Influence of Shear Walls on Optimizing Seismic Internal Force Distribution of RC Structures
-
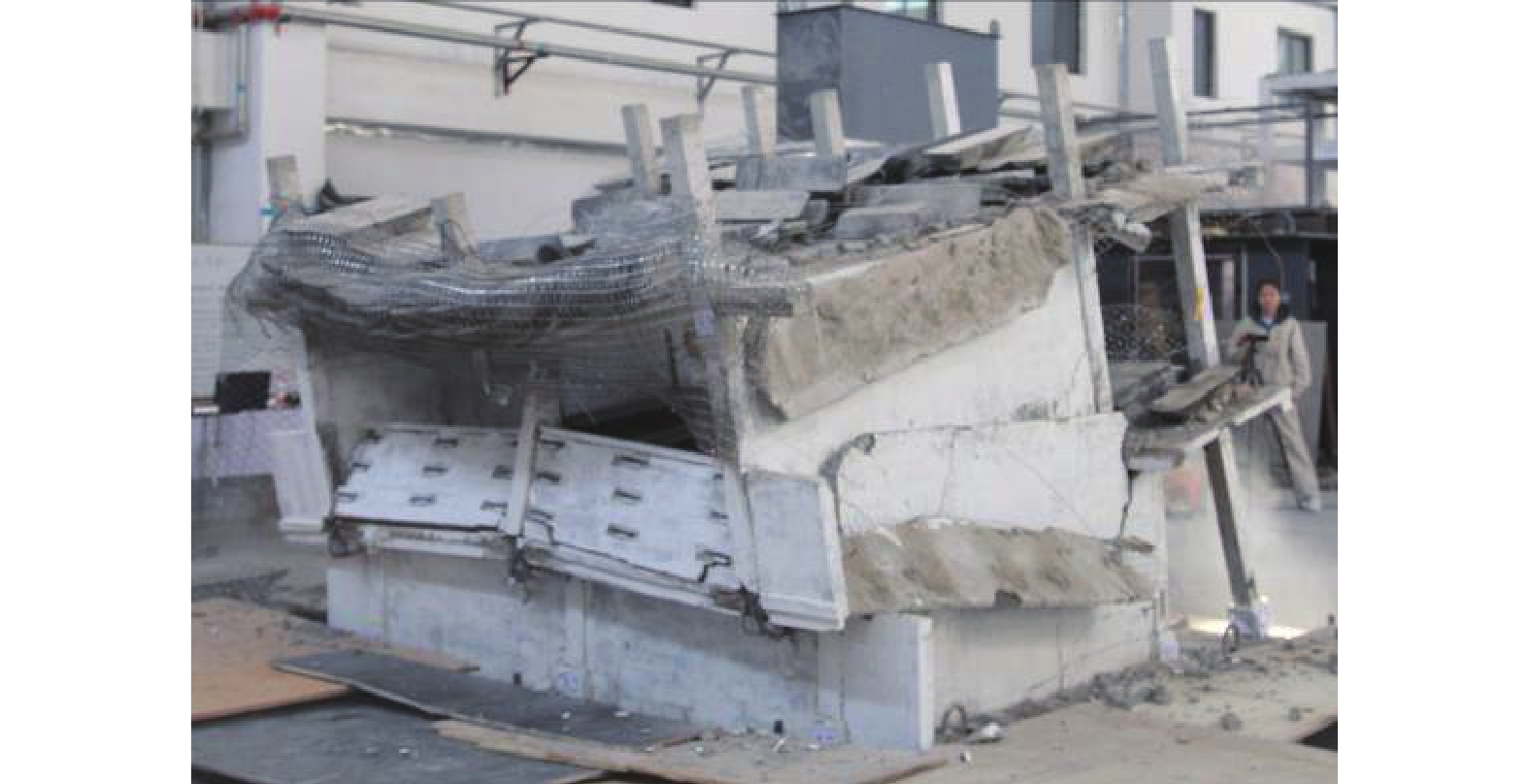
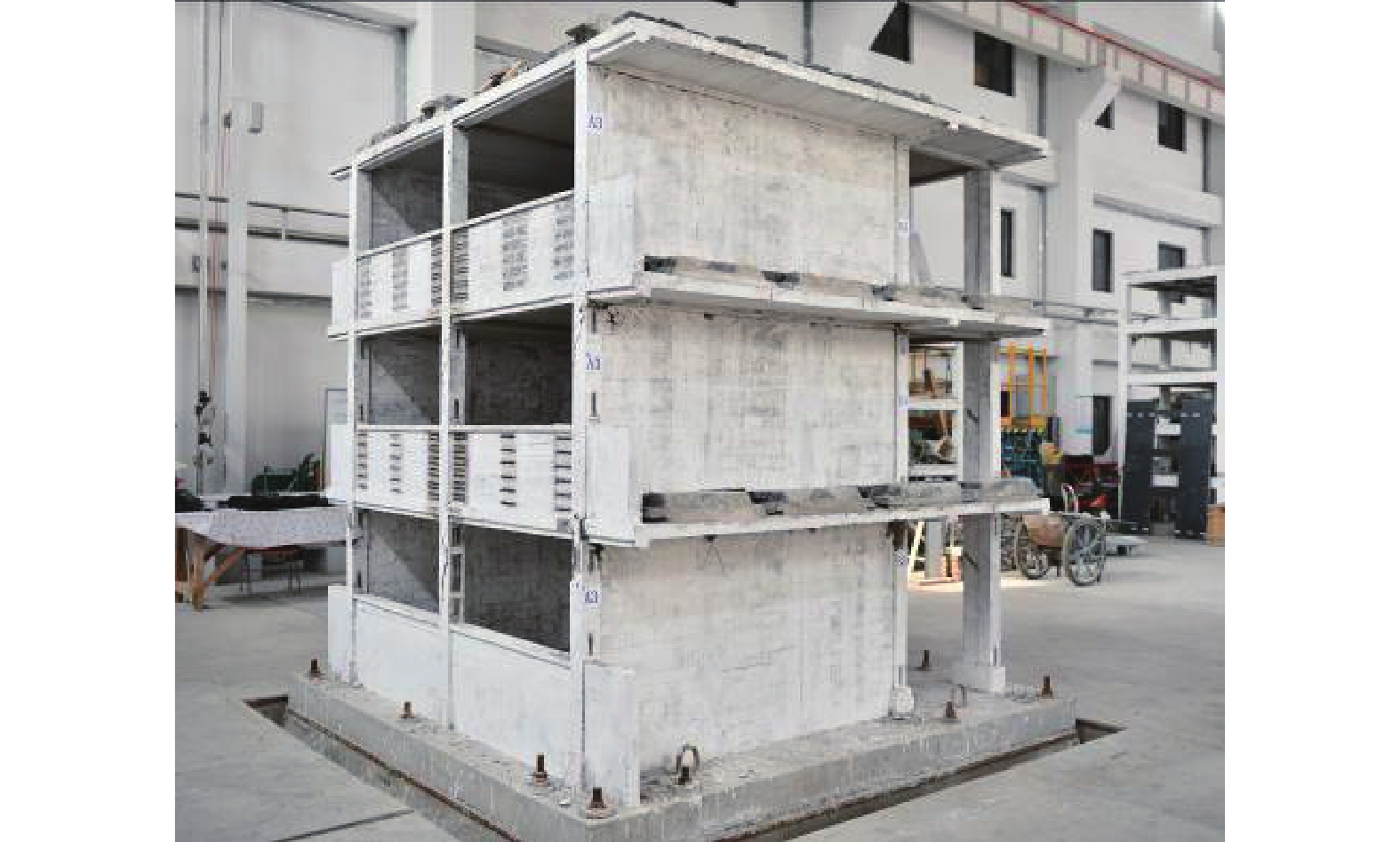
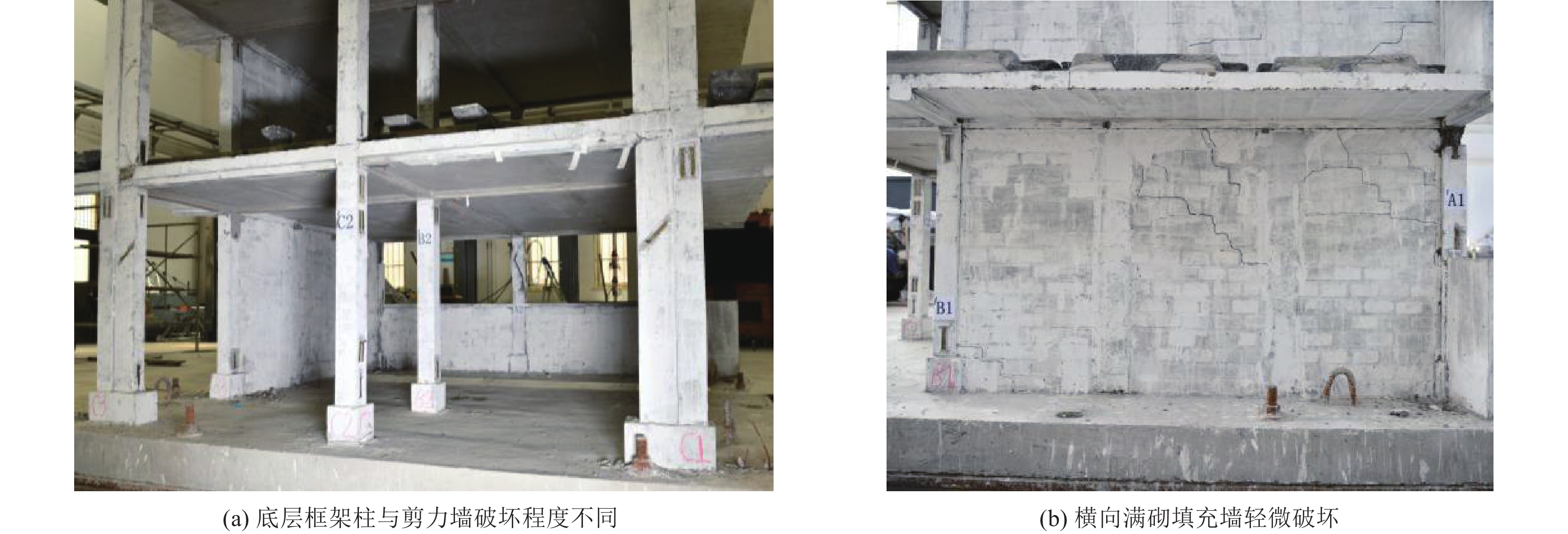
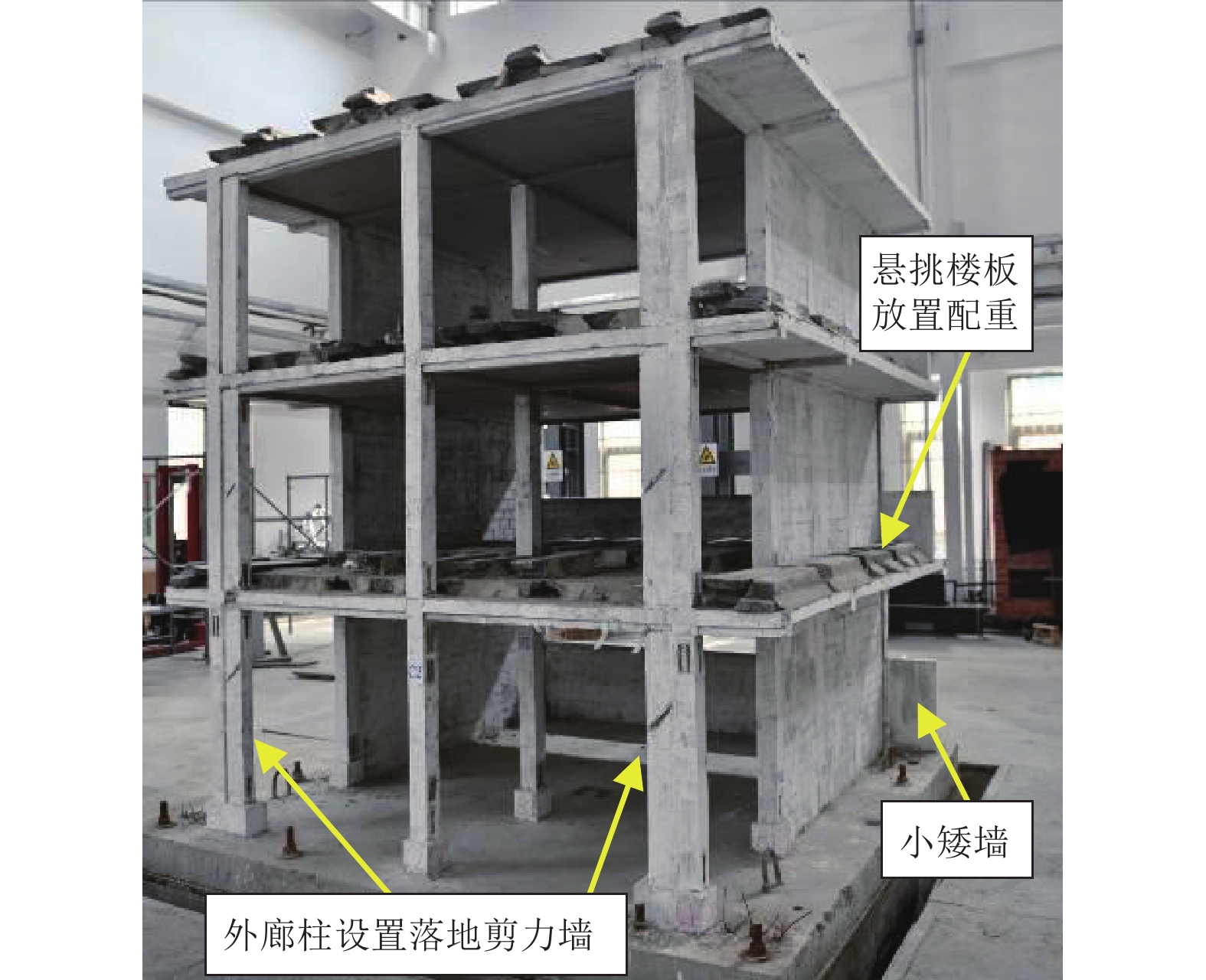
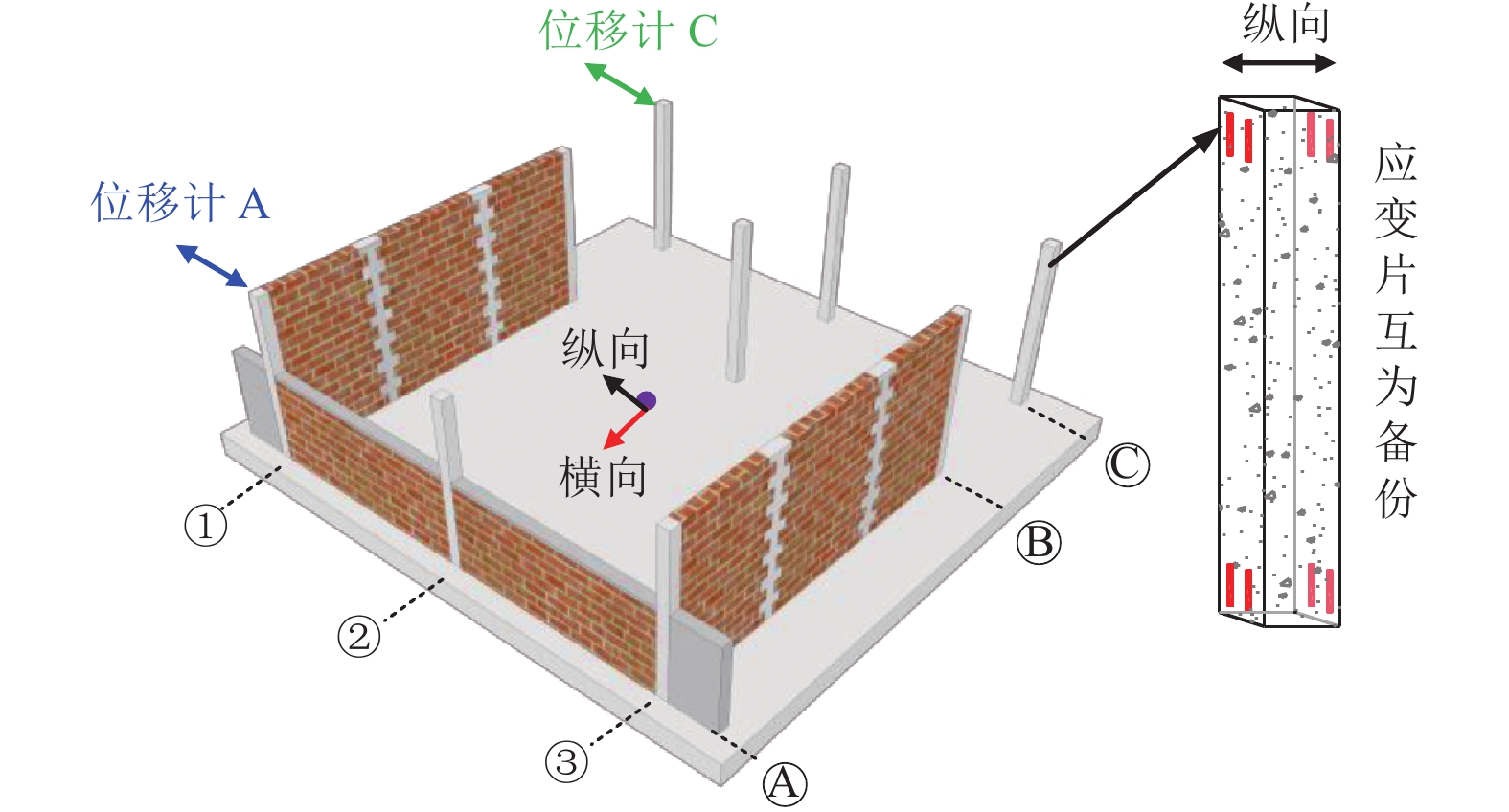
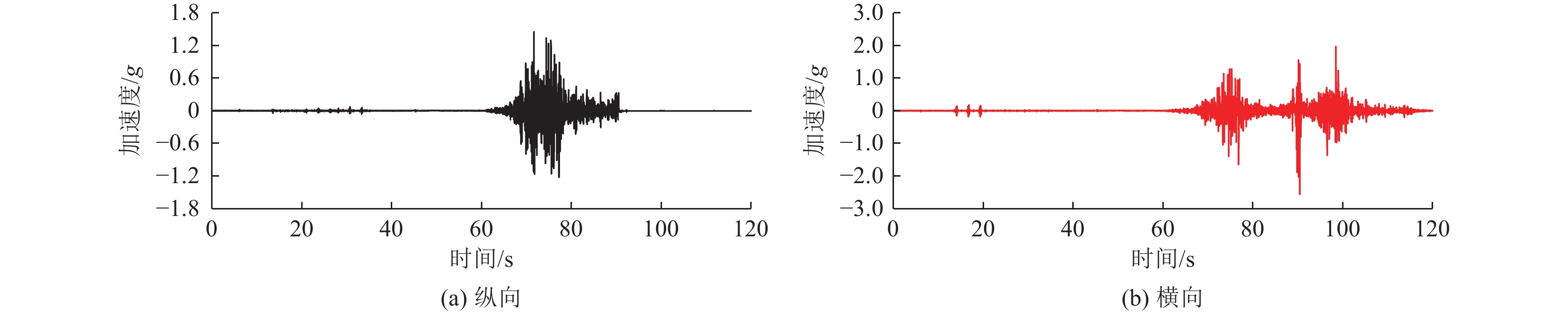
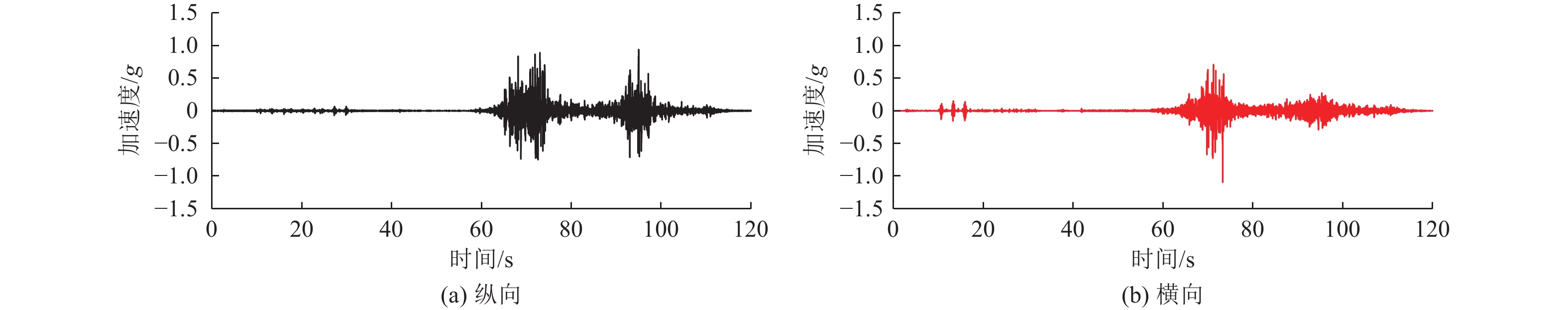
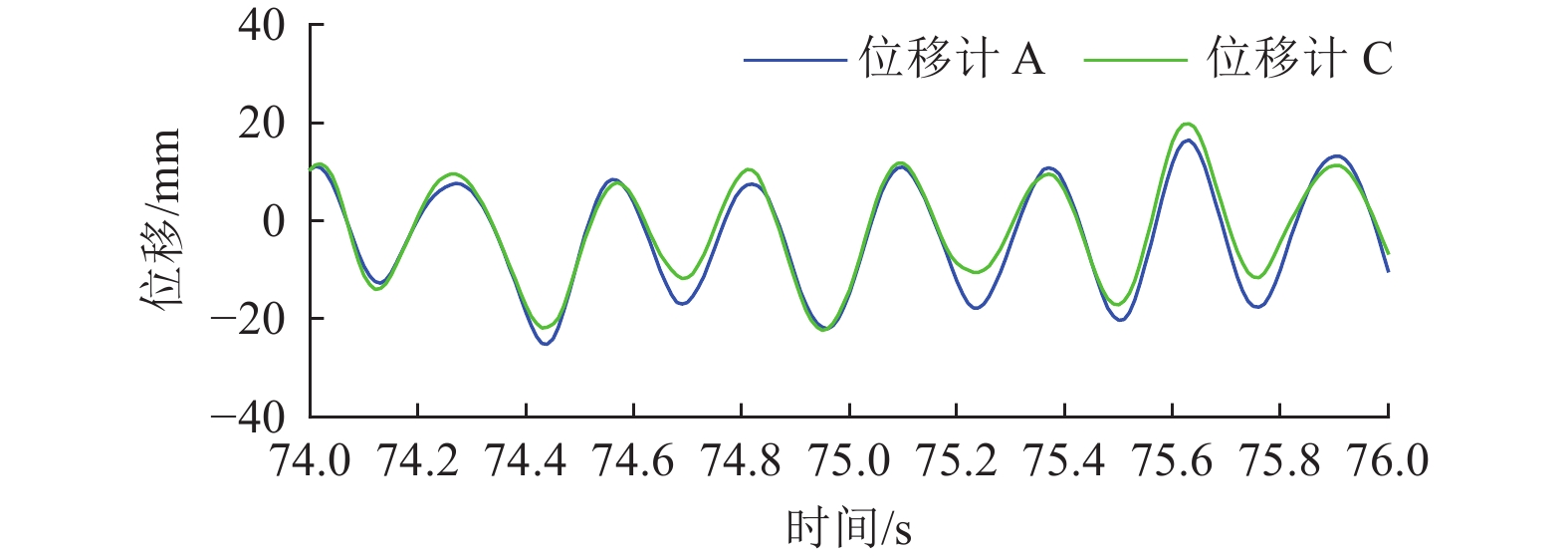
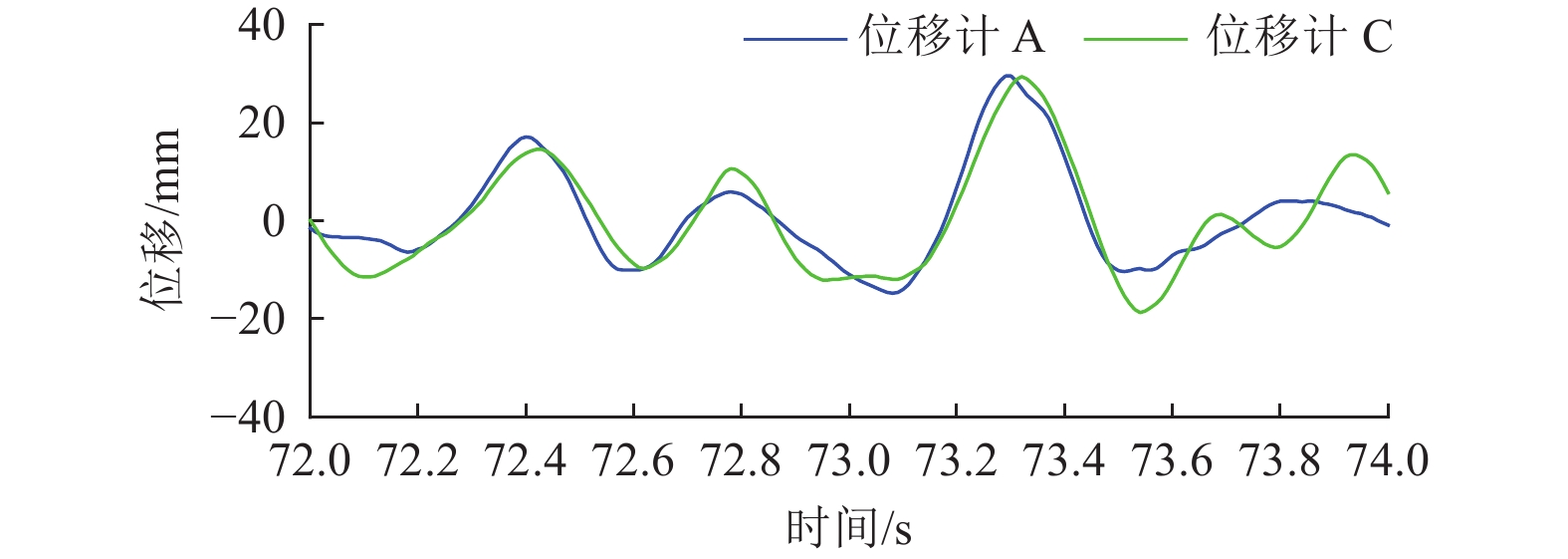
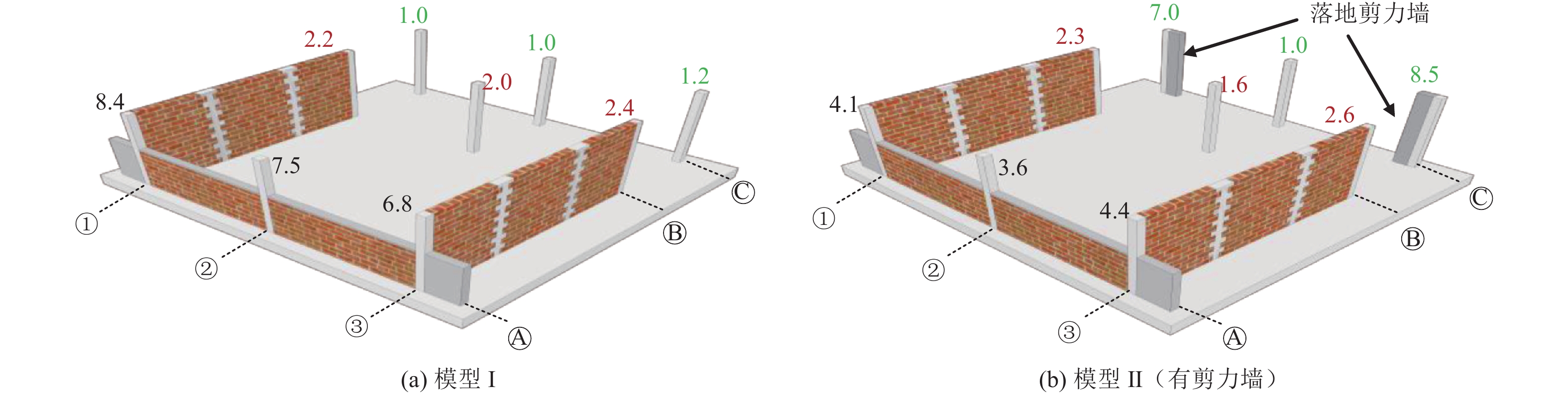
摘要: 为研究地震作用下钢筋混凝土框架结构倒塌机理,验证基于内力分配得到的抗倒塌措施的合理性,设计2组缩尺比例为1∶4的框架结构模型并开展振动台对比试验,单次双向输入地震动峰值加速度为1.0 g,分析地震作用下填充墙-框架结构变形模式和破坏特点,对比分析有、无落地剪力墙框架结构柱间内力分配规律。研究结果表明,填充墙影响框架结构整体变形及柱破坏模式,横向满砌填充墙约束结构扭转变形,即使在双向地震作用下,偏心结构也未发生扭转;由于窗下半高连续填充墙的约束作用,窗间柱抗侧刚度变大,在地震作用下承担的地震剪力是不受半高连续填充墙约束柱的6~8倍;设置落地剪力墙可优化底层柱间地震剪力分配,使框架柱地震剪力分配趋于均匀,避免结构因“凝震聚力”而发生倒塌,实现“大震不倒”。Abstract: In order to investigate the collapse mechanism of the RC frames and verify the rationality of the anti-collapse measures based on the internal force distribution under the earthquake, two models with the scale ratio of 1:4 were designed and the shaking table tests were conducted. In this paper, the structure deformation and column failure of the RC frame structures with infilled walls suffered from bidirectional earthquake reappeared in detail, and the internal force distribution of each column in the structures with or without shear walls was compared. Results show that the infilled walls have significant effects on the columns. The transverse filled walls can restrain the torsion of the structure. Thus, even under the bidirectional earthquake, the eccentric structures do not twist. Due to the restraints of the half-height continuous infilled walls under the window, the seismic shear force of the window column is 6-8 times that of unconstrained ones. The comparison of internal force distribution between columns based on strain of the column shows that the shear walls can optimize the distribution of seismic shear forces among the columns, make the internal force distribution of the columns on each axis balanced, and avoid the structure collapse.
-
Key words:
- RC frame /
- Earthquake collapse /
- Shear walls /
- Internal force distribution /
- Shaking table test
-
表 1 试验模型主要相似关系
Table 1. The similarity ratio of the experimental model
项目 相似比 模型Ⅰ
(人工质量13.4 t)模型Ⅱ
(人工质量11.6 t)长度lr 0.25 0.25 弹性模量Er 0.55 0.55 材料密度ρr 2.20 2.20 应力σr 0.55 0.55 时间tr 0.50 0.50 速度vr 0.50 0.50 加速度ar 1.00 1.00 表 2 不同时刻模型Ⅰ底层柱端应变
Table 2. The strain of the columns of model Ⅰ at different moments
时间t/s 柱端应变/με A/①轴柱 A/②轴柱 A/③轴柱 B/①轴柱 B/②轴柱 B/③轴柱 C/①轴柱 C/②轴柱 C/③轴柱 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 6.14 25 24 49 18 26 16 13 12 18 16 10 17 8 10 9 8 9 11 7.20 21 20 41 15 22 14 11 10 15 13 9 14 7 8 8 7 8 9 14.28 83 74 144 62 73 46 41 35 53 49 30 53 23 30 28 25 28 35 17.13 69 62 124 50 63 39 37 31 47 43 27 47 20 26 25 21 25 31 20.12 79 70 138 54 73 44 39 32 50 45 31 50 23 27 26 22 28 32 24.32 51 45 103 30 48 29 32 25 39 35 23 38 17 21 19 16 21 25 表 3 不同时刻模型Ⅱ底层柱端应变
Table 3. The strain of the columns of model Ⅱ at different moments
时间t/s 柱端应变/με A/①轴柱 A/②轴柱 A/③轴柱 B/①轴柱 B/②轴柱 B/③轴柱 C/①轴柱(带剪力墙) C/②轴柱 C/③轴柱(带剪力墙) 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 上端 下端 12.33 23 31 45 29 14 46 29 36 28 39 35 38 3 56 9 31 2 68 14.73 35 50 67 45 23 67 43 52 40 57 52 55 2 79 14 47 1 100 19.34 33 46 62 42 22 63 42 51 39 55 50 53 1 78 14 45 1 96 21.29 51 81 99 74 32 105 65 79 60 84 77 80 1 117 25 71 2 146 25.02 44 61 82 59 27 85 51 62 48 67 61 65 3 95 17 55 1 115 26.43 53 81 99 72 34 104 62 75 57 81 76 79 4 113 22 67 1 139 表 4 底层框架柱计算参数
Table 4. The column parameters of two models
编号 h/mm y/mm Iz/mm4 等效计算方法示意 A/①轴柱,A/③轴柱 380 40.00 5.12×106 
A/②轴柱 380 40.00 3.41×106 B/①轴柱,B/③轴柱 740 40.00 5.12×106 B/②轴柱 740 40.00 3.41×106 C/②轴柱 740 40.00 3.41×106 C/①轴柱,C/③轴柱 740 40.00 3.41×106 C/①轴柱,C/③轴柱(带剪力墙) 740 88.22 3.94×107 注:表中右图为横墙对柱纵向抗侧刚度影响的等效计算方法示意,用于估算模型Ⅰ和模型Ⅱ的A/①轴柱、A/③轴柱、B/①轴柱、B/③轴柱与横墙组合体的惯性矩。 表 5 不同时刻模型Ⅰ底层柱地震剪力
Table 5. The shear force of the columns of model Ⅰ at different moments
时间t/s 地震剪力/N A/①轴柱 A/②轴柱 A/③轴柱 B/①轴柱 B/②轴柱 B/③轴柱 C/①轴柱 C/②轴柱 C/③轴柱 6.14 421 384 361 111 100 119 53 50 59 7.20 352 321 309 93 82 102 44 44 50 14.28 1 349 1 179 1 022 336 299 366 156 156 185 17.13 1 126 995 876 300 265 327 135 135 164 20.12 1 280 1 098 1 005 314 279 357 147 141 176 24.32 824 761 661 252 217 269 112 103 135 表 6 不同时刻模型Ⅱ底层柱地震剪力
Table 6. The shear force of the columns of model Ⅱ at different moments
时间t/s 地震剪力/N A/①轴柱 A/②轴柱 A/③轴柱 B/①轴柱 B/②轴柱 B/③轴柱 C/①轴柱
(带剪力墙)C/②轴柱 C/③轴柱
(带剪力墙)12.33 464 424 516 287 197 322 908 118 1 077 14.73 730 640 774 419 285 472 1 247 179 1 554 19.34 679 594 730 410 276 454 1 216 173 1 493 21.29 1 134 990 1 177 635 423 693 1 816 282 2 278 25.02 902 806 962 499 338 556 1 508 212 1 785 26.43 1 151 978 1 185 604 406 684 1 801 261 2 155 -
顾祥林, 黄庆华, 汪小林等, 2012. 地震中钢筋混凝土框架结构倒塌反应的试验研究与数值仿真. 土木工程学报, 45(9): 36—45Gu X. L. , Huang Q. H. , Wang X. L. , et al. , 2012. Spatial collapse responses of reinforced concrete frame structures under earthquakes-test study and numerical simulation. China Civil Engineering Journal, 45(9): 36—45. (in Chinese) 郭迅, 2010. 汶川地震震害与抗倒塌新认识. 土木建筑与环境工程, 32(S2): 28—29. 李小军, 于爱勤, 甘朋霞等, 2008. 汶川8.0级地震北川县城区灾害调查与分析. 震灾防御技术, 3(4): 352—362 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2008.04.004Li X. J. , Yu A. Q. , Gan P. X. , et al. , 2008. Survey and analysis of the disaster and engineering damage of Beichuan county seat in MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 3(4): 352—362. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2008.04.004 李英民, 罗文文, 韩军, 2013. 钢筋混凝土框架结构强震破坏模式的控制. 土木工程学报, 46(5): 85—92 doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.05.021Li Y. M. , Luo W. W. , Han J. , 2013. Control of failure mechanism for RC frame structure under strong earthquakes. China Civil Engineering Journal, 46(5): 85—92. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.05.021 林超, 郭子雄, 黄群贤等, 2018. 足尺砌体填充墙RC框架抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 39(9): 30—37Lin C. , Guo Z. X. , Huang Q. X. , et al. , 2018. Experimental study on seismic behavior of full-scale infilled RC frames. Journal of Building Structures, 39(9): 30—37. (in Chinese) 刘伯权, 苏佶智, 马煜东等, 2019. 多层多跨钢筋混凝土平面框架拟静力倒塌试验研究. 土木工程学报, 52(8): 24—39 doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2019.08.003Liu B. Q. , Su J. Z. , Ma Y. D. , et al. , 2019. Pseudo-static collapse experiment of multi-story multi-span reinforced concrete plane frames. China Civil Engineering Journal, 52(8): 24—39. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2019.08.003 骆欢, 杜轲, 孙景江等, 2017. 地震作用下钢筋混凝土框架结构倒塌全过程振动台试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 38(12): 49—56Luo H. , Du K. , Sun J. J. , et al. , 2017. Shaking table test on complete collapse process of RC frame structure subjected to earthquake. Journal of Building Structures, 38(12): 49—56. (in Chinese) 曲哲, 和田章, 叶列平, 2011. 摇摆墙在框架结构抗震加固中的应用. 建筑结构学报, 32(9): 11—19Qu Z. , He T. Z. , Ye L. P. , 2011. Seismic retrofit of frame structures using rocking wall system. Journal of Building Structures, 32(9): 11—19. (in Chinese) 苏幼坡, 张玉敏, 王绍杰等, 2009. 从汶川地震看提高建筑结构抗倒塌能力的必要性和可行性. 土木工程学报, 42(5): 25—32 doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2009.05.010Su Y. P. , Zhang Y. M. , Wang S. J. , et al. , 2009. The necessity and feasibility of enhancing seismic design of structures based on the Wenchuan earthquake. China Civil Engineering Journal, 42(5): 25—32. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2009.05.010 王波, 2017. 典型RC框架结构地震倒塌机理研究. 三河: 防灾科技学院.Wang B., 2017. Experimental study on collapse mechanism of typical RC frame structures. Sanhe: Institute of Disaster Prevention. (in Chinese) 王波, 郭迅, 宣越, 2020. 基于新视角的震害分析——以四川长宁6.0级地震为例. 震灾防御技术, 15(3): 496—509 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200303Wang B. , Guo X. , Xuan Y. , 2020. Analysis of earthquake damage from a new perspective: a case study of Changning M6.0 earthquake in Sichuan Province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(3): 496—509. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200303 王中阳, 车佳玲, 张尚荣等, 2018. 基于能量方法设计的RC框架结构易损性分析. 震灾防御技术, 13(3): 524—533Wang Z. Y. , Che J. L. , Zhang S. R. , et al. , 2018. Seismic fragility analysis of RC frame structure based on energy balance. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 524—533. (in Chinese) 徐超, 刘健, 温增平等, 2016. 汶川地震中某RC框架结构的震害分析与模拟. 震灾防御技术, 11(3): 542—551 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20160310Xu C. , Liu J. , Wen Z. P. , et al. , 2016. Damage analysis and simulation of a RC frame structure in the Wenchuan earthquake. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 11(3): 542—551. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20160310 许卫晓, 孙景江, 杜轲等, 2015. 阶梯墙框架结构体系的抗震性能分析. 工程力学, 32(2): 139—146Xu W. X. , Sun J. J. , Du K. , et al. , 2015. Seismic performance analysis of stepped wall-frame structure. Engineering Mechanics, 32(2): 139—146. (in Chinese) 闫培雷, 孙柏涛, 张昊宇, 2014. 芦山7.0级强烈地震钢筋混凝土框架结构教学楼震害. 土木工程学报, 47(S1): 24—28Yan P. L. , Sun B. T. , Zhang H. Y. , 2014. Seismic damage to RC frame teaching buildings in Lushan MS7.0 earthquake. China Civil Engineering Journal, 47(S1): 24—28. (in Chinese) 杨伟松, 郭迅, 许卫晓等, 2015. 增设翼墙RC框架结构的抗震性能研究. 振动与冲击, 34(24): 144—152Yang W. S. , Guo X. , Xu W. X. , et al. , 2015. Seismic behaviors of RC frames retrofitted with wing walls. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 34(24): 144—152. (in Chinese) 袁新星, 2018. RC框架结构“强柱弱梁”问题的探讨. 三河: 防灾科技学院.Yuan X. X. , 2018. Discussion on “strong column weak beam” of RC frame structure. Sanhe: Institute of Disaster Prevention. (in Chinese) 张望喜, 庞博, 徐帅, 2019. 基于IDA和易损性分析的RC框架结构底层柱端弯矩增大系数. 重庆大学学报, 42(5): 37—45Zhang W. X. , Pang B. , Xu S. , 2019. Research on bottom column end moment amplification factor of RC frame based on incremental dynamic analysis and fragility analysis. Journal of Chongqing University, 42(5): 37—45. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2010. GB 50011—2010 建筑抗震设计规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, 2010. GB 50011—2010 Code for seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese) 周晓洁, 李忠献, 续丹丹等, 2015. 柔性连接填充墙框架结构抗震性能试验. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 48(2): 155—166Zhou X. J. , Li Z. X. , Xu D. D. , et al. , 2015. Experiment on seismic behavior of flexible connection masonry infilled frame structure. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 48(2): 155—166. (in Chinese) Penava D. , Sarhosis V. , Kožar I. , et al. , 2018. Contribution of RC columns and masonry wall to the shear resistance of masonry infilled RC frames containing different in size window and door openings. Engineering Structures, 172: 105—130. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.06.007 Peng Q. M. , Zhou X. J. , Yang C. H. , 2018. Influence of connection and constructional details on masonry-infilled RC frames under cyclic loading. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 108: 96—110. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.02.009 -




 下载:
下载: