Impact of Different Source Incidence Angles on Seismic Response of Submarine Basin
-
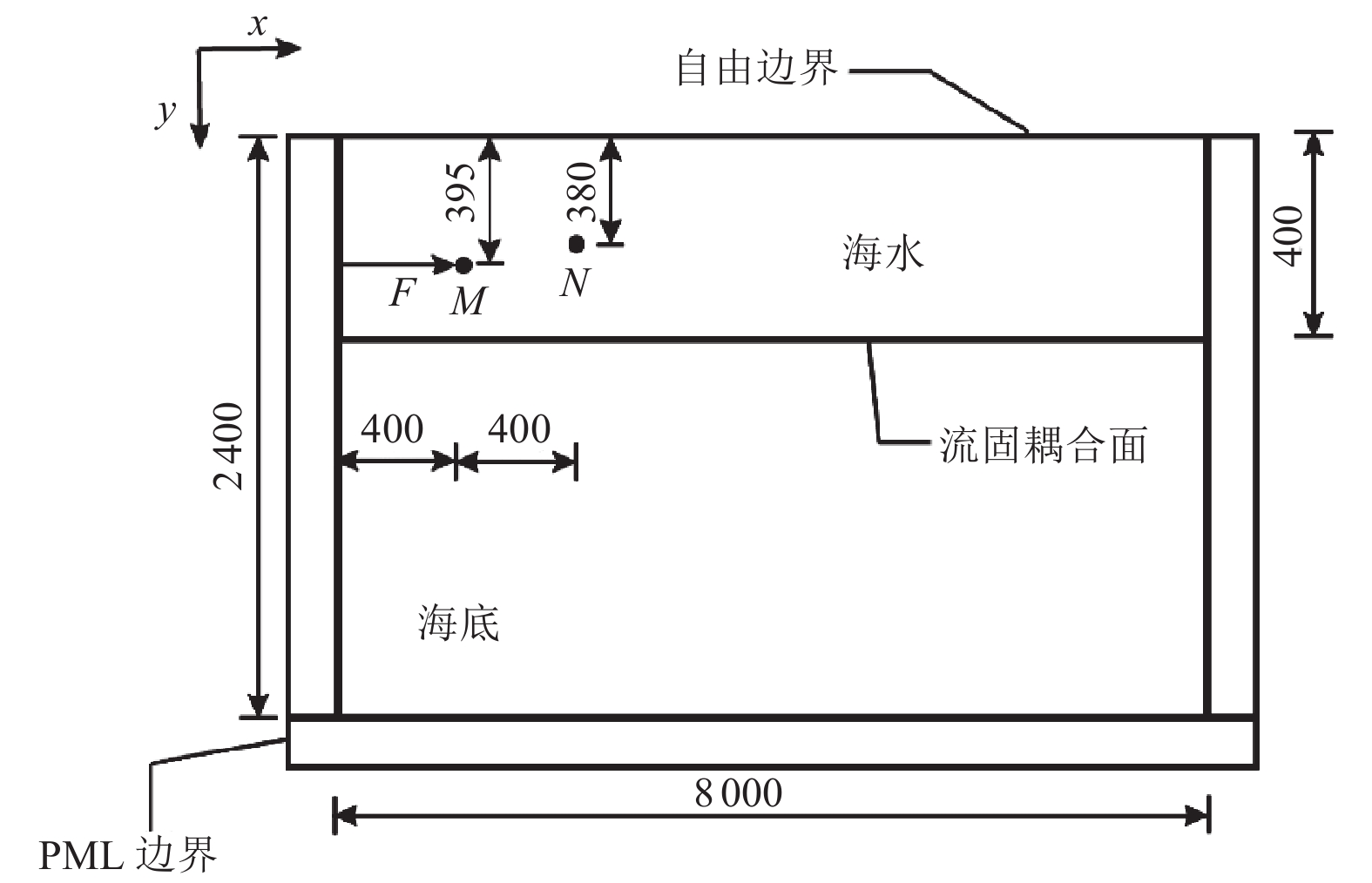
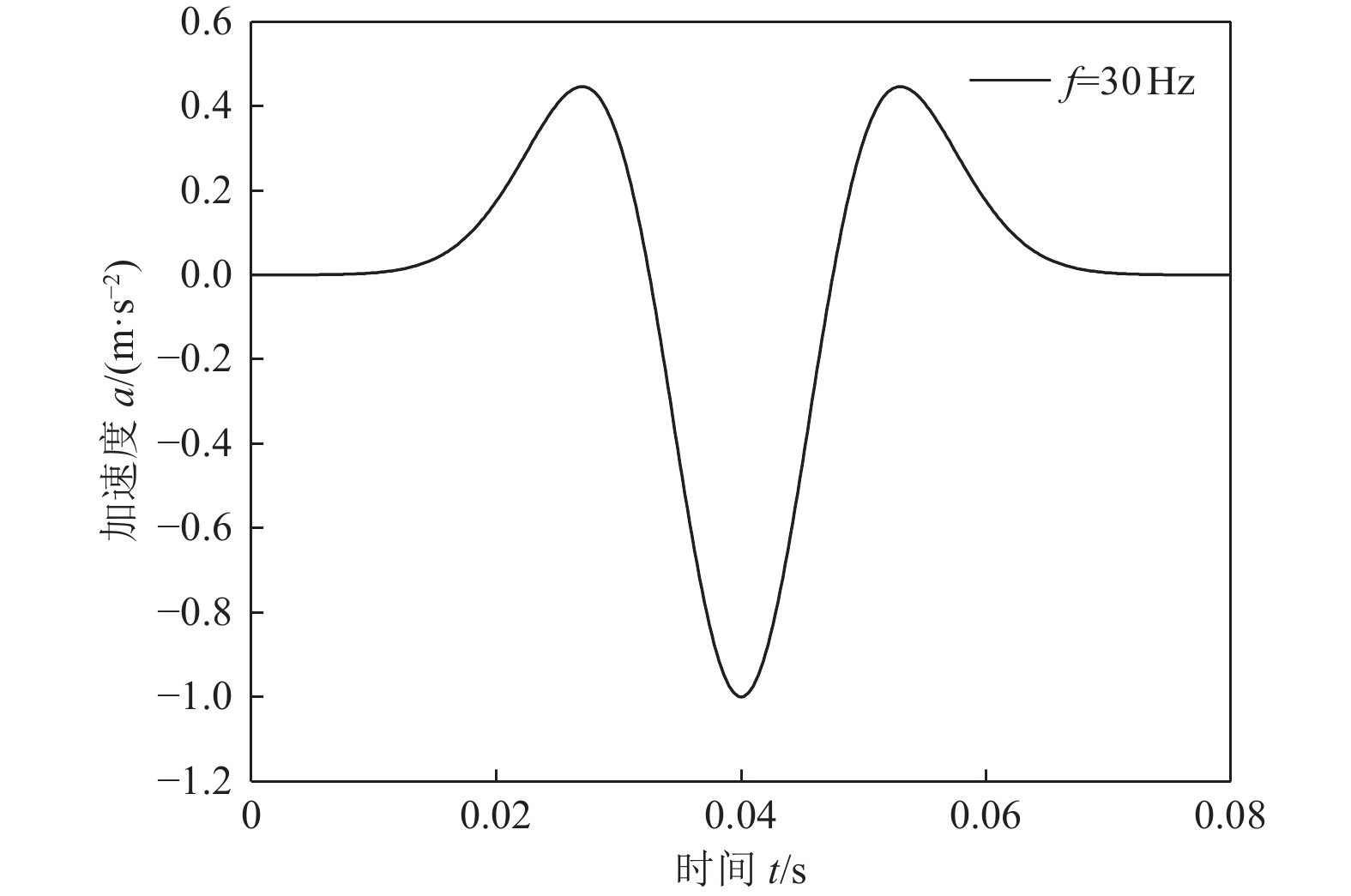
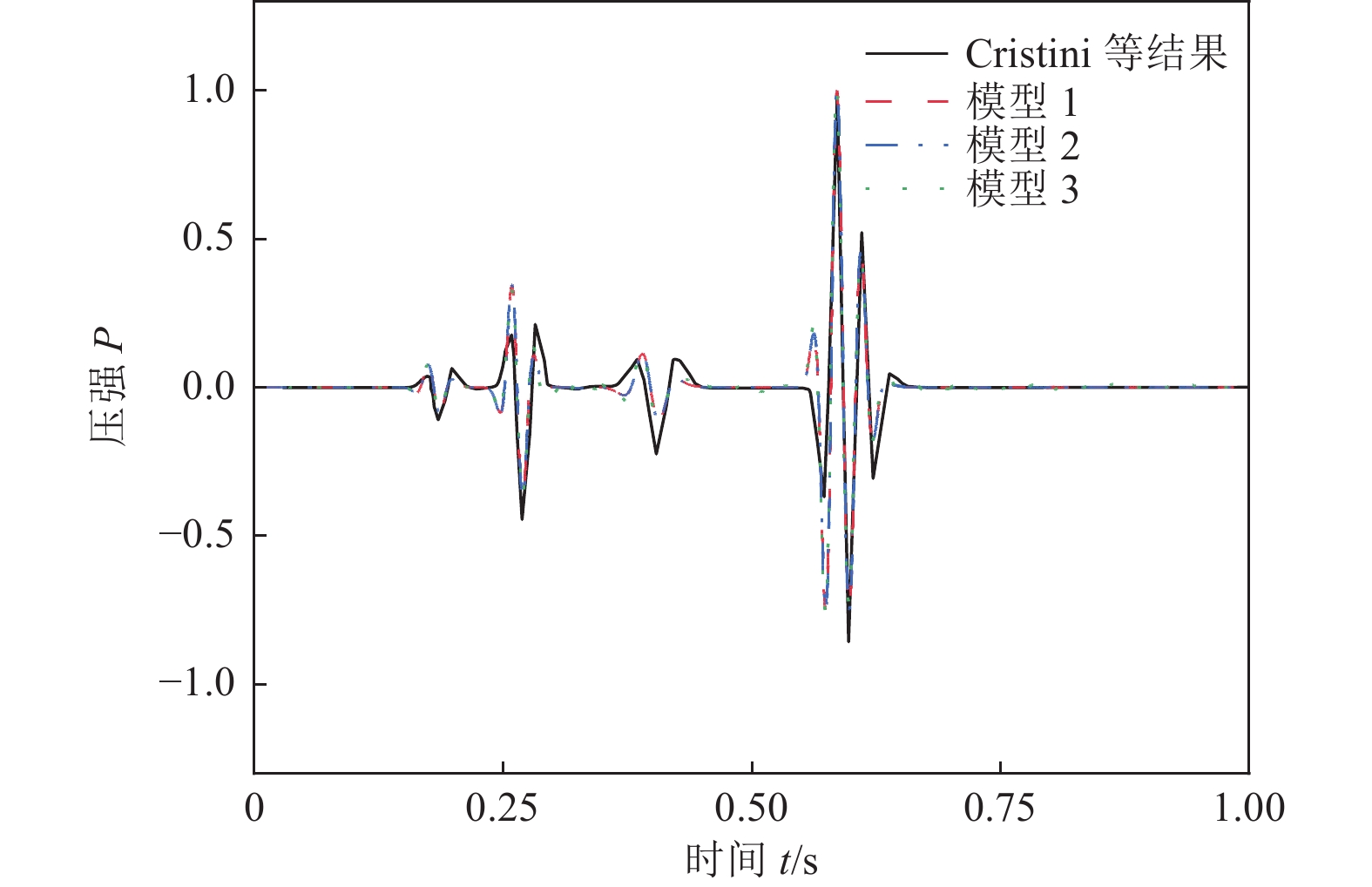
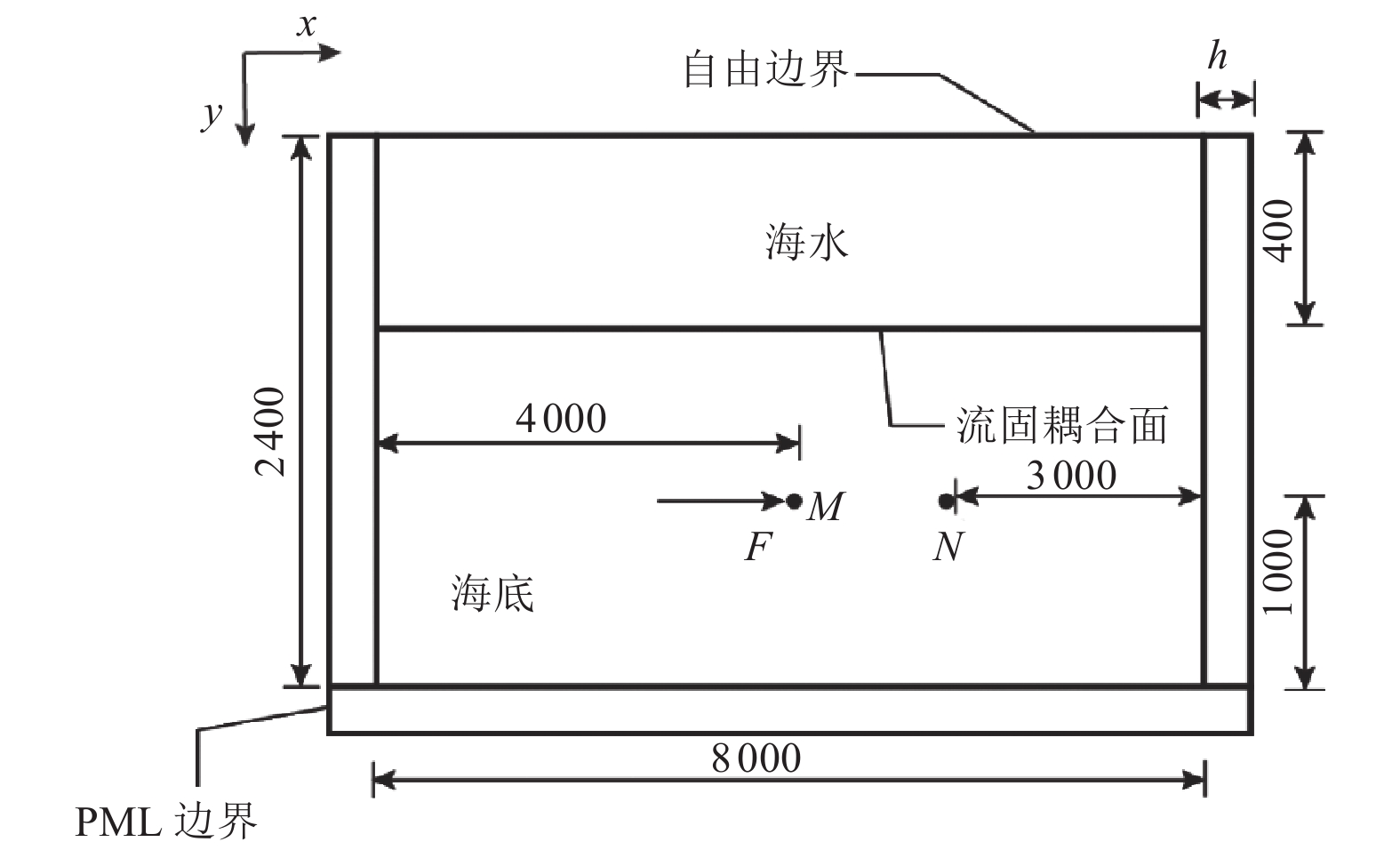
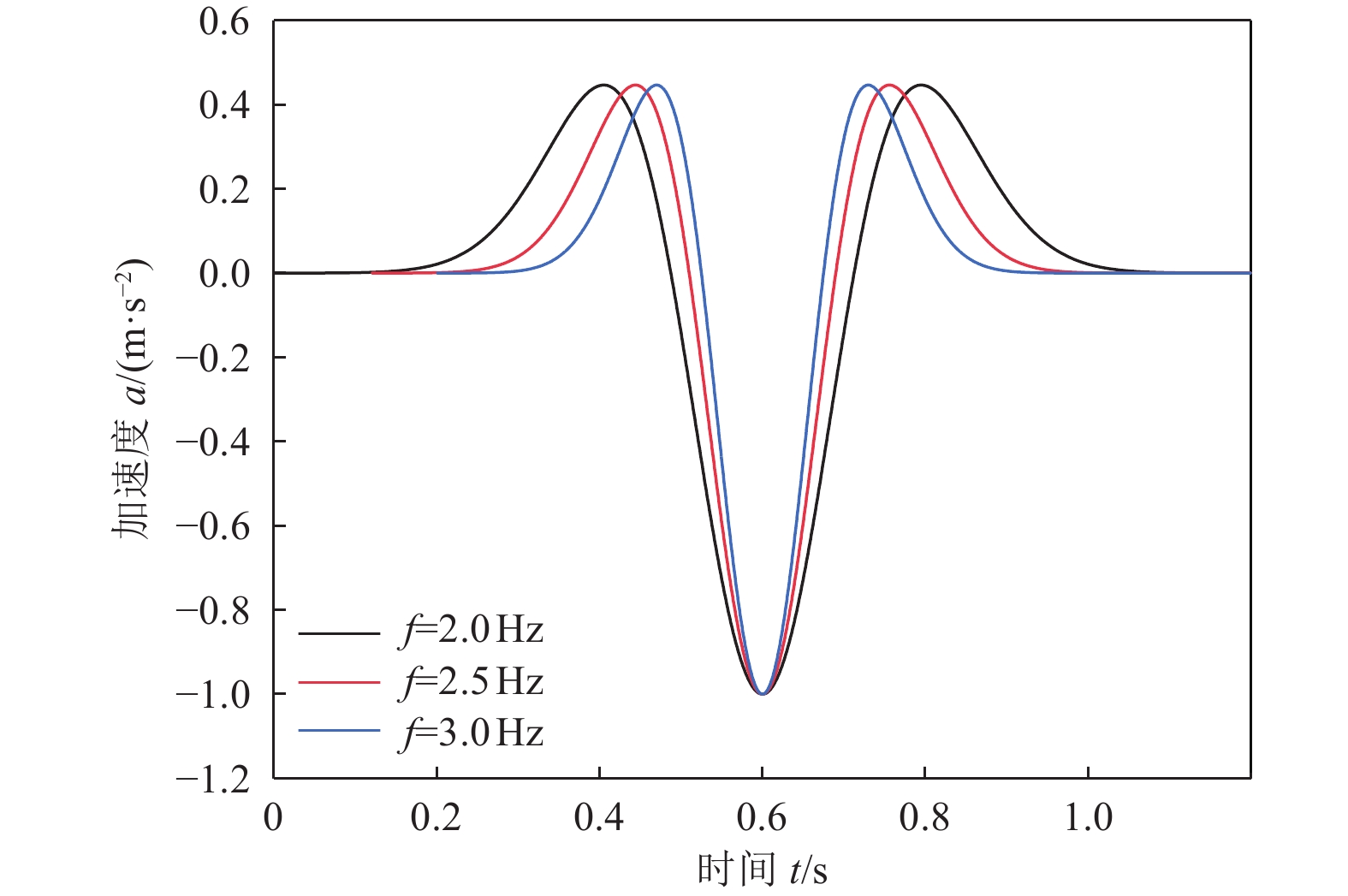
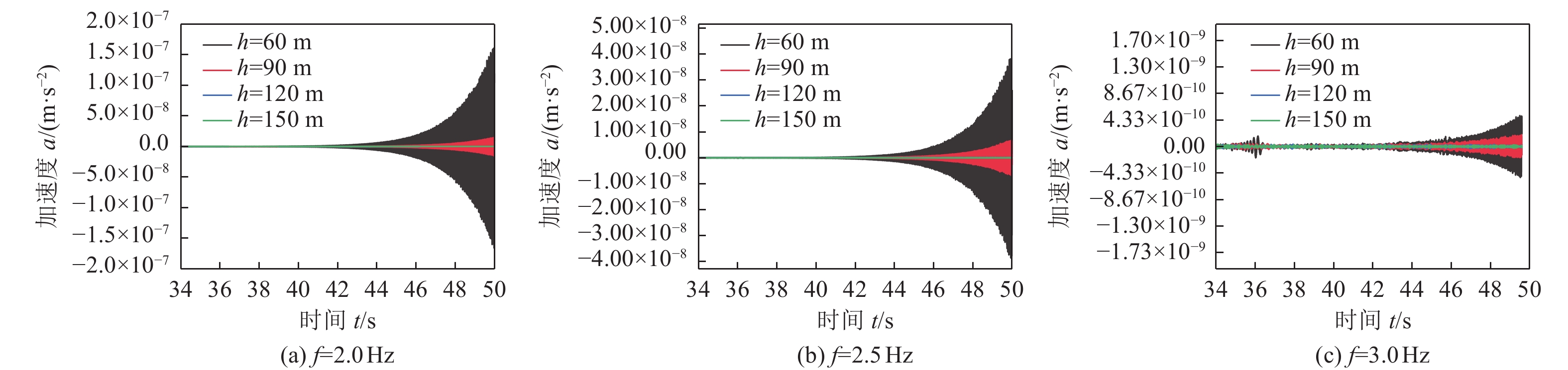
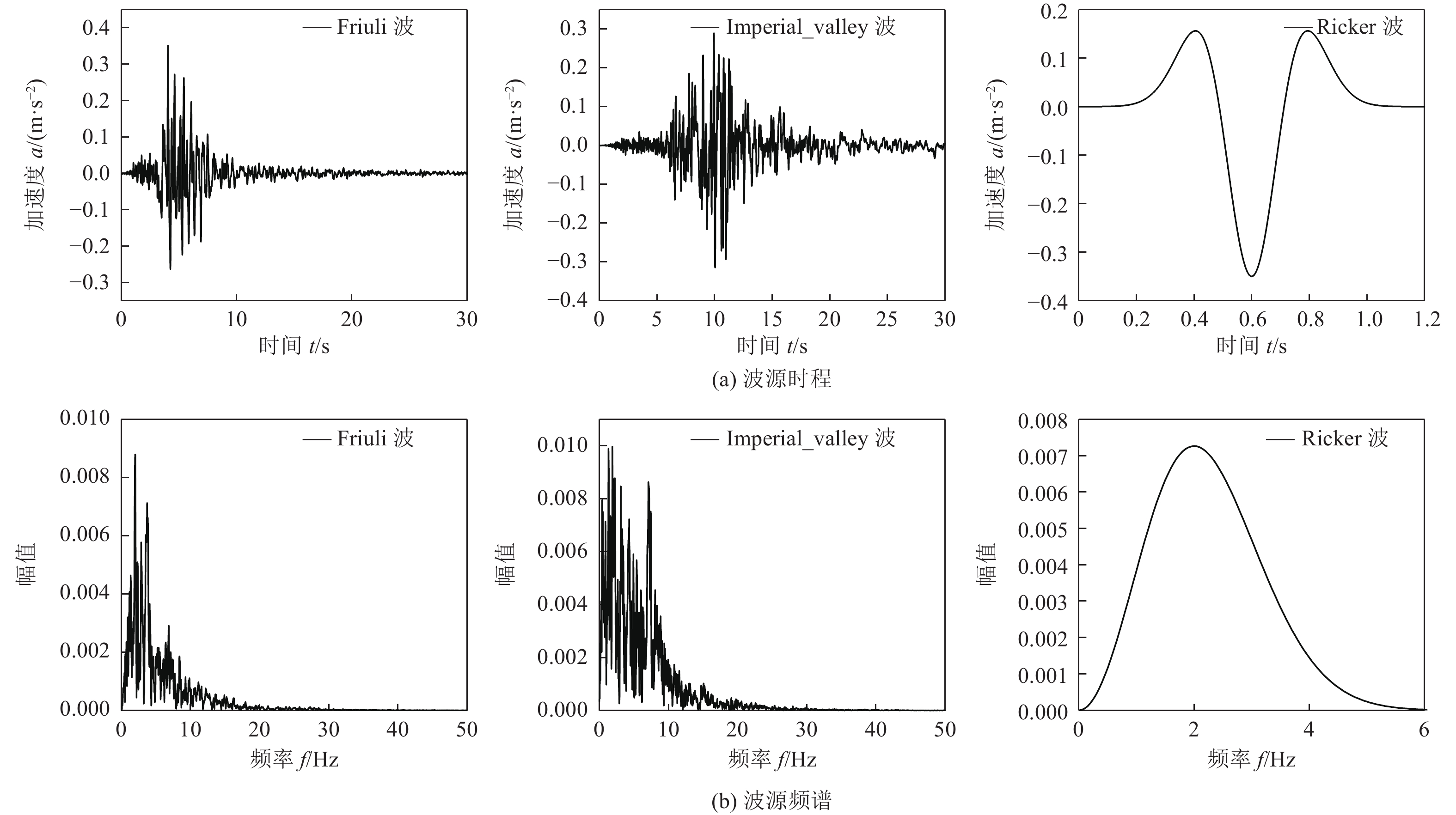
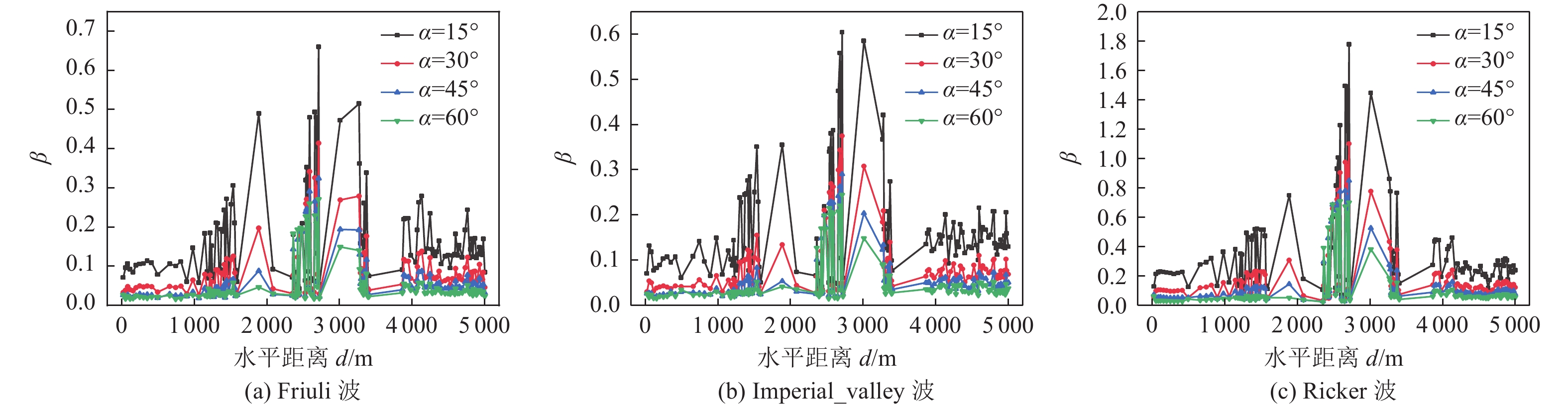
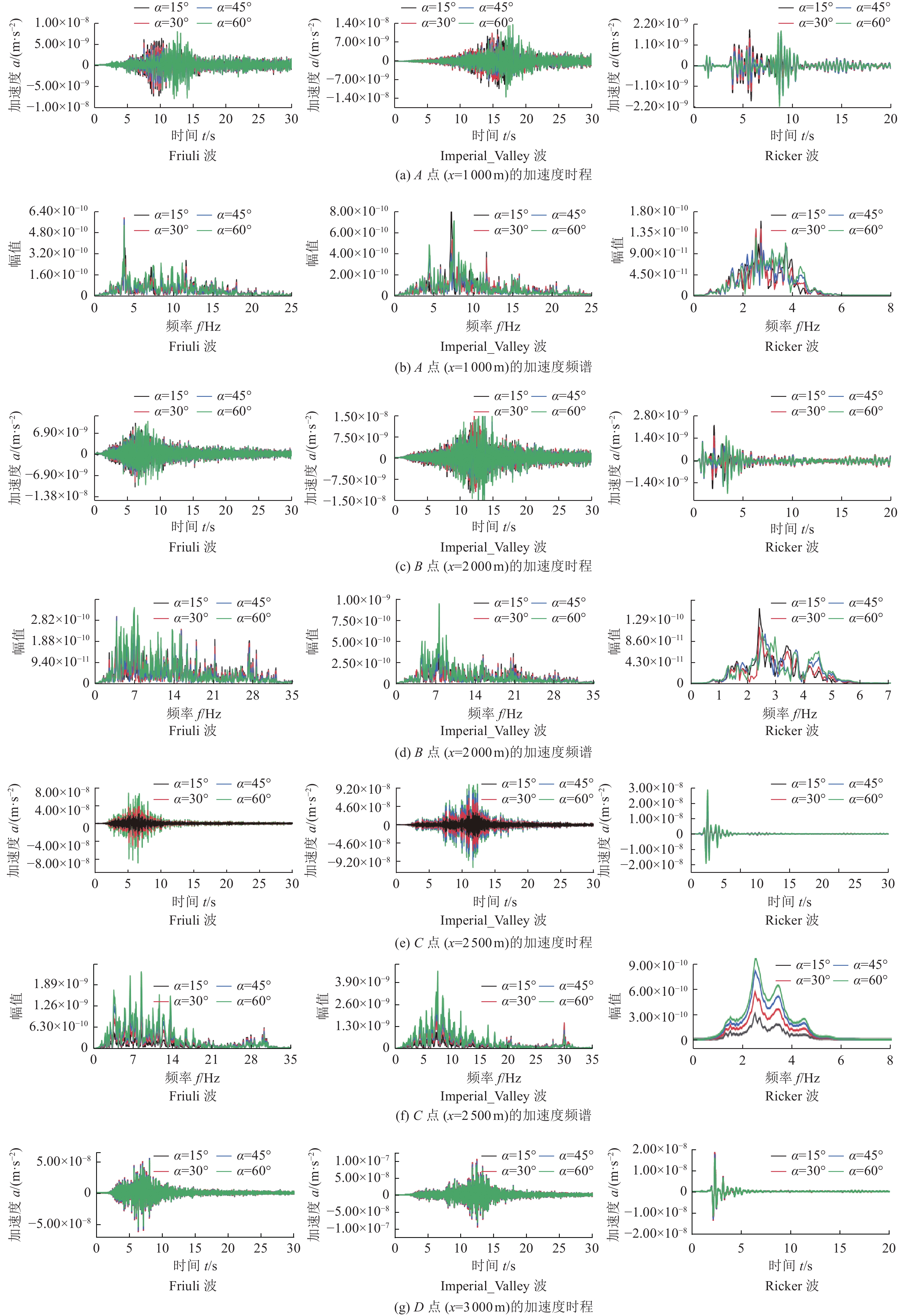
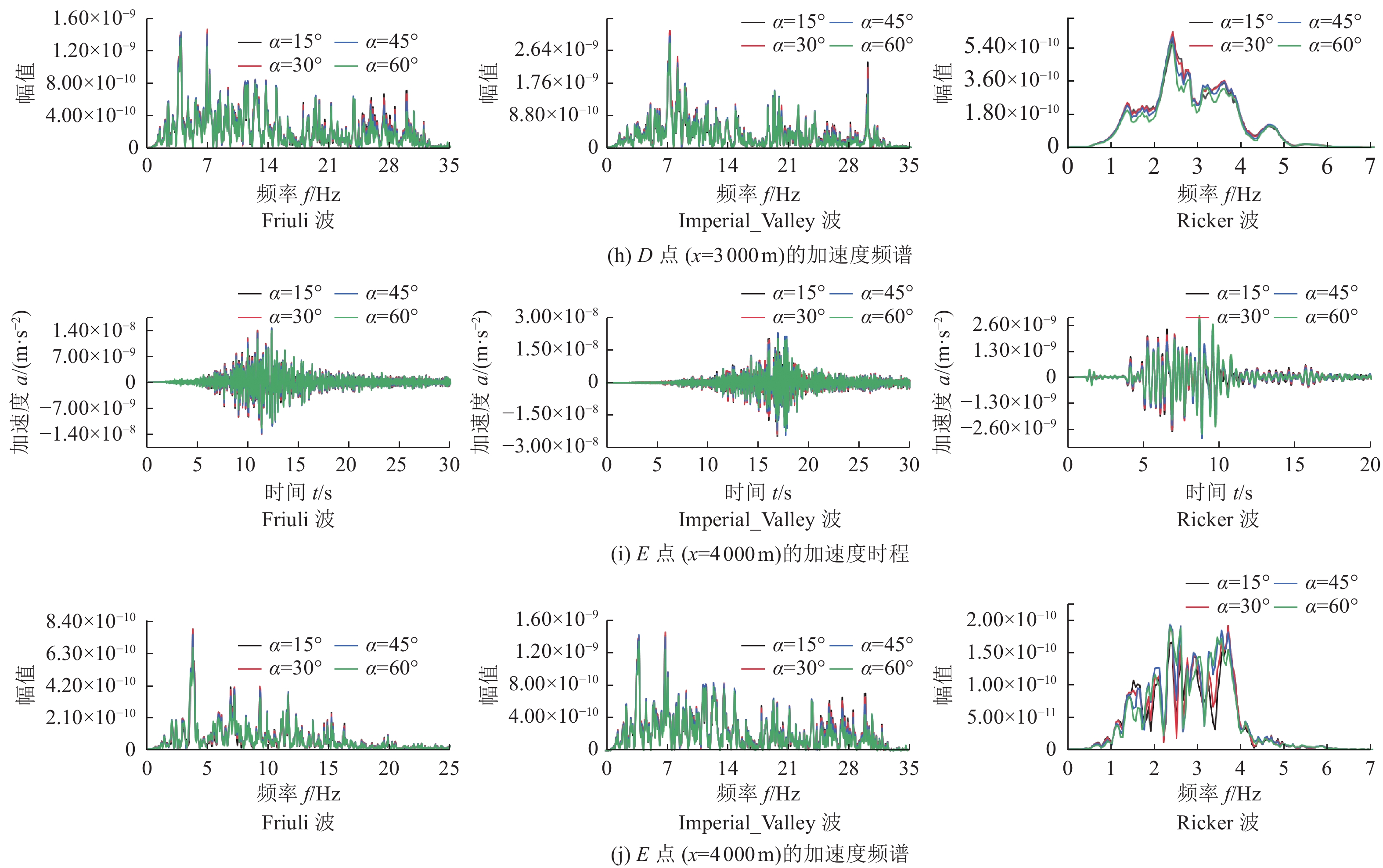
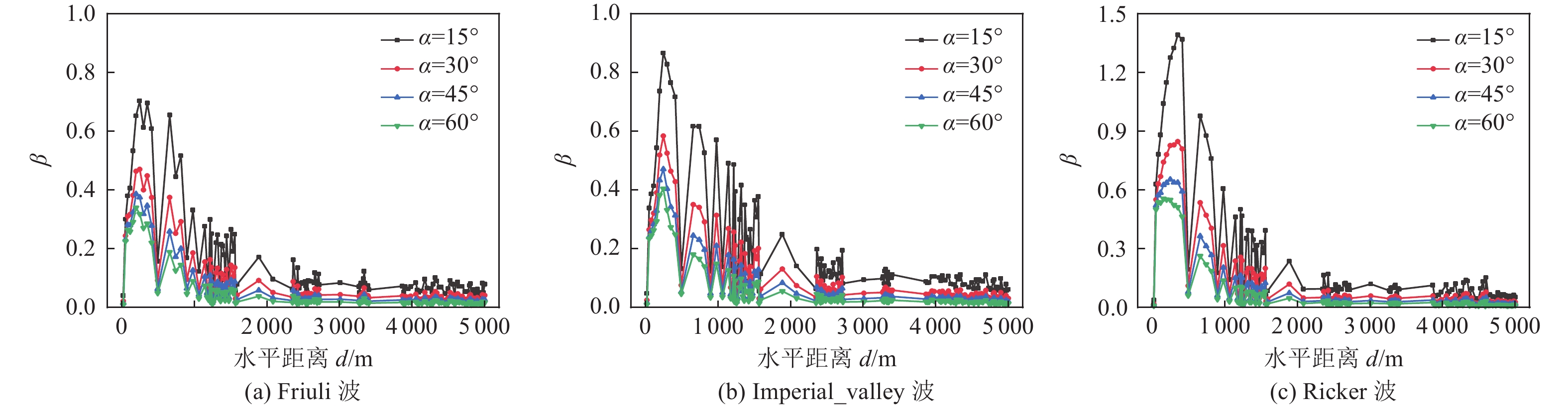
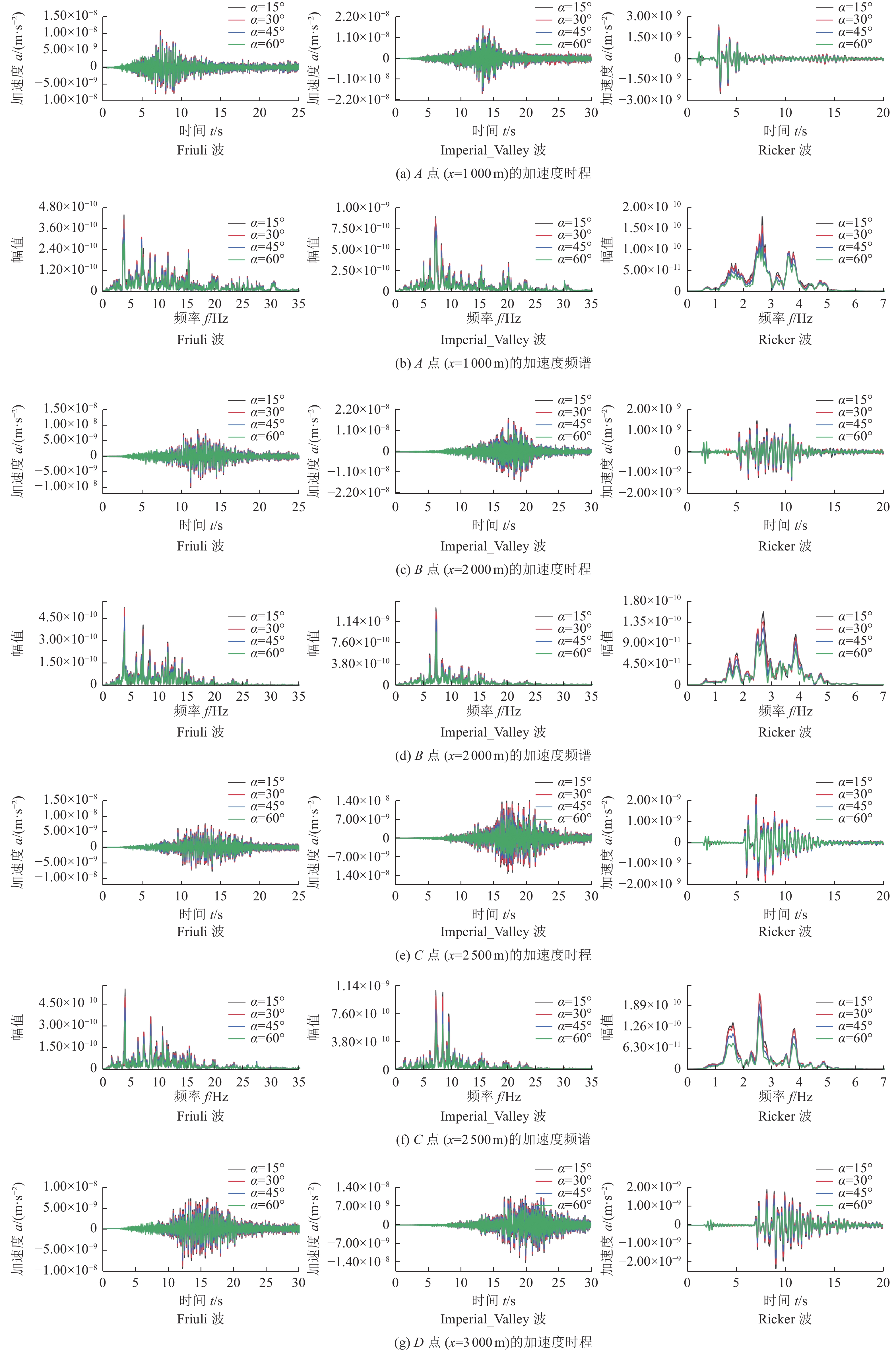
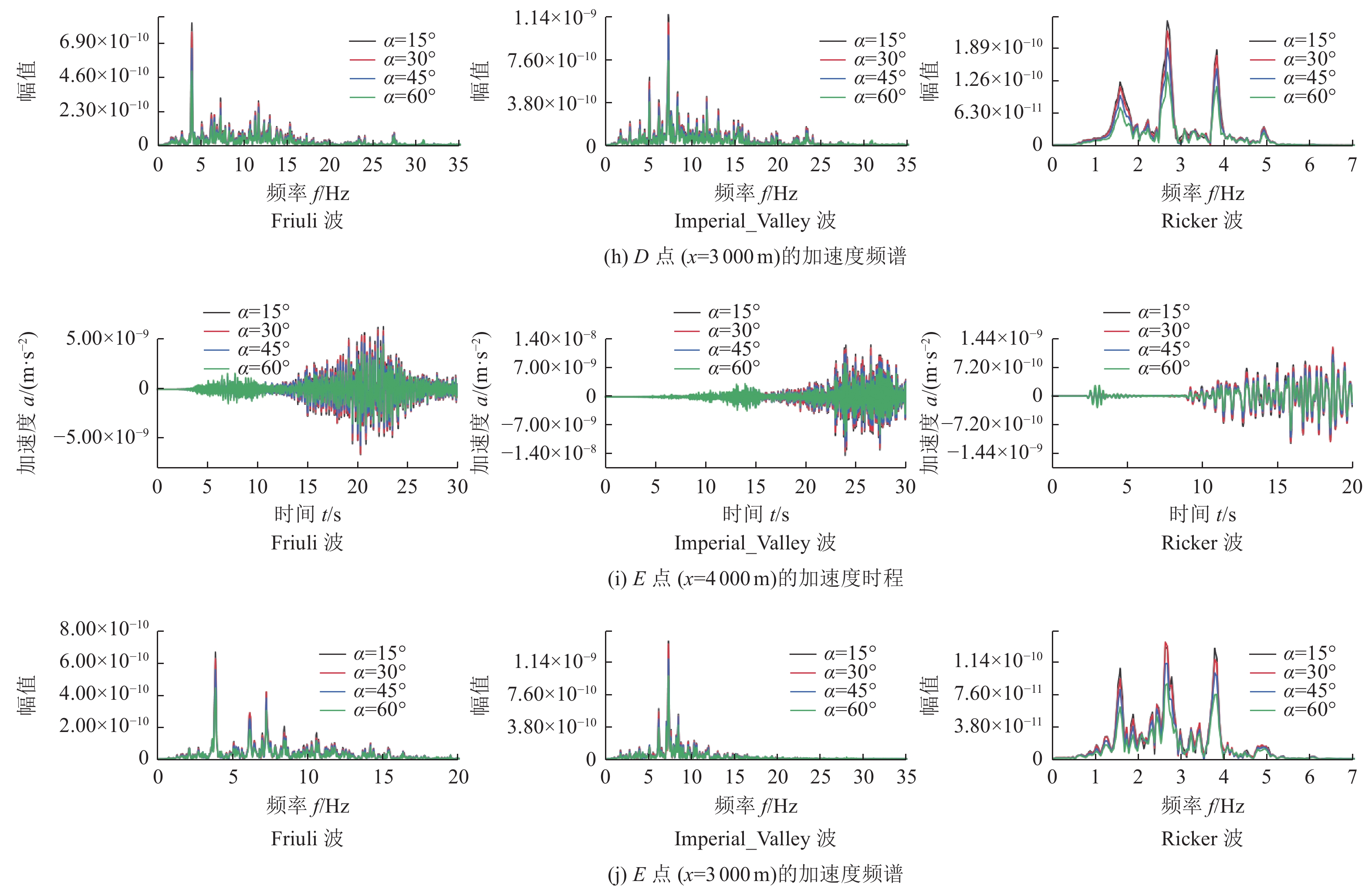
摘要: 为研究地震作用对海底盆地的影响,在分析网格大小和PML边界厚度对计算精度影响的基础上,综合考虑了海水、盆地内不规则地形以及多层介质等因素,运用谱元法理论建立了礼乐盆地地震动分析二维模型,研究了盆地在不同震源入射角下的响应。结果表明:在考虑流固耦合的情况下,网格尺寸为四分之一波长时即可取得较高精度,PML边界厚度至少为2个波长时方可达到理想效果。震源的不同会影响放大系数的大小及频谱特征。当地震波从盆地中部入射时,随着震源入射角的增大,放大系数逐渐减小;在不同震源入射角下,盆地不同位置的加速度时程及频谱特征差异较大。当地震波从左侧入射时,放大系数的分布规律与地震波从盆地中部入射时有所不同;在不同的震源入射角下,盆地不同位置的加速度时程及频谱特征差异较小。在研究盆地地震相关问题时,海水、地形以及多层介质的影响是不可忽视的。Abstract: In order to study the influence of seismic action on the submarine basin, based on the analysis of the influence of grid size and PML boundary thickness on the calculation accuracy, a two-dimensional seismic analysis model of the Lile basin is established by using the spectral element method, taking into account the factors of seawater, irregular topography in the basin and multi-layer media, and the response of the basin at different incident angles of earthquake sources is studied. The results show that high accuracy can be achieved when the mesh size is a quarter wavelength and the PML boundary thickness is at least two wavelengths when considering the fluid-solid coupling. The magnification factor and spectrum characteristics are influenced by the source. When seismic waves are incident from the middle of the basin, the amplification coefficient decreases with the increase of the incident angle of the source. Acceleration time history and frequency spectrum characteristics differ greatly in different locations of the basin at different source incidence angles. When the seismic wave is incident from the left side, the distribution law of the amplification coefficient is different from that when the seismic wave is incident from the middle of the basin. Acceleration time history and spectrum characteristics differ slightly in different locations of the basin at different source incidence angles. The influence of seawater, topography and multi-layered media can not be ignored in the study of basin earthquake-related problems.
-
Key words:
- Basin /
- Spectral element method /
- Ground motion
-
表 1 模型介质参数
Table 1. Model media parameters
介质 $ \rho $/(kg·m−3) Vp/(m·s−1) Vs/(m·s−1) 海水 1000 1500 — 黏土 1650 1650 218 砂土 1800 1697 264 岩石 2100 2135 485 -
丁海平, 朱重洋, 于彦彦, 2017. P, SV波斜入射下凹陷地形地震动分布特征. 振动与冲击, 36(12): 88—92, 98 doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.12.015Ding H. P. , Zhu C. Y. , Yu Y. Y. , 2017. Characteristic of ground motions of a canyon topography under inclined P and SV waves. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 36(12): 88—92, 98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.12.015 董阳, 2016. 谱元法在海洋声学中的应用. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学.Dong Y. , 2016. The spectral element method applied to ocean acoustic. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University. (in Chinese) 孔曦骏, 李鸿晶, 2021. 基于谱元模型的带斜坡覆水场地地震动效应分析. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 43(2): 264—272 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7627.2021.02.018Kong X. J. , Li H. J. , 2021. Spectral element analysis of seismic effects for overlying water fields with side slopes. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 43(2): 264—272. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7627.2021.02.018 李颂, 杨树春, 仝志刚等, 2012. 南海南部礼乐盆地深水区烃源岩生烃潜力研究. 天然气地球科学, 23(6): 1070—1076Li S. , Yang S. C. , Tong Z. G. , et al. , 2012. Study on the hydrocarbon generation potential of source rocks in Lile Basin, Southern South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience, 23(6): 1070—1076. (in Chinese) 李伟华, 赵成刚, 2003. 圆弧形凹陷饱和土场地对平面P波散射问题的解析解. 地球物理学报, 46(4): 539—546Li W. H. , Zhao C. G. , 2003. An analytical solution for the diffraction of plane P-waves by circular cylindrical canyons in a fluid-saturated porous media half space. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 46(4): 539—546. (in Chinese) 刘少林, 杨顶辉, 徐锡伟等, 2021. 模拟地震波传播的三维逐元并行谱元法. 地球物理学报, 64(3): 993—1005Liu S. L. , Yang D. H. , Xu X. W. , et al. , 2021. Three-dimensional element-by-element parallel spectral-element method for seismic wave modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(3): 993—1005. (in Chinese) 彭浩天, 2018. 起伏地表下弹性波传播数值模拟方法对比研究. 成都: 西南石油大学. 苏波, 李怀良, 刘少林等, 2019. 修正辛格式有限元法的地震波场模拟. 地球物理学报, 62(4): 1440—1452Su B. , Li H. L. , Liu S. L. , et al. , 2019. Modified symplectic scheme with finite element method for seismic wavefield modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(4): 1440—1452. (in Chinese) 孙龙涛, 孙珍, 詹文欢等, 2010. 南沙海域礼乐盆地油气资源潜力. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 35(1): 137—145 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014Sun L. T. , Sun Z. , Zhan W. H. , et al. , 2010. Petroleum potential prediction of the Lile basin in Nansha. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(1): 137—145. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014 谭文卓, 吴帮玉, 李博等, 2020. 梯形网格伪谱法地震波场模拟. 石油地球物理勘探, 55(6): 1282—1291 doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2020.06.014Tan W. Z. , Wu B. Y. , Li B. , et al. , 2020. Seismic wave simulation using a trapezoid grid pseudo-spectral method. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 55(6): 1282—1291. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2020.06.014 万子轩, 2020. 基于谱元法的山体地形效应模拟研究. 成都: 成都理工大学.Wan Z. X. , 2020. Investigations of mountain topographic effects based on spectral element method. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese) 魏成前, 2021. 平面波入射下二维成层盆地地震动放大特征研究. 苏州: 苏州科技大学.Wei C. Q. , 2021. Research on characteristics of ground motion amplification in two-dimensional layered basins under plane wave incidence. Suzhou: Suzhou University of Science and Technology. (in Chinese) 姚铭, 高刚, 周游等, 2017. 基于有限差分法的地震波数值模拟研究综述. 能源与环保, 39(10): 75—79, 85Yao M. , Gao G. , Zhou Y. , et al. , 2017. Summarization of numerical simulation of seismic wave based on minite difference method. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 39(10): 75—79, 85. (in Chinese) 禹乐, 于彦彦, 丁海平, 2020. 内源作用下盆地倾角对地表地震动放大特征的影响. 地震工程与工程振动, 40(5): 97—106 doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2020.05.97.yul.010Yu L. , Yu Y. Y. , Ding H. P. , 2020. Effect of basin slope angle on ground motion amplification characteristics under internal point source. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 40(5): 97—106. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2020.05.97.yul.010 张田升, 吴自银, 赵荻能等, 2019. 南海礼乐盆地海底麻坑地貌及成因分析. 海洋学报, 41(3): 106—120Zhang T. S. , Wu Z. Y. , Zhao D. N. , et al. , 2019. The morphologies and genesis of pockmarks in the Reed Basin, South China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao, 41(3): 106—120. (in Chinese) 赵成刚, 王磊, 李伟华, 2008. 具有饱和土沉积层的充水河谷对平面瑞雷波的散射. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1567—1573 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.032Zhao C. G. , Wang L. , Li W. H. , 2008. Scattering of plane Rayleigh waves by circular-arc alluvial valleys with saturated soil deposits and water layer. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(5): 1567—1573. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.032 朱重洋, 丁海平, 于彦彦, 2016. SV波入射下有无覆盖层凹陷地形的地面运动比较. 苏州科技学院学报(工程技术版), 29(2): 33—37Zhu C. Y. , Ding H. P. , Yu Y. Y. , 2016. Comparison of canyon ground motion with or without covering soil layers under SV wave incidence. Journal of Suzhou University of Science and Technology (Engineering and Technology), 29(2): 33—37. (in Chinese) Antonietti P. F. , Ferroni A. , Mazzieri I. , et al. , 2018. Numerical modeling of seismic waves by discontinuous spectral element methods. ESAIM: Proceedings and Surveys, 61: 1—37. doi: 10.1051/proc/201861001 Chen B. K. , Du Y. J. , Shi Y. , et al. , 2021. Seismic analysis of isolated continuous bridge considering influence of seawater and site condition. Shock and Vibration, 2021: 7599715. Cristini P. , Komatitsch D. , 2012. Some illustrative examples of the use of a spectral-element method in ocean acoustics. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 131(3): EL229—EL235. doi: 10.1121/1.3682459 Graves R. W. , Pitarka A. , Somerville P. G. , 1998. Ground-motion amplification in the Santa Monica area: effects of shallow basin-edge structure. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 88(5): 1224—1242. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0880051224 Komatitsch D. , Barnes C. , Tromp J. , 2000. Wave propagation near a fluid-solid interface: a spectral-element approach. Geophysics, 65(2): 623—631. doi: 10.1190/1.1444758 Lee J., 2013. Earthquake site effect modeling in the Granada basin using a 3-D indirect boundary element method. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 63: 102—115. Patera A. T. , 1984. A spectral element method for fluid dynamics: laminar flow in a channel expansion. Journal of Computational Physics, 54(3): 468—488. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(84)90128-1 -




 下载:
下载: