Analytical Solution for the Longitudinal Response of Tunnels under Combined Seismic-fault Misalignment
-
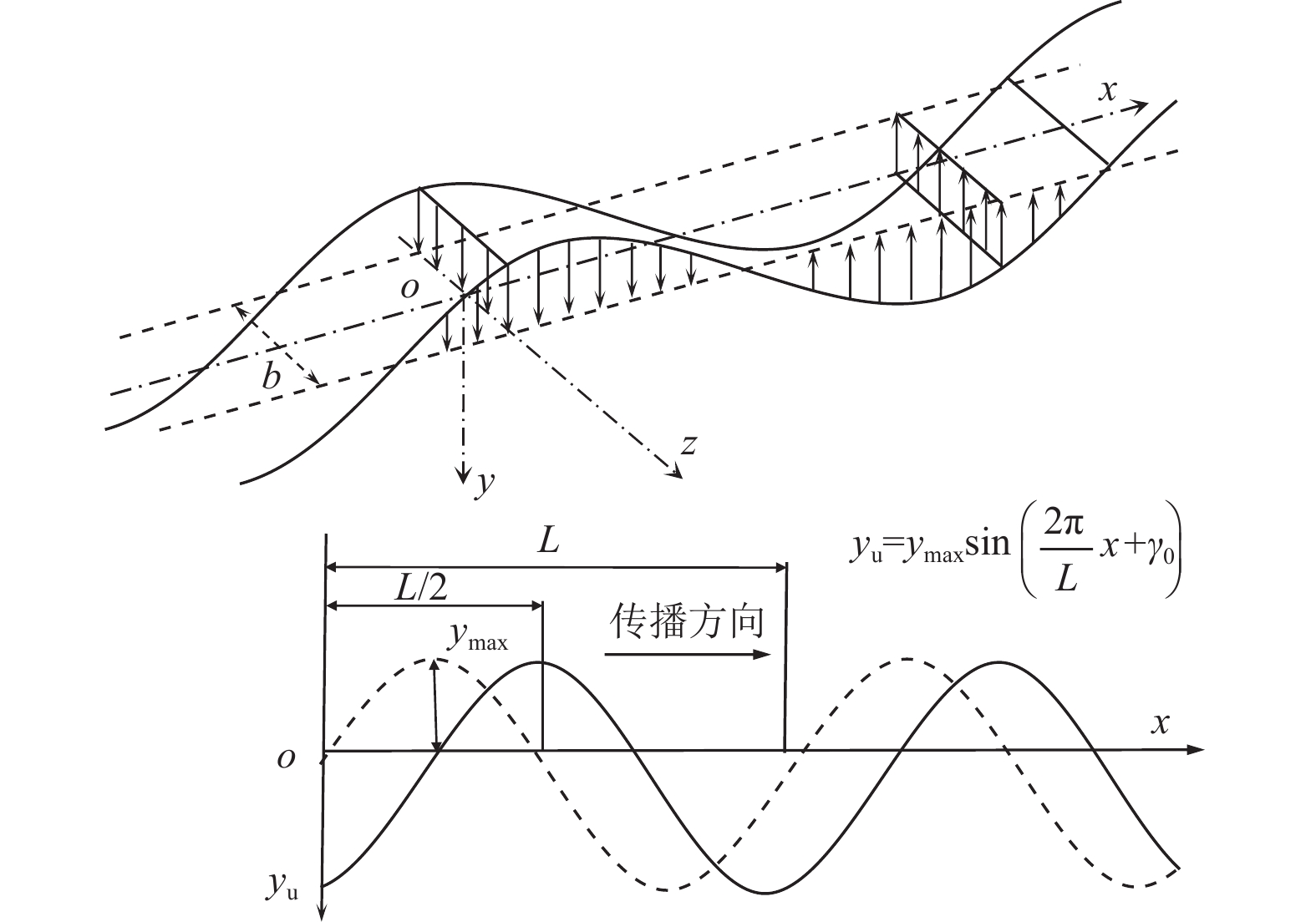
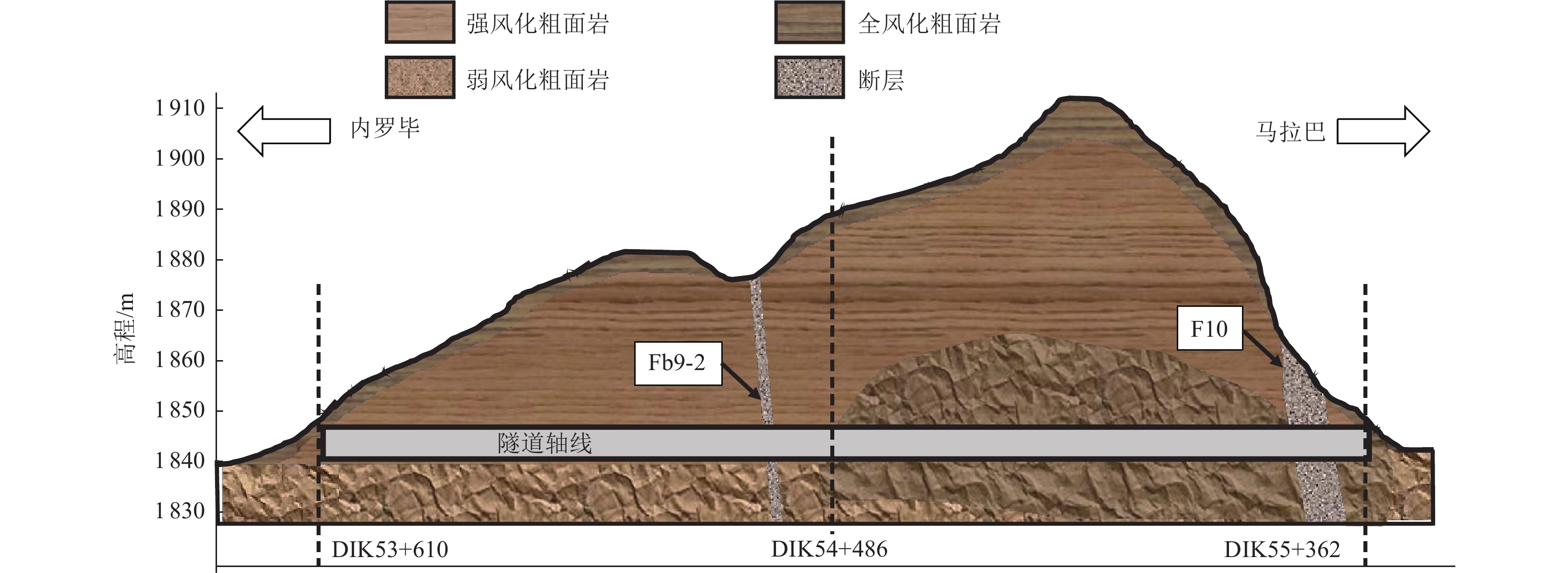
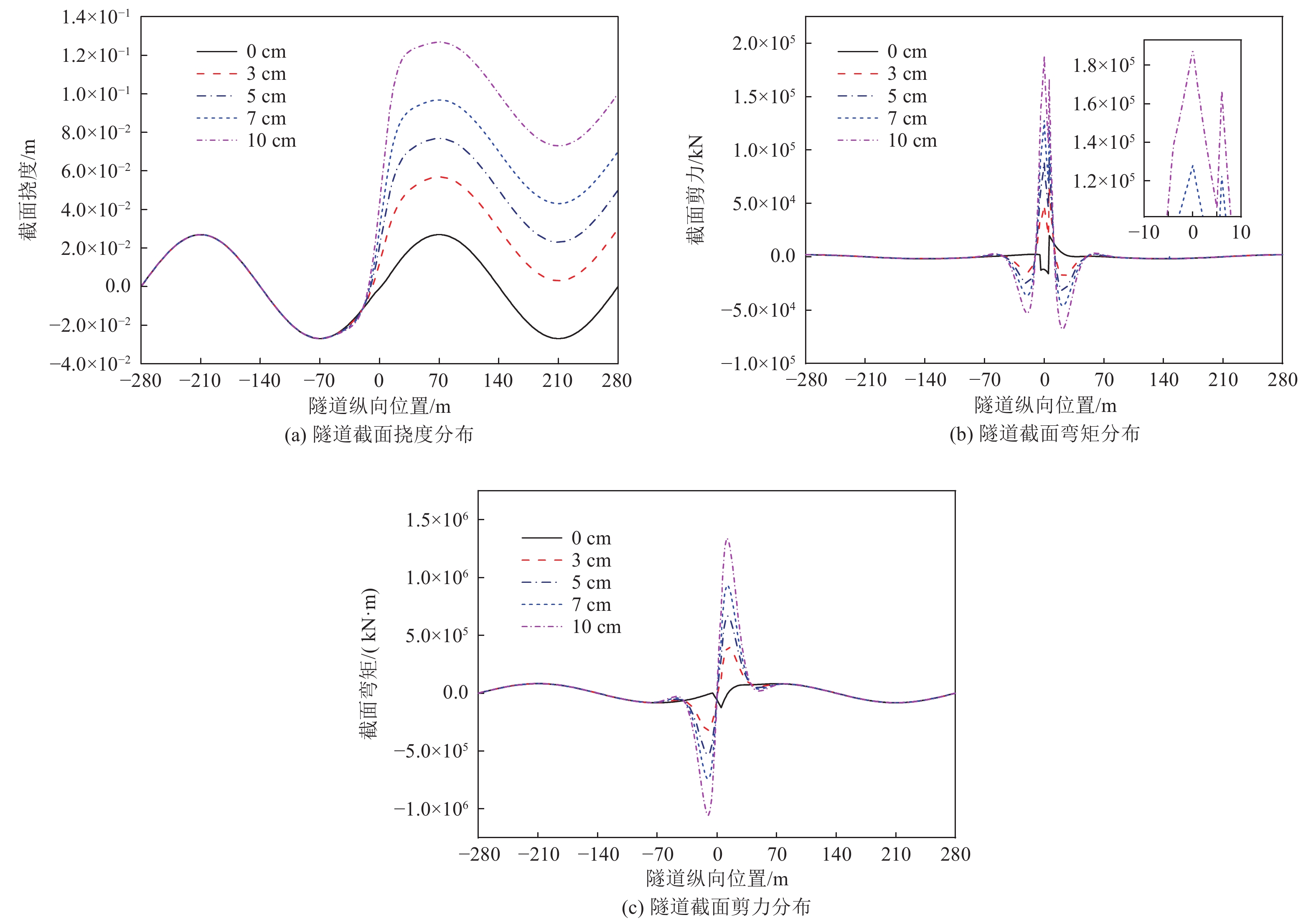
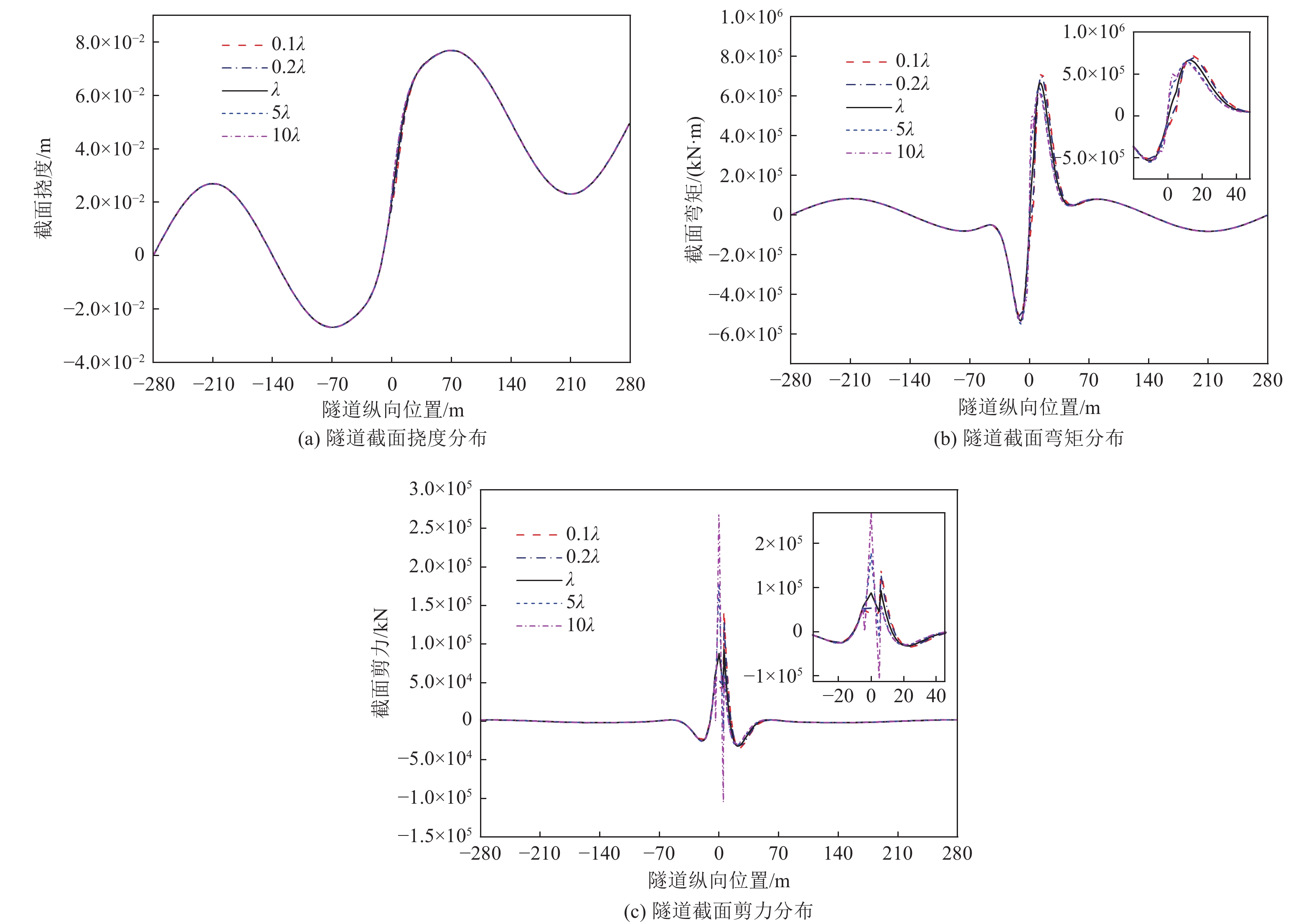
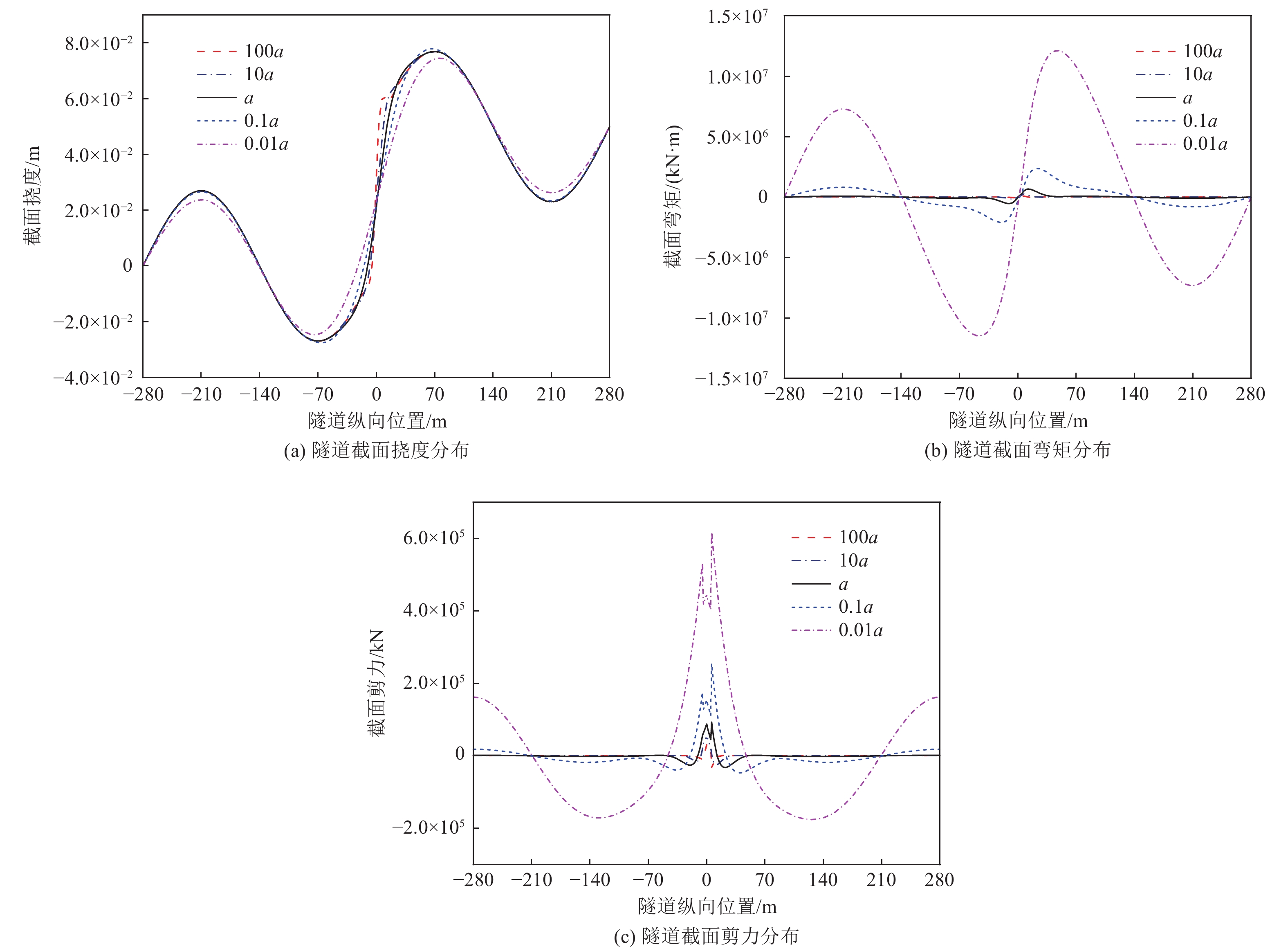
摘要: 隧道穿越地震活动断层带时可能遭受严重破坏,以内马铁路一期三标段工程为依托,对地震动和断层错动联合作用下隧道结构纵向响应进行研究。针对穿越断层破碎带的隧道结构,基于地下结构抗震拟静力法,将其简化为弹性地基梁,并将地震动和断层错动位移简化为作用在隧道上的静荷载,建立地震动和断层错动联合作用下隧道纵向响应理论模型并进行求解,利用有限元数值模拟方法验证解析解的正确性。通过解析解进行参数敏感性分析,揭示断层错动位移、两侧围岩地基系数与断层破碎带地基系数比及围岩与隧道结构刚度比对隧道结构纵向响应的影响规律。研究结果表明,断层错动位移增加使隧道结构截面弯矩、剪力峰值接近线性增加,隧道内力沿隧道纵向分布的影响范围不变,且断层破碎带界面出现了截面剪力突变;两侧围岩地基系数与断层破碎带地基系数比对隧道结构截面剪力的影响较大,在地震动和断层错动联合作用下隧道结构剪力在断层破碎带界面急剧减小;随着围岩与隧道结构刚度比的减小,地震动引起的隧道挠度减小,断层错动作用引起的隧道挠度变化范围增大,同时隧道结构内力响应明显增大。Abstract: China is one of the countries that has the most severe seismic hazards in the world, and tunnels may suffer severe damage when crossing seismically active fault zones. In this paper, the longitudinal response of the tunnel structure under the joint action of earthquake and fault misalignment is investigated based on the third standard section of the first phase of the Nairobi-Malaba railway as a project. For the tunnel structure crossing the fault fragmentation zone, based on the idea of seismic anthropomorphism of underground structure, it is simplified into elastic foundation beam, and the ground vibration and fault misalignment displacement are simplified into static load acting on the tunnel, the theoretical model of tunnel longitudinal response under the joint action of earthquake - fault misalignment is established and solved, and the correctness of the analytical solution is verified by using the finite element numerical simulation method. Parametric sensitivity analysis is carried out to reveal the influence of the fault misalignment displacement, the ratio of the foundation coefficient of the surrounding rock to the foundation coefficient of the fault fragmentation zone, and the ratio of the surrounding rock to the tunnel structure stiffness on the longitudinal response of the tunnel structure. The results show that the increase of fault misalignment displacement makes the tunnel structure cross-sectional moment and tunnel structure cross-sectional shear peak close to linear increase, the influence range of tunnel internal force distribution along the tunnel longitudinal direction remains unchanged, and there is a sudden change of cross-sectional shear at the interface of fault fragmentation zone; the ratio of surrounding rock foundation coefficient and fault fragmentation zone foundation coefficient on both sides has a greater influence on the tunnel structure cross-sectional shear, under the combined effect of earthquake - fault misalignment tunnel The shear force of the tunnel structure decreases sharply at the interface of the fault zone; the ratio of surrounding rock to tunnel structure stiffness decreases, the tunnel deflection caused by the earthquake decreases, and the range of deflection caused by fault misalignment increases, while the internal force response of the tunnel structure increases significantly.
-
Key words:
- Tunnel /
- Seismic shaking /
- Fault dislocation /
- Analytical solution /
- Foundation beam /
- Quasi-static method
-
表 1 计算参数
Table 1. Calculation parameter table
材料 弹性模量/GPa 围岩泊松比 围岩密度/(kg·m−3) 地基系数/MPa 隧道截面惯性矩/m4 隧道宽度/m 强风化粗面岩 6.5 0.32 2 400 1 083.4 — — 断层破碎带 2.0 0.30 2 200 332.7 — — 隧道衬砌 35.0 0.20 — — 173.63 6.2 -
甘星球, 徐锋, 王晓伟等, 2021. 断层错动隧道地震响应规律及减震模拟研究. 现代隧道技术, 58(3): 100—106Gan X. Q. , Xu F. , Wang X. W. , et al. , 2021. Simulation study on seismic response laws and seismic mitigation measures of tunnels under fault dislocation. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 58(3): 100—106. (in Chinese) 耿萍, 吴川, 唐金良等, 2012. 穿越断层破碎带隧道动力响应特性分析. 岩石力学与工程学报, 31(7): 1406—1413Geng P. , Wu C. , Tang J. L. , et al. , 2012. Analysis of dynamic response properties for tunnel through fault fracture zone. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 31(7): 1406—1413. (in Chinese) 何川, 李林, 张景等, 2014. 隧道穿越断层破碎带震害机理研究. 岩土工程学报, 36(3): 427—434He C. , Li L. , Zhang J. , et al. , 2014. Seismic damage mechanism of tunnels through fault zones. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 36(3): 427—434. (in Chinese) 刘国钊, 乔亚飞, 何满潮等, 2020. 活动性断裂带错动下隧道纵向响应的解析解. 岩土力学, 41(3): 923—932Liu G. Z. , Qiao Y. F. , He M. C. , et al. , 2020. An analytical solution of longitudinal response of tunnels under dislocation of active fault. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 41(3): 923—932. (in Chinese) 刘学增, 王煦霖, 林亮伦, 2013.75°倾角正断层黏滑错动对公路隧道影响的模型试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 32(8): 1714—1720Liu X. Z. , Wang X. L. , Lin L. L. , 2013. Model experiment on effect of normal fault with 75° dip angle stick-slip dislocation on highway tunnel. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 32(8): 1714—1720. (in Chinese) 孙飞, 张志强, 易志伟, 2019. 正断层黏滑错动对地铁隧道结构影响的模型试验研究. 岩土力学, 40(8): 3037—3044, 3053Sun F. , Zhang Z. Q. , Yi Z. W. , 2019. Model experimental study of the influence of normal fault with stick-slip dislocation on subway tunnel structure. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(8): 3037—3044, 3053. (in Chinese) 王明年, 崔光耀, 2011. 高烈度地震区隧道设置减震层的减震原理研究. 土木工程学报, 44(8): 126—131Wang M. N. , Cui G. Y. , 2011. Study of the mechanism of shock absorption layer in the supporting system of tunnels in highly seismic areas. China Civil Engineering Journal, 44(8): 126—131. (in Chinese) 文鑫涛, 李华玥, 段乙好等, 2021. 2020年中国大陆地震灾害损失述评. 震灾防御技术, 16(4): 651—656.Wen X. T., Li H. Y., Duan Y. H., et al., 2021. Earthquake disasters loss on Chinese mainland in 2020. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(4): 651−656. (in Chinese) 闫高明, 申玉生, 高波等, 2019. 穿越黏滑断层分段接头隧道模型试验研究. 岩土力学, 40(11): 4450—4458Yan G. M. , Shen Y. S. , Gao B. , et al. , 2019. Experimental study of stick-slip fault crossing segmental tunnels with joints. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(11): 4450—4458. (in Chinese) 张景, 何川, 耿萍等, 2017. 穿越软硬突变地层盾构隧道纵向地震响应振动台试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 36(1): 68—77 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0103Zhang J. , He C. , Geng P. , et al. , 2017. Shaking table tests on longitudinal seismic response of shield tunnel through soft-hard stratum junction. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 36(1): 68—77. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0103 Anastasopoulos I. , Gerolymos N. , Drosos V. , et al. , 2008. Behaviour of deep immersed tunnel under combined normal fault rupture deformation and subsequent seismic shaking. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 6(2): 213—239. doi: 10.1007/s10518-007-9055-0 Baziar M. H. , Nabizadeh A. , Lee C. J. , et al. , 2014. Centrifuge modeling of interaction between reverse faulting and tunnel. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 65: 151—164. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.04.008 Fan L. , Chen J. L. , Peng S. Q. , et al. , 2020. Seismic response of tunnel under normal fault slips by shaking table test technique. Journal of Central South University, 27(4): 1306—1319. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4368-0 Hashash Y. M. A. , Hook J. J. , Schmidt B. , et al. , 2001. Seismic design and analysis of underground structures. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 16(4): 247—293. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(01)00051-7 Liang L. J. , Xu C. J. , Zhu B. T. , et al. , 2020. Theoretical method for an elastic infinite beam resting on a deformable foundation with a local subsidence. Computers and Geotechnics, 127: 103740. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103740 Shen Y. S. , Wang Z. Z. , Yu J. , et al. , 2020. Shaking table test on flexible joints of mountain tunnels passing through normal fault. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 98: 103299. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103299 St John C. M. , Zahrah T. F. , 1987. Aseismic design of underground structures. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2(2): 165—197. doi: 10.1016/0886-7798(87)90011-3 Tsinidis G. , De Silva F. , Anastasopoulos I. , et al. , 2020. Seismic behaviour of tunnels: from experiments to analysis. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 99: 103334. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103334 Vesić A. B. , 1961. Bending of beams resting on isotropic elastic solid. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, 87(2): 35—53. doi: 10.1061/JMCEA3.0000212 Wang J. N., 1993. Seismic design of tunnels: a simple state-of-the-art design approach. New York: Parsons Brinckerhoff Quade & Douglas. Inc. Yan G. M. , Shen Y. S. , Gao B. , et al. , 2020. Damage evolution of tunnel lining with steel reinforced rubber joints under normal faulting: an experimental and numerical investigation. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 97: 103223. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.103223 Yu H. T. , Zhang Z. W. , Chen J. T. , et al. , 2018. Analytical solution for longitudinal seismic response of tunnel liners with sharp stiffness transition. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 77: 103—114. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.04.001 Zhen C. , Qian S. , Gui-Min Z. , et al. , 2022. Response and mechanism of a tunnel subjected to combined fault rupture deformation and subsequent seismic excitation. Transportation Geotechnics, 34: 100749. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2022.100749 Zhong Z. L. , Wang Z. , Zhao M. , et al. , 2020. Structural damage assessment of mountain tunnels in fault fracture zone subjected to multiple strike-slip fault movement. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 104: 103527. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103527 -



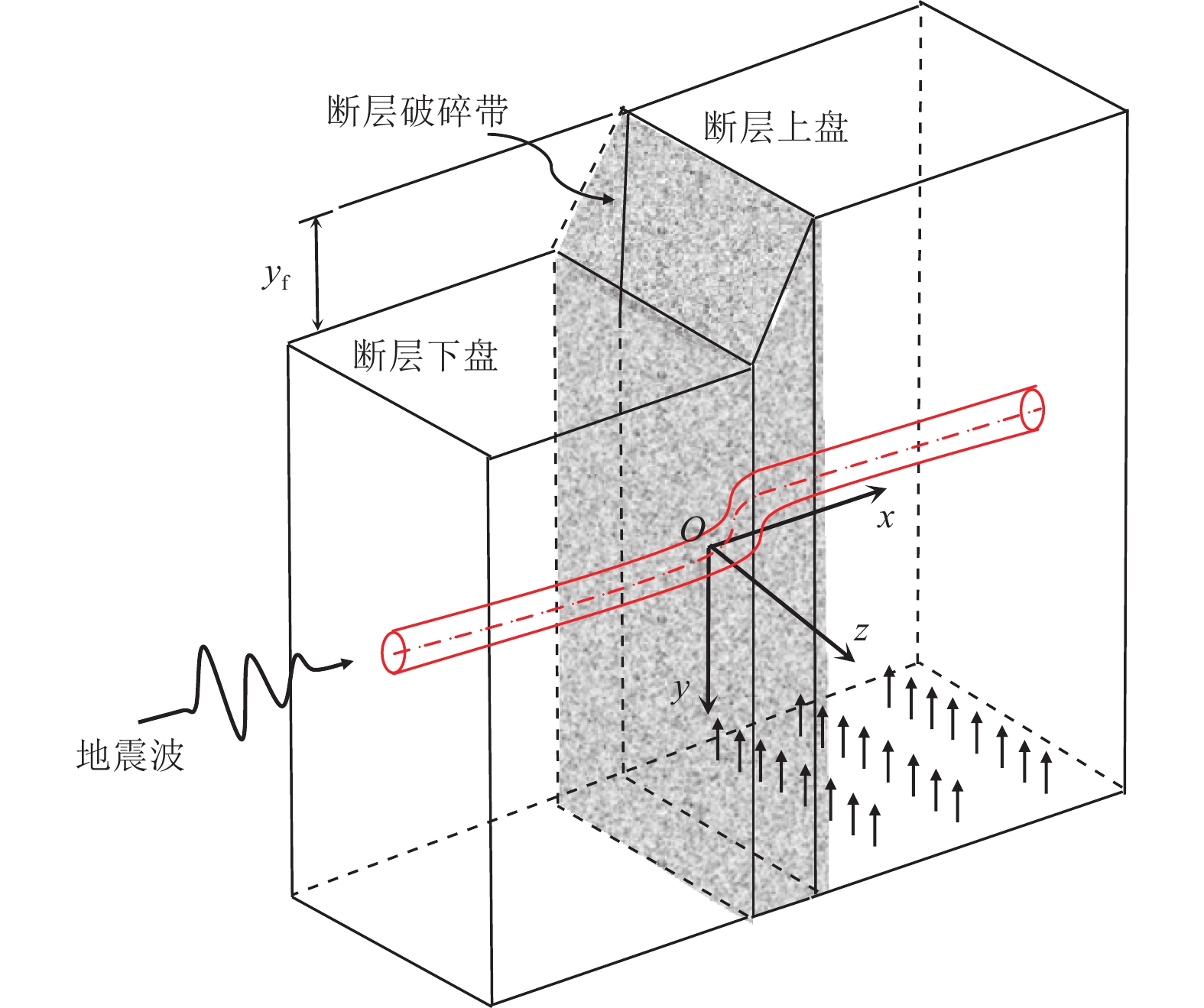
 下载:
下载: