Evidence of Late Pleistocene Activity and Seismic Risk Significance of Chengnan Fault in Binbei Area
-
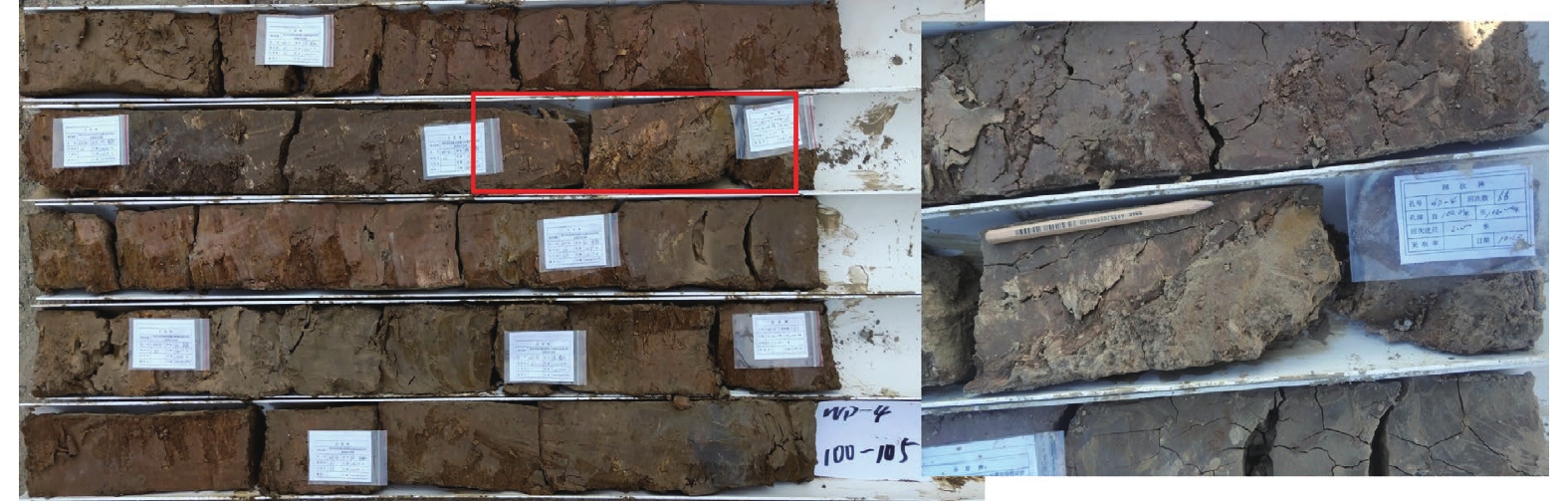
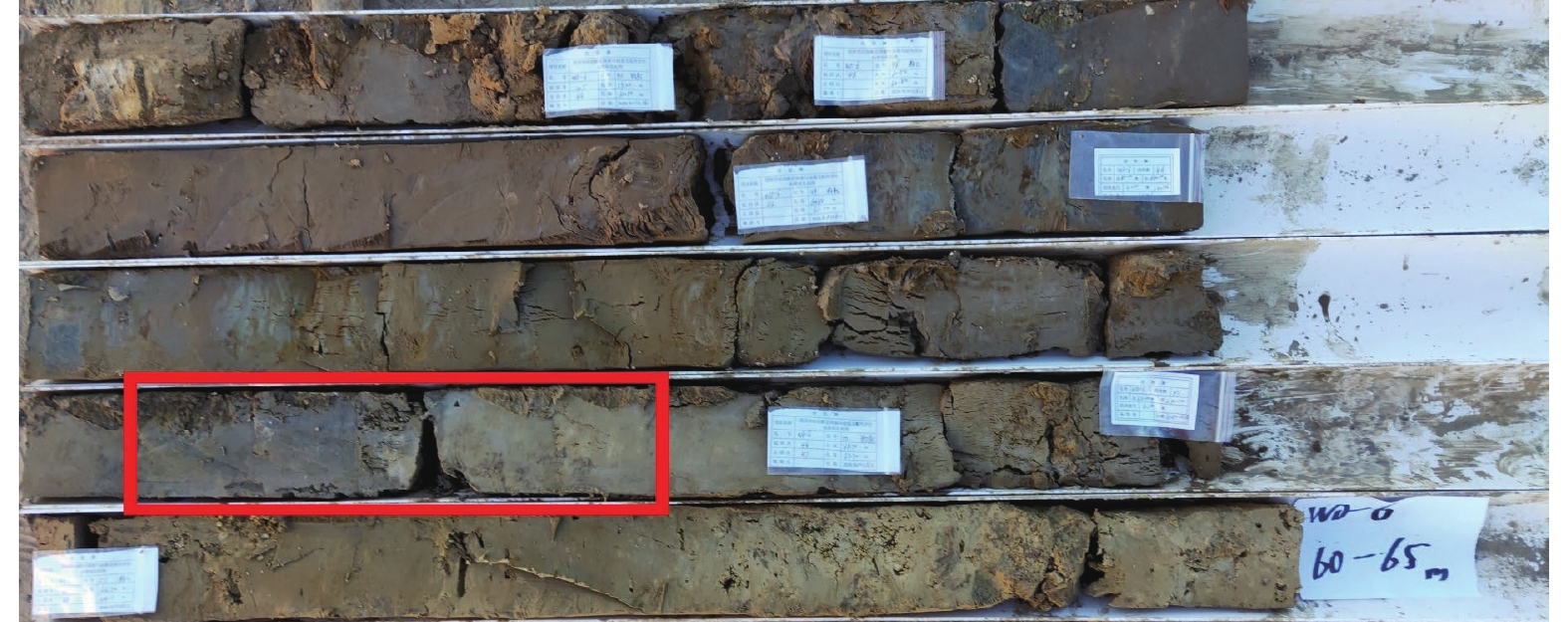
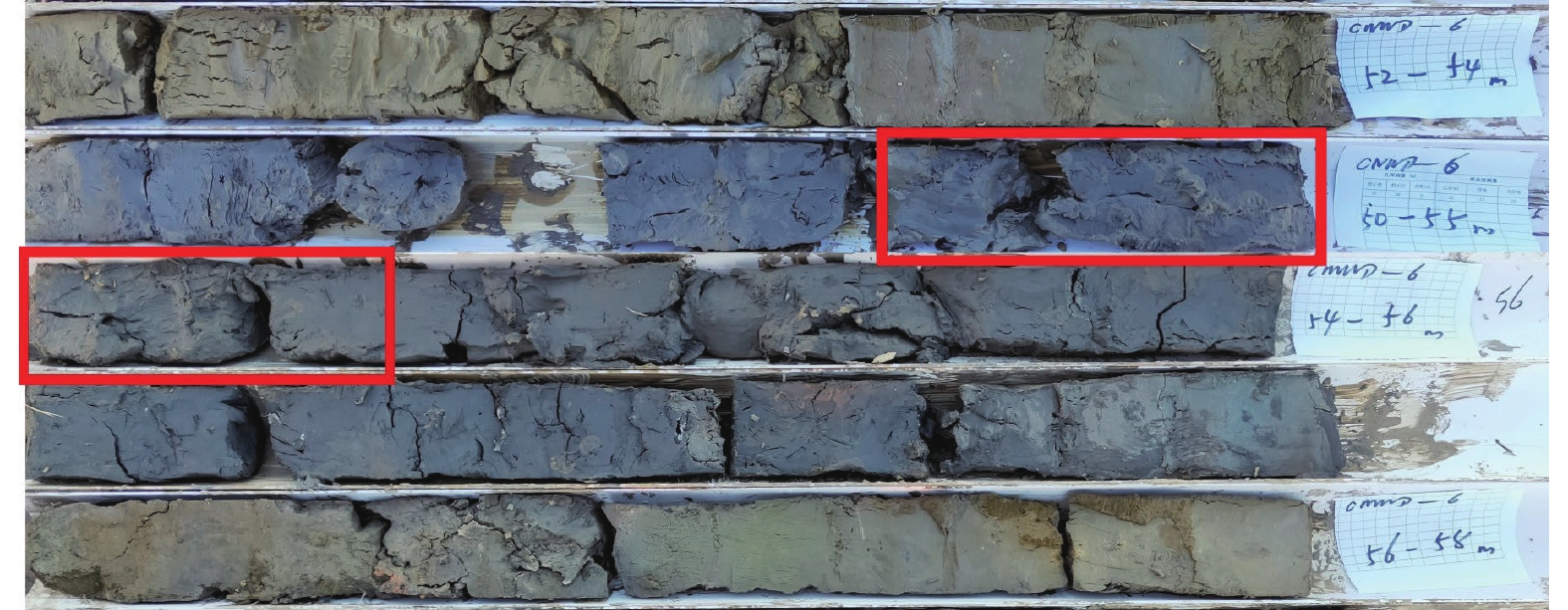
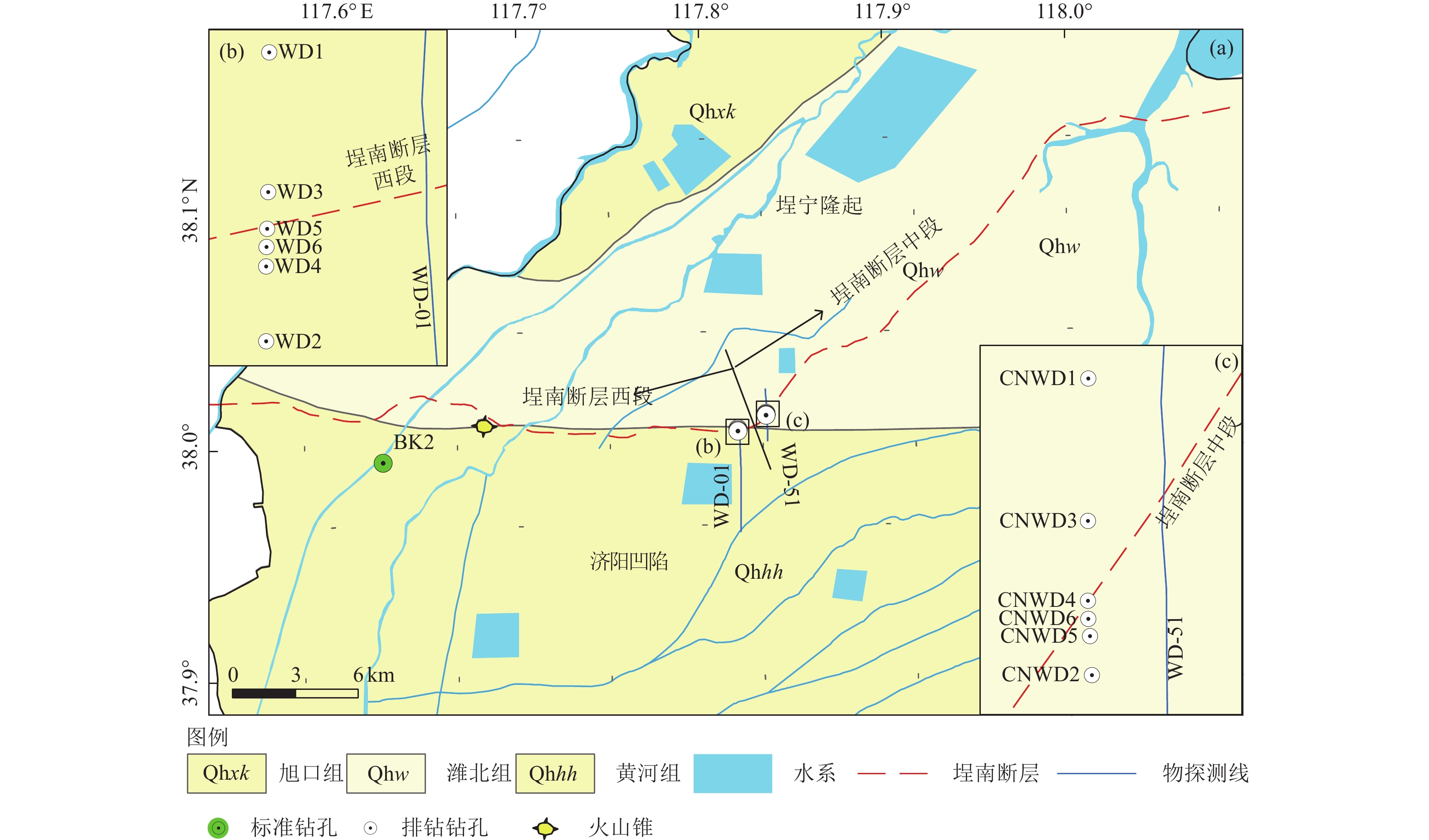
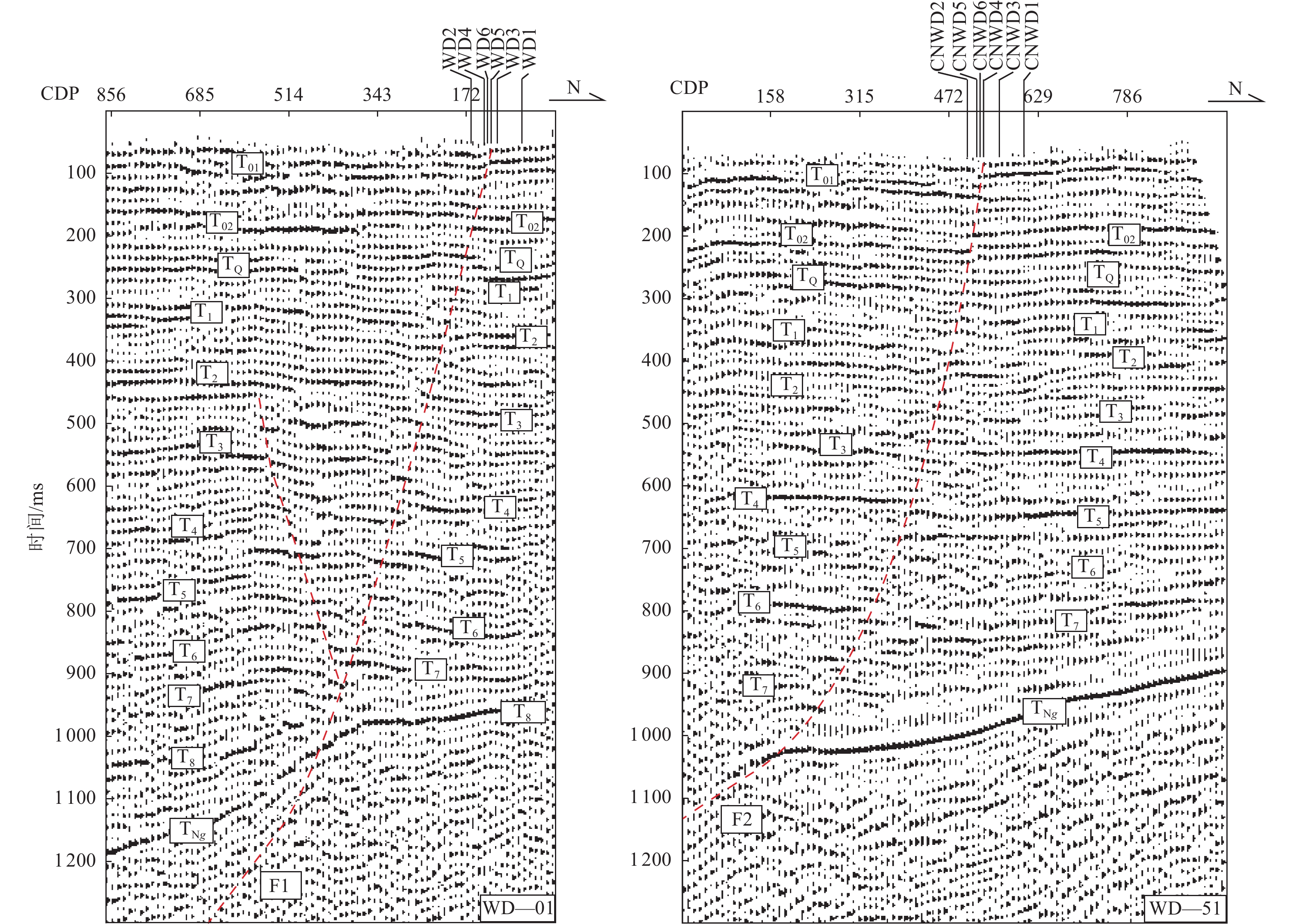
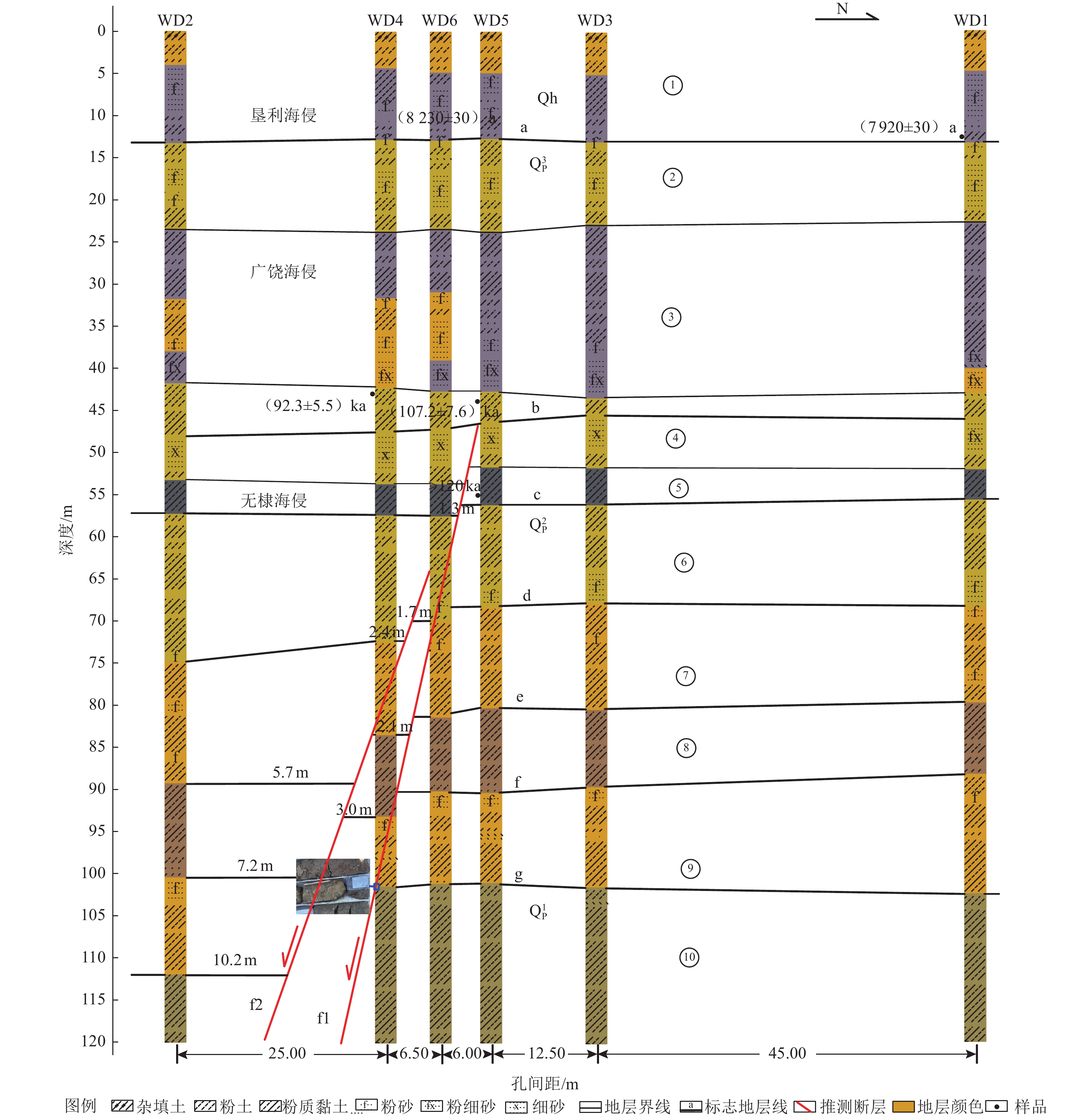
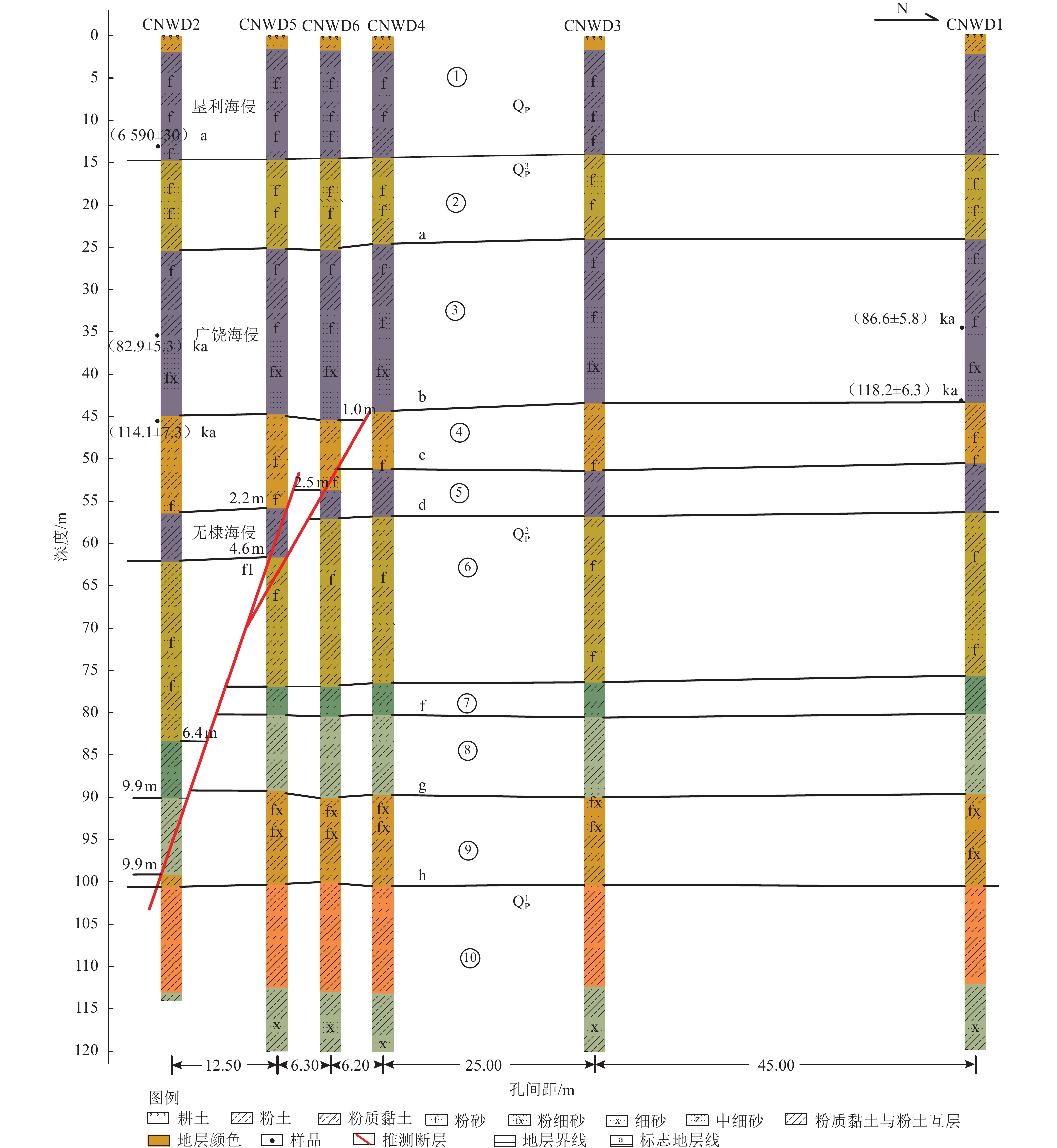
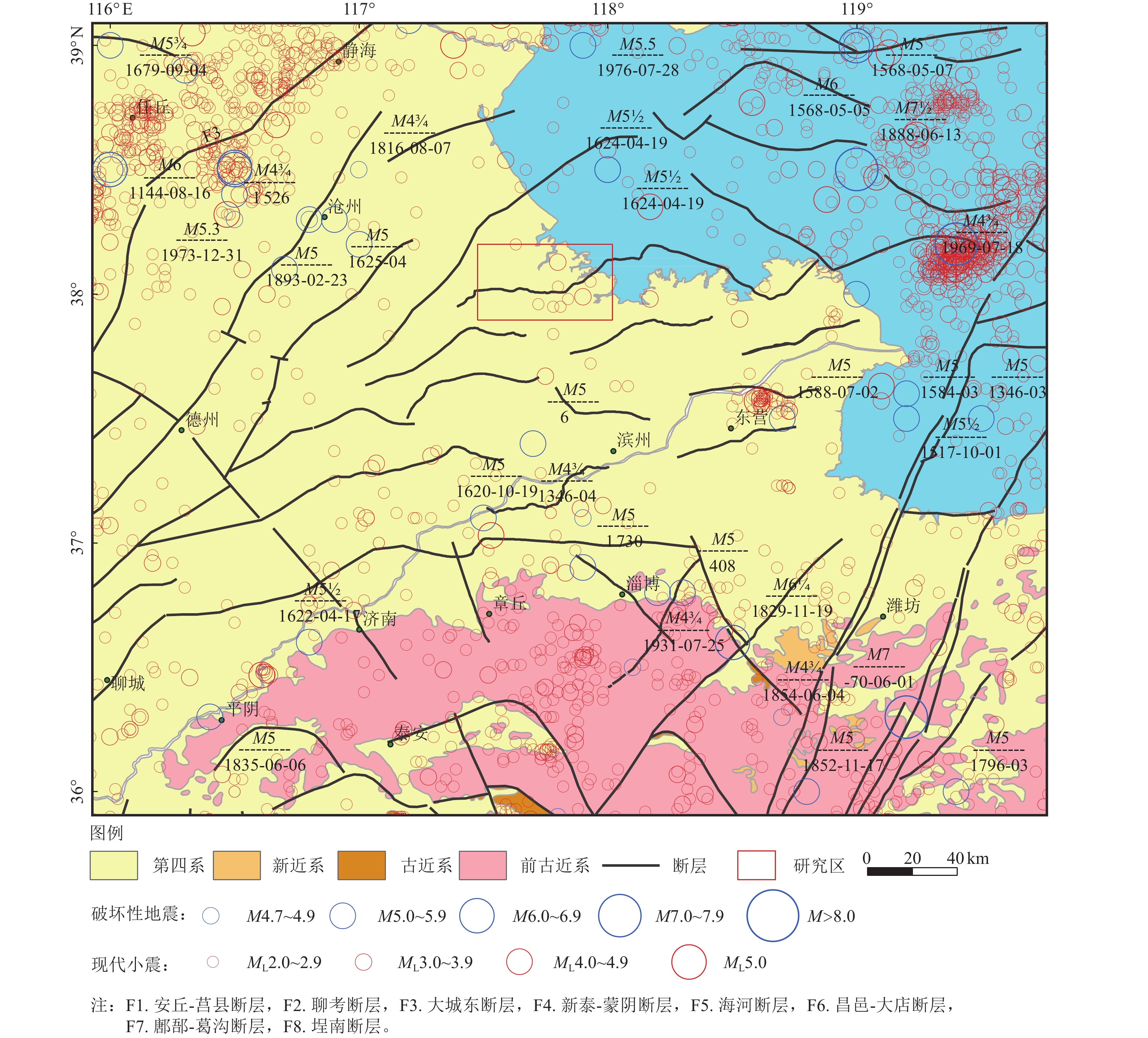
摘要: 埕南断层是埕宁隆起与济阳凹陷的边界断层,也是滨北地区1条规模最大的重要断层,采用浅层地震勘探和钻孔联合剖面探测相结合的方法,确定了埕南断层准确位置,探明了断层的产状,揭露了上断点深度。钻探结果显示,埕南断层为正断特征,倾向南或南东,倾角70°~80°,断层上断点埋深44.3~46.4 m,断距1.0~1.3 m。通过年代学测试确定了错断地层的年代,获得埕南断层错断晚更新世地层的证据,埕南断层晚更新世活动证据的发现对滨北地区地震危险性再认识具有重要意义和价值。Abstract: Chengnan fault is the boundary fault between chengning uplift and Jiyang depression, and it is also an important fault with the largest scale in Binbei area. Combining with the shallow seismic exploration and composite drilling section exploration, the accurate location of Chengnan fault is determined, The occurrence of the fault is proved and the depth of the upper breakpoint is revealed. The drilling results show that Chengnan fault is characterized by normal fault, dipping South or southeast, with an inclination of about 70 °~80 °. The buried depth of the breakpoint on the fault is 44.3~46.4 m, and the vertical displacement is 0.8~1.2 m. The age of the faulted strata is determined through chronological test, and the evidence of the faulted late Pleistocene strata of Chengnan fault is obtained. The discovery of the evidence of the late Pleistocene activity of Chengnan fault is of great significance and value to the re understanding of the seismic risk in Binbei area.e seismic risk in Binbei area.
-
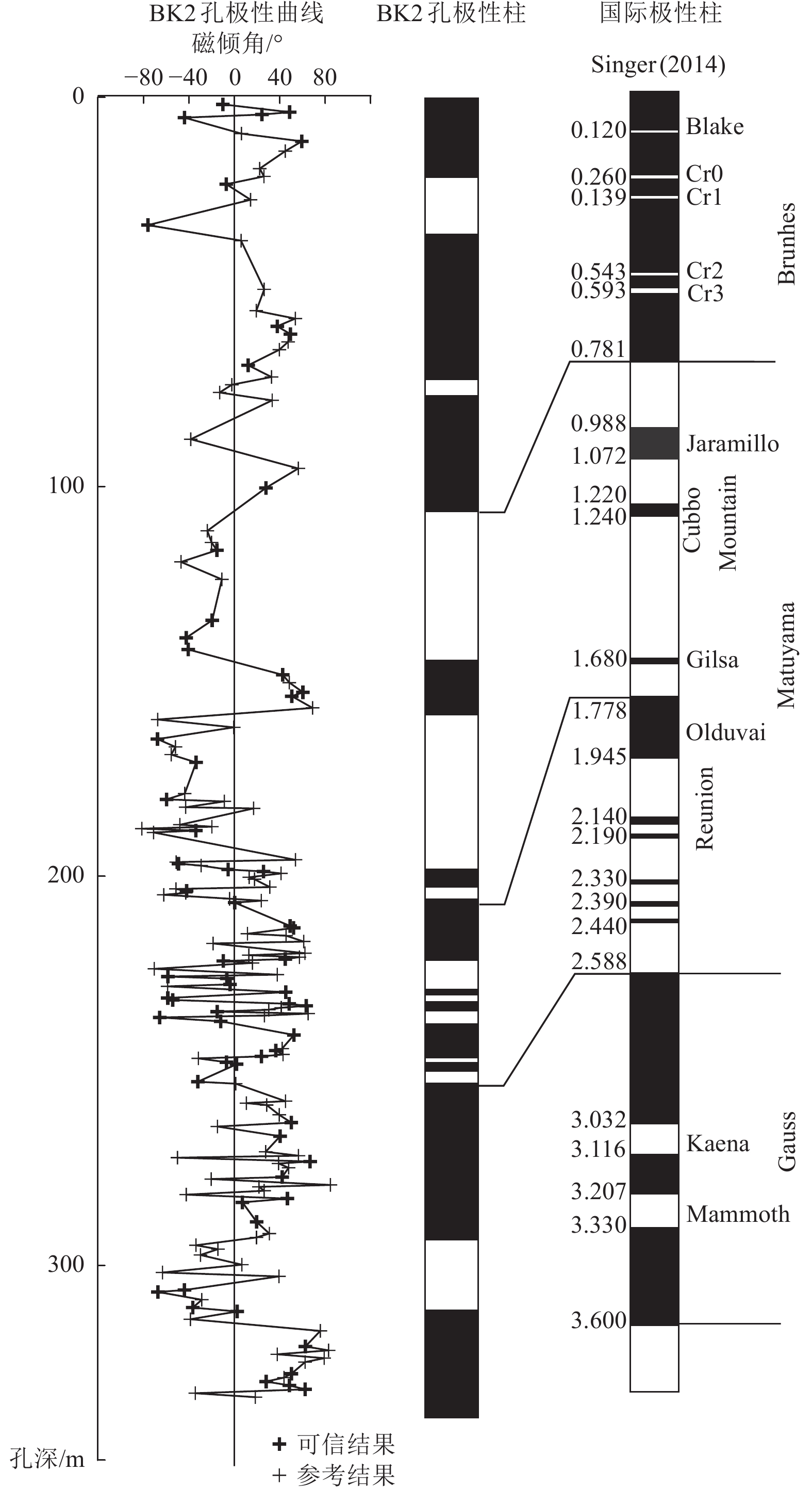
表 1 BK2孔样品光释光年龄及参数
Table 1. Photoluminescence age and parameters of samples in hole BK2
样品编号 样品岩性 样品埋深/m 环境剂量率/Gy·ka−1 等效剂量/Gy 释光年龄/ka BK2-1 粉质黏土 3.2 2.7±0.3 11.2±0.8 4.2±0.3 BK2-2 粉土 8.0 2.7±0.3 27.4±4.8 10.0±1.8 BK2-4 粉砂 15.0 2.5±0.3 30.3±3.0 12.1±1.2 BK2-5 黏土 18.4 2.5±0.3 112.4±12.4 44.8±4.9 BK2-6 粉土 22.7 2.4±0.2 122.4±16.4 50.8±6.8 BK2-8 粉质黏土 32.0 2.4±0.2 131.4±9.8 54.8±4.1 BK2-9 粉质黏土 36.0 2.8±0.2 231.4±17.4 82.6±6.2 BK2-11 粉砂 44.0 2.4±0.2 199.1±12.6 82.9±5.3 BK2-C4 粉土 56.5 2.4±0.2 279.1±14.1 116.2±5.9 BK2-14 粉质黏土 57.0 2.5±0.3 299.1±16.5 118.2±6.6 表 2 BK2孔第四系厚度划分
Table 2. Quaternary thickness division of hole BK2
系 统 阶 厚度/m 特征 第
四
系
Q全新统Qh / 14.4 上部为黄褐色粉土、粉质黏土互层,下部棕褐色、灰褐色粉土、粉质黏土互层。以灰褐色调与下伏的褐黄色粉砂相区别。 更新统QP 萨拉乌苏阶${\rm{Q}}_{\rm{p}}^3 $ 37.6 顶部为褐黄色、棕黄色粉砂、粉质黏土、粉土,含钙质结核、铁锰结核,中部为厚层黄褐色粉砂、粉土,底部为黄褐色粉质黏土。 周口店阶${\rm{Q}}_{\rm{p}}^2 $ 54.2 多个完整或不完整的黄褐色黏土-粉质黏土-粉土-粉砂-中细砂沉积韵律。底部以较深色调的黄褐色粉砂与下伏的浅色调粉质黏土相区分。 泥河湾阶${\rm{Q}}_{\rm{p}}^1 $ 137.8 薄层或中薄层的黄褐色、褐黄色粉质黏土、粉土、粉砂沉积旋回,夹厚层的黏土、粉砂层,底部剪影的褐黄色黏土,含较多铁锰氧化物,钙质结核直径可达4 cm。 -
[1] 蔡雄飞, 廖计华, 蔡海磊等, 2007. 第四系冲、洪积物的识别标志和研究意义. 海洋地质动态, 23(1): 10—12, 16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.01.003Cai X. F. , Liao J. H. , Cai H. L. , et al. , 2007. Identification mark and research significance of Quaternary alluvium and proluvium. Marine Geology Letters, 23(1): 10—12, 16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.01.003 [2] 曹筠, 冉勇康, 许汉刚等, 2015. 宿迁城市活动断层探测多方法技术运用的典型案例. 地震地质, 37(2): 430—439 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.007Cao J. , Ran Y. K. , Xu H. G. , et al. , 2015. Typical case analysis on application of multi-method detection technique to active fault exploration in Suqian city. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 430—439. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.007 [3] 柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测——以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地震地质, 28(4): 536—546 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002Chai C. Z. , Meng G. K. , Du P. , et al. , 2006. Comprehensive multi-level exploration of buried active fault: an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 28(4): 536—546. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002 [4] 邓起东, 2002. 城市活动断裂探测和地震危险性评价问题. 地震地质, 24(4): 601—605 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.015Deng Q. D. , 2002. Exploration and seismic hazard assessment of active faults in urban areas. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 601—605. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.015 [5] 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2003. 城市活动断裂探测的方法和技术. 地学前缘, 10(1): 93—104 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012Deng Q. D. , Xu X. W. , Zhang X. K. , et al. , 2003. Methods and techniques for surveying and prospecting active faults in urban areas. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 93—104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012 [6] 杜彦男, 吴孔友, 刘寅等, 2020. 断陷盆地边界断裂结构特征及物性差异定量评价——以车镇凹陷埕南断裂为例. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 56(3): 405—417Du Y. N. , Wu K. Y. , Liu Y. , et al. , 2020. The development of fault zone architecture of deep buried boundary faults in the rift basin: a case from the Chengnan Fault of the Chezhen depression. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 56(3): 405—417. (in Chinese) [7] 方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金等, 2002. 探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法. 地震地质, 24(4): 606—613 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016Fang S. M. , Zhang X. K. , Liu B. J. , et al. , 2002. Geophysical methods for the exploration of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 606—613. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016 [8] 何付兵, 徐锡伟, 郑桂森等, 2018. 探索第四纪钻探岩心沉积物颜色测量新方法. 地震地质, 40(4): 920—934 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.04.014He F. B. , Xu X. W. , Zheng G. S. , et al. , 2018. A new method for color measurement of Quaternary drilling core deposits. Seismology and Geology, 40(4): 920—934. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.04.014 [9] 花鑫升, 石金虎, 谭雅丽等, 2018. 浅层地震勘探资料揭示汤东断裂特征. 震灾防御技术, 13(2): 276—283 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180203Hua X. S. , Shi J. H. , Tan Y. L. , et al. , 2018. The characteristics of the Tangdong fault revealed by shallow seismic survey. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(2): 276—283. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180203 [10] 李金森, 王恩福, 张正墨等, 1994. 高分辨率浅层地震勘探在探测隐伏断层中的应用. 东北地震研究, 10(4): 50—54Li J. S. , Wang E. F. , Zhang Z. M. , et al. , 1994. Application of high-resolution shallow seismic prospecting to detecting hidden faults. Seismological Research of Northeast China, 10(4): 50—54. (in Chinese) [11] 李守军, 陈宇慧, 赵秀丽等, 2016. 潍坊北部晚第四纪介形类与环境演变研究. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 35(1): 1—11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2016.01.001Li S. J. , Chen Y. H. , Zhao X. L. , et al. , 2016. Late quaternary ostracoda and environmental evolution in the North Weifang. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 35(1): 1—11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2016.01.001 [12] 李小艳, 赵泉鸿, 姚政权等, 2015. 渤海百万年以来的海侵记录: BH08孔有孔虫和介形类证据. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 35(6): 93—108Li X. Y. , Zhao Q. H. , Yao Z. Q. , et al. , 2015. Transgressive records of last million years in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from foraminifera and ostracoda of core BH08. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 35(6): 93—108. (in Chinese) [13] 刘保金, 孙振国, 赵成斌等, 1999. 延庆—怀来地区高分辨率浅地震反射剖面. 地震地质, 21(4): 425—430 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.04.018Liu B. J. , Sun Z. G. , Zhao C. B. , et al. , 1999. Shallow seismic reflection profiling with high-resolution in Yanqing-Huailai region. Seismology and Geology, 21(4): 425—430. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.04.018 [14] 刘保金, 张先康, 方盛明等, 2002. 城市活断层探测的高分辨率浅层地震数据采集技术. 地震地质, 24(4): 524—532 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006Liu B. J. , Zhang X. K. , Fang S. M. , et al. , 2002. Acquisition technique of high-resolution shallow seismic data for surveying of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 524—532. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006 [15] 刘保金, 姬继法, 徐朝繁等, 2006. 共偏移距地震反射波方法用于城市活断层探测. 地震地质, 28(3): 411—418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.03.009Liu B. J. , Ji J. F. , Xu Z. F. , et al. , 2006. Application of common offset seismic reflection method to urban active fault survey. Seismology and Geology, 28(3): 411—418. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.03.009 [16] 刘华国, 吴小江, 李峰等, 2018. 马袅-铺前断裂中段全新世活动特征研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(3): 588—599 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180310Liu H. G. , Wu X. J. , Li F. , et al. , 2018. Active characteristics of the middle segment of Maniao-Puqian fault in the Holocene. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 588—599. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180310 [17] 潘纪顺, 刘保金, 朱金芳等, 2002. 城市活断层高分辨率地震勘探震源对比试验研究. 地震地质, 24(4): 533—541 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.007Pan J. S. , Liu B. J. , Zhu J. F. , et al. , 2002. Comparative experiment on seismic sources in high-resolution seismic exploration for urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 533—541. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.007 [18] 童国榜, 羊向东, 王苏民等, 1998. 第四纪气候事件的孢粉记录. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 18(3): 13—22Tong G. B. , Yang X. D. , Wang S. M. , et al. , 1998. Sporopollen records from Quaternary climatic events. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 18(3): 13—22. (in Chinese) [19] 王海峰, 杨剑萍, 庞效林等, 2016. 鲁北平原晚第四纪地层结构及沉积演化. 沉积学报, 34(1): 90—101Wang H. F. , Yang J. P. , Pang X. L. , et al. , 2016. Stratigraphic structure and sedimentary evolution during Late Quaternary in Lubei Plain. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 34(1): 90—101. (in Chinese) [20] 王华林, 陈锦太, 耿杰等, 1991. 胜利油田及邻近地区断裂活动性研究. 西北地震学报, 13(1): 78—84Wang H. L. , Chen J. T. , Geng J. , et al. , 1991. A study on fault activity in and near Shengli Oil Field. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 13(1): 78—84. (in Chinese) [21] 王蛟, 姜在兴, 陈世悦, 2005. 渤海湾盆地车镇凹陷古近系层序地层与隐蔽油气藏. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 35(2): 163—169Wang J. , Jiang Z. X. , Chen S. Y. , 2005. Sequence stratigraphy and subtle hydrocarbon reservoir of paleogene in Chezhen Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 35(2): 163—169. (in Chinese) [22] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华等, 1981. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究. 地质学报, 55(1): 1—13Wang P. X., Min Q. B., Bian Y. H., et al., 1981, Strata of Quaternary transgressions in East China: a preliminary study. Acta Geologica Sinica, 55(1): 1—13. (in Chinese) [23] 王强, 李从先, 2009. 中国东部沿海平原第四系层序类型. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 29(4): 39—51Wang Q. , Li C. X. , 2009. The type of quaternary sequence in the East China coastal plain. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 29(4): 39—51. (in Chinese) [24] 王世进, 张成基, 刘海坤等, 1999. 山东省第四纪地质研究新进展. 山东地质, 15(2): 1—8Wang S. J. , Zhang C. J. , Liu H. K. , et al. , 1999. Advances on the Quaternary geological study in Shandong province. Geology of Shandong, 15(2): 1—8. (in Chinese) [25] 武奉霞, 2014. 埕南断层演化规律研究. 内蒙古石油化工, 40(16): 119-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7981.2014.16.047 [26] 向宏发, 方仲景, 张晚霞等, 1993. 北京平原区隐伏断裂晚第四纪活动性的初步研究. 地震学报, 15(3): 358—388. [27] 向宏发, 2003. 隐伏活动构造探测研究的若干问题讨论. 地震地质, 25(3): 460—466 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.03.011Xiang H. F. , 2003. Some problems in the exploration and research of buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 25(3): 460—466. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.03.011 [28] 徐朝繁, 张先康, 朱金芳等, 2002. 复杂介质结构中折射界面的哈格多恩原理波前成像. 地震地质, 24(4): 542—548 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.008Xu Z. F. , Zhang X. K. , Zhu J. F. , et al. , 2002. Refractor imaging in complex structures by using Hagedoorn wavefront reconstruction principle. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 542—548. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.008 [29] 张家震, 马士忠, 王新峰等, 2005. 车镇凹陷北部陡坡带下古生界油气分布控制因素. 西南石油学院学报, 27(4): 5—8Zhang J. Z. , Ma S. Z. , Wang X. F. , et al. , 2005. The control factors of hydrocarbon distributing of the lower palaeozoic in the northern abrupt slope of Chezhen sag. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 27(4): 5—8. (in Chinese) [30] 张鹏, 李丽梅, 许汉刚等, 2014. 徐州活动断层探测项目主要断层活动性研究. 震灾防御技术, 9(4): 801—812 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20140407Zhang P. , Li L. M. , Xu H. G. , et al. , 2014. Identification of fault activity in “urban active fault exploration and seismic risk assessment in Xuzhou city”. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 9(4): 801—812. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20140407 [31] 张祖陆, 1995. 渤海莱州湾南岸平原黄土阜地貌及其古地理意义. 地理学报, 50(5): 464—470 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.05.010Zhang Z. L. , 1995. Loess mounds on the Laizhou Bay Ptain South of Bohai Sea and their paleogeographic implicatiom. Acta Geographica Sinica, 50(5): 464—470. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.05.010 [32] 赵成斌, 孙振国, 刘保金等, 1999. 邢台地震区浅部构造特征及其与深部构造的耦合关系. 地震地质, 21(4): 417—424 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.04.017Zhao C. B. , Sun Z. G. , Liu B. J. , et al. , 1999. A study of the shallow Structural characteristics and the coupling relation between deep and shallow structures in Xingtai earthquake area. Seismology and Geology, 21(4): 417—424. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.04.017 [33] 赵秀丽, 章磊, 张祥玉等, 2017. 山东省潍坊北部第四系有孔虫及古环境意义. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 36(1): 1—10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2017.01.001Zhao X. L. , Zhang L. , Zhang X. Y. , et al. , 2017. The quaternary foraminifera and Paleoenvironments in northern Weifang, Shandong province. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 36(1): 1—10. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2017.01.001 [34] 周月玲, 彭远黔, 陈建强等, 2018. 河西务断裂活动性的综合探测研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(3): 610—618 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180312Zhou Y. L. , Peng Y. Q. , Chen J. Q. , et al. , 2018. Comprehensive survey and study on the activity of the Hexiwu Fault in Langfang area, Hebei province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 610—618. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180312 [35] Aitken M. J. , 1998. An introduction to optical dating. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 39—50. [36] Singer B. S. , 2014. A Quaternary geomagnetic instability time scale. Quaternary Geochronology, 21: 29—52. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2013.10.003 -



 下载:
下载: