Study on Seismic Activity of Reservoir in Complex Tectonic Environment −Take Nuozhadu Hydropower Station as An Example
-
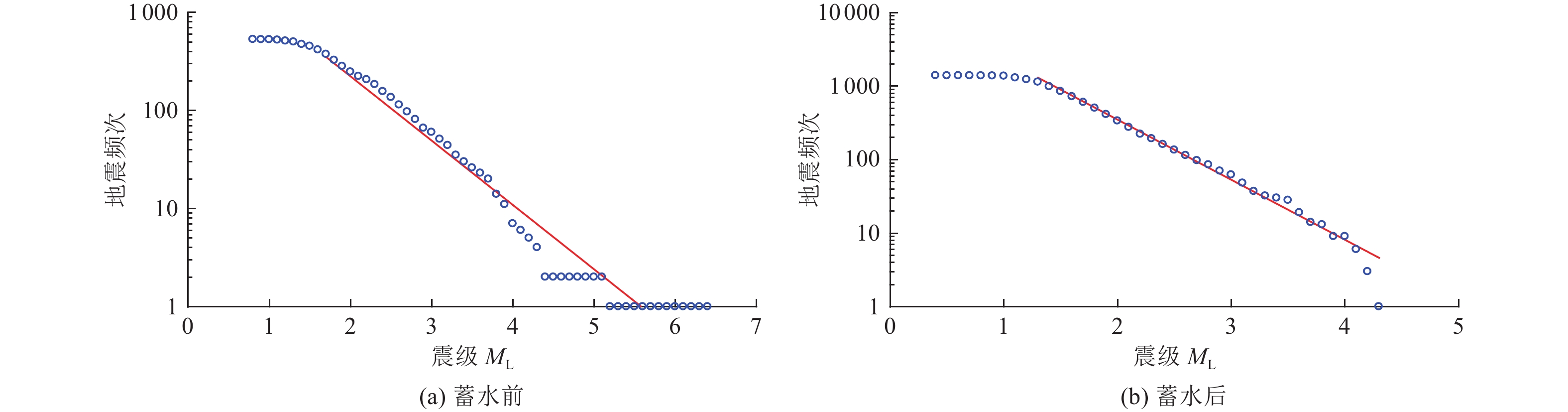
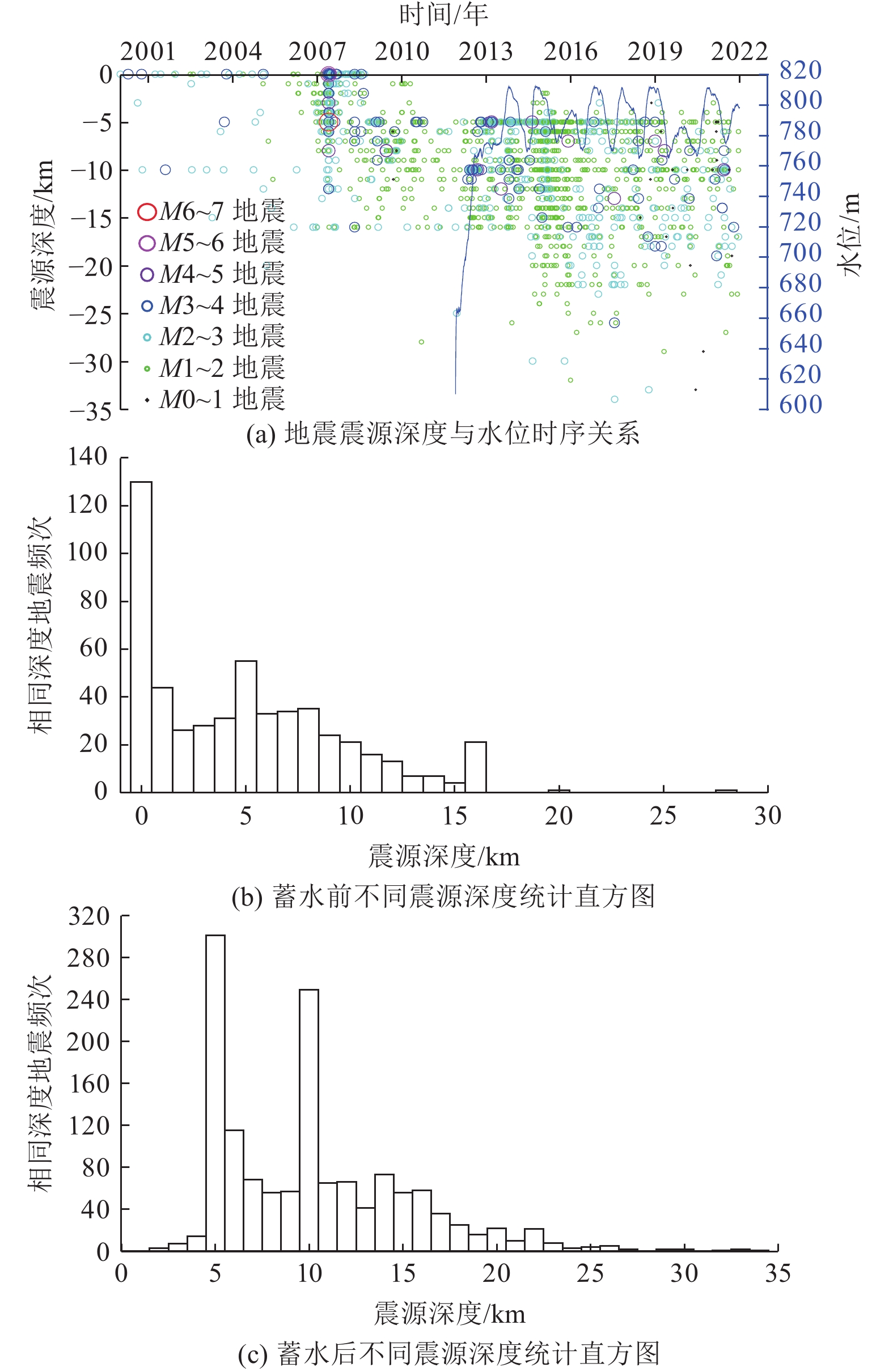
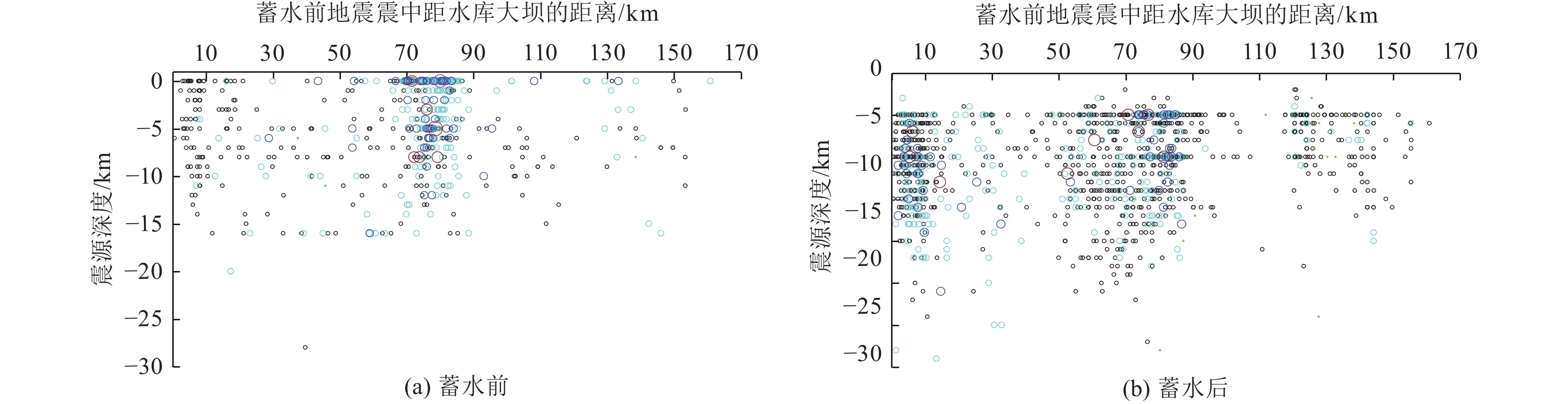
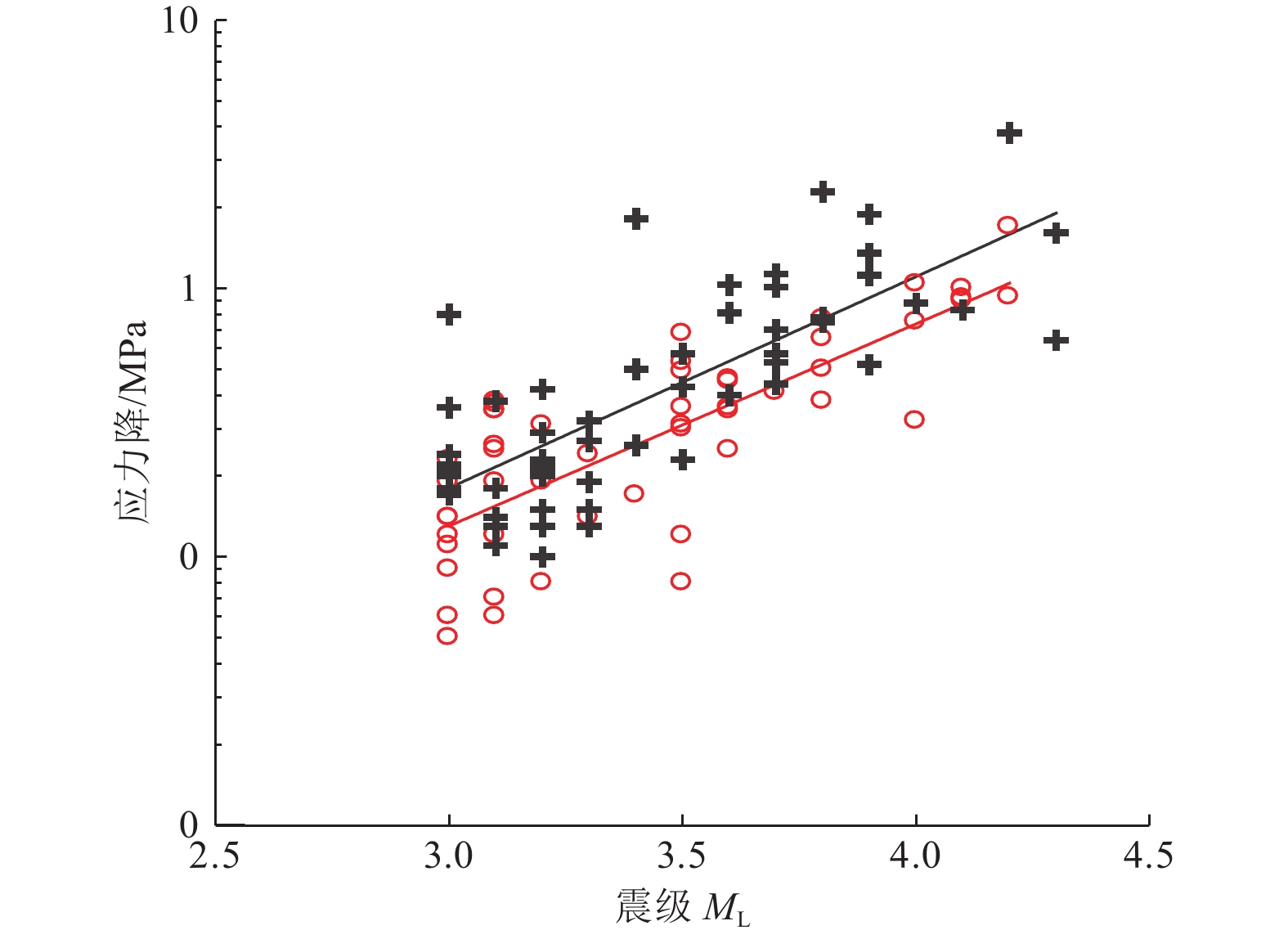
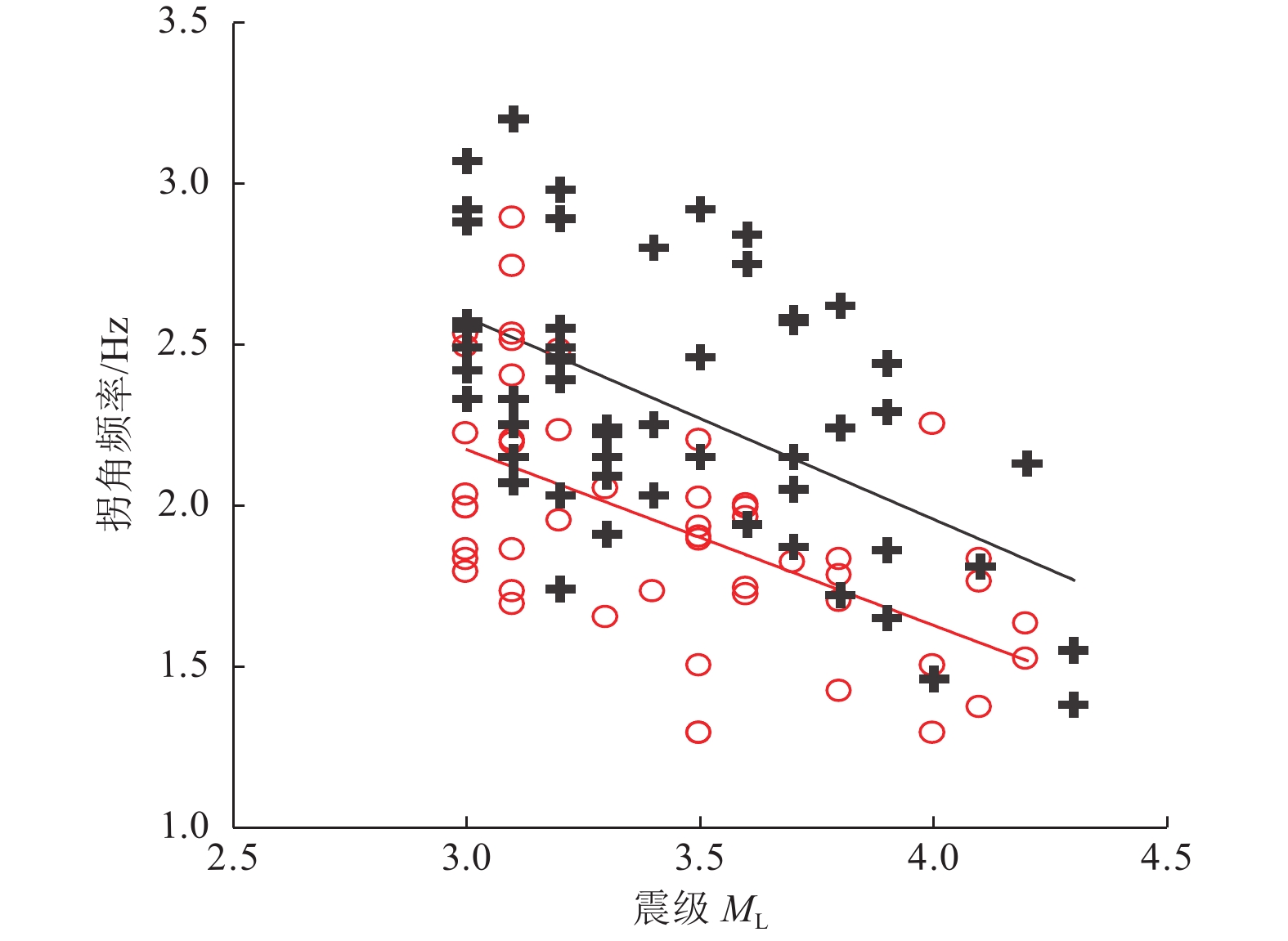
摘要: 糯扎渡水电站位于澜沧江中下游,该地区构造环境复杂,活动断层发育,地震频发。本文利用区域构造、糯扎渡库区水荷载变化、云南省区域地震台网2000—2021年地震监测资料,对糯扎渡水库区域断层性质、库水位荷载变化、地震震源参数和水库蓄水前后的地震活动空间等进行综合分析。研究结果表明,糯扎渡水库影响区及附近区域活断层密集,构造环境复杂且存在应力水平较高区域,蓄水前库区地震活动强度较高。伴随蓄水量的增加,微小地震活动频度和强度逐渐增强,显示出蓄水对库区内断层上的应力分布具有明显的扰动作用。蓄水后水库坝区附近和澜沧江库区中段窝拖寨断层区的地震活动频度和强度有所增强,普洱大河库段地震活动强度则低于区域背景地震,但微小地震活动的频度有所上升,且与库水位的周期性变化有一定的相关性。地震活动的空间位置与库区内复杂的构造断层密切相关。在区域构造应力和库区水加、卸载的共同作用下,构成了糯扎渡水库影响区微小地震时间、空间、强度的活动图像。未来区内地震活动仍将受到区域构造应力影响和水位变化及水的渗透作用影响,其地震活动强度可能达到5.0级左右。Abstract: Nuozhadu Hydropower Station (NHS) is located at the middle and lower reaches of the Lancang River, where the tectonic environment is complex with massive active faults and frequent earthquakes. In this paper we comprehensively analyzed the characteristics of regional faults, the variation of water level load in NHS, focal parameters, and the spatial distribution, frequency and intensity of seismicity before and after impoundment, based on the regional tectonics, the variation of water load, and the seismic monitoring data of Yunnan regional seismic network from 2000 to 2021. The results show that the affected areas in and around the reservoir have densely distributed active faults and tectonic environment with high stress level, and higher intensity of seismic activities before impoundment. The frequency and intensity of micro-seismic activities gradually increase on the rise of water level, indicating that water storage has a significant disturbance on the stress distribution along the faults. After impoundment, however, the intensity of seismic activities is lower than that of regional background earthquakes, but the frequency of micro-earthquakes increases and intensifies, which is correlated with the periodic change of reservoir water level. The spatial distribution of seismic activities is closely related to the complex faults in the area. The activity pattern of time, space and intensity of micro-earthquakes in the affected area of NHS are constructed by the joint action of regional tectonic stress and water loading and unloading. Seismicity in the region will still respond to the regional tectonic stress, the change of water level and the infiltration of water in the future and the magnitude may reach about M5.0.1)
1 2 叶建庆、李勇、徐誉宸等,2018.糯扎渡库区及邻区水库地震监测总结与地震活动特征研究报告(2008年—2017年). -
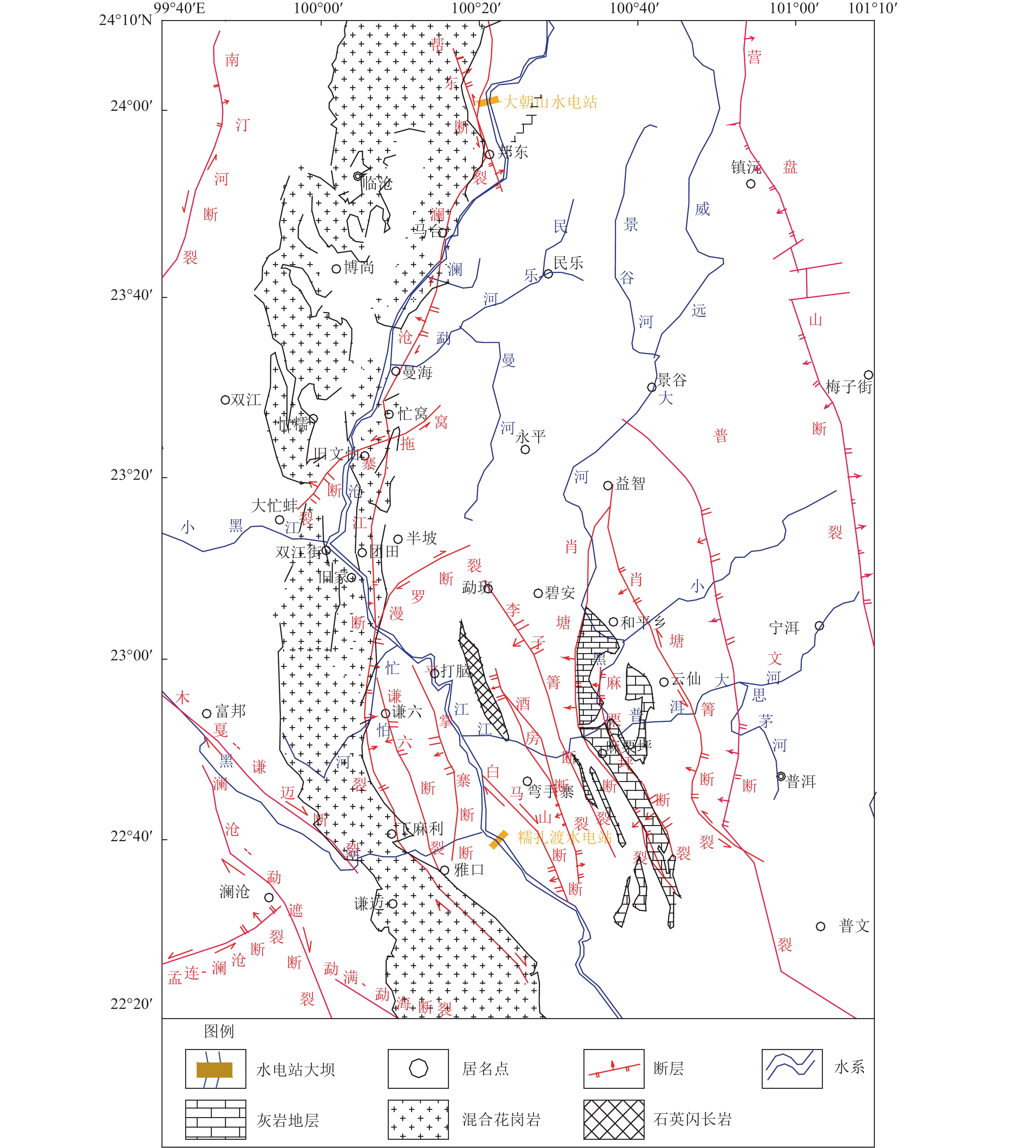
表 1 糯扎渡库区及邻近地区主要断裂活动特征
Table 1. Major faults activity characteristics of Nuozhadu hydropower station and affected area
断裂名称 断裂长度/km 产状 断裂性质 最新活动年代 地震活动 走向 倾向 倾角/(°) 澜沧江断裂 800 NNW SE 近直立,
微向西倾右旋走滑 10万年以内 永平、鲁史附近发生过5.5级地震 南汀河断裂 210 NE — 40~50 左旋走滑压扭 第四纪 1941年耿马大寨7级地震、1988年11月7.2级地震 营盘山断裂 140 NS SE 60 — 更新世 第四纪以来活动减弱 邦东断裂 50 NW NE 40~70 左旋,北为正断,
南为逆断10万年以内 历史上发生过多次中震 窝拖寨断裂 26.5 NE NW — 左旋 全新世 现代有多次中震记载 漫罗断裂 38 NE — — 平移断层 — — 孟连-澜沧断裂 150 NE NW 70~80 左旋 全新世 1952年孟连-澜沧交界6.5级地震、1984年4月
孟连6.4级地震、1995年7月中缅边境7.3级地震木戛-谦迈断裂 120 NW SW/NE 60~80 右旋走滑 全新世 1988年澜沧7.6级地震 澜沧-勐遮断裂 160 NW SW 60~80 右旋走滑 全新世 1988年11月6日澜沧-耿马7.6级地震的6.7级强余震
发生在断裂北段,现代小震活动频繁谦六断裂 92 SN W — 逆断 中更新世中晚期 — 平掌寨断裂 90 NS W/E — 正断层、逆断 前第四纪 近现代无地震记载 白马山断裂 35 NW SW — 正倾滑断裂 中更新世中期 断裂东侧现代有地震活动记载 酒房断裂 50 NNW NE 80 逆断 中更新世 断裂中段有中震记载 普文断裂 220 NNW — — — — 2014年12月7日普文断裂北西(隐伏)延长段上发生的
景谷6.6级地震是距今最近的一次强震肖塘断裂 100 SE W 45 逆断 前第四纪 现代有中强震记载 肖塘箐断裂 — NS W — 压扭左旋 第四纪 断裂中段东侧及南段现代有强震记载 麻栗坪断裂 40 NNW SW — 逆断 第四纪 断裂中段东侧现代有中强震记载,断裂南段有小震记载 李子箐断裂 40 NW SW — 逆断 第四纪 断裂南段近代有中强震记载 表 2 糯扎渡水库蓄水后水位年变幅度
Table 2. Annual variation of water level after Nuozhadu hydropower station impoundment
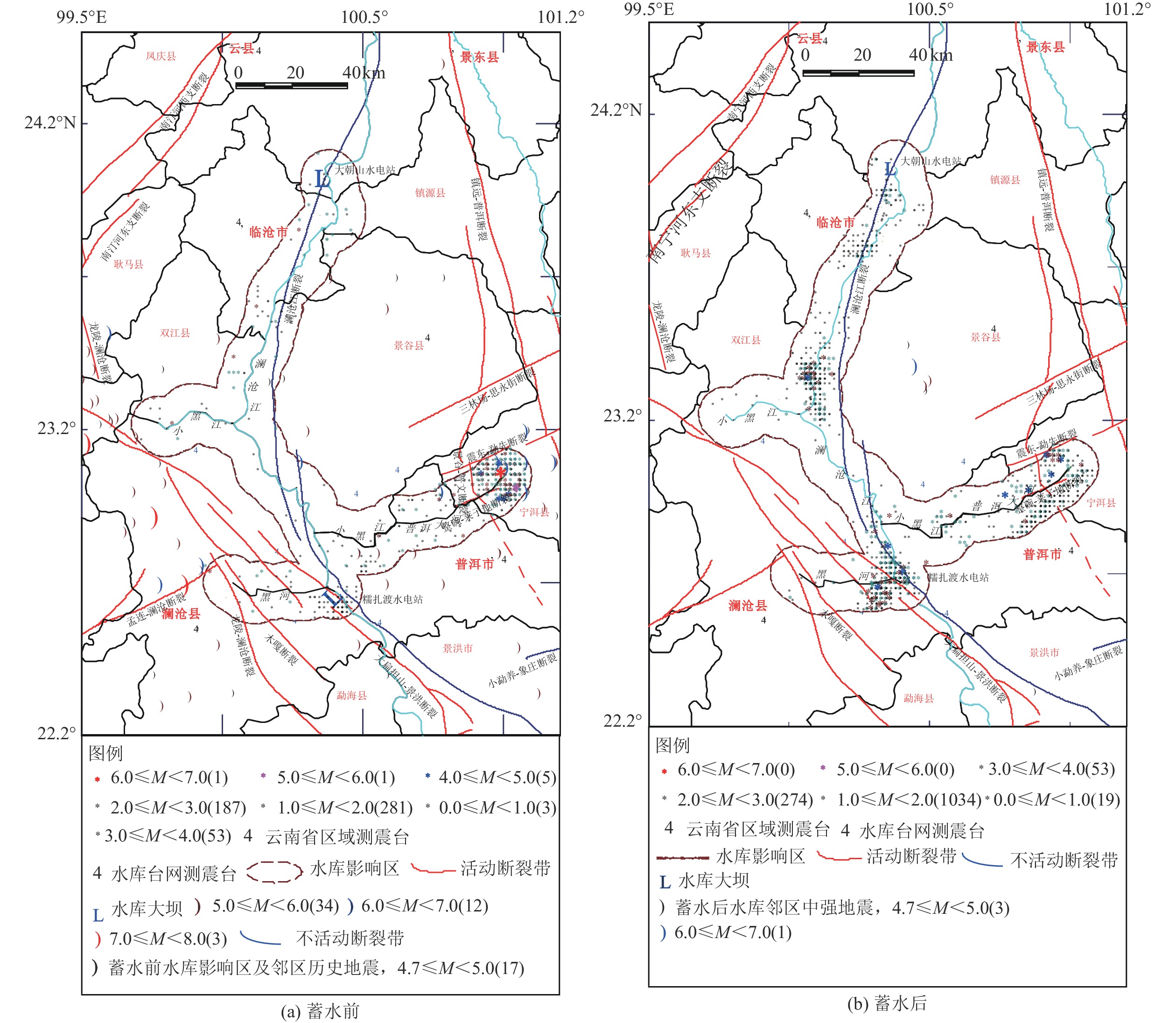
年份/年 极低位时间/(年-月-日) 极低位值/m 极高位时间/(年-月-日) 极高位值/m 变化幅度/m 2011 2011-11-29 610.33 2011-12-17 666.23 55.90 2012 2012-01-02 663.04 2012-12-31 774.69 111.65 2013 2013-03-16 771.27 2013-10-18 812.09 40.82 2014 2014-06-16 769.35 2014-10-24 812.34 42.99 2015 2015-07-01 770.05 2015-12-31 795.26 35.41 2016 2016-06-05 770.38 2016-11-01 812.31 41.93 2017 2017-07-04 770.03 2017-10-26 811.73 41.70 2018 2018-06-06 765.12 2018-10-30 811.93 46.81 2019 2019-06-19 765.40 2019-01-29 811.12 45.72 2020 2020-06-26 766.70 2020-12-03 811.61 44.91 2021 2021-07-05 774.97 2021-10-21 807.54 32.57 表 3 蓄水后糯扎渡水库影响区内地震活动情况
Table 3. Seismic activity after impoundment in Nuozhadu hydropower station adjacent region
年份/年 频次/次 最小震级/级 3.0级以上地震
次数/次最大地震发震时间/
(年-月-日)震级/级 震源深度/km 距坝区距离/km 距库岸距离/km 震中参考位置 2012 189 1.0 12 2012-09-18 4.2 10 82.0 0.5 窝拖寨断裂 2013 176 1.1 12 2013-07-21 4.2 12 53.0 4.8 普洱大河支库附近 2014 183 1.0 6 2014-08-27 4.1 5 71.0 8.0 普洱大河支库尾段 2015 327 1.0 4 2015-12-08 4.0 7 6.2 2.0 黑河支库附近 2016 101 1.0 2 2016-11-06 3.8 5 75.0 5.0 普洱大河支库尾段 2017 97 1.0 4 2017-07-29 4.0 13 14.0 0.0 澜沧江主库段 2018 91 0.4 5 2018-08-28 3.8 5 76.0 5.0 普洱大河支库尾段 2019 77 0.4 7 2019-01-06 4.1 7 74.0 3.0 普洱大河支库尾段 2019-05-11 4.1 8 61.0 1.0 普洱大河支库附近 2020 64 0.7 2 2020-03-27 3.6 13 54.0 7.0 普洱大河支库附近 2021 81 0.4 8 2021-06-20 4.3 10 5.4 5.4 澜沧江主库附近 -
曹颖, 叶建庆, 李丹宁等, 2015. 云南省糯扎渡水库蓄水前后地震活动性研究. 地震研究, 38(2): 189—195Cao Y. , Ye J. Q. , Li D. N. , et al. , 2015. Study of seismicity in Nuozhadu reservoir area before and after the water storage. Journal of Seismological Research, 38(2): 189—195. (in Chinese) 常廷改, 胡晓, 2018. 水库诱发地震研究进展. 水利学报, 49(9): 1109—1122Chang T. G. , Hu X. , 2018. Research progress on reservoir induced earthquake. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 49(9): 1109—1122. (in Chinese) 陈厚群, 徐泽平, 李敏, 2009. 关于高坝大库与水库地震的问题. 水力发电学报, 28(5): 1—7Chen H. Q. , Xu Z. P. , Li M. , 2009. Discussion on the relationship between large reservoirs and seismicity. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 28(5): 1—7. (in Chinese) 国家地震局震害防御司, 1995. 中国历史强震目录(公元前23世纪-公元1911年). 北京: 地震出版社. 华卫, 陈章立, 郑斯华等, 2012. 水库诱发地震与构造地震震源参数特征差异性研究——以龙滩水库为例. 地球物理学进展, 27(3): 924—935 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.03.013Hua W. , Chen Z. L. , Zheng S. H. , et al. , 2012. Differences existing in characteristics of source parameters between reservoir induced seismicity and tectonic earthquake——a case study of Longtan reservoir. Progress in Geophysics, 27(3): 924—935. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.03.013 李志祥, 毛玉平, 谢建斌等, 2008. 糯扎渡水电站水库诱发地震预测. 地震研究, 31(S2): 633—641Li Z. X. , Mao Y. P. , Xie J. B. , et al. , 2008. Prediction of Earthquake Induced by Nuozhadu Reservoir in Yunnan. Journal of Seismological Research, 31(S2): 633—641. (in Chinese) 陆丽娟, 张帆, 黄树生等, 2014. 广西龙滩库区地震震源参数定标关系. 震灾防御技术, 9(S1): 648—656 doi: 10.11899/zzfy2014s111Lu L. J. , Zhang F. , Huang S. S. , et al. , 2014. Scaling relations of source parameters for moderate and small earthquake at Longtan reservoir in Guangxi Province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 9(S1): 648—656. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy2014s111 罗建伟, 李勇, 叶建庆, 2020. 溪洛渡水库影响区地震活动性分析. 地震研究, 43(1): 118—124Luo J. W. , Li Y. , Ye J. Q. , 2020. Seismic activity analysis in the Xiluodu reservoir affected area. Journal of Seismological Research, 43(1): 118—124. (in Chinese) 毛玉平, 王洋龙, 李朝才, 2004 a. 澜沧江中段水利枢纽工程水库诱发地震的地震地质环境分析. 地震研究, 27(S1): 63—69Mao Y. P. , Wang Y. L. , Li C. C. , 2004 a. Study on the seismogeological background of dam-induced earthquake of major dam along the middle segment of Lancang River. Journal of Seismological Research, 27(S1): 63—69. (in Chinese) 毛玉平, 王洋龙, 李朝才, 2004 b. 小湾库区水库诱发地震的地质环境分析. 地震研究, 27(4): 339—343Mao Y. P. , Wang Y. L. , Li C. C. , 2004 b. Seismo-geological ambiance analyses of reservoir-induced earthquake in Xiaowan area. Journal of Seismological Research, 27(4): 339—343. (in Chinese) 秦嘉政, 钱晓东, 叶建庆, 2012. 云南地震活动与数字地震台网. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 34(S2): 1—7Qin J. Z. , Qian X. D. , Ye J. Q. , 2012. Earthquake activity and the regional digital telemetric seismic network in Yunnan. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 34(S2): 1—7. (in Chinese) 苏有锦, 李永莉, 李忠华等, 2003. 川滇地区区域地震目录完整性最小震级分析. 地震研究, 26(S1): 10—16Su Y. J. , Li Y. L. , Li Z. H. , et al. , 2003. Analysis of minimum complete magnitude of earthquake catalog in Sichuan - Yunnan Region. Journal of Seismological Research, 26(S1): 10—16. (in Chinese) 中国地震局震害防御司, 1999. 中国近代地震目录(公元1912年-1990年 MS≥4.7). 北京: 中国科学技术出版社. 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 2008. GB/T 21075—2007 水库诱发地震危险性评价. 北京: 中国标准出版社.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. 2008. GB/T 21075—2007 Reservoir-induced earthquake hazard assessment. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 2015. GB/T 31077—2014 水库地震监测技术要求. 北京: 中国标准出版社.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. 2015. GB/T 31077—2014 Technical requirement of reservoir earthquake monitoring. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) Brune J. N. , 1970. Tectonic stress and the spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(26): 4997—5009. doi: 10.1029/JB075i026p04997 Carder D. S. , 1945. Seismic investigations in the Boulder Dam area, 1940-1944, and the influence of reservoir loading on local earthquake activity. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 35(4): 175—192. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0350040175 Simpson D. W. , Leith W. S. , Scholz C. H. , 1988. Two types of reservoir-induced seismicity. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 78(6): 2025—2040. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0780062025 Talwani P., 1997. On the nature of reservoir-induced seismicity. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 150(3—4): 473—492. -



 下载:
下载: