Analysis of Ground Motion Characteristics of Typical Slope Terrain
-
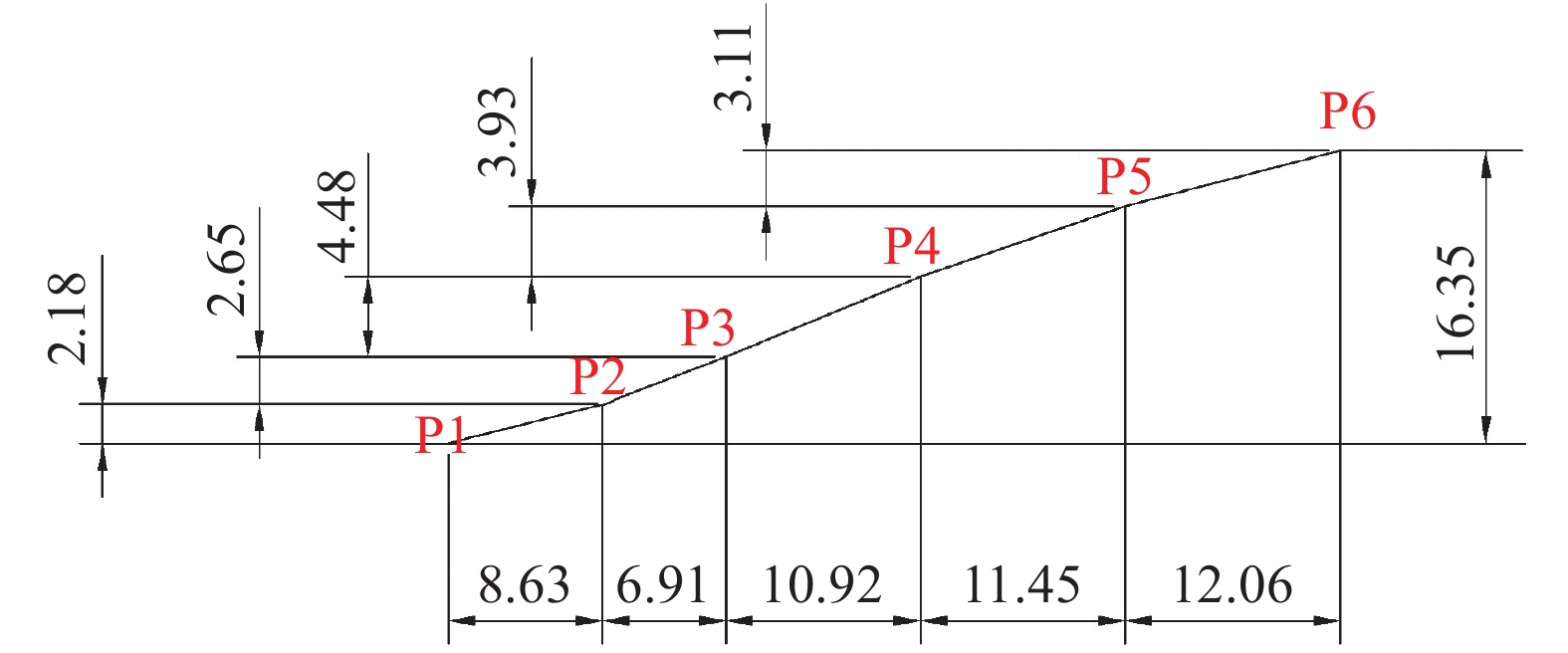
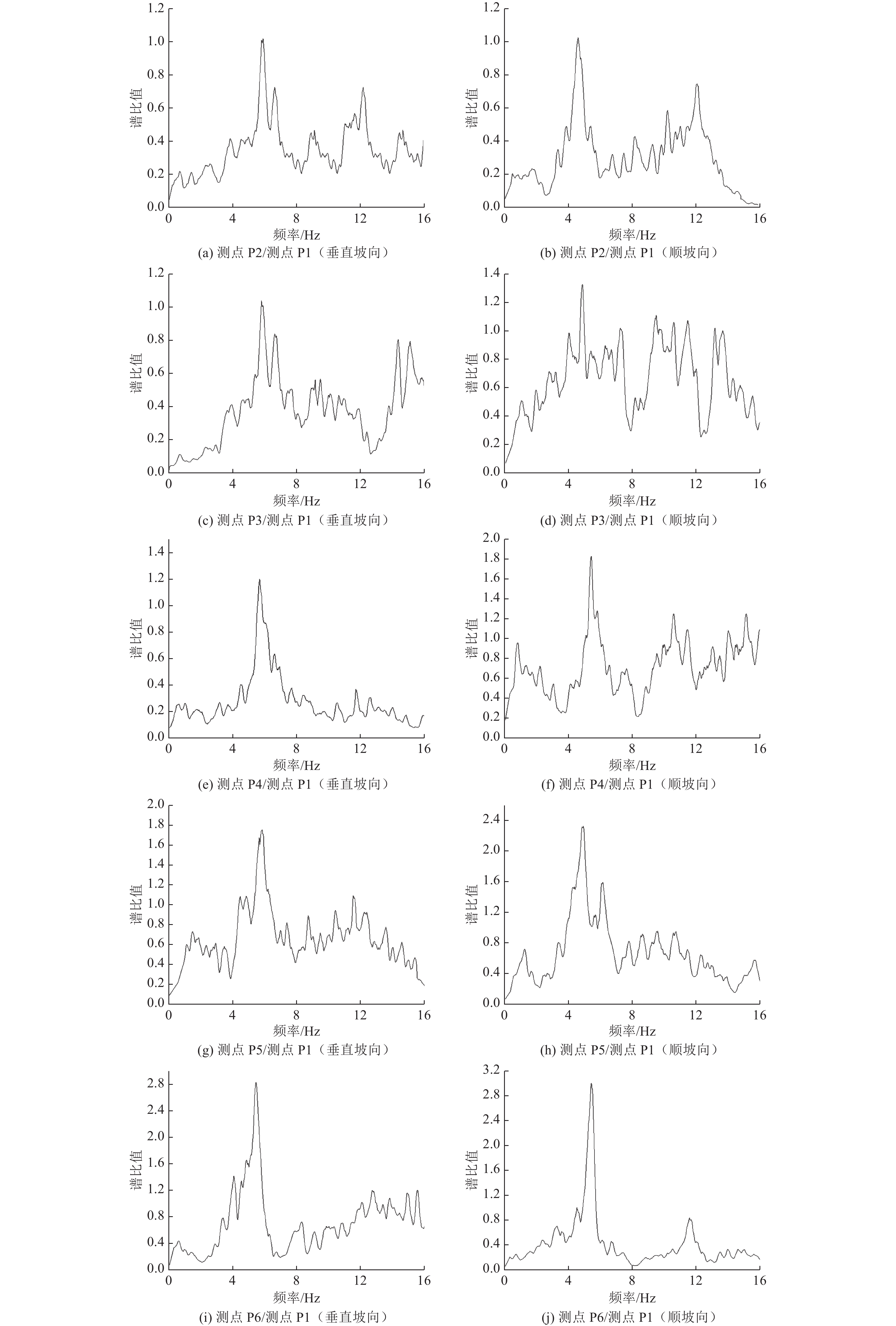
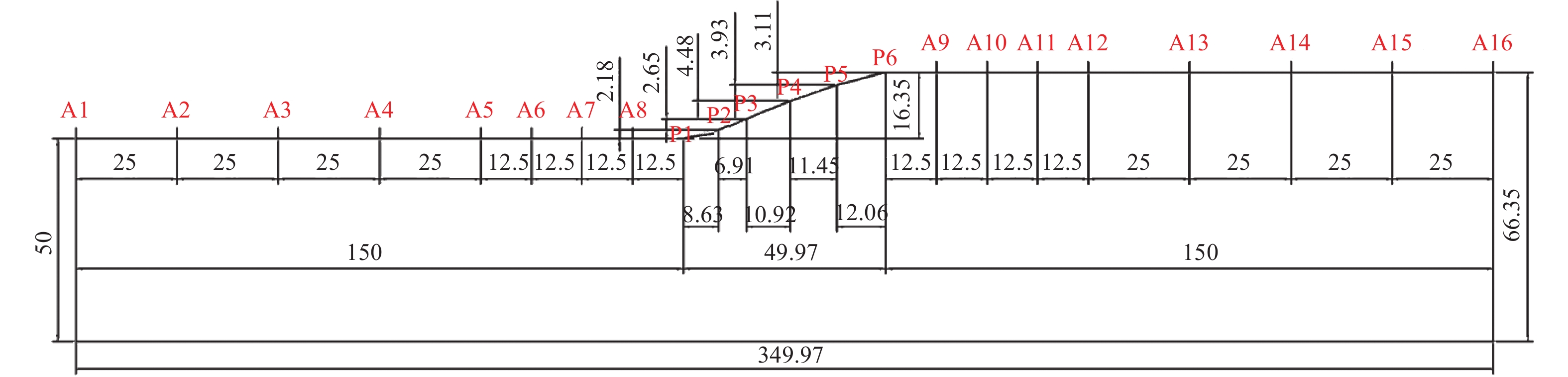
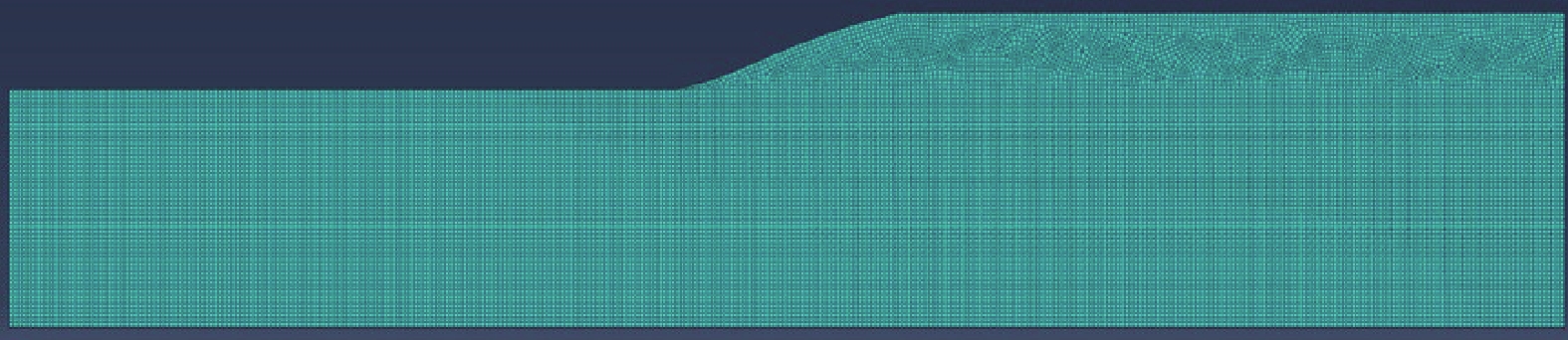
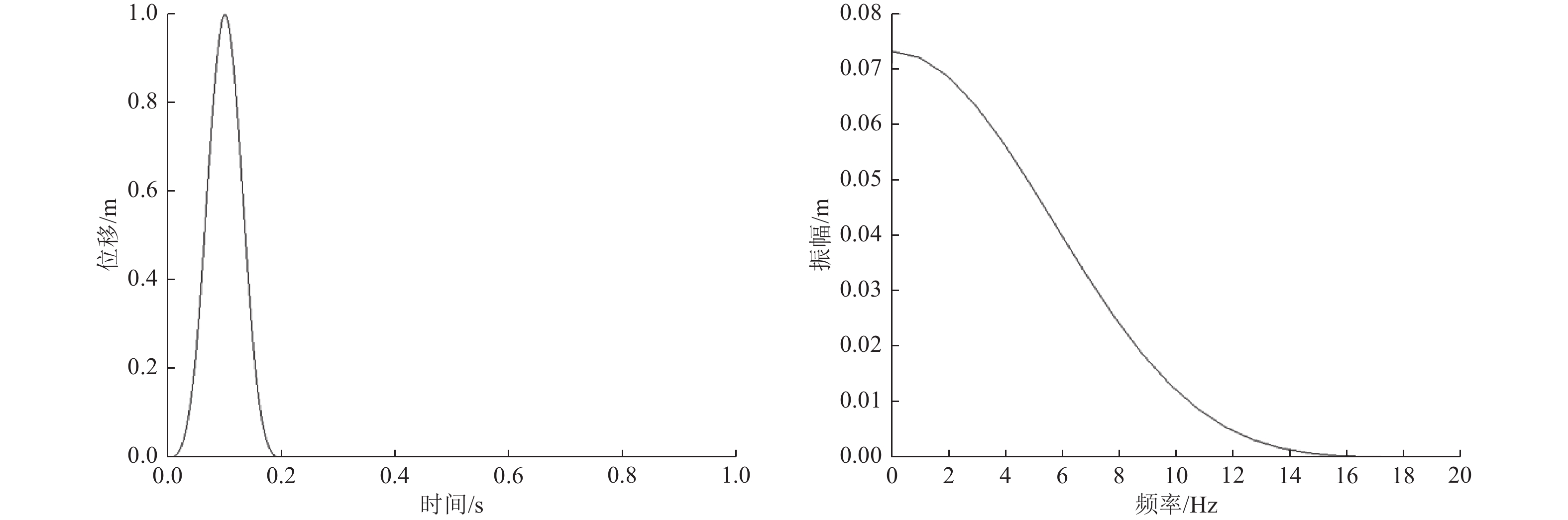
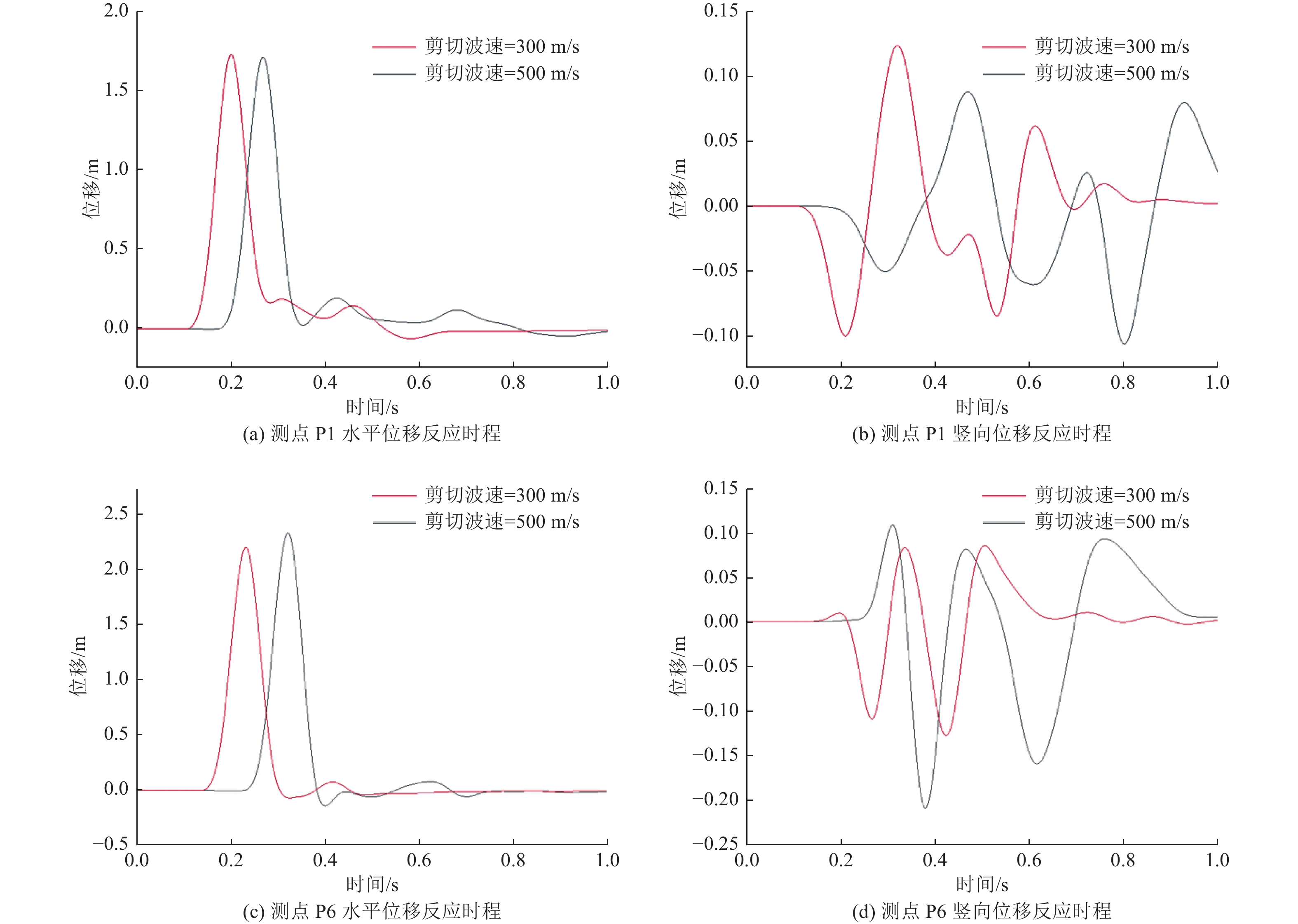
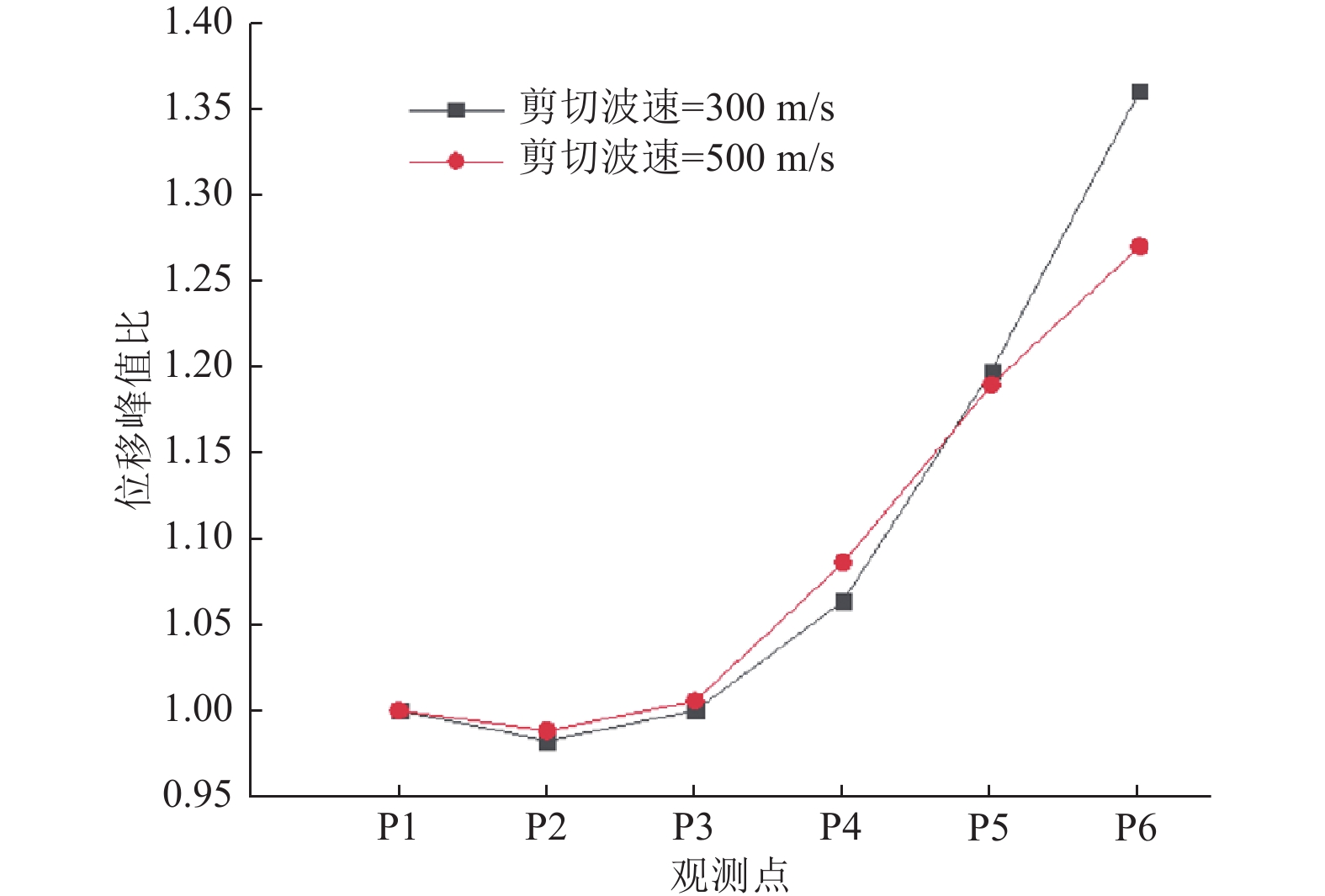
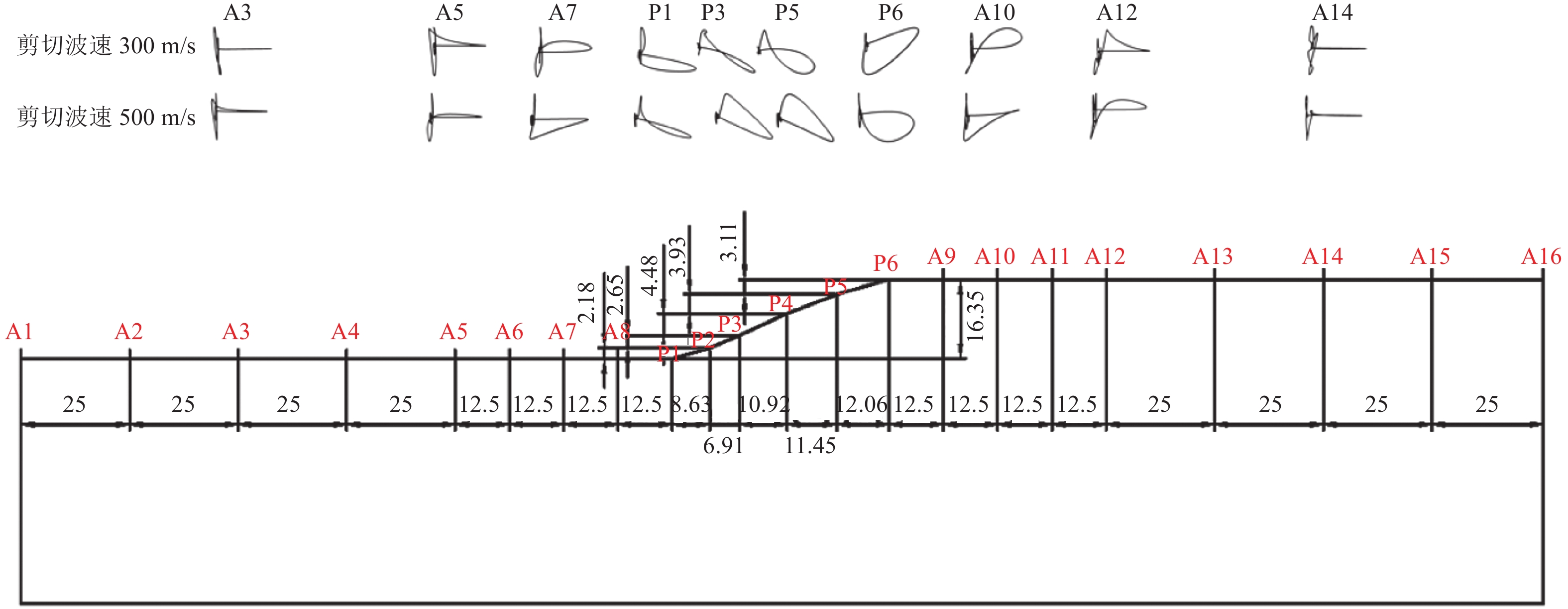
摘要: 以云南鲁甸6.5级地震中房屋建筑破坏严重的龙头山集镇斜坡地形为例,通过地脉动测试分析得出斜坡及坡顶测点相对于坡脚参考点谱比峰值均>1,顺坡向谱比峰值大于垂直坡向谱比峰值,且谱比峰值从斜坡坡脚到坡顶逐渐增大,坡顶处约为3;顺坡向谱比峰值对应的频率为4.57~5.39 Hz,垂直坡向谱比峰值对应的频率稍高,为5.42~5.96 Hz。通过结合黏弹性边界的时域动力有限元方法分析斜坡地形在垂直入射地震动作用下的响应,数值模拟结果表明,斜坡坡顶处的位移放大作用显著,坡脚处放大作用较小;介质剪切波速对斜坡地震动的影响较明显,尤其是坡顶点处不同介质剪切波速模型位移峰值差异较大。由于斜坡地形复杂的散射效应,在斜坡及附近测点均出现明显的转换面波,坡顶点处波形转换最显著。数值模拟结果进一步验证了龙头山集镇依坡而建的房屋建筑破坏严重是由局部地形地震动放大效应与地震动差动共同作用引起的。Abstract: Taking the slope topography of Longtoushan market town, which was seriously damaged in the MS6.5 earthquake in Ludian, Yunnan Province, as an example, through the analysis of ground pulsation test, it is found that the peak spectral ratio of the slope and the measuring point at the slope top relative to the reference point at the slope toe is > 1, the peak spectral ratio in the slope direction is greater than that in the vertical slope direction, and the peak spectral ratio gradually increases from the slope toe to the slope top, and the peak spectral ratio at the slope top is about 3; The frequency corresponding to the peak value of the slope direction spectrum is 4.57 ~ 5.39 Hz, and the frequency corresponding to the peak value of the vertical slope direction spectrum is slightly higher, 5.42 ~ 5.96 Hz. The time domain dynamic finite element method combined with viscoelastic boundary is used to analyze the response of slope terrain under vertical incident ground motion. The numerical simulation results show that the displacement amplification at the top of slope is significant, and the amplification at the foot of slope is small; The influence of medium shear wave velocity on the ground motion of slope is obvious, especially the displacement peak value of different medium shear wave velocity models at the top of slope is different. Due to the complex scattering effect of the slope topography, there are obvious converted surface waves at the slope and nearby observation points, and the waveform conversion at the top of the slope is the most significant. The numerical simulation results further verify that the serious damage of the buildings built along the slope in Longtoushan market town is caused by the combined effect of local terrain ground motion amplification and seismic differential.
-
Key words:
- Slope topography /
- Surface wave /
- Shear wave velocity /
- Scattering effect /
- Seismic response /
- Finite element analysis
-
表 1 斜坡测点及坡顶测点相对于坡脚测点地脉动谱比
Table 1. Spectral ratio results of measuring points relative to slope
测点编号 方向 谱比卓越频率/Hz 谱比峰值 P2 垂直坡向 5.96 1.01 顺坡向 4.57 1.03 P3 垂直坡向 5.79 1.04 顺坡向 4.85 1.33 P4 垂直坡向 5.66 1.20 顺坡向 5.36 1.83 P5 垂直坡向 5.81 1.76 顺坡向 4.89 2.33 P6 垂直坡向 5.42 2.83 顺坡向 5.39 3.01 -
邓鹏, 2020. 单体边坡地形的地震动力响应及其放大效应的数值分析. 地震学报, 42(3): 349—361 doi: 10.11939/jass.20190133Deng P. , 2020. Numerical parametric study of seismic dynamic response and amplification effects of slope topography. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 42(3): 349—361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11939/jass.20190133 丁海平, 于彦彦, 郑志法, 2017. P波斜入射陡坎地形对地面运动的影响. 岩土力学, 38(6): 1716—1724, 1732Ding H. P. , Yu Y. Y. , Zheng Z. F. , 2017. Effects of scarp topography on seismic ground motion under inclined P waves. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 38(6): 1716—1724, 1732. (in Chinese) 顾亮, 丁海平, 于彦彦, 2017. SV波斜入射陡坎地形对地面运动的影响. 自然灾害学报, 26(4): 39—47Gu L. , Ding H. P. , Yu Y. Y. , 2017. Effects of scarp topography on seismic ground motion under inclined SV waves. Journal of Natural Disasters, 26(4): 39—47. (in Chinese) 郝明辉, 张郁山, 2014. 凸起地形对地震动特性的影响. 地震学报, 36(5): 883—894Hao M. H. , Zhang Y. S. , 2014. Analysis of terrain effect on the properties of ground motion. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 36(5): 883—894. (in Chinese) 郝明辉, 张郁山, 赵凤新, 2021. 坡地地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 震灾防御技术, 16(2): 229—236 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210201Hao M. H. , Zhang Y. S. , Zhao F. X. , 2021. Analysis of slope terrain effect on the properties of ground motion. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(2): 229—236. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210201 廖振鹏, 杨柏坡, 袁一凡, 1981. 三维地形对地震地面运动的影响. 地震工程与工程振动, 1(1): 56—77 doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.1981.01.007Liao Z. P. , Yang B. P. , Yuan Y. F. , 1981. Effects of three-dimensional topography on earthquake ground motion. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 1(1): 56—77. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.1981.01.007 廖振鹏, 1984. 近场波动问题的有限元解法. 地震工程与工程振动, 4(2): 1—14 doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.1984.02.005Liao Z. P. , 1984. A finite element method for near-field wave motion in heterogeneous materials. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 4(2): 1—14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.1984.02.005 刘必灯, 周正华, 刘培玄等, 2011. SV波入射情况下V型河谷地形对地震动的影响分析. 地震工程与工程振动, 31(2): 17—24Liu B. D. , Zhou Z. H. , Liu P. X. , et al. , 2011. Influence of V-shaped canyon site on ground motions for incident SV waves. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 31(2): 17—24. (in Chinese) 刘晶波, 宝鑫, 谭辉等, 2020. 土-结构动力相互作用分析中基于内部子结构的地震波动输入方法. 土木工程学报, 53(8): 87—96Liu J. B. , Bao X. , Tan H. , et al. , 2020. Seismic wave input method for soil-structure dynamic interaction analysis based on internal substructure. China Civil Engineering Journal, 53(8): 87—96. (in Chinese) 唐为民, 马淑芝, 刘小浪等, 2019. 地形地貌条件对边坡动力响应规律的影响. 长江科学院院报, 36(11): 98—103, 109 doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20180443Tang W. M. , Ma S. Z. , Liu X. L. , et al. , 2019. Influence of topographic and geomorphic conditions on the dynamic response of slope acceleration. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 36(11): 98—103, 109. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20180443 万子轩, 梁春涛, 罗永红, 2020. 斜坡地形效应模拟研究. 防灾科技学院学报, 22(1): 1—9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2020.01.001Wan Z. X. , Liang C. T. , Luo Y. H. , 2020. Numerical simulation study on slope topographic effects. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 22(1): 1—9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2020.01.001 王荐霖, 王运生, 辛聪聪, 2018. 九寨沟MS4.5级地震斜坡体及覆盖层的动响应分析. 中国科技论文, 13(21): 2401—2407 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2018.21.001Wang J. L. , Wang Y. S. , Xin C. C. , 2018. Analysis of slope and overburden seismic response during the Jiuzhaigou MS4.5 earthquake. China Sciencepaper, 13(21): 2401—2407. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2018.21.001 夏坤, 董林, 李璐, 2019. 黄土斜坡动力响应特征分析. 地震工程学报, 41(3): 694—701 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.03.694Xia K. , Dong L. , Li L. , 2019. Dynamic response characteristics of loess slopes. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 41(3): 694—701. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.03.694 张迎宾, 柳静, 唐云波等, 2021. 考虑边坡地形效应的地震动力响应分析. 地震工程学报, 43(1): 142—153Zhang Y. B. , Liu J. , Tang Y. B. , et al. , 2021. Dynamic response analysis of seismic slopes considering topographic effect. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 43(1): 142—153. (in Chinese) Ashford S. A. , Sitar N. , 1997. Analysis of topographic amplification of inclined shear waves in a steep coastal bluff. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 87(3): 692—700. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0870030692 Jeong S. , Asimaki D. , Dafni J. , et al. , 2019. How topography-dependent are topographic effects? Complementary numerical modeling of centrifuge experiments. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 116: 654—667. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.10.028 Kagami H. , Okada S. , Shiono K. , et al. , 1986. Observation of 1- to 5-second microtremors and their application to earthquake engineering. Part III. A two-dimensional study of Site effects in the San Fernando Valley. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 76(6): 1801—1812. Shabani M. J. , Shamsi M. , Ghanbari A. , 2021. Slope topography effect on the seismic response of mid-rise buildings considering topography-soil-structure interaction. Earthquakes and Structures, 20(2): 187—200. Zhang Y. B. , Chen G. Q. , Zheng L. , et al. , 2013. Effects of geometries on three-dimensional slope stability. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 50(3): 233—249. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0279 -




 下载:
下载: