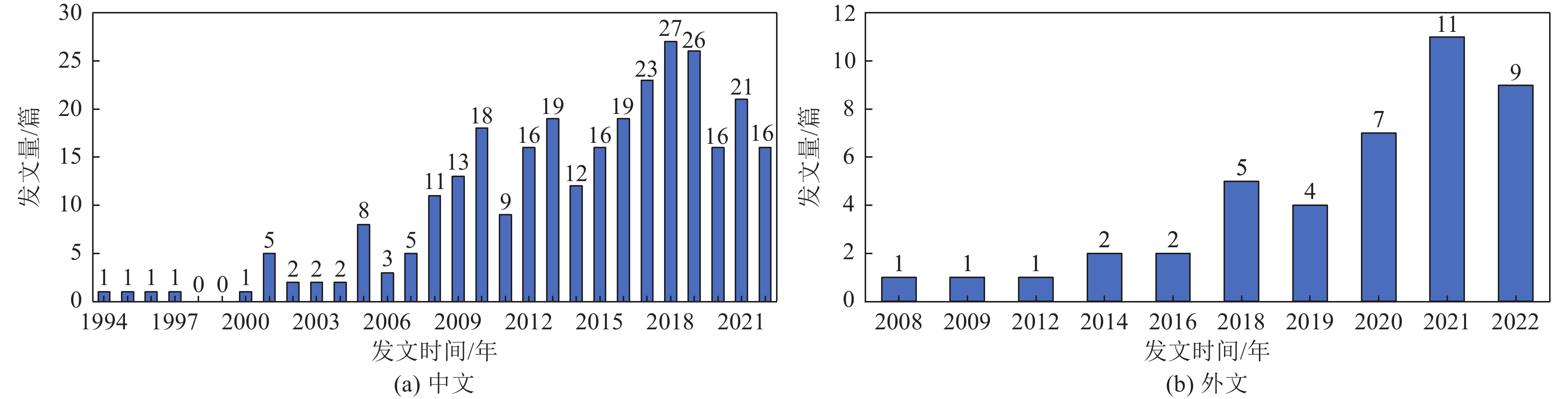
|
白广斌, 赵杰, 汪宇, 2012. 地下结构工程抗震分析方法综述. 防灾减灾学报, 28(1): 20—26Bai G. B. , Zhao J. , Wang Y. , 2012. Review of methods for antiseismic research of underground engineering. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 28(1): 20—26. (in Chinese)
|
|
蔡丽雯, 黄勇, 何静等, 2022.2022年青海门源6.9级地震交通系统震害与启示. 地震工程与工程振动, 42(4): 8—16Cai L. W. , Huang Y. , He J. , et al. , 2022. Earthquake damage and enlightenment from traffic system in 2022 Qinghai Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 42(4): 8—16. (in Chinese)
|
|
陈庆, 郑颖人, 陈剑杰, 2013. 花岗岩隧道地震响应机理及减震技术探析. 振动与冲击, 32(10): 149—156Chen Q. , Zheng Y. R. , Chen J. J. , 2013. Analysis of seismic responses of granite tunnel under earthquake effect and related aseismic measures. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 32(10): 149—156. (in Chinese)
|
|
陈之毅, 谈忠傲, 楼梦麟, 2016. 地下结构抗震设计方法整体强制反应位移法. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 44(8): 1145—1152Chen Z. Y. , Tan Z. A. , Lou M. L. , 2016. Integral forced displacement method for seismic design of underground structures. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 44(8): 1145—1152. (in Chinese)
|
|
陈之毅, 刘文博, 陈炜, 2020. 多层地铁车站结构性能试验研究. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 48(6): 811—820Chen Z. Y. , Liu W. B. , Chen W. , 2020. Performance experiment of a multi-story subway station. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 48(6): 811—820. (in Chinese)
|
|
崔光耀, 伍修刚, 王明年等, 2017. 汶川8.0级大地震公路隧道震害调查与震害特征. 现代隧道技术, 54(2): 9—16Cui G. Y. , Wu X. G. , Wang M. N. , et al. , 2017. Earthquake damages and characteristics of highway tunnels in the 8.0-magnitude Wenchuan earthquake. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 54(2): 9—16. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 刘洪涛, 路德春等, 2017. 装配整体式地铁车站侧墙底节点抗震性能研究. 土木工程学报, 50(4): 38—47Du X. L. , Liu H. T. , Lu D. C. , et al. , 2017. Study on seismic performance of sidewall joints in assembled monolithic subway station. China Civil Engineering Journal, 50(4): 38—47. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 李洋, 许成顺等, 2018 a. 1995年日本阪神地震大开地铁车站震害原因及成灾机理分析研究进展. 岩土工程学报, 40(2): 223—236Du X. L. , Li Y. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2018 a. Review on damage causes and disaster mechanism of Daikai subway station during 1995 Osaka-Kobe Earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 40(2): 223—236. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 刘洪涛, 许成顺等, 2018 b. 不同轴压比下装配整体式地铁车站拼装柱抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 39(11): 11—19Du X. L. , Liu H. T. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2018 b. Experimental study on seismic performance of precast column in assembled monolithic subway station under different axial compression ratio. Journal of Building Structures, 39(11): 11—19. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 刘洪涛, 许成顺等, 2019 a. 装配整体式地铁车站纵断面方向梁板柱中节点抗震性能研究. 建筑结构学报, 40(9): 95—103Du X. L. , Liu H. T. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2019 a. Study on seismic performance of beam-column-slab interior joints in longitudinal section of assembled monolithic subway station. Journal of Building Structures, 40(9): 95—103. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 刘洪涛, 许成顺等, 2019b-09-27. 一种自复位装配式地铁车站柔性抗震结构: 中国, 106351494B.
|
|
杜修力, 许紫刚, 许成顺等, 2019 c. 摩擦摆支座在地下地铁车站结构中的减震效果研究. 工程力学, 36(9): 60—67, 88Du X. L. , Xu Z. G. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2019 c. Seismic mitigation effect analysis on friction pendulum bearing applied in the underground subway station. Engineering Mechanics, 36(9): 60—67, 88. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 阴孟莎, 刘洪涛等, 2019 d. 柱脚可更换的地下结构抗震截断柱技术性能分析. 震灾防御技术, 14(3): 524—534Du X. L. , Yin M. S. , Liu H. T. , et al. , 2019 d. Analysis of technical performance of underground structure seismic truncated columns with replaceable column foot. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(3): 524—534. (in Chinese)
|
|
杜修力, 刘迪, 许成顺等, 2021. 橡胶支座在浅埋地下框架结构中的减震效果研究. 岩土工程学报, 43(10): 1761—1770Du X. L. , Liu D. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2021. Seismic mitigation effect of shallow-covered underground frame station with rubber bearings. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 43(10): 1761—1770. (in Chinese)
|
|
付继赛, 庄海洋, 王旭等, 2018. 地下连续墙连接方式对地铁车站结构地震反应的影响研究. 自然灾害学报, 27(6): 42—50Fu J. S. , Zhuang H. Y. , Wang X. , et al. , 2018. Influence of diaphragm wall connection mode on earthquake response of subway station structure. Journal of Natural Disasters, 27(6): 42—50. (in Chinese)
|
|
傅游, 王浩蓉, 2020. 基于Web of Science的国际区块链技术文献计量分析. 图书情报导刊, 5(12): 67—75Fu Y. , Wang H. R. , 2020. Bibliometric analysis on international blockchain technology based on Web of Science. Journal of Library and Information Science, 5(12): 67—75. (in Chinese)
|
|
高峰, 石玉成, 严松宏等, 2005. 隧道的两种减震措施研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 24(2): 222—229Gao F. , Shi Y. C. , Yan S. H. , et al. , 2005. Study of two shock absorption measures in tunnel. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 24(2): 222—229. (in Chinese)
|
|
耿萍, 何川, 晏启祥, 2013. 隧道结构抗震分析方法现状与进展. 土木工程学报, 46(S1): 262—268Geng P. , He C. , Yan Q. X. , 2013. The current situation and prospect of seismic analysis methods for tunnel structure. China Civil Engineering Journal, 46(S1): 262—268. (in Chinese)
|
|
韩俊艳, 郭之科, 李满君等, 2021. 纵向非一致激励下非均匀场地中埋地管道的振动台试验研究. 岩土工程学报, 43(6): 1147—1156Han J. Y. , Guo Z. K. , Li M. J. , et al. , 2021. Shaking table tests on buried pipelines in inhomogeneous soil under longitudinal non-uniform seismic excitation. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 43(6): 1147—1156. (in Chinese)
|
|
侯剑华, 胡志刚, 2013. CiteSpace软件应用研究的回顾与展望. 现代情报, 33(4): 99—103Hou J. H. , Hu Z. G. , 2013. Review on the application of CiteSpace at home and abroad. Journal of Modern Information, 33(4): 99—103. (in Chinese)
|
|
黄胜, 陈卫忠, 杨建平等, 2009. 地下工程地震动力响应及抗震研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 28(3): 483—490Huang S. , Chen W. Z. , Yang J. P. , et al. , 2009. Research on earthquake-induced dynamic responses and aseismic measures for underground engineering. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 28(3): 483—490. (in Chinese)
|
|
黄胜, 2010. 高烈度地震下隧道破坏机制及抗震研究. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所).Huang S., 2010. Research on failure mechanism and aseismic measures for underground engineering under high intensity earthquake. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Rock & Soil Mechanics Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. R. China. (in Chinese)
|
|
孔令俊, 2014. 大型钢筋混凝土箱涵结构拟静力试验与数值分析. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学.Kong L. J. , 2014. Pseudo-static test and numerical analysis of large reinforced concrete box culvert. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology. (in Chinese)
|
|
李亮, 杨晓慧, 杜修力, 2014. 地下结构地震反应计算的改进的反应位移法. 岩土工程学报, 36(7): 1360—1364Li L. , Yang X. H. , Du X. L. , 2014. Improved response displacement method for evaluating seismic responses of underground structures. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 36(7): 1360—1364. (in Chinese)
|
|
李晟, 庄海洋, 王伟等, 2021. 采用不同中柱的单层地铁地下车站结构抗震性能对比研究. 岩土工程学报, 43(10): 1905—1914Li S. , Zhuang H. Y. , Wang W. , et al. , 2021. Seismic performance of single-story subway station structures with different types of intermediate columns. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 43(10): 1905—1914. (in Chinese)
|
|
李育枢, 2006. 山岭隧道地震动力响应及减震措施研究−以国道318线黄草坪隧道为例. 上海: 同济大学.Li Y. S., 2006. Study on earthquake responses and vibration-absorption measures for mountain tunnel−A case study of Huangcaoping tunnel on No. 318 national highway. Shanghai: Tongji University. (in Chinese)
|
|
林刚, 罗世培, 倪娟, 2009. 地铁结构地震破坏及处理措施. 现代隧道技术, 46(4): 36—41, 47Lin G. , Luo S. P. , Ni J. , 2009. Damages of metro structures due to earthquake and corresponding treatment measures. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 46(4): 36—41, 47. (in Chinese)
|
|
林皋, 1990 a. 地下结构抗震分析综述(上). 世界地震工程, (2): 1—10.
|
|
林皋, 1990 b. 地下结构抗震分析综述(下). 世界地震工程, (3): 1—10, 42.
|
|
刘晶波, 李彬, 谷音, 2005. 地铁盾构隧道地震反应分析. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 45(6): 757—760Liu J. B. , Li B. , Gu Y. , 2005. Seismic response analysis of shielded subway tunnels. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 45(6): 757—760. (in Chinese)
|
|
刘晶波, 王文晖, 赵冬冬, 2013. 地下结构横截面地震反应拟静力计算方法对比研究. 工程力学, 30(1): 105—111Liu J. B. , Wang W. H. , Zhao D. D. , 2013. Comparison of the pseudo-static methods for seismic analysis of the underground structures. Engineering Mechanics, 30(1): 105—111. (in Chinese)
|
|
刘晶波, 王东洋, 谭辉等, 2019. 隧道纵向地震反应分析的反应位移法对比. 振动与冲击, 38(21): 104—111, 132Liu J. B. , Wang D. Y. , Tan H. , et al. , 2019. Response displacement methods for longitudinal seismic response analysis of tunnel structures. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 38(21): 104—111, 132. (in Chinese)
|
|
刘如山, 胡少卿, 石宏彬, 2007. 地下结构抗震计算中拟静力法的地震荷载施加方法研究. 岩土工程学报, 29(2): 237—242Liu R. S. , Hu S. Q. , Shi H. B. , 2007. Study on seismic loading of pseudo-static approach used in the seismic design of underground structure. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 29(2): 237—242. (in Chinese)
|
|
卢大伟, 李小军, 2010. 中国大陆强震动观测发展研究. 国际地震动态, (10): 35—42Lu D. W. , Li X. J. , 2010. Study on development of strong motion observation in China. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (10): 35—42. (in Chinese)
|
|
马超, 王作虎, 路德春等, 2020. CFRP加固地铁车站结构中柱地震损伤评价研究. 岩土工程学报, 42(12): 2249—2256Ma C. , Wang Z. H. , Lu D. C. , et al. , 2020. Seismic damage evaluation of CFRP-strengthened columns in subway stations. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 42(12): 2249—2256. (in Chinese)
|
|
倪茜, 卫林斌, 2018. 减震层作用下地铁车站结构的三维减震分析. 西安科技大学学报, 38(3): 459—465Ni Q. , Wei L. B. , 2018. Three-dimensional shock absorption analysis of metro station structure based on seismic layer. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 38(3): 459—465. (in Chinese)
|
|
孙铁成, 高波, 叶朝良, 2007. 地下结构抗震减震措施与研究方法探讨. 现代隧道技术, 44(3): 1—5, 10Sun T. C. , Gao B. , Ye Z. L. , 2007. Discussion on anti-seismic and seismic-relieving measures and corresponding research methods for underground structures. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 44(3): 1—5, 10. (in Chinese)
|
|
陶连金, 李卓遥, 安军海等, 2018. 地铁车站工程应用叠层橡胶支座隔震效果的研究. 公路, 63(7): 328—333Tao L. J. , Li Z. Y. , An J. H. , et al. , 2018. Study of isolation effect for laminated rubber bearing applied in the metro station engineering. Highway, 63(7): 328—333. (in Chinese)
|
|
王雪剑, 庄海洋, 陈国兴等, 2017. 地下连续墙对叠合墙式地铁车站结构地震反应的影响研究. 岩土工程学报, 39(8): 1435—1443Wang X. J. , Zhuang H. Y. , Chen G. X. , et al. , 2017. Effect of diaphragm wall on earthquake responses of an underground subway station. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 39(8): 1435—1443. (in Chinese)
|
|
许成顺, 许紫刚, 杜修力等, 2017. 地下结构抗震简化分析方法比较研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 37(2): 65—80Xu C. S. , Xu Z. G. , Du X. L. , et al. , 2017. Comparative study of simplified methods for seismic analysis of underground structure. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 37(2): 65—80. (in Chinese)
|
|
许成顺, 汪洋筱珊, 杜修力等, 2021. 分体柱在地下车站结构中的减震效果研究. 岩土工程学报, 43(4): 624—633Xu C. S. , Wang Y. X. S. , Du X. L. , et al. , 2021. Seismic mitigation effects of split columns in underground station structures. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 43(4): 624—633. (in Chinese)
|
|
徐琨鹏, 2019. 地下结构拟静力抗震分析方法及推覆试验研究. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Xu K. P., 2019. Study on Pseudo-static Seismic analysis method of underground structures and pushover test. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese)
|
|
闫冠宇, 许成顺, 张梓鸿等, 2022. 考虑水平-竖向地震作用效应的地下结构离心机振动台试验方法适用性研究. 建筑结构学报, doi: 10.14006/j. jzjgxb. 2022.0397.Yan G. Y., Xu C. S., Zhang Z. H., et al., 2022. Study on applicability of centrifuge shaking table test method for underground structure considering horizontal-vertical seismic effects. Journal of Building Structures, doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2022.0397. (in Chinese)
|
|
杨林德, 季倩倩, 郑永来等, 2003. 软土地铁车站结构的振动台模型试验. 现代隧道技术, 40(1): 7—11Yang L. D. , Ji Q. Q. , Zheng Y. L. , et al. , 2003. Shaking table test on metro station structures in soft soil. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 40(1): 7—11. (in Chinese)
|
|
袁勇, 陈之毅, 2014. 城市地下空间抗震与安全. 上海: 同济大学出版社.
|
|
岳粹洲, 郑永来, 2015. 埋深对地下结构地震反应特点的影响研究. 长江科学院院报, 32(11): 78—81Yue C. Z. , Zheng Y. L. , 2015. Research of the influence of embedded depth on seismic response of underground structure. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 32(11): 78—81. (in Chinese)
|
|
卓越, 李治国, 高广义, 2021. 隧道注浆技术的发展现状与展望. 隧道建设(中英文), 41(11): 1953—1963Zhuo Y. , Li Z. G. , Gao G. Y. , 2021. Development status and prospect of tunnel grouting technology. Tunnel Construction, 41(11): 1953—1963. (in Chinese)
|
|
邹炎, 2015. 地下结构地震反应规律和抗震设计方法研究. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Zou Y., 2015. Study on seismic response laws and seismic design methods of underground structures. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese)
|
|
川岛一彦, 1994. 地下构筑物の耐震设计.
|
|
川西智浩, 清野純史, 井澤淳, 2014. 開削トンネルの破壊箇所と耐力の関係把握のための静的載荷実験. 第33回地震工学研宄凳表会講論文集, 70(4): 1734-1741.Kawanishi T., Kiyono J., Izawa J., 2014. Static loading tests of cut and cover tunnel to grasp a relationship between a process of failure and strength. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Ser. A1 (Structural Engineering & Earthquake Engineering (SE/EE)), 70(4): 1734—1741(in Japanese)
|
|
Adalier K. , Abdoun T. , Dobry R. , et al. , 2003. Centrifuge modelling for seismic retrofit design of an immersed tube tunnel. International Journal of Physical Modelling in Geotechnics, 3(2): 23—35. doi: 10.1680/ijpmg.2003.030203
|
|
Al-Kheetan M. J. , Ghaffar S. H. , Madyan O. A. , et al. , 2020. Development of low absorption and high-resistant sodium acetate concrete for severe environmental conditions. Construction and Building Materials, 230: 117057. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117057
|
|
An X. H. , Shawky A. A. , Maekawa K. , 1997. The collapse mechanism of a subway station during the great Hanshin earthquake. Cement and Concrete Composites, 19(3): 241—257. doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(97)00014-0
|
|
Azadi M. , Hosseini S. M. M. M. , 2010. Analyses of the effect of seismic behavior of shallow tunnels in liquefiable grounds. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 25(5): 543—552. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2010.03.003
|
|
Cattoni E. , Tamagnini C. , 2020. On the seismic response of a propped r. c. diaphragm wall in a saturated clay. Acta Geotechnica, 15(4): 847—865.
|
|
Chen G. X. , Wang Z. H. , Zuo X. , et al. , 2013. Shaking table test on the seismic failure characteristics of a subway station structure on liquefiable ground. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 42(10): 1489—1507.
|
|
Chen G. X. , Chen S. , Qi C. Z. , et al. , 2015 a. Shaking table tests on a three-arch type subway station structure in a liquefiable soil. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 13(6): 1675—1701. doi: 10.1007/s10518-014-9675-0
|
|
Chen G. X. , Chen S. , Zuo X. , et al. , 2015 b. Shaking-table tests and numerical simulations on a subway structure in soft soil. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 76: 13—28. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.12.012
|
|
Chen J. T. , Yuan Y. , Yu H. T. , 2019 a. Dynamic response of segmental lining tunnel. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 43(3): 660—682.
|
|
Chen S. , Zhuang H. Y. , Quan D. Z. , et al. , 2019 b. Shaking table test on the seismic response of large-scale subway station in a loess site: a case study. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 123: 173—184. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.04.023
|
|
Chen Z. Y. , Chen W. , Bian G. Q. , 2014. Seismic performance upgrading for underground structures by introducing shear panel dampers. Advances in Structural Engineering, 17(9): 1343—1357. doi: 10.1260/1369-4332.17.9.1343
|
|
Chen Z. Y. , Zhou Y. , 2019 c. Seismic performance of framed underground structures with self-centering energy-dissipation column base. Advances in Structural Engineering, 22(13): 2809—2822. doi: 10.1177/1369433219852043
|
|
Dabiri R. , Notash N. H. , 2020. Evaluation of geofoam effects on seismic response in cantilever retaining wall. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 38(2): 2097—2116. doi: 10.1007/s10706-019-01151-1
|
|
Huh J. , Tran Q. H. , Haldar A. , et al. , 2017. Seismic vulnerability assessment of a shallow two-story underground RC box structure. Applied Sciences, 7(7): 735. doi: 10.3390/app7070735
|
|
Huo H. , Bobet A. , Fernández G. , et al. , 2006. Analytical solution for deep rectangular structures subjected to far-field shear stresses. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 21(6): 613—625. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2005.12.135
|
|
Hushmand A. , Dashti S. , Davis C. , et al. , 2016. A centrifuge study of the influence of site response, relative stiffness, and kinematic constraints on the seismic performance of buried reservoir structures. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 88: 427—438. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.06.011
|
|
Iwatate T., Kobayashi Y., Kusu H., et al., 2000. Investigation and shaking table tests of subway structures of the Hyogoken-Nanbu earthquake. In: Proceedings of the 12 th World conference on Earthquake Engineering. Auckland: New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering Upper Hutt, 1043—1051.
|
|
Jiang J. W. , Xu C. S. , El Naggar H. M. , et al. , 2021. Improved pushover method for seismic analysis of shallow buried underground rectangular frame structure. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 140: 106363. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106363
|
|
Jiang J. W. , El Naggar M. H. , Huang W. T. , et al. , 2022. Seismic vulnerability analysis for shallow-buried underground frame structure considering 18 existing subway stations. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 162: 107479. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107479
|
|
Jiang L. Z. , Chen J. , Li J. , 2010. Seismic response of underground utility tunnels: shaking table testing and FEM analysis. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 9(4): 555—567. doi: 10.1007/s11803-010-0037-x
|
|
Keykhosropour L. , Lemnitzer A. , 2022. Seismic response behavior of deep flexible underground structures in sand-insights from an experimental–numerical investigation. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 20(10): 5205—5231. doi: 10.1007/s10518-022-01388-x
|
|
Kim D. S. , Konagai K. , 2001. Key parameters governing the performance of soft tunnel coating for seismic isolation. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 30(9): 1333—1343.
|
|
Li W. T. , Chen Q. J. , 2020. Seismic damage evaluation of an entire underground subway system in dense urban areas by 3 D FE simulation. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 99: 103351. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103351
|
|
Liu H. B., Song E. X., 2006. Working mechanism of cutoff walls in reducing uplift of large underground structures induced by soil liquefaction. Computers and Geotechnics, 33(4—5): 209—221.
|
|
Lu C. C. , Hwang J. H. , 2019 a. Nonlinear collapse simulation of Daikai Subway in the 1995 Kobe earthquake: necessity of dynamic analysis for a shallow tunnel. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 87: 78—90. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.02.007
|
|
Lu D. C. , Wu C. Y. , Ma C. , et al. , 2020. A novel segmental cored column for upgrading the seismic performance of underground frame structures. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 131: 106011. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.106011
|
|
Lu L. M. , Qiu J. N. , Yuan Y. , et al. , 2019 b. Large-scale test as the basis of investigating the fire-resistance of underground RC substructures. Engineering Structures, 178: 12—23. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.09.083
|
|
Ma C. , Lu D. C. , Du X. L. , 2018. Seismic performance upgrading for underground structures by introducing sliding isolation bearings. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 74: 1—9. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.01.007
|
|
Manohar D. R. , Anbazhagan P. , 2021. Shear strength characteristics of geosynthetic reinforced rubber-sand mixtures. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 49(4): 910—920. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.12.015
|
|
Penzien J. , 2000. Seismically induced racking of tunnel linings. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 29(5): 683—691.
|
|
Sakyi K. S. , Benjamin K. , Godson K. , 2018. Seismic response analysis of underground structures. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 8(5): 48—71.
|
|
Samata S. , Ohuchi H. , Matsuda T. , 1997. A study of the damage of subway structures during the 1995 Hanshin-Awaji earthquake. Cement and Concrete Composites, 19(3): 223—239. doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(97)00018-8
|
|
Sandoval E. , Bobet A. , 2020. Effect of input frequency on the seismic response of deep circular tunnels. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 139: 106421. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106421
|
|
Shawky A. A. , 1994. Nonlinear static and dynamic analysis for underground reinforced concrete. 東京大学.
|
|
Wang G. B. , Ba F. , Miao Y. , et al. , 2022. Design of multi-array shaking table tests under uniform and non-uniform earthquake excitations. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 153: 107114. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.107114
|
|
Wang W. , Feng K. , Wang Y. C. , et al. , 2021. A solution of subgrade modulus for response displacement method of circular underground structures. Shock and Vibration, 2021: 3654147.
|
|
Xu C. S. , Zhang Z. H. , Li Y. , et al. , 2021. Seismic response and failure mechanism of underground frame structures based on dynamic centrifuge tests. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 50(7): 2031—2048.
|
|
Yang D. , Naesgaard E. , Byrne P. M. , et al. , 2004. Numerical model verification and calibration of George Massey Tunnel using centrifuge models. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 41(5): 921—942. doi: 10.1139/t04-039
|
|
Yu H. T. , Li Y. X. , Shao X. Y. , et al. , 2021. Virtual hybrid simulation method for underground structures subjected to seismic loadings. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 110: 103831. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.103831
|
|
Zarnani S. , Bathurst R. J. , 2009. Numerical parametric study of expanded polystyrene (EPS) geofoam seismic buffers. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 46(3): 318—338. doi: 10.1139/T08-128
|
|
Zhang Z. H. , Li Y. , Xu C. S. , et al. , 2021. Study on seismic failure mechanism of shallow buried underground frame structures based on dynamic centrifuge tests. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 150: 106938. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.106938
|
|
Zhu T. , Wang R. , Zhang J. M. , 2021. Evaluation of various seismic response analysis methods for underground structures in saturated sand. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 110: 103803. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103803
|
|
Zhuang H. Y. , Wang R. , Shi P. X. , et al. , 2019. Seismic response and damage analysis of underground structures considering the effect of concrete diaphragm wall. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 116: 278—288. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.09.052
|
|
Zhuang H. Y. , Yang J. , Chen S. , et al. , 2021. Statistical numerical method for determining seismic performance and fragility of shallow-buried underground structure. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 116: 104090. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104090
|
|
Zou Y. , Liu H. B. , Jing L. P. , et al. , 2017. A pseudo-static method for seismic responses of underground frame structures subjected to increasing excitations. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 65: 106—120. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.02.006
|




 下载:
下载: