(2): 250—259. (in Chinese)
|
|
Chen Y. C. , Sung Q. C. , Cheng K. Y. , 2003. Along-strike variations of morphotectonic features in the Western Foothills of Taiwan: tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis. Geomorphology, 56(1—2): 109—137. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(03)00059-X
|
|
Clark M. K. , Royden L. H. , 2000. Topographic ooze: building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow. Geology, 28(8): 703—706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
|
|
Fu B. H. , Shi P. L. , Guo H. D. , et al. , 2011. Surface deformation related to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, and mountain building of the Longmen Shan, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 805—824. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.011
|
|
Howard A. D. , Kerby G. , 1983. Channel changes in Badlands. GSA Bulletin, 94(6): 739—752. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1983)94<739:CCIB>2.0.CO;2
|
|
Hubbard J. , Shaw J. H. , 2009. Uplift of the Longmen Shan and Tibetan Plateau, and the 2008 Wenchuan (M=7.9) earthquake. Nature, 458(7235): 194—197. doi: 10.1038/nature07837
|
|
Kirby E. , Whipple K. X. , Tang W. Q. , et al. , 2003. Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Inferences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B4): 2217.
|
|
Kirby E., Ouimet W., 2011. Tectonic geomorphology along the eastern margin of Tibet: Insights into the pattern and processes of active deformation adjacent to the Sichuan Basin. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 353(1): 165—188.
|
|
Liu-Zeng J., Wen L., Oskin M., et al., 2011. Focused modern denudation of the Longmen Shan margin, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(11): Q11007.
|
|
Meng Q. R. , Hu J. M. , Wang E. , et al. , 2006. Late Cenozoic denudation by large-magnitude landslides in the eastern edge of Tibetan Plateau. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 243(1—2): 252—267. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.12.008
|
|
Parker R. N. , Densmore A. L. , Rosser N. J. , et al. , 2011. Mass wasting triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake is greater than orogenic growth. Nature Geoscience, 4(7): 449—452. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1154
|
|
Pike R. J. , Wilson S. E. , 1971. Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral, and geomorphic area-altitude analysis. GSA Bulletin, 82(4): 1079—1084. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1971)82[1079:ERHIAG]2.0.CO;2
|
|
Ren J. J. , Xu X. W. , Yeats R. S. , et al. , 2013. Latest Quaternary paleoseismology and slip rates of the Longriba fault zone, eastern Tibet: Implications for fault behavior and strain partitioning. Tectonics, 32(2): 216—238. doi: 10.1002/tect.20029
|
|
Royden L. H. , Burchfiel B. C. , King R. W. , et al. , 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in Eastern Tibet. Science, 276(5313): 788—790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788
|
|
Schwanghart W. , Scherler D. , 2014. TopoToolbox 2 – MATLAB-based software for topographic analysis and modeling in Earth surface sciences. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2(1): 1—7. doi: 10.5194/esurf-2-1-2014
|
|
Snyder N. P. , Whipple K. X. , Tucker G. E. , et al. , 2000. Landscape response to tectonic forcing: Digital elevation model analysis of stream profiles in the Mendocino triple junction region, northern California. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112(8): 1250—1263. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1250:LRTTFD>2.0.CO;2
|
|
Strahler A. N. , 1952. Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. GSA Bulletin, 63(11): 1117—1142. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1952)63[1117:HAAOET]2.0.CO;2
|
|
Wang Y. Z. , Zhang H. P. , Zheng D. W. , et al. , 2017. Coupling slope–area analysis, integral approach and statistic tests to steady-state bedrock river profile analysis. Earth Surface Dynamics, 5(1): 145—160 doi: 10.5194/esurf-5-145-2017
|
|
Whipple K., Wobus C. W., Crosby B. T., et al., 2007. New tools for quantitative geomorphology: extraction and interpretation of stream profiles from digital topographic data [EB/OL]. (2007-01-01)[2023-11-10].https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Cameron-Wobus/publication/268056101_New_Tools_for_Quantitative_Geomorphology_Extraction_and_Interpretation_of_Stream_Profiles_from_Digital_Topographic_Data/links/54f9bf970cf29a9fbd7c51d4/New-Tools-for-Quantitative-Geomorphology-Extraction-and-Interpretation-of-Stream-Profiles-from-Digital-Topographic-Data.pdf.
|




 下载:
下载: