Test and Analysis of Foundation Vibration Caused by the High-speed Train
-
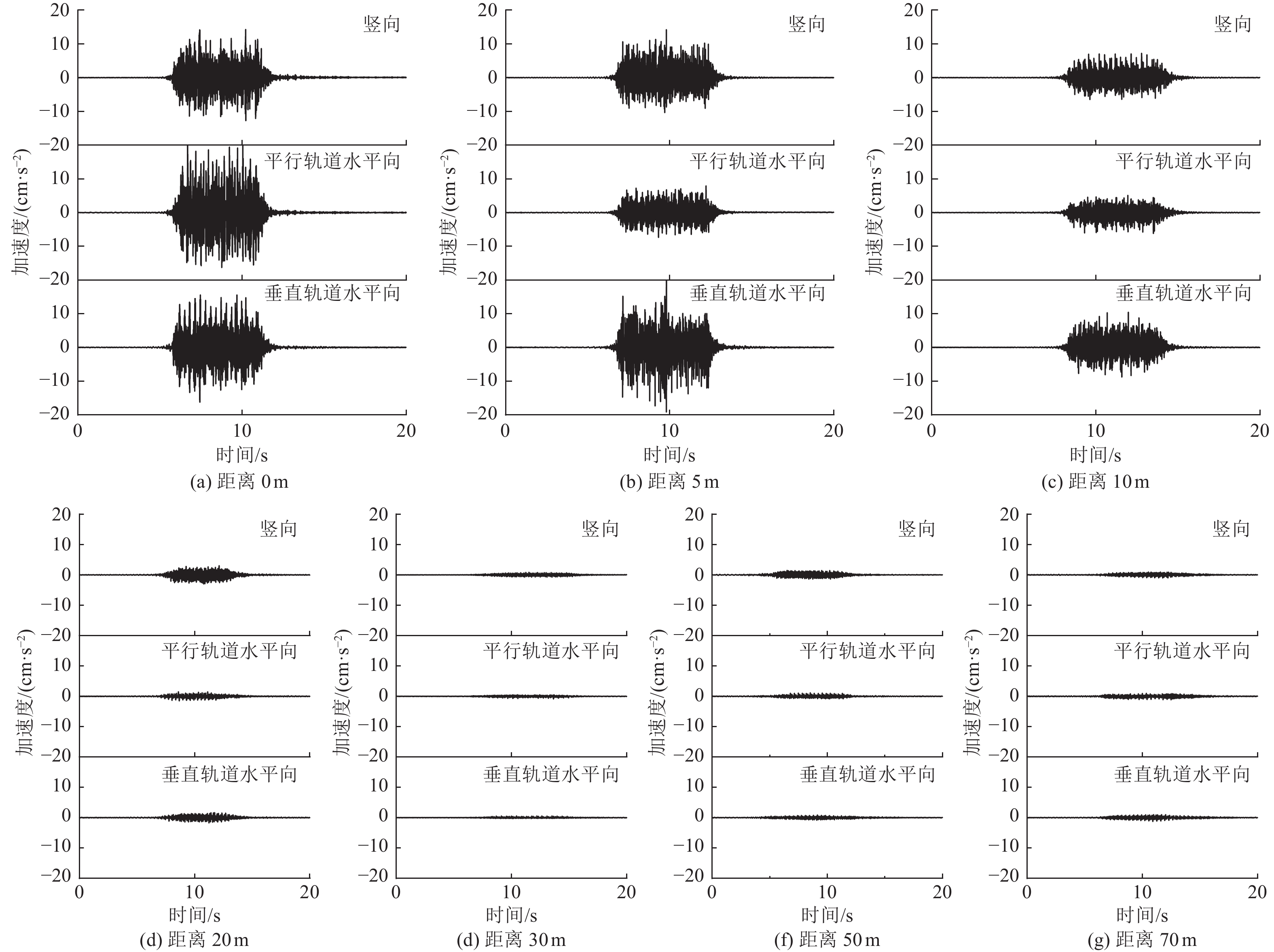
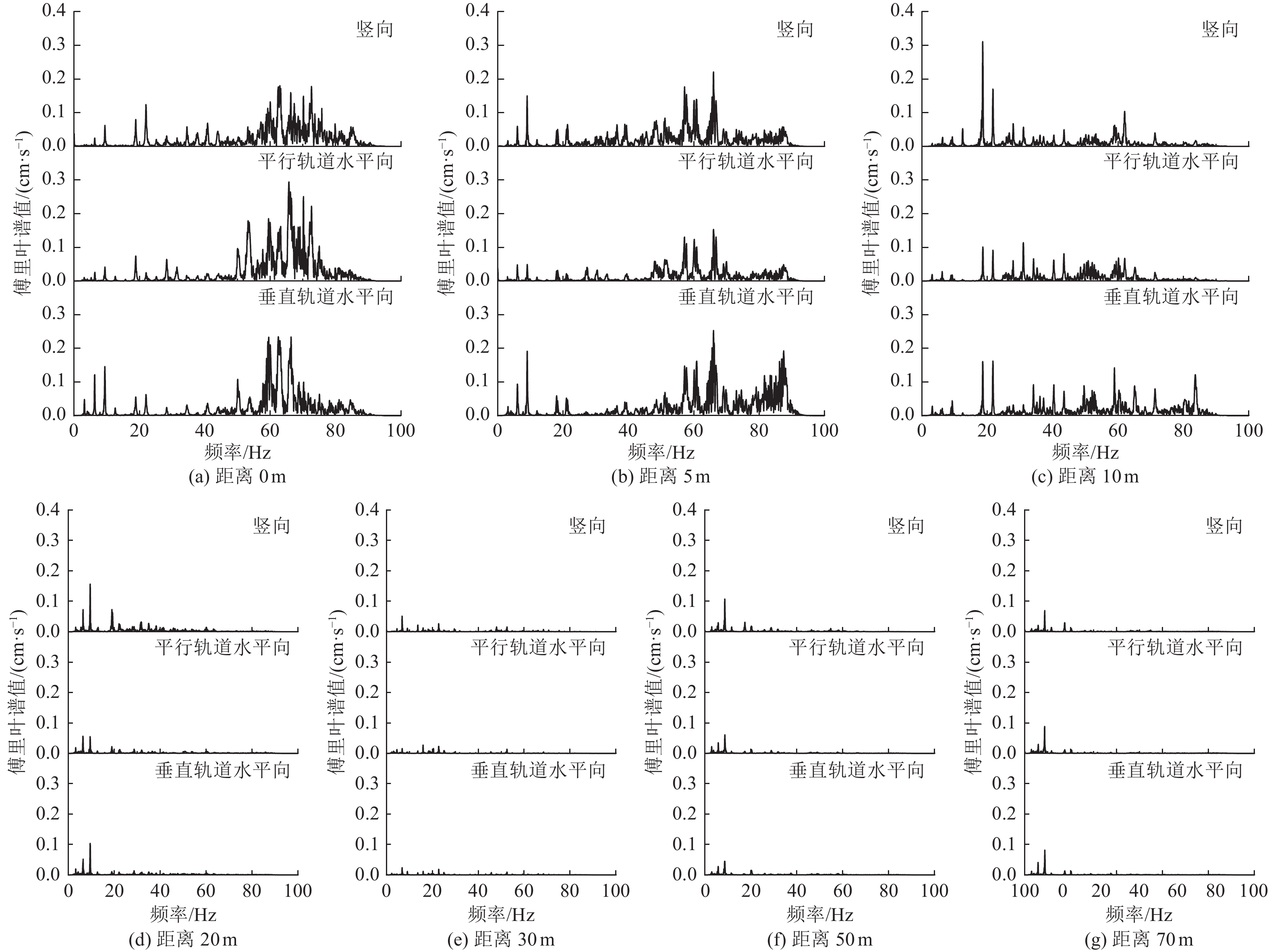
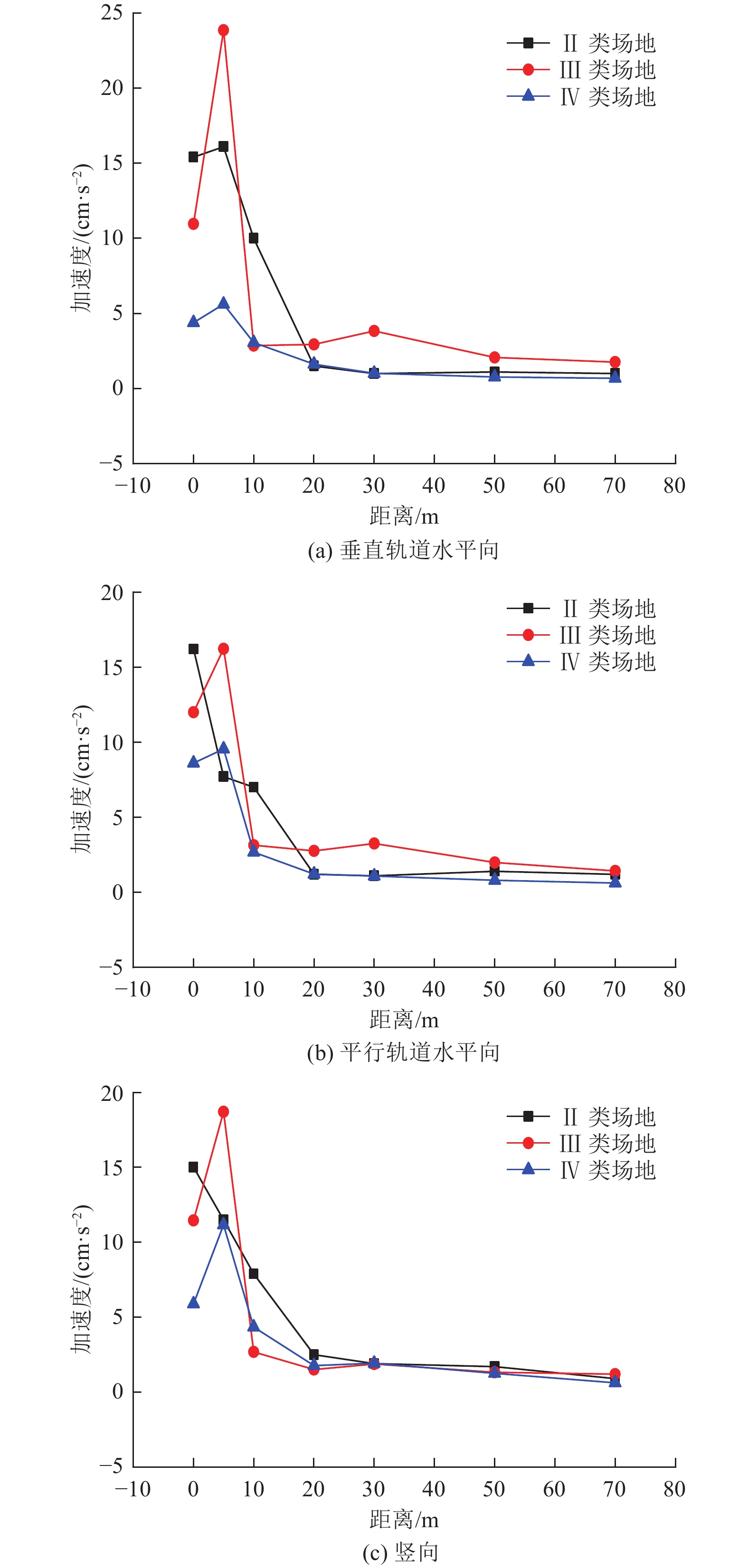
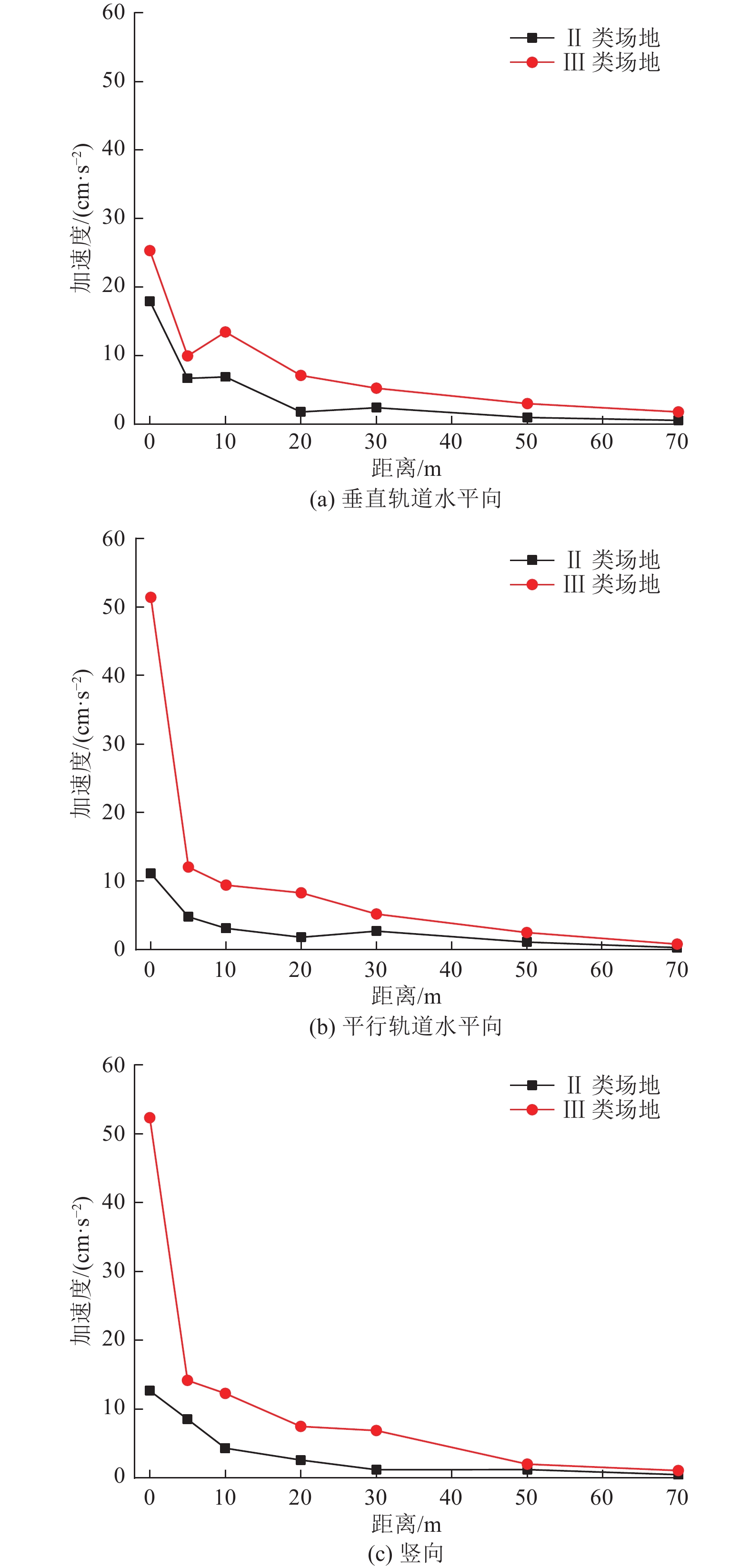
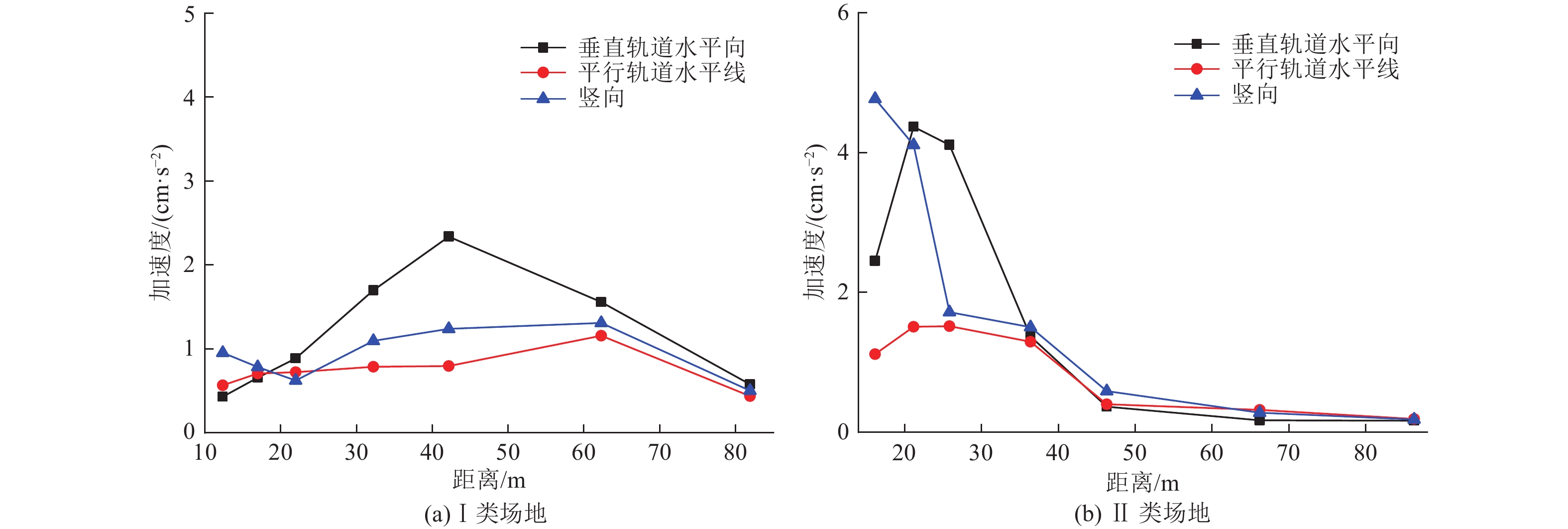
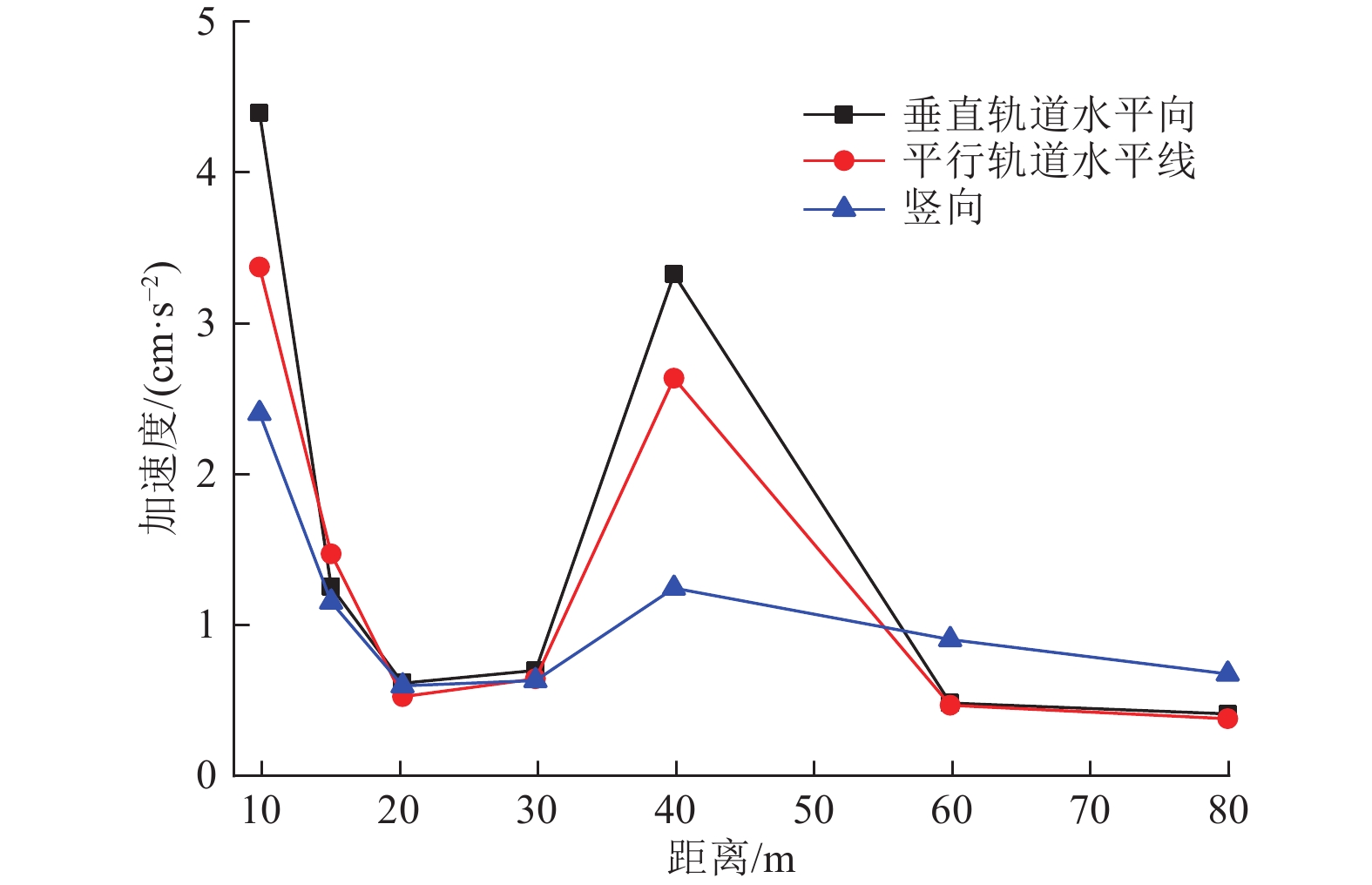
摘要: 为分析高速列车运行引起的地表处振动峰值加速度随距轨道中心线距离的变化特征,选择8个不同场地类型及路基形式的工程场地进行高速列车运行引起的地表振动加速度测试。研究结果表明,高速列车引起的地表振动加速度随距轨道中心线距离的变化特征因场地条件和路基形式的不同存在显著差异;Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ类场地条件下,高速列车引起的地表三分量振动加速度均随距轨道中心线距离的增加而减小,且距轨道近距离处峰值加速度衰减较快,远距离处衰减较慢,Ⅰ类场地条件下,高速列车引起的地表振动加速度随距轨道中心线距离的增加呈先增大后减小的趋势;对于相同路基形式的高速铁路,Ⅲ类场地条件下地表振动峰值加速度随距轨道中心线距离的增加减小速度最快,Ⅱ类场地次之,Ⅳ类场地衰减最慢。Abstract: By choosing 8 cases including elevated subgrade of high and low bridge pier, embankment subgrade and cutting type subgrade under different site condition, in-situ observation were carried out for ground vibration acceleration caused by high speed railway at different distances from the center line of the orbit. The results show that the ground vibration acceleration caused by high-speed trains with the horizontal distance vary significantly with the different site conditions and the subgrade forms. In general, the ground vibration acceleration induced by high-speed trains decreases with the distance increase from the center line of the track under site conditions of class II, III and IV, and the peak acceleration decreases quickly near the orbit, then decreases slowly at long distance from orbit. However, under the site condition of class I, the ground vibration acceleration increases first and then decreases with the increase in distance from the center line of the track. In addition, under the same subgrade condition, the ground peak acceleration decreases fastest with the increase of distance from the center line of the track on site of class III, then on site of class II, and slowest on site of class IV.
-
Key words:
- Vibration Acceleration /
- Subgrade /
- Site Conditions /
- Foundation /
- Vibration Test
-
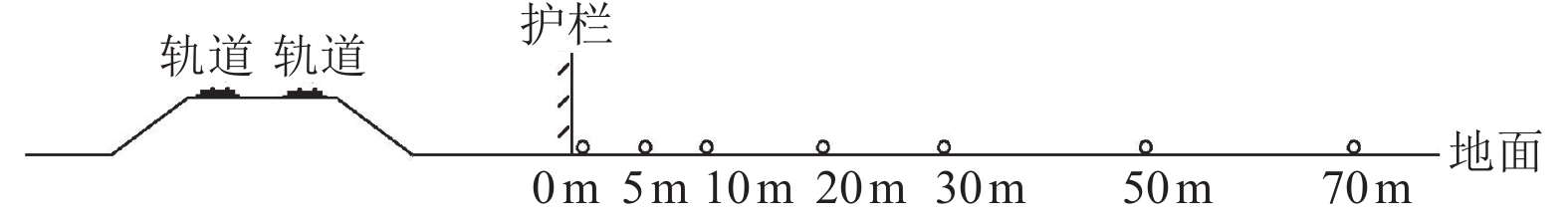
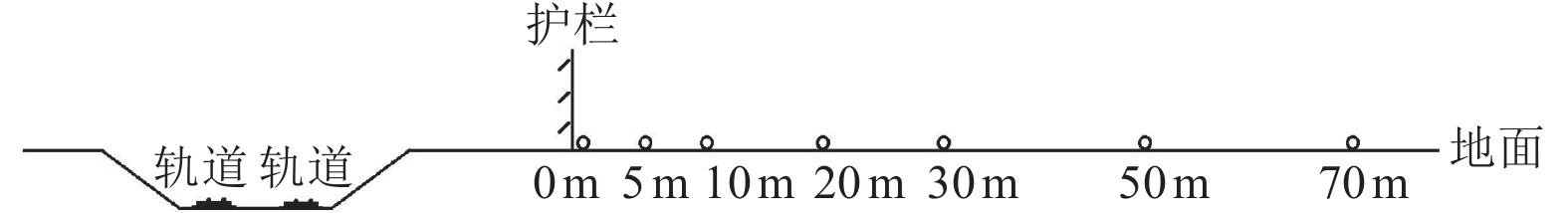
表 1 高速铁路环境振动影响现场测试工况
Table 1. High-speed rail environmental vibration impact field test conditions information
路基形式 场地类型 测试地点 测试内容 高墩高架式(桥墩高度≥10 m) Ⅱ类 南京市浦口区(桥墩高约12 m) 地表不同距离处振动加速度 Ⅲ类 无锡市锡山区(桥墩高约10.5 m) Ⅳ类 苏州市昆山市(桥墩高约10.5 m) 低墩高架式(桥墩高度≤7 m) Ⅱ类 宿州市埇桥区(桥墩高约6.5 m) Ⅲ类 德州市齐河县(桥墩高约5 m) 路堤式 Ⅱ类 枣庄市峄城区 Ⅰ类 徐州市贾汪区 路堑式 Ⅱ类 济宁市邹城市 -
葛勇, 张希黔, 肖正直等, 2010. 无碴轨动车组运行引起的场地振动试验研究. 振动与冲击, 29(11): 209—212, 241Ge Y. , Zhang X. Q. , Xiao Z. Z. , et al. , 2010. A test of the ground vibrations induced by ballastless truck running. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 29(11): 209—212, 241. (in Chinese) 贺玉龙, 周青, 杨立中, 2012.350 km/h高速铁路高架桥环境振动的测试分析. 噪声与振动控制, 32(1): 170—173He Y. L. , Zhou Q. , Yang L. Z. , 2012. Environmental vibration test and analysis of viaduct bridge of 350 km/h high-speed railway. Noise and Vibration Control, 32(1): 170—173. (in Chinese) 刘厚毅, 周游, 钟康明等, 2018. 场地条件对高速铁路地基土振动影响的研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(4): 893—902Liu H. Y. , Zhou Y. , Zhong K. M. , et al. , 2018. Variation characteristics of foundation soil vibration caused by high speed train with depth under different site conditions. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(4): 893—902. (in Chinese) 王逢朝, 夏禾, 吴萱, 1999. 列车振动对环境及建筑物的影响分析. 北方交通大学学报, 23(4): 13—17Wang F. C. , Xia H. , Wu X. , 1999. Vibration effects of trains on surrounding environments and buildings. Journal of Northern Jiaotong University, 23(4): 13—17. (in Chinese) 王金凤, 贺玉龙, 2012. 高速铁路运营引发的环境振动研究综述. 工业安全与环保, 38(1): 43—45, 48Wang J. F. , He Y. L. , 2012. Studies on environmental vibration induced by high-speed railways operations. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 38(1): 43—45, 48. (in Chinese) 王玉石, 李小军, 梅泽洪等, 2014. 高速列车引起的地震动及其对地震信息检测的影响分析. 地震工程与工程振动, 34(S1): 28—33Wang Y. S. , Li X. J. , Mei Z. H. , et al. , 2014. Analysis on ground motions induced by high-speed trains and its influence on information detection of earthquake. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 34(S1): 28—33. (in Chinese) 夏禾, 曹艳梅, 2004. 轨道交通引起的环境振动问题. 铁道科学与工程学报, 1(1): 44—51Xia H. , Cao Y. M. , 2004. Problem of railway traffic induced vibrations of environments. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 1(1): 44—51. (in Chinese) 尹皓, 李耀增, 辜小安等, 2010. 高速铁路环境振动特性研究. 铁道劳动安全卫生与环保, 37(1): 32—36Yin H. , Li Y. Z. , Gu X. A. , et al. , 2010. Study of the environmental vibration characteristic of high-speed railroad. Railway Occupational Safety Health & Environmental Protection, 37(1): 32—36. (in Chinese) 郁雯, 刘杰, 刘航等, 2021. 连续型隔振屏障在高速铁路环境振动问题治理中的应用研究. 震灾防御技术, 16(1): 157—164Yu W. , Liu J. , Liu H. , et al. , 2021. Based on the infinite element boundary analysis, the study of the effect of continuous barrier on the environmental vibration of high-speed railway. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(1): 157—164. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2010. GB 50011—2010 建筑抗震设计规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 18—20Ministry of Housing and Urban-rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2010. GB 50011—2010 Code for seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 18—20. (in Chinese) Connolly D. P. , Kouroussis G. , Woodward P. K. , et al. , 2014. Field testing and analysis of high speed rail vibrations. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 67: 102—118. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.08.013 Connolly D. P. , Alves Costa P. , Kouroussis G. , et al. , 2015. Large scale international testing of railway ground vibrations across Europe. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 71: 1—12. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.01.001 Degrande G. , Schillemans L. , 2001. Free field vibrations during the passage of a thalys high-speed train at variable speed. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 247(1): 131—144. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.2001.3718 Galvín P. , Domínguez J. , 2009. Experimental and numerical analyses of vibrations induced by high-speed trains on the Córdoba–Málaga line. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 29(4): 641—657. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.07.001 Ju S. H., Lin H. T., Huang J. Y., 2009. Dominant frequencies of train-induced vibrations. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 319(1—2): 247—259. Kouroussis G., Connolly D. P., Olivier B., et al., 2016. Railway cuttings and embankments: Experimental and numerical studies of ground vibration. Science of the Total Environment, 557—558: 110—122. Zhai W. M. , Wei K. , Song X. L. , et al. , 2015. Experimental investigation into ground vibrations induced by very high speed trains on a non-ballasted track. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 72: 24—36. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.02.002 -



 下载:
下载: