The Analysis on Seismic Response Control of Long-span Suspension Bridge
-
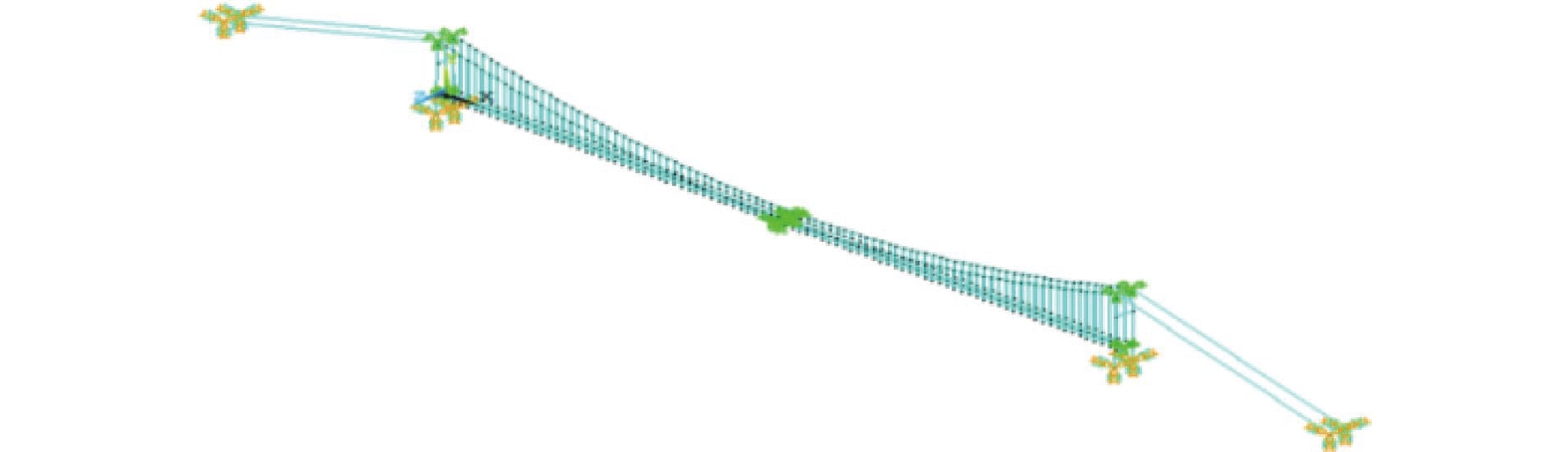
摘要: 以主跨为1 490 m的润扬长江大桥为背景,采用ANSYS软件建立结构有限元模型,计算大跨度悬索桥动力特性。对黏滞阻尼器和软钢阻尼器进行参数敏感性分析,得出控制大跨度悬索桥地震响应的最优参数值,并分析一致激励和行波激励作用下黏滞阻尼器和软钢阻尼器减震效果。研究结果表明,黏滞阻尼器和软钢阻尼器对塔梁相对位移有较好的控制效果,但会使塔底内力有所增加;就位移控制而言,软钢阻尼器的效果更好;在低视波速区间内,黏滞阻尼器和软钢阻尼器减震效果明显存在波动特征;随着视波速的逐渐增大,黏滞阻尼器和软钢阻尼器减震效果受视波速的影响逐渐减小,悬索桥地震响应逐渐平缓,并趋于一致激励作用下的对应值。Abstract: Taking Runyang Yangtze River Bridge with 1490 m main span as the background, the structural finite element model is established by ANSYS software, and the dynamic characteristics of long-span suspension bridge are calculated. The parameter sensitivity analysis of viscous damper and mild steel damper is carried out, the optimal parameter value for controlling the seismic responses of long-span suspension bridge is obtained, and the damping effects of the two dampers under uniform excitation and traveling wave excitation are analyzed. The results show that the above two dampers have good control effect on the relative displacement of tower beam, but they will increase the internal force at the bottom of the tower; in terms of displacement control, the effect of mild steel damper is better; in the range of low apparent wave velocity, the damping effect of the two damping devices has obvious fluctuation characteristics; with the increment of apparent wave velocity, the damping effect is gradually reduced, stabilized and close to the case of uniform excitation.
-
表 1 悬索桥动力特性分析
Table 1. Dynamic characteristic analysis of suspension bridge
阶次 频率/Hz 振型描述 阶次 频率/Hz 振型描述 1 0.049 857 一阶对称侧弯 11 0.210 620 一阶反对称扭转 2 0.090 090 一阶反对称竖弯 12 0.214 330 主缆振动 3 0.130 630 一阶对称竖弯 13 0.247 290 主缆振动 4 0.131 430 一阶反对称侧弯 14 0.262 390 二阶对称侧弯 5 0.181 000 主缆振动 15 0.264 240 三阶对称竖弯 6 0.182 400 二阶对称竖弯 16 0.291 330 主缆振动 7 0.184 910 主缆振动 17 0.316 890 主缆振动+扭转 8 0.186 160 主缆振动+主梁扭转 18 0.326 400 三阶反对称竖弯 9 0.187 020 一阶对称扭转 19 0.328 770 主缆振动 10 0.200 630 二阶反对称竖弯 20 0.330 460 主缆振动 表 2 TCU102波输入下软钢阻尼器响应峰值
Table 2. Peak values of responses of mild steel damper under TCU102 wave input
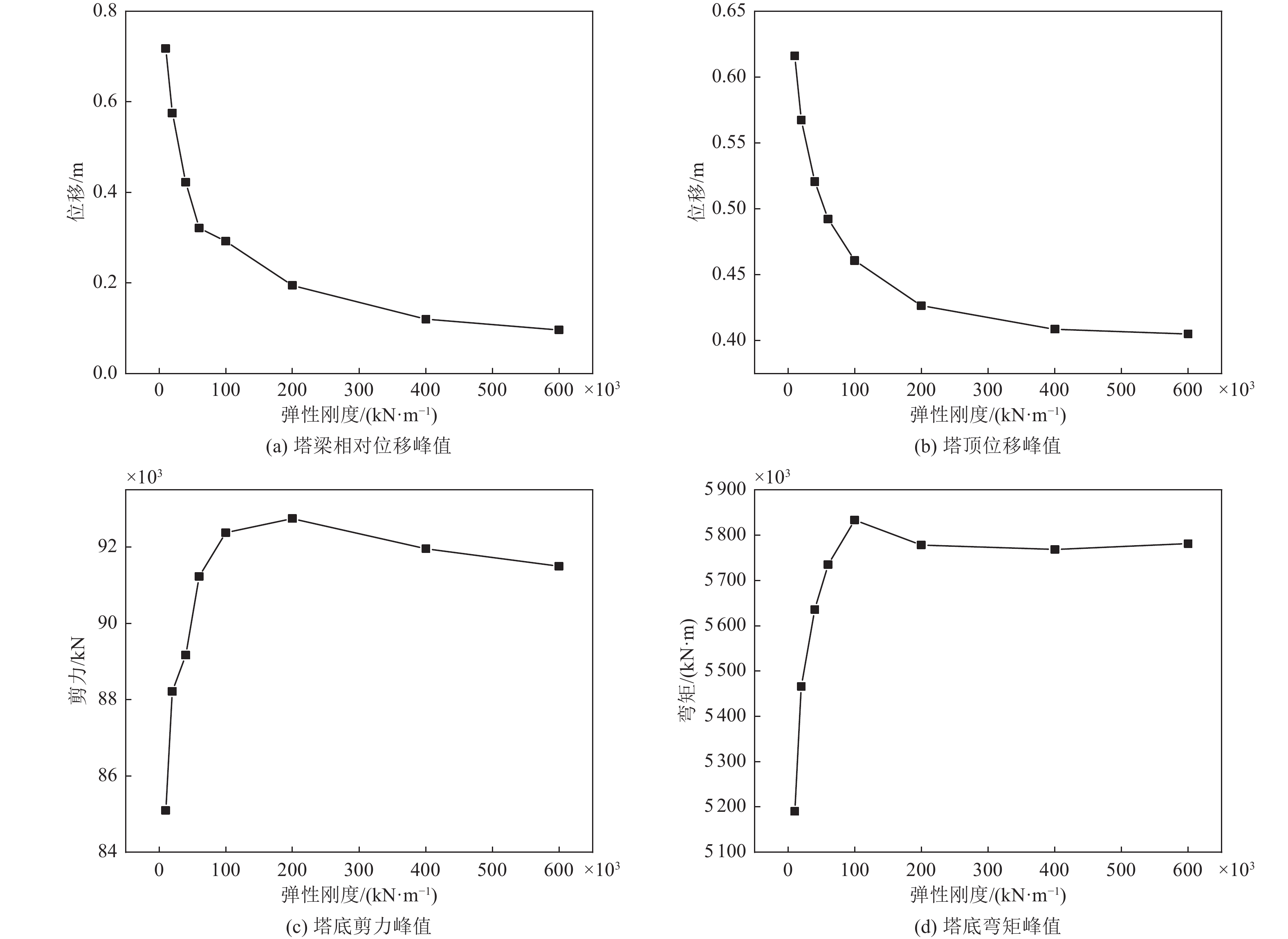
屈服荷载/kN 南塔阻尼器位移/m 北塔阻尼器位移/m 南塔阻尼器阻尼力/kN 北塔阻尼器阻尼力/kN 900 0.817 2 0.806 9 11 800 11 800 2 000 0.694 2 0.692 1 3 587 3 663 4 000 0.553 1 0.596 4 4 967 4 833 6 000 0.456 3 0.449 1 6 239 6 091 9 000 0.246 1 0.240 8 9 496 9 113 20 000 0.089 7 0.076 1 8 872 8 650 40 000 0.016 8 0.014 1 8 085 8 239 50 000 0.005 4 0.004 9 7 758 7 963 表 3 悬索桥结构关键部位地震响应与减震效果对比
Table 3. Comparison of seismic responses and shock absorbing effect on key positions of suspension bridge structure
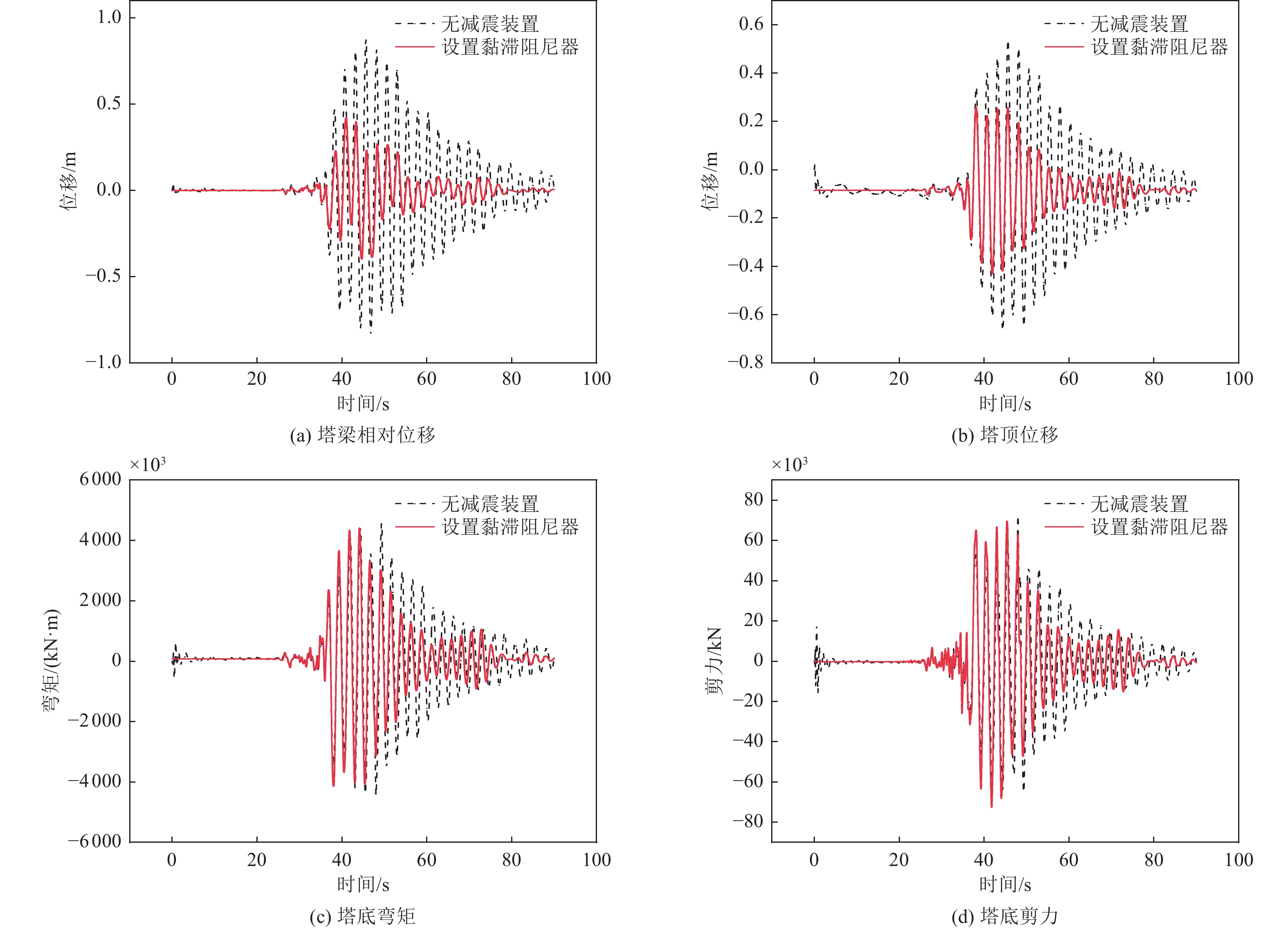
减震装置 塔梁相对位移/m 减震率η/% 塔顶位移/m 减震率η/% 塔底弯矩/(kN·m) 减震率η/% 塔底剪力/kN 减震率η/% 无减震装置 0.874 9 — 0.664 8 — 4 564.11×103 — 72.48×103 — 黏滞阻尼器 0.421 6 51.8 0.430 8 35.2 4 411.13×103 3.4 72.55×103 −0.1 软钢阻尼器 0.194 6 77.8 0.426 5 35.8 5 778.02×103 −26.6 92.75×103 −27.9 表 4 行波效应下悬索桥结构关键部位位移响应与减震效果对比
Table 4. Comparison of displacement response shock absorbing effect on key positions of suspension bridge structure under traveling wave effect
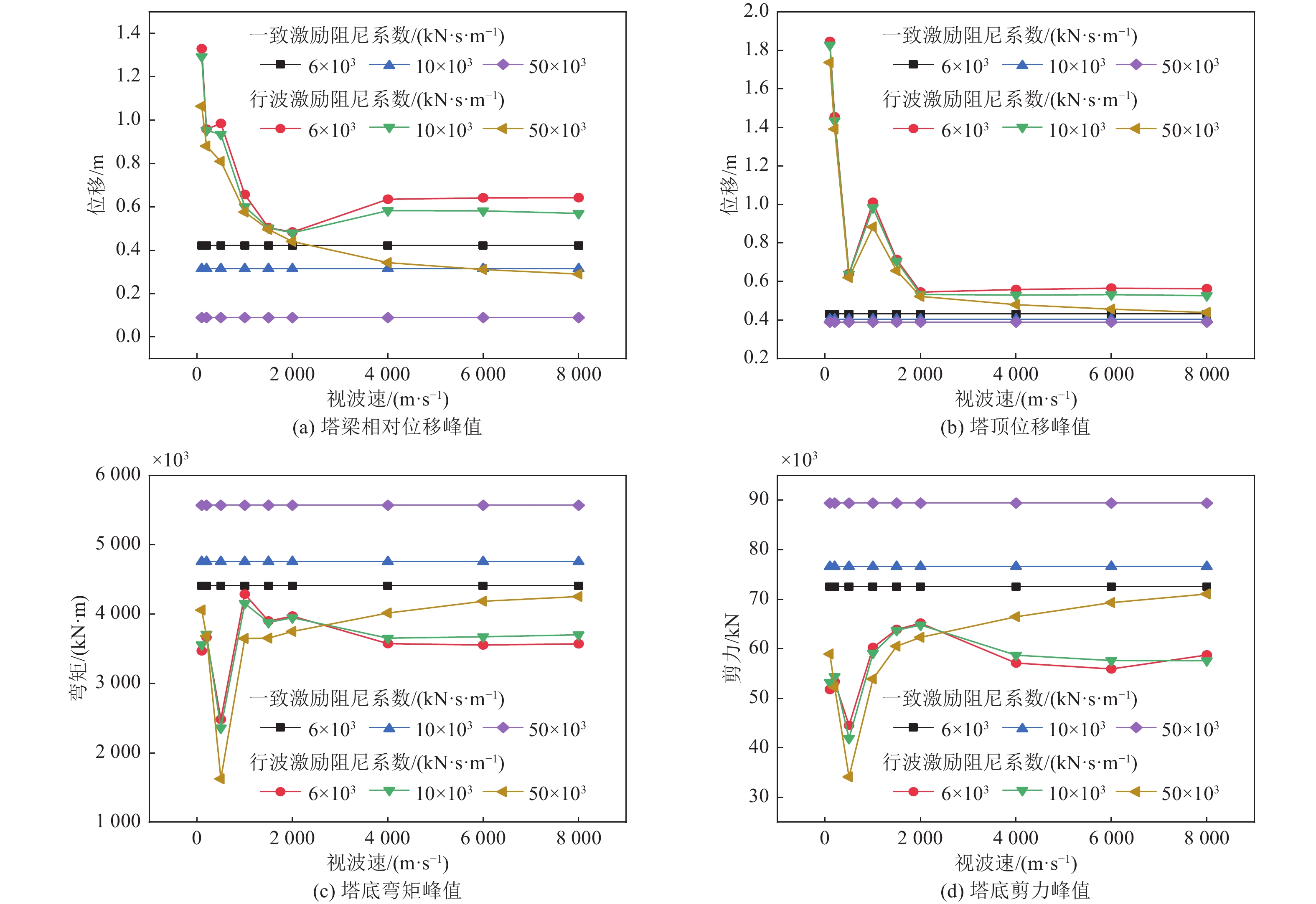
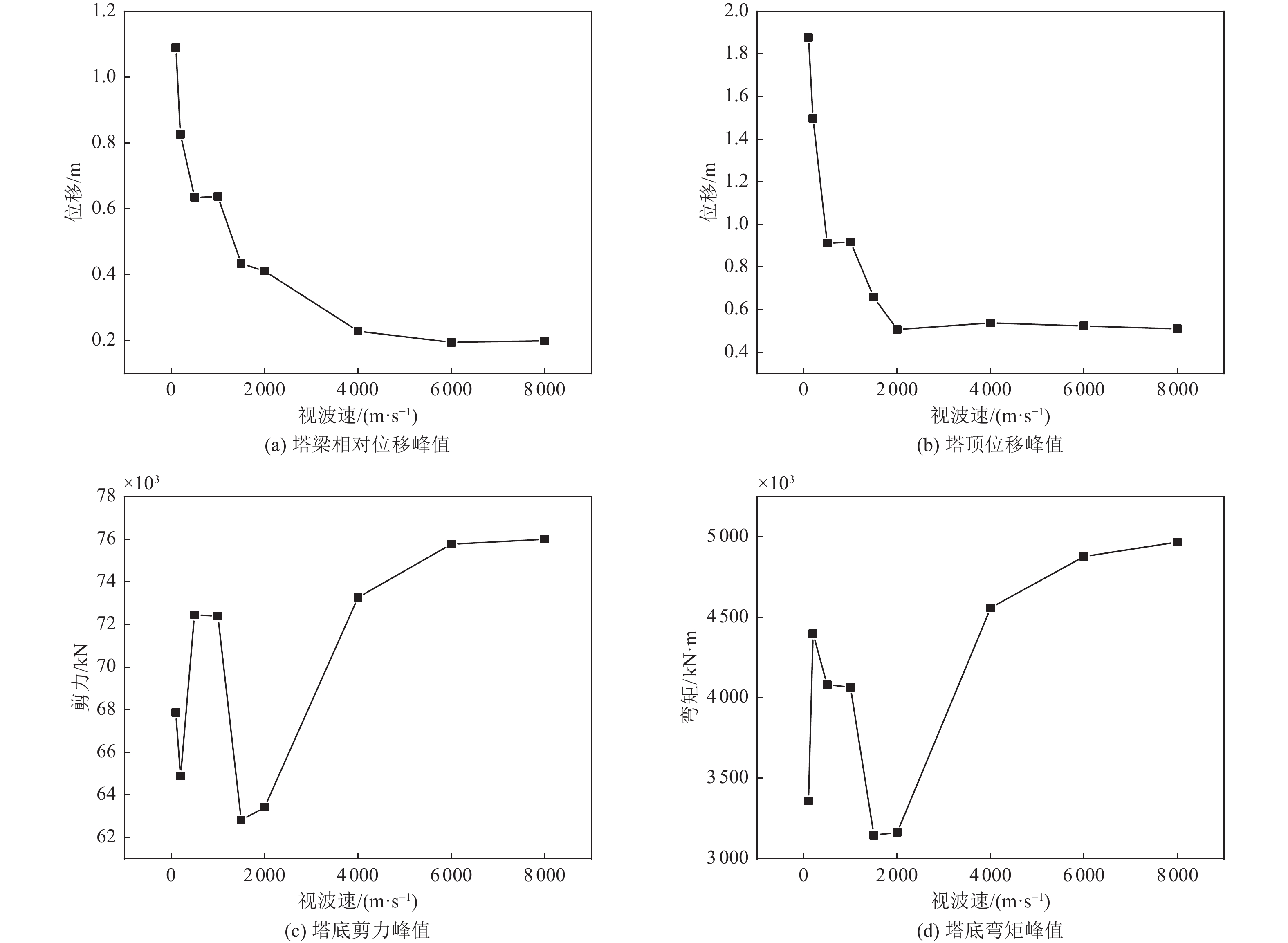
视波速/(m·s−1) 塔梁相对位移减震率η/% 塔顶位移减震率η/% 黏滞阻尼器 软钢阻尼器 黏滞阻尼器 软钢阻尼器 100 4.32 21.57 1.69 1.06 200 6.49 19.41 2.87 2.67 500 9.62 41.73 0.46 −42.45 1 000 20.46 22.88 5.41 14.09 1 500 2.19 15.77 1.59 9.47 2 000 8.48 22.31 4.45 11.22 4 000 15.75 69.66 10.18 13.49 6 000 20.36 75.88 11.61 18.36 8 000 23.31 76.16 12.24 20.53 表 5 行波效应下悬索桥结构关键部位内力响应减震效果对比
Table 5. Comparison of internal force response shock absorbing effect on key positions of suspension bridge structures
视波速/(m·s−1) 塔底弯矩减震率η/% 塔底剪力减震率η/% 黏滞阻尼器 软钢阻尼器 黏滞阻尼器 软钢阻尼器 100 −3.28 −2.98 −8.17 −41.79 200 16.66 15.92 17.73 3.08 500 13.65 −41.92 11.54 −43.90 1 000 8.23 12.98 11.41 −6.41 1 500 0.79 19.93 0.43 2.16 2 000 0.89 21.08 1.07 3.75 4 000 7.36 −1.52 1.40 −26.46 6 000 16.95 −6.88 11.31 −20.13 8 000 19.28 −12.27 9.16 −17.46 -
姜涛, 张哲, 邱文亮, 2014. 一座自锚式悬索桥的减振设计. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 38(2): 371—374 doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2014.02.030Jiang T. , Zhang Z. , Qiu W. L. , 2014. Application of viscous damper on self-anchored suspension bridge. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 38(2): 371—374. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2014.02.030 李钢, 李宏男, 2006. 新型软钢阻尼器的减震性能研究. 振动与冲击, 25(3): 66—72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.03.015Li G. , Li H. N. , 2006. Study on vibration reduction of structure with a new type of mild metallic dampers. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 25(3): 66—72. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.03.015 李丽, 赵国峰, 李吉等, 2020. 一致激励与多点激励对悬索桥地震响应影响分析. 震灾防御技术, 15(2): 252—259 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200203Li L. , Zhao G. F. , Li J. , et al. , 2020. Analysis of the influence of uniform excitation and multi-point excitation on the seismic response of suspension bridge. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(2): 252—259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200203 卢长炯, 卢明奇, 2021. 基于黏滞阻尼器的单跨悬索桥地震位移响应控制. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 38(2): 98—103Lu C. J. , Lu M. Q. , 2021. Seismic displacement responses control of single span suspension bridges based on viscous dampers. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science), 38(2): 98—103. (in Chinese) 沈禹, 谈华顺, 王献挚等, 2020. 考虑行波效应的大跨度矮塔斜拉桥耐震时程分析. 工程力学, 37(3): 131—141, 148Shen Y. , Tan H. S. , Wang X. Z. , et al. , 2020. Application of the endurance time method to seismic-induced pounding analysis for long-span extradosed cable-stayed bridges considering wave passage effects. Engineering Mechanics, 37(3): 131—141, 148. (in Chinese) 王浩, 李爱群, 2014. ANSYS大跨度桥梁高等有限元分析与工程实例. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. 王新敏, 李义强, 许宏伟, 2011. ANSYS结构分析单元与应用. 北京: 人民交通出版社. 王亚欣, 李武生, 王贵春等, 2021. 江津观音岩长江大桥减震分析. 结构工程师, 37(1): 90—96Wang Y. X. , Li W. S. , Wang G. C. , et al. , 2021. Shock absorption analysis of Jiangjin Guanyinyan Yangtze river bridge. Structural Engineers, 37(1): 90—96. (in Chinese) 闫聚考, 李建中, 彭天波等, 2017. 不同纵向约束体系多塔悬索桥行波效应研究. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 38(6): 874—880Yan J. K. , Li J. Z. , Peng T. B. , et al. , 2017. Effect of wave passage on seismic response of multi-tower suspension bridge under different longitudinal constraint systems. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 38(6): 874—880. (in Chinese) 严琨, 王立新, 姜慧, 2017. 伸缩缝刚度对大跨度悬索桥动力特性的影响. 震灾防御技术, 12(3): 667—676Yan K. , Wang L. X. , Jiang H. , 2017. Dynamic characteristics of long-span suspension bridge with variability of stiffness of expansion joints. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(3): 667—676. (in Chinese) 易富, 杜常博, 王伟等, 2019. 基于人工地震波作用下大跨度悬索桥多点激励地震响应分析. 地震工程学报, 41(2): 278—285 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.02.278Yi F. , Du C. B. , Wang W. , et al. , 2019. Seismic response of long-span suspension bridges under multi-support excitation based on artificial seismic waves. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 41(2): 278—285. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.02.278 张玉平, 王浩, 邹仲钦, 2018. 大跨度三塔悬索桥弹塑性软钢阻尼器减震控制. 振动与冲击, 37(23): 226—233Zhang Y. P. , Wang H. , Zou Z. Q. , 2018. Aseismic control of a long-span triple-tower suspension bridge with elastic-plastic steel dampers. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 37(23): 226—233. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2008. JTG/T B02—01—2008 公路桥梁抗震设计细则. 北京: 人民交通出版社.Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China, 2008. JTG/T B02—01—2008 Guidelines for seismic design of highway bridges. Beijing: China Communications Press. (in Chinese) Apaydın N. M. , 2010. Earthquake performance assessment and retrofit investigations of two suspension bridges in Istanbul. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 30(8): 702—710. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.02.011 Kandemir E. C. , Mazda T. , Nurui H. , et al. , 2011. Seismic retrofit of an existing steel arch bridge using viscous damper. Procedia Engineering, 14: 2301—2306. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.07.290 Ras A. , Boumechra N. , 2016. Seismic energy dissipation study of linear fluid viscous dampers in steel structure design. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 55(3): 2821—2832. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2016.07.012 Semenov M. E. , Solovyov A. M. , Meleshenko P. A. , et al. , 2020. Efficiency of hysteretic damper in oscillating systems. Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena, 15: 43. doi: 10.1051/mmnp/2019053 Wang H. , Zhou R. , Zong Z. H. , et al. , 2012. Study on seismic response control of a single-tower self-anchored suspension bridge with elastic-plastic steel damper. Science China Technological Sciences, 55(6): 1496—1502. doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-4826-5 Yao J. T. P. , 1972. Concept of structural control. Journal of the Structural Division, 98(7): 1567—1574. doi: 10.1061/JSDEAG.0003280 Zheng Y. , Xiao X. , Zhi L. H. , et al. , 2015. Evaluation on impact interaction between abutment and steel girder subjected to nonuniform seismic excitation. Shock and Vibration, 2015: 981804. -



 下载:
下载: