Research on Seismic Performance of Multi-drum Ancient Columns Based on Particle Dampers
-
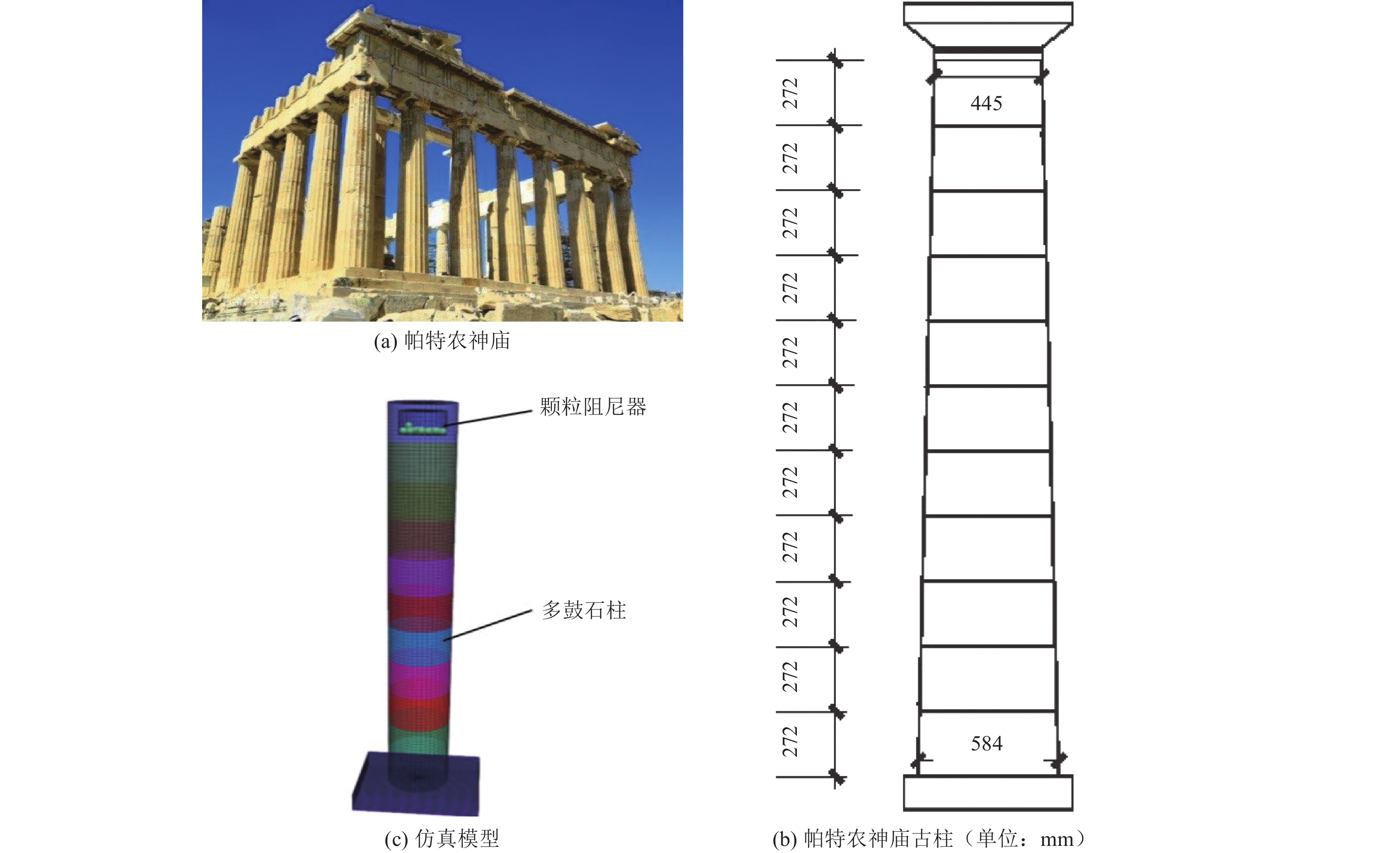
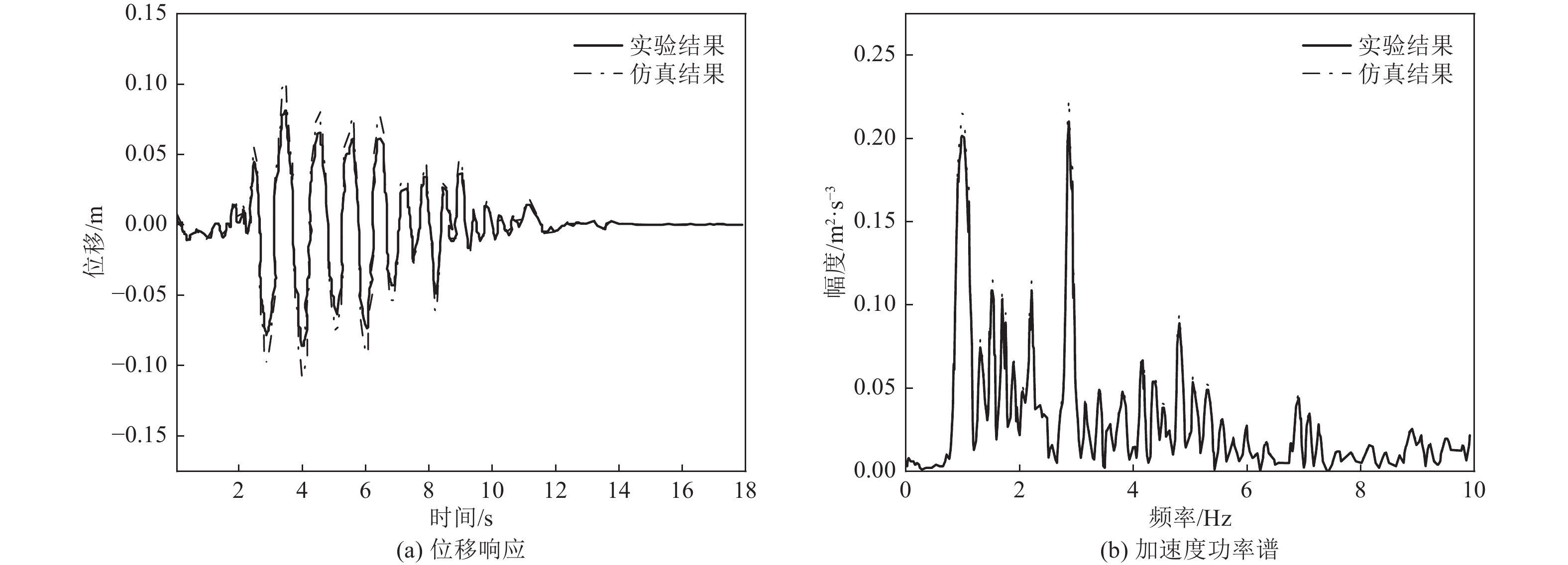
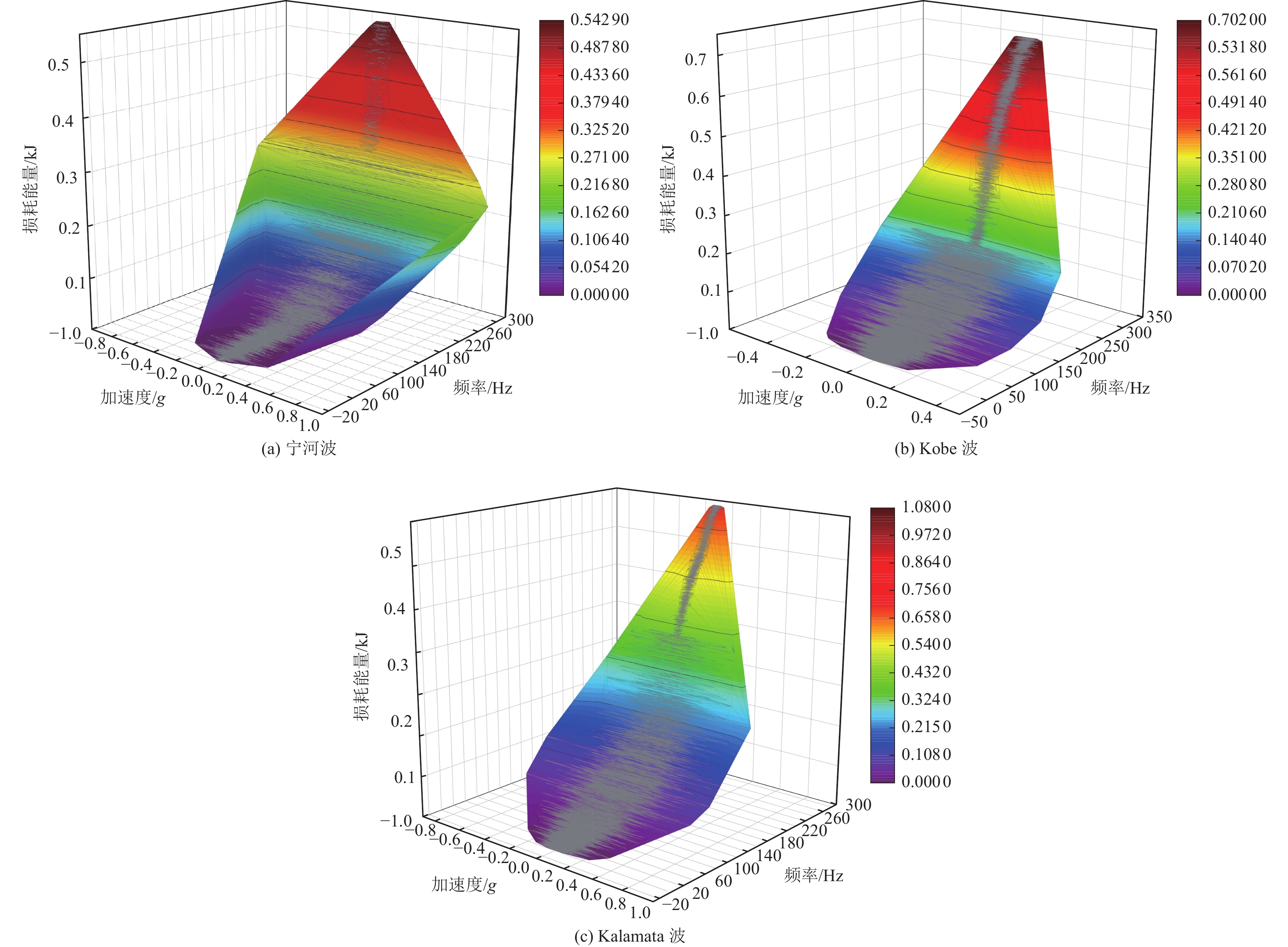
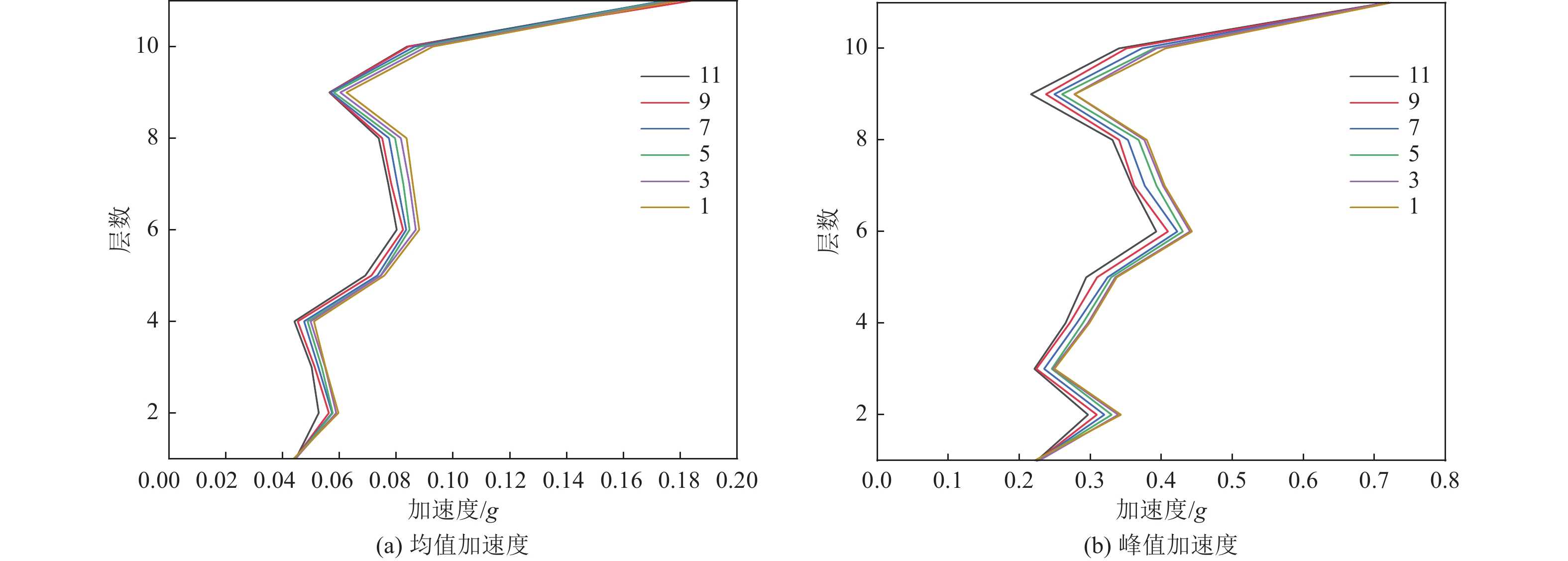
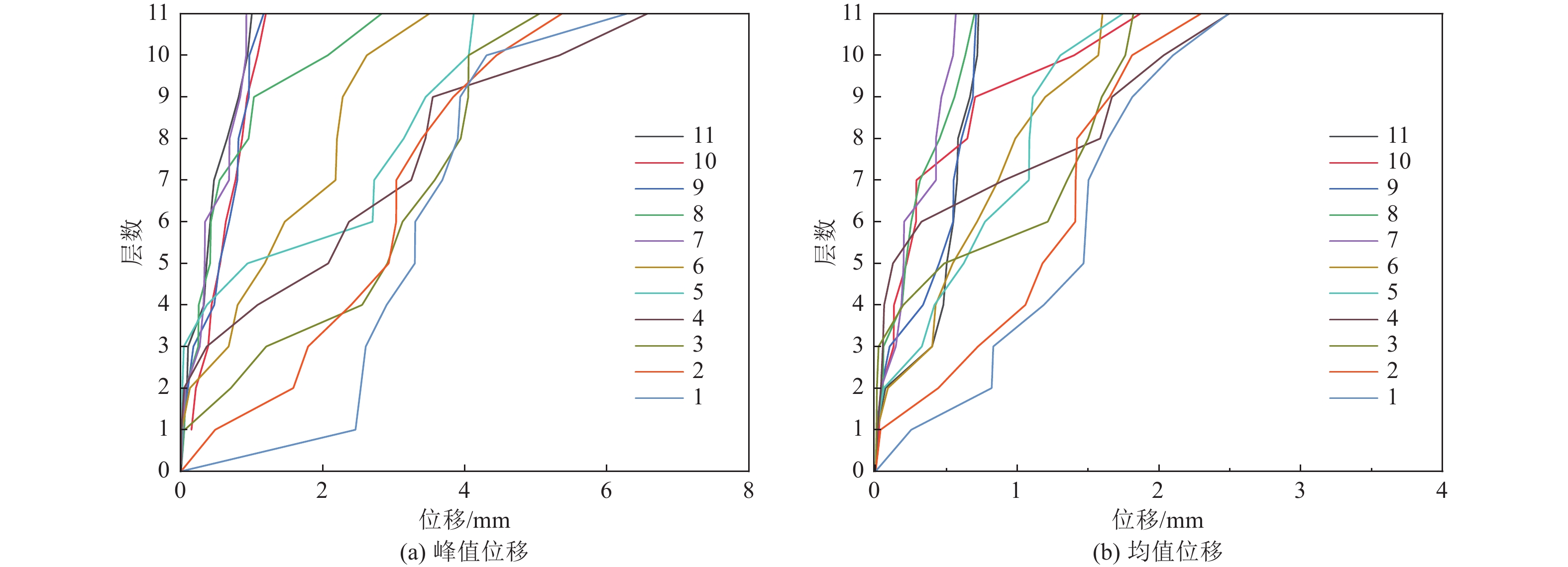
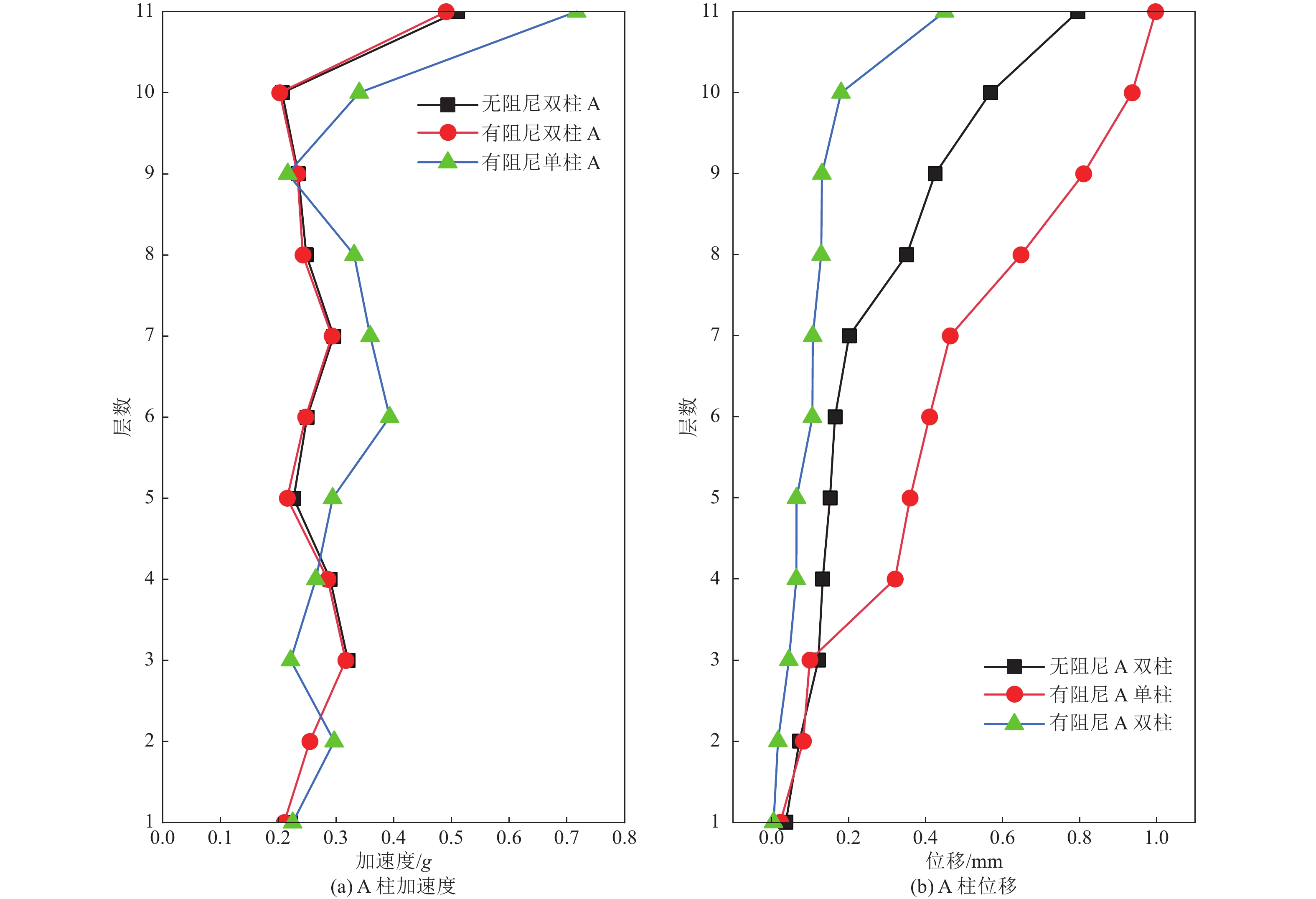
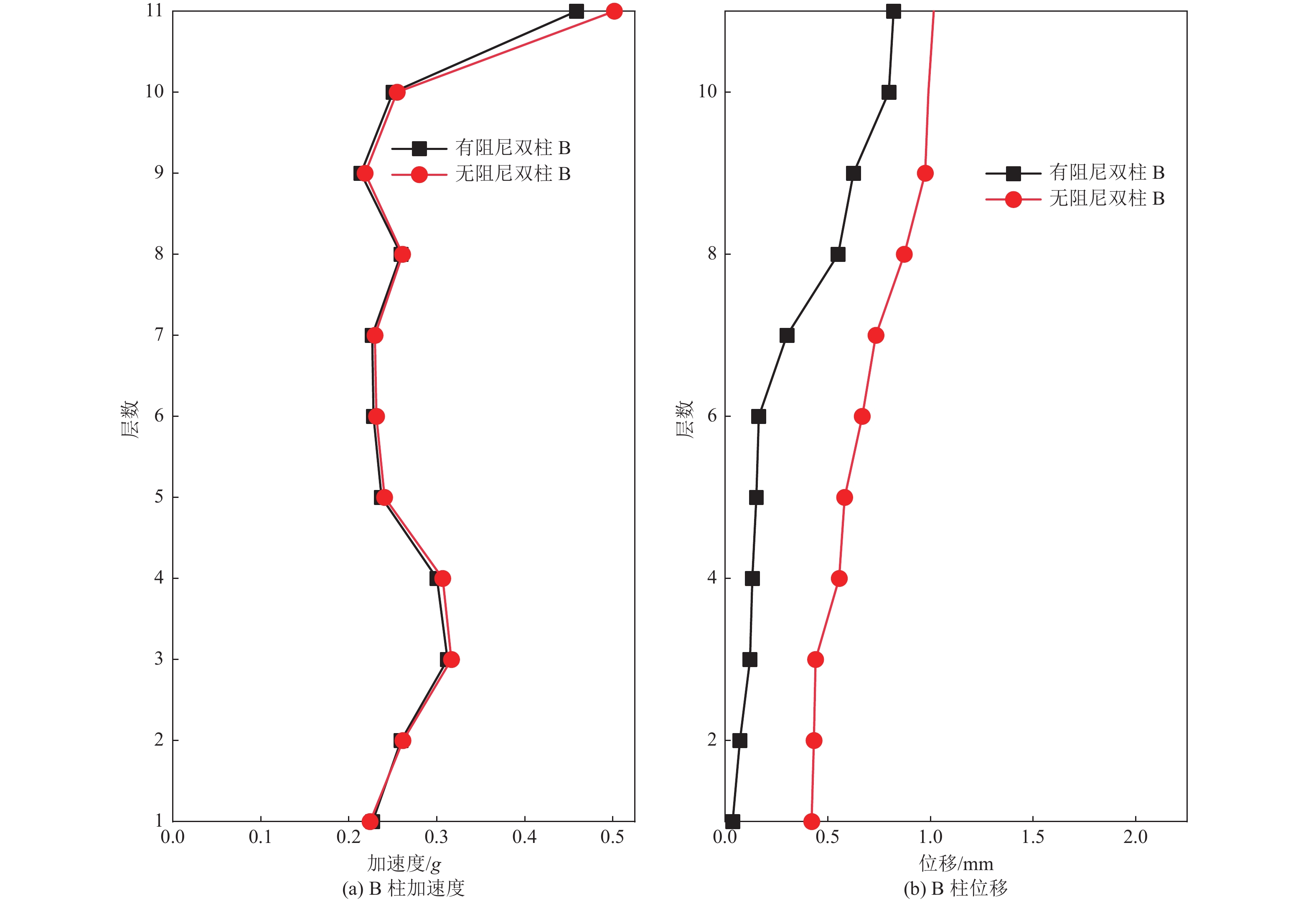
摘要: 为保护地震作用下历史遗迹帕特农神庙多鼓石柱,提出将破损的石鼓替换为填充颗粒的空鼓,以减轻多鼓石柱动力响应。本文基于PFC3D与FLAC3D软件,实现了离散-有限耦合作用,模拟了附有颗粒阻尼器帕特农神庙多鼓型石柱,研究了颗粒阻尼器对帕特农神庙石柱的减震效果,并分析地震强度、频率、阻尼器位置等因素对减震效果的影响。研究结果表明,将颗粒阻尼器替换破损的空鼓,PFC3D与FLAC3D耦合计算结果与试验结果基本一致,减震效果显著,说明耦合分析方法研究颗粒阻尼器抗震性能具有较高的可靠性;地震强度不同时,分层颗粒阻尼器仍可较好地耗散能量;颗粒阻尼器对结构的减震性能受激励频率的影响显著,频率越高,减震效果越好;颗粒阻尼器布置在古柱中上部减震效果优于布置在古柱下部。Abstract: In order to protect the multi drum stone column of Parthenon temple under earthquake, it is proposed to replace the damaged stone drum with an empty drum filled with particles to reduce the dynamic response of the multi drum stone column. Based on PFC3D and FLAC3D platforms, this paper realizes the discrete finite joint action, simulates the multi drum stone column of Parthenon temple with particle damper, explores the damping effect of particle damper on the stone column of Parthenon temple, and studies the factors affecting the damping effect of particle damper, such as seismic intensity, frequency, damper position and so on. The results show that the coupling results of PFC3D and FLAC3D are basically consistent with the experimental results, and the damping effect is remarkable, which shows that the coupling analysis method has high reliability in studying the seismic performance of particle damper; When the earthquake intensity is different, the layered particle damper can still dissipate energy better; The damping performance of particle damper is significantly affected by the excitation frequency. The higher the frequency, the better the damping effect; The damping effect of the damper arranged at the upper end of the ancient column is better than that arranged at the lower part of the ancient column. The results of the study are of reference to the earthquake-resistant protection of similar stone-type ancient buildings in China.
-
Key words:
- Historic buildings /
- Multi drum stone column /
- Particle damper /
- Damping control /
- Seismic performance
-
表 1 不同地震强度下结构顶鼓加速度和位移响应
Table 1. Acceleration and displacement response of the structure with different earthquake intensity
地震波
类型加速度
幅值/g阻尼器
位置加速度
峰值/$ \mathit{g} $加速度
均方根/$ \mathit{g} $位移峰值/
mm位移均
方根/mm无阻尼器
加速度均方根/$ \mathit{g} $无阻尼器位移
均方根/mm加速度均方根
减震率/%位移均方根
减震率/%Kalamata1986 0.245 顶鼓 1.044 49 0.212 76 13.526 0 1.926 0.264 42 2.889 0 13.9 33.3 0.200 顶鼓 0.694 80 0.100 40 7.717 2 1.718 0.166 30 2.583 9 39.6 31.0 0.100 顶鼓 0.458 66 0.084 55 5.885 0 0.942 0.114 54 1.318 8 26.2 28.5 0.050 顶鼓 0.250 91 0.047 46 3.451 0 0.093 0.064 07 0.126 2 25.9 25.8 表 2 不同激励频率下结构顶鼓加速度和位移响应
Table 2. Acceleration and displacement responses of the structure with different excitation frequencies
地震波
类型加速度
幅值/g阻尼器
位置加速度
峰值/$ \mathit{g} $加速度
均方根/$ \mathit{g} $位移峰值/
mm位移均
方根/mm无阻尼器加速度
均方根/$ \mathit{g} $无阻尼器位移
均方根/mm加速度均方根
减震率/%位移均方根
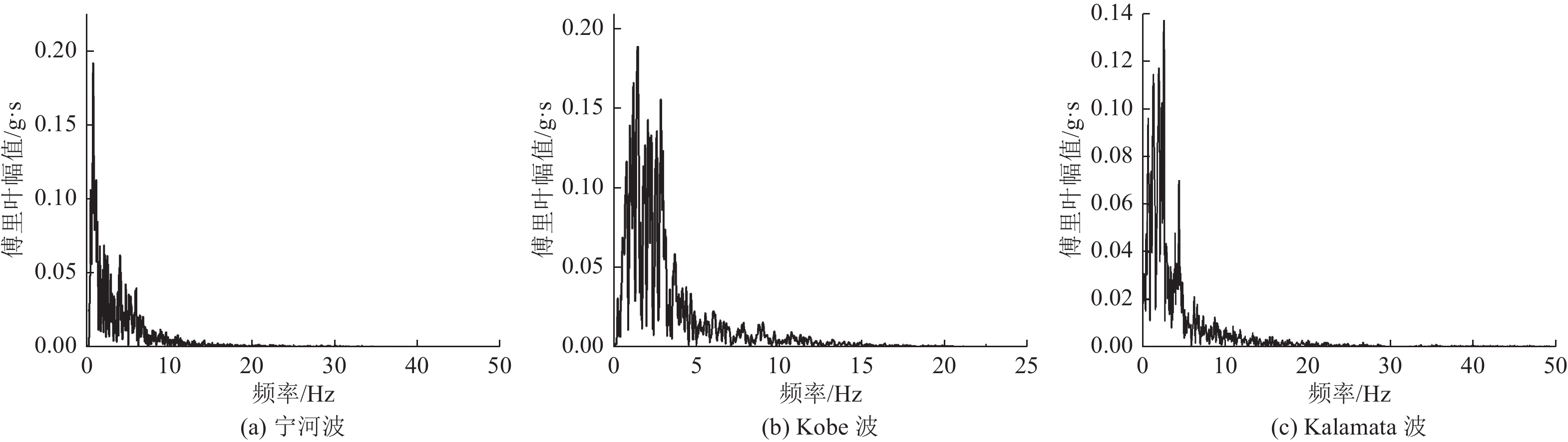
减震率/%宁河波 0.2 顶鼓 0.589 5 0.089 9 7.100 8 1.621 0 0.119 3 2.133 0 24.6 24.0 Kobe波 0.2 顶鼓 0.621 3 0.094 6 7.487 8 1.513 7 0.146 8 2.300 8 35.5 34.2 Kalamata波 0.2 顶鼓 0.694 8 0.100 4 7.717 2 1.718 2 0.166 3 2.583 9 39.6 31.0 -
[1] 贾晗曦, 林均岐, 刘金龙, 2019. 建筑结构地震易损性分析研究综述. 震灾防御技术, 14(1): 42—51 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190105Jia H. X. , Lin J. Q. , Liu J. L. , 2019. Review of seismic fragility analysis of building structure. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(1): 42—51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190105 [2] 鲁正, 吕西林, 闫维明, 2012. 颗粒阻尼器减震控制的试验研究. 土木工程学报, 45(S1): 243—247Lu Z. , Lü X. L. , Yan W. M. , 2012. Experimental investigation into the vibration control effects of particle dampers. China Civil Engineering Journal, 45(S1): 243—247. (in Chinese) [3] 鲁正, 吕西林, 闫维明, 2013. 颗粒阻尼技术研究综述. 振动与冲击, 32(7): 1—7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.07.001Lu Z. , Lü X. L. , Yan W. M. , 2013. A survey of particle damping technology. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 32(7): 1—7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.07.001 [4] 鲁正, 王佃超, 吕西林, 2014. 调谐质量阻尼器与颗粒阻尼器对比试验研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 34(S1): 738—742Lu Z. , Wang D. C. , Lü X. L. , 2014. Comparative experimental study of particle damper and tuned mass damper. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 34(S1): 738—742. (in Chinese) [5] 施卫星, 李晓玮, 鲁正, 2013. 具有不同表面特性的物体碰撞全过程分析. 地震工程与工程振动, 33(2): 110—116Shi W. X. , Li X. W. , Lu Z. , 2013. Study on the whole process of the collision between concerning objects with different surface characters. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 33(2): 110—116. (in Chinese) [6] 张奎, 闫维明, 王瑾等, 2017. 简谐波作用下颗粒阻尼器性能试验研究. 工业建筑, 47(9): 75—80Zhang K. , Yan W. M. , Wang J. , et al. , 2017. Experimental research on the performance of particle dampers under harmonic excitation. Industrial Construction, 47(9): 75—80. (in Chinese) [7] Fang J. L. , Wang X. P. , Chen T. N. , et al. , 2018. Research on the energy dissipation mechanism of nonobstructive particle dampers based on the dense granular flow theory. Journal of Vibration and Control, 24(4): 682—693. doi: 10.1177/1077546316649533 [8] Hu L. , Huang Q. B. , Liu Z. X. , 2008. A non-obstructive particle damping model of DEM. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 4(1): 45—51. doi: 10.1007/s10999-007-9053-z [9] Luo Z. Y. , Yan W. M. , Xu W. B. , et al. , 2019. Experimental research on the multilayer compartmental particle damper and its application methods on long-period bridge structures. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 13(4): 751—766. doi: 10.1007/s11709-018-0509-z [10] Papalou A. , Strepelias E. , Roubien D. , et al. , 2015. Seismic protection of monuments using particle dampers in multi-drum columns. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 77: 360—368. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.06.004 [11] Veeramuthuvel P., Shankar K., Sairajan K. K., 2016. Experimental investigation of particle damper-based vibration suppression in printed circuit board for spacecraft applications. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 230(7): 1299—1311. -



 下载:
下载: