Earthquake Damage Prediction Method of Seawall Engineering Considering Site Liquefaction
-
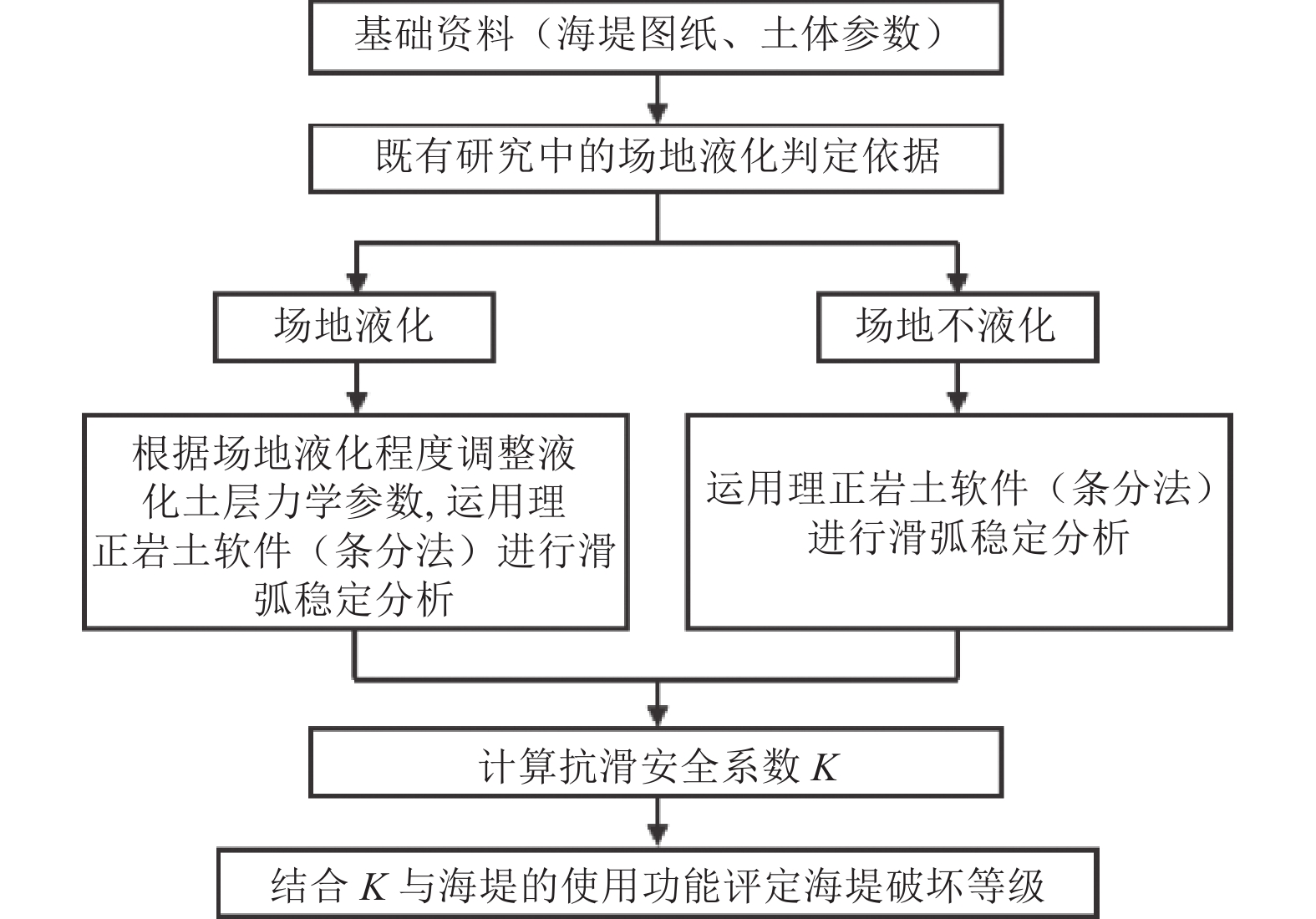
摘要: 为合理进行海堤工程震害预测,通过改变液化土层力学参数的方法考虑场地液化对海堤抗滑稳定性的影响,综合海堤本体结构抗滑安全系数和场地液化程度,提出新的海堤工程震害预测方法,并给出海堤破坏等级划分标准。以某海堤工程为算例,采用理正岩土分析软件建立海堤抗滑稳定性分析模型,进行不同地震烈度下海堤震害预测。研究结果表明,场地液化对海堤地震稳定性有较大影响,依托的海堤工程满足当地7度抗震设防要求,但8度时可发生中等破坏,存在较高的地震灾害风险,宜采取有针对性的加固措施。Abstract: In order to reasonably predict the seismic damage of seawall engineering, it considers the influence of site liquefaction on the anti-sliding stability of seawall by changing the mechanical parameters of liquefied soil layer. Based on the anti-sliding safety factor of seawall structure and the degree of site liquefaction, a new seismic damage prediction method of seawall engineering is proposed, and the classification standard of seawall damage grade is given. Taking a seawall project as an example, the anti-sliding stability analysis model of seawall was established by using Lizheng geotechnical analysis software, and the seismic damage prediction of seawall under different seismic intensities was carried out. The results show that the site liquefaction has a great influence on the seismic stability of the seawall. The seawall project meets the local seismic fortification requirements of 7 degree, but it enters medium damage at 8 degree, and there is a high risk of earthquake disasters. Targeted reinforcement measures should be taken.
-
表 1 计算参数修正方法
Table 1. Calculation parameter correction method
场地液化程度 黏聚力c 内摩擦角 未液化 c φ 轻微液化 0.92c~0.99c 0.82φ~0.99φ 中等液化 0.80c~0.91c 0.60φ~0.81φ 严重液化 0.68c~0.79c 0.42φ~0.59φ 表 2 海堤滑坡与抗滑安全系数最小值的关系
Table 2. Relationship between seawall landslide and minimum safety factor of anti-sliding
抗滑安全系数最小值 海堤状态 $ {K_{\rm{s}}} \in \left( {0\;,\;1.05} \right) $ 滑坡 $ {K_{\rm{s}}} = 1.05 $ 临界 $ {K_{\rm{s}}} \in \left( {1.05\;,\; + \infty } \right) $ 不滑坡 表 3 海堤破坏等级评定方法
Table 3. Evaluation method of seawall damage grade
破坏等级 评定依据 基本完好 海堤抗滑安全系数最小值>1.05,且海堤地基未液化 轻微破坏 海堤抗滑安全系数最小值>1.05,且海堤地基轻微液化 中等破坏 海堤抗滑安全系数最小值>1.05,且海堤地基中等液化 严重破坏 海堤抗滑安全系数最小值>1.05,且海堤地基严重液化 毁坏 海堤抗滑安全系数最小值<1.05 表 4 不同破坏等级海堤破坏现象和功能状态
Table 4. Phenomena and engineering state corresponding to seawall damage grades
破坏等级 破坏现象和功能状态 基本完好 堤坝表面完好,无须维修能够继续使用 轻微破坏 堤坝表面有轻微裂痕,局部维修后能继续使用 中等破坏 堤坝表面有较多裂缝,加固后方能使用 严重破坏 堤坝表面多处开裂,局部坍塌,大修后方能使用 毁坏 堤坝坍塌,海堤使用功能丧失,需重建 表 5 场地液化程度判定结果
Table 5. Determination results of site liquefaction degree
地震加速度值 场地液化程度 0.10 g 不发生液化 0.15 g 中等液化 0.20 g及以上 严重液化 表 6 模型计算参数
Table 6. Calculation parameters of the model
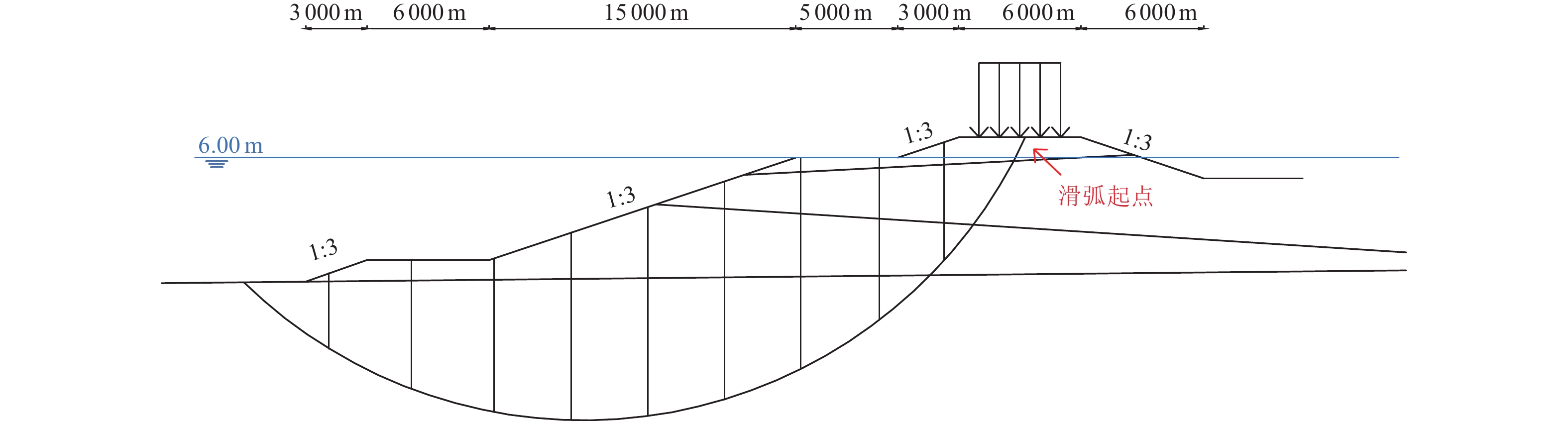
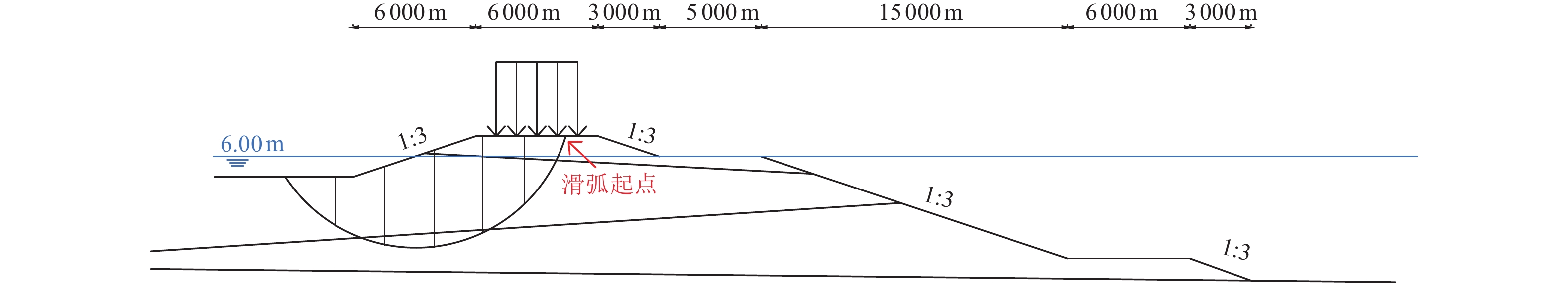
参数 地震强度/g 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.80 土体重度/(kN·m−3) 土层1 18.07 18.07 18.07 18.07 18.07 18.07 18.07 土层2 19.52 19.52 19.52 19.52 19.52 19.52 19.52 土体黏聚力/kPa 土层1 16.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 土层2 13.00 13.00 10.40 8.84 8.84 8.84 8.84 土体内摩擦角/(°) 土层1 18.00 18.00 18.00 18.00 18.00 18.00 18.00 土层2 29.00 29.00 17.40 12.18 12.18 12.18 12.18 表 7 海堤土层高程分布
Table 7. Soil layer distribution map of seawall
土层种类 土层高程/m 粉土 −1.170~−0.370 粉质黏土 −8.070~−1.170 粉土 −11.270~−8.070 粉质黏土 −14.470~−11.270 表 8 海堤地震稳定性分析结果
Table 8. Seawall seismic stability analysis results
地震强度/g 外坡迎浪面海堤抗滑安全系数 内坡背浪面海堤抗滑安全系数 考虑液化 不考虑液化 考虑液化 不考虑液化 0.05 1.327 1.327 1.990 1.990 0.10 1.180 1.180 1.746 1.746 0.15 1.137 1.148 1.702 1.692 0.20 1.043 1.119 1.598 1.603 0.30 0.963 1.064 1.421 1.528 0.40 0.895 1.003 1.238 1.467 0.80 0.772 0.972 1.048 1.381 表 9 海堤震害预测结果
Table 9. Forecast results of sea wall earthquake damage
地震强度/g 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.80 Fsy 1.327 1.180 1.137 1.043 0.963 0.895 0.772 Fsb 1.990 1.746 1.702 1.598 1.421 1.238 1.048 液化程度 不发生液化 不发生液化 中等液化 严重液化 严重液化 严重液化 严重液化 震害等级 基本完好 基本完好 中等破坏 严重破坏 毁坏 毁坏 毁坏 -
白铭学, 张苏民, 1990. 高烈度地震时黄土地层的液化移动. 工程勘察, (6): 1—5Bai M. X. , Zhang S. M. , 1990. Landslide induced by liquefaction of loessial soil during earthquake of high intensity. Geotechnical Investigation and Surveying, (6): 1—5. (in Chinese) 蔡为武, 1999. 水工建筑物抗震设计探讨. 水利水电科技进展, 19(4): 21—24Cai W. W. , 1999. Antiseismic design of hydraulic structures. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 19(4): 21—24. (in Chinese) 陈晓平, 黄井武, 张黎明等, 2007. 软基海堤结构稳定性研究. 岩土力学, 28(12): 2495—2500Chen X. P. , Huang J. W. , Zhang L. M. , et al. , 2007. Stability study for coastal levee on soft foundation. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 28(12): 2495—2500. (in Chinese) 郭翔, 张发明, 孙梦雅等, 2016. 高潮位作用下施工期海堤抗滑稳定性研究. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版), 33(2): 82—85Guo X. , Zhang F. M. , Sun M. Y. , et al. , 2016. Study on the stability against sliding of seawalls in construction period under the action of high tide level. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 33(2): 82—85. (in Chinese) 胡彩清, 2014. 筒型基础在地震荷载下土体液化及承载性能研究. 天津: 天津大学.Hu C. Q., 2014. Research of soil liquefaction and bearing performance of bucket foundation under seismic load. Tianjin: Tianjin University. (in Chinese) 蒋清国, 2015. 液化地层下地铁工程抗地震液化措施研究. 震灾防御技术, 10(1): 95—107Jiang Q. G. , 2015. Anti-liquefaction measures for subway engineering in liquefiable soil layers. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(1): 95—107. (in Chinese) 李家宁, 2007. 孤东海堤坝身地震稳定性评价. 现代企业教育, (18): 81. 卢盛松, 姜朴, 孙德安, 1987. 海堤地震反应及稳定性分析. 河海大学学报, 15(6): 65—71Lu S. S. , Jiang P. , Sun D. A. , 1987. Sesmic responsibility and stability analysis of sea bank. Journal of Hohai University, 15(6): 65—71. (in Chinese) 卢永金, 何友声, 刘桦, 2005. 海堤设防标准探讨. 中国工程科学, 7(12): 17—23Lu Y. J. , He Y. S. , Liu Y. , 2005. Research on seawall flood defense criteria. Engineering Science, 7(12): 17—23. (in Chinese) 毛昶熙, 段祥宝, 毛佩郁等, 1999. 海堤结构型式及抗滑稳定性计算分析. 水利学报, (11): 30—37Mao C. X. , Duan X. B. , Mao P. Y. , et al. , 1999. Analysis on structural shape of sea dyke and its sliding stability. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, (11): 30—37. (in Chinese) 毛昶熙, 段祥宝, 毛佩郁等, 2000. 海堤护坡块体的稳定性分析. 水利学报, (8): 32—38, 45Mao C. X. , Duan X. B. , Mao P. Y. , et al. , 2000. Analysis on stability of revetment block in sea dyke. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, (8): 32—38, 45. (in Chinese) 蒲高军, 冯秀丽, 2005. 孤东海堤海域浅层地基土地震效应分析. 油气田地面工程, 24(4): 16—17. 时振梁, 李裕澈, 张晓东, 2002. 中国地震区划图应用和工程抗震. 中国工程科学, 4(8): 20—25Shi Z. L. , Li Y. C. , Zhang X. D. , 2002. Earthquake resistant engineering and application of seismic zonation map of China. Engineering Science, 4(8): 20—25. (in Chinese) 孙锋, 潘蓉, 周群等, 2014. 某核电厂软基海堤地震动力响应规律及工程对策探讨. 工程抗震与加固改造, 36(5): 138—142Sun F. , Pan Y. , Zhou Q. , et al. , 2014. Study on dynamic response analysis and engineering countermeasure of coastal levee on soft soil foundation of nuclear power Plant. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 36(5): 138—142. (in Chinese) 孙晓东, 王丹, 2010. 土的黏聚力取值分析. 辽宁建材, (3): 39—41Sun X. D. , Wang D. , 2010. Analysis of cohesive force of soil. Liaoning Building Materials, (3): 39—41. (in Chinese) 王明星, 石洋, 芦俊波等, 2013. 德商高速鄄城至菏泽段震动液化地基处理方案. 北方交通, (6): 37—39Wang M. X. , Shi Y. , Lu J. B. , et al. , 2013. Treatment scheme for vibration liquefaction foundation of Juancheng to Heze section in Deshang expressway. Northern Communications, (6): 37—39. (in Chinese) 夏元友, 熊海丰, 2004. 边坡稳定性影响因素敏感性人工神经网络分析. 岩石力学与工程学报, 23(16): 2703-2707Xia Y. Y. , Xiong H. F. , 2004. Sensibility analysis of slope stability based on artificial neural network. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23(16): 2703-2707. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2009. GB/T 24336—2009 生命线工程地震破坏等级划分. 北京: 中国标准出版社.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2009. GB/T 24336—2009 Classification of earthquake damage to lifeline engineering. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国建设部, 2008. JGJ 94—2008 建筑桩基技术规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2017. GB 51254—2017 高填方地基技术规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. GB 51254—2017 Technical code for deep filled ground. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese) 周斌, 李蕾, 李先梅, 2004. 胜利油田孤东海堤地震液化及稳定性评价. 华南地震, 24(3): 25—31Zhou B. , Li L. , Li X. M. , 2004. Earthquake sand liquefaction and evaluation of dam stability for Gudong Sea Wall in Shengli oil field. South China Journal of Seismology, 24(3): 25—31. (in Chinese) Yasuhara K. , Yang S. S. , Horikawa I. , et al. , 2018. Settlement of river dykes and their adjacent residences on soft clay deposits after the Tohoku-Pacific Ocean earthquake in 2011. Geotechnical Engineering Journal of the SEAGS & AGSSEA, 49(2): 41—48. -



 下载:
下载: