The Late Quaternary Activity Characteristics of the Dulan South Fault in the Qaidam Block
-
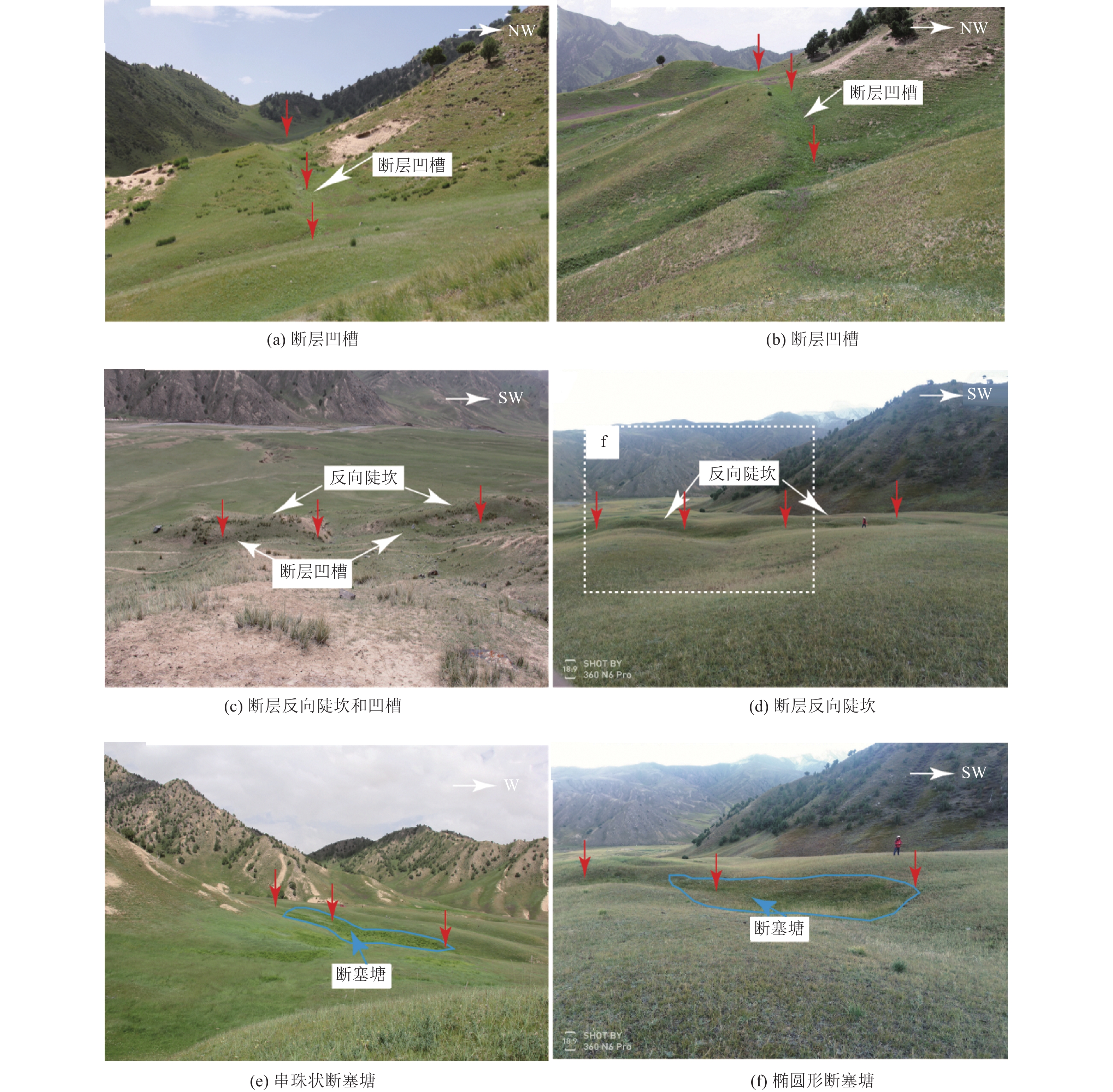
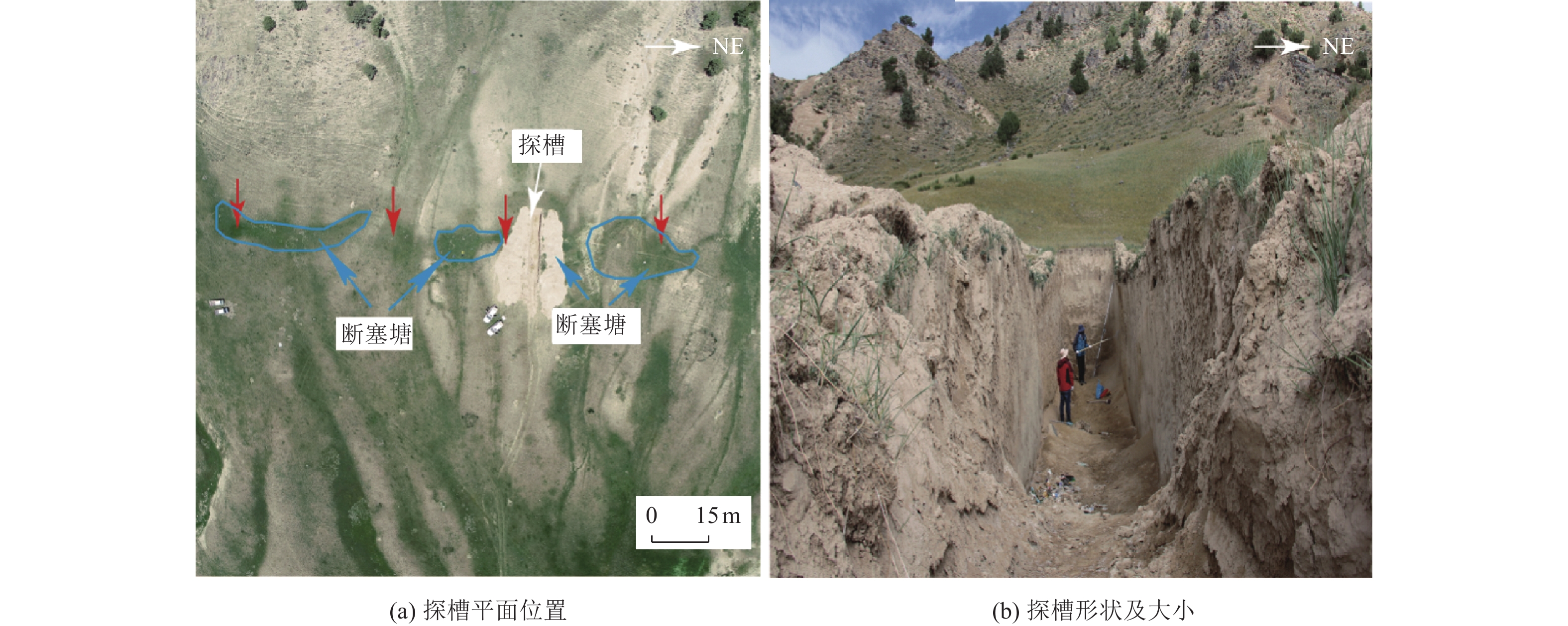
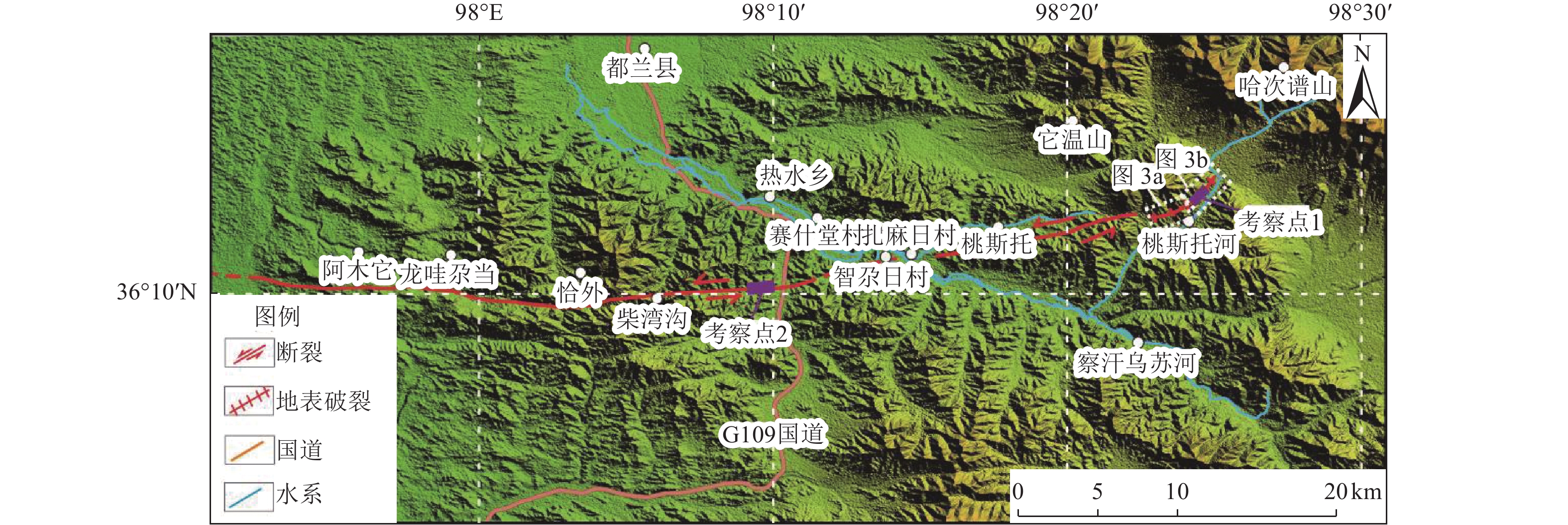
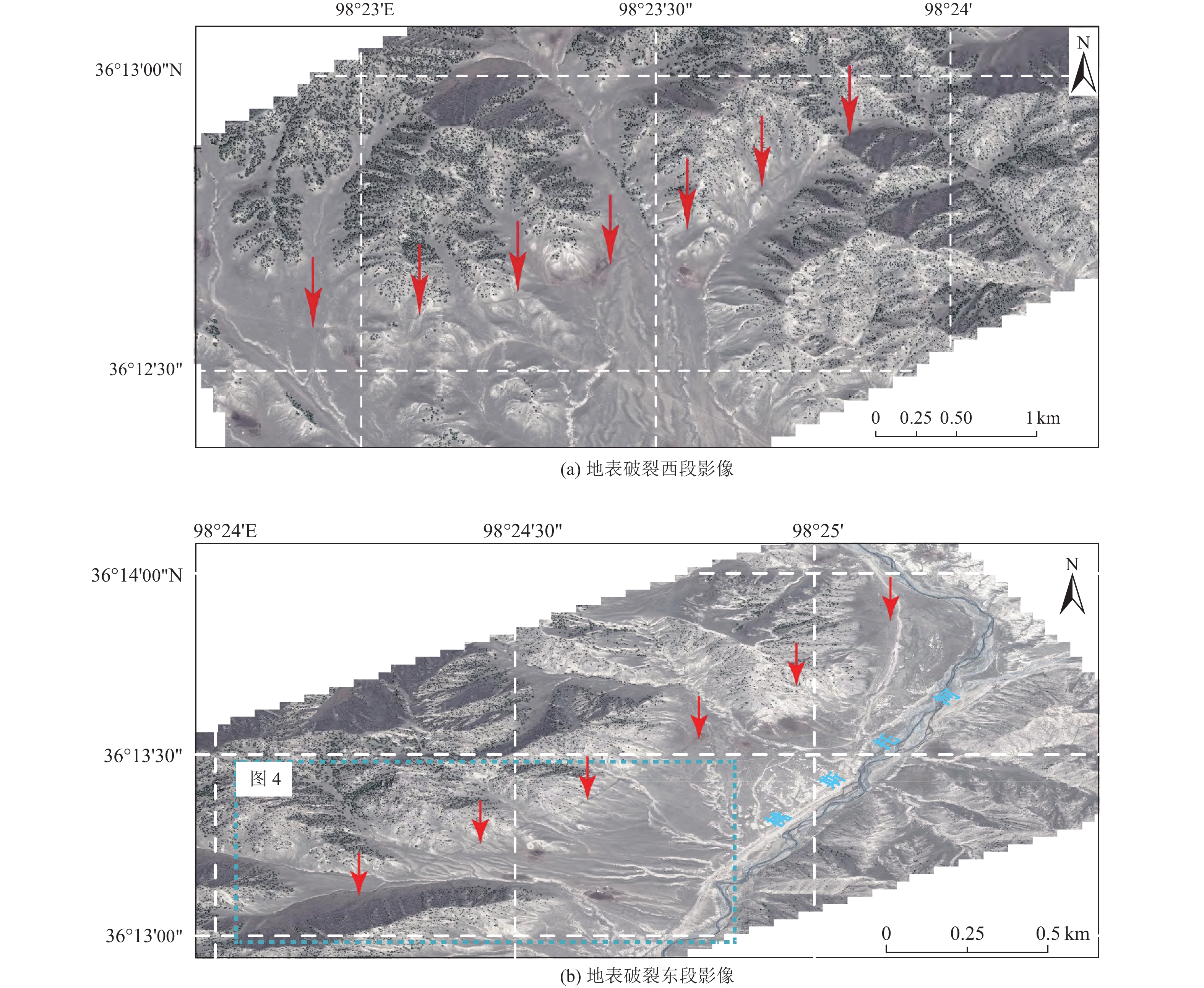
摘要: 青藏高原是新生代期间印度与欧亚板块持续强烈陆陆碰撞作用下形成的陆内活动造山带,发育了复杂的活动断裂系统,并成为东亚显著的陆内强震活动区。已有学者对高原活动断裂的研究多集中于地块边界带上,缺少对块体内部变形的研究。近期在开展青海省海西州都兰县察汗乌苏镇地震小区划工作中,调查发现在柴达木地块东南部的都兰次级断块内部存在明显的晚第四纪活断层−都兰南断裂。通过对都兰南断裂开展详细的野外地质调查、高分辨率遥感影像解译和无人机低空摄影精细测量等,得到该断裂的构造地貌特征、空间几何展布及运动特性,并通过开挖探槽和地质测年等,对其最新活动时代及滑动速率等进行初步约束。研究结果表明,该断裂为全长约43 km、全新世活动的左旋走滑断裂,并在其东段存在长约6 km的地表破裂带。在该断裂东段,地表的晚第四纪累积左旋位移达(14.5±1.8)m,西段的左旋走滑量为(6.7±0.8)m,初步估算其东段的水平走滑速率为1.56~1.9 mm/a,西段的水平走滑速率为0.9~1.16 mm/a。该断裂的发现及全新世活动的厘定表明,青藏高原内部活动构造变形样式复杂,断块内部通常存在不同程度的弥散变形。因此,断块内部的强震危险性不容忽视。该活动断裂的发现为认识都兰次级断块内部变形样式、应变分配等提供了参考,为都兰地区地震危险性的认知提供了支撑,对防御和减轻区域地震灾害风险具有一定指导意义。Abstract: The Qinghai Tibet Plateau is an intracontinental active orogenic belt formed under the continuous strong continental collision between India and Eurasia during the Cenozoic era. It has developed an extremely complex active fault system and has become an extremely significant intracontinental strong earthquake activity area in East Asia. Previous studies on active faults in the plateau have focused more on the boundary zone of the block, but paid less attention to the internal deformation of the block. Recently, during the seismic zoning of Chahanwusu Town, Dulan County, Haixi Prefecture, Qinghai Province, it was found that there was an obvious late Quaternary active fault - Dulan South fault in the Dulan secondary fault block in the southeast of Qaidam block. Through detailed field geological survey, high-resolution remote sensing image interpretation and low altitude photography fine measurement of the Dulan South fault, the structural and geomorphic characteristics, spatial geometric distribution and movement characteristics of the fault are obtained. The latest activity age and sliding rate are preliminarily constrained by excavation of trench and geological dating. The results show that the fault is a 43 km long, Holocene left lateral strike slip fault, and there is a 6 km long surface fracture zone at its east end. In the east section of the fault, the accumulated left lateral displacement of the surface in the late Quaternary is (14.5 ± 1.8) m, and the left lateral strike slip of the west section is (6.7 ± 0.8) m. It is preliminarily estimated that the horizontal strike slip rate in the east section is about 1.56~1.9 mm/a, and that in the west section is about 0.9~1.16 mm/a. The discovery of the fault and the determination of Holocene activity indicate that the active tectonic deformation style in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau is very complex, and there is usually dispersion deformation in the fault block with different degrees. Therefore, the risk of strong earthquakes in the fault block cannot be ignored. The new discovery of this active fault provides an important basis for understanding the internal deformation style and strain distribution of Dulan sub-fault block, provides strong support for the recognition of seismic risk in Dulan area, and has a certain guiding significance for the prevention and mitigation of regional seismic disaster risk.
-
Key words:
- Dulan South fault /
- Holocene activities /
- Surface rupture /
- Left lateral strike slip /
- Motion rate
-
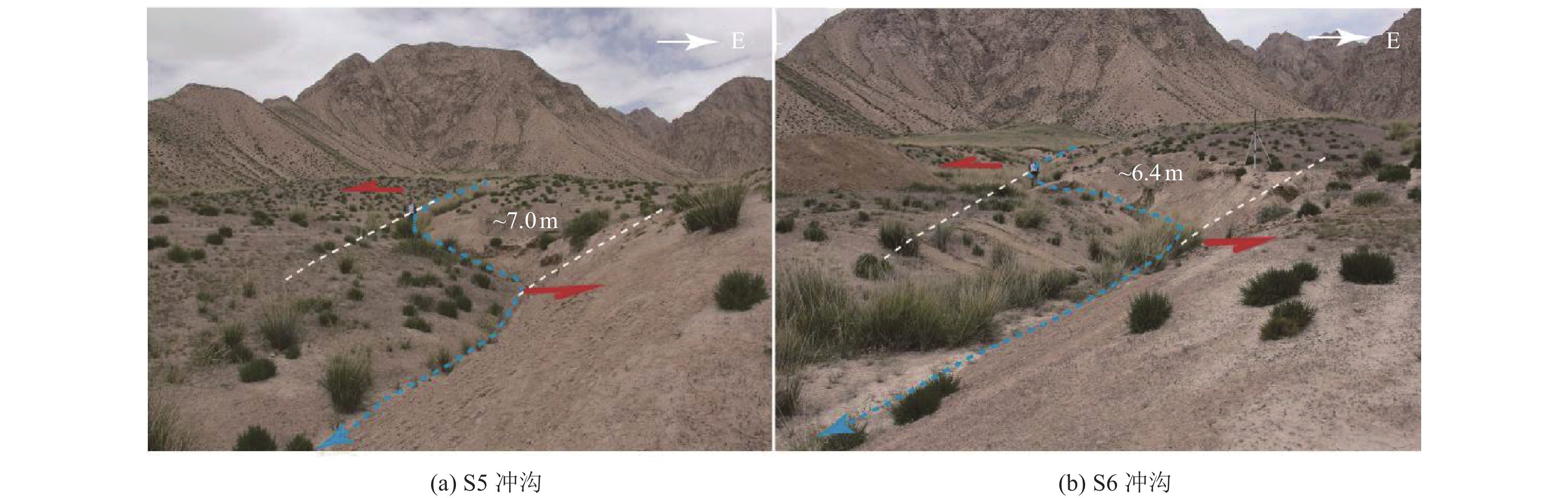
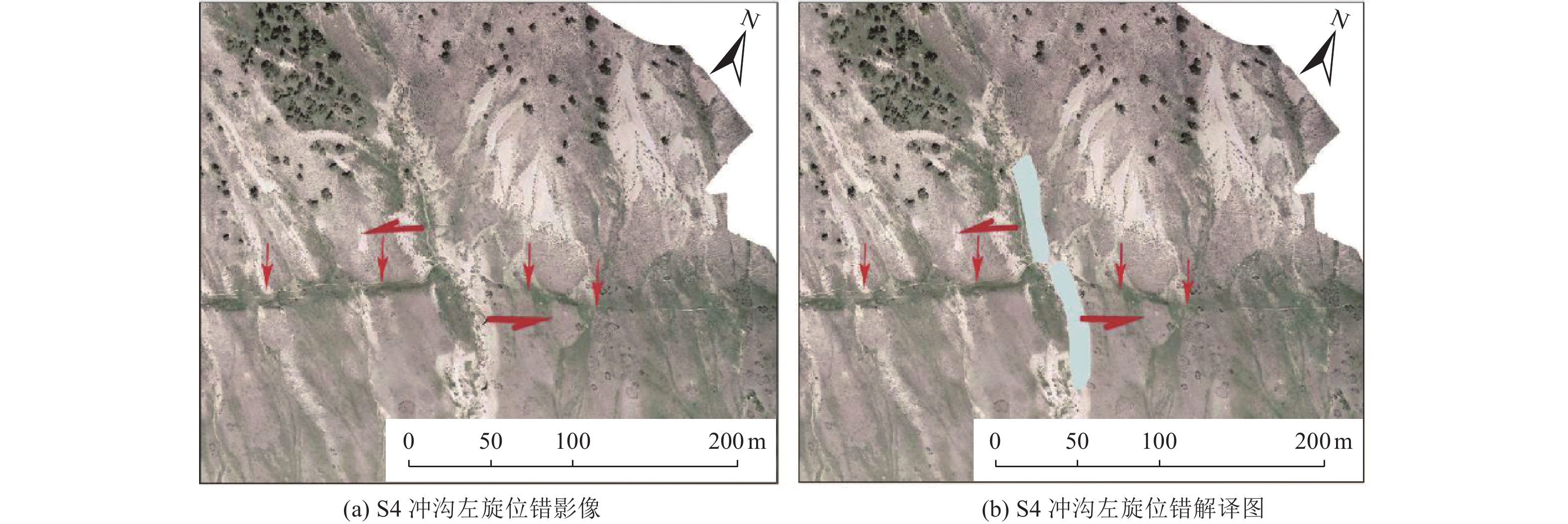
表 1 地表破裂沿线冲沟左旋位错实测位移
Table 1. Measured displacement table of left-handed dislocation of gullies along the surface rupture
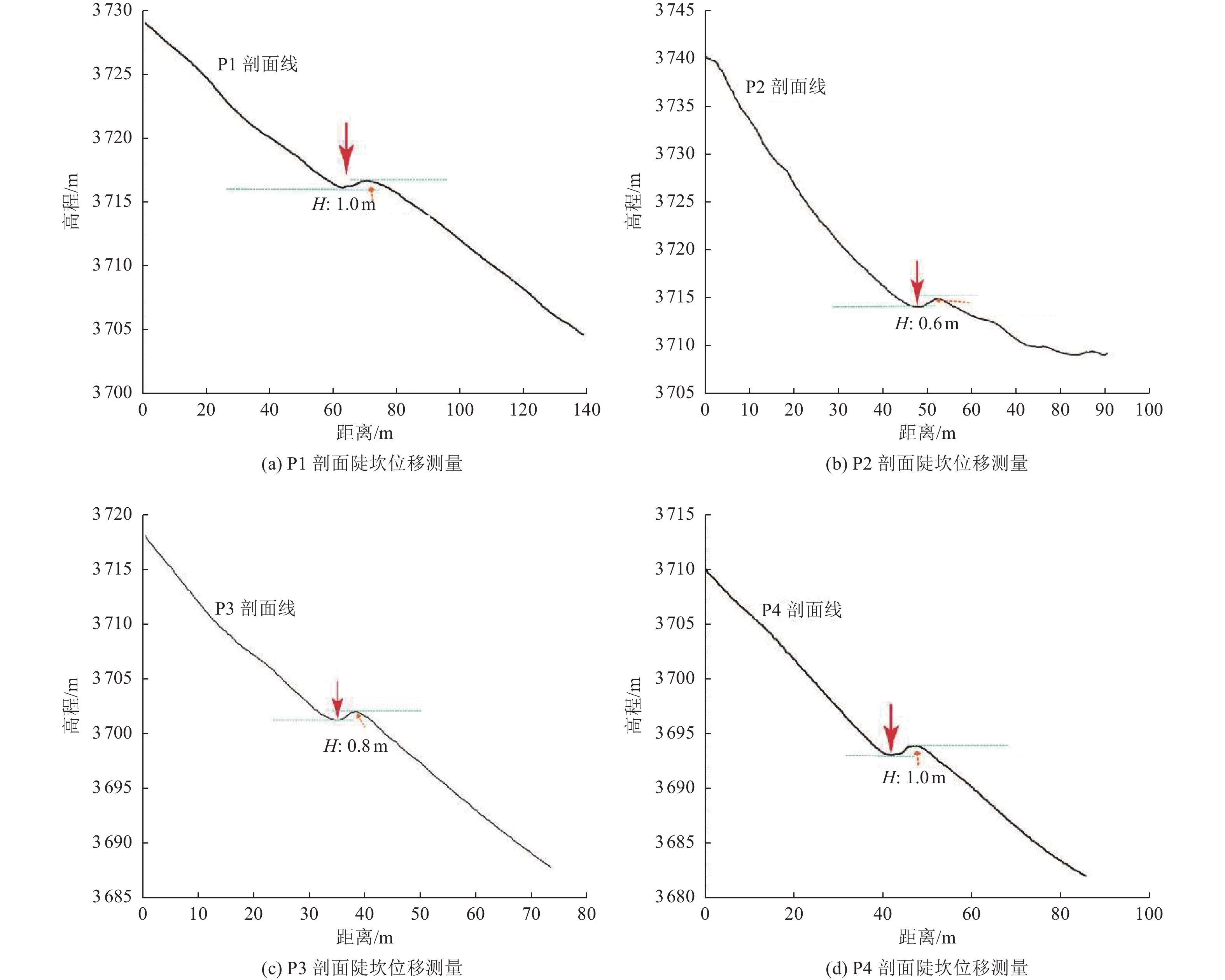
实测水平位移点 水平位移/m 平均水平位移/m S1 11.7±1.2 14.5±1.8 S2 14.5±1.5 S3 15.8±1.5 S4 16.0±1.6 表 2 断层陡坎垂直高度实测位移
Table 2. Measured displacement of vertical height of fault scarp
实测垂直位移点 垂直位移/m 平均垂直位移/m P1 1.0 0.85 P2 0.6 P3 0.8 P4 1.0 表 3 断裂沿线冲沟左旋位错实测位移
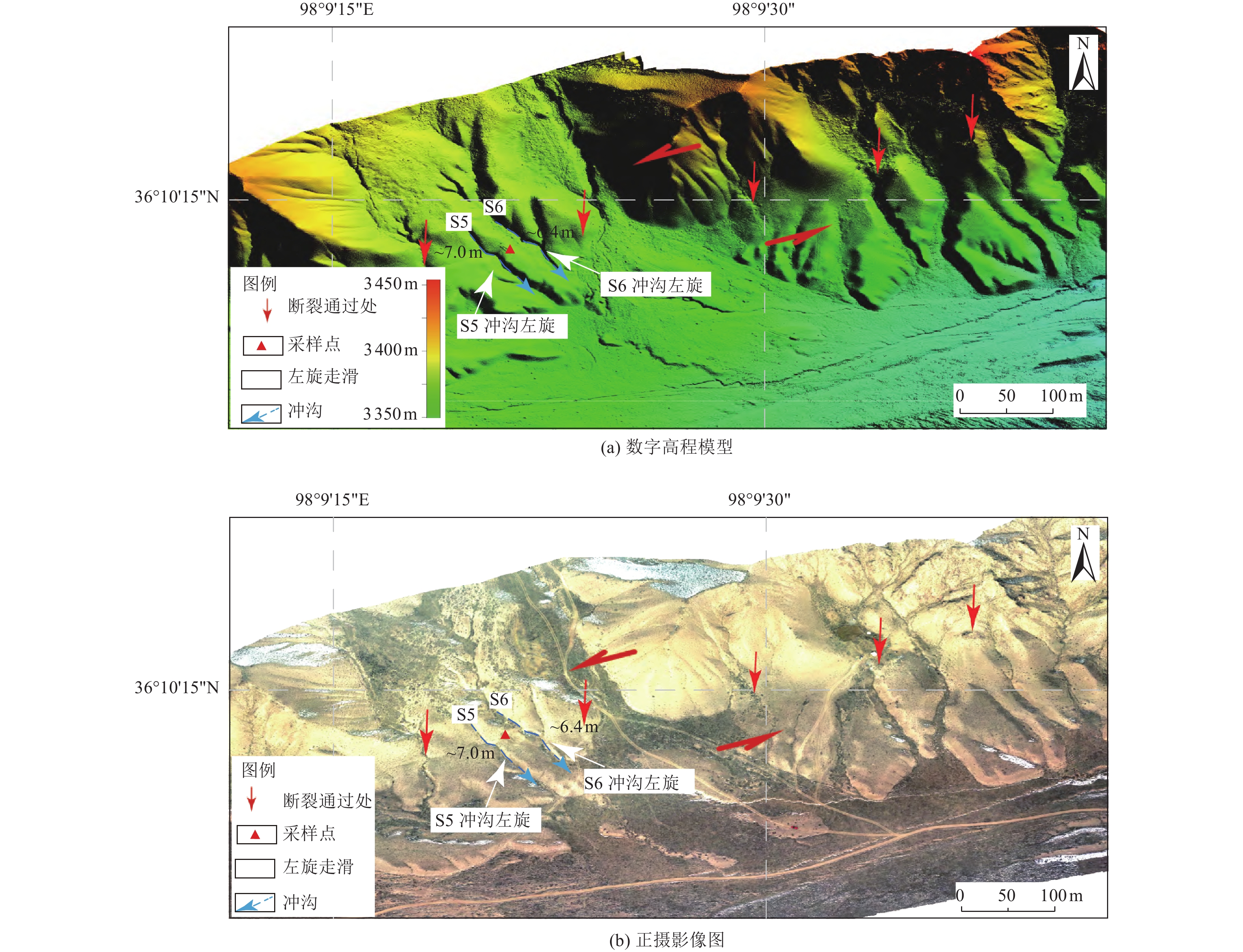
Table 3. Measured displacement table of gully left-handed dislocation along the fault
实测水平位移点 水平位移/m 平均水平位移/m S5 7.0±0.8 6.7±0.8 S6 6.4±0.8 表 4 桃斯托河西北岸探槽14C样品测试结果
Table 4. Test results of 14C sample from trench on the north west bank of taosto river
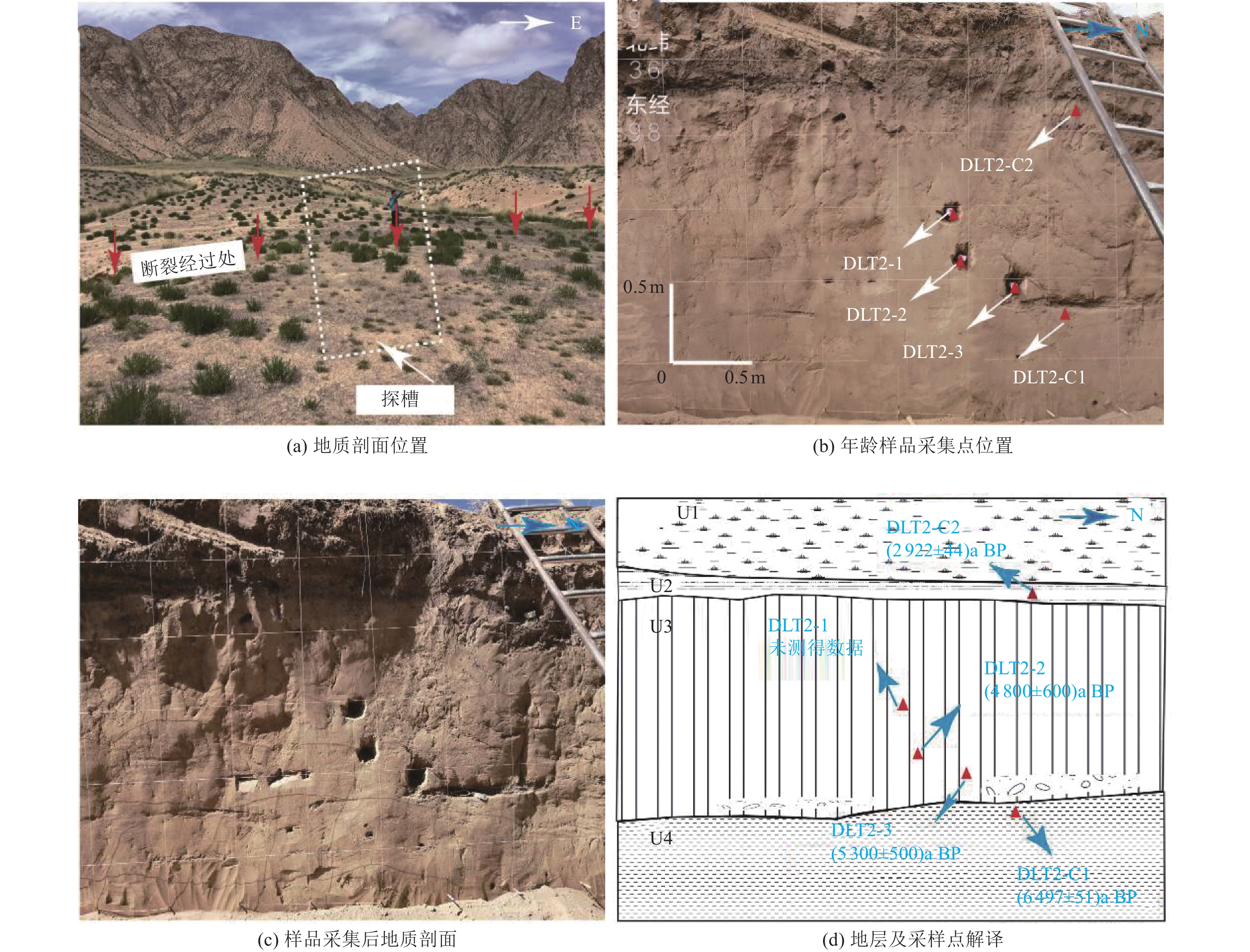
实验室编号 样品号 取样位置 测年物质 常规放射性碳年代/a BP 树轮校正2σ/Cal a BP Beta-536481 DLT1-C2 U4地层 泥炭 4 820±30 5 533±41 Beta-536483 DLT1-C4 U5地层 泥炭 7 600±30 8 397±21 表 5 G109国道以西探槽OSL样品测试结果
Table 5. Test results of OSL sample trench from the trench to west of G109 national highway
实验室编号 样品号 取样位置 环境剂量率/(Gy·ka−1) 测年物质 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka — DLT2-1 U3地层 — 未取得测试数据 — — 2020_1_22 DLT2-2 U3地层 3.646±0.160 粉质黏土 17.58±1.97 4.8±0.6 2020_1_23 DLT2-3 U3地层 3.653±0.162 细砂 19.41±1.44 5.3±0.5 表 6 G109国道以西探槽14C样品测试结果
Table 6. Test results of 14C sample from the trench to the west of G109 national highway
实验室编号 样品号 取样位置 测年物质 常规放射性碳年代/a BP 树轮校正2σ/Cal a BP Beta-570283 DLT2-C1 U4地层 泥炭 5 710±30 6 497±51 Beta-570284 DLT2-C2 U2地层 泥炭 2 820±30 2 922±44 -
邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康等, 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020—1030.Deng Q. D. , Zhang P. Z. , Ran Y. K. , et al. , 2003. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(4): 356—372. 盖海龙, 姚生海, 杨丽萍等, 2021. 青海玛多“5·22”MS7.4级地震的同震地表破裂特征、成因及意义. 地质力学学报, 27(6): 899—912 doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.073Gai H. L. , Yao S. H. , Yang L. P. , et al. , 2021. Characteristics and causes of coseismic surface rupture triggered by the "5.22" MS7.4 Earthquake in Maduo, Qinghai, and their significance. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 899—912. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.073 哈广浩, 任治坤, 刘金瑞等, 2021. 青海都兰地区夏日哈活动断裂带的发现及其构造意义. 地震地质, 43(3): 614—629 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.009Ha G. H. , Ren Z. K. , Liu J. R. , et al. , 2021. New discovery of Xiariha fault zone around Dulan area, Qinghai province and its tectonic implications. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 614—629. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.009 李智敏, 苏鹏, 黄帅堂等, 2018. 日月山断裂德州段晚更新世以来的活动速率研究. 地震地质, 40(3): 656—671 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.011Li Z. M. , Su P. , Huang S. T. , et al. , 2018. Slip rates of the Riyue MT. fault at Dezhou segment since late pleistocene. Seismology and Geology, 40(3): 656—671. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.011 李忠武, 陈桂华, 2022. 基于无人机倾斜航空摄影三维点云测量同震倾滑变形研究——以2021年玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂为例. 震灾防御技术, 17(1): 46—55 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20220105Li Z. W. , Chen G. H. , 2022. Measurement of co-seismic dip-slip based on 3 D point clouds from UAV oblique photogrammetry——a case study of surface rupture of the 2021 Maduo MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 17(1): 46—55. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20220105 王光明, 吴中海, 彭关灵等, 2021.2021年5月21日漾濞MS6.4地震的发震断层及其破裂特征: 地震序列的重定位分析结果. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 662—678 doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.055Wang G. M. , Wu Z. H. , Peng G. L. , et al. , 2021. Seismogenic fault and it's rupture characteristics of the 21 May, 2021 Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake: Analysis results from the relocation of the earthquake sequence. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 662—678. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.055 吴果, 孙浩越, 吕丽星等, 2022.2022年青海门源MS6.9地震后冷龙岭断裂未来强震的水平位错量评估. 震灾防御技术, 17(2): 308—315 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20220211Wu G. , Sun H. Y. , Lv L. X. , et al. , 2022. Assessment of horizontal displacements for future strong earthquakes on the Lenglongling fault after the 2022 MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake, Qinghai province, China. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 17(2): 308—315. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20220211 徐锡伟, 2006. 活动断层、地震灾害与减灾对策问题. 震灾防御技术, 1(1): 7—14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.01.002Xu X. W. , 2006. Active faults, associated earthquake disaster distribution and policy for disaster reduction. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(1): 7—14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.01.002 徐锡伟, 郭婷婷, 刘少卓等, 2016. 活动断层避让相关问题的讨论. 地震地质, 38(3): 477—502 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001Xu X. W. , Guo T. T. , Liu S. Z. , et al. , 2016. Discussion on issues associated with setback distance from active fault. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 477—502. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔等, 2020. 柴达木盆地北缘断裂(锡铁山段)的构造地貌特征与晚第四纪活动速率. 地震地质, 42(6): 1385—1400 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.008Yao S. H. , Gai H. L. , Yin X. , et al. , 2020. Tectonic geomorphology and quaternary slip rate of the Xitieshan section of the northern margin fault of Qaidam basin. Seismology and Geology, 42(6): 1385—1400. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.008 袁道阳, 2003. 青藏高原东北缘晚新生代以来的构造变形特征与时空演化. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Yuan D. Y., 2003. Tectonic deformation features and space-time evolution in northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau since the late Cenozoic time. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese) 袁道阳, 张培震, 刘百篪等, 2004. 青藏高原东北缘晚第四纪活动构造的几何图像与构造转换. 地质学报, 78(2): 270—278 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2004.02.017Yuan D. Y. , Zhang P. Z. , Liu B. C. , et al. , 2004. Geometrical imagery and tectonic transformation of late quaternary active tectonics in northeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(2): 270—278. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2004.02.017 张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪等, 2013. 中国大陆的活动断裂、地震灾害及其动力过程. 中国科学: 地球科学, 43(10): 1607—1620 doi: 10.1360/zd-2013-43-10-1607Zhang P. Z. , Deng Q. D. , Zhang Z. Q. , et al. , 2013. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 43(10): 1607—1620. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/zd-2013-43-10-1607 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2018. GB/T 36072—2018 活动断层探测. 北京: 中国标准出版社.Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2018. GB/T 36072—2018 Surveying and prospecting of active fault. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) Molnar P. , Stock J. M. , 2009. Slowing of India's convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics. Tectonics, 28(3): TC3001. Yuan D. Y., Champagnac J. D., Ge W. P., et al., 2011. Late Quaternary right-lateral slip rates of faults adjacent to the Lake Qinghai, northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau. GSA Bulletin, 123(9—10): 2016—2030. Zhang P. Z. , Shen Z. K. , Wang M. , et al. , 2004. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan plateau from global positioning system data. Geology, 32(9): 809—812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1 -




 下载:
下载: