Shaking Table Test Study on Seismic Response of Soil-structure Cluster Interaction System
-
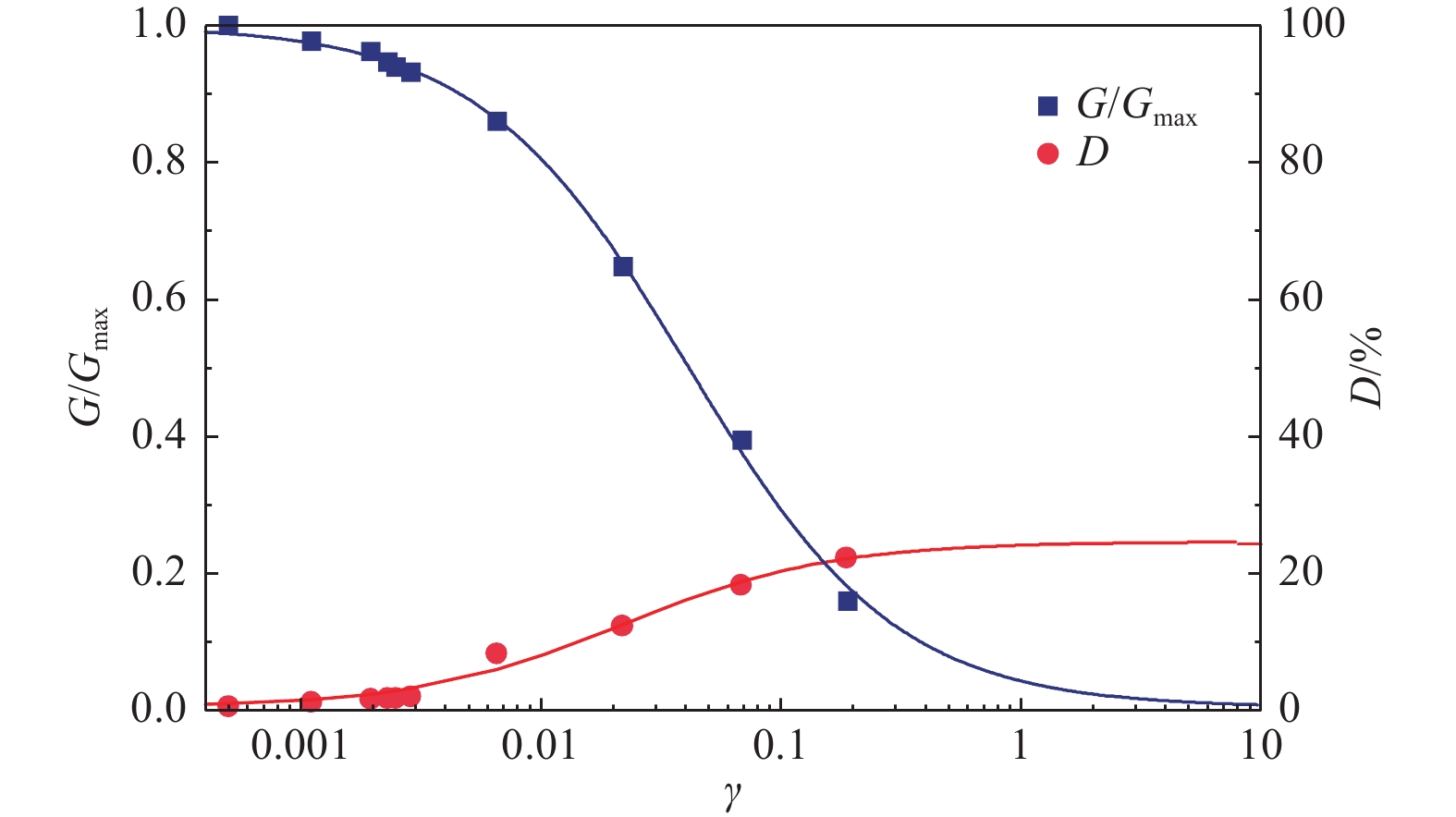
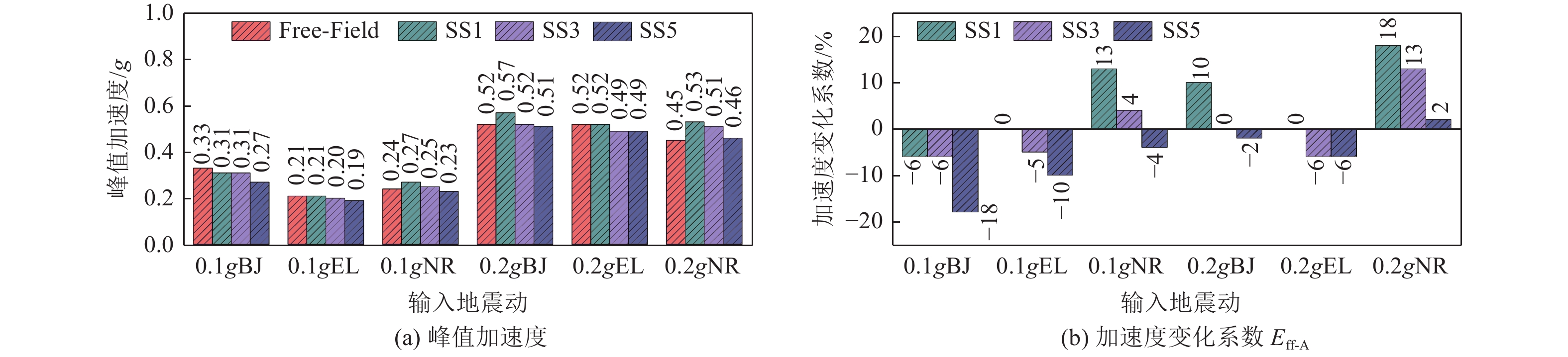
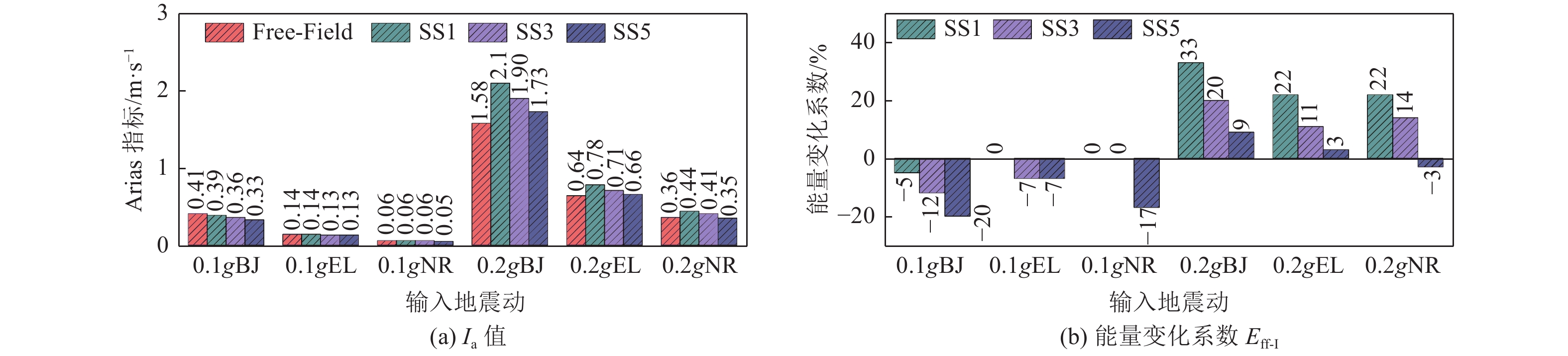
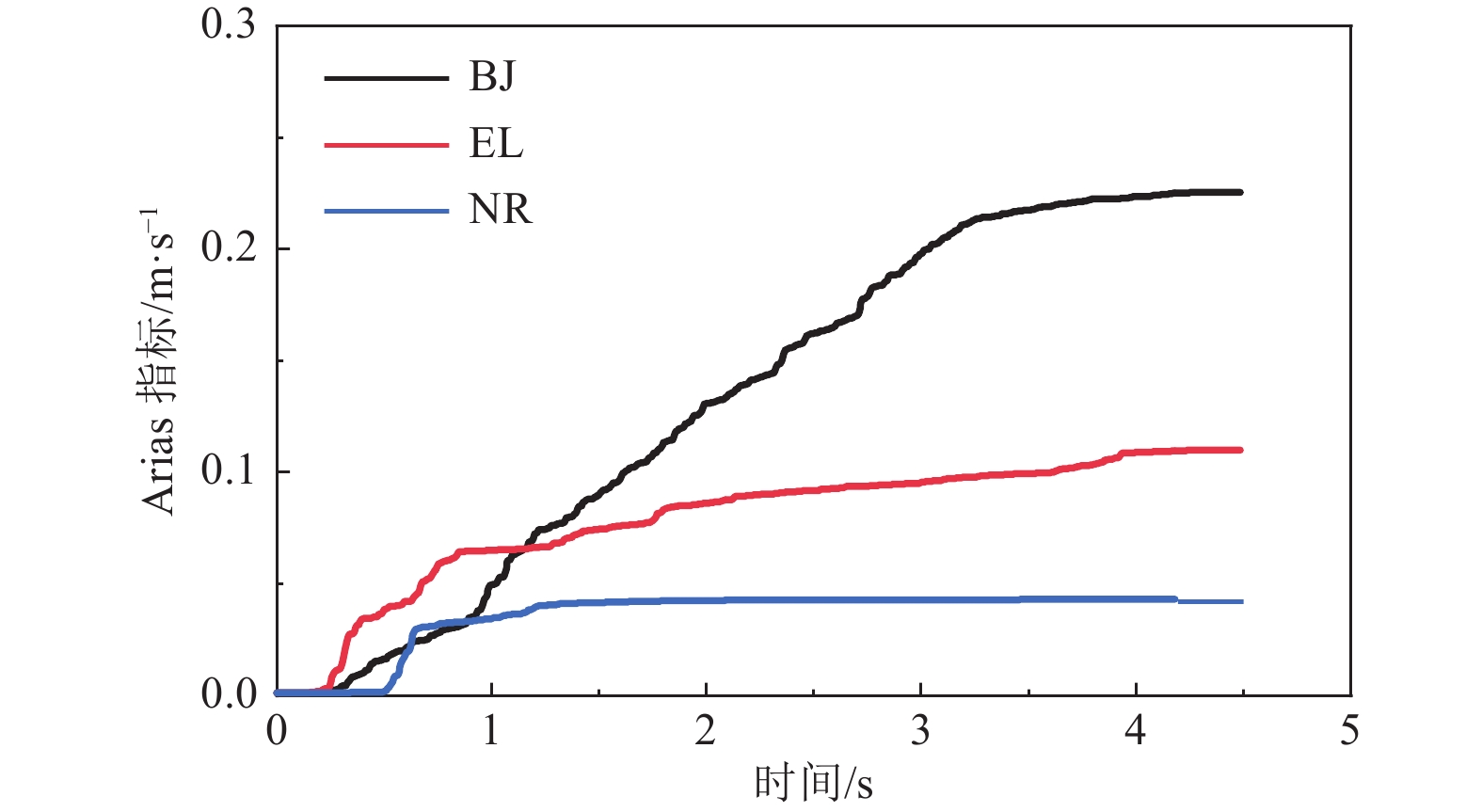
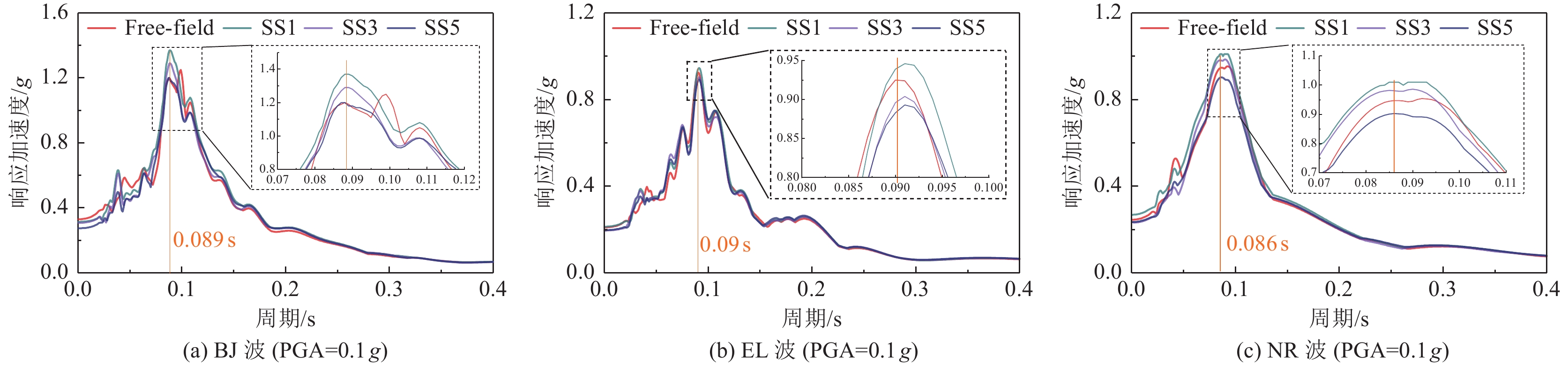
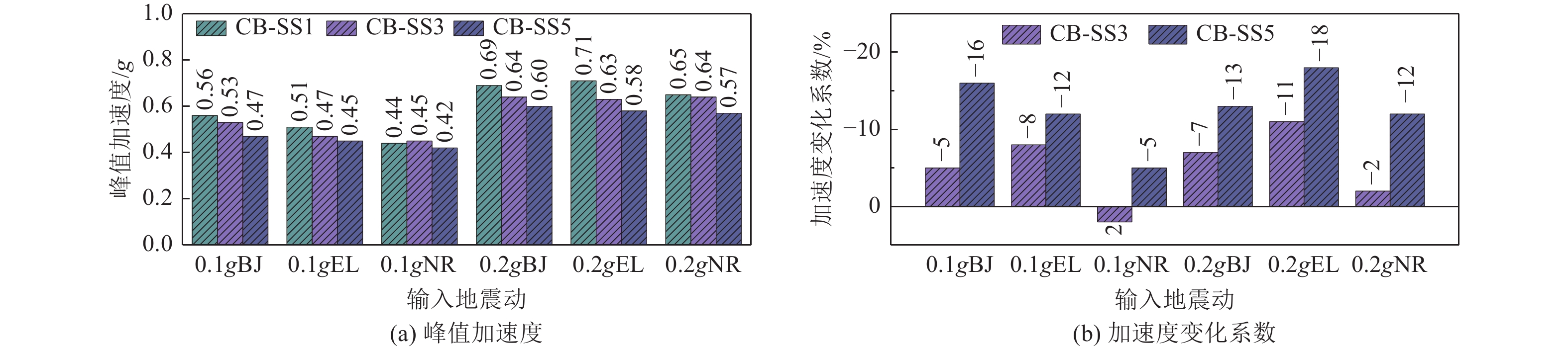
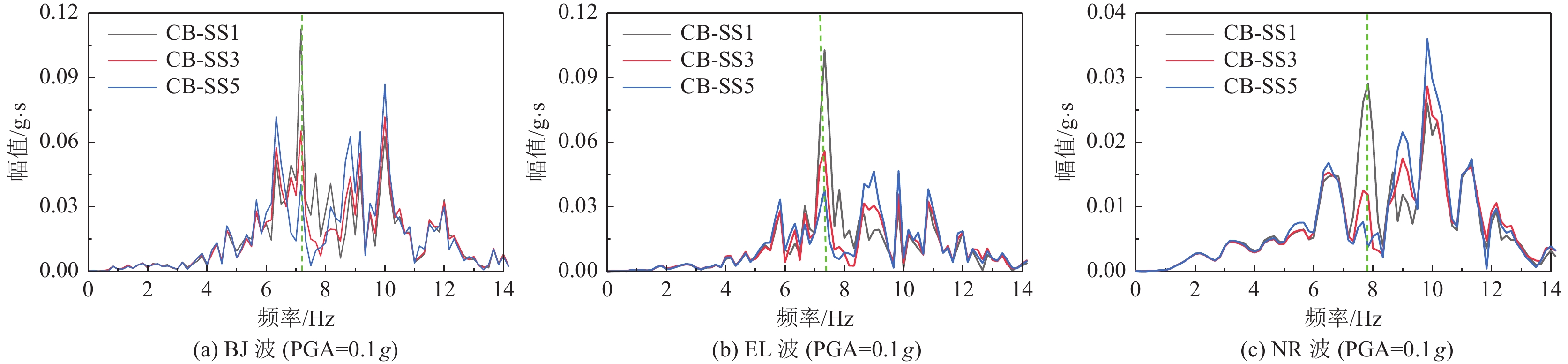
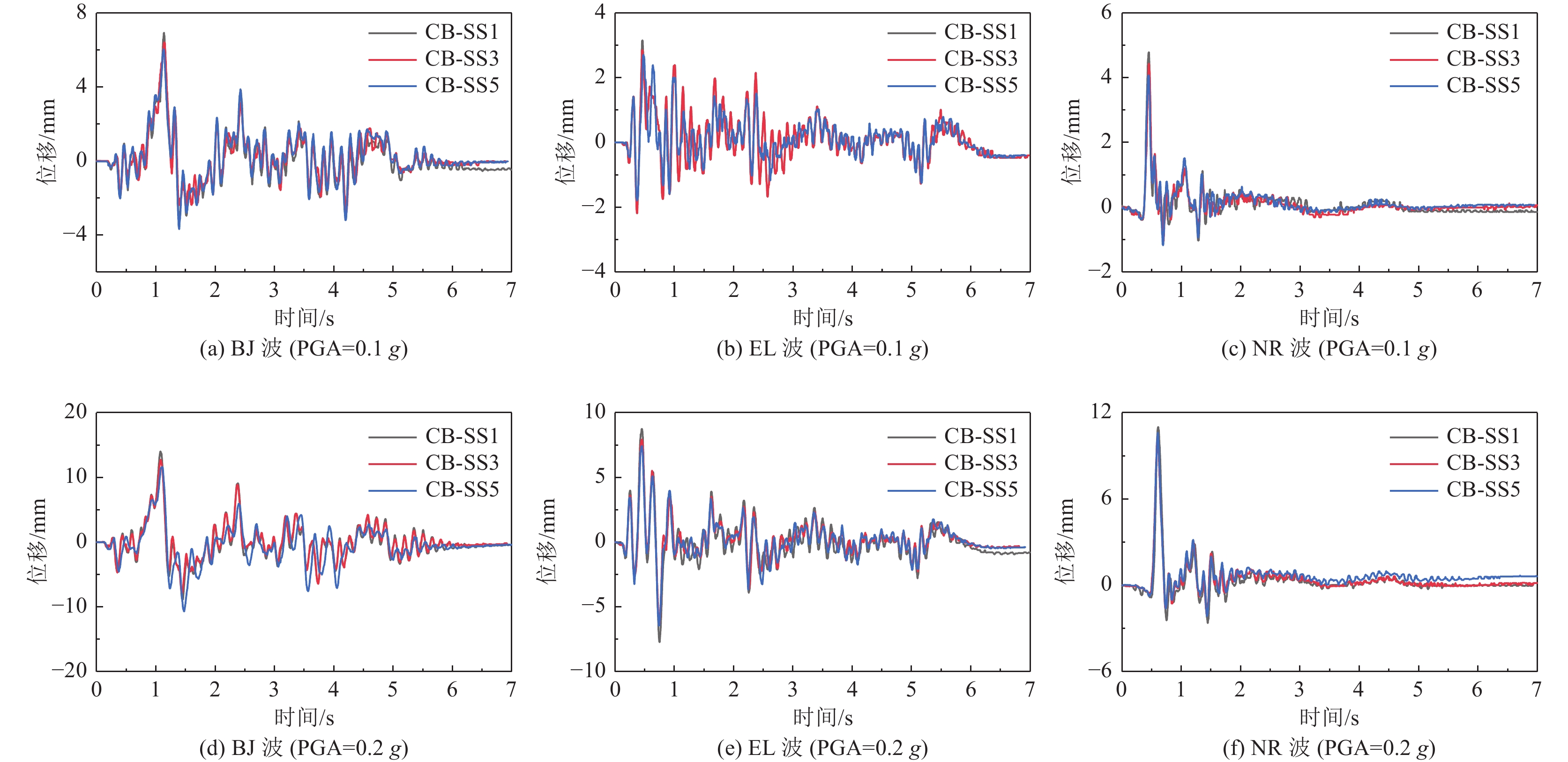
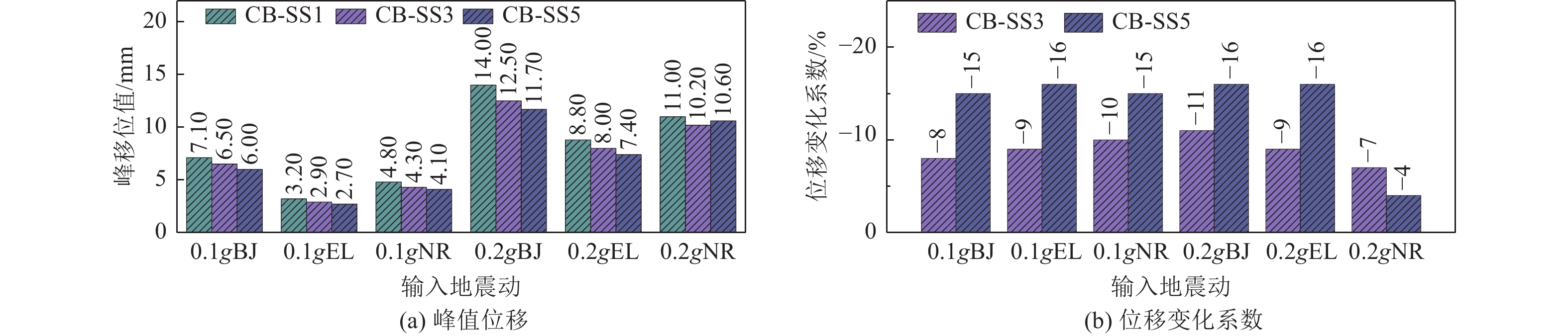
摘要: 设计并开展一系列土-结构群相互作用体系振动台试验,考虑结构数量、地震动类型与幅值等参数,研究土-结构群相互作用对结构及场地土响应的影响,并对模型土参数确定方法进行分析。研究结果表明,地表建筑物的存在并不总是减小自由场地面运动,但地面运动随着地表结构数量的增加而降低;土-结构群相互作用对位于结构群中心的结构响应影响最大,且会放大土体卓越频率附近的响应成分;不同评价指标之间具有不同的侧重点,但均可较好地评价结构群之间的相互作用;输入地震动的总能量越高,土-结构群相互作用越明显。
-
关键词:
- 振动台试验 /
- 土-结构相互作用 /
- 结构-土-结构相互作用 /
- 土-结构群相互作用
Abstract: A series of shaking table tests of soil-structure (group) interaction systems are designed and implemented in the paper, the parameters such as the number of structures, and the type and amplitude of ground motion are considered to explore the influence of the SSCI effect on the structure and site soil response. And the methods to determine model soil parameters are discussed. The comparative analysis based on the test results shows that: (1) the existence of surface buildings does not always reduce the ground motion of the free field, but the ground motion decreases with the increase of the number of surface structures. (2) The SSCI effect has the greatest impact on the structural response at the center of the structure group, and it also will amplify the response components near the predominant frequency of the soil. (3) Different evaluation indicators have different emphases, However, they both can evaluate the interaction between structural groups well; (4) the higher the total energy of the input ground motion, the more obvious the SSCI effect. -
表 1 相似系数与相似关系
Table 1. Similarity coefficient and similarity relation
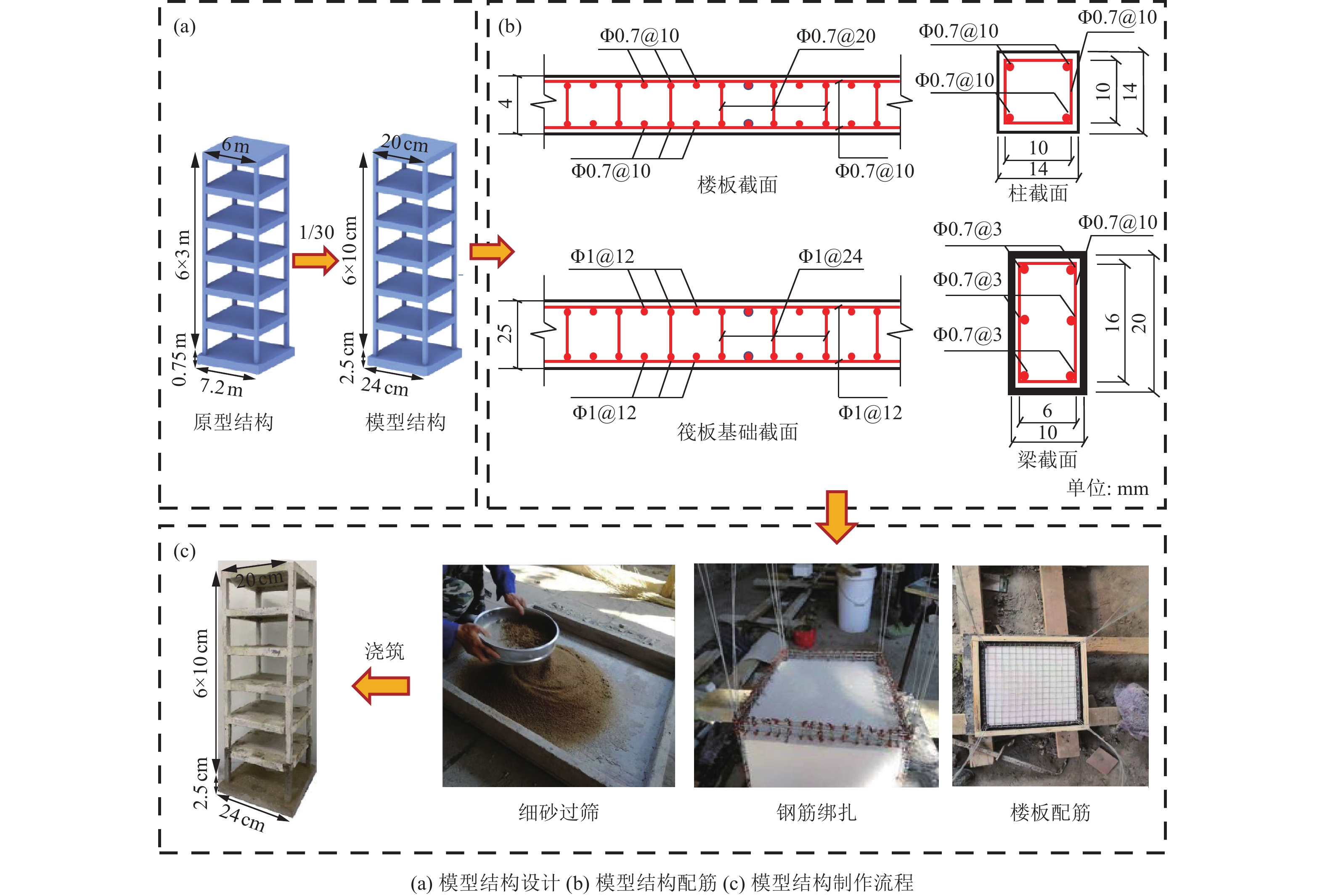
特征类型 物理量 相似关系 相似系数 几何特征 几何尺寸 SL 1/30 材料特征 弹性模量 SE 0.462 等效密度 Sρ=SE/(SaSL) 6.923 应变 Sε= Sσ/ SE 1 应力 Sσ 0.462 质量 Sm= SσSL2/ Sa 0.000 256 动力特征 时间 St = SL/ (SE / Sρ)−0.5 0.129 频率 Sf = SL−0.5Sa0.5 7.746 位移 SL 1/30 速度 Sv= (SL/ Sa)0.5 0.258 加速度 Sa 2 表 2 加载工况
Table 2. Test loading cases
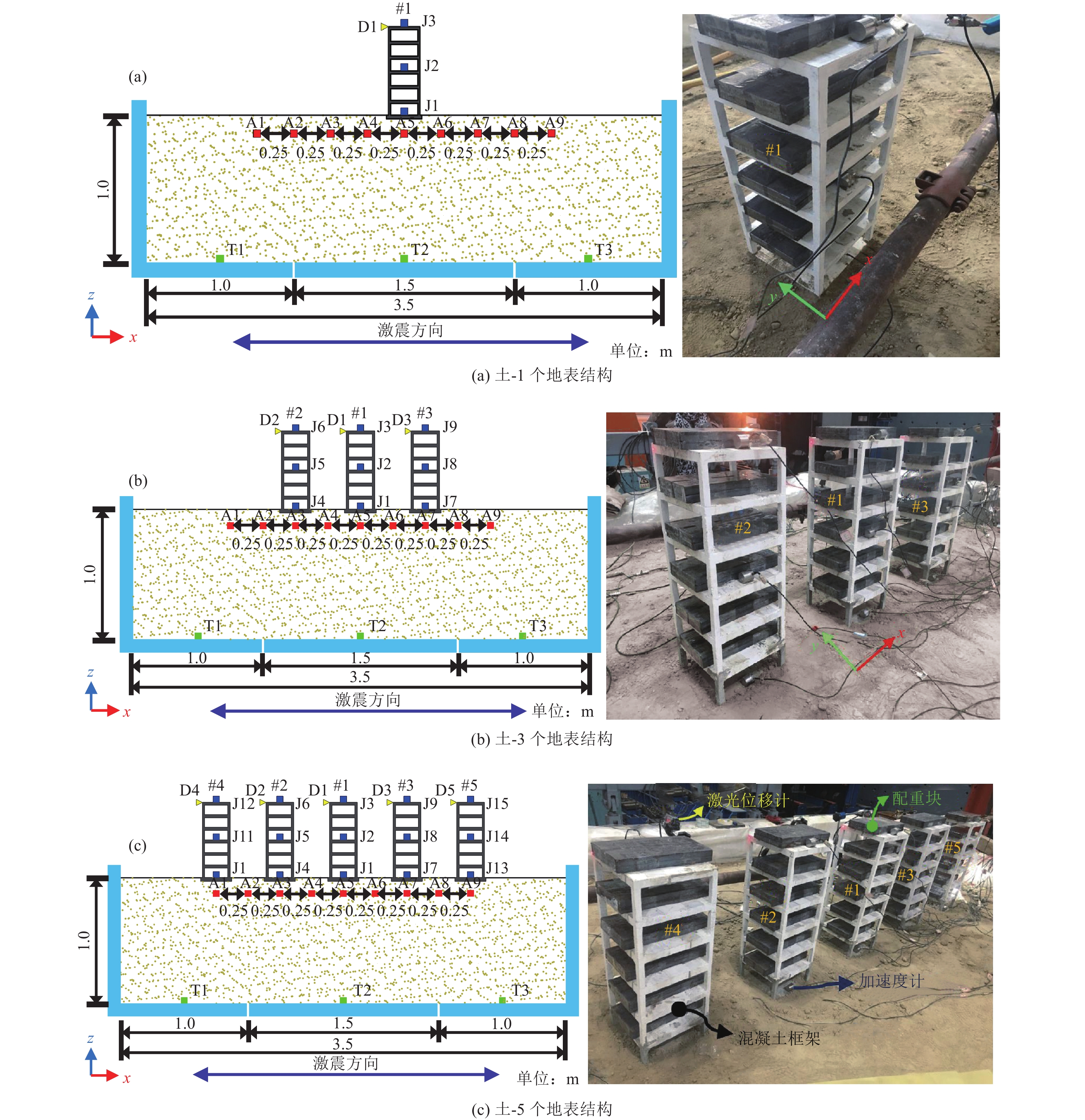
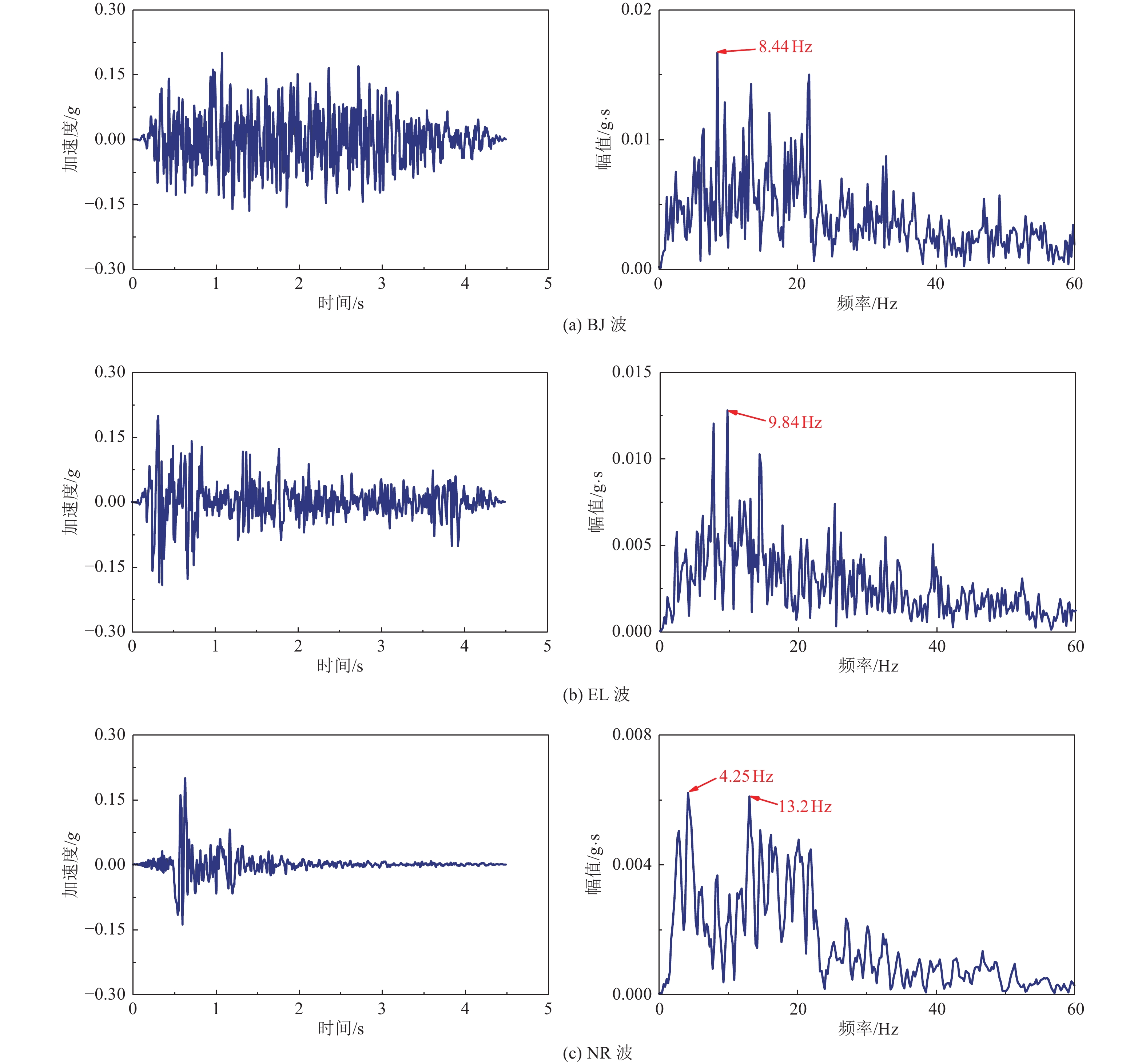
编号 自由场 土-1个地表结构 土-3个地表结构 土-5个地表结构 输入波 地震动峰值加速度PGA/g 输入波 地震动峰值加速度PGA/g 输入波 地震动峰值加速度PGA/g 输入波 地震动峰值加速度PGA/g 1 WN 0.05 WN 0.05 WN 0.05 WN 0.05 2 EL 0.1 EL 0.1 EL 0.1 EL 0.1 3 BJ 0.1 BJ 0.1 BJ 0.1 BJ 0.1 4 NR 0.1 NR 0.1 NR 0.1 NR 0.1 5 EL 0.2 EL 0.2 EL 0.2 EL 0.2 6 BJ 0.2 BJ 0.2 BJ 0.2 BJ 0.2 7 NR 0.2 NR 0.2 NR 0.2 NR 0.2 -
巴振宁, 慕少聪, 赵靖轩等, 2022. 基于动力学震源模型的三维沉积盆地直下型断层地震动模拟. 震灾防御技术, 17(3): 431—441Ba Z. N. , Mu S. C. , Zhao J. X. , et al. , 2022. Ground motion simulation of three-dimensional sedimentary basin based on directly-beneath fault dynamic source model. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 17(3): 431—441. (in Chinese) Aji H. D. B. , Wuttke F. , Dineva P. , 2022. 3 D structure-soil-structure interaction in an arbitrary layered half-space. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 159: 107352. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107352 Aldaikh H. , Alexander N. A. , Ibraim E. , et al. , 2015. Two dimensional numerical and experimental models for the study of structure-soil-structure interaction involving three buildings. Computers & Structures, 150: 79—91. Aldaikh H. , Alexander N. A. , Ibraim E. , et al. , 2016. Shake table testing of the dynamic interaction between two and three adjacent buildings (SSSI). Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 89: 219—232. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.08.012 Anand V. , Kumar S. R. S. , 2018. Seismic soil-structure interaction: a state-of-the-art review. Structures, 16: 317—326. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2018.10.009 Ayala F. , Sáez E. , Magna-Verdugo C. , 2022. Computational modelling of dynamic soil-structure interaction in shear wall buildings with basements in medium stiffness sandy soils using a subdomain spectral element approach calibrated by micro-vibrations. Engineering Structures, 252: 113668. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113668 Bard P. Y., Chazelas J. L., Guéguen P., et al., 2008. Site-city interaction. In: Oliveira C. S., Roca A., Goula X., eds., Assessing and Managing Earthquake Risk. Dordrecht: Springer, 91—114. Barrios G. , Larkin T. , Chouw N. , 2021. Experimental study of the seismic response of a structure set amongst closely adjacent structures. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 50(14): 3771—3791. Dijckmans A. , Coulier P. , Jiang J. , et al. , 2015. Mitigation of railway induced ground vibration by heavy masses next to the track. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 75: 158—170. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.04.003 Ge Q. , Xiong F. , Xie L. W. , et al. , 2019. Dynamic interaction of soil-Structure cluster. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 123: 16—30. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.04.020 Hardin B. O. , Drnevich V. P. , 1972. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 98(7): 667—692. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001760 Isbiliroglu Y. , Taborda R. , Bielak J. , 2015. Coupled soil-structure interaction effects of building clusters during earthquakes. Earthquake Spectra, 31(1): 463—500. doi: 10.1193/102412EQS315M Kumar N. , Narayan J. P. , 2018. Quantification of site-city interaction effects on the response of structure under double resonance condition. Geophysical Journal International, 212(1): 422—441. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx397 Kumar N. , Narayan J. P. , 2019. Effects of site-city interaction and polarization of the incident S-wave on the transfer function and fundamental frequency of structures. Natural Hazards, 97(2): 747—774. doi: 10.1007/s11069-019-03671-8 Li W. T. , Chen Q. J. , 2020. Seismic damage evaluation of an entire underground subway system in dense urban areas by 3 D FE simulation. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 99: 103351. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103351 Long H. , Wang Z. C. , Zhang C. S. , et al. , 2021. Nonlinear study on the structure-soil-structure interaction of seismic response among high-rise buildings. Engineering Structures, 242: 112550. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112550 Schwan L. , Boutin C. , Padrón L. A. , et al. , 2016. Site-city interaction: theoretical, numerical and experimental crossed-analysis. Geophysical Journal International, 205(2): 1006—1031. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw049 Wang G. B. , Ba F. , Miao Y. , et al. , 2022 a. Design of multi-array shaking table tests under uniform and non-uniform earthquake excitations. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 153: 107114. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.107114 Wang J. S. , Guo T. , Du Z. Y. , 2022 b. Experimental and numerical study on the influence of dynamic structure-soil-structure interaction on the responses of two adjacent idealized structural systems. Journal of Building Engineering, 52: 104454. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104454 Wang J. S. , Guo T. , Du Z. Y. , et al. , 2022 c. Shaking table tests and parametric analysis of dynamic interaction between soft soil and structure group. Engineering Structures, 256: 114041. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.114041 -



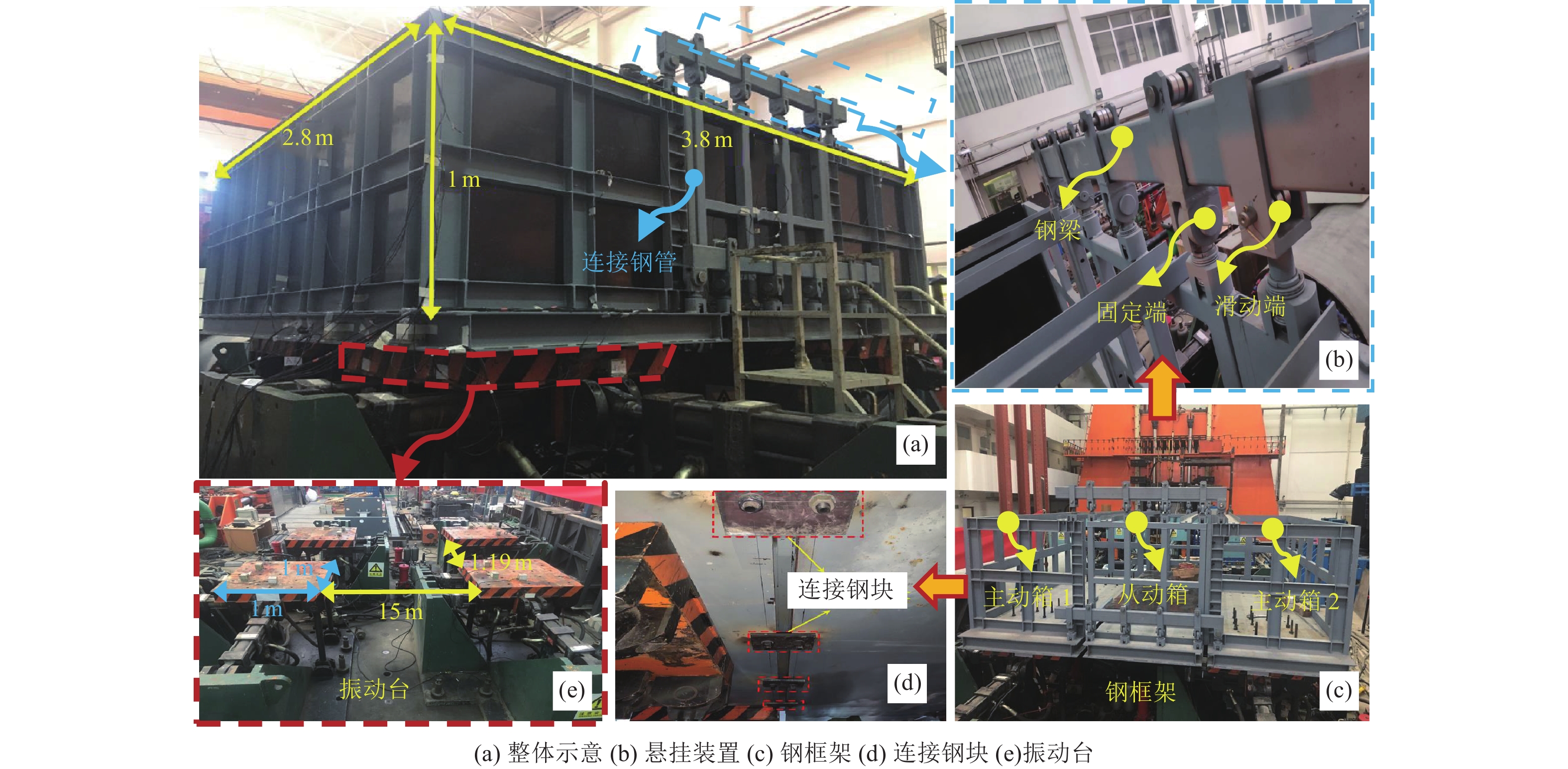
 下载:
下载: