Data Flow Monitoring and Analysis of Earthquake Early Warning System
-
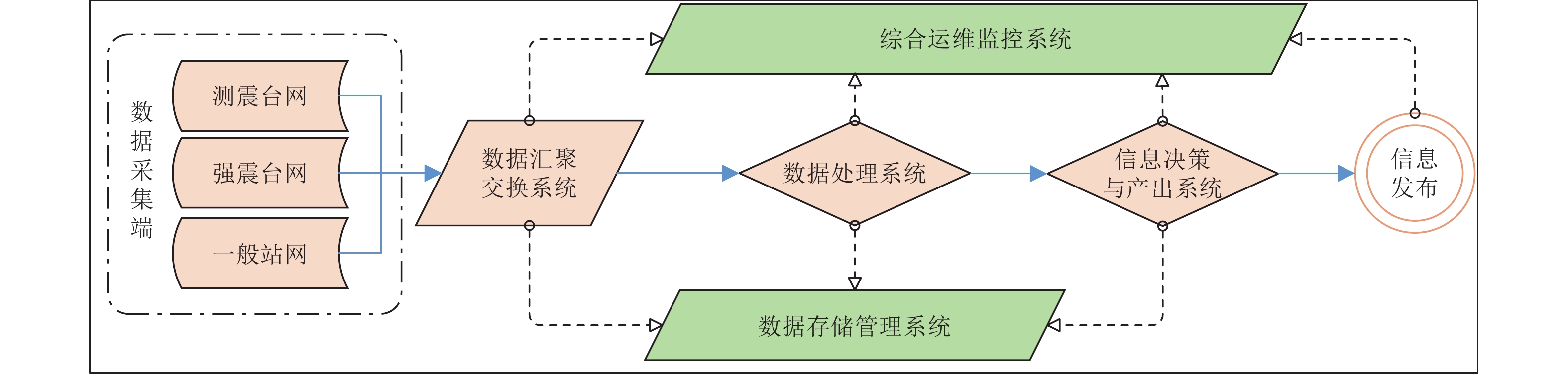
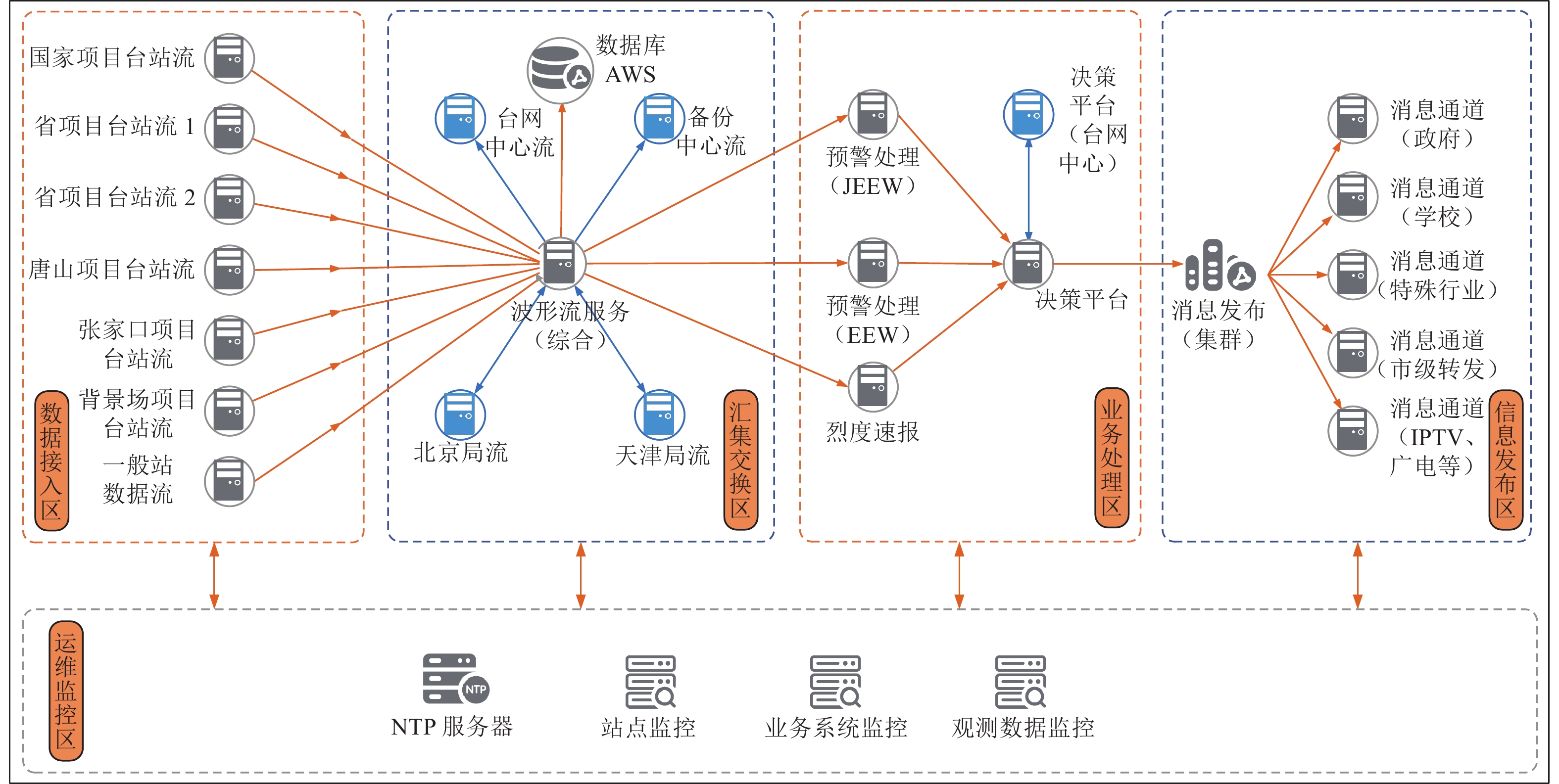
摘要: 为实现地震预警网络环境实时监控与分析,明确各业务系统之间的数据流向和范围,根据地震预警系统业务分区梳理关键业务、网段和终端,并通过数据流分析实现地震预警系统网络流量监控。通过数据包采集与解码技术,实现对主要业务系统关键指标的监控,从而对地震预警系统的网络访问性能、系统服务性能、应用响应性能等关键指标进行综合监控与分析,实现以业务为核心的网络环境监控与支撑。Abstract: This paper studies the data flow monitoring of the Earthquake Early Warning system based on the connection of the core components. We sort out the key servers, network segments and terminals of the EEW system, and then analysis the data flow, extract key indicators by data packet acquisition and decoding technology, so as to comprehensively monitor and analyze the key performance indicators such as network access performance, system service performance and application response performance of the full life cycle of EEW system.
-
表 1 核心应用
Table 1. List of core applications
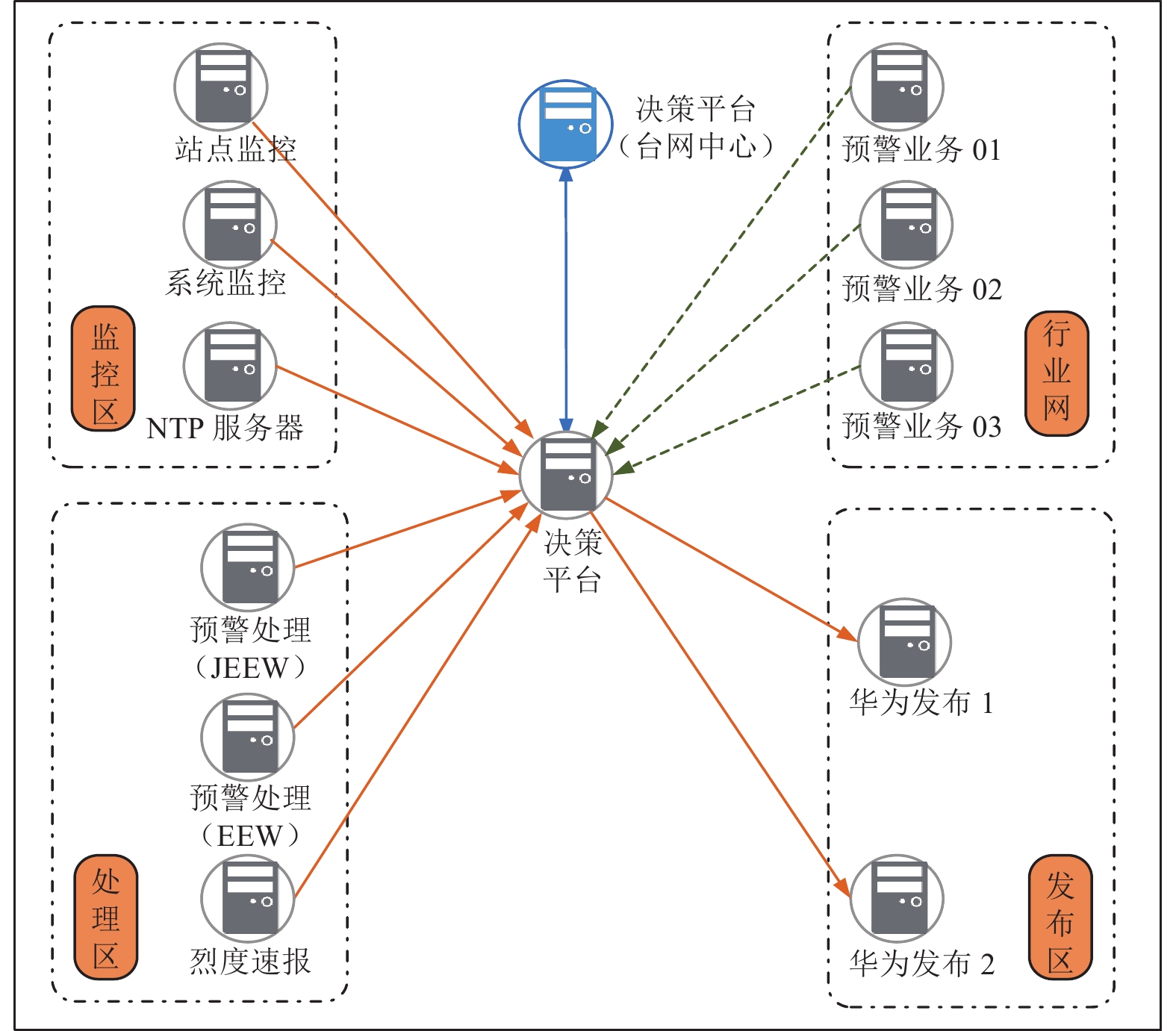
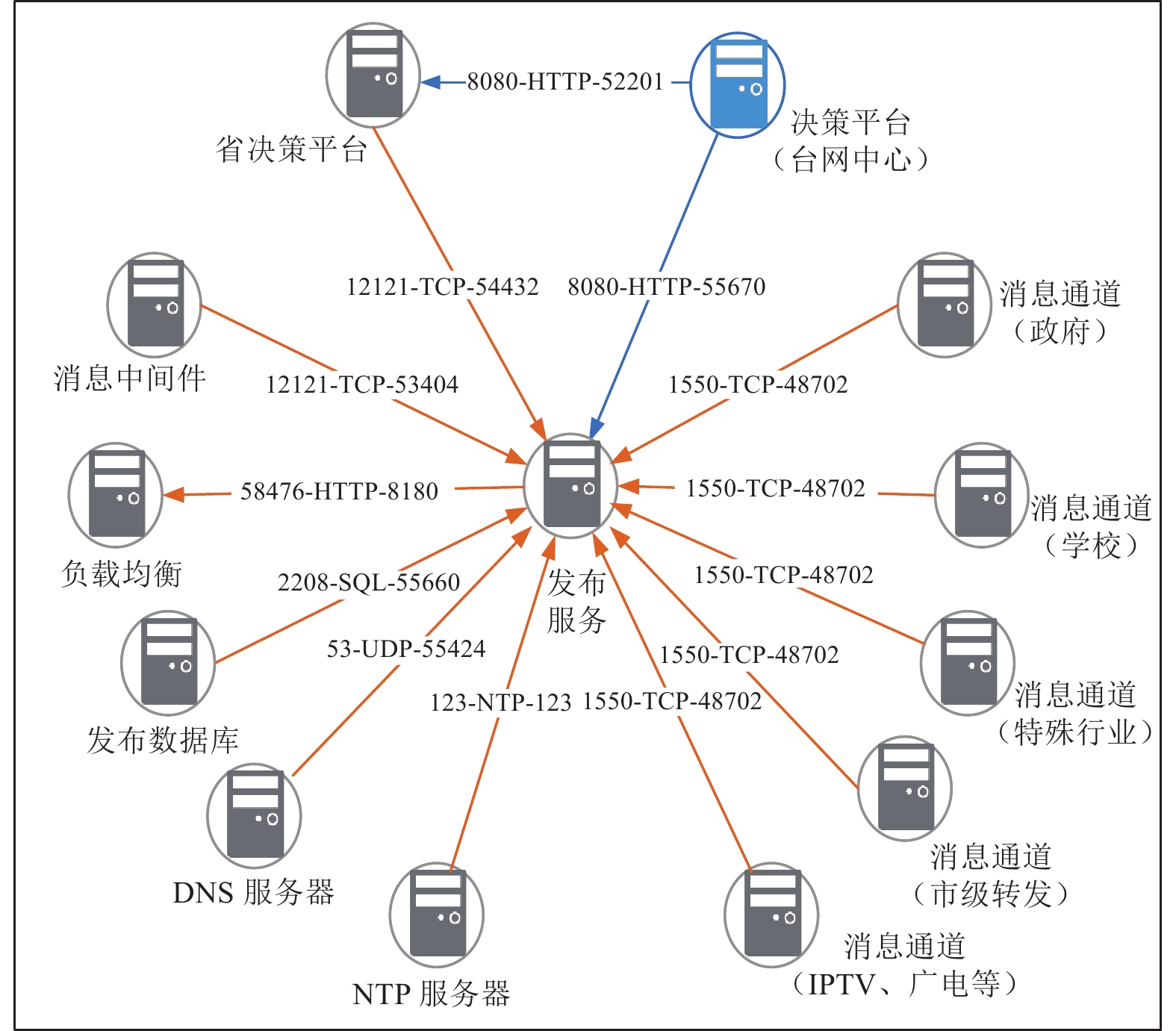
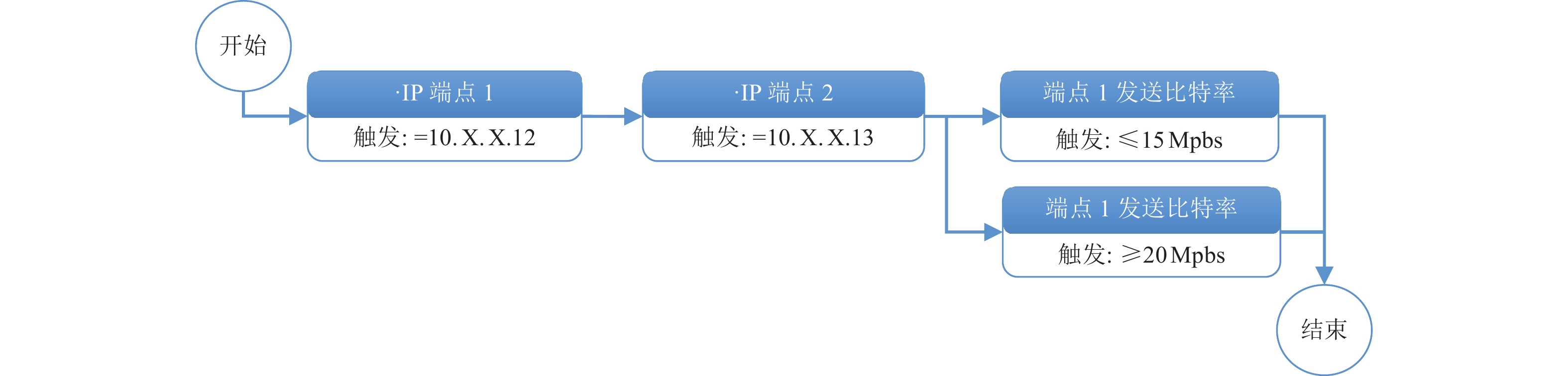
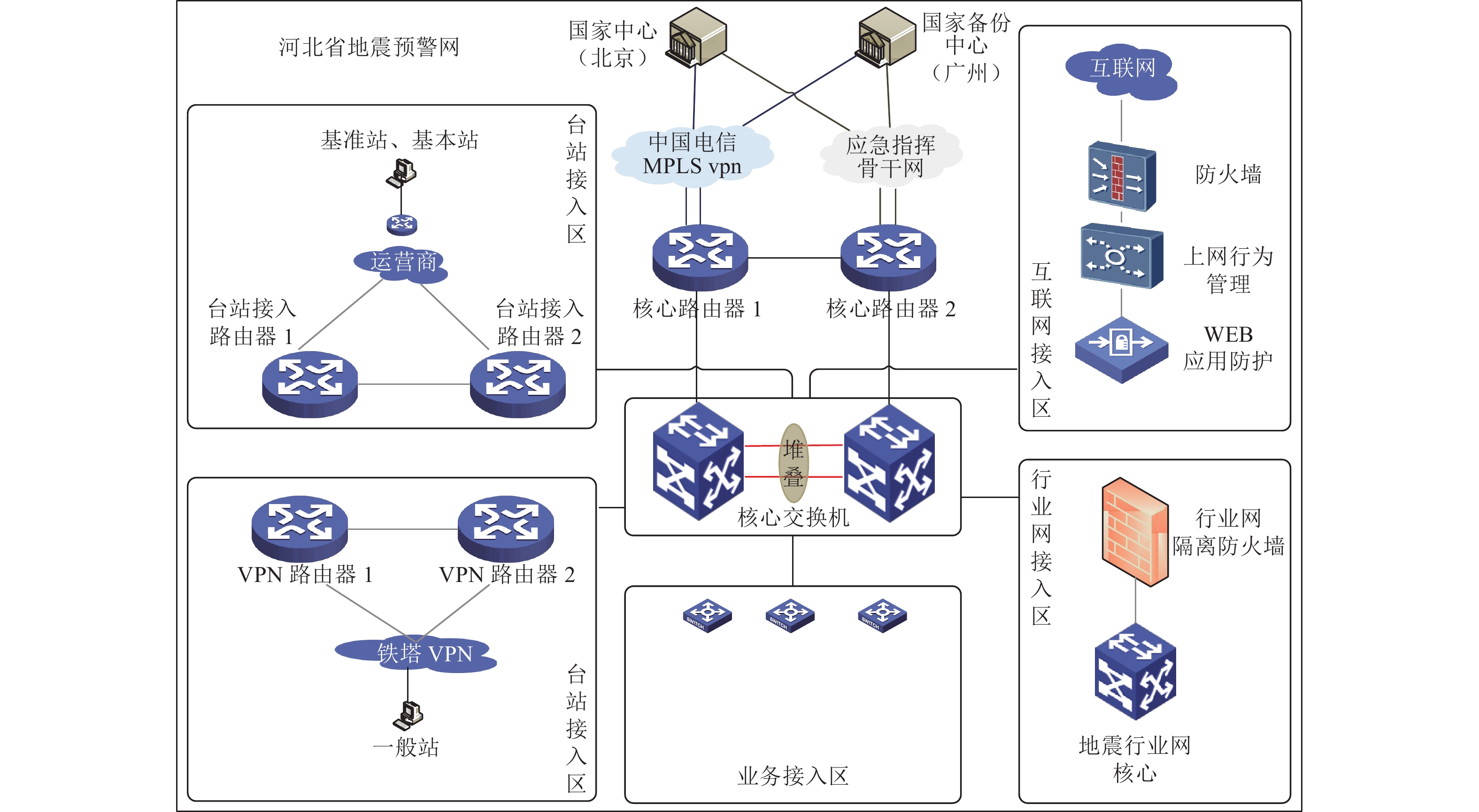
业务分区 分系统部署单元 部署方式 IP地址 数据接入区 波形流服务(分流服务) 物理机 10.×.×.5(国家项目台站流) 10.×.×.6(省项目台站流1) 10.×.×.7(省项目台站流2) 10.×.×.8(唐山台站流) 10.×.×.9(张家口台站流) 10.×.×.10(背景场台站流) 10.×.×.11(一般站) 汇集交换区 波形流服务(综合) 物理机 10.×.×.12 波形流服务(触发流) 物理机 10.×.×.13 波形流服务(台网中心) 未知 10.×.×.14 波形流服务(备份中心) 未知 10.×.×.15 波形流服务(北京局) 未知 10.×.×.16 波形流服务(天津局) 未知 10.×.×.17 业务处理区 预警处理软件(JEEW) 物理机 10.×.×.18 预警处理软件(EEW) 物理机 10.×.×.19 烈度速报 物理机 10.×.×.20 决策平台 物理机 10.×.×.21 决策平台(台网中心) 未知 10.×.×.22 数据存储区 数据存储AWS 物理机 10.×.×.23 信息发布区 信息发布子系统 集群 10.×.×.24;10.×.×.25 消息中间件 主备 10.×.×.26 消息通道:预警终端政府 集群 10.×.×.27 消息通道:预警终端学校 集群 10.×.×.28 消息通道:PC端、通信运营商、新闻媒体通道、特殊行业通道 集群 10.×.×.29 消息通道:市级转发通道 集群 10.×.×.30;10.×.×.31 Nginx(负载均衡) 主备 10.×.×.32 MYSQL(紧急地震信息服务) 主备 10.×.×.12 预警转发平台(IPTV、广电等预警信息发布) 集群 10.×.×.33 运维监控区 站点监控 集群(负载均衡) 10.×.×.34 业务系统监控/预警终端 10.×.×.35 观测数据监控 主备 10.×.×.36 NTP 单机 10.×.×.37 表 2 预警业务网段划分
Table 2. Network segments of EEW system
地址段划分 业务分区 VLAN 网关 10.×.0.0/24 专线预警发布区(接入政府专线) 2100 10.×.0.254 10.×.1.0/24 互联网对外发布区 2101 10.×.1.254 10.×.2.0/24 DMZ区 2102 10.×.2.254 10.×.7.0/24 预警数据交换区 2107 10.×.7.254 10.×.8.0/24 预警数据处理区 2108 10.×.8.254 10.×.9.0/24 预警数据存储与备份区 2109 10.×.9.254 10.×.10.0/24 预警运行监控与展示区 2110 10.×.10.254 10.×.11.0/24 预警数据信息服务区 2111 10.×.11.254 10.×.13.0/24 预警系统安全管理区 2113 10.×.13.254 10.×.63.0/24 测试区 2163 10.×.63.254 表 3 预警台站网段划分
Table 3. Network segments of EEW stations
地市 台站数 网段 总带宽/Mbps 廊坊 9 15.×.4.0/22 18 保定 17 15.×.8.0/22 34 邢台 16 15.×.12.0/22 32 唐山 13 15.×.16.0/22 26 沧州 13 15.×.20.0/22 26 邯郸 15 15.×.24.0/22 30 衡水 11 15.×.28.0/22 22 承德 5 15.×.32.0/22 10 石家 4 15.×.36.0/22 8 张家口 34 15.×.40.0/22 68 表 4 监控指标
Table 4. Network monitoring metrics
监控类别 监控指标名称 网络性能 数据流量
(上行和下行)3次握手平均RTT
(客户端、服务端)ACK时延
(客户端、服务端)丢包率 重传率 丢包重传比 应用性能 响应时间 超时比例 交易次数 交易响应率 主机性能 会话数量 连接状态 服务器窗口尺寸 客户端窗口尺寸 表 5 主要应用监控指标
Table 5. Monitoring metrics of core applications
类别 监控指标 波形流服务
(综合)台网中心流交换 广东流服务
(备份)北京流交换 波形流服务
(分流)流服务
(一般站)决策
系统连接类型 长连接 长连接 长连接 长连接 长连接 短连接 短连接 网络性能 比特率/Mbps 142.84 21.85 22.49 19.30 6.20 9.54 0.064 上行比特率/Mbps 1.79 20.07 20.45 16.28 2.14 8.37 0.032 下行比特率/Mbps 141.05 1.79 2.05 3.02 4.06 1.18 0.032 客户端平均ACK时延/ms 2.85 1 693.50 0.00 1.86 1.27 282.38 29.08 服务器平均ACK时延/ms 1.18 15.95 39.41 0.00 26.04 34.30 33.10 TCP重传率/% 0.09 0 0.03 0 0 0.39 0 应用性能 平均响应时间/ms 0.39 0 0 0 0 1.48 0.31 服务器响应平均传输时间/ms 0.05 0 0 0 0 137.73 1.13 主机性能 活动会话数 10 1 1 1 134 552 10 客户端平均窗口大小/KB 662.78 1.00 1.00 164.92 9.38 18.82 382.75 服务器平均窗口大小/KB 37.33 5.45 25.48 64.19 8.32 62.77 56.84 注:监控时间段为2022年3月15日08:05—2022年3月15日08:10。 表 6 台站链路监控指标
Table 6. Monitoring metrics of station links
地市 台站数 数据流量/Kbps 上行流量/Kbps 上行丢包数/个 TCP重传率/% 客户端3次握手
平均RTT/ms服务器3次握手
平均RTT/ms平均ACK
时延/ms廊坊 9 161.78 141.77 1 386 0 13.33 0.01 20.73 张家口 34 492.07 453.99 44 0 16.70 75.95 38.07 保定 17 324.12 288.55 2 278 0.01 71.19 1.29 19.47 邢台 16 285.91 250.55 2 856 0 8.11 0.17 20.54 唐山 13 251.64 231.60 1 862 0 165.34 1.29 25.08 沧州 13 229.89 203.44 9 675 0.01 45.67 0.59 20.24 邯郸 15 218.83 201.43 0 0 82.60 0.22 39.12 衡水 11 207.44 184.05 1 539 0 4.24 0.43 19.72 承德 5 89.99 83.03 217 0.01 11.66 4.62 27.13 石家庄 4 81.67 73.84 549 0.02 1.27 0.28 18.11 -
陈军华, 王忠民, 2006. BGP/MPLS VPN实现原理. 计算机工程, 32(23): 124—126Chen J. H. , Wang Z. M. , 2006. Theory and implementation of BGP/MPLS VPN. Computer Engineering, 32(23): 124—126. (in Chinese) 陈琳, 南洋, 2017. 一种面向大规模系统域网络性能管理系统. 计算机工程与科学, 39(9): 1588—1593Chen L. , Nan Y. , 2017. A performance management system for large-scale system area networks. Computer Engineering & Science, 39(9): 1588—1593. (in Chinese) 凯文 R. 福尔, W. 理查德·史蒂文斯, 2016. TCP/IP详解-卷1: 协议. 吴英, 张玉, 许昱伟, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 423—427Fall K. R., Stevens W. R., 2016. TCP/IP illustrated-volume 1: the protocols. Wu Y., Zhang Y., Xu Y. H., trans. Beijing: China Machine Press, 423—427. (in Chinese) 刘恩海, 刘微, 樊世燕等, 2015. 增强的NetFlow数据采集系统设计与实现. 计算机工程与设计, 36(5): 1150—1155Liu E. H. , Liu W. , Fan S. Y. , et al. , 2015. Design and implementation of enhanced Netflow data collection system. Computer Engineering and Design, 36(5): 1150—1155. (in Chinese) 孙路强, 张春莉, 徐小远等, 2020. 地震综合信息多渠道发布系统设计与实现. 震灾防御技术, 15(3): 563—570Sun L. Q. , Zhang C. L. , Xu X. Y. , et al. , 2020. Design and implementation of multi-channel release system of seismic comprehensive information. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(3): 563—570. (in Chinese). 王红蕾, Walter M. , 高景春等, 2019. 美国地震预警系统ShakeAlert测试与评估. 国际地震动态, (5): 17—25Wang H. L. , Walter M. , Gao J. C. , et al. , 2019. Instruction of earthquake early warning ShakeAlert testing platform. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (5): 17—25. (in Chinese) 王俊, 刘红桂, 周昱辰, 2021. 地震预警技术的应用与展望. 防灾减灾工程学报, 41(4): 874—882Wang J. , Liu H. G. , Zhou Y. C. , 2021. Application and prospect of earthquake early warning technology. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 41(4): 874—882. (in Chinese) 王颀, 刘丰, 张彬等, 2021. SNMP与NetStream流量监控方法的对比分析. 海洋信息, 36(3): 18—25Wang Q. , Liu F. , Zhang B. , et al. , 2021. Comparative analysis of SNMP and netstream traffic monitoring methods. Marine Information, 36(3): 18—25. (in Chinese) 许可, 郭巍, 高也等, 2019. 天津简易烈度计地震预警试验区建设. 震灾防御技术, 14(2): 456—463Xu K. , Guo W. , Gao Y. , et al. , 2019. Development of simple intensity meter in Tianjin early warn experimental site. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(2): 456—463. (in Chinese) 张红才, 金星, 李军等, 2013. 地震预警系统研究及应用进展. 地球物理学进展, 28(2): 706—719Zhang H. C. , Jin X. , Li J. , et al. , 2013. Progress of research and application of earthquake early warning system (EEWs). Progress in Geophysics, 28(2): 706—719. (in Chinese) Allen R. M. , Melgar D. , 2019. Earthquake early warning: advances, scientific challenges, and societal needs. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 47: 361—388. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-053018-060457 Ganguli S., Bhalla V., Prasad P., 2018. Gartner magic quadrant for network performance monitoring and diagnostics. (2018-02-21)[2022-04-21].https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3859467. Given D. D., Allen R. M., Baltay A. S., et al., 2018. Revised technical implementation plan for the ShakeAlert system—An earthquake early warning system for the West Coast of the United States. Reston: USGS, 15—17. Peng C. Y. , Jiang P. , Ma Q. , et al. , 2022. Chinese nationwide earthquake early warning system and its performance in the 2022 Lushan M6.1 earthquake. Remote Sensing, 14(17): 4269. doi: 10.3390/rs14174269 Saito H. , Chusho T. , 2005. Development of performance evaluation system for network systems by client observation. Electronics and Communications in Japan (Part I: Communications), 88(2): 71—80. doi: 10.1002/ecja.20083 Siswanto A., Syukur A., Kadir E. A., et al., 2019. Network traffic monitoring and analysis using packet sniffer. In: 2019 International Conference on Advanced Communication Technologies and Networking (CommNet). Rabat: IEEE, 1—4. -



 下载:
下载: