Research on Transmission Tower Damage Assessment Caused by Earthquake and Landslide
-
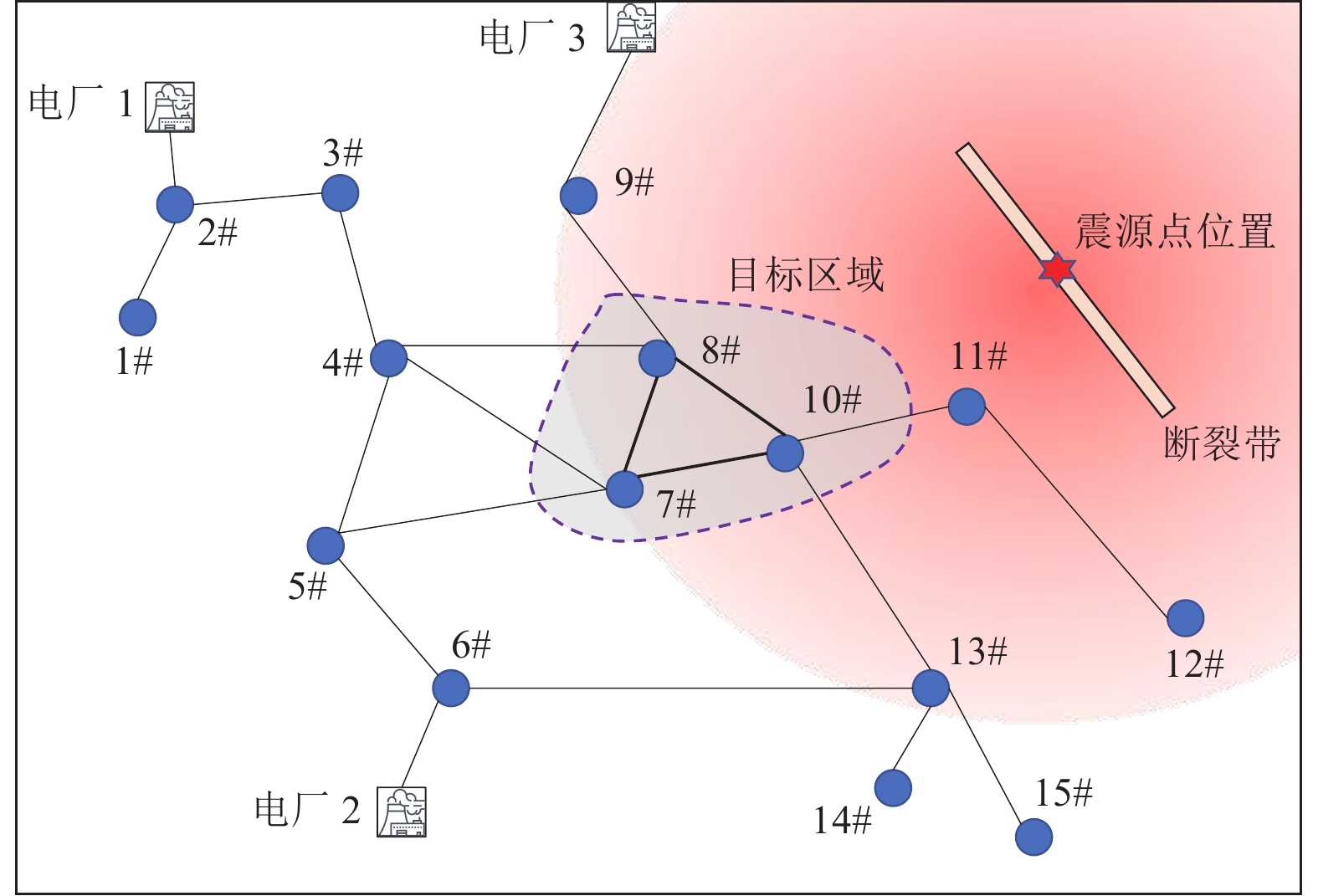
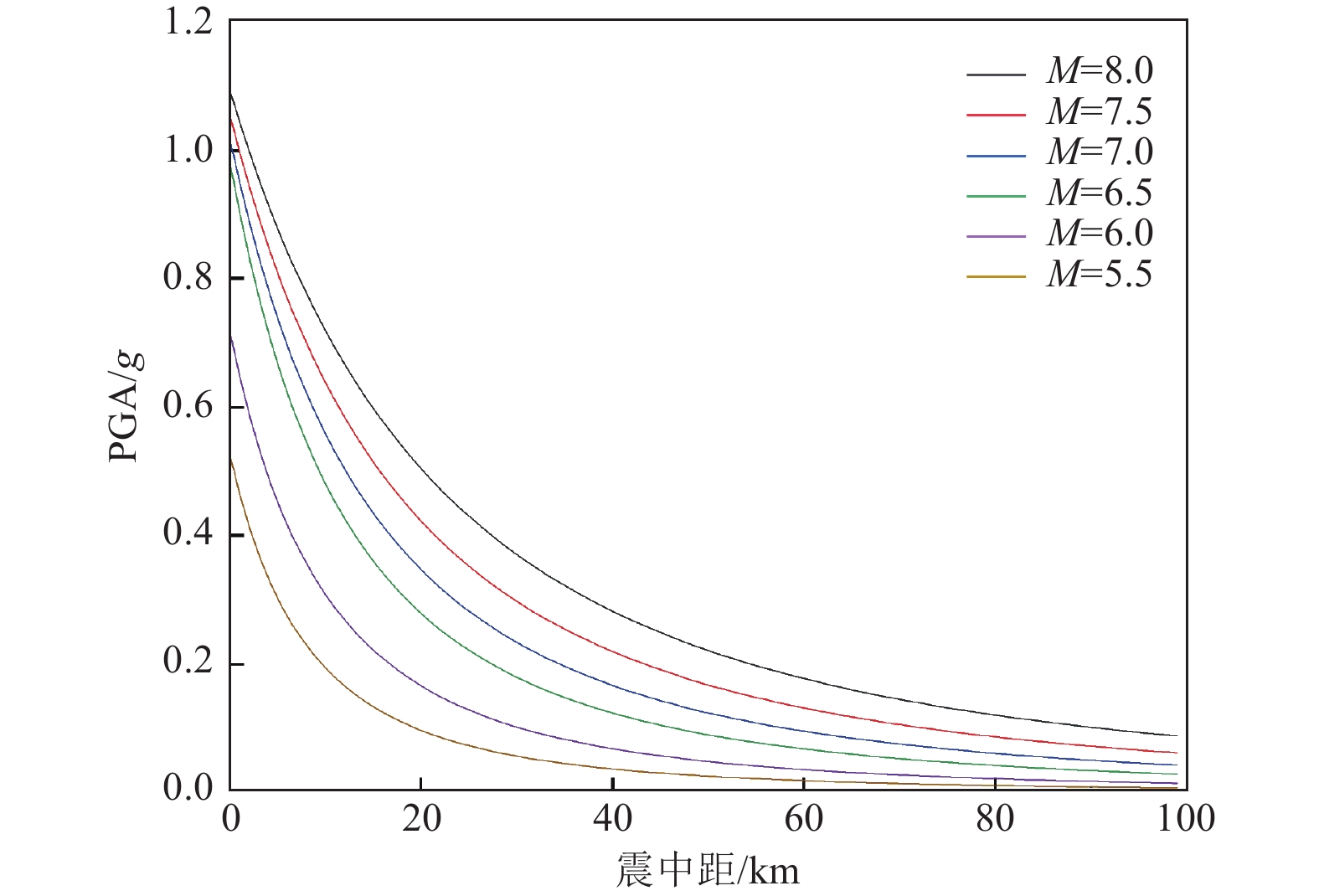
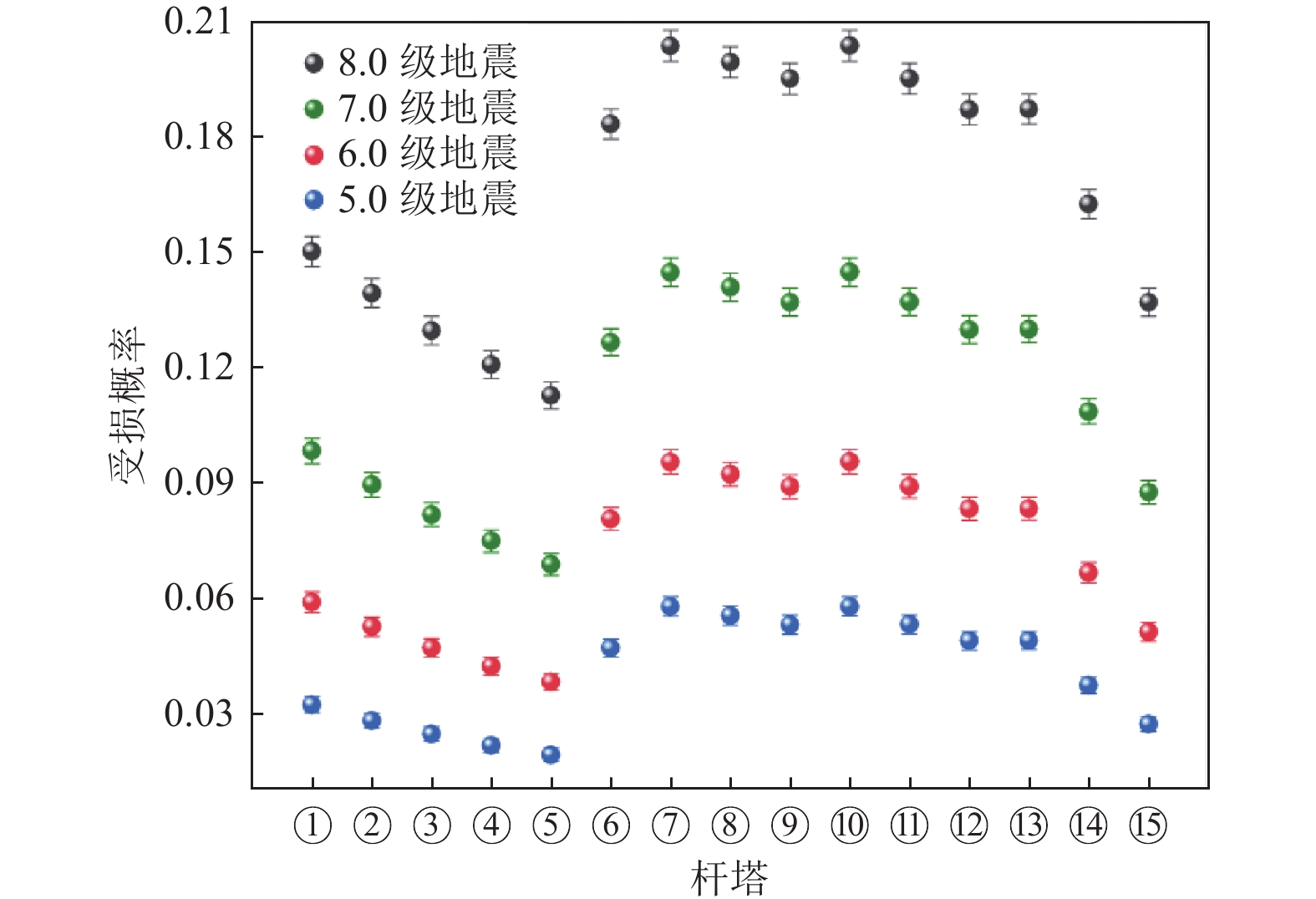
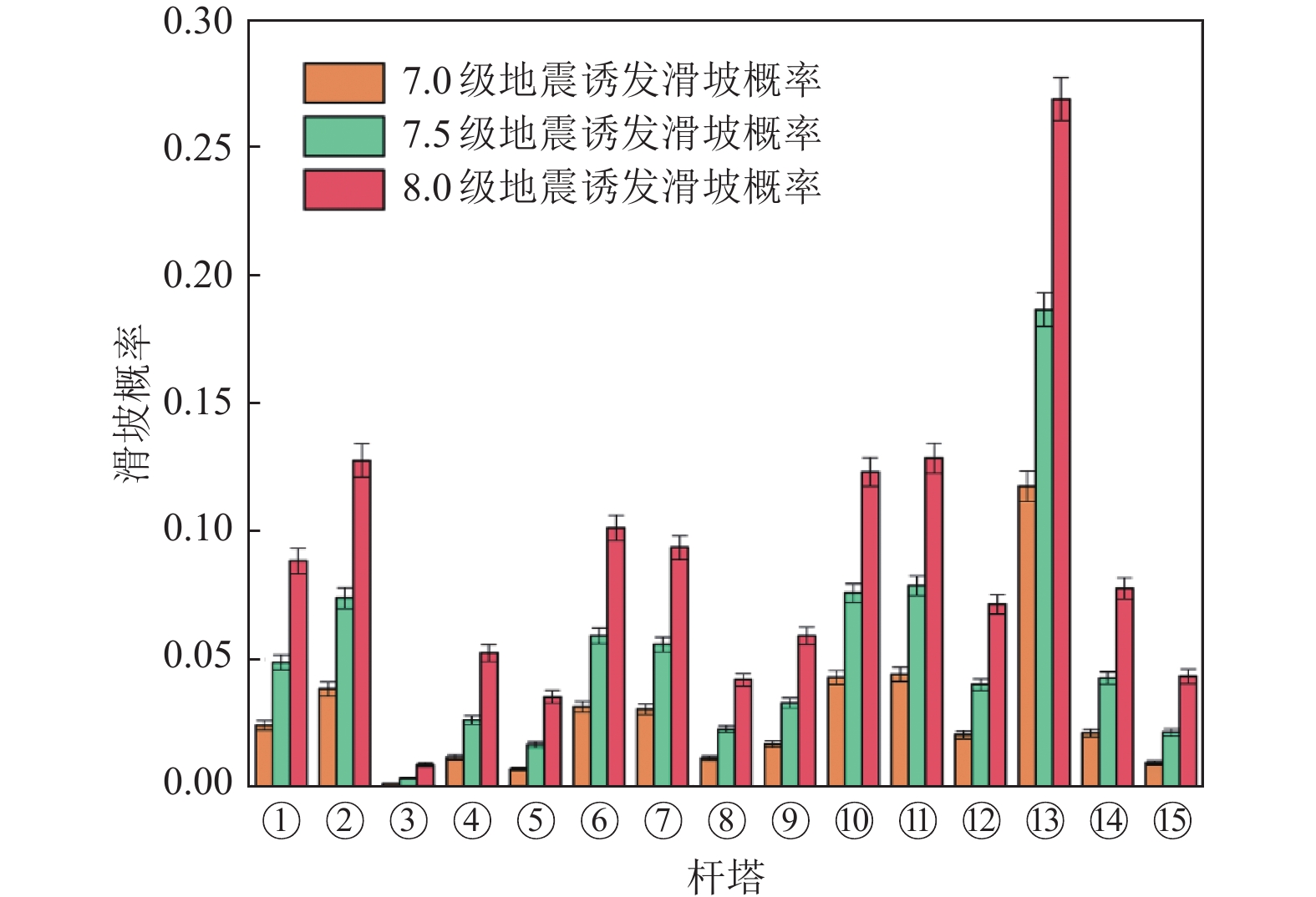
摘要: 为快速评估地震与滑坡灾害对输电杆塔的损毁作用,辅助风险防控措施制定与应急指挥人员决策,研究输电杆塔在地震与滑坡灾害中的损失概率模型。使用蒙特卡洛方法模拟地震震级与震源点坐标,结合峰值地面加速度与脆弱性曲线构建输电杆塔震损概率模型。基于Newmark理论与材料力学原理,构建地震诱发滑坡概率模型及杆塔滑坡冲击损毁概率模型。对我国西南部某区域输电杆塔进行地震与滑坡灾损分析,得到研究区域内各输电杆塔震损概率及滑坡冲击损毁概率。研究结果表明,输电杆塔损毁概率随震级的增大而增大,震级相同时输电杆塔损毁概率主要取决于震中距。滑坡体高度及杆塔与坡脚距离是影响杆塔损毁概率的主要因素,较高处的滑坡体下落时将重力势能转化为动能,进而冲击作用于杆塔,而较小的杆塔与坡脚距离将导致摩擦损耗较小。对于损毁概率较高的杆塔,应采取避让、迁移等措施,降低滑坡灾害的影响。Abstract: In order to evaluate the damage effect of earthquake and landslide disasters on transmission towers, assisting in the formulation of risk prevention and control measures and the decision-making of emergency commanders, this paper studies the loss probability model of transmission towers in earthquake and landslide disasters. The Monte Carlo method is used to simulate the earthquake magnitude and focal point coordinates, and combined with the peak ground acceleration (PGA) and vulnerability curve, the seismic loss probability model of transmission tower is constructed; Based on Newmark theory and the principle of material mechanics, the probability model of earthquake induced landslide and the impact damage probability model of tower landslide are constructed. The earthquake and landslide disaster damage analysis of transmission towers in a region in Southwest China is carried out, and the earthquake damage probability and landslide impact damage probability of transmission towers in the study area are obtained. The results show that the damage probability of transmission tower increases obviously with the increase of earthquake magnitude, and the damage probability of transmission tower mainly depends on the epicenter distance. The height of the landslide mass and the distance between the tower and the slope toe are the main factors affecting the damage probability of the tower. The falling of the landslide mass at a higher height will convert the greater gravitational potential energy into kinetic energy and then impact the tower, while the shorter distance between the tower and the slope toe will also lead to less friction loss. For the towers with high damage probability, effective planning such as avoidance and relocation should be adopted to reduce the impact of landslide disaster on the transmission grid.
-
Key words:
- Power transmission tower /
- Damage evaluation /
- Fragility curve /
- Newmark theory /
- Monte-Carlo method
-
表 1 杆塔主要参数
Table 1. Tower parameters
杆塔 材质 弹性模量/(kN·mm−2) 相关线路 ① 钢/Q345 200 7#-8# ② 200 ③ 200 ④ 200 ⑤ 钢/Q235 206 ⑥ 钢/Q235 206 7#-10# ⑦ 206 ⑧ 206 ⑨ 206 ⑩ 206 ⑪ 钢/Q345 200 ⑫ 200 ⑬ 钢/Q345 200 8#-10# ⑭ 200 ⑮ 200 表 2 滑坡冲击作用下杆塔参数与损毁概率
Table 2. Tower parameters and damage probability under landslide impact
杆塔 岩土组成 滑坡体高度/m 杆塔与坡脚距离/m 杆塔损毁概率 ① 碎石块堆积体 58.64 12.05 0.46 ② 61.61 7.840 0.61 ③ 22.33 13.20 0.07 ④ 60.66 15.84 0.55 ⑤ 47.21 9.030 0.23 ⑥ 黏土碎石 25.28 6.420 0.13 ⑦ 17.54 9.110 0.06 ⑧ 16.15 11.520 0.04 ⑨ 20.88 5.570 0.10 ⑩ 16.26 11.010 0.03 ⑪ 17.22 12.510 0.05 ⑫ 23.36 8.530 0.11 ⑬ 碎石块堆积体 56.32 7.760 0.52 ⑭ 44.75 5.450 0.38 ⑮ 73.06 9.830 0.40 -
陈波, 王芳, 肖本夫, 2021. “情景-应对”型理论体系的发展及其在地震灾害应急管理中的应用探讨. 震灾防御技术, 16(4): 605—616Chen B. , Wang F. , Xiao B. F. , 2021. The development of “scenario-response” theoretical system and its application in earthquake disaster emergency management. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(4): 605—616. (in Chinese) 陈强, 王建, 熊小伏等, 2020. 一种降雨诱发滑坡灾害下输电杆塔的监测与预警方法. 电力系统保护与控制, 48(3): 147—155Chen Q. , Wang J. , Xiong X. F. , et al. , 2020. Monitoring and early warning method for transmission tower under rainfall-induced landslide disaster. Power System Protection and Control, 48(3): 147—155. (in Chinese) 陈晓利, 单新建, 张凌等, 2019. 地震诱发滑坡的快速评估方法研究: 以2017年MS 7.0级九寨沟地震为例. 地学前缘, 26(2): 312—320Chen X. L. , Shan X. J. , Zhang L. , et al. , 2019. Quick assessment of earthquake-triggered landslide hazards: a case study of the 2017 MS 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(2): 312—320. (in Chinese) 邓创, 刘友波, 刘俊勇等, 2016. 考虑降雨诱发次生地质灾害的电网风险评估方法. 电网技术, 40(12): 3825—3832Deng C. , Liu Y. B. , Liu J. Y. , et al. , 2016. A risk assessment method of power grid considering secondary geological hazards caused by rainfall weather. Power System Technology, 40(12): 3825—3832. (in Chinese) 丁宝荣, 孙景江, 李小东等, 2014. 地震烈度和地震动参数相关性研究进展及讨论. 地震工程与工程振动, 34(5): 7—20Ding B. R. , Sun J. J. , Li X. D. , et al. , 2014. Research progress and discussion of the correlation between seismic intensity and ground motion parameters. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 34(5): 7—20. (in Chinese) 葛华, 陈启国, 王德伟, 2013. 地震滑坡危险性评价及编图——以映秀震中区为例. 中国地质, 40(2): 644—652Ge H. , Chen Q. G. , Wang D. W. , 2013. The assessment and mapping of seismic landslide hazards: a case study of Yingxiu area, Sichuan Province. Geology in China, 40(2): 644—652. (in Chinese) 郭星, 2008. 基于蒙特卡罗模拟的概率地震危险性分析方法. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所.Guo X., 2008. The use of Monte Carlo simulation methods in Probabilistic Seismic hazard assessment. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 何剑, 屠竞哲, 孙为民等, 2020. 美国加州“8·14”、“8·15”停电事件初步分析及启示. 电网技术, 44(12): 4471—4478He J. , Tu J. Z. , Sun W. M. , et al. , 2020. Preliminary analysis and lessons of California power outage events on august 14 and 15, 2020. Power System Technology, 44(12): 4471—4478. (in Chinese) 贺海磊, 郭剑波, 谢强, 2011. 电气设备的地震灾害易损性分析. 电网技术, 35(4): 25—28 doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2011.04.002He H. L. , Guo J. B. , Xie Q. , 2011. Vulnerability analysis of power equipments caused by earthquake disaster. Power System Technology, 35(4): 25—28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2011.04.002 黄发明, 陈佳武, 范宣梅等, 2021. 降雨型滑坡时间概率的逻辑回归拟合及连续概率滑坡危险性建模. 地球科学. (2021-11-02). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20211101.2007.018.html.Huang F. M., Chen J. W., Fan X. M., et al., 2021. Logistic regression fitting of rainfall-induced landslide occurrence probability and continuous landslide hazard prediction modelling. Earth Science. (2021-11-02). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20211101.2007.018.html. (in Chinese) 雷霞, 郑国鑫, 胡益, 2021. 地震灾害下配电网的脆弱性分析及弹性提升措施. 电网技术, 45(9): 3674—3680Lei X. , Zheng G. X. , Hu Y. , 2020. Vulnerability analysis and resilience improvement of distribution network under earthquake disasters. Power System Technology, 45(9): 3674—3680. (in Chinese) 李雪婧, 吴健, 高孟潭等, 2018. 基于阿里亚斯烈度估值的概率性地震危险性分析——以四川丹棱县及其周缘为例. 地震工程学报, 40(3): 555—561Li X. J. , Wu J. , Gao M. T. , et al. , 2018. Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis based on arias intensity: a case study in Danling county, Sichuan province and its surrounding area. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 40(3): 555—561. (in Chinese) 李雪婧, 高孟潭, 徐伟进, 2019. 基于Newmark模型的概率地震滑坡危险性分析方法研究——以甘肃天水地区为例. 地震学报, 41(6): 795−807.Li X. J., Gao M. T., Xu W. J., 2019. Probabilistic seismic slope displacement hazard analysis based on Newmark displacement model: Take the area of Tianshui, Gansu Province, China as an example. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 41(6): 795—807. (in Chinese) 李莹甄, 殷娜, 李小晗, 2014. 不同震级标度转换关系研究概述. 地震工程学报, 36(1): 80—87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2014.01.0080Li Y. Z. , Yin N. , Li X. H. , 2014. Review of the conversional relationship for different magnitude scales. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 36(1): 80—87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2014.01.0080 梁黄彬, 谢强, 2022. 特高压换流站系统的地震易损性分析. 电网技术, 45(2): 551—557Liang H. B. , Xie Q. , 2022. Seismic vulnerability analysis of UHV converter station system. Power System Technology, 45(2): 551—557. (in Chinese) 廖景高, 赵其华, 刘宇等, 2014. 基于Monte-Carlo的滑坡失稳概率计算研究. 长江科学院院报, 31(7): 29—33Liao J. G. , Zhao Q. H. , Liu Y. , et al. , 2014. Study on the probability of landslide failure by Monte-Carlo method. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 31(7): 29—33. (in Chinese) 林高聪, 潘书华, 叶振南, 2021. 基于Newmark法的设定地震滑坡危险性评估. 桂林理工大学学报, 41(3): 525—532Lin G. C. , Pan S. H. , Ye Z. N. , 2021. Assessment of landslide risk based on Newmark and preset earthquake. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 41(3): 525—532. (in Chinese) 刘甲美, 2015. 概率地震滑坡危险性区划方法及应用. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所.Liu J. M., 2015. Probabilistic seismic landslide hazard zonation method and its application. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 刘军, 谭明, 宋立军等, 2019.2017年5月11日新疆塔什库尔干MS 5.5地震震害特征分析. 震灾防御技术, 14(1): 231—238 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190122Liu J. , Tan M. , Song L J. , et al. , 2019. Analysis on the disaster characteristics of the 2017 Taxkorgan MS 5.5 earthquake in Xinjiang. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(1): 231—238. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190122 刘善琪, 李永兵, 田会全等, 2013. 影响b值计算误差的Monte Carlo实验研究. 地震, 33(4): 135—144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2013.04.014Liu S. Q. , Li Y. B. , Tian H. Q. , et al. , 2013. Monte Carlo experiments on the influencing factors of b value calculation errors. Earthquake, 33(4): 135—144. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2013.04.014 蒲书豪, 任光明, 王滨等, 2020. 基于改进分析方法的滑坡失稳概率研究. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 47(3): 367—373 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2020.03.10Pu S. H. , Ren G. M. , Wang B. , et al. , 2020. Study on probability of landslide instability based on improved analysis method. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 47(3): 367—373. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2020.03.10 邱丹丹, 吴燕玲, 宋世杰, 2021. 基于Newmark模型的地震诱发滑坡易发性分析方法的研究. 防灾科技学院学报, 23(1): 54—58 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2021.01.008Qiu D. D. , Wu Y. L. , Song S. J. , 2021. Susceptibility analysis method of earthquake-induced landslide based on newmark model. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 23(1): 54—58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2021.01.008 史海欧, 张希, 林本海等, 2021. 基于Arias烈度维度扩展概念下十字异形、方形桩屏障隔振作用对比研究. 振动与冲击, 40(22): 259—266 doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.22.035Shi H. O. , Zhang X. , Lin B. H. , et al. , 2021. Vibration isolation effect of cross and square piles based on the concept of dimension expansion of Arias intensity. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 40(22): 259—266. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.22.035 舒荣星, 2018. 电网地震安全性与地震可恢复性评价理论研究. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Shu R. X., 2018. Research on the seismic safety and resilience evaluation theory of power grid. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 孙江玉, 刘创, 欧阳敏等, 2018. 地震灾害下电网性能研究综述——以弹性视角为主. 自然灾害学报, 27(2): 14—23 doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2018.0202Sun J. Y. , Liu C. , Ouyang M. , et al. , 2018. Review of performance studies on electric power grids under seismic hazards—with a focus on resilience perspective. Journal of Natural Disasters, 27(2): 14—23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2018.0202 谭洋洋, 杨洪耕, 徐方维等, 2016. 降雨型滑坡诱发电网连锁故障风险评估模型研究. 科学技术与工程, 16(33): 8—13, 28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.33.002Tan Y. Y. , Yang H. G. , Xu F. W. , et al. , 2016. The research on risk assessment model of power grid cascading failures caused by rainfall-induced landslides. Science Technology and Engineering, 16(33): 8—13, 28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.33.002 汤奕, 徐香香, 陈彬等, 2020. 降雨滑坡灾害对输电杆塔故障的时空强在线预警. 中国电力, 53(1): 56—65Tang Y. , Xu X. X. , Chen B. , et al. , 2020. Space-time-intensity online early-warning of transmission tower faults by caused rainfall-induced landslides. Electric Power, 53(1): 56—65. (in Chinese) 王秀英, 聂高众, 马牧军, 2012. 地震滑坡灾害评估中地震影响因素的联合应用. 地震学报, 34(1): 76—84Wang X. Y. , Nie G. Z. , Ma M. J. , 2012. Application of multiple ground motion factors in earthquake-induced landslide hazard evaluation. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 34(1): 76—84. (in Chinese) 徐光兴, 姚令侃, 李朝红等, 2012. 基于汶川地震强震动记录的边坡永久位移预测模型. 岩土工程学报, 34(6): 1131—1136Xu G. X., Yao L. K., Li C. H., et al. Predictive models for permanent displacement of slopes based on recorded strong-motion data of Wenchuan Earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 34(6): 1131—1136. (in Chinese) 严道波, 文劲宇, 杜治等, 2021.2021年得州大停电事故分析及其对电网规划管理的启示. 电力系统保护与控制, 49(9): 121—128 doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.210358Yan D. B. , Wen J. Y. , Du Z. , et al. , 2021. Analysis of Texas blackout in 2021 and its enlightenment to power system planning management. Power System Protection and Control, 49(9): 121—128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.210358 严敏嘉, 张佳敏, 谭思蓉等, 2022. 地震作用下岩坡稳定性研究现状与发展. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 55(1): 29—38Yan M. J. , Zhang J. M. , Tan S. R. , et al. , 2022. Research status and development of rock slope stability analysis under seismic conditions. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 55(1): 29—38. (in Chinese) 于永清, 李光范, 李鹏等, 2008. 四川电网汶川地震电力设施受灾调研分析. 电网技术, 32(11): T1—T6 doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2008.11.021Yu Y. Q. , Li G. F. , Li P. , et al. , 2008. Investigation and analysis of electric equipment damage in Sichuan power grid caused by Wenchuan earthquake. Power System Technology, 32(11): T1—T6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2008.11.021 俞言祥, 李山有, 肖亮, 2013. 为新区划图编制所建立的地震动衰减关系. 震灾防御技术, 8(1): 24—33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2013.01.003Yu Y. X. , Li S. Y. , Xiao L. , 2013. Development of ground motion attenuation relations for the new seismic hazard map of China. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 8(1): 24—33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2013.01.003 张丽波, 郭将, 刘晓, 2016. 响应面法与蒙特卡洛法边坡可靠性评价方法对比研究. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 49(5): 779—786Zhang L. B. , Guo J. , Liu X. , 2016. Comparative study of methodologies between response surface methods and Monte Carlo methods in slope reliability analysis. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 49(5): 779—786. (in Chinese) 张中近, 2017. 电力设施地震经济损失快速评估. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Zhang Z. J., 2017. Rapid evaluation of electric power facility economic loss caused by earthquake. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) 郑光, 许强, 巨袁臻等, 2018.2017年8月28日贵州纳雍县张家湾镇普洒村崩塌特征与成因机理研究. 工程地质学报, 26(1): 223—240Zheng G. , Xu Q. , Ju Y. Z. , et al. , 2018. The pusacun rockavalanche on August 28, 2017 in Zhangjiawan Nayongxian, Guizhou: characteristics and failure mechanism. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(1): 223—240. (in Chinese) 郑国鑫, 雷霞, 王湘等, 2020. 地震灾害模拟及配电网的风险评估. 电工技术学报, 35(24): 5218—5226 doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.191495Zheng G. X. , Lei X. , Wang X. , et al. , 2020. Earthquake simulation and risk assessment of distribution network. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 35(24): 5218—5226. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.191495 朱凌, 陈涛威, 周晨等, 2019. 考虑风速风向联合分布的大风灾害下电力断线倒塔概率预测. 电力系统保护与控制, 47(2): 115—122 doi: 10.7667/PSPC180109Zhu L. , Chen T. W. , Zhou C. , et al. , 2019. Probability prediction of transmission line breakage and tower topple over under wind disaster considering the joint distribution of wind speed and wind direction. Power System Protection and Control, 47(2): 115—122. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7667/PSPC180109 Aven T. , 2011. On some recent definitions and analysis frameworks for risk, vulnerability, and resilience. Risk Analysis, 31(4): 515—522. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2010.01528.x Bahrampouri M. , Rodriguez-Marek A. , Green R. A. , 2021. Ground motion prediction equations for Arias Intensity using the Kik-net database. Earthquake Spectra, 37(1): 428—448. doi: 10.1177/8755293020938815 Crowley H. , Bommer J. J. , 2006. Modelling seismic hazard in earthquake loss models with spatially distributed exposure. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 4(3): 249—273. doi: 10.1007/s10518-006-9009-y del Gaudio V. , Wasowski J. , 2004. Time probabilistic evaluation of seismically induced landslide hazard in Irpinia (Southern Italy). Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 24(12): 915—928. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.06.019 Federal Emergency Management Agency(FEMA), 2012. HAZUS, Multi-hazard Loss Estimation Methodology, Earthquake Mode. Washington D. C. : Department of Homeland Security, Federal Emergency Management Agency. Jibson R. W. , 1993. Predicting earthquake-induced landslide displacements using Newmark's sliding block analysis. Transportation Research Record, 1411: 9—17. Jibson R. W., 2011. Methods for assessing the stability of slopes during earthquakes—A retrospective. Engineering Geology, 122(1—2): 43—50. Jibson R. W., Harp E. L., Schulz W., et al., 2006. Large rock avalanches triggered by the M 7.9 Denali Fault, Alaska, earthquake of 3 November 2002. Engineering Geology, 83(1—3): 144—160. Pitilakis K. , Franchin P. , Khazai B. , et al. , 2014. SYNER-G: systemic seismic vulnerability and risk assessment of complex urban, utility, lifeline systems and critical facilities: methodology and applications. Dordrecht: Springer, 157—184. Raschke M. , Bilis E. , Kröger W. , 2011. Vulnerability of the Swiss electric power transmission grid against natural hazards. In: Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference on Applications of Statistics and Probability in Civil Engineering. Zurich: ETH Zurich, 1407—1414. Rathje E. M. , Saygili G. , 2008. Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis for the sliding displacement of slopes: scalar and vector approaches. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 134(6): 804—814. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:6(804) Travasarou T. , Bray J. D. , Abrahamson N. A. , 2003. Empirical attenuation relationship for Arias intensity. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 32(7): 1133—1155. -



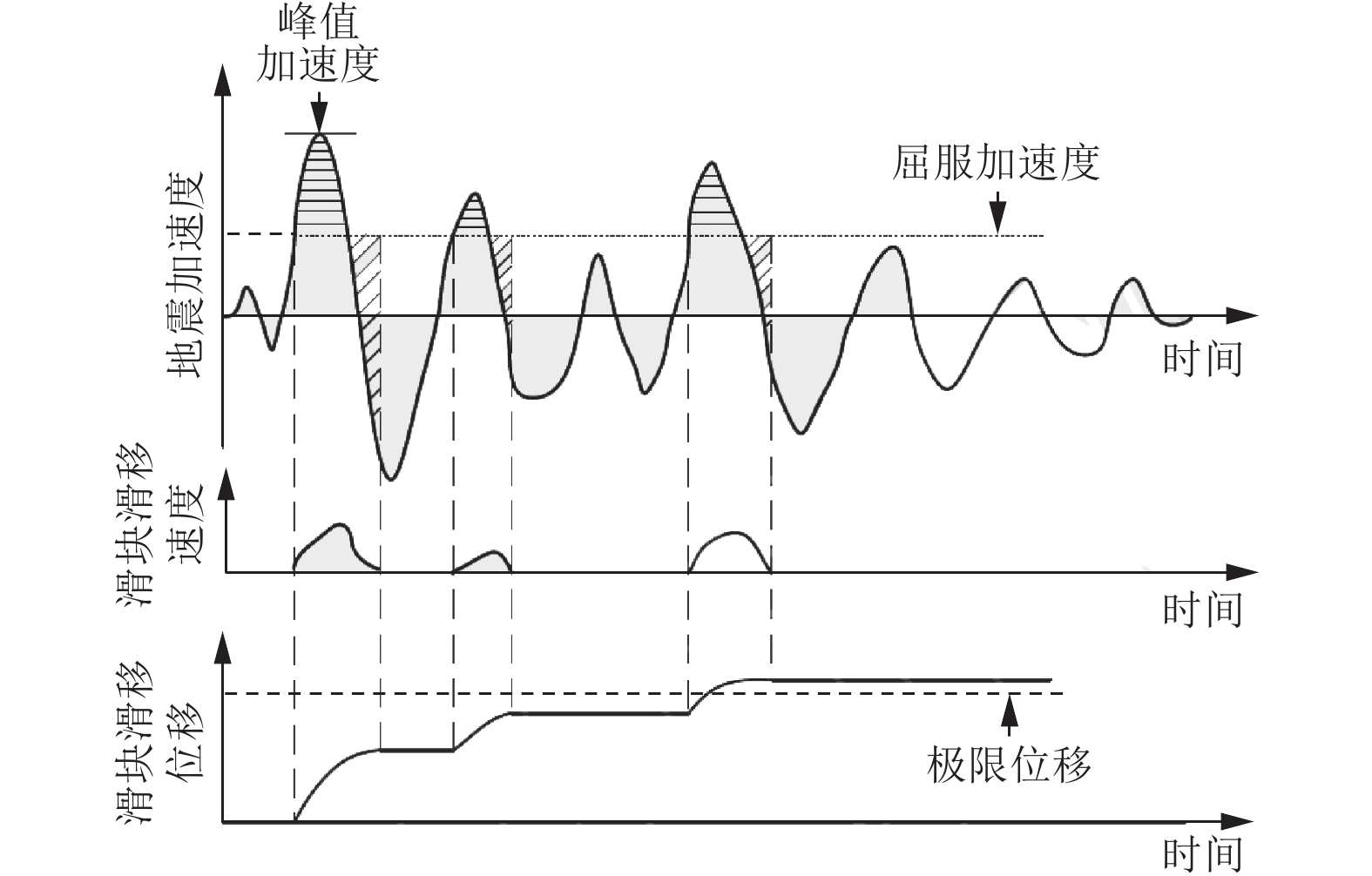
 下载:
下载: