Research on Regional Stacking of Broadband Seismic Records at Hongshan Station in Hebei Province
-
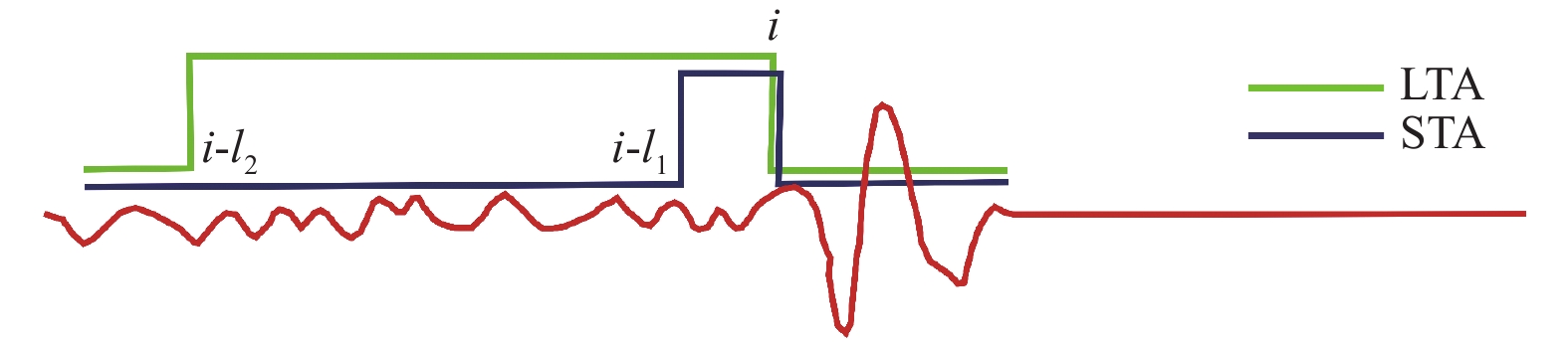
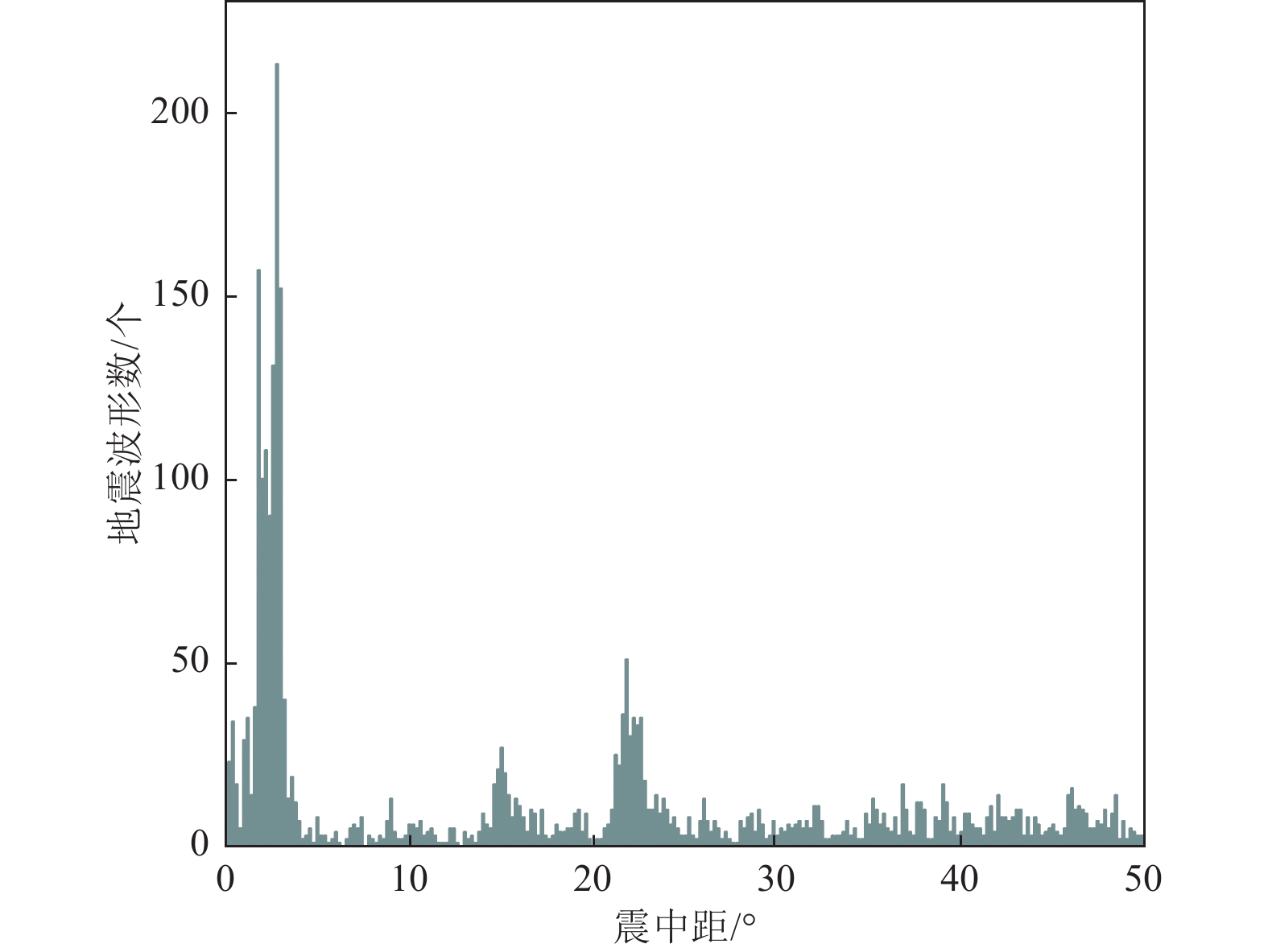
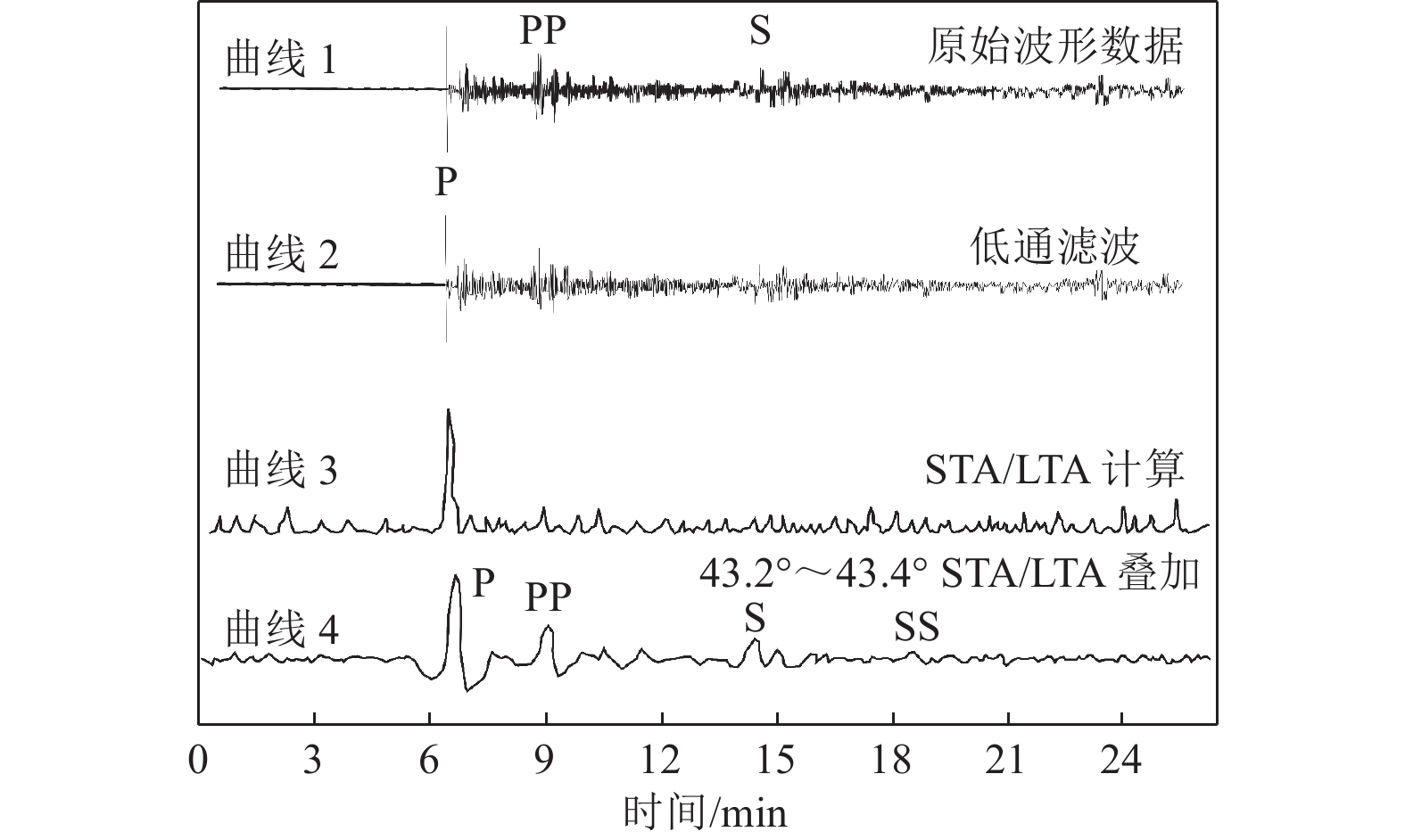
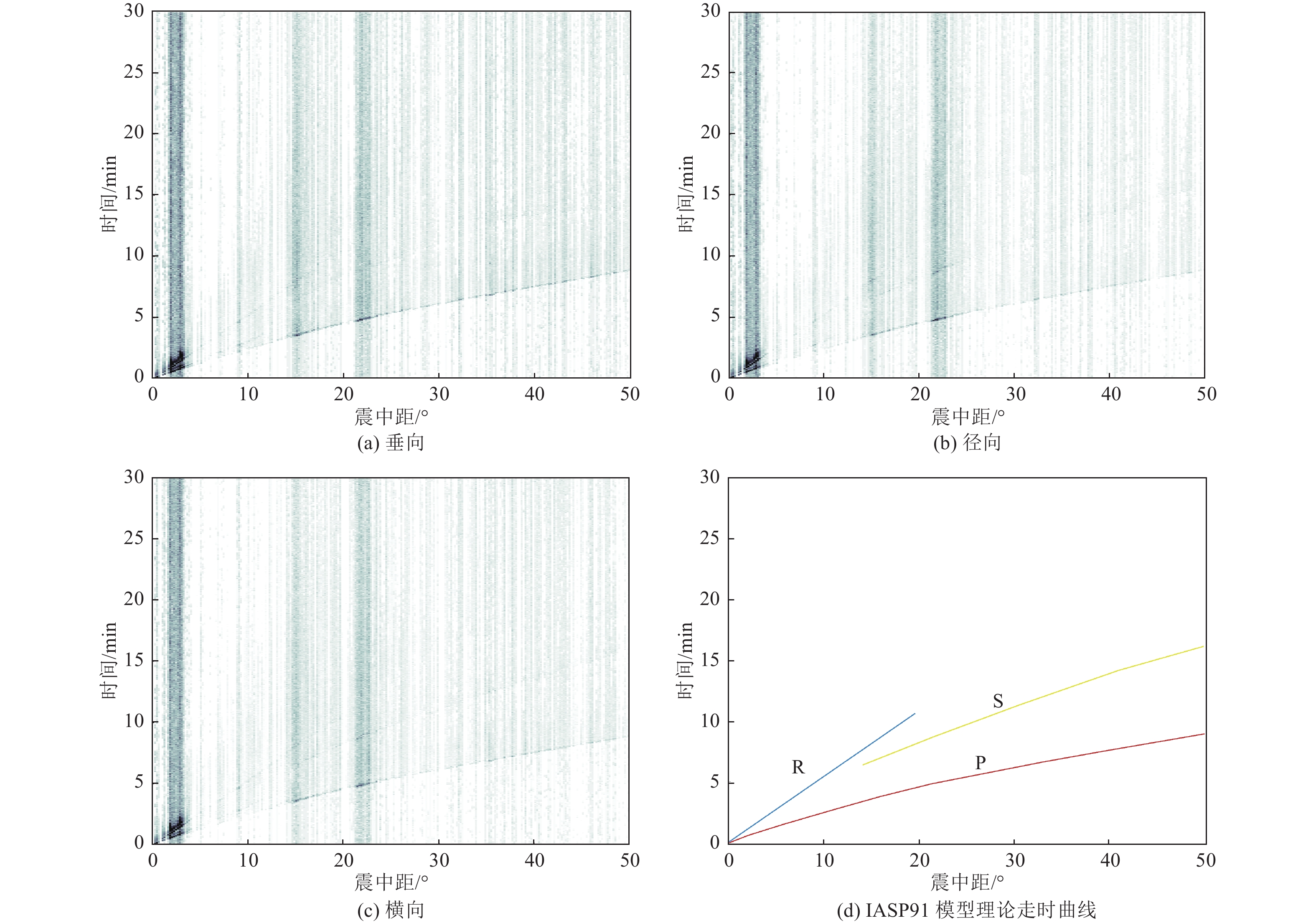
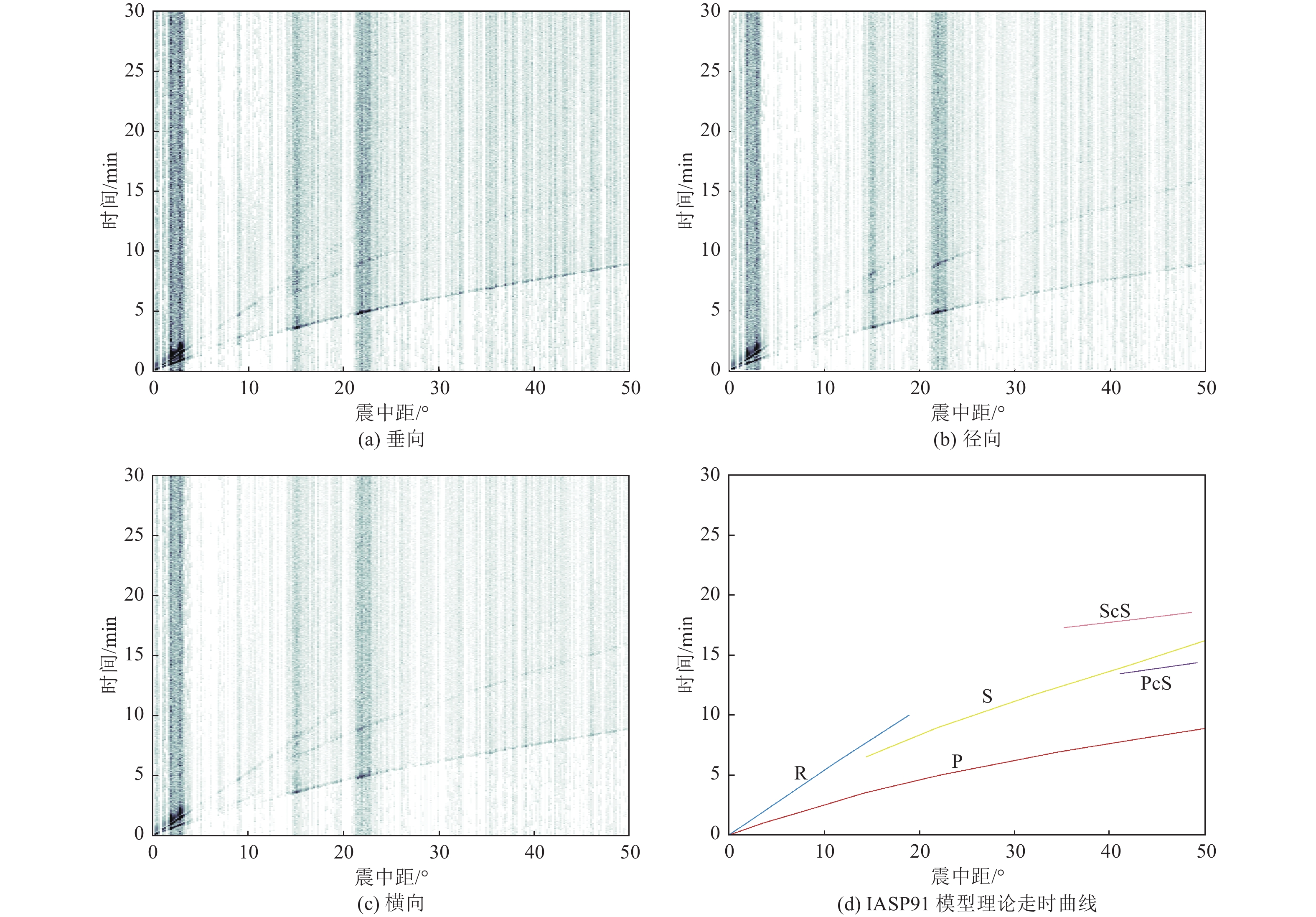
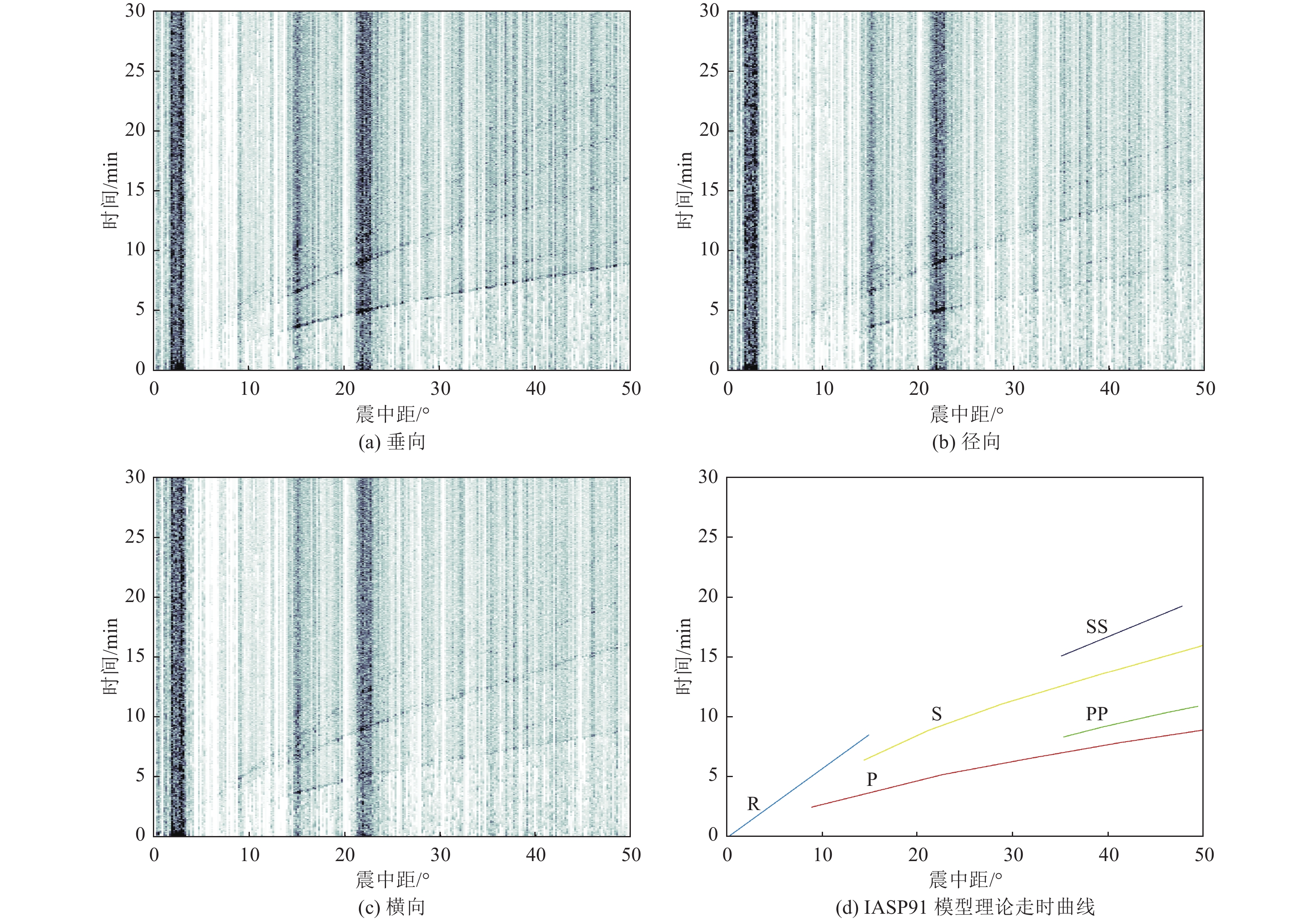
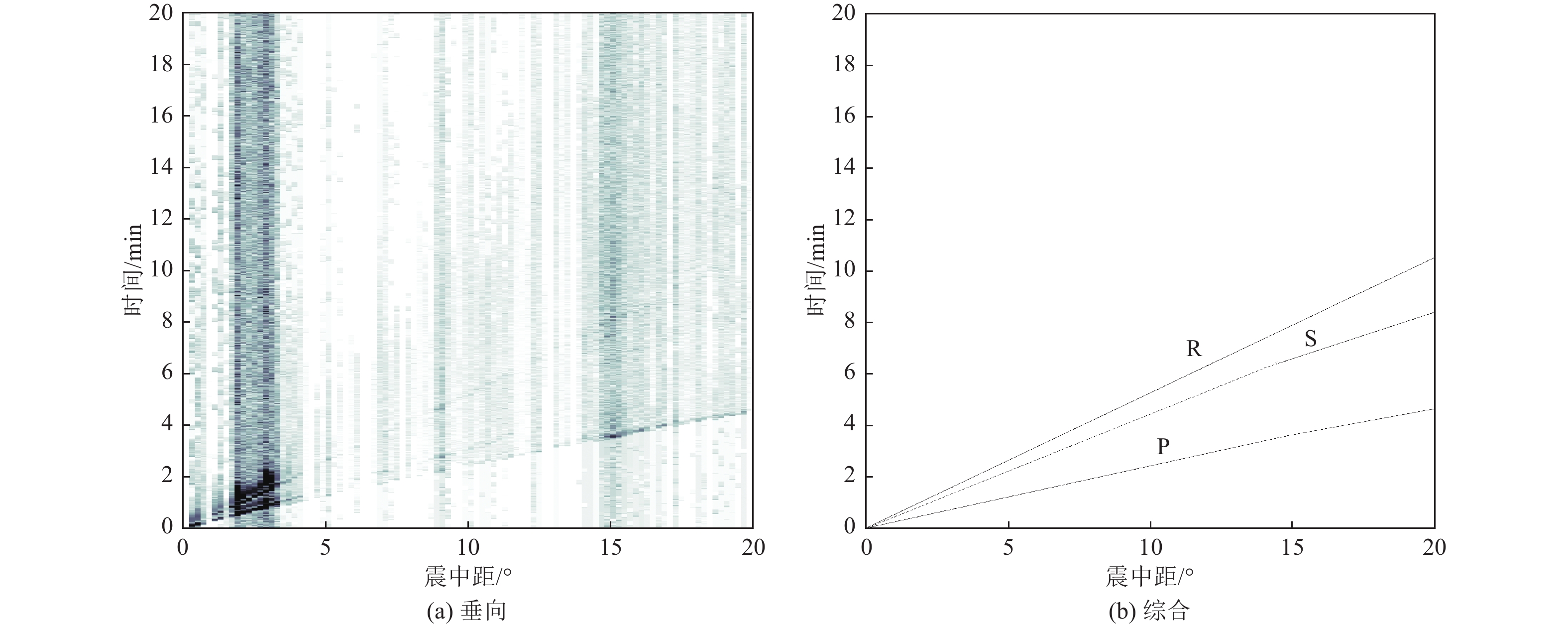
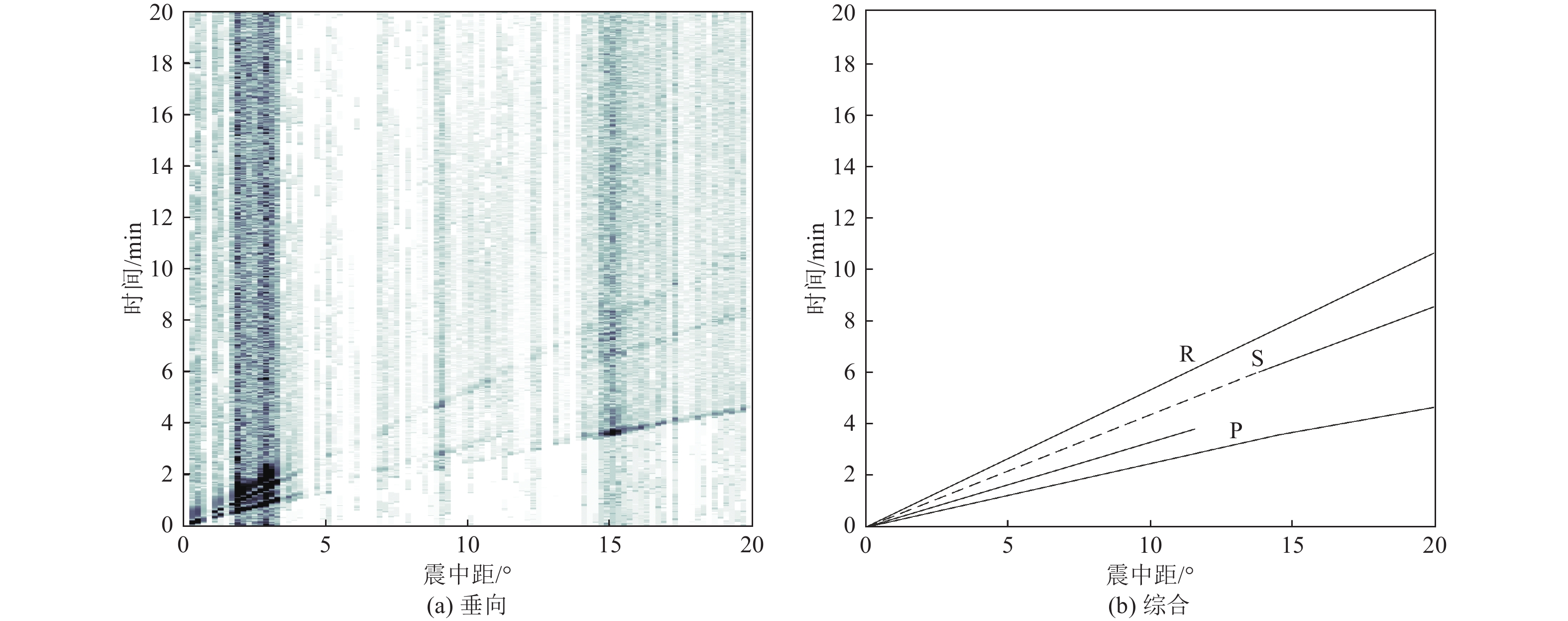
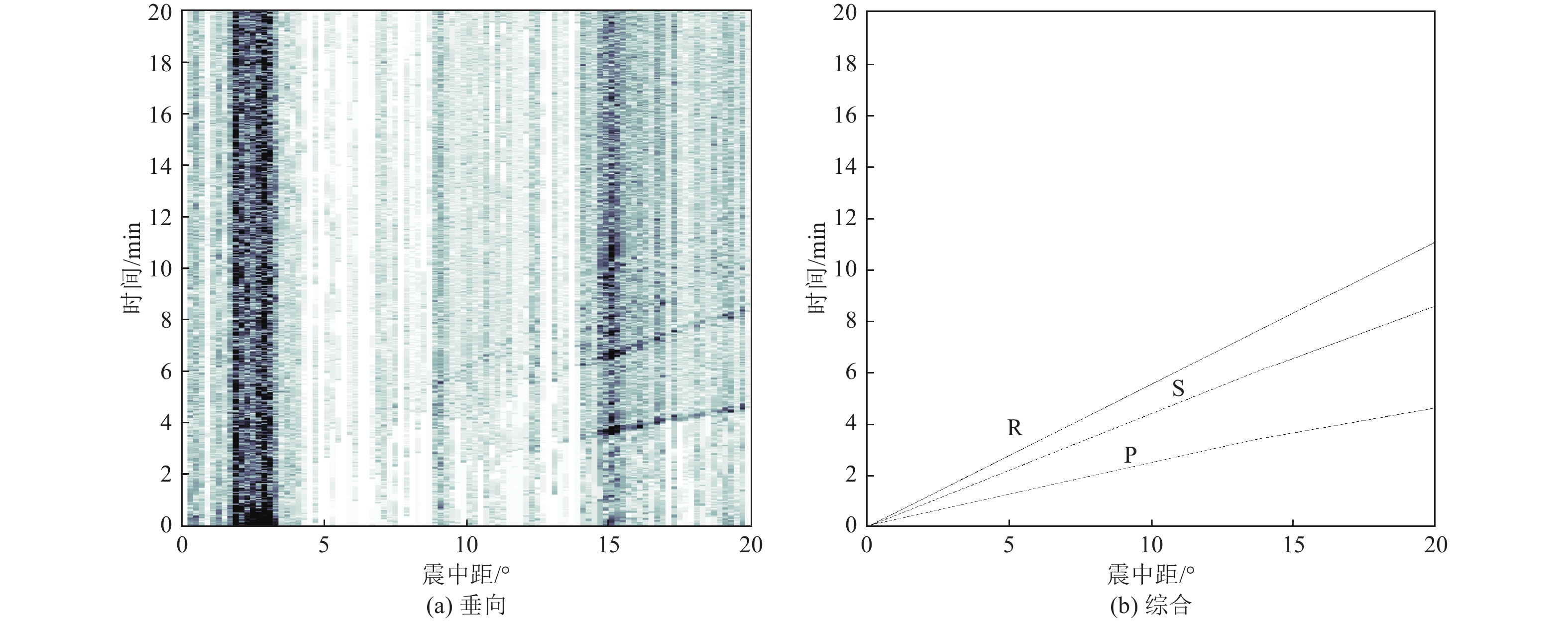
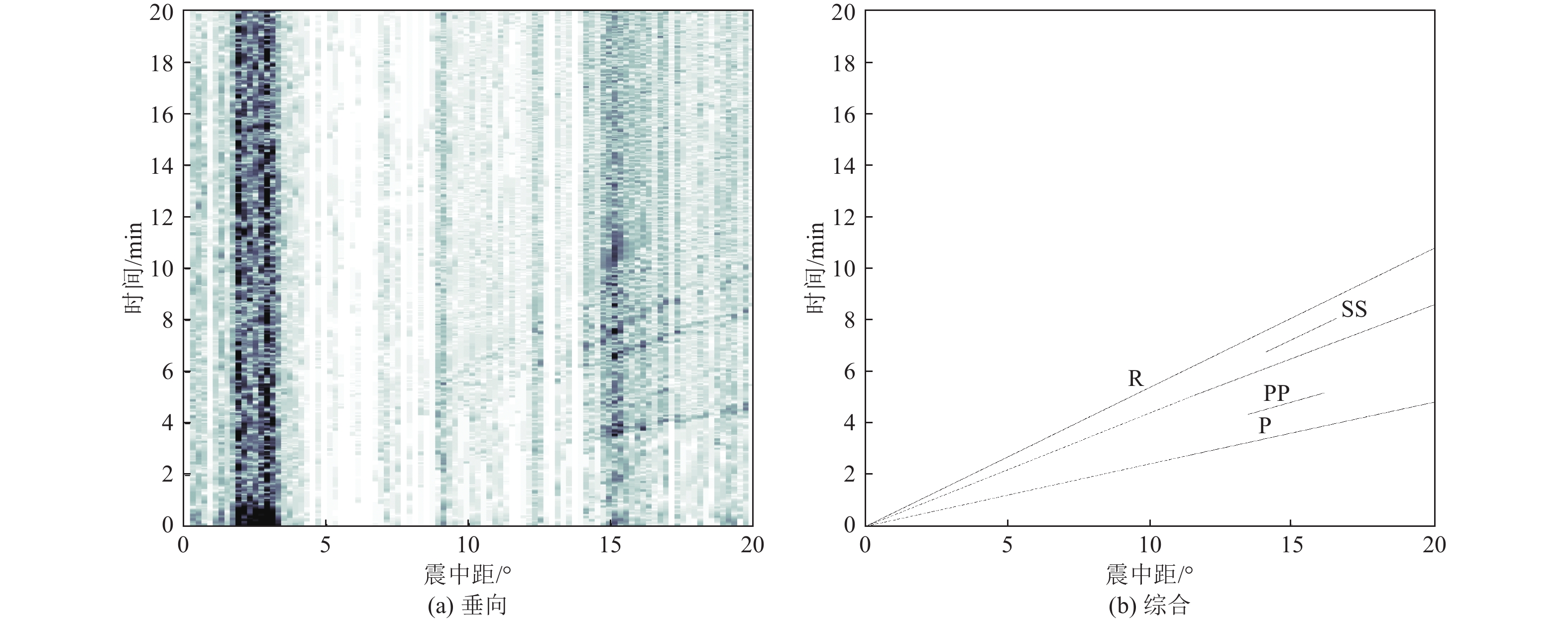
摘要: 可靠的震相走时是地震预警技术中精确测定震源位置和发震时刻的基础,本文运用STA/LTA震相识别技术,针对单台(河北红山台)2009—2021年共计12年积累的地震记录进行叠加计算,得到了红山台记录到的区域地震各震相走时曲线。结果显示,震中距0°~50°范围内红山台共成像7种震相的走时曲线,分别为P、S、PP、SS、PcS、ScS以及R面波震相,且随着组合参数变化,叠加成像的震相种类、震中距范围、清晰度均有所不同。此外,通过绘制各震相走时曲线发现,震中距0°~15°范围内,P波、S波及R波走时曲线基本呈线性变化,震中距0°~15°范围内计算得到红山台区域地震P波传播速度为7.5 km/s左右,S波传播速度为4.2 km/s左右,R波传播速度为3.5 km/s左右,介于P波和S波之间存在一个震相的走时痕迹,波速为5.4 km/s左右。本工作对于提升红山台震中距≤1000 km的地震预警定位精度有指导意义。Abstract: Reliable seismic phase travel time plays a fundamental role in the accurate determination of source position and occurrence time in earthquake early warning technology. In this paper, the STA/LTA phase identification technology is used for the first time to stack the seismic records accumulated by a single station (Hebei Hongshan station) for 12 years from 2009 to 2021, and the travel time curves of each seismic phase recorded by Hongshan station are imaged. The results show that the travel time curves of seven known seismic phases in Hongshan station are P, S, PP, SS, PcS, ScS, and R surface wave phases in the range of 0° to 50° epicenter distance. With the change of combination parameters, the types of seismic phases, epicentral distance range, and definition of superimposed imaging are different. In addition, by drawing the travel time curves of each seismic phase, it is found that the travel time curves of P wave, S wave, and R wave basically change linearly within the epicenter distance of 0° to 15°. Within the epicenter distance of 0° to15°, it is calculated that the seismic P-wave propagation velocity in Hongshantai area is about 7.5 km/s, S-wave propagation velocity is about 4.2 km/s and R-wave propagation velocity is about 3.5 km/s. There is a trace of seismic phase travel time between P wave and S wave, and the wave propagation velocity is about 5.4 km/s.
-
Key words:
- Seismic phase /
- Superposition /
- STA / LTA /
- Seismic record
-
表 1 数据处理参数组合
Table 1. Data processing parameter combination
组合序号 滤波 STA/s LTA/s 1 高通0.5 Hz 1.0 9 2 高通0.167 Hz 2.0 20 3 低通0.1 Hz 3.0 30 4 低通0.033 Hz 4.5 45 -
冯太林, 张学工, 李衍达等, 2001. 折射波地震记录叠加成像方法研究. 地球物理学报, 44(1): 129—134Feng T. L. , Zhang X. G. , Li Y. D. , et al. , 2001. Research on methodology of stack imaging of refractive seismic recording. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 44(1): 129—134. (in Chinese) 蒋振武, 吴律, 1995. 井间地震反射波叠加成像的DLCDP法. 石油地球物理勘探, 30(4): 495—504Jiang Z. W. , Wu L. , 1995. DLCDP method for the stacking and imaging of crossborehole seismic reflection waves. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 30(4): 495—504. (in Chinese) 李启成, 何书耕, 2019. 用振幅变化长短时均值比实现地震预警中P波自动拾取. 地震工程学报, 41(1): 138—146Li Q. C. , He S. G. , 2019. Automatic picking up of P-wave first arrival in earthquake early warning using STA/LTA method. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 41(1): 138—146. (in Chinese) 李希元, 胡望水, 张楠等, 2020. 连续子波反射叠加合成地震记录方法. 大庆石油地质与开发, 39(2): 133—138Li X. Y. , Hu W. S. , Zhang N. , et al. , 2020. Synthetic seismic recording method by the continuous wavelet-reflection superposition. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 39(2): 133—138. (in Chinese) 刘晓明, 赵君杰, 王运敏等, 2017. 基于改进的STA/LTA方法的微地震P波自动拾取技术. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 38(5): 740—745Liu X. M. , Zhao J. J. , Wang Y. M. , et al. , 2017. Automatic picking of microseismic events P-wave arrivals based on improved method of STA/LTA. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 38(5): 740—745. (in Chinese) 芦俊, 王赟, 季玉新等, 2018. 多分量地震数据的成像技术. 地球物理学报, 61(8): 3499—3514Lu J. , Wang Y. , Ji Y. X. , et al. , 2018. Imaging techniques of multi-component seismic data. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(8): 3499—3514. (in Chinese) 乔红丽, 张常在, 2018. 云计算环境下震前震源异常次声波自动识别方法. 地震工程学报, 40(6): 1331—1336Qiao H. L. , Zhang C. Z. , 2018. Automatic identification of anomalous infrasonic waves prior to earthquake in cloud computing environment. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 40(6): 1331—1336. (in Chinese) 秦满忠, 沈旭章, 张元生等, 2014. 利用兰州小孔径地震台阵资料叠加观测走时曲线. 地震学报, 36(1): 59—69Qin M. Z. , Shen X. Z. , Zhang Y. S. , et al. , 2014. Observed travel-time curves by stacking records from Lanzhou small aperture seismic array. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 36(1): 59—69. (in Chinese) 孙印, 潘素珍, 刘明军, 2018. 天然地震识别与震相自动拾取技术进展. 中国地震, 34(4): 606—620Sun Y. , Pan S. Z. , Liu M. J. , 2018. Seismic phase identification associated with the automatic pickup technology and its application. Earthquake Research in China, 34(4): 606—620. (in Chinese) 岳玉波, 张建磊, 张超阳等, 2020. 基于时变数据映射的地震叠加成像方法. 石油地球物理勘探, 55(2): 331—340Yue Y. B. , Zhang J. L. , Zhang C. Y. , et al. , 2020. Seismic data stacking based on time-varying mapping. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 55(2): 331—340. (in Chinese) 赵哲, 2018. 基于STA/LTA法的地震波初至时间提取方法. 中国科技信息, (9): 83—84. Astiz L. , Earle P. , Shearer P. , 1996. Global stacking of broadband seismograms. Seismological Research Letters, 67(4): 8—18. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.67.4.8 Earle P. S. , 1999. Polarization of the earth’s teleseismic wavefield. Geophysical Journal International, 139(1): 1—8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.1999.00908.x Okal E. A., Cansi Y., 1998. Detection of PKJKP at intermediate periods by progressive multi-channel correlation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 164(1—2): 23—30. Shearer P. M. , 1991. Imaging global body wave phases by stacking long-period seismograms. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 96(B12): 20353—20364. doi: 10.1029/91JB00421 Shearer P. M. , Rychert C. A. , Liu Q. Y. , 2011. On the visibility of the inner-core shear wave phase PKJKP at long periods. Geophysical Journal International, 185(3): 1379—1383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05011.x Stevenson P. R. , 1976. Microearthquakes at Flathead Lake, Montana: a study using automatic earthquake processing. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 66(1): 61—80. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0660010061 Walck M. C. , Clayton R. W. , 1984. Analysis of upper mantle structure using wave field continuation of P waves. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 74(5): 1703—1719. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0740051703 -




 下载:
下载: