Research on Reverse Time Migration of Different Phases from OBN Stations
-
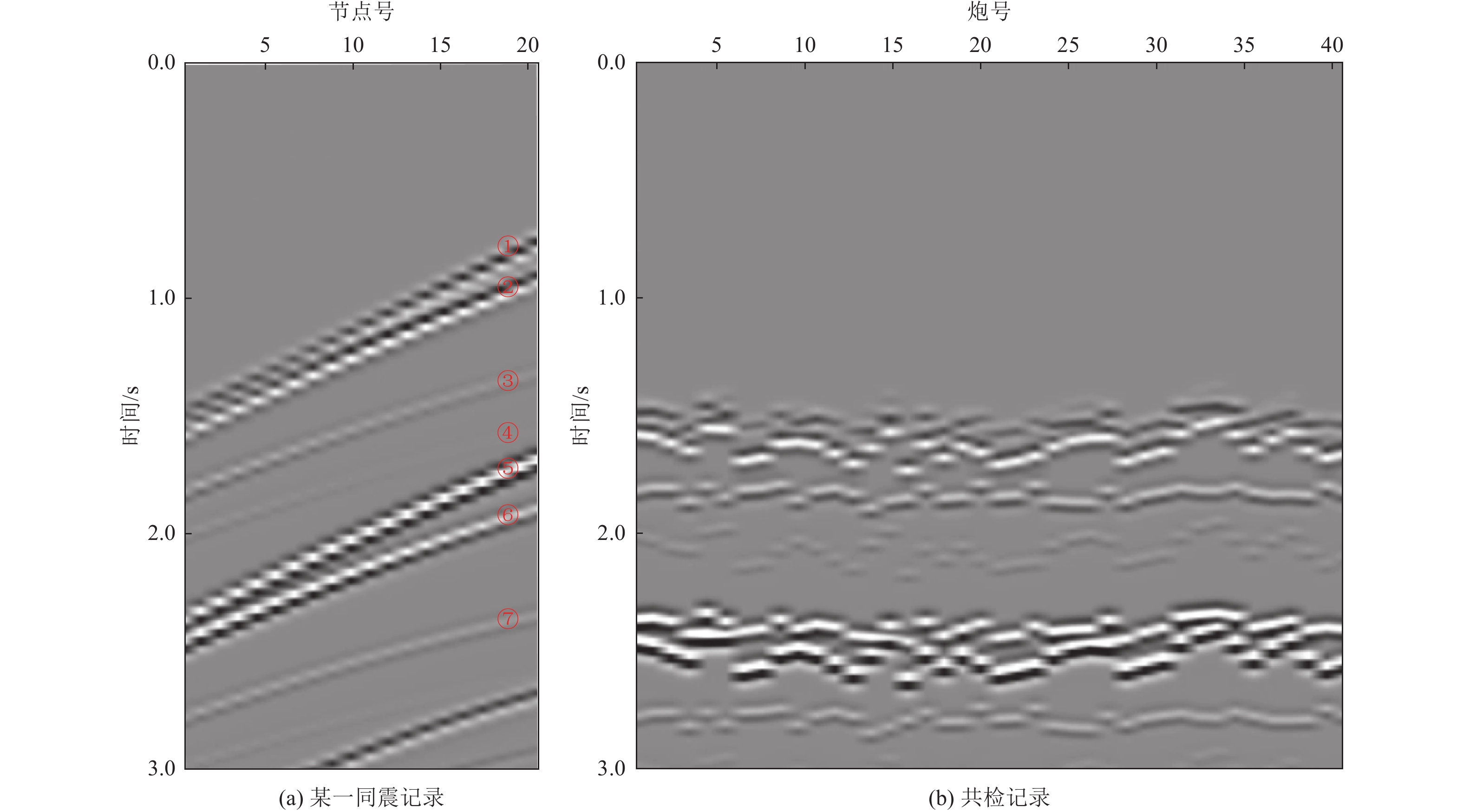
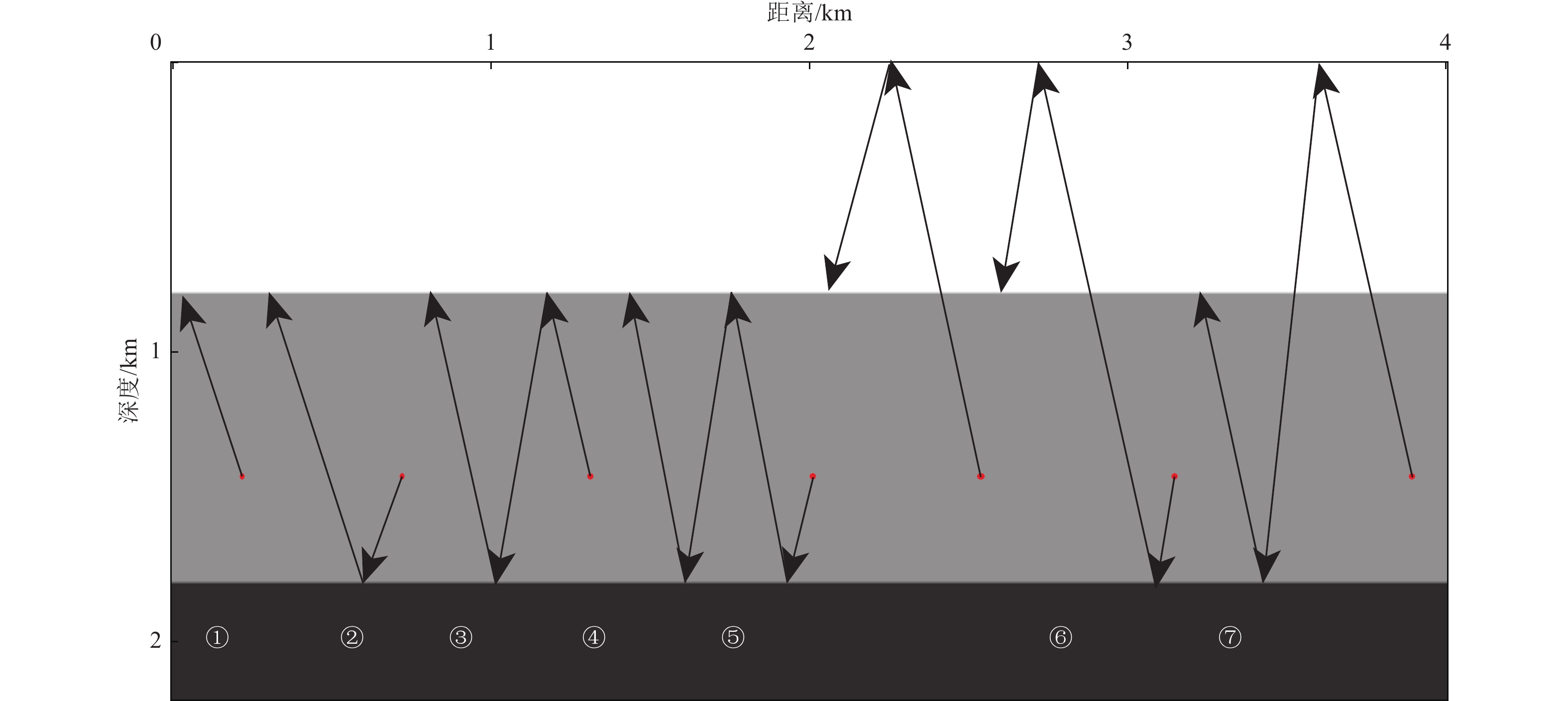
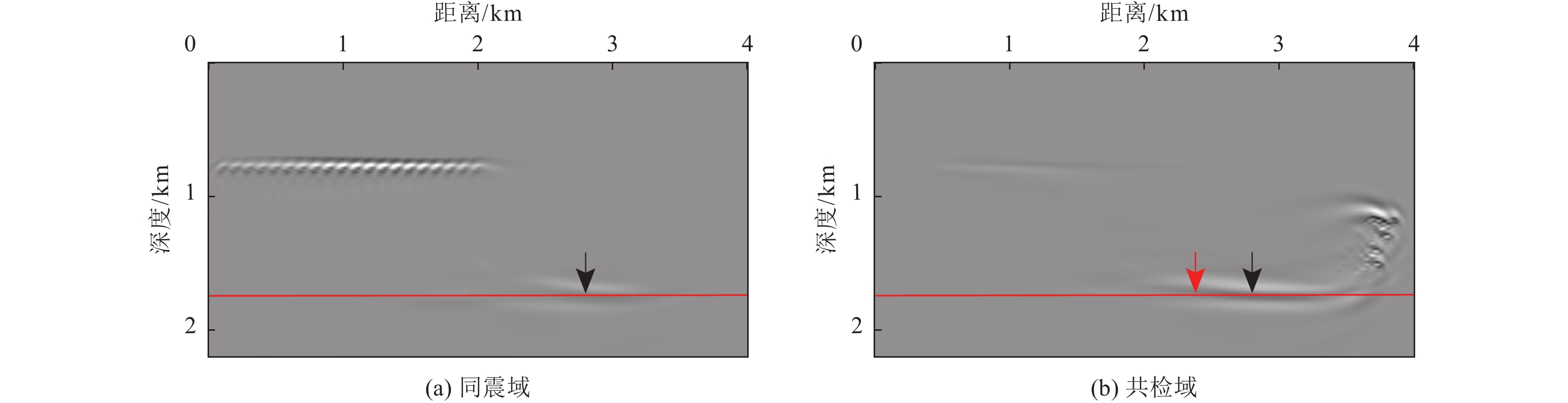
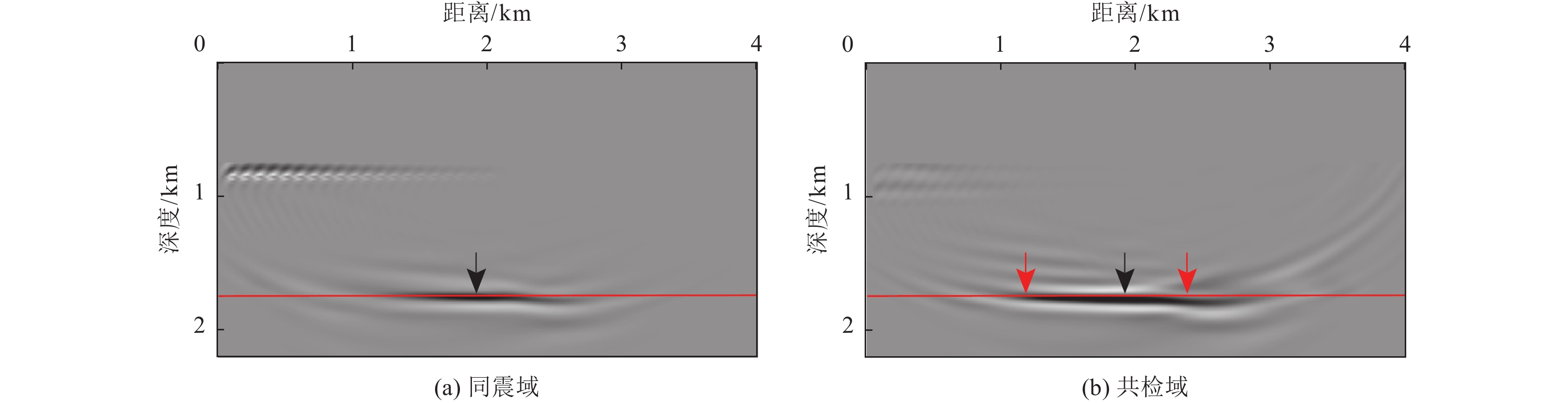
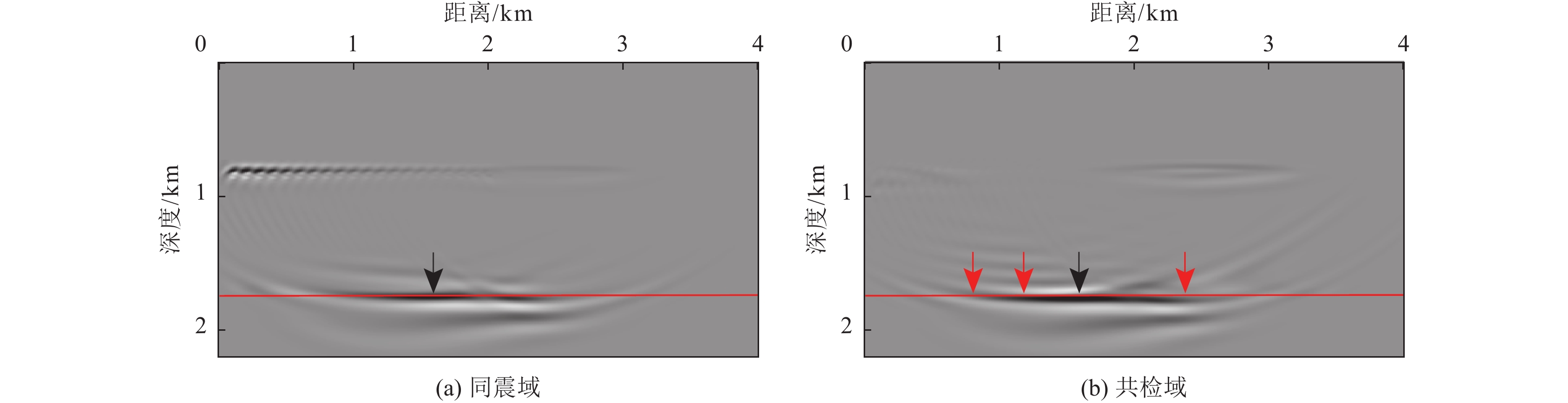
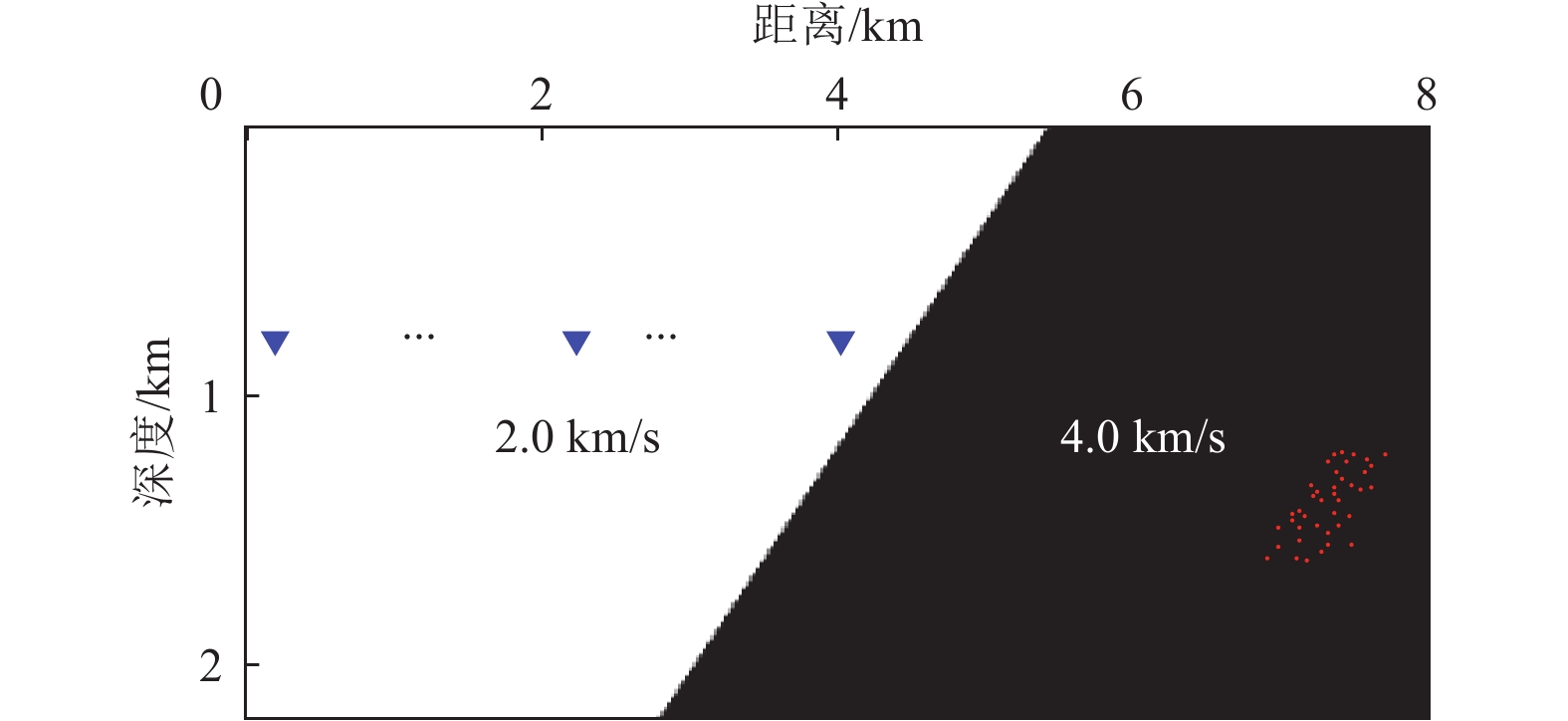
摘要: 对近海海域进行地壳速度结构高精度成像有助于深入了解我国近海地震活动、深部孕震构造条件,揭示海域构造特征及其相互作用模式,为海域地震区划和风险评估提供基础支撑。在海底节点观测系统中,由于海底、海平面等强波阻抗差界面的存在,台站记录了较多强能量的后续震相。与初至震相相比,后续震相在地球内部来回反射,传播路径长、携带构造信息多,充分利用后续震相有望获得高精度的地下构造成像结果。逆时偏移是勘探地球物理中精度较高的成像方法之一,且易于实现。将逆时偏移算法引入海底节点初至震相和后续震相成像,采用常规逆时偏移对反射震相进行偏移,对上行一阶海底震相、上行一阶后续震相成像均进行镜像法逆时偏移,通过修改逆时偏移框架,实现初至震相的成像。研究结果表明,逆时偏移能够有效对反射震相进行地下偏移归位;采用镜像法逆时偏移对上行一阶海底震相、上行一阶自由表面震相进行成像,能够有效增大成像范围;修改逆时偏移框架,初至震相能够对断层进行准确定位。Abstract: High-precision imaging of the velocity structure of the crust in offshore sea concentrates to understanding of the seismic activity and deep seismogenic environments, revealing the tectonic features and their interaction patterns, and providing basic supports for seismic risk assessment. Due to the existence of interfaces with strong impedance differences such as the seafloor and the free surface, the ocean bottom nodes (OBN) monitoring station records many seismic later phases with strong energy. The later phases propagate back and forth in the Earth’s interior and therefore the later phases carry more structural information than the first arriving phases. Inversions using later phases can promote the generation of high-quality subsurface structural imaging results. Reverse time migration (RTM) is one of the high-precision and widely-used imaging methods in exploration geophysics and it is convenient to implement. In this paper, RTM algorithm is introduced into the imaging of the first and later arrival phases of the OBN stations: the conventional RTM is used to migrate the reflected phases; the up-going first-order sea-floor-related phases and the up-going first-order free-surface-related phases can be processed by mirror RTM; by modifying the framework of RTM, the imaging of the first arriving phases are realized. Numerical experiments demonstrate that RTM can effectively migrate the reflected phases, mirror RTM of the first-order later phases can effectively increase the image quality and enlarge the illumination ranges, and the modified RTM of first arriving phases can accurately locate faults.
-
Key words:
- Seismic later phases /
- Reverse time migration (RTM) /
- Ocean bottom nodes (OBN) /
- Imaging
-
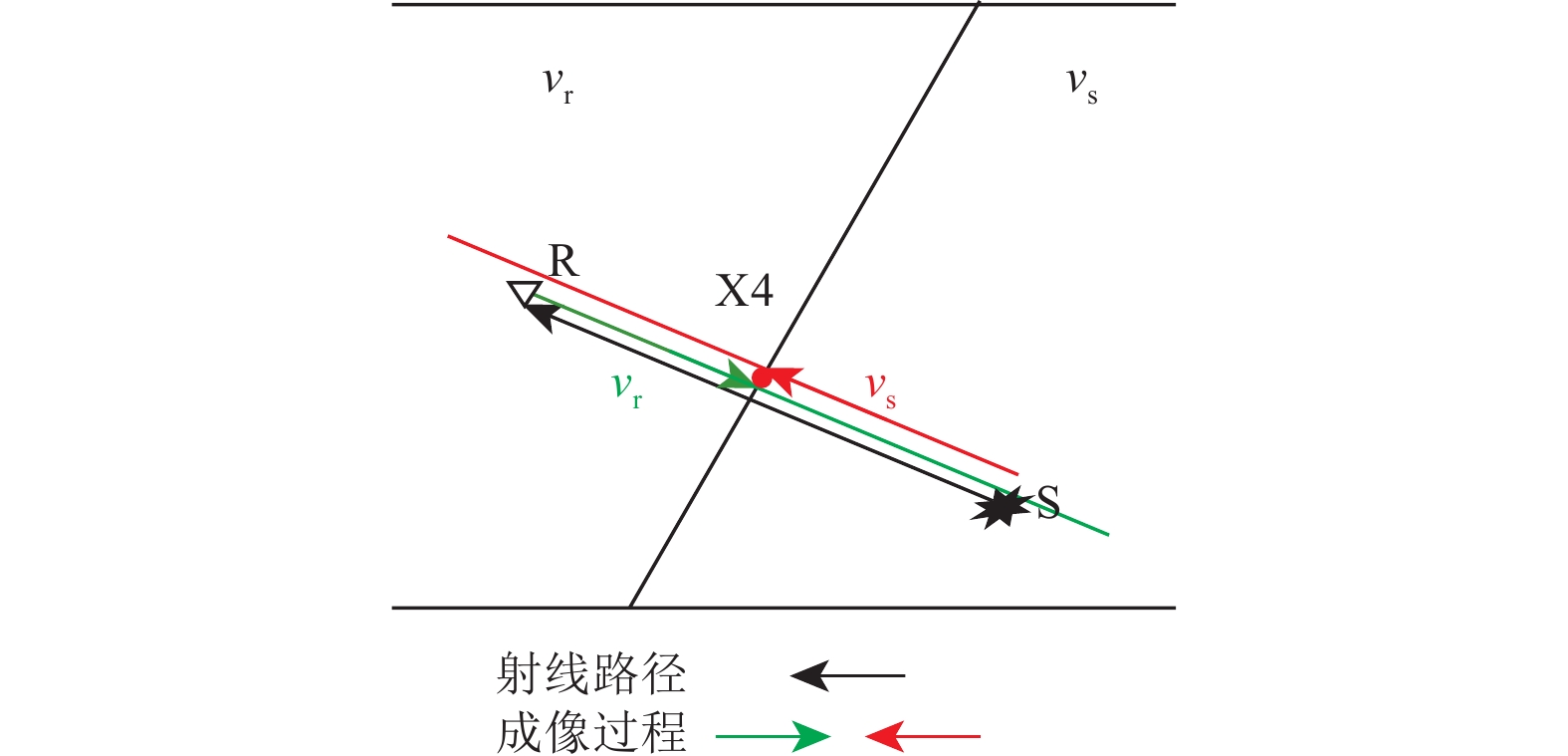
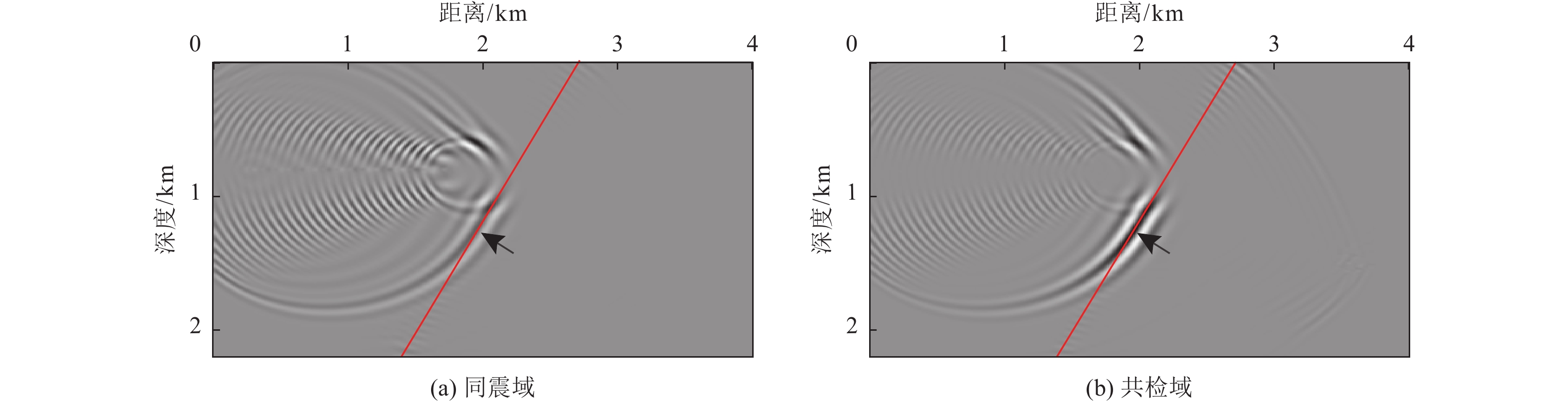
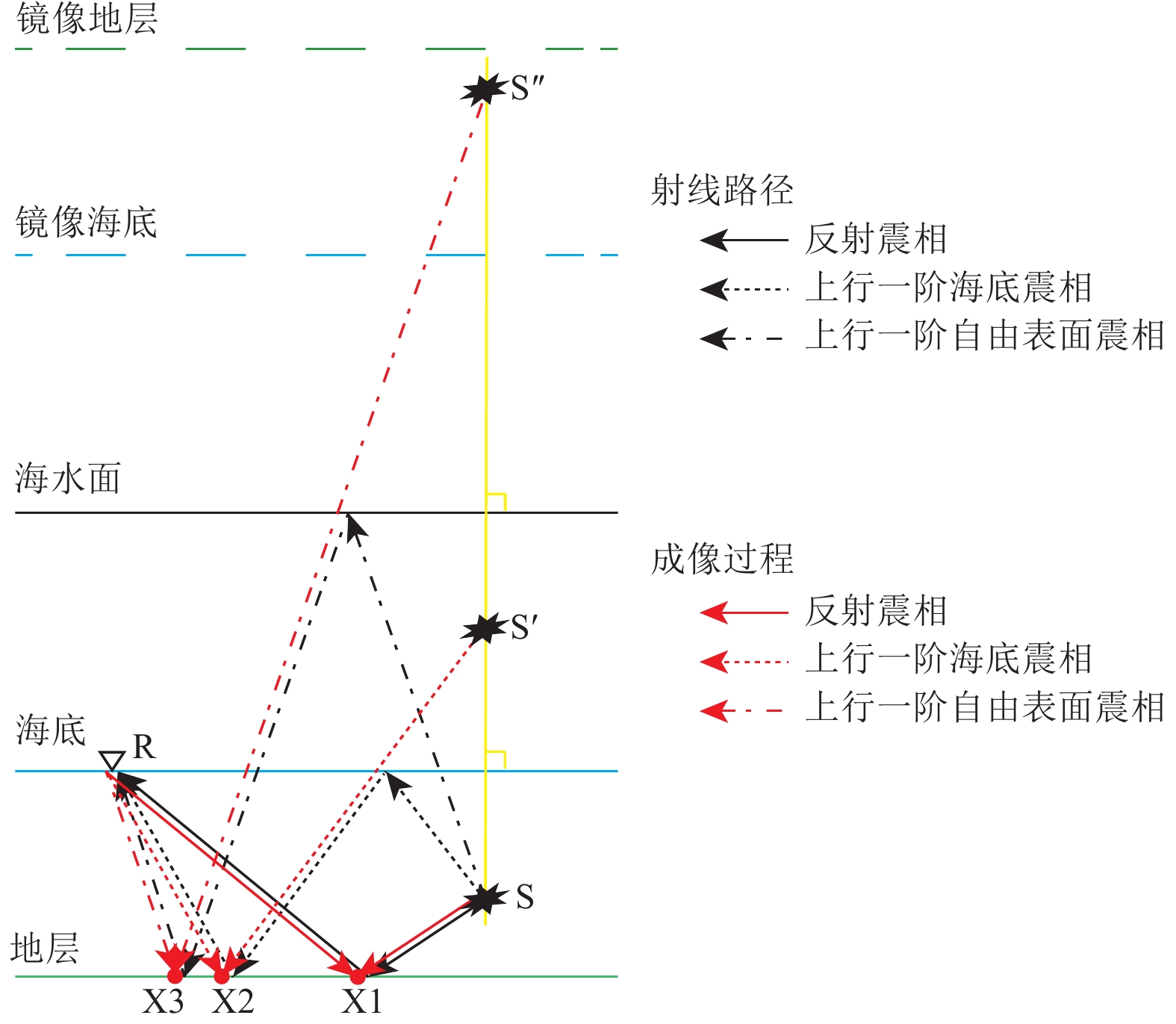
图 1 反射震相
$ {P}_{{\rm{d}}}{P}_{{\rm{u}}} $ 、上行一阶海底震相$ {{P}_{{\rm{wu}}}P}_{{\rm{wd}}}{P}_{{\rm{u}}} $ 、上行一阶自由表面震相$ {{P}_{{\rm{u}}}P}_{{\rm{d}}}{P}_{{\rm{u}}} $ 射线路径及成像过程示意注:S表示震源点,S'表示以海底为镜像面而翻折的虚拟震源点,S''表示以海水面为镜像面而翻折的虚拟震源点,R表示OBN台站,X1、X2与X3分别表示反射震相、上行一阶海底震相与上行一阶自由表面震相逆时偏移成像点。
Figure 1. Illuminations of raypaths and imaging procedures of the seismic later phases
-
高战武, 缑亚森, 钟慧等, 2021. 中国东部海域断裂构造格架与地震活动研究. 震灾防御技术, 16(1): 11—18Gao Z. W. , Gou Y. S. , Zhong H. , et al. , 2021. Fault structure frame and seismicity in the sea on the EastSide of Chinese mainland. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(1): 11—18. (in Chinese) 李小军, 李娜, 陈苏, 2021. 中国海域地震区划及关键问题研究. 震灾防御技术, 16(1): 1—10Li X. J. , Li N. , Chen S. , 2021. Study on seismic zoning in China sea area and its key issues. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(1): 1—10. (in Chinese) 刘伊克, 刘学建, 张延保, 2018. 地震多次波成像. 地球物理学报, 61(3): 1025—1037Liu Y. K. , Liu X. J. , Zhang Y. B. , 2018. Migration of seismic multiple reflections. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(3): 1025—1037. (in Chinese) 齐诚, 刘璐惜, 2008. 对后续震相的认识促进了地震层析成像的发展. 地学前缘, 15(1): 232—241Qi C. , Liu L. X. , 2008. Importance of later-phase data in seismic tomography. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(1): 232—241. (in Chinese) 夏少红, 丘学林, 徐辉龙等, 2011. 天然地震后续PmP震相走时特征及在地壳结构成像中的作用——以日本东北活火山地区为例. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(2): 141—148.Xia S. H. , Qiu X. L. , Xu H. L. , et al. , 2011. Characteristics of PmP phases from earthquakes and their role in crustal tomography: An active volcanic area example, northeastern Japan. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(5): 640—646. 张延保, 2020. 基于逆时偏移地震多次波成像. 北京: 中国科学院大学. 郑忆康, 王一博, 徐嘉亮等, 2015. 数据自相关多次波偏移成像. 地球物理学报, 58(3): 993—1001Zheng Y. K. , Wang Y. B. , Xu J. L. , et al. , 2015. Imaging multiples by data to data migration. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(3): 993—1001. (in Chinese) 郑忆康, 王一博, 常旭等, 2016. 单程波角度域内压制多次波偏移假象. 地球物理学报, 59(12): 4584—4593Zheng Y. K. , Wang Y. B. , Chang X. , et al. , 2016. Eliminating migration artifacts in angle domain based on one-way wave equation migration of multiples. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(12): 4584—4593. (in Chinese) Alerini M. , Traub B. , Ravaut C. , et al. , 2009. Prestack depth imaging of ocean-bottom node data. Geophysics, 74(6): WCA57—WCA63. doi: 10.1190/1.3204767 Baysal E. , Kosloff D. D. , Sherwood J. W. C. , 1983. Reverse time migration. Geophysics, 48(11): 1514—1524. doi: 10.1190/1.1441434 Dash R. , Spence G. , Hyndman R. , et al. , 2009. Wide-area imaging from OBS multiples. Geophysics, 74(6): Q41—Q47. doi: 10.1190/1.3223623 Grion S. , Exley R. , Manin M. , et al. , 2007. Mirror imaging of OBS data. First Break, 25(11): 37—42. Huang X. Y. , Yang D. H. , Tong P. , et al. , 2016. Wave equation-based reflection tomography of the 1992 Landers earthquake area. Geophysical Research Letter, 43(5): 1884—1892. doi: 10.1002/2016GL067717 Katzman R. , Holbrook W. S. , Paull C. K. , 1994. Combined vertical-incidence and wide-angle seismic study of a gas hydrate zone, Blake Ridge. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 99(B9): 17975—17995. doi: 10.1029/94JB00662 Korenaga J. , Holbrook W. S. , Singh S. C. , et al. , 1997. Natural gas hydrates on the southeast U. S. margin: Constraints from full waveform and travel time inversions of wide-angle seismic data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B7): 15345—15365. Kumar D. , Sen M. K. , Bangs N. L. , 2006. Seismic characteristics of gas hydrates at Hydrate Ridge, offshore Oregon. The Leading Edge, 25(5): 610—614. doi: 10.1190/1.2202665 Liu X. J. , Liu Y. K. , Khan M. , 2018. Fast least-squares reverse time migration of VSP free-surface multiples with dynamic phase-encoding schemes. Geophysics, 83(4): S321—S332. doi: 10.1190/geo2017-0419.1 Liu Y. K. , Chang X. , Jin D. G. , et al. , 2011. Reverse time migration of multiples for subsalt imaging. Geophysics, 76(5): WB209—WB216. doi: 10.1190/geo2010-0312.1 Liu Y. K. , Liu X. J. , Osen A. , et al. , 2016. Least-squares reverse time migration using controlled-order multiple reflections. Geophysics, 81(5): S347—S357. doi: 10.1190/geo2015-0479.1 Mienert J., Bünz S., Guidard S., et al., 2005. Ocean bottom seismometer investigations in the Ormen Lange area offshore mid-Norway provide evidence for shallow gas layers in subsurface sediments. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 22(1—2): 287—297. Ravasi M. , Vasconcelos I. , Curtis A. , et al. , 2015. Vector-acoustic reverse time migration of Volve ocean-bottom cable data set without up/down decomposed wavefields. Geophysics, 80(4): S137—S150. doi: 10.1190/geo2014-0554.1 Reiter E. C. , Toksoz M. N. , Keho T. H. , et al. , 1991. Imaging with deep-water multiples. Geophysics, 56(7): 1081–1086. doi: 10.1190/1.1443119 Romero L. A. , Ghiglia D. C. , Ober C. C. , et al. , 2000. Phase encoding of shot records in prestack migration. Geophysics, 65(2): 426–436. doi: 10.1190/1.1444737 Shiraishi K., No T., Gou F. J., 2022. Seismic reflection imaging of deep crustal structures via reverse time migration using offshore wide-angle seismic data on the eastern margin of the Sea of Japan. Earth, Planets and Space, 74(1): 28. Verschuur D. J. , Berkhout A. J. , 2011. Seismic migration of blended shot records with surface-related multiple scattering. Geophysics, 76(1): A7—A13. doi: 10.1190/1.3521658 Xia S. H. , Zhao D. P. , Qiu X. L. , et al. , 2007. Mapping the crustal structure under active volcanoes in central Tohoku, Japan using P and PmP data. Geophysical Research Letter, 34(10): 325—327. Zhang Y. B. , Liu Y. K. , Liu X. J. , et al. , 2020. Reverse time migration using water-bottom-related multiples. Geophysical Prospecting, 68(2): 446—465. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12851 Zhang Y. B. , Liu Y. K. , Yi J. , et al. , 2021. Fast Least-squares reverse time migration of OBN down-going multiples. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 730476. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.730476 Zhao D. P., Todo S., Lei J. S., 2005. Local earthquake reflection tomography of the Landers aftershock area. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 235(3—4): 623—631. Zheng Y. K. , Wang Y. B. , Chang X. , 2016. Eliminating artifacts in migration of surface-related multiples: An application to marine data. Interpretation, 4(4): SQ51—SQ57. doi: 10.1190/INT-2016-0020.1 Zheng Y. K. , Wang Y. B. , Chang X. , 2019. Least-squares data-to-data migration: An approach for migrating free-surface-related multiples. Geophysics, 84(2): S83—S94. doi: 10.1190/geo2018-0080.1 -






 下载:
下载: