Research on Building Data Spatialization Based on Feature Partition
-
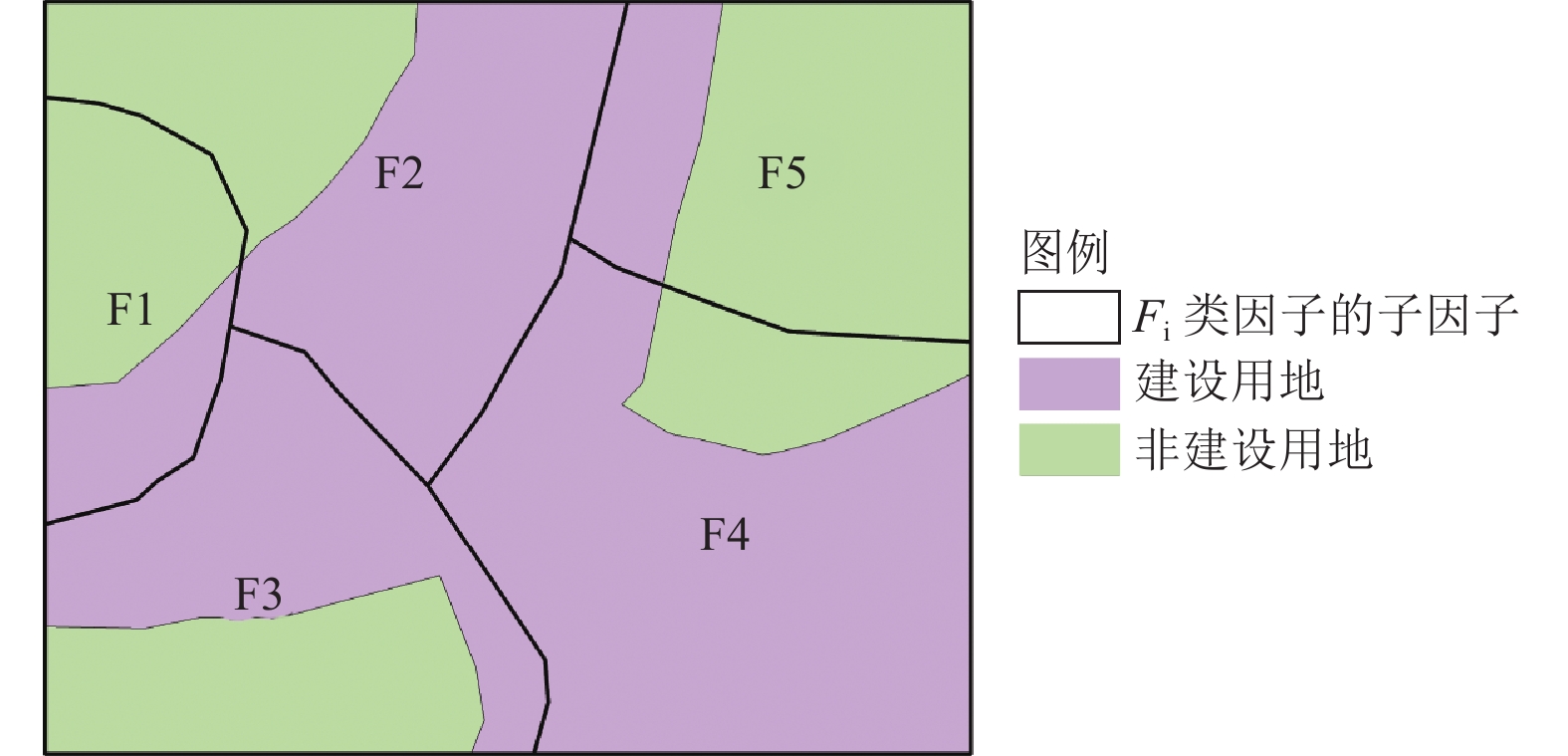
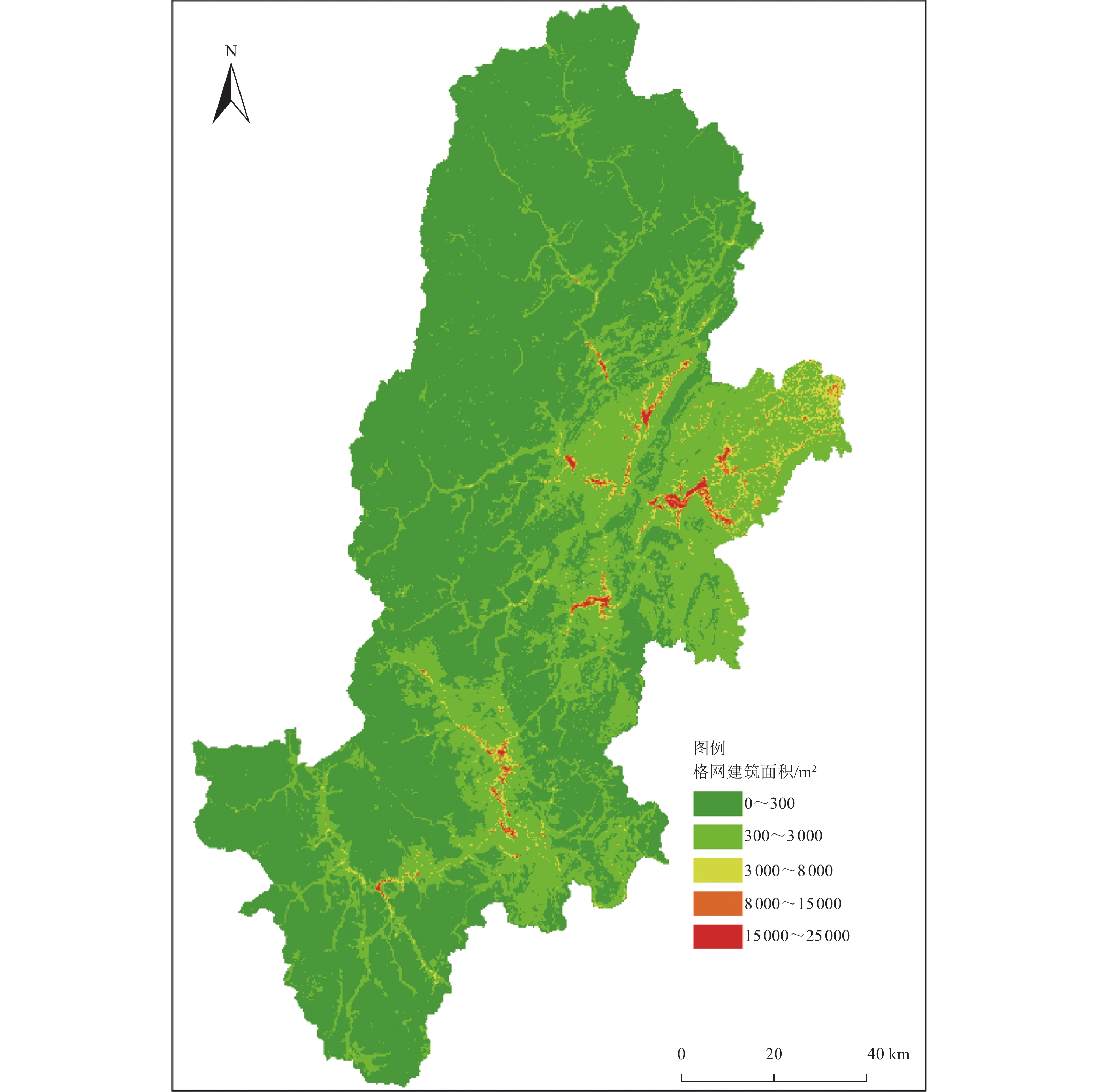
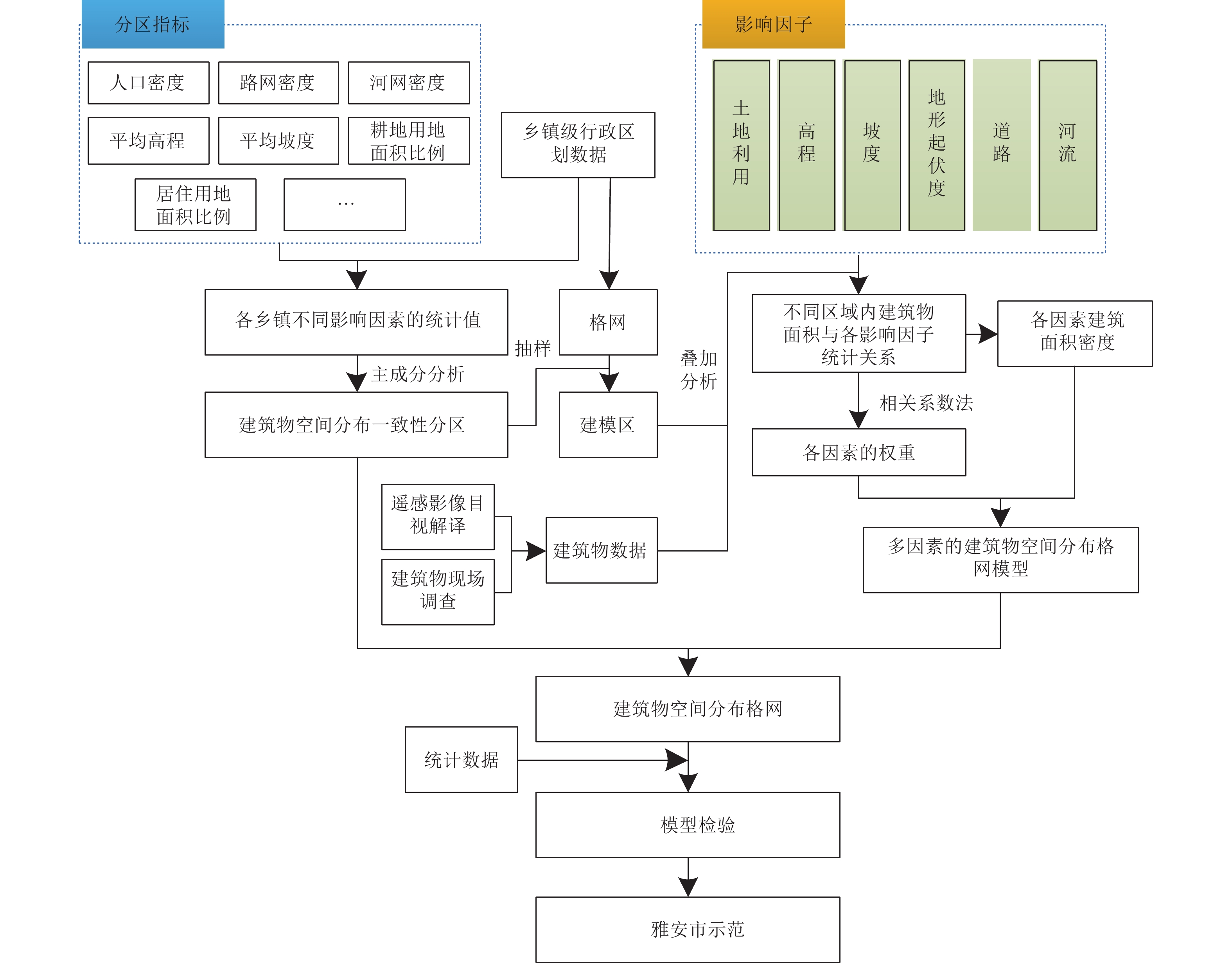
摘要: 针对现有基于多因素的建筑空间分布格网化模型未考虑建筑物空间分布异质性的问题,提出基于特征分区的建筑物数据空间化模型。以四川省雅安市为例,利用影响建筑物空间分布的因子进行建筑物特征一致性分区,选取土地利用、高程、坡度、坡向、河流距离、道路距离、地形起伏度7类影响因子,基于分区结果分别研究建筑物空间分布与各影响因子之间的关系,分区构建基于多因素的建筑物数据空间化模型,生成雅安市300 m格网建筑物空间分布数据。研究结果表明,分区构建的建筑物空间分布格网化模型有效提高了建筑物空间分布数据的精确度与准确性。Abstract: Aiming at the problem that the existed models do not consider the heterogeneity of building in spatial distribution, a gridding method of building data based on feature partition is proposed in this paper. Taking Ya'an City, Sichuan Province, as an example, the factors affecting the spatial distribution of buildings are used to partition the consistency of building characteristics. Seven influencing factors including land use, elevation, slope, aspect, river distance, road distance and topographic relief are selected. Based on the zoning results, the relationship between the spatial distribution of buildings and various influencing factors is studied respectively. The spatial gridding model of buildings based on multi factors is constructed, and the spatial distribution data of 300 m grid buildings in Ya'an City are generated. The results show that the gridding model of building spatial distribution constructed by zoning effectively improves the precision and accuracy of building spatial distribution data.
-
Key words:
- Building /
- Feature partition /
- Space distribution /
- Gridding /
- Ya'an
-
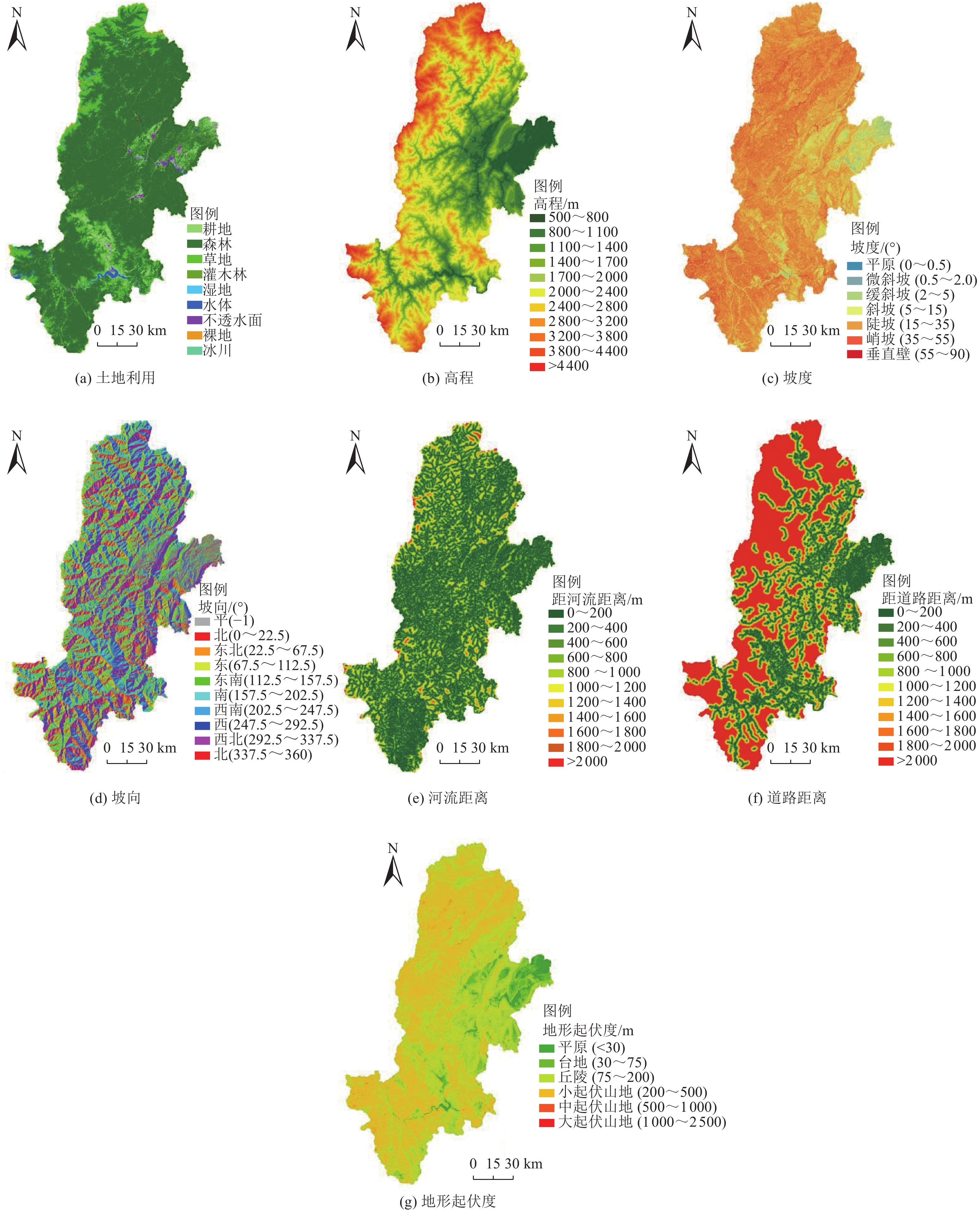
表 1 影响因子子类分级
Table 1. Classification of influencing factors
土地利用 高程/m 坡度/(°) 坡向/(°) 河流距离/m 道路距离/m 地形起伏度/m 耕地 500~800 平原
(0~0.5)平缓坡
(−1)0~200 0~200 平原(<30) 森林 800~1 100 微斜坡(0.5~2) 向阳坡(135~225) 200~400 200~400 台地
(30~70)草地 1 100~1 400 缓斜坡(2~5) 向阳坡
(45~135,
225~315)400~600 400~600 丘陵
(70~200)灌木林 1 400~1 700 斜坡
(5~15)阴坡(0~45,
315~360)600~800 600~800 小起伏山地(200~500) 湿地 1 700~2 000 陡坡
(15~35)— 800~1 000 800~1 000 中起伏山地(500~1 000) 水体 2 000~2 400 峭坡
(35~55)— 1 000~1 200 1 000~1 200 大起伏山地(1 000~2 500) 不透水面 2 400~2 800 垂直壁
(55~90)— 1 200~1 400 1 200~1 400 极大起伏山地(>2 500) 裸地 2 800~3 200 — — 1 400~1 600 1 400~1 600 — 冰川 3 200~3 800 — — 1 600~1 800 1 600~1 800 — — 3 800~4 400 — — 1 800~2 000 1 800~2 000 — — >4 400 — — >2 000 >2 000 — 表 2 雅安市不同特征分区抽样统计的各类因子权重
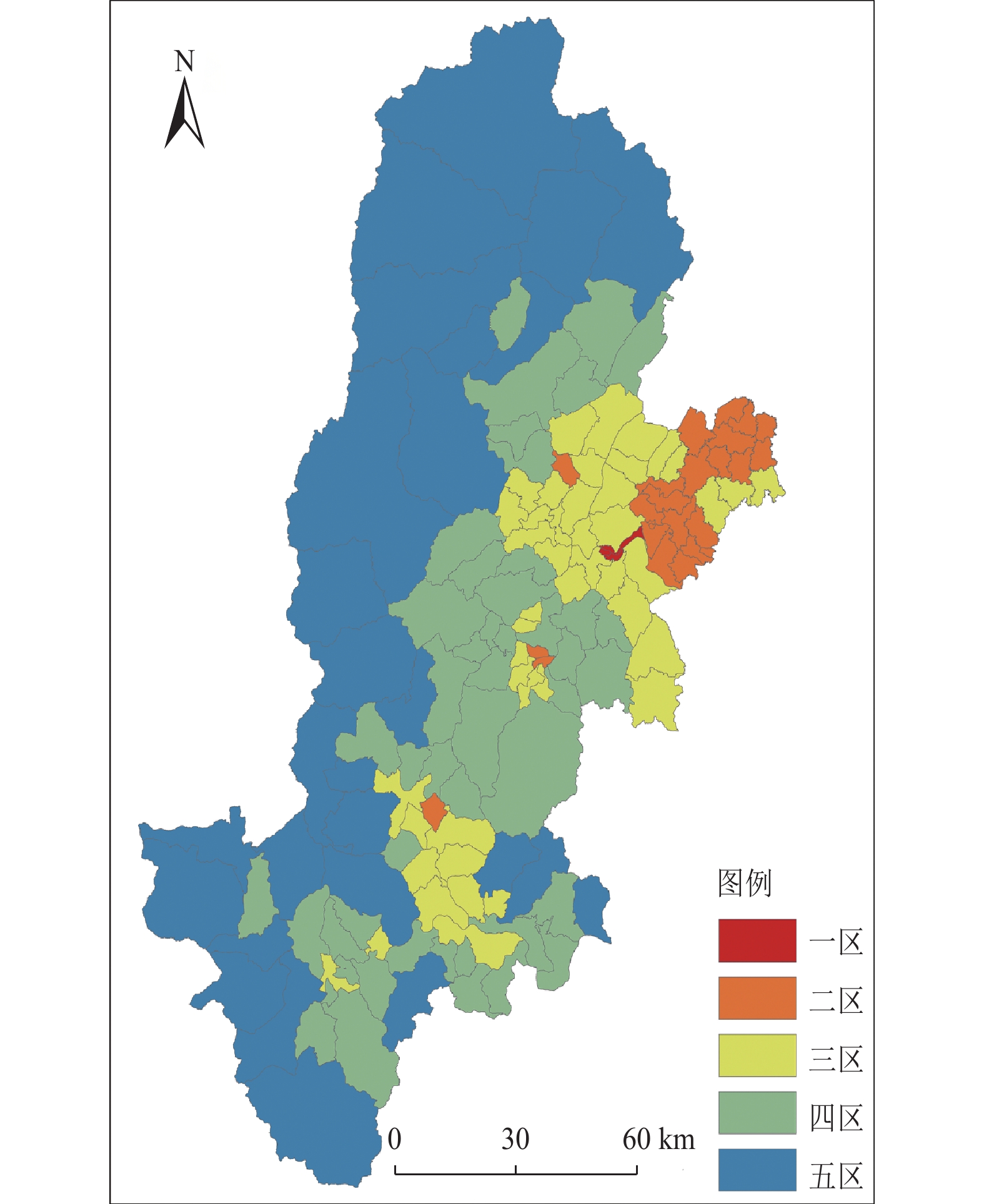
Table 2. Weights of various factors in sampling statistics in different regions of Ya'an city
分区 区域划分 权重 土地利用 高程 坡度 坡向 河流距离 道路距离 地形起伏度 一区 建设用地 — — 0.263 0.108 — 0.300 0.329 非建设用地 0.244 — 0.225 0.164 0.064 0.083 0.220 二区 建设用地 — — 0.230 0.231 0.144 0.159 0.236 非建设用地 0.163 — 0.178 0.154 0.187 0.141 0.177 三区 建设用地 — 0.216 0.213 0.156 — 0.217 0.198 非建设用地 0.227 0.177 0.224 — — 0.183 0.189 四区 建设用地 — 0.089 0.195 0.185 0.169 0.148 0.214 非建设用地 0.236 0.183 0.221 — — 0.175 0.185 五区 建设用地 — 0.176 0.183 0.169 0.156 0.147 0.170 非建设用地 0.156 0.168 0.192 0.180 — 0.148 0.157 表 3 相对误差分级统计
Table 3. Statistics of relative error classification
分级 数目 比例/% 严重低估,<−50% 794 4.7 一般低估,[−50%,−20%) 602 3.6 较准确估计,[−20%,20%] 12 568 74.7 一般高估,(20%,50%] 1 228 7.3 严重高估,>50% 1 626 9.7 -
陈振拓, 李志强, 丁文秀等, 2012. 面向防震减灾的人口数据空间化研究——以2007年宁洱地震灾区为例. 震灾防御技术, 7(3): 273—284Chen Z. T. , Li Z. Q. , Ding W. X. , et al. , 2012. Study of spatial population distribution in earthquake disaster reduction——a case study of 2007 Ning’er earthquake. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 7(3): 273—284. (in Chinese) 程晓亮, 饶芬芳, 2008. 不同地形环境下道路、河流对人口分布影响的分析——以黄山市为例. 资源开发与市场, 24(5): 417—419 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2008.05.012Cheng X. L. , Rao F. F. , 2008. Analysis of influence of road, river on population distribution under different terrain environment——take Huangshan City as an example. Resource Development & Market, 24(5): 417—419. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2008.05.012 丁文秀, 李志强, 卓力格图等, 2015. 四川省房屋数据空间化及在芦山7.0级地震灾情快速评估中的应用. 灾害学, 30(2): 128—132 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2015.02.025Ding W. X. , Li Z. Q. , Zhuoli G. T. , et al. , 2015. Housing data spatialization in Sichuan Province and its application in fast assessment on Lushan M7.0 earthquake disaster. Journal of Catastrophology, 30(2): 128—132. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2015.02.025 谷国梁, 王晓蕾, 李雅静等, 2016. 天津市面向震害快速评估的房屋和人口空间化研究. 地震, 36(2): 149—158Gu G. L. , Wang X. L. , Li Y. J. , et al. , 2016. Spatialization of population and housing data in Tianjin oriented to rapid earthquake loss assessment. Earthquake, 36(2): 149—158. (in Chinese) 韩贞辉, 2013. 基于震害分类的房屋数据格网化研究. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Han Z. H. , 2013. Study on the grid of housing data based on the classification of earthquake damage. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 韩贞辉, 李志强, 陈振拓等, 2013. 人口、房屋数据空间化及其在震灾快速评估中的应用——以彝良地震为例. 地震地质, 35(4): 894—906Han Z. H. , Li Z. Q. , Chen Z. T. , et al. , 2013. Population, housing statistics data spatialization research in the application of rapid earthquake loss assessment—a case of Yiliang earthquake. Seismology and Geology, 35(4): 894—906. (in Chinese) 江东, 杨小唤, 王乃斌等, 2002. 基于RS、GIS的人口空间分布研究. 地球科学进展, 17(5): 734—738Jiang D. , Yang X. H. , Wang N. B. , et al. , 2002. Study on spatial distribution of population based on remote sensing and GIS. Advance in Earth Science, 17(5): 734—738. (in Chinese) 李皓, 张合, 吕国军, 2018. 基于遥感影像的建筑数据构建研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(1): 168—176Li H. , Zhang H. , Lv G. J. , 2018. Construction of building data based on remote sensing images. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(1): 168—176. (in Chinese) 孙柏涛, 张桂欣, 2017. 中国大陆建筑物地震灾害风险分布研究. 土木工程学报, 50(9): 1—7Sun B. T. , Zhang G. X. , 2017. Study on seismic disaster risk distribution of buildings in mainland China. China Civil Engineering Journal, 50(9): 1—7. (in Chinese) 王龙, 王晓青, 丁香等, 2007. 基于遥感和GIS的建筑物震害损失评估方法研究与实现. 地震, 27(4): 77—83Wang L. , Wang X. Q. , Ding X. , et al. , 2007. Study on loss assessment of construction earthquake damage based on remote sensing and GIS. Earthquake, 27(4): 77—83. (in Chinese) 王晓青, 丁香, 王龙等, 2009. 四川汶川8级大地震灾害损失快速评估研究. 地震学报, 31(2): 205—211Wang X. Q. , Ding X. , Wang L. , et al. , 2009. A study on fast earthquake loss assessment and its application to 2008 Wenchuan M8 earthquake. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 31(2): 205—211. (in Chinese) 王志涛, 马祎, 马东辉, 2019. 基于城市规划的建筑物地震灾害风险评估研究. 武汉理工大学学报(信息与管理工程版), 41(6): 549—554Wang Z. T. , Ma Y. , Ma D. H. , 2019. Research on seismic risk assessment of buildings based on urban planning. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Information & Management Engineering), 41(6): 549—554. (in Chinese) 徐国栋, 袁艺, 方伟华等, 2011. 玉树7.1级地震震后损失快速评估. 地震工程与工程振动, 31(1): 114—123Xu G. D. , Yuan Y. , Fang W. H. , et al. , 2011. Fast loss assessment of M7.1 Yushu earthquake. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 31(1): 114—123. (in Chinese) 杨海霞, 2015. 建筑物空间分布格网化方法研究. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所.Yang H. X. , 2015. Research on gridding method of buildings’ spatial distribution. Beijing: Institute of Earthquake Science, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 杨海霞, 王晓青, 窦爱霞等, 2015. 基于RS和GIS的建筑物空间分布格网化方法研究. 地震, 35(3): 136—146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.03.014Yang H. X. , Wang X. Q. , Dou A. X. , et al. , 2015. Multi-source and multi-factor gridding method of building distribution based on RS and GIS. Earthquake, 35(3): 136—146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.03.014 曾祥贵, 2013. 基于影响因子分级和居民地指数密度的人口数据空间化——以梅江流域为例. 南昌: 江西师范大学.Zeng X. G. , 2013. Influencing factors classification and residential area index density based spatialization of population data——taking Meijiang River basin as an example. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University. (in Chinese) Gong P. , Wang J. , Yu L. , et al. , 2013. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: first mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 34(7): 2607—2654. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.748992 Li C. C. , Gong P. , Wang J. , et al. , 2017. The first all-season sample set for mapping global land cover with Landsat-8 data. Science Bulletin, 62(7): 508—515. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2017.03.011 -



 下载:
下载: